Red and Yellow Hypergiants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. General Properties
2.1. Observational Characteristics
| Star | SpTy | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Milky Way | |||
| AH Sco | M4-5 Ia-Iab | 3.57 | 5.52 |
| HR 5171A | K0 0-Ia | 3.70 | 5.70 |
| IRAS 17163-3907 | A3-A6Ia | 3.90 | 5.70 |
| IRC +10420 | F8Ia+-A2I | 3.93–3.81 | 5.70 |
| KW Sgr | M0I-M4Ia | 3.57 | 5.24 |
| Cep | M2Ia+ | 3.57 | 5.42 |
| MY Cep | M7-M7.5 | 3.45 | 5.48 |
| NML Cyg | M6Ia | 3.49 | 5.50 |
| Cas | F8pIa-K0pIa | 3.86–3.56 | 5.48 |
| RSG C1 1–13 | M3/K2 | 3.71 | 5.48 |
| RSG C2 2–49 | K4 | 3.60 | 5.60 |
| RW Cep | K0-K2 | 3.71 | 5.48 |
| S Per | M4Ia | 3.53 | 5.30 |
| UY Sct | M2-M4Ia-Iab | 3.53 | 5.53 |
| V602 Car | M3 Ia-Iab | 3.54 | 5.14 |
| VX Sgr | M4Ia-(M8) | 3.49 | 5.40 |
| VY CMa | M4Ia+ | 3.54 | 5.43 |
| LMC | |||
| HD 269953 | G0 | 3.78 | 5.70 |
| MG 73–59 | K0I | 3.66 | 5.60 |
| Sk-69-148 | K0I | 3.66 | 5.60 |
| WOH G64 | M-G: | 3.70–3.51 | 5.65 |
| M31/33 | |||
| M31-00444453 | F0Ia | 3.87 | 5.60 |
| M33 N093351 | F0Ia | 3.87 | 5.40 |
| M33 N125093 | F0-F2 | 3.85 | 5.50 |
| Var A | F0:-M4: | 3.88–3.54 | 5.70 |
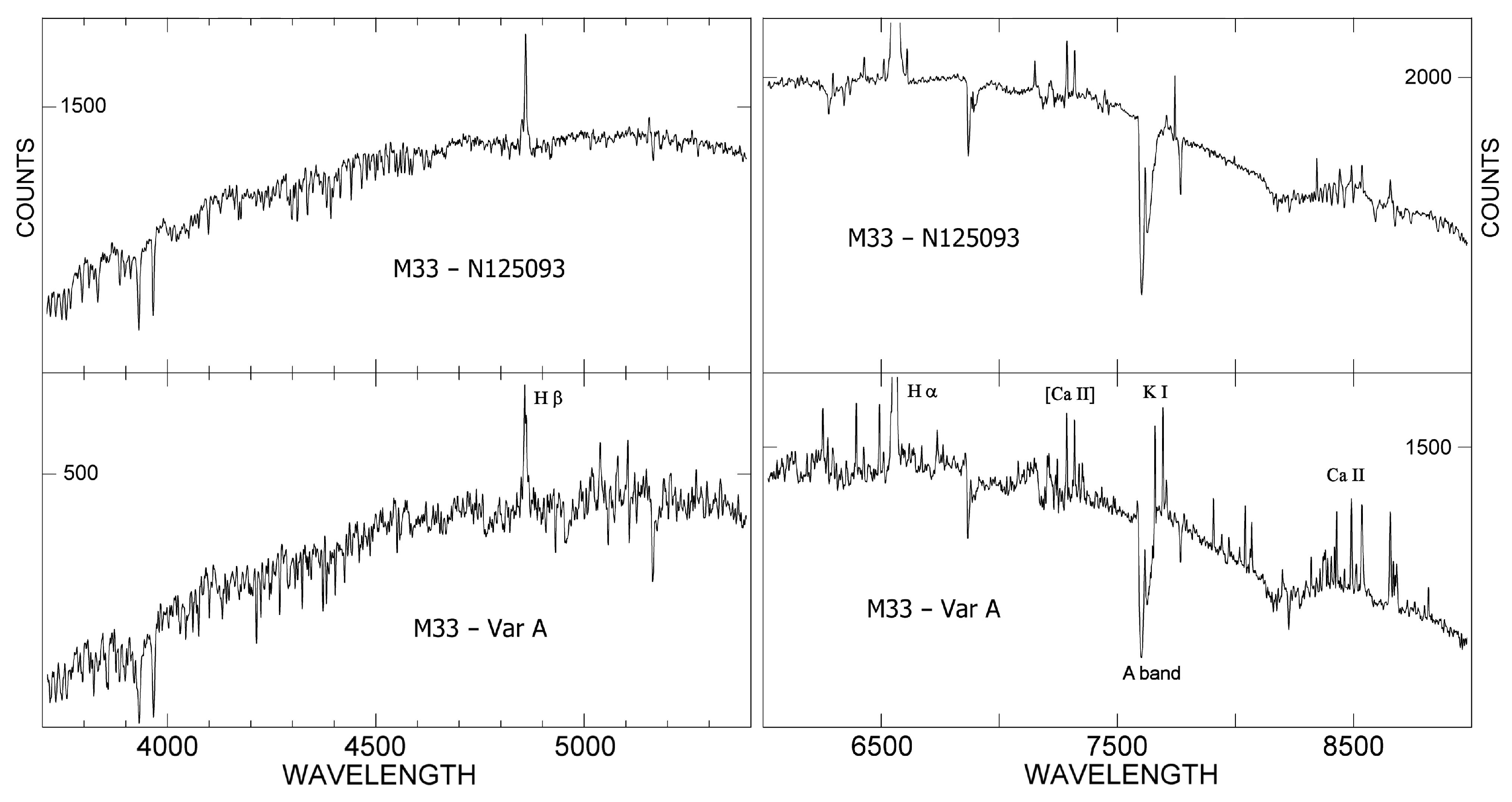

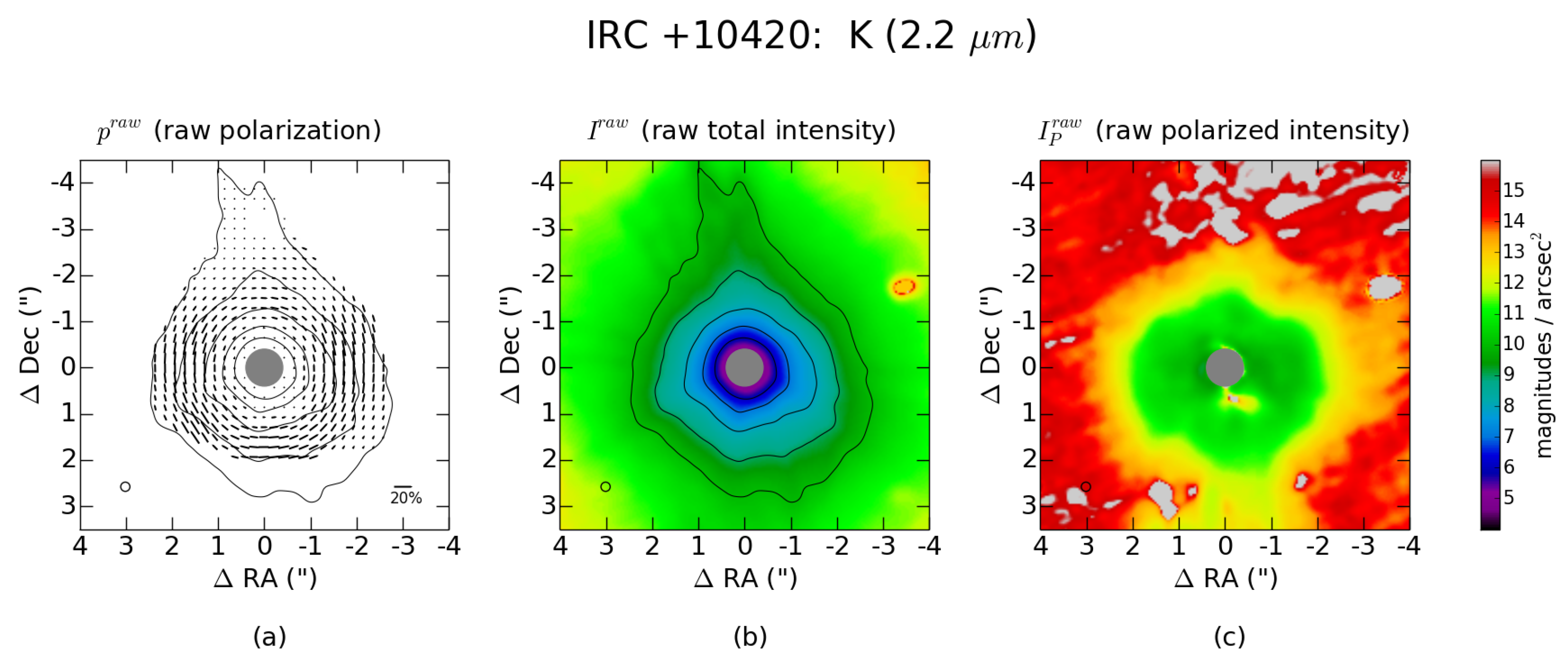
2.2. Evolution
2.3. High Spatial Resolution Observations
2.4. Extreme Mass Loss and Massive Outflows
3. Transits on the H-R Diagram and Post RSG Evolution
4. Summary
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HRD | Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram, H-R Diagram |
| RSG | red supergiant |
| SED | spectral energy distribution |
| VLBI | Very Long Baseline Interferometry |
| AU | Astronomical Unit |
References
- Keenan, P.C. Luminosities of the M-Type Variables of Small Range. Astrophys. J. 1942, 95, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feast, M.W.; Thackeray, A.D. Red supergiants in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1956, 116, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jager, C. The yellow hypergiants. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 1998, 8, 145–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, P.C. Classification of supergiants of types G, K, and M. Contrib. Kitt Peak Natl. Obs. 1971, 554, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K. Studies of luminous stars in nearby galaxies. III. Comments on the evolution of the most massive stars in the Milky Way and the Large Magellanic Cloud. Astrophys. J. 1979, 232, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M. Studies of luminous stars in nearby galaxies. I. Supergiants and O stars in the Milky Way. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1978, 38, 309–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, D.; Humphreys, R.M.; Jones, T.J.; Marengo, M.; Gehrz, R.D.; Helton, L.A.; Hoffmann, W.F.; Skemer, A.J.; Hinz, P.M. Searching for Cool Dust in the Mid-to-Far Infrared: The Mass-Loss Histories of the Hypergiants μ Cep, VY CMa, IRC +10420, and ρ Cas. Astron. J. 2016, 151, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.S.; Humphreys, R.M.; Jones, T.J. Luminous and Variable Stars in M31 and M33. III. The Yellow and Red Supergiants and Post-red Supergiant Evolution. Astrophys. J. 2016, 825, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.S.; Jones, T.J.; Humphreys, R.M.; Ertel, S.; Hinz, P.M.; Hoffmann, W.F.; Stone, J.; Spalding, E.; Vaz, A. Thermal