Abstract
The inevitable fate of massive stars in the initial mass range of ≈8– in the red supergiant (RSG) phase is a core-collapse supernova (SN) explosion, although some stars may collapse directly to a black hole. We know that this is the case, since RSGs have been directly identified and characterized for a number of supernovae (SNe) in pre-explosion archival optical and infrared images. RSGs likely all have some amount of circumstellar matter (CSM), through nominal mass loss, although evidence exists that some RSGs must experience enhanced mass loss during their lifetimes. The SNe from RSGs are hydrogen-rich Type II-Plateau (II-P), and SNe II-P at the low end of the luminosity range tend to arise from low-luminosity RSGs. The typical spectral energy distribution (SED) for such RSGs can generally be fit with a cool photospheric model, whereas the more luminous RSG progenitors of more luminous SNe II-P tend to require a greater quantity of dust in their CSM to account for their SEDs. The SN II-P progenitor luminosity range is –5.2. The fact RSGs are known up to leads to the so-called “RSG problem”, which may, in the end, be a result of small number of available statistics to date.
1. Introduction
It had long been speculated that red supergiants (RSGs) were the progenitors of supernovae (SNe), catastrophic explosions arising from the gravitational-collapse endpoints of stars with initial, zero-age main sequence masses [1] (see Ekström & Georgy in this volume). As such, the resulting SNe should be dominated by strong hydrogen lines in their spectra [2], given the massive RSG hydrogen envelope, i.e., they are SNe of Type II [3], and the light curves should exhibit an extended “plateau” in their luminosity [4,5,6]. More modern theoretical analyses have further strengthened this connection, through detailed modeling of both the SN photometric and spectroscopic evolution, e.g., [7,8,9,10,11,12,13].
One must consider the observed properties of SNe in the context of their progenitors. They are inextricably linked. Substantial heterogeneity exists in both the overall shapes and the peak luminosities of Type II SNe (SNe II) [14], with implications for diversity in progenitor properties at the time of explosion. Classically, SN II light curves were separated into II-Plateau (II-P) and II-Linear (II-L) [15], with possible spectroscopic differences exemplified by a weaker P-Cygni profile in the H line [16]. More recently, the light-curve shape distinction has become less clear with significantly more data available [14,17,18], although large samples appear to indicate that SNe with higher expansion velocities have higher luminosities, higher radioactive 56Ni masses, shorter (≲100-day) plateau durations, and more rapidly declining light curves [19,20]. At the other extreme are low-luminosity SNe II, with peak luminosities at least an order of magnitude lower than average, underluminous exponential declines in the light-curve tail, ∼10% of the average 56Ni mass, and significantly lower expansion velocities [21,22].
Recent sophisticated modeling has impressively simulated SN II-P light curves through radiative transport of shock-deposited and radioactively powered energy through the RSG stellar ejecta [23], successfully reproducing the observations of the radiative breakout of the shock wave through the outer RSG envelope [24].
Neutrino heating, together with neutrino-driven—albeit chaotic— turbulence, appears to be the main mechanism driving explosion in massive stars, although an understanding of stellar evolution to core collapse has not yet converged [25]. Whereas empirical (and possibly theoretical) correlations may exist between initial progenitor mass; ejecta expansion velocity; and, therefore, explosion energy [26,27,28,29,30] (however, see [31,32]), recent 3D core-collapse SN models point more toward explosion energy as a function of, say, progenitor mantle binding energy and, more importantly, a core “compactness parameter” [33] rather than initial progenitor mass [25]. We point out that explosions have also been modeled as jet-driven [34,35,36].
We know that many RSGs are often-irregular, long-period variables (LPVs; e.g., [37,38,39]). We also know that many, if not all, RSGs have at least some circumstellar matter (CSM, e.g., [40]) beyond their photospheres, often dusty [41,42], as a result of mass loss during this phase of stellar evolution [43,44]. We observe evidence for a CSM layer above the photosphere via short-lived so-called “flash” emission features in early-time optical spectra for a number of SNe II [45]. The interaction of the SN shock with the dense CSM can lead to enhanced luminosity in the early-time light curves [46,47]. In fact, if the CSM is sufficiently dense, the breakout of the SN shock can be significantly delayed [48,49].
A question then emerges: What is the origin of the CSM around RSGs, and, then, at what rate and at what interval does it emerge before explosion, especially when the CSM is particularly dense? Theoretical evolutionary models include baseline empirical prescriptions of mass loss [50,51] (∼; different, higher mass-loss rate prescriptions have been presented elsewhere [52]; see also van Loon in this volume and [53]). However, these rates are not nearly high enough to account for the amount and densities of the CSM that are inferred from a number of SN observations, which, in several, cases also imply short-time-scale (days to decades) mass-loss episodes prior to explosion.
Enhanced mass loss (∼–) can be driven pulsationally by internal convective shocks [54] induced by nuclear flashes [55] or convectively driven wave heating [56,57], which, toward the end of the RSG phase during late-stage nuclear burning, could lead to higher mass-loss rates [58] or eruptive outbursts during the final year or years prior to explosion [59,60,61], when turbulence and pulsations are most vigorous. (A “superwind” could develop from internal dynamical instabilities; however, this may only be the case for the most massive RSGs [62].) Such a precursor event has been observed for at least one normal SN II-P [63]. Other recent studies have provided alternatives to outbursts, e.g., a late-time effervescent zone [64] or a wave-driven chromospheric layer [65] to account for the immediate dense CSM above RSGs. Binary interaction may offer yet another mechanism [66].
Several indirect observational constraints on SN progenitors include the modeling of SN light curves via progenitor population synthesis [67], probing late-time ejecta [68,69], analyzing circumstellar gas ionized by the early ultraviolet/X-ray radiation from the SN blast [45,70,71], and inferring ages and turnoff masses from the SN’s local stellar and interstellar environment ([72,73,74,75]; however, see [76]). Of course, the surest means to understand the nature of the progenitor is to directly identify and characterize it as it was some time before it exploded. The first SN II to have its progenitor identified in this way was SN 1987A, although the SN was peculiar in its properties. In addition, ironically, the progenitor was identified as blue, not red, supergiant Sanduleak 202 [77,78] (the unanticipatedly unusual progenitor could possibly be explained by a merger of two stars [79]). The first SN II-P progenitor to be characterized from pre-SN imaging as an RSG was SN 2003gd [80,81]. Subsequent identifications up to a certain point in time have been reviewed and discussed elsewhere [82,83,84,85]. In the remainder of this article, we provide a further and more current review.
2. Direct Identification of RSGs as SN Progenitors
A summary of all of the direct identifications of SN II-P progenitors to date is given in Table 1. Like SN 1987A, the host galaxies of SN 2004et [86,87], SN 2008bk [88,89,90], and SN 2012A [91,92] were nearby enough (≲10 Mpc) that the progenitors could be identified in ground-based image data (this was strikingly true for SN 2008bk, whose host is at 3.4 Mpc, and data of high quality in multiple photometric bands were available). All of the remaining examples involve images taken prior to each SN with the high spatial resolution of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The SN 2003gd progenitor identification was a hybrid of HST data at shorter optical wavelengths and ground-based images at longer wavelengths. A number of cases also included infrared data from the Spitzer Space Telescope.

Table 1.
Direct identification of RSGs as SN progenitors.
The precise location of the progenitor is generally established based on high-resolution images of the SN itself, usually when the SN is still bright, using either the HST or adaptive optics-assisted ground-based observations (AO). A notable exception is SN 2022acko, for which the SN was serendipitously imaged by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST); those data were astrometrically aligned with the pre-SN HST imaging to pinpoint the progenitor site [113].
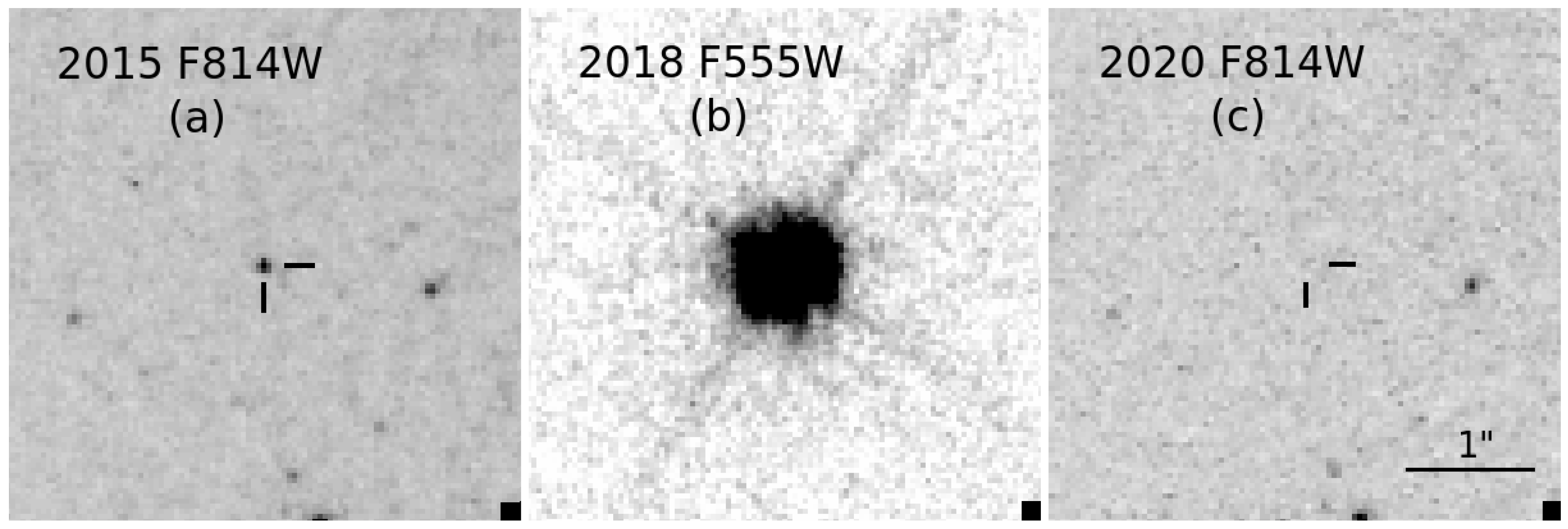
In Figure 1, we show one example of direct progenitor identification for SN 2018aoq in NGC 4151 (see also [110]). The leftmost panel shows the RSG progenitor in the HST F814W (∼I) band, the site of which was serendipitously imaged more than 2 years prior to its explosion. The precise location of the progenitor was pinpointed using an image of the SN itself we obtained with the HST in 2018 in the F555W band (∼V). We revisited the site again in 2020 with the HST in the F814W band, confirming that the RSG was, indeed, the progenitor based on its disappearance [127].
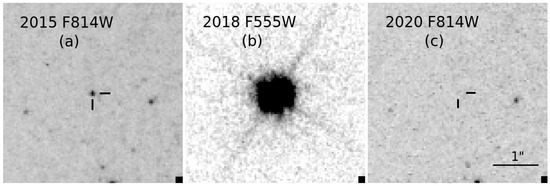
Figure 1.
(a) Portion of an HST image of the host galaxy of SN 2018aoq obtained in the F814W band in December 2015. (b) Portion of an HST image of the SN itself obtained in the F555W band in April 2018. (c) Portion of an HST image of the SN field obtained in the F814W band in December 2020. The position of the SN site in panels (a,c) is indicated with tick marks. The image data were all obtained with the Wide-Field Camera 3 (WFC3) instrument. The panels are all shown at the same scale and orientation. North is up, and east is to the left. (See also [110,127]).
In Table 1, we provide both the host galaxy name and the inferred bolometric luminosity of the RSG progenitor relative to the Sun (). In the literature on each of the progenitors, the initial mass(), is generally inferred for the stars. However, we resist including these here and list just the luminosity instead. This is since the mapping from luminosity to initial mass, via theoretical stellar evolutionary tracks, can be fraught with additional uncertainties and open to interpretation [128], particularly given that the various available model tracks [129,130,131] for a given do not all terminate at the same locus on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram, due, at least in part, to different input assumptions made in the modeling.
Many of the cases involve detection of the progenitor only in one band, with upper limits on detection in other bands, especially early on in the pursuit of direct progenitor identifications, e.g., SN 2005cs [94,95]. Typically, these one- or two-band detections have since been converted to luminosity estimates via bolometric corrections for RSGs [132,133,134]. When more than two photometric bands are available, model fits can be applied to the resulting observed spectral energy distributions (SEDs), then integrated over wavelengths to obtain luminosity estimates.
In practice, a limit exists on how far away the host can be while still being able to detect or resolve an individual luminous star. For the HST, that limit is ≲20–30 Mpc, beyond which crowding and confusion become insurmountable issues; for ground-based optical and near-infrared (and even the Spitzer telescope in the mid-infrared range), that limit is far more restrictive. In nearly equal numbers to the progenitor detections are non-detections, many as a result of the depth (or lack thereof) of the pre-SN imaging, given either the exposure time, the host distance, or both, as listed in Table 2. In a few of these cases, the resulting upper limits provided useful constraints on the progenitor’s luminosity, which are provided in the table.

Table 2.
Upper limits on progenitor detection.