Emission in the Southwest Clump of VY CMa. Astron. J. 2019, 157, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K.; Gehrz, R.D.; Schuster, M.T.; Krautter, J. The Asymmetric Nebula Surrounding the Extreme Red Supergiant Vy Canis Majoris. Astron. J. 2001, 121, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K.; Ruch, G.; Wallerstein, G. High-Resolution, Long-Slit Spectroscopy of VY Canis Majoris: The Evidence for Localized High Mass Loss Events. Astron. J. 2005, 129, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Helton, L.A.; Jones, T.J. The Three-Dimensional Morphology of VY Canis Majoris. I. The Kinematics of the Ejecta. Astron. J. 2007, 133, 2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Smith, N.; Davidson, K.; Jones, T.J.; Gehrz, R.T.; Mason, C.G.; Hayward, T.L.; Houck, J.R.; Krautter, J. HST and Infrared Images of the Circumstellar Environment of the Cool Hypergiant IRC +10420. Astron. J. 1997, 114, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiffany, C.; Humphreys, R.M.; Jones, T.J.; Davidson, K. The Morphology of IRC +10420’s Circumstellar Ejecta. Astron. J. 2010, 140, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, M.T.; Marengo, M.; Hora, J.L.; Fazio, G.G.; Humphreys, R.M.; Gehrz, R.D.; Hinz, P.M.; Kenworthy, M.A.; Hoffmann, W.F. Imaging the Cool Hypergiant NML Cygni’s Dusty Circumstellar Envelope with Adaptive Optics. Astrophys. J. 2009, 699, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Edwards, J.L.; Humphreys, R.M.; Ziurys, L.M. Molecules and Outflows in NML Cygni: New Insights from a 1 mm Spectral Line Survey. Astrophys. J. 2021, 920, L38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudmaijer, R.D.; Koumpia, E. Multiple shell ejections on a 100 yr timescale from a massive yellow hypergiant. Orig. Outflows Evolved Stars 2022, 366, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K.; Smith, N. Crossing the Yellow Void: Spatially Resolved Spectroscopy of the Post-Red Supergiant IRC +10420 and Its Circumstellar Ejecta. Astron. J. 2002, 124, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudmaijer, R.D. High resolution spectroscopy of the post-red supergiant IRC +10420: I. The data. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1998, 129, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Helmel, G.; Jones, T.J.; Gordon, M.S. Exploring the Mass-loss Histories of the Red Supergiants. Astron. J. 2020, 160, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K.; Grammer, S.; Kneeland, N.; Martin, J.C.; Weis, K.; Burggraf, B. Luminous and Variable Stars in M31 and M33. I. The Warm Hypergiants and Post-red Supergiant Evolution. Astrophys. J. 2013, 773, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekström, S.; Georgy, C.; Eggenberger, P.; Meynet, G.; Mowlavi, N.; Wyttenbach, A.; Granada, A.; Decressin, T.; Hirschi, R.; Frischknecht, U.; et al. Grids of stellar models with rotation. I. Models from 0.8 to 120 Modot at solar metallicity (Z = 0.014). Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 537, A146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.S.; Humphreys, R.M. Red Supergiants, Yellow Hypergiants, and Post-RSG Evolution. Galaxies 2019, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, K. Radiation-Driven Stellar Eruptions. Galaxies 2020, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.J.; Humphreys, R.M.; Gehrz, R.D.; Lawrence, G.F.; Zickgraf, F.-J.; Moseley, H.; Casey, S.; Glaccum, W.J.; Koch, C.J.; Pina, R.; et al. IRC +10420: A Cool Hypergiant near the Top of the H-R Diagram. Astrophys. J. 1993, 411, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Jones, T.J.; Polomski, E.; Koppelman, M.; Helton, A.; McQuinn, K.; Gehrz, R.D.; Woodward, C.E.; Wagner, R.M.; Gordon, K.; et al. M33’s Variable A: A Hypergiant Star More Than 35 YEARS in Eruption. Astron. J. 2006, 131, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Sanchez, G.; Kalitsounaki, M.; de Wit, S.; Antoniadis, K.; Bonanos, A.Z.; Zapartas, E.; Boutsia, K.; Christodoulou, E.; Maravelias, G.; Soszynski, I.; et al. The dramatic transition of the extreme Red Supergiant WOH G64 to a Yellow Hypergiant. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.19329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smartt, S.J.; Eldridge, J.J.; Crockett, R.M.; Maund, J.R. The death of massive stars—I. Observational constraints on the progenitors of Type II-P supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 395, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasor, E.R.; Davies, B. The evolution of red supergiants to supernova in NGC 2100. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 463, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasor, E.R.; Smith, N.; Jencson, J.E. The red supergiant progenitor luminosity problem. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.14027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walmswell, J.J.; Eldridge, J.J. Circumstellar dust as a solution to the red supergiant supernova progenitor problem. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 419, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, C.D.; Foley, R.J. The dusty progenitor star of the Type II supernova 2017eaw. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 481, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasor, E.R.; Davies, B.; Smith, N.; Bastian, N. Discrepancies in the ages of young star clusters; evidence for mergers? MNRAS 2019, 486, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesneau, O.; Meilland, A.; Chapellier, E.; Millour, F.; van Genderen, A.M.; Nazé, Y.; Smith, N.; Spang, A.; Smoker, J.V.; Dessart, L.; et al. The yellow hypergiant HR 5171 A: Resolving a massive interacting binary in the common envelope phase. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 563, A71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siódmiak, N.; Meixner, M.; Ueta, T.; Sugerman, B.E.K.; Van de Steene, G.C.; Szczerba, R. Hubble Space Telescope Snapshot Survey of Post-AGB Objects. Astrophys. J. 2008, 677, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumpia, E.; Oudmaijer, R.D.; Graham, V.; Banyard, G.; Black, J.H.; Wichittanakom, C.; Ababakr, K.M.; de Wit, W.-J.; Millour, F.; Lagadec, E.; et al. Optical and near-infrared observations of the Fried Egg Nebula. Multiple shell ejections on a 100 yr timescale from a massive yellow hypergiant. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 635, A183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W.F.; Fazio, G.G.; Shivanandan, K.; Hora, J.L.; Deutsch, L.K. MIRAC: A mid-infrared array camera for astronomy. Proc. SPIE 1993, 1946, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.J.; Shenoy, D.; Humphreys, R. The Recent Mass Loss History of the Hypergiant RW Cep. Res. Notes Am. Astron. Soc. 2023, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, D.P.; Jones, T.J.; Humphreys, R.M.; Marengo, M.; Leisenring, J.M.; Nelson, M.J.; Wilson, J.C.; Skrutskie, M.F.; Hinz, P.M.; Hoffmann, W.F.; et al. Adaptive Optics Imaging of VY Canis Majoris at 2–5 μm with LBT/LMIRCam. Astron. J. 2013, 146, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittkowski, M.; Chiavassa, A.; Baron, F.; Freytag, B.; Höfner, S.; Paladini, C. Investigating mass loss from RSG and AGB stars using the new VLTI-MATISSE imaging instrument. In Proceedings of the 20.5th Cambridge Workshop on Cool Stars, Stellar Systems, and the Sun (CS20.5), Online, 2–4 March 2021; Volume 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnaka, K.; Hofmann, K.-H.; Weigelt, G.; van Loon, J.T.; Schertl, D.; Goldman, S.R. Imaging the innermost circumstellar environment of the red supergiant WOH G64 in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 691, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scicluna, P.; Siebenmorgen, R.; Wesson, R.; Blommaert, J.A.D.L.; Kasper, M.; Voshchinnikov, N.V.; Wolf, S. Large dust grains in the wind of VY Canis Majoris. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 584, L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittkowski, M.; Hauschildt, P.H.; Arroyo-Torres, B.; Marcaide, J.M. Fundamental properties and atmospheric structure of the red supergiant VY Canis Majoris based on VLTI/AMBER spectro-interferometry. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 540, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumpia, E.; Oudmaijer, R.D.; de Wit, W.-J.; Mérand, A.; Black, J.H.; Ababakr, K.M. Tracing a decade of activity towards a yellow hypergiant. The spectral and spatial morphology of IRC +10420 at au scales. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 515, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloppenborg, B.; van Belle, G. Optical Interferometry of Giants and Supergiants. In Giants of Eclipse: Theζ Aurigae Stars and Other Binary Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 408, pp. 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, H.M.; Benson, J.A.; Carleton, N.P.; Coldwell, C.; Lacasse, M.G.; Nisenson, P.; Panasyuk, A.; Papaliolios, C.; Pearlman, M.R.; Reasenberg, R.D.; et al. First 2.2 micron Results From the IOTA Interferometer. Astron. J. 1995, 109, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragland, S.; Traub, W.A.; Berger, J.-P.; Danchi, W.C.; Monnier, J.D.; Willson, L.A.; Carleton, N.P.; Lacasse, M.G.; Millan-Gabet, R.; Pedretti, E.; et al. First Surface-resolved Results with the Infrared Optical Telescope Array Imaging Interferometer: Detection of Asymmetries in Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars. Astrophys. J. 2006, 652, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anugu, N.; Gies, D.R.; Roettenbacher, R.M.; Monnier, J.D.; Montargés, M.; Mérand, A.; Baron, F.; Schaefer, G.H.; Shepard, K.A.; Kraus, S.; et al. Time Evolution Images of the Hypergiant RW Cephei during the Rebrightening Phase Following the Great Dimming. Astrophys. J. 2024, 973, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, R.P.; Baron, F.R.; Monnier, J.D.; Paladini, C.; Anderson, M.D.; Martinez, A.O.; Schaefer, G.H.; Che, X.; Chiavassa, A.; Connelley, M.S.; et al. Long Term Evolution of Surface Features on the Red Supergiant AZ Cyg. Astrophys. J. 2021, 919, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anugu, N.; Baron, F.; Monnier, J.D.; Gies, D.R.; Roettenbacher, R.M.; Schaefer, G.H.; Montargès, M.; Kraus, S.; Le Bouquin, J.