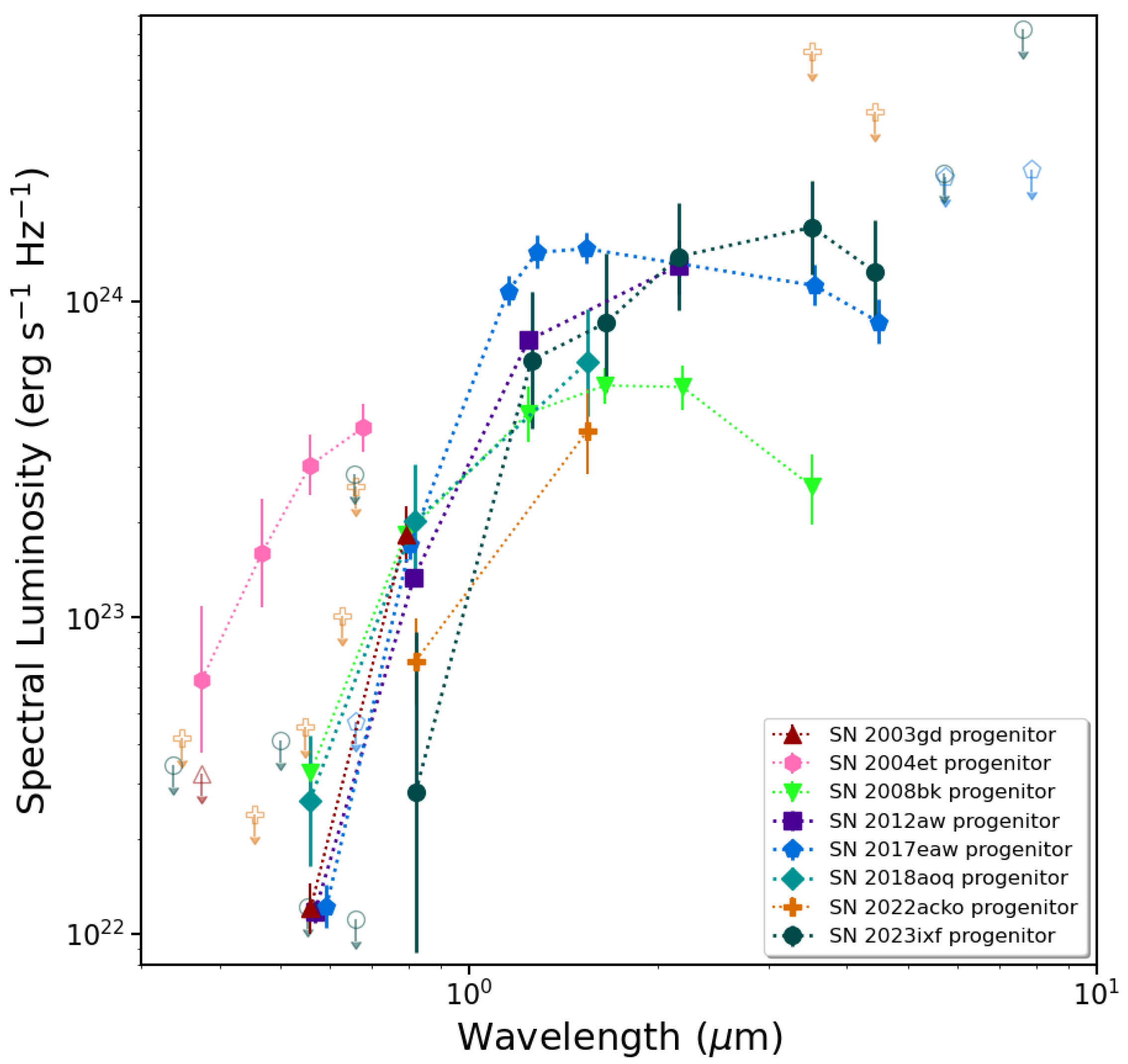
We show absolute SEDs for several of the detected progenitors listed in Table 1 in Figure 2. The observed SEDs were all corrected both for assumptions of galactic foreground and internal host galaxy reddening, as well as for the assumed distance to each of the hosts. As one can see, first, the SEDs were not all been equally sampled across wavelengths, since we are completely beholden to whatever available archival imaging data serendipitously included the SN site. Secondly, with the caveat that the statistics are still quite small, the SEDs have generally different shapes relative to one another; the variety of shapes most likely arise from differing amounts of intrinsic reddening in (i.e., dustiness of) the circumstellar environments of the progenitors. This is not entirely surprising, since we do not expect the apparent SEDs of RSGs to be the same, given the rich variety of SED shapes for, e.g., galactic RSGs [42]. We should not expect all massive stars to have the same properties at the end of their lives; therefore, each RSG is an individual. Lastly, the detected progenitors span a range of at least an order of magnitude in luminosity, as can be seen as well in Table 1, from to 5.5. This is, to the first order, consistent with the expected range of (∼8–) for massive stars that terminate as RSGs (however, we discuss this further in Section 3).
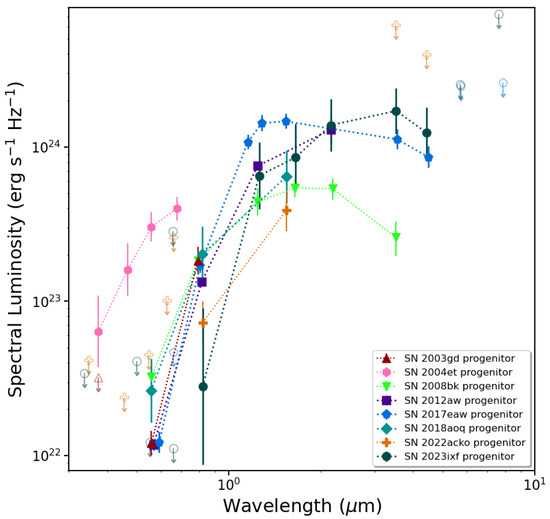
Figure 2.
A comparison of the spectral energy distributions (SEDs) for several resolved RSG progenitors of SNe II-P (see Table 1). Photometric bands for which there are measurements are shown as filled symbols, and upper-limit estimates are presented as open symbols. SEDs are all corrected for both galactic foreground and internal host galaxy reddening, as well as the assumed distances to the hosts.
We must stress here that we have been using the term “progenitor” rather cavalierly so far. A star identified at the precise location of an SN is only a candidate progenitor until the star has demonstrably vanished. This requires patient vigilance to determine whether the SN has faded sufficiently below the luminosity of the candidate, with the wait time occasionally exacerbated by any lingering light as a result of CSM interaction. For many of the SNe in Table 1, the candidates have been shown to have disappeared, reinforcing the likelihood that these were the actual progenitors [99,127,150,151,152,153,154]. One important caveat to this is that we cannot outright eliminate the possibility that dust has formed around the SN and obscured or otherwise dimmed the light. We expect dust to form over the time span of years in the SN ejecta from massive star explosions [155]. Additionally, unresolved binaries or multiple-star systems certainly can appear as single stars at the distances of the host galaxies. We would expect this to occur quite frequently, since the multiplicity fraction is ≳70% for (primary) stars with [156]. It is also possible that an identified progenitor is a chance superposition of two or more stars, again, given the host distances. In fact, the yellow star associated with SN 2008cn [98] appears, in retrospect, to have been a combination of a blue and a red (probably supergiant) star [99]. Similarly, the progenitor of SN 2013ej also appears to be the near-superposition of a blue and a red star, although their photocenters are just slightly displaced from one another [106].
2.1. Progenitors of Low-Luminosity SNe
Several of the SNe in Table 1 for which an RSG progenitor has been identified were low-luminosity events, including SN 2003gd [157], SN 2004A [93], SN 2005cs [158], SN 2008bk [89,159], SN 2018aoq [160], and SN 2022acko [161] (likely also SN 2006my [162]). Interestingly, the SED for these progenitors can be fit essentially with a bare photosphere, with effective temperatures in the range of –3700 K. This is typified by, e.g., the case of the SN 2018aoq progenitor (see Figure 1), for which the multi-band SED was fit by a 3500 K stellar atmosphere model with minimal, if any, additional CSM extinction [110].
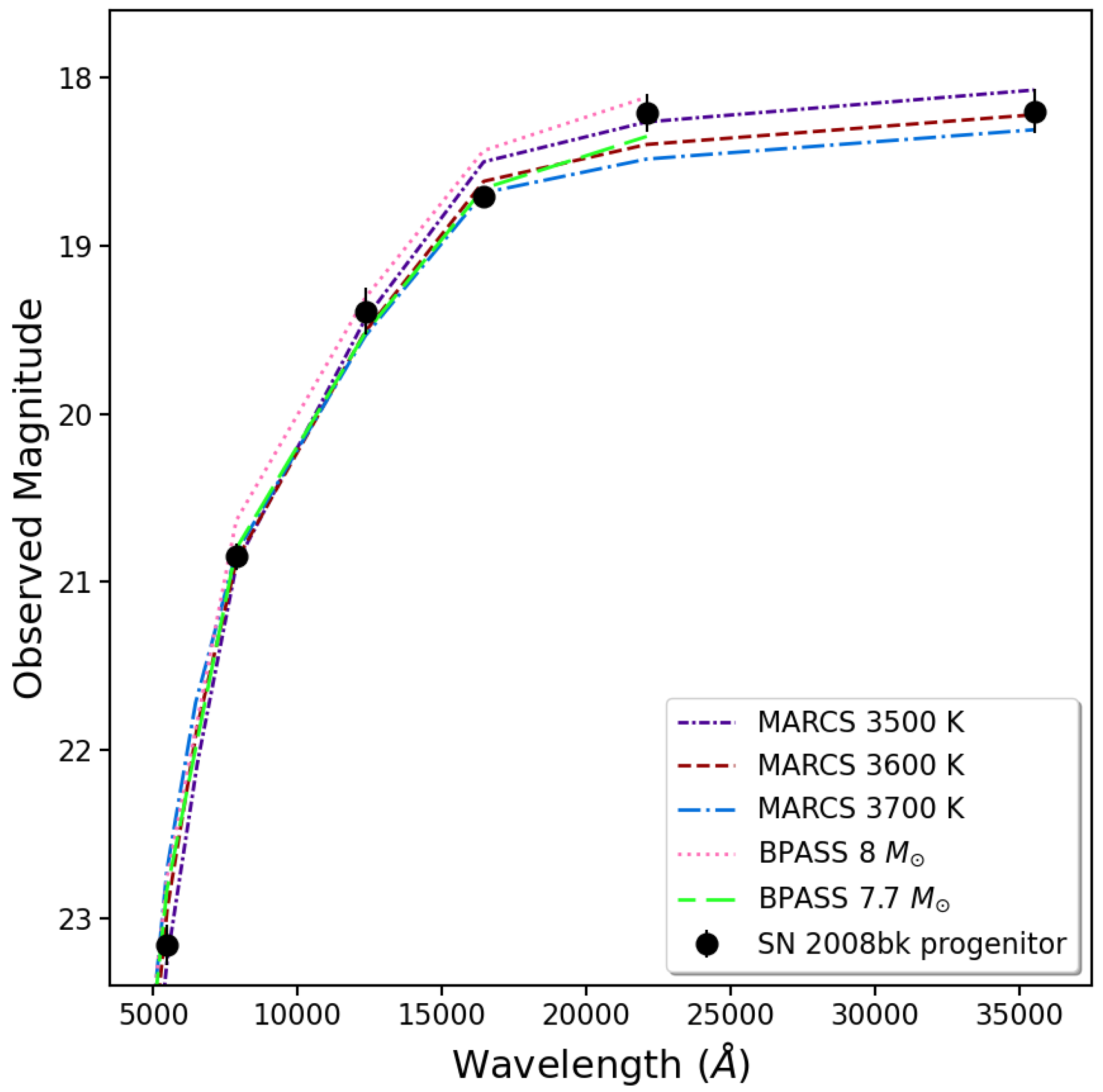
We also illustrate this for the SN 2008bk progenitor in Figure 3. Correcting the photometry [89] for the contributions of fainter stars, as seen with the HST, within the ground-based point-spread function (PSF) to the overall brightness of the progenitor in each band (see also [90]), we present the SED for the progenitor in the figure. For comparison with the corrected SED, we show MARCS stellar atmospheres at subsolar metallicity ( [163]) at , 3600, and 3700 K, as well as the SEDs at the endpoints of two BPASS model single-star evolutionary tracks [131]. One can see that all of the photospheres provide excellent fits to the full observed SED. In addition, the endpoints of the 7.7 and tracks are roughly consistent with the SED to 2.2 µm. The and for the two model endpoints are 3555 K and 4.51 and 3550 K and 4.59, respectively. The main point here is that any effect of extinction as a result of CSM dust on the stellar SED is minimal, at least to wavelengths ≲ 3.5 µm. The luminosity implied for the SN 2008bk progenitor is consistent with the overall limiting luminosity for low-luminosity SNe II-P, i.e., . Fits to the SEDs of these progenitors generally—and specifically in the cases of SN 2008bk and SN 2018aoq—appear to imply that –.
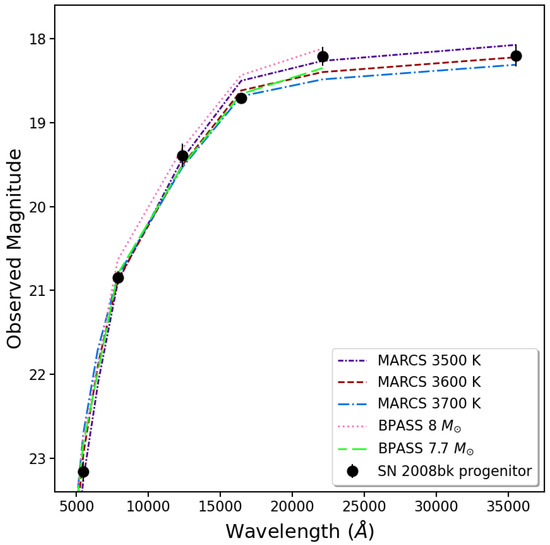
Figure 3.
Previously unpublished, corrected SED for the progenitor of SN 2008bk [89] (see also [90]). The ground-based photometry for the star was adjusted for the contributions of fainter stars, visible with the HST, within the point-spread function in each band. Shown for comparison are MARCS model stellar atmospheres at subsolar metallicity (; [163]) at 3500, 3600, and 3700 K. Also shown are the endpoint SEDs of BPASS model single-star evolutionary tracks at a similar metallicity, at and . All of the models were reddened, assuming mag (from the Galactic foreground [164], via the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database [NED]) and . The assumed distance to the SN is Mpc [89].
One notable and unresolved case is the low-luminosity SN 2018zd. This event was a collapse either as a result of an electron-capture (EC) reaction in a degenerate ONeMg core of an – super-asymptotic giant branch (SAGB) star [109] or of a more standard Fe core in an RSG [165]. The ambiguity arises from a large uncertainty in the host distance (∼6–18 Mpc). Assuming a distance on the short side, ≤10 Mpc, the detected star at the SN position, indeed, had properties more consistent with a those of an SAGB than an RSG [109].
We point out that the SN 2022acko progenitor may have been straddling the SAGB/RSG boundary as well, with –4.5 [113]. Although SN 2005cs was only somewhat underluminous on the light-curve plateau, it suffered a large fall from the plateau to an extraordinarily underluminous radioactive tail, likely resulting from a very low 56Ni mass (∼) synthesized in the explosion [158]. The luminosity estimates for the progenitor, –4.5 [94,95], are also indicative of a similarly lower-mass progenitor.
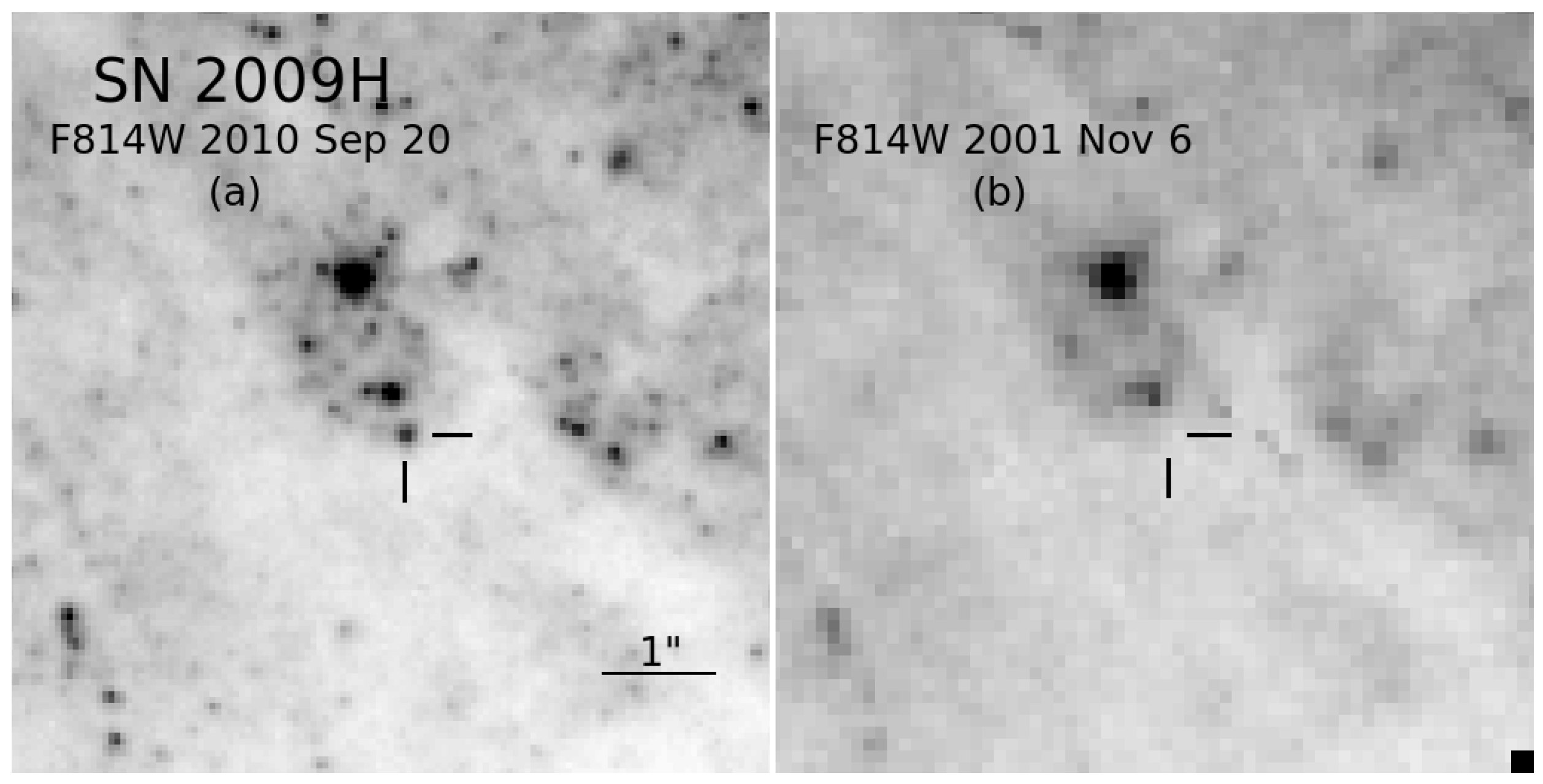
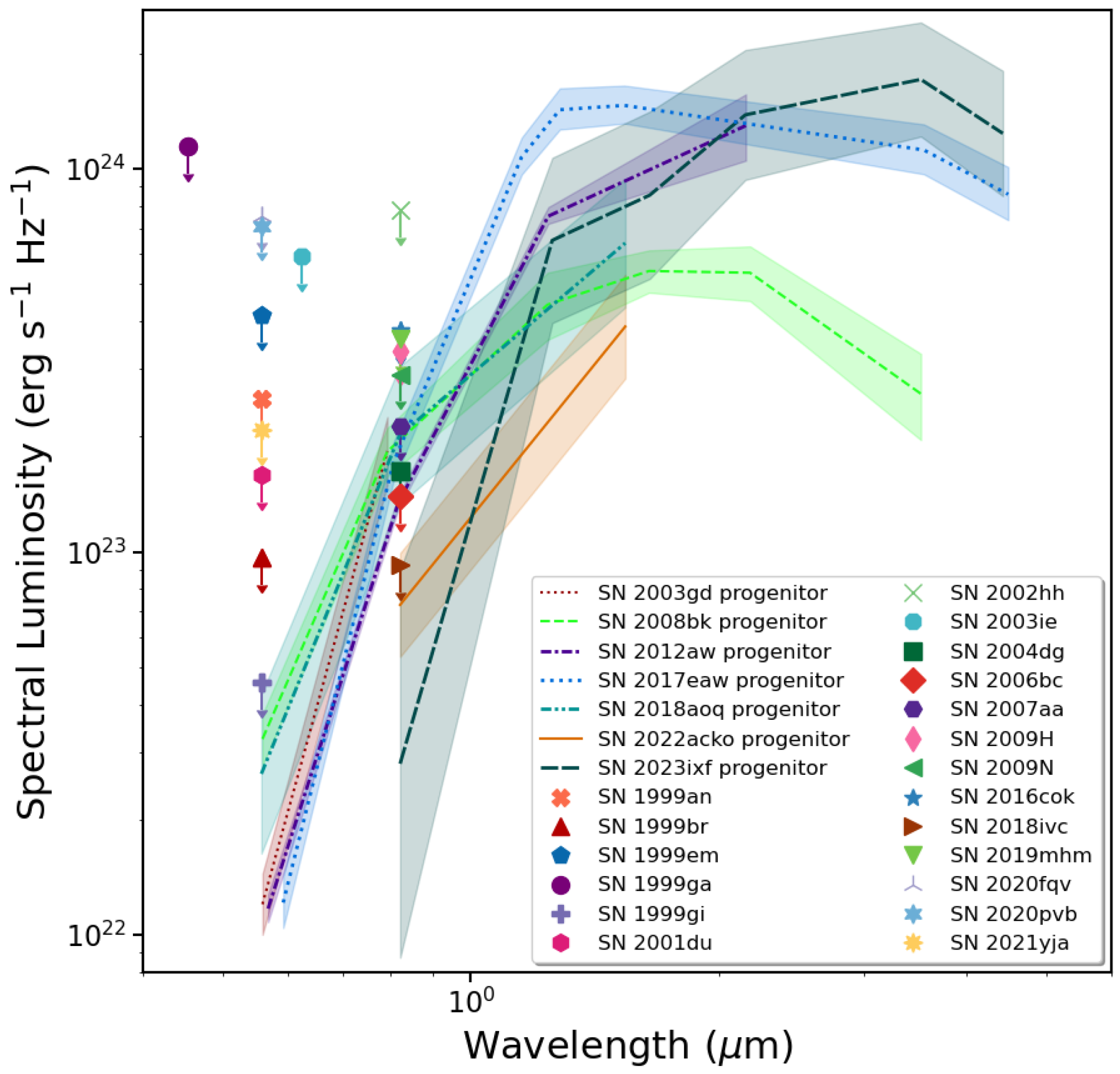
What, if anything, can we glean from the upper limits to progenitor detections presented in Table 2? These limits were all estimated in optical photometric HST bands, e.g., F555W or F814W. A previously unpublished example for SN 2009H is shown in Figure 4. What has been generally done in the literature is to infer a luminosity constraint by, e.g., adjusting the brightness limits in these bands with RSG bolometric corrections [132,133,134], in a similar way as for a number of the actual detections (e.g., [139]) (see Section 2). However, this method may have led to luminosity underestimates [166,167]. We show the upper limits from Table 2 in Figure 5 and compare these to the intrinsic SEDs of several of the direct detections (Figure 2), with the intent of imposing luminosity constraints from this comparison.
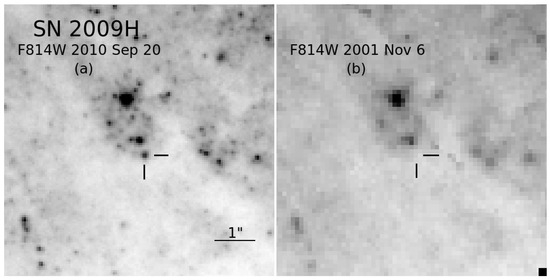
Figure 4.
(a) A portion of an HST image of SN 2009H obtained in the F814W band on 2010 September 20 UT; the SN is indicated by tick marks. (b) A portion of an archival, pre-explosion HST image, also in the F814W band, from 6 November 2001; the precise location of the SN site, based on astrometric registration with the image in panel (a) is indicated by tick marks. Both images are shown at the same scale and orientation. North is up, and east is to the left.
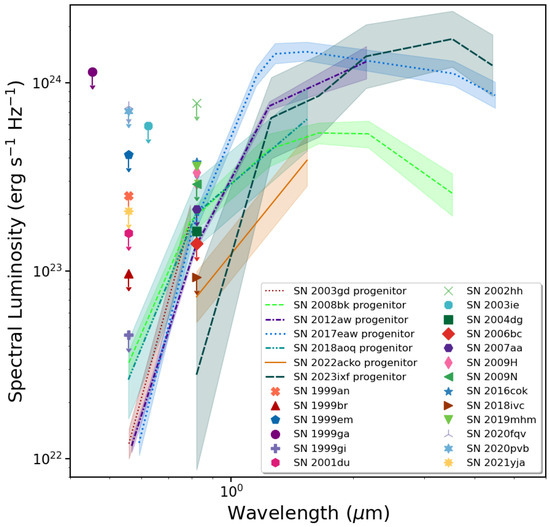
What is readily obvious from Figure 5 is that the upper limits for several of the SNe do not provide meaningful constraints at all on the progenitor luminosities (contrary to what has been inferred in the literature for these events). However, some of the limits do, in a limited way. Based on the blue end of the SEDs of the progenitor detections and the luminosities associated with those stars (see Table 1), we can infer at least relatively useful, although approximate, luminosity upper limits, and for several cases, we can also place approximate lower limits. We provide these estimates in Table 2. The lowest lower-luminosity constraints arise from the observed limits being indicative of a progenitor at least as luminous as the detected low-luminosity progenitors (e.g., SN 2008bk; ). The upper luminosity constraints arise from comparison with, e.g., the SN 2023ixf progenitor SED; therefore, the progenitor was likely no more luminous than that (; see Section 2.3). The optically based limits have little constraining power (since most of the emission from an RSG is at longer wavelengths) and, had detection limits been available, particularly in the near-IR range, we would likely have been able to place far more stringent luminosity constraints, again, treating the known progenitor SEDs as templates.
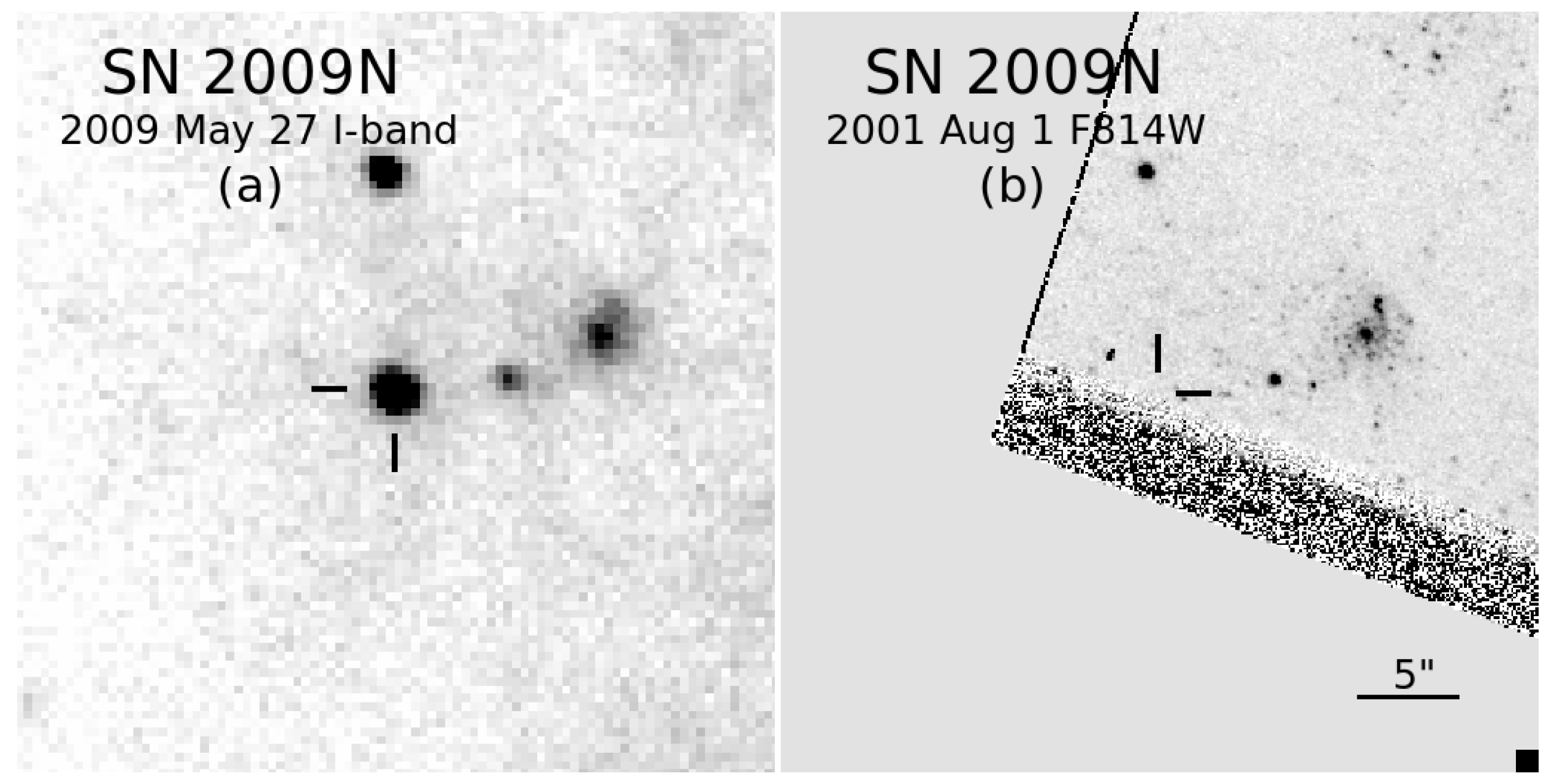
With regards to the low-luminosity SNe II-P, the limits on detection of a progenitor only likely pertain to SN 2009N (see Figure 6), which had spectral properties similar to low-luminosity events, yet had photometric similarities to more intermediate-luminosity SNe II-P [168].
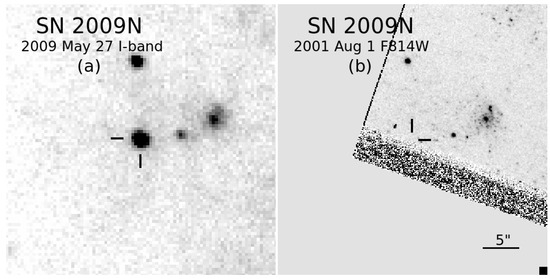
Figure 6.
(a) A portion of an image of SN 2009N obtained with the Palomar Observatory 1.5 m telescope (in California, USA) in the I band on 27 May 2009; the SN is indicated by tick marks. (b) A portion of an archival, pre-explosion HST image in the F814W band from 1 August 2001; the approximate location of the SN site, based on astrometric registration with the image in the panel (a), is indicated by tick marks. Note the extreme proximity to the detector edge of the site of the SN progenitor. These images were not previously presented [168]. Both images are shown approximately at the same scale and orientation. North is up, and east is to the left.