-B.; Anderson, M.D.; et al. CHARA Near-infrared Imaging of the Yellow Hypergiant Star ρ Cassiopeiae: Convection Cells and Circumstellar Envelope. Astrophys. J. 2024, 974, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, T. Massive dust clumps in the envelope of the red supergiant VY Canis Majoris. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 627, A114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beck, E.; Vlemmings, W.; Muller, S.; Black, J.H.; O’gorman, E.; Richards, A.M.S.; Baudry, A.; Maercker, M.; Decin, L.; Humphreys, E.M. ALMA observations of TiO2 around VY Canis Majoris. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 580, A36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Richards, A.M.S.; Humphreys, R.M.; Richards, A.M.S.; Humphreys, R.M.; Humphreys, R.M.; Decin, L.; Decin, L.; Ziurys, L.M.; Ziurys, L.M. ALMA Reveals Hidden Morphologies in the Molecular Envelope of VY Canis Majoris. Astrophys. J. 2023, 954, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallström, S.H.J.; Lagadec, E.; Muller, S.; Black, J.H.; Cox, N.L.J.; Galván-Madrid, R.; Justtanont1, K.; Longmore, S.; Olofsson1, H.; Oudmaijer, R.D.; et al. ALMA Compact Array observations of the Fried Egg nebula. Evidence for large-scale asymmetric mass-loss from the yellow hypergiant IRAS 17163-3907. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 597, A99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, S.; Lim, J.; Kwok, S.; Muthu, C. Probing the Mass-Loss History of the Yellow Hypergiant IRC +10420. Astrophys. J. 2009, 697, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decin, L.; Richards, A.M.S.; Millar, T.J.; Baudry, A.; De Beck, E.; Homan, W.; Smith, N.; Van de Sande, M.; Walsh, C. ALMA-resolved salt emission traces the chemical footprint and inner wind morphology of VY Canis Majoris. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 592, A76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, L.; Kemball, A.; Jonas, J. Simultaneous VLBA polarimetric observations of the v = {1,2} J = 1–0 and v = 1, J = 2–1 SiO maser emission towards VY CMa: Maser morphology and pumping. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 436, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, A.M.S.; Yates, J.A.; Cohen, R.J. MERLIN observations of water maser proper motions in VY Canis Majoris. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 299, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakawa, K.; Yates, J.A.; Richards, A.M.S.; Cohen, R.J. The radially expanding molecular outflow of VX Sagittarii. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 344, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- tat Wong, K.; Lim, J. Dense Molecular Clumps in the Envelope of the Yellow Hypergiant IRC +10420. Astrophys. J. 2017, 851, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Reid, M.J.; Menten, K.M.; Zheng, X.W. Distance and Kinematics of the Red Hypergiant VY CMa: Very Long Baseline Array and Very Large Array Astrometry. Astrophys. J. 2012, 744, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.K.; Hirota, T.; Honma, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Bushimata, T.; Imai, H.; Iwadate, K.; Jike, T.; Kameno, S.; Kameya, O.; et al. Distance to VY Canis Majoris with VERA. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2008, 60, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shen, Z.-Q.; Xu, Y. Measuring the Distance of VX Sagittarii with SiO Maser Proper Motions. Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 7, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Bonanos, A.Z.; Jiang, B.; Zapartas, E.; Gao, J.; Ren, Y.; Lam, M.I.; Wang, T.; Maravelias, G.; Gavras, P.; et al. Evolved massive stars at low-metallicity. V. Mass-loss rate of red supergiant stars in the Small Magellanic Cloud. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 676, A84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Yang, M.; Gao, J.; Chen, B.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, B. Mass-loss Rate of Highly Evolved Stars in the Magellanic Clouds. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2024, 275, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, E.; Vlemmings, W.; Richards, A.M.S.; Baudry, A.; Beck, E.D.; Decin, L.; Harper, G.M.; Humphreys, E.M.; Kervella, P.; Khouri, T.; et al. ALMA observations of anisotropic dust mass loss in the inner circumstellar environment of the red supergiant VY Canis Majoris. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 573, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Richards, A.M.S.; Davidson, K.; Singh, A.P.; Decin, L.; Ziurys, L.M. The Hidden Clumps in VY CMa Uncovered by the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array. Astron. J. 2024, 167, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.R.; Whiteoak, J.B.; Hughes, S.M.G.; Bessell, M.S.; Gardner, F.F.; Hyland, A.R. OH/IR Stars in the Magellanic Clouds. Astrophys. J. 1992, 397, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatzel, W.; Kraus, M. Instabilities in the yellow hypergiant domain. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 529, 4947–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quataert, E.; Shiode, J. Wave-driven mass loss in the last year of stellar evolution: Setting the stage for the most luminous core-collapse supernovae. MNRAS 2012, 423, L92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Fuller, J. A Diversity of Wave-driven Presupernova Outbursts. Astrophys. J. 2021, 906, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Jones, T.J. Episodic Gaseous Outflows and Mass Loss from Red Supergiants. Astron. J. 2022, 163, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervella, P.; Perrin, G.; Chiavassa, A.; Ridgway, S.T.; Cami, J.; Haubois, X.; Verhoelst, T. The close circumstellar environment of Betelgeuse. II. Diffraction-limited spectro-imaging from 7.76 to 19.50 μm with VLT/VISIR. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 531, A117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadlovský, D.; Granzer, T.; Weber, M.; Kravchenko, K.; Krtička, J.; Dupree, A.K.; Chiavassa, A.; Strassmeier, K.G.; Poppenhäger, K. The Great Dimming of Betelgeuse: The photosphere as revealed by tomography over the past 15 yr. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 685, A124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Ariste, A.; Georgiev, S.; Mathias, P.; Lèbre, A.; Wavasseur, M.; Josselin, E.; Konstantinova-Antova, R.; Roudier, T. Three-dimensional imaging of convective cells in the photosphere of Betelgeuse. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 661, A91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.J.; Humphreys, R.M.; Helton, L.A.; Gui, C.; Huang, X. The Three-Dimensional Morphology of VY Canis Majoris. II. Polarimetry and the Line-of-Sight Distribution of the Ejecta. Astron. J. 2007, 133, 2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emslie, A.G.; Dennis, B.R.; Shih, A.Y.; Chamberlin, P.C.; Mewaldt, R.A.; Moore, C.S.; Share, G.H.; Vourlidas, A.; Welsch, B.T. Global Energetics of Thirty-Eight Large Solar Eruptive Events. Astrophys. J. 2012, 759, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montez, R.; Kastner, J.H.; Humphreys, R.M.; Turok, R.L.; Davidson, K. Constraints on the Surface Magnetic Fields and Age of a Cool Hypergiant: Xmm-Newton X-ray Observations of VY CMa. Astrophys. J. 2015, 800, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevon, J.; Millour, F.; Cruzalèbes, P.; Paladini, C.; Scicluna, P.; Matter, A.; Chiavassa, A.; Montargès, M.; Cannon, E.; Allouche, F.; et al. Images of Betelgeuse with VLTI/MATISSE across the Great Dimming. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 527, L88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, V.L.; Drake, J.J.; Patnaude, D. Non-detection of Betelgeuse in X-rays. In The Astronomer’s Telegram; SAO Astrophysics Data System: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; p. 13501. [Google Scholar]
- Plachinda, S.; Butkovskaya, V.; Shulyak, D.; Pankov, N.; Tsymbal, V. Magnetic fields of red giants and supergiants: A review of spectropolarimetric observations. Acta Astrophys. Taurica 2022, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlemmings, W.H.T.; Diamond, P.J.; van Langevelde, H.J. Circular polarization of water masers in the circumstellar envelopes of late type stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 394, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlemmings, W.H.T.; van Langevelde, H.J.; Diamond, P.J. The magnetic field around late-type stars revealed by the circumstellar H2O masers. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 434, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlemmings, W.H.T.; Khouri, T.; Martí-Vidal, I.; Tafoya1, D.; Baudry, A.; Etoka, S.; Humphreys, E.M.L.; Jones, T.J.; Kemball, A.; O’Gorman, E.; et al. Magnetically aligned dust and SiO maser polarisation in the envelope of the red supergiant VY Canis Majoris. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 603, A92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, B.-G.; Lazarian, A.; Vaillancourt, J.E. Interstellar Dust Grain Alignment. ARAA 2015, 53, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurière, M.; Donati, J.-F.; Konstantinova-Antova, R.; Perrin, G.; Petit, P.; Roudier, T. The magnetic field of Betelgeuse: A local dynamo from giant convection cells? Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 516, L2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidelman, W.P.; McKellar, A. Double Lines in the Spectrum of ρ Cassiopeiae. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1957, 69, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyarchuk, A.A.; Boyarchuk, M.E.; Petrov, P.P. Spectral variability of the supergiant rho CAS in 1985–1986. Tartu Astrofuus. Obs. Teated 1998, 92, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Lobel, A.; Dupree, A.K.; Stefanik, R.P.; Torres, G.; Israelian, G.; Morrison, N.; de Jager, C.; Nieuwenhuijzen, H.; Ilyin, I.; Musaev, F. High-Resolution Spectroscopy of the Yellow Hypergiant ρ Cassiopeiae from 1993 through the Outburst of 2000–2001. Astrophys. J. 2003, 583, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Jones, T.J.; Gehrz, R.D. The Enigmatic Object Variable A in M33. Astron. J. 1987, 94, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, J.H.; Frogel, J.A.; Schwering, P.B.W. Two Supergiants in the Large Magellanic Cloud with Thick Dust Shells. Astrophys. J. 1986, 302, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerlund, B.E.; Olander, N.; Hedin, B. Supergiant and giant M type stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1981, 43, 267–295. [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Jones, T.J.; Martin, J.C. Yellow Supergiants and Post-red Supergiant Evolution in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Astron. J. 2023, 166, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn-Wallenstein, T.Z.; Levesque, E.M.; Davenport, J.R.A.; Neugent, K.F.; Morris, B.M.; Bostroem, K.A. The Properties of Fast Yellow Pulsating Supergiants: FYPS Point the Way to Missing Red Supergiants. Astrophys. J. 2022, 940, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn-Wallenstein, T.Z.; Levesque, E.M.; Neugent, K.F.; Davenport, J.R.A.; Morris, B.M.; Gootkin, K. Short-term Variability of Evolved Massive Stars with TESS. II. A New Class of Cool, Pulsating Supergiants. Astrophys. J. 2020, 902, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmeister, C. Mitteilungen über neuentdeckte Veränderliche Sterne. Astron. Nachrichten 1964, 288, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, E.W.; Liller, W. Photometric histories of six infrared objects and three highly reddened blue supergiants. Astrophys. J. 1978, 225, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Strecker, D.W.; Murdock, T.L.; Low, F.J. IRC +10420—Another Eta Carinae? Astrophys. J. 1973, 179, L49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudmaijer, R.D.; Geballe, T.R.; Waters, L.B.F.M.; Sahu, K.C. Discovery of near-infrared hydrogen line emission in the peculiar F8 hypergiant IRC +10420. Astron. Astrophys. 1994, 281, L33. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, B.; Oudmaijer, R.D.; Sahu, K.C. Integral-Field Spectroscopy of the Post-Red Supergiant IRC +10420: Evidence for an Axisymmetric Wind. Astrophys. J. 2007, 671, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shenoy, D.P.; Jones, T.J.; Packham, C.; Lopez-Rodriguez, E. Probing Hypergiant Mass Loss with Adaptive Optics Imaging and Polarimetry in the Infrared: MMT-Pol and LMIRCam Observations of IRC +10420 and VY Canis Majoris. Astron. J. 2015, 150, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, M.; Boyer, M.; Arendt, R.G.; Larsson, J.; Fransson, C.; Rest, A.; Ravi, A.P.; Park, S.; Cigan, P.; Temim, T.; et al. Deep JWST/NIRCam imaging of Supernova 