The nearby (∼14 Mpc) SN 2020jfo appears to be something of an unusual puzzle. The light-curve properties of the SN are consistent with more luminous SNe, including a short plateau duration of ≲65 days [111,112,169,170]; however, a single-band progenitor detection at HST F814W was underluminous relative to what would be expected for luminous, relatively massive RSGs, which could also imply enhanced CSM dust [111]. Furthermore, analyses of the late-time spectra were indicative of a star with a moderate initial mass of ∼[111,112,169,170]. However, the progenitor may also have been detected with the Spitzer telescope, and, as measured at these wavelengths, the total SED could be fit with a quite cool (∼2900 K), low-luminosity () blackbody; even including a consideration of CSM dust raised the luminosity estimate only somewhat to , which further implies a low initial mass [112]. Based on all of this, it is unclear whether SN 2020jfo should really be considered a low-luminosity SN, even though the inferred properties of its progenitor, at this point, at least, are consistent with those of other low-luminosity SN progenitor stars (see also [171]).
In summary, all in all, low-luminosity SNe II-P appear to arise from relatively lower-luminosity RSGs, for which dust in the CSM is likely relatively limited in quantity. One can infer that these RSGs are also at the low end of the possible range in initial mass for progenitors, i.e., –. Some of these progenitors may have been in a transitional state between EC-SN and Fe core-collapse SN.
2.2. Progenitors of More Luminous SNe
The remaining SNe in Table 1 with identified progenitors appear to have arisen from RSGs with higher luminosities () based on the analyses of the stars’ observed properties (although, this demarcation is somewhat arbitrary and not yet well-defined). Since the CSM dust production rate appears to be correlated with [41,42] (the mass of CSM dust may also increase as the RSG progenitor approaches explosion [58]), the effect of dust on the observed SED is expected to be larger for higher-luminosity progenitors.
If one examines Figure 2, then this is effectively what one sees. The presence of and necessity for including CSM dust became particularly apparent when attempting to fit the observed SED of the SN 2012aw progenitor [104]. The reddened overall shape of the SED, compared to that of a bare photosphere, is evident, as the dust in the CSM reprocesses the UV/blue photospheric emission into the infrared range. This was even more conspicuous in the detailed multiband SED of the SN 2017eaw progenitor [107,108]. The lone attempt to characterize the SN 2024ggi progenitor so far resulted in a luminosity [124]. All of these RSG progenitors had luminosities at explosion approaching 100,000 Suns.
As one can see from Figure 2 the SED for the SN 2004et progenitor is unusual relative to the SEDs of the other SN progenitors (including for low-luminosity SNe). It looks quite unlike the expected SED of an RSG — the luminosity of the star in the blue is far higher than that of any of the other progenitors presumed to be RSGs. The SN 2004et progenitor was characterized solely based on ground-based image data. Subsequent observations of the field with the HST revealed that other, fainter stars within the PSF may have contaminated the light from the observed progenitor itself. However, even accounting for this contamination only reduces the observed flux in each band by ∼ mag or so, and the SED is still better characterized by a luminous star hotter than the M type, i.e., a yellow supergiant [87]. What may be the case is that the detected star is actually a composite of more than one star. We will not really know until the SN has significantly faded; however, this may well be a long wait, since SN 2004et continues to exhibit signs of CSM interaction, as well as the formation of dust [172].
The progenitor requiring the largest amount of CSM dust to date in its characterization is SN 2023ixf, and we reserve a separate discussion for the next subsection (Section 2.3).
Have there been SN II-P progenitors more luminous than ? The modeling of the two-band detection of the SN 2009ib progenitor in HST archival data led to an estimate of [101], although the SN itself was assessed possibly to be of low luminosity (or, at least, at the transition from low to more normal luminosity). Based on a single HST band (F814W) detection, however, the progenitor of SN 2012ec was estimated to have had [105], which would imply that it was one of the most luminous (and potentially most massive) known RSG progenitors, which, unlike for SN 2009ib, is not entirely inconsistent with the observed properties of the SN itself [105,173].
Whereas the overwhelming majority of the identified progenitors were well-isolated spatially, we have already noted that the SN 2008cn progenitor candidate [98] was likely a blend of the RSG with a superposed (or companion) blue star [99] (we note that the progenitor candidate was distinctly variable with a period days [98]) and that the SN 2013ej progenitor was partially confused with the presence of a blue neighbor [106]. Therefore, it was very difficult to measure and accurately characterize the brightness of the star before explosion, despite indications that both were quite luminous. Although data were scant, the observed properties of SN 2008cn indicated that it was a luminous SN II-P [98]. SN 2013ej was somewhat unusual in that it was a slow-rising [174] and fast-declining, luminous SN II-P or II-L [175,176,177,178] that was also powered, at later times, by the interaction of the SN shock with the CSM [179]. The observed properties of SN 2009hd, particularly its fast decline, pointed to it being a possible SN II-L; substantial uncertainty existed as to whether the progenitor was actually identified due to the level of confusion in its environment, even at HST resolution, and the fact the SN observations indicated that the line of sight to the star is heavily dust-obscured [100]. Nevertheless, the likelihood is that it was a luminous RSG.
As discussed in Section 2.1, approximate constraints on the luminosity of a progenitor can be estimated from the observed limits on the progenitor’s detection. Lower luminosity constraints can be placed based on comparison of the detection limits with the least dusty SEDs of the lower-luminosity progenitors, and upper luminosity constraints can be established based on comparison with the most dusty SED, i.e., for SN 2023ixf. In three cases of moderate- to higher-luminosity SNe II (SN 2004dg [180], SN 2007aa [14,19], and SN 2018ivc [145]), we can infer that the star was at least as luminous as the SN 2008bk progenitor () and, in one case, (SN 2006bc), at least as luminous as the SN 2012aw progenitor ().
2.3. The SN 2023ixf Progenitor as a Special Example
SN 2023ixf occurred in the nearly face-on Messier 101 (NGC 5457) at a distance of 6.85 Mpc, in close proximity within the host to giant H ii region NGC 5471. As such, the SN generated tremendous excitement very soon after discovery, at 14.9 mag, with classification as an SN II, and immediately became the target of intense scrutiny by a number of investigators working across the full gamut of wavelengths. Given the closeness and prominence of the host and interest in the nearby H ii region, a veritable treasure trove of archival data, both ground- and space-based, were available. In particular, the host had been observed over numerous epochs with Spitzer. (In fact, due to the relative scarcity of pre-explosion optical imaging data in which the star was detected, HST contributed comparatively little to our knowledge of this SN progenitor.) It became readily evident that the star (which could be straightforwardly isolated in Spitzer data with a high degree of certainty based on its equatorial coordinates alone) was highly variable. In fact, it was possible to describe the star classification as a semi-regular, LPV (period –1100 days [115,118]), not unlike many known RSGs in the local group. This, in itself, was an astonishing discovery.
The existence of exquisite multi-epoch photometry at various bands over years before explosion also helped rule out any dramatic changes in the star’s luminosity up to days the SN, effectively ruling out the occurrences of any pre-SN outbursts, eruptions, or other catastrophic late-time mass loss [115,118,121,181,182,183]. Therefore, the origin of the dense CSM inferred around SN 2023ixf must have occurred via some other mechanism.
With the wealth of pre-explosion data, the proximity and brightness of the SN, and the relative isolation and ease of identification of the progenitor candidate, a number of investigators undertook the construction of appraisals of the progenitor’s properties. Beyond the general agreement that resulted in the analysis of the star’s variability, as mentioned above, and the overall recognition that the CSM was especially dusty, the approaches of these various investigations and their results were, by and large, disparate for a number of reasons. From the start, the measurement techniques for obtaining photometry from the existing HST, Spitzer, and ground-based near-IR data significantly diverged: For the HST data, most studies employed the Dolphot package v2.0 [184], while one [116] used DAOPHOT [185] and yet another used a tool developed by the authors [123]. In principle, everyone should have obtained the same numbers; however, even those using Dolphot arrived at different values based on different parameter settings, pre-processing steps, and so on. For measurements from the Spitzer image data, one study applied aperture photometry to the pipeline-processed mosaics [120]; another applied DAOPHOT PSF fitting to these mosaics [115], another employed DoPHOT [186] on the mosaics [117], while yet another [118] used the MOPEX [187] and APEX MultiFrame [188] packages v18.5.6 as advised by the Spitzer project. Needless to say, again, a range of output values was obtained. In Figure 2, we show the SED constructed by VanDyk [122] from HST F814W to Spitzer 4.5 µm, for which the uncertainties included the estimated amount of variability in each band.
Next, the approaches to model fitting to the various SEDs differed. Several of the studies [114,117,119,120,121,123] used the dust radiative-transfer code (DUSTY) [189], together with MARCS atmospheres [163] as the input light source; another [122] used PHOENIX atmospheres [190] instead. Two studies [115,122] used GRAMS models [191,192], in lieu of or in addition to DUSTY. About half of the studies adopted silicate-rich dust for the CSM, whereas roughly the other half adopted carbon-rich dust (although the CSM around known RSGs tends to have little to no C-rich dust [42]).
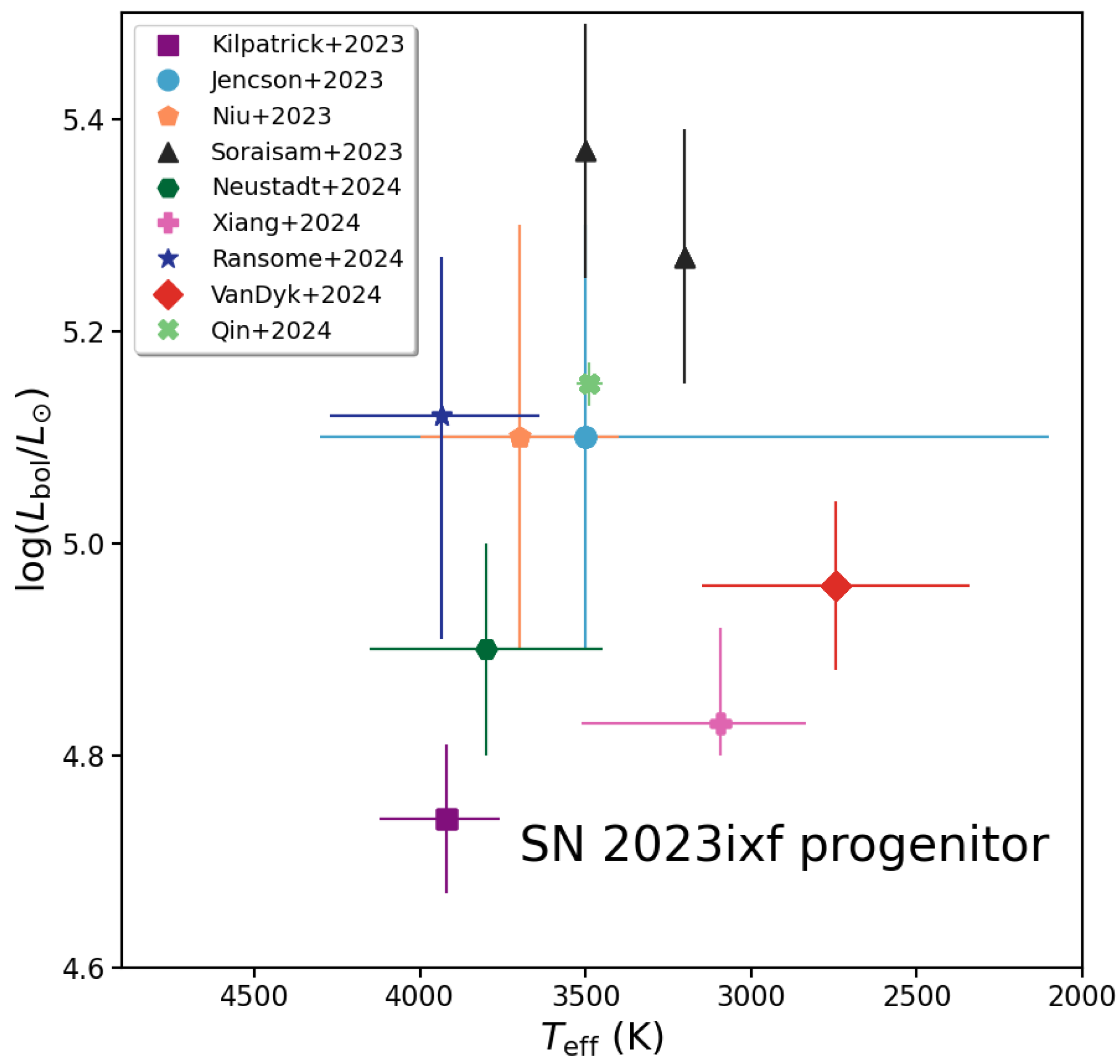
The net result of all of these various assumptions and approaches is an astonishing level of disagreement on the bolometric luminosity and effective temperature of the star years to days before it exploded (see Figure 7). This might have been expected if little data had been available to construct the star’s SED. However, in this case, we had an astounding level of multi-band data available, from the UV to the mid-infrared band. Given that, we should have been able to sharply define this one star’s characteristics; therefore, it is frustrating that the results have not converged. Technically, from a statistical standpoint, the various values for and do agree with each other in the ensemble, to within all of their estimated uncertainties; one could compute a weighted mean and uncertainty in each of K and . However, it is disappointing that, given the very high quality of the available data for the star, we have to place such large overall uncertainties on these inferred values.
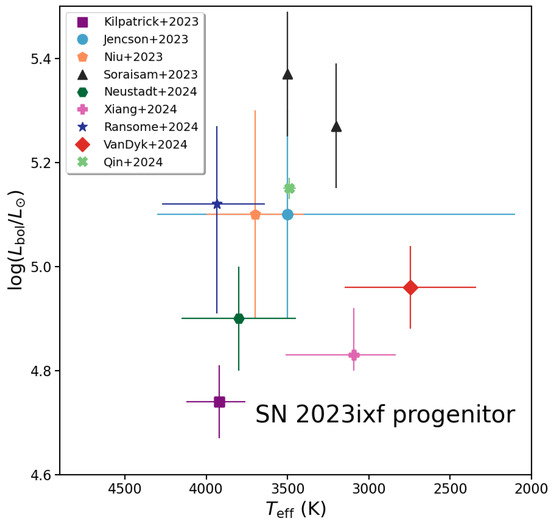
Figure 7.
Comparison of the various estimates of the bolometric luminosity () and the effective temperature () of the SN 2023ixf RSG progenitor based on either SED fitting or via a P-L relation applied to the variable star [114,115,117,118,119,120,121,122,123].
How we [118] approached this analysis was to carefully measure the fluxes or estimate upper limits of detection based on the available HST, Spitzer, and ground-based near-IR imaging data over all of the available epochs, then perform a variability analysis of the resulting light curves. We estimated a period of days for the star over years before explosion. From this period, assuming two different values, we inferred bolometric luminosities from an established RSG period–luminosity (P-L) relation, with both values being on the high side (–5.4). Next, we averaged the various epochs in the IR to arrive at global values, including the amplitude of the flux variability into the overall uncertainty in each band (for the single HST band in which the star was detected, we adopted a representative amplitude based on other cool variable giants). Then, we formally fit the SED with both GRAMS and DUSTY, assuming Si-rich dust, and obtained consistent results (and likely more stringent ones than from the P-L relation) of –5.04 and –3150 K (68% credible intervals) [122]. As can be seen in Figure 7, these are on the lower-luminosity and (considerably) cooler side. Lest it be a consideration that our estimated properties were fanciful and unrealistic, we found a direct galactic analog, RSG IRC −10414, with strikingly similar properties [193,194]. (We did not necessarily intend, in our analysis, to suggest that IRC −10414 is also nearing explosion.) Interestingly, we concluded that the SN 2023ixf progenitor, like IRC −10414 (and Betelgeuse [195] and Cep [196]), may have had an interstellar bow shock.
Even with the surprising disparity in the inferred properties of the SN 2023ixf progenitor (with the overall disagreement, it is unfortunate that the community will likely just randomly pick from the various results when referencing this progenitor in the future), we were able to characterize this candidate star in extraordinary and unprecedented detail. We will likely not have the opportunity for a similar or superior breakthrough until an SN occurs in a host galaxy with multi-band JWST coverage. Although the level of certainty is exceedingly high that the candidate was, indeed, the progenitor, this still requires confirmation when the SN has sufficiently faded (see the discussion in Section 1).
3. Discussion
The key observationally driven advances in our understanding of SN II-P progenitors and their link to RSGs have only been made possible by the direct identification of progenitors in pre-explosion archival images. The statistics are still amazingly too small to draw any broad conclusions about SN II-P progenitors, despite previous attempts at this. Accumulating sufficient statistics on SN progenitors requires both time and patience; thus, every new example is highly welcomed and informative. Although upper limits of detection have provided some coarse indications of progenitor characteristics, only actual progenitors and progenitor system identifications will continue to advance this line of study in finer detail.
As a community, we have generally found that low-luminosity SNe arise from lower-luminosity (–4.7; and lower ) RSGs [197]. Given a normal initial mass function within host galaxies in the local Universe, we would expect these progenitors to be predominant. These RSGs appear to have less (and less dusty) CSM prior to explosion, and in a few cases, the stars may dwell near the boundary of RSG and SAGB, perishing as either a core-collapse or electron-capture event. Whereas low-luminosity SNe II-P possess a certain degree of observational homogeneity, both in photometric and spectroscopic properties [22,198], higher-luminosity SNe are more heterogeneous in their properties, preventing us from clearly distinguishing what is “normal” from what is more extreme. If anything, a continuum of properties likely exists, starting at the low-luminosity floor [10,14,17,18,19]. We likely see this reflected in the diversity of observed progenitor characteristics for RSGs with . Suffice it to say that the mass, extent, and dust content of CSM is substantially higher for progenitors of more luminous explosions.
Target-of-opportunity programs with both the HST and AO, observing young SNe II-P to identify progenitor candidates, have been ongoing for the last two decades and necessitate the virtual equivalent of a long-term program because of the relatively low rate of viable candidates. (JWST has yet to be purposely used in this capacity, although it has serendipitously it has [113].) Over time we, as a community, have successfully amassed constraints on dozens of interesting SNe and their progenitors. Every new progenitor identification is precious, and each has greatly advanced our understanding of SN explosion physics, stellar evolution, and progenitor mass-loss history, particularly by putting the characteristics of each SN in context with the properties of its directly identified progenitor.
The “Red Supergiant Problem”
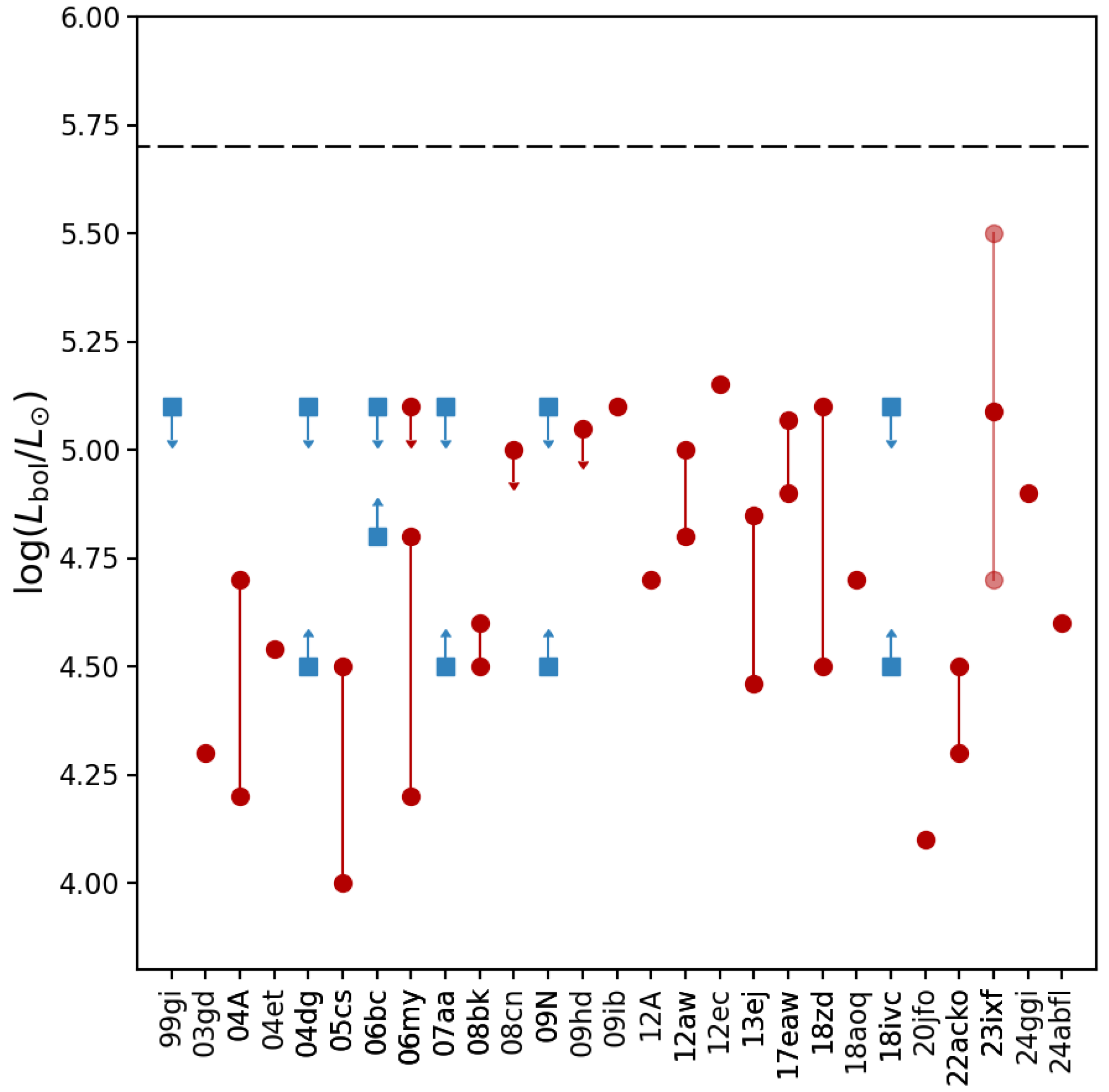
This brings us to one last topic on RSGs as SN progenitors. As one can see from Figure 8, the luminosities derived for the SN progenitors, both from direct identifications and from limits on detection, all tend to top out at (with the possible exception of the upper range of the luminosity estimate for the SN 2023ixf progenitor) and generally fall well below the empirical Humphreys–Davidson limit [199] on the luminosities of local-group cool supergiants (; see also Humphreys and Jones & Humphreys in this volume). The apparent fact that no SN II-P progenitor has, so far, been found closer to this limit, even though such luminous RSGs exist in the local Universe, is a puzzle. Why are we not finding highly luminous RSG SN progenitors? This so-called “red supergiant problem” has been debated intensively in the literature [82,84,128,200,201], and various explanations have been offered to help solve this conundrum: from CSM dust [202] to bolometric correction [134], statistics [201,203], and alternative evolutionary pathways for the highest-luminosity (most initially massive) RSGs [204]. The fact that the fate of the most massive RSGs may depend on the core compactness parameter [205] can lead to mass ranges that terminate in failed explosions, leading directly to black-hole formation [33,206].
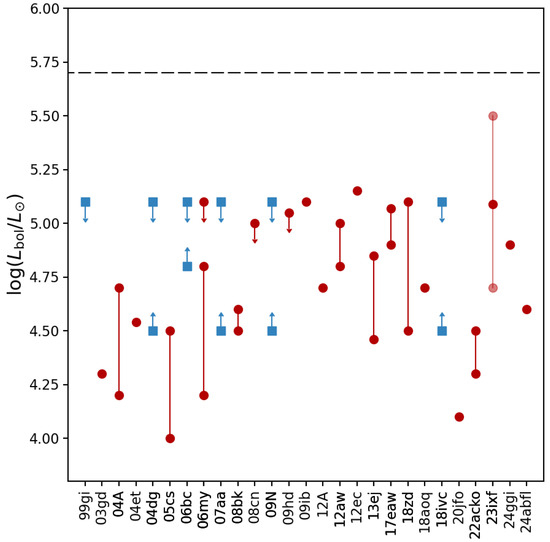
Figure 8.
Comparison of the estimates of the bolometric luminosity () for all of the SNe II-P considered here. The red circles are the estimates from direct progenitor identification, whereas the blue squares are estimates we made here based on the non-detection limits. In the case of SN 2023ixf, we show the range in the luminosity estimates, as well as the weighted mean (see Section 2.3). Also shown is the Humphreys–Davidson limit [199] (see also Humphreys and Jones & Humphreys in this volume).
The search was then underway for RSGs that simply failed to explode [207,208] or experienced very low-energy SNe [209]. A promising candidate source, “NGC 6946-BH1”, was isolated [210], although according to analysis of recent JWST observations, its origin remains ambiguous [211,212]; possibilities include a stellar merger [212] manifested as an intermediate-luminosity optical transient [213] or luminous red nova [214].
Possibly a simpler means of explaining, or attempting to explain away, the RSG problem is by taking into account the full SEDs of RSGs, from the optical to the mid-IR. Since many of the SN progenitor identifications are in a single band, the question asked is, how much divergence is the inferred luminosity from the actual luminosity; it has essentially been argued that the inference is underluminous, and taking this into account, one could statistically eliminate the existence of an “RSG problem [166,167]”, although the assumed luminosities for identified progenitors differ to a fair extent from those we have presented here.
We would argue that the RSG problem remains to be adequately challenged observationally. The sample still needs to be at least doubled [128]. Therefore, every new SN II with a progenitor identification further augments the luminosity (mass) distribution.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All data used in this review are publicly available.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| 3D | Three-Dimensional |
| CSM | Circumstellar Matter (or Medium) |
| EC | Electron Capture |
| HST | Hubble Space Telescope |
| IR | Infrared |
| JWST | James Webb Space Telescope |
| II-L | II-Linear |
| II-P | II-Plateau |
| LPV | Long-Period Variable |
| NED | NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database |
| Ni | Nickel |
| P-L | Period-Luminosity |
| PSF | Point Spread Function |
| RSG | Red Supergiant |
| SAGB | Super Asymptotic Giant Branch |
| SED | Spectral Energy Distribution |
| SN | Supernova |
| SNe | Supernovae |
References
- Woosley, S.E.; Weaver, T.A. The physics of supernova explosions. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 24, 205–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branch, D.; Falk, S.W.; McCall, M.L.; Rybski, P.; Uomoto, A.K.; Wills, B.J. The type II SN 1979c in M 100 and the distance to the Virgo cluster. Astrophys. J. 1981, 244, 780–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkowski, R. Spectra of Supernovae. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1941, 53, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, S.W.; Arnett, W.D. A Theoretical Model for Type II Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1973, 180, L65–L68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, R.A. The hydrodynamics of type II supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1976, 207, 872–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, W.D. Analytic solutions for light curves of supernovae of Type II. Astrophys. J. 1980, 237, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessart, L.; Blondin, S.; Brown, P.J.; Hicken, M.; Hillier, D.J.; Holl, S.T.; Immler, S.; Kirshner, R.P.; Milne, P.; Modjaz, M.; et al. Using Quantitative Spectroscopic Analysis to Determine the Properties and Distances of Type II Plateau Supernovae: SN 2005cs and SN 2006bp. Astrophys. J. 2008, 675, 644–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, D.J.; Dessart, L. Time-dependent radiative transfer calculations for supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 424, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessart, L.; Hillier, D.J.; Waldman, R.; Livne, E. Type II-Plateau supernova radiation: Dependences on progenitor and explosion properties. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 433, 1745–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejcha, O.; Prieto, J.L. A Global Model of The Light Curves and Expansion Velocities of Type II-plateau Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2015, 799, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, D.J.; Dessart, L. Photometric and spectroscopic diversity of Type II supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 631, A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessart, L.; Hillier, D.J. The difficulty of inferring progenitor masses from type-II-Plateau supernova light curves. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 625, A9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, J.A.; Bildsten, L.; Paxton, B. Inferring Explosion Properties from Type II-Plateau Supernova Light Curves. Astrophys. J. 2019, 879, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.P.; González-Gaitán, S.; Hamuy, M.; Gutiérrez, C.P.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Olivares, E.F.; Phillips, M.M.; Schulze, S.; Antezana, R.; Bolt, L.; et al. Characterizing the V-band Light-curves of Hydrogen-rich Type II Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2014, 786, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Barbon, R.; Ciatti, F.; Rosino, L. Photometric properties of type II supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. 1979, 72, 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel, E.M. On the Early Spectroscopic Distinction of Type II Supernovae. Astron. J. 1996, 111, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, S.; Howell, D.A.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Graham, M.L.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Arcavi, I.; Bildsten, L.; Jerkstr, A.; McCully, C.; Pastorello, A.; et al. The diversity of Type II supernova versus the similarity in their progenitors. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 459, 3939–3962. [Google Scholar]
- Faran, T.; Poznanski, D.; Filippenko, A.V.; Chornock, R.; Foley, R.J.; Ganeshalingam, M.; Leonard, D.C.; Li, W.; Modjaz, M.; Serduke, F.J.D.; et al. A sample of Type II-L supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 445, 554–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, C.P.; Anderson, J.P.; Hamuy, M.; González-Gaitan, S.; Galbany, L.; Dessart, L.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Phillips, M.M.; Morrell, N.; Folatelli, G. Type II Supernova Spectral Diversity. II. Spectroscopic and Photometric Correlations. Astrophys. J. 2017, 850, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, D.; Howell, D.A.; Moriya, T.J.; Goldberg, J.A.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Arcavi, I.; Anderson, J.P.; Gutiérrez, C.P.; Burke, J.; McCully, C.; et al. Luminous Type II Short-Plateau Supernovae 2006Y, 2006ai, and 2016egz: A Transitional Class from Stripped Massive Red Supergiants. Astrophys. J. 2021, 913, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Zampieri, L.; Pastorello, A.; Turatto, M.; Cappellaro, E.; Benetti, S.; Altavilla, G.; Mazzali, P.; Hamuy, M. Peculiar, low-luminosity Type II supernovae: Low-energy explosions in massive progenitors? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 338, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Zampieri, L.; Turatto, M.; Cappellaro, E.; Meikle, W.P.S.; Benetti, S.; Branch, D.; Baron, E.; Patat, F.; Armstrong, M.; et al. Low-luminosity Type II supernovae: Spectroscopic and photometric evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 347, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, B.T.-H.; Goldberg, J.A.; Bildsten, L.; Kasen, D. Comparing Moment-based and Monte Carlo Methods of Radiation Transport Modeling for Type II-Plateau Supernova Light Curves. Astrophys. J. 2020, 898, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, J.A.; Jiang, Y.-F.; Bildsten, L. Shock Breakout in Three-dimensional Red Supergiant Envelopes. Astrophys. J. 2022, 933, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, A.; Wang, T.; Vartanyan, D. Physical Correlations and Predictions Emerging from Modern Core-Collapse Supernova Theory. Astrophys. J. 2024, 964, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, K.; Tominaga, N.; Umeda, H.; Kobayashi, C.; Maeda, K. Nucleosynthesis yields of core-collapse supernovae and hypernovae, and galactic chemical evolution. Nucl. Phys. A 2006, 777, 424–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznanski, D. An emerging coherent picture of red supergiant supernova explosions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 436, 3224–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Müller, B.; Heger, A.; Liptai, D.; Cameron, J.B. A simple approach to the supernova progenitor-explosion connection. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 460, 742–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.; Bersten, M.C. Mass discrepancy analysis for a select sample of Type II-Plateau supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 629, A124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, A.; Radice, D.; Vartanyan, D.; Nagakura, H.; Skinner, M.A.; Dolence, J.C. The overarching framework of core-collapse supernova explosions as revealed by 3D FORNAX simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 491, 2715–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejcha, O.; Thompson, T.A. The Landscape of the Neutrino Mechanism of Core-collapse Supernovae: Neutron Star and Black Hole Mass Functions, Explosion Energies, and Nickel Yields. Astrophys. J. 2015, 801, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejcha, O.; Prieto, J.L. On the Intrinsic Diversity of Type II-Plateau Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2015, 806, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, E.; Ott, C.D. Black Hole Formation in Failing Core-Collapse Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2011, 730, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, S.M.; Wheeler, J.C.; Milosavljević, M. Aspherical Core-Collapse Supernovae in Red Supergiants Powered by Nonrelativistic Jets. Astrophys. J. 2009, 696, 953–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papish, O.; Nordhaus, J.; Soker, N. A call for a paradigm shift from neutrino-driven to jet-driven core-collapse supernova mechanisms. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 448, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soker, N. The Role of Jets in Exploding Supernovae and in Shaping their Remnants. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 22, 122003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothers, R.; Leung, K.C. Luminosities, masses and periodicities of massive red supergiants. Astron. Astrophys. 1971, 10, 290–300. [Google Scholar]
- Kiss, L.L.; Szabó, G.M.; Bedding, T.R. Variability in red supergiant stars: Pulsations, long secondary periods and convection noise. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 372, 1721–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soraisam, M.D.; Bildsten, L.; Drout, M.R.; Bauer, E.B.; Gilfanov, M.; Kupfer, T.; Laher, R.R.; Masci, F.; Prince, T.A.; Kulkarni, S.R.; et al. Variability of Red Supergiants in M31 from the Palomar Transient Factory. Astrophys. J. 2018, 859, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loon, J.T.; Groenewegen, M.A.T.; de Koter, A.; Trams, N.R.; Waters, L.B.F.M.; Zijlstra, A.A.; Whitelock, P.A.; Loup, C. Mass-loss rates and luminosity functions of dust-enshrouded AGB stars and red supergiants in the LMC. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 351, 559–572. [Google Scholar]
- Massey, P.; Plez, B.; Levesque, E.M.; Olsen, K.A.G.; Clayton, G.C.; Josselin, E. The Reddening of Red Supergiants: When Smoke Gets in Your Eyes. Astrophys. J. 2005, 634, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoelst, T.; van der Zypen, N.; Hony, S.; Decin, L.; Cami, J.; Eriksson, K. The dust condensation sequence in red supergiant stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 498, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauron, N.; Josselin, E. The mass-loss rates of red supergiants and the de Jager prescription. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 526, A156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Helmel, G.; Jones, T.J.; Gordon, M.S. Exploring the Mass-loss Histories of the Red Supergiants. Astron. J. 2020, 160, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Khazov, D.; Yaron, O.; Gal-Yam, A.; Manulis, I.; Rubin, A.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Arcavi, I.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Ofek, E.O.; Cao, Y.; et al. Flash Spectroscopy: Emission Lines from the Ionized Circumstellar Material around <10-day-old Type II Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2016, 818, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Moriya, T.J.; Yoon, S.-C.; Gräfener, G.; Blinnikov, S.I. Immediate dense circumstellar environment of supernova progenitors caused by wind acceleration: Its effect on supernova light curves. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 469, L108–L112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, V.; Piro, A.L.; Fuller, J.; Van Dyk, S.D. The Influence of Late-stage Nuclear Burning on Red Supergiant Supernova Light Curves. Astrophys. J. 2020, 891, L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förster, F.; Moriya, T.J.; Maureira, J.C.; Anderson, J.P.; Blinnikov, S.; Bufano, F.; Cabrera-Vives, G.; Clocchiatti, A.; de Jaeger, T.; Estévez, P.A.; et al. The delay of shock breakout due to circumstellar material evident in most type II supernovae. Nat. Astron. 2018, 2, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, E.A.; Irani, I.; Chen, P.; Gal-Yam, A.; Schulze, S.; Perley, D.A.; Sollerman, J.; Filippenko, A.V.; Shenar, T.; Yaron, O.; et al. The complex circumstellar environment of supernova 2023ixf. Nature 2024, 627, 759–762. [Google Scholar]
- de Jager, C.; Nieuwenhuijzen, H.; van der Hucht, K.A. Mass loss rates in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. Astron. Astrophys. 1988, 72, 259–289. [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuijzen, H.; de Jager, C. Parametrization of stellar rates of mass loss as functions of the fundamental stellar parameters M, L, and R. Astron. Astrophys. 1990, 231, 134–136. [Google Scholar]
- Van Loon, J.T.; Marshall, J.R.; Zijlstra, A.A. Dust-enshrouded giants in clusters in the Magellanic Clouds. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 442, 597–613. [Google Scholar]
- Beasor, E.R.; Davies, B.; Smith, N.; Van Loon, J.T.; Gertz, R.D.; Figer, D.F. A new mass-loss rate prescription for red supergiants. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 5994–6006. [Google Scholar]
- Josselin, E.; Plez, B. Atmospheric dynamics and the mass loss process in red supergiant stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 469, 671–680. [Google Scholar]
- Moriya, T.; Tominaga, N.; Blinnikov, S.I.; Baklanov, P.V.; Sorokina, E.I. Supernovae from red supergiants with extensive mass loss. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiode, J.H.; Quataert, E. Setting the Stage for Circumstellar Interaction in Core-Collapse Supernovae. II. Wave-driven Mass Loss in Supernova Progenitors. Astrophys. J. 2014, 780, 96. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, J. Pre-supernova outbursts via wave heating in massive stars—I. Red supergiants. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 470, 1642–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Beasor, E.R.; Davies, B. The evolution of red supergiants to supernova in NGC 2100. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 463, 1269–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Yaron, O.; Perley, D.A.; Gal-Yam, A.; Groh, J.H.; Horesh, A.; Ofek, E.O.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Sollerman, J.; Fransson, C.; Rubin, A.; et al. Confined dense circumstellar material surrounding a regular type II supernova. Nat. Phys. 2017, 13, 510–517. [Google Scholar]
- Bruch, R.J.; Gal-Yam, A.; Schulze, S.; Yaron, O.; Yang, Y.; Soumagnac, M.; Rigault, M.; Strotjohann, N.L.; Ofek, E.; Sollerman, J.; et al. A Large Fraction of Hydrogen-rich Supernova Progenitors Experience Elevated Mass Loss Shortly Prior to Explosion. Astrophys. J. 2021, 912, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.; Plez, B.; Petrault, M. Explosion imminent: The appearance of red supergiants at the point of core-collapse. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 517, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.-C.; Cantiello, M. Evolution of Massive Stars with Pulsation-driven Superwinds During the Red Supergiant Phase. Astrophys. J. 2010, 717, L62–L65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson-Galán, W.V.; Dessart, L.; Jones, D.O.; Margutti, R.; Coppejans, D.L.; Dimitriadis, G.; Foley, R.J.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Matthews, D.J.; Rest, S.; et al. Final Moments. I. Precursor Emission, Envelope Inflation, and Enhanced Mass Loss Preceding the Luminous Type II Supernova 2020tlf. Astrophys. J. 2022, 924, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Soker, N. A Pre-explosion Effervescent Zone for the Circumstellar Material in SN 2023ixf. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 23, 081002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, J.; Tsuna, D. Boil-off of red supergiants: Mass loss and type II-P supernovae. Open J. Antennas Propag. 2024, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, T.; Sawada, R. Binary Interaction Can Yield a Diversity of Circumstellar Media around Type II Supernova Progenitors. Astrophys. J. 2024, 963, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge, J.J.; Xiao, L.; Stanway, E.R.; Rodrigues, N.; Guo, N.-Y. Supernova lightCURVE POPulation Synthesis I: Including interacting binaries is key to understanding the diversity of type II supernova lightcurves. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2018, 35, e049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milisavljevic, D.; Fesen, R.A.; Chevalier, R.A.; Kirshner, R.P.; Challis, P.; Turatto, M. Late-time Optical Emission from Core-collapse Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2012, 751, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerkstr, A.; Fransson, C.; Maguire, K.; Smartt, S.; Ergon, M.; Spyromilio, J. The progenitor mass of the Type IIP supernova SN 2004et from late-time spectral modeling. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 546, A28. [Google Scholar]
- Gezari, S.; Dessart, L.; Basa, S.; Martin, D.C.; Neill, J.D.; Woosley, S.E.; Hillier, D.J.; Bazin, G.; Forster, K.; Friedman, P.G.; et al. Probing Shock Breakout with Serendipitous GALEX Detections of Two SNLS Type II-P Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2008, 683, L131–L134. [Google Scholar]
- Gal-Yam, A.; Arcavi, I.; Ofek, E.O.; Ben-Ami, S.; Cenko, S.B.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Cao, Y.; Yaron, O.; Tal, D.; Silverman, J.M.; et al. A Wolf-Rayet-like progenitor of SN 2013cu from spectral observations of a stellar wind. Nature 2014, 509, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.P.; Habergham, S.M.; James, P.A.; Hamuy, M. Progenitor mass constraints for core-collapse supernovae from correlations with host galaxy star formation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 424, 1372–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maund, J.R. The resolved stellar populations around 12 Type IIP supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 469, 2202–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncarayakti, H.; Anderson, J.P.; Galbany, L.; Maeda, K.; Hamuy, M.; Aldering, G.; Arimoto, N.; Doi, M.; Morokuma, T.; Usuda, T. Constraints on core-collapse supernova progenitors from explosion site integral field spectroscopy. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 613, A35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.F.; Hillis, T.J.; Murphy, J.W.; Gilbert, K.; Dalcanton, J.J.; Dolphin, A.E. Constraints for the Progenitor Masses of Historic Core-collapse Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2018, 860, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapartas, E.; de Mink, S.E.; Justham, S.; Smith, N.; Renzo, M.; de Koter, A. Effect of binary evolution on the inferred initial and final core masses of hydrogen-rich, Type II supernova progenitors. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 645, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneborn, G.; Altner, B.; Kirshner, R.P. The Progenitor of SN 1987A: Spatially Resolved Ultraviolet Spectroscopy of the Supernova Field. Astrophys. J. 1987, 323, L35–L39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walborn, N.R.; Prevot, M.L.; Prevot, L.; Wamsteker, W.; Gonzalez, R.; Gilmozzi, R.; Fitzpatrick, E.L. The spectrograms of Sanduleak -69 202, precursor to supernova 1987A in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Astron. Astrophys. 1989, 219, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Podsiadlowski, P.; Joss, P.C.; Rappaport, S. A merger model for SN 1987A. Astron. Astrophys. 1990, 227, L9–L12. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Li, W.; Filippenko, A.V. On the progenitor of the Type II-plateau supernova 2003gd in M74. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2003, 115, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smartt, S.J.; Maund, J.R.; Hendry, M.A.; Tout, C.A.; Gilmore, G.F.; Mattila, S.; Benn, C.R. Detection of a red supergiant progenitor star of a Type II-plateau supernova. Science 2004, 303, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smartt, S.J.; Eldridge, J.J.; Crockett, R.M.; Maund, J.R. The death of massive stars—I. Observational constraints on the progenitors of Type II-P supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 395, 1409–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Smartt, S.J. Progenitors of Core-Collapse Supernovae. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 47, 63–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smartt, S.J. Observational Constraints on the Progenitors of Core-Collapse Supernovae: The Case for Missing High-Mass Stars. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2015, 32, e016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, S.D. The direct identification of core-collapse supernova progenitors. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2017, 375, 20160277. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Filippenko, A.V.; Cuillandre, J.-C. On the Progenitor of the Type II Supernova 2004et in NGC 6946. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2005, 117, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Crockett, R.M.; Smartt, S.J.; Pastorello, A.; Eldridge, J.J.; Stephens, A.W.; Maund, J.R.; Mattila, S. On the nature of the progenitors of three Type II-P supernovae: 2004et, 2006my and 2006ov. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 410, 2767–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, S.; Smartt, S.J.; Eldridge, J.J.; Maund, J.R.; Crockett, R.M.; Danziger, I.J. VLT Detection of a Red Supergiant Progenitor of the Type II-P Supernova 2008bk. Astrophys. J. 2008, 688, L91–L94. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Davidge, T.J.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Taubenberger, S.; Li, W.; Levesque, E.M.; Howerton, S.; Pignata, G.; Morrell, N.; Hamuy, M.; et al. Supernova 2008bk and Its Red Supergiant Progenitor. Astron. J. 2012, 143, 19. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, D.; Kotak, R.; Fraser, M.; Mattila, S.; Pietrzyński, G.; Prieto, J.L. Revisiting the progenitor of the low-luminosity type II-plateau supernova, SN 2008bk. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 645, L7. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto, J.L.; Osip, D.; Palunas, P. Candidate Progenitor of the Type II SN 2012A in the Near-IR. Astron. Telegr. 2012, 3863. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasella, L.; Cappellaro, E.; Fraser, M.; Pumo, M.L.; Pastorello, A.; Pignata, G.; Benetti, S.; Bufano, F.; Dennefeld, M.; Harutyunyan, A.; et al. Comparison of progenitor mass estimates for the Type IIP SN 2012A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 434, 1636–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendry, M.A.; Smartt, S.J.; Crockett, R.M.; Maund, J.R.; Gal-Yam, A.; Moon, D.S.; Cenko, S.B.; Fox, D.W.; Kudritzki, R.P.; Benn, C.R.; et al. SN 2004A: Another Type II-P supernova with a red supergiant progenitor. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 369, 1303–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maund, J.R.; Smartt, S.J.; Danziger, I.J. The progenitor of SN 2005cs in the Whirlpool Galaxy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 364, L33–L37. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Filippenko, A.V.; Cuillandre, J.-C.; Jha, S.; Bloom, J.S.; Riess, A.G.; Livio, M. Identification of the Red Supergiant Progenitor of Supernova 2005cs: Do the Progenitors of Type II-P Supernovae Have Low Mass? Astrophys. J. 2006, 641, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, X.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Cuillandre, J.-C.; Foley, R.J.; Filippenko, A.V. On the Progenitors of Two Type II-P Supernovae in the Virgo Cluster. Astrophys. J. 2007, 661, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, D.C.; Gal-Yam, A.; Fox, D.B.; Cameron, P.B.; Johansson, E.M.; Kraus, A.L.; Le Mignant, D.; van Dam, M.A. An Upper Mass Limit on a Red Supergiant Progenitor for the Type II-Plateau Supernova SN 2006my. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2008, 874, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Elias-Rosa, N.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Li, W.; Morrell, N.; Gonzalez, S.; Hamuy, M.; Filippenko, A.V.; Cuillandre, J.-C.; Foley, R.J.; Smith, N. On the Progenitor of the Type II-Plateau SN 2008cn in NGC 4603. Astrophys. J. 2009, 706, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Maund, J.R.; Fraser, M.; Reilly, E.; Ergon, M.; Mattila, S. Whatever happened to the progenitors of supernovae 2008cn, 2009kr and 2009md? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 3207–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias-Rosa, N.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Li, W.; Silverman, J.M.; Foley, R.J.; Ganeshalingam, M.; Mauerhan, J.C.; Kankare, E.; Jha, S.; Filippenko, A.V.; et al. The Massive Progenitor of the Possible Type II-Linear Supernova 2009hd in Messier 66. Astrophys. J. 2011, 742, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takáts, K.; Pignata, G.; Pumo, M.L.; Paillas, E.; Zampieri, L.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Benetti, S.; Bufano, F.; Cappellaro, E.; Ergon, M.; et al. SN 2009ib: A Type II-P supernova with an unusually long plateau. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, 3137–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Cenko, S.B.; Poznanski, D.; Arcavi, I.; Gal-Yam, A.; Filippenko, A.V.; Silverio, K.; Stockton, A.; Cuillandre, J.-C.; Marcy, G.W.; et al. The Red Supergiant Progenitor of Supernova 2012aw (PTF12bvh) in Messier 95. Astrophys. J. 2012, 756, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, M.; Maund, J.R.; Smartt, S.J.; Botticella, M.-T.; Dall’Ora, M.; Inserra, C.; Tomasella, L.; Benetti, S.; Ciroi, S.; Eldridge, J.J.; et al. Red and Dead: The Progenitor of SN 2012aw in M95. Astrophys. J. 2012, 759, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanek, C.S.; Khan, R.; Dai, X. On Absorption by Circumstellar Dust, with the Progenitor of SN 2012aw as a Case Study. Astrophys. J. 2012, 759, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maund, J.R.; Fraser, M.; Smartt, S.J.; Botticella, M.-T.; Barbarino, C.; Childress, M.; Gal-Yam, A.; Inserra, C.; Pignata, G.; Reichart, D.; et al. Supernova 2012ec: Identification of the progenitor and early monitoring with PESSTO. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, L102–L106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, M.; Maund, J.R.; Smartt, S.J.; Kotak, R.; Lawrence, A.; Bruce, A.; Valenti, S.; Yuan, F.; Benetti, S.; Chen, T.-W.; et al. On the progenitor of the Type IIP SN 2013ej in M74. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, L56–L60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, C.D.; Foley, R.J. The dusty progenitor star of the Type II supernova 2017eaw. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 481, 2536–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Zheng, W.; Maund, J.R.; Brink, T.G.; Srinivasan, S.; Andrews, J.E.; Smith, N.; Leonard, D.C.; Morozova, V.; Filippenko, A.V.; et al. The Type II-plateau Supernova 2017eaw in NGC 6946 and Its Red Supergiant Progenitor. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, D.; Howell, D.A.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Goldberg, J.A.; Maeda, K.; Moriya, T.J.; Tominaga, N.; Nomoto, K.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Arcavi, I.; et al. The electron-capture origin of supernova 2018zd. Nat. Astron. 2021, 5, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, D.; Kotak, R.; Fraser, M.; Sim, S.A.; Benetti, S.; Smartt, S.J.; Mattila, S.; Ashall, C.; Callis, E.; Elias-Rosa, N.; et al. A progenitor candidate for the type II-P supernova SN 2018aoq in NGC 4151. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 622, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollerman, J.; Yang, S.; Schulze, S.; Strotjohann, N.-L.; Jerkstr, A.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Kool, E.C.; Barbarino, C.; Brink, T.G.; Bruch, R.; et al. The Type II supernova SN 2020jfo in M 61, implications for progenitor system, and explosion dynamics. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 655, A105. [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick, C.D.; Izzo, L.; Bentley, R.O.; Chambers, K.C.; Coulter, D.A.; Drout, M.R.; de Boer, T.; Foley, R.J.; Gall, C.; Halford, M.R.; et al. Type II-P supernova progenitor star initial masses and SN 2020jfo: Direct detection, light-curve properties, nebular spectroscopy, and local environment. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 524, 2161–2185. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Bostroem, K.A.; Zheng, W.; Brink, T.G.; Fox, O.D.; Andrews, J.E.; Filippenko, A.V.; Dong, Y.; Hoang, E.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; et al. Identifying the SN 2022acko progenitor with JWST. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 524, 2186–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, C.D.; Foley, R.J.; Jacobson-Galán, W.V.; Piro, A.L.; Smartt, S.J.; Drout, M.R.; Gagliano, A.; Gall, C.; Hjorth, J.; Jones, D.O.; et al. SN 2023ixf in Messier 101: A Variable Red Supergiant as the Progenitor Candidate to a Type II Supernova. Astrophys. J. 2023, 952, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jencson, J.E.; Pearson, J.; Beasor, E.R.; Lau, R.M.; Andrews, J.E.; Bostroem, K.A.; Dong, Y.; Engesser, M.; Gomez, S.; Guolo, M.; et al. A Luminous Red Supergiant and Dusty Long-period Variable Progenitor for SN 2023ixf. Astrophys. J. 2023, 952, L30. [Google Scholar]
- Pledger, J.L.; Shara, M.M. Possible Detection of the Progenitor of the Type II Supernova SN 2023ixf. Astrophys. J. 2023, 953, L14. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.; Sun, N.-C.; Maund, J.R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Liu, J. The Dusty Red Supergiant Progenitor and the Local Environment of the Type II SN 2023ixf in M101. Astrophys. J. 2023, 955, L15. [Google Scholar]
- Soraisam, M.D.; Szalai, T.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Andrews, J.E.; Srinivasan, S.; Chun, S.-H.; Matheson, T.; Scicluna, P.; Vasquez-Torres, D.A. The SN 2023ixf Progenitor in M101. I. Infrared Variability. Astrophys. J. 2023, 957, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Neustadt, J.M.M.; Kochanek, C.S.; Smith, M.R. Constraints on pre-SN outbursts from the progenitor of SN 2023ixf using the large binocular telescope. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 527, 5366–5373. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, D.; Mo, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, L. The dusty and extremely red progenitor of the type II supernova 2023ixf in Messier 101. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2024, 67, 219514. [Google Scholar]
- Ransome, C.L.; Villar, V.A.; Tartaglia, A.; Gonzalez, S.J.; Jacobson-Galán, W.V.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Margutti, R.; Foley, R.J.; Grayling, M.; Ni, Y.Q.; et al. SN 2023ixf in Messier 101: The Twilight Years of the Progenitor as Seen by Pan-STARRS. Astrophys. J. 2024, 965, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Srinivasan, S.; Andrews, J.E.; Soraisam, M.; Szalai, T.; Howell, S.B.; Isaacson, H.; Matheson, T.; Petigura, E.; Scicluna, P.; et al. The SN 2023ixf Progenitor in M101. II. Properties. Astrophys. J. 2023, 968, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.-J.; Zhang, K.; Bloom, J.; Sollerman, J.; Zimmerman, E.A.; Irani, I.; Schulze, S.; Gal-Yam, A.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Coughlin, M.W.; et al. The progenitor star of SN 2023ixf: A massive red supergiant with enhanced, episodic pre-supernova mass loss. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 534, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Mo, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Lin, H.; Chen, L.; Song, C.; Liu, L.-D.; Wang, Z.; et al. The Red Supergiant Progenitor of Type II Supernova 2024ggi. Astrophys. J. 2024, 969, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, B.; Cheng, Q.; Guo, B.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Xiong, J.; Meng, X.; Chen, X.; et al. The Red Supergiant Progenitor of the Type II Supernova 2024abfl. Astrophys. J. 2024; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Groenewegen, M.A.T.; Sloan, G.C.; Soszyński, I.; Petersen, E.A. Luminosities and mass-loss rates of SMC and LMC AGB stars and red supergiants. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 506, 1277–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; de Graw, A.; Baer-Way, R.; Zheng, W.; Filippenko, A.V.; Fox, O.D.; Smith, N.; Brink, T.G.; de Jaeger, T.; Kelly, P.L.; et al. The disappearances of six supernova progenitors. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 519, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.; Beasor, E.R. The ‘red supergiant problem’: The upper luminosity boundary of Type II supernova progenitors. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 493, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, A.; Marigo, P.; Girardi, L.; Salasnich, B.; Dal Cero, C.; Rubele, S.; Nanni, A. PARSEC: Stellar tracks and isochrones with the PAdova and TRieste Stellar Evolution Code. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 427, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Dotter, A.; Conroy, C.; Cantiello, M.; Paxton, B.; Johnson, B.D. Mesa Isochrones and Stellar Tracks (MIST). I. Solar-scaled Models. Astrophys. J. 2016, 823, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanway, E.R.; Eldridge, J.J. Re-evaluating old stellar populations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 479, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, E.M.; Massey, P.; Olsen, K.A.G.; Plez, B.; Josselin, E.; Maeder, A.; Meynet, G. The Effective Temperature Scale of Galactic Red Supergiants: Cool, but Not As Cool As We Thought. Astrophys. J. 2005, 628, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, E.M.; Massey, P.; Olsen, K.A.G.; Plez, B.; Maeder, A.; Meynet, G. The Effective Temperatures and Physical Properties of Magellanic Cloud Red Supergiants: The Effects of Metallicity. Astrophys. J. 2006, 645, 1102–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, B.; Beasor, E.R. The initial masses of the red supergiant progenitors to Type II supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 474, 2116–2128. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Li, W.; Filippenko, A.V. A Search for Core-Collapse Supernova Progenitors in Hubble Space Telescope Images. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2003, 115, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Maund, J.R.; Smartt, S.J. Hubble Space Telescope imaging of the progenitor sites of six nearby core-collapse supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 360, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Smartt, S.J.; Gilmore, G.F.; Tout, C.A.; Hodgkin, S.T. The Nature of the Progenitor of the Type II-P Supernova 1999em. Astrophys. J. 2002, 565, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Pastorello, A.; Crockett, R.M.; Martin, R.; Smartt, S.J.; Altavilla, G.; Benetti, S.; Botticella, M.T.; Cappellaro, E.; Mattila, S.; Maund, J.R.; et al. SN 1999ga: A low-luminosity linear type II supernova? Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 500, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Smartt, S.J.; Gilmore, G.F.; Trentham, N.; Tout, C.A.; Frayn, C.M. An Upper Mass Limit for the Progenitor of the Type II-P Supernova SN 1999gi. Astrophys. J. 2001, 556, L29–L32. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Li, W.; Filippenko, A.V. On the Progenitor of Supernova 2001du in NGC 1365. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2003, 115, 448–452. [Google Scholar]
- Smartt, S.J.; Maund, J.R.; Gilmore, G.F.; Tout, C.A.; Kilkenny, D.; Benetti, S. Mass limits for the progenitor star of supernova 2001du and other Type II-P supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 343, 735–749. [Google Scholar]
- Mattila, S.; Fraser, M.; Smartt, S.J.; Meikle, W.P.S.; Romero-Cañizales, C.; Crockett, R.M.; Stephens, A. Supernovae and radio transients in M82. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar]
- Maíz-Apellániz, J.; Bond, H.E.; Siegel, M.H.; Lipkin, Y.; Maoz, D.; Ofek, E.O.; Poznanski, D. The Progenitor of the Type II-P SN 2004dj in NGC 2403. Astrophys. J. 2004, 615, L113–L116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanek, C.S.; Fraser, M.; Adams, S.M.; Sukhbold, T.; Prieto, J.L.; Müller, T.; Bock, G.; Brown, J.S.; Dong, S.; Holoien, T.W.S.; et al. Supernova progenitors, their variability and the Type IIP Supernova ASASSN-16fq in M66. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 3347–3360. [Google Scholar]
- Bostroem, K.A.; Valenti, S.; Sand, D.J.; Andrews, J.E.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Galbany, L.; Pooley, D.; Amaro, R.C.; Smith, N.; Yang, S.; et al. Discovery and Rapid Follow-up Observations of the Unusual Type II SN 2018ivc in NGC 1068. Astrophys. J. 2020, 895, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, J.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Dimitriadis, G.; Foley, R.J.; Piro, A.L.; Rest, A.; Rojas-Bravo, C. The Type II-P Supernova 2019mhm and Constraints on its Progenitor System. Astrophys. J. 2023, 949, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Tinyanont, S.; Ridden-Harper, R.; Foley, R.J.; Morozova, V.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Dimitriadis, G.; DeMarchi, L.; Gagliano, A.; Jacobson-Galán, W.V.; Messick, A.; et al. Progenitor and close-in circumstellar medium of type II supernova 2020fqv from high-cadence photometry and ultra-rapid UV spectroscopy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 512, 2777–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias-Rosa, N.; Brennan, S.J.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Pastorello, A.; Kozyreva, A.; Lundqvist, P.; Fraser, M.; Anderson, J.P.; Cai, Y.-Z.; et al. SN 2020pvb: A Type IIn-P supernova with a precursor outburst. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 686, A13. [Google Scholar]
- Vasylyev, S.S.; Filippenko, A.V.; Vogl, C.; Brink, T.G.; Brown, P.J.; de Jaeger, T.; Matheson, T.; Gal-Yam, A.; Mazzali, P.A.; Modjaz, M.; et al. Early-time Ultraviolet Spectroscopy and Optical Follow-up Observations of the Type IIP Supernova 2021yja. Astrophys. J. 2022, 934, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maund, J.R.; Smartt, S.J. The Disappearance of the Progenitors of Supernovae 1993J and 2003gd. Science 2009, 324, 486–488. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyk, S.D. An Echo of Supernova 2008bk. Astron. J. 2013, 146, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Maund, J.R.; Reilly, E.; Mattila, S. A late-time view of the progenitors of five Type IIP supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 438, 938–958. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Lee, J.C.; Anderson, J.; Andrews, J.E.; Calzetti, D.; Bright, S.N.; Ubeda, L.; Smith, L.J.; Sabbi, E.; Grebel, E.K.; et al. LEGUS Discovery of a Light Echo Around Supernova 2012aw. Astrophys. J. 2015, 806, 195. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, M. The disappearance of the progenitor of SN 2012aw in late-time imaging. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 456, L16–L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, A.; Cherchneff, I. Condensation of dust in the ejecta of Type II-P supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 575, A95. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Han, Z. Binary stars in the new millennium. PrPNP 2024, 134, 104083. [Google Scholar]
- Hendry, M.A.; Smartt, S.J.; Maund, J.R.; Pastorello, A.; Zampieri, L.; Benetti, S.; Turatto, M.; Cappellaro, E.; Meikle, W.P.S.; Kotak, R.; et al. A study of the Type II-P supernova 2003gd in M74. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 359, 906–926. [Google Scholar]
- Pastorello, A.; Valenti, S.; Zampieri, L.; Navasardyan, H.; Taubenberger, S.; Smartt, S.J.; Arkharov, A.A.; Bärnbantner, O.; Barwig, H.; Benetti, S.; et al. SN 2005cs in M51—II. Complete evolution in the optical and the near-infrared. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 394, 2266–2282. [Google Scholar]
- Lisakov, S.M.; Dessart, L.; Hillier, J.D.; Waldman, R.; Livne, E. A study of the low-luminosity Type II-Plateau supernova 2008bk. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 466, 34–48. [Google Scholar]
- Tsvetkov, D.Y.; Pavlyuk, N.N.; Vozyakova, O.V.; Shatsky, N.I.; Tatarnikov, A.M.; Nikiforova, A.A.; Baklanov, P.V.; Blinnikov, S.I.; Ushakova, M.G.; Larionova, E.G.; et al. Type II-P Supernova SN 2018aoq in NGC 4151: Light Curves, Models, and Distance. Astron. Lett. 2021, 47, 291–306. [Google Scholar]
- Bostroem, K.A.; Dessart, L.; Hillier, D.J.; Lundquist, M.; Andrews, J.E.; Sand, D.J.; Dong, Y.; Valenti, S.; Haislip, J.; Hoang, E.T.; et al. SN 2022acko: The First Early Far-ultraviolet Spectra of a Type IIP Supernova. Astrophys. J. 2023, 953, L18. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, K.; Di Carlo, E.; Smartt, S.J.; Pastorello, A.; Tsvetkov, D.Y.; Benetti, S.; Spiro, S.; Arkharov, A.A.; Beccari, G.; Botticella, M.T.; et al. Optical and near-infrared coverage of SN 2004et: Physical parameters and comparison with other Type IIP supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 404, 981–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, B.; Edvardsson, B.; Eriksson, K.; Jørgensen, U.G.; Nordlund, Å.; Plez, B. A grid of MARCS model atmospheres for late-type stars. I. Methods and general properties. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 486, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlafly, E.F.; Finkbeiner, D.P. Measuring Reddening with Sloan Digital Sky Survey Stellar Spectra and Recalibrating SFD. Astrophys. J. 2011, 737, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Vinkó, J.; Zhai, Q.; Zhang, T.; Filippenko, A.V.; Brink, T.G.; Zheng, W.; Wyrzykowski, Ł.; Mikołajczyk, P.; et al. SN 2018zd: An unusual stellar explosion as part of the diverse Type II Supernova landscape. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 498, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, S.; Horiuchi, S.; Ashall, C. The Red Supergiant Problem: As Seen from the Local Group’s Red Supergiant Populations. Astrophys. J. 2024; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Beasor, E.R.; Smith, N.; Jencson, J.E. The Red Supergiant Progenitor Luminosity Problem. Astrophys. J. 2025, 979, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takáts, K.; Pumo, M.L.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Pastorello, A.; Pignata, G.; Paillas, E.; Zampieri, L.; Anderson, J.P.; Vinkó, J.; Benetti, S.; et al. SN 2009N: Linking normal and subluminous Type II-P SNe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 438, 368–387. [Google Scholar]
- Teja, R.S.; Singh, A.; Sahu, D.K.; Anupama, G.C.; Kumar, B.; Nayana, A.J. SN 2020jfo: A Short-plateau Type II Supernova from a Low-mass Progenitor. Astrophys. J. 2020, 930, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Ailawadhi, B.; Dastidar, R.; Misra, K.; Roy, R.; Hiramatsu, D.; Howell, D.A.; Brink, T.G.; Zheng, W.; Galbany, L.; Shahbandeh, M.; et al. Photometric and spectroscopic analysis of the Type II SN 2020jfo with a short plateau. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 519, 248–270. [Google Scholar]
- Utrobin, V.P.; Chugai, N.N. Uncommon SN 2020jfo: Ordinary explosion of 8 M⊙ red supergiant with dense wind. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 527, 6227–6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbandeh, M.; Sarangi, A.; Temim, T.; Szalai, T.; Fox, O.D.; Tinyanont, S.; Dwek, E.; Dessart, L.; Filippenko, A.V.; Brink, T.G.; et al. JWST observations of dust reservoirs in type IIP supernovae 2004et and 2017eaw. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 523, 6048–6060. [Google Scholar]
- Barbarino, C.; Dall’Ora, M.; Botticella, M.T.; Della Valle, M.; Zampieri, L.; Maund, J.R.; Pumo, M.L.; Jerkstr, A.; Benetti, S.; Elias-Rosa, N.; et al. SN 2012ec: Mass of the progenitor from PESSTO follow-up of the photospheric phase. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 448, 2312–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, S.; Sand, D.; Pastorello, A.; Graham, M.L.; Howell, D.A.; Parrent, J.T.; Tomasella, L.; Ochner, P.; Fraser, M.; Benetti, S.; et al. The first month of evolution of the slow-rising Type IIP SN 2013ej in M74. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 438, L101–L105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Sutaria, F.; Kumar, B.; Duggal, C.; Misra, K.; Brown, P.J.; Singh, M.; Dwarkadas, V.; York, D.G.; Chakraborti, S.; et al. SN 2013ej: A Type IIL Supernova with Weak Signs of Interaction. Astrophys. J. 2015, 806, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Brown, P.J.; Zampieri, L.; Pumo, M.L.; Zhang, T.; Chen, J.; Mo, J.; Zhao, X. SN 2013ej in M74: A Luminous and Fast-declining Type II-P Supernova. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhungana, G.; Kehoe, R.; Vinko, J.; Silverman, J.M.; Wheeler, J.C.; Zheng, W.; Marion, G.H.; Fox, O.D.; Akerlof, C.; Biro, B.I.; et al. Extensive Spectroscopy and Photometry of the Type IIP Supernova 2013ej. Astrophys. J. 2016, 822, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Jerkstr, A.; Valenti, S.; Sollerman, J.; Seitenzahl, I.R.; Pastorello, A.; Schulze, S.; Chen, T.-W.; Childress, M.J.; Fraser, M.; et al. 450 d of Type II SN 2013ej in optical and near-infrared. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 461, 2003–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauerhan, J.C.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Johansson, J.; Hu, M.; Fox, O.D.; Wang, L.; Graham, M.L.; Filippenko, A.V.; Shivvers, I. Asphericity, Interaction, and Dust in the Type II-P/II-L Supernova 2013EJ in Messier 74. Astrophys. J. 2017, 834, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harutyunyan, A.H.; Pfahler, P.; Pastorello, A.; Taubenberger, S.; Turatto, M.; Cappellaro, E.; Benetti, S.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Navasardyan, H.; Valenti, S.; et al. ESC supernova spectroscopy of non-ESC targets. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 488, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flinner, N.; Tucker, M.A.; Beacom, J.F.; Shappee, B.J. No UV-bright Eruptions from SN 2023ixf in GALEX Imaging 15–20 yr Before Explosion. Res. Notes Am. Astron. Soc. 2023, 7, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, D.; Tsuna, D.; Berger, E.; Itagaki, K.; Goldberg, J.A.; Gomez, S.; De, K.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Bostroem, K.A.; Brown, P.J.; et al. From Discovery to the First Month of the Type II Supernova 2023ixf: High and Variable Mass Loss in the Final Year before Explosion. Astrophys. J. 2023, 955, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Sand, D.J.; Valenti, S.; Bostroem, K.A.; Andrews, J.E.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Hoang, E.; Janzen, D.; Jencson, J.E.; Lundquist, M.; et al. A Comprehensive Optical Search for Pre-explosion Outbursts from the Quiescent Progenitor of SN 2023ixf. Astrophys. J. 2023, 957, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin, A. DOLPHOT: Stellar Photometry. Astrophysics Source Code Library, Record Ascl: 1608.013. Available online: https://ascl.net/1608.013 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Stetson, P.B. DAOPHOT: A Computer Program for Crowded-Field Stellar Photometry. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1987, 99, 191–222. [Google Scholar]
- Schechter, P.L.; Mateo, M.; Saha, A. DoPHOT, A CCD Photometry Program: Description and Tests. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1993, 105, 1342–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Makovoz, D.; Khan, I. Mosaicking with MOPEX. In Astronomical Data Analysis Software and Systems XIV; ASP Conference Series; THE ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY OF THE PACIFIC: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 347, pp. 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Makovoz, D.; Marleau, F.R. Point-Source Extraction with MOPEX. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2005, 117, 1113–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Ivezic, Z.; Nenkova, M.; Elitzur, M. DUSTY: Radiation Transport in a Dusty Environment. Astrophysics Source Code Library, Record Ascl: 9911.001. Available online: https://ascl.net/9911.001 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Kučinskas, A.; Hauschildt, P.H.; Ludwig, H.-G.; Brott, I.; Vansevixcxius, V.; Lindegren, L.; Tanabé, T.; Allard, F. Broad-band photometric colors and effective temperature calibrations for late-type giants. I. Z = 0.02. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 442, 281–308. [Google Scholar]
- Sargent, B.A.; Srinivasan, S.; Meixner, M. The Mass-loss Return from Evolved Stars to the Large Magellanic Cloud. IV. Construction and Validation of a Grid of Models for Oxygen-rich AGB Stars, Red Supergiants, and Extreme AGB Stars. Astrophys. J. 2011, 728, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, S.; Sargent, B.A.; Meixner, M. The mass-loss return from evolved stars to the Large Magellanic Cloud. V. The GRAMS carbon-star model grid. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 532, A54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvaramadze, V.V.; Menten, K.M.; Kniazev, A.Y.; Langer, N.; Mackey, J.; Kraus, A.; Meyer, D.M.-A.; Kamiński, T. IRC -10414: A bow-shock-producing red supergiant star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 437, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messineo, M.; Brown, A.G.A. A Catalog of Known Galactic K-M Stars of Class I Candidate Red Supergiants in Gaia DR2. Astron. J. 2019, 158, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Noriega-Crespo, A.; van Buren, D.; Cao, Y.; Dgani, R. A Parsec-Size Bow Shock around Betelgeuse. Astron. J. 1997, 114, 837–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, N.L.J.; Kerschbaum, F.; van Marle, A.-J.; Decin, L.; Ladjal, D.; Mayer, A.; Groenewegen, M.A.T.; van Eck, S.; Royer, P.; Ottensamer, R.; et al. A far-infrared survey of bow shocks and detached shells around AGB stars and red supergiants. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 537, A35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisakov, S.M.; Dessart, L.; Hillier, D.J.; Waldman, R.; Livne, E. Progenitors of low-luminosity Type II-Plateau supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, 3863–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiro, S.; Pastorello, A.; Pumo, M.L.; Zampieri, L.; Turatto, M.; Smartt, S.J.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Valenti, S.; Agnoletto, I.; et al. Low luminosity Type II supernovae—II. Pointing towards moderate mass precursors. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, 2873–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K. Studies of luminous stars in nearby galaxies. III. Comments on the evolution of the most massive stars in the Milky Way and the Large Magellanic Cloud. Astrophys. J. 1979, 232, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanek, C.S. On the red supergiant problem. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 493, 4945–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.; Beasor, E.R. ‘On the red supergiant problem’: A rebuttal, and a consensus on the upper mass cut-off for II-P progenitors. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 496, L142–L146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walmswell, J.J.; Eldridge, J.J. Circumstellar dust as a solution to the red supergiant supernova progenitor problem. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 419, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strotjohann, N.L.; Ofek, E.O.; Gal-Yam, A. A Bias-corrected Luminosity Function for Red Supergiant Supernova Progenitor Stars. Astrophys. J. 2024, 964, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhbold, T.; Woosley, S.E. The Compactness of Presupernova Stellar Cores. Astrophys. J. 2014, 783, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, S.; Nakamura, K.; Takiwaki, T.; Kotake, K.; Tanaka, M. The red supergiant and supernova rate problems: Implications for core-collapse supernova physics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 445, L99–L103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanek, C.S. Constraints on core collapse from the black hole mass function. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 446, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Gerke, J.R.; Kochanek, C.S.; Stanek, K.Z. The search for failed supernovae with the Large Binocular Telescope: First candidates. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, 3289–3305. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, S.M.; Kochanek, C.S.; Gerke, J.R.; Stanek, K.Z. The search for failed supernovae with the Large Binocular Telescope: Constraints from 7 yr of data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 469, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar]
- Lovegrove, E.; Woosley, S.E. Very Low Energy Supernovae from Neutrino Mass Loss. Astrophys. J. 2013, 769, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, S.M.; Kochanek, C.S.; Gerke, J.R.; Stanek, K.Z.; Dai, X. The search for failed supernovae with the Large Binocular Telescope: Confirmation of a disappearing star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 468, 4968–4981. [Google Scholar]
- Kochanek, C.S.; Neustadt, J.M.M.; Stanek, K.Z. The Search for Failed Supernovae with the Large Binocular Telescope: The Mid-infrared Counterpart to N6946-BH1. Astrophys. J. 2024, 962, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Beasor, E.R.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Smith, N.; Davies, B.; Jencson, J.E.; Pearson, J.; Sand, D.J. JWST Reveals a Luminous Infrared Source at the Position of the Failed Supernova Candidate N6946-BH1. Astrophys. J. 2024, 964, 171. [Google Scholar]
- Kashi, A.; Soker, N. Type II intermediate-luminosity optical transients (ILOTs). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 3299–3305. [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz, T.; Kamiński, T.; Melis, C.; Gromadzki, M.; Menten, K.; Su, K. OGLE-2002-BLG-360: A dusty anomaly among red nova remnants. Astron. Astrophys. 2025; submitted. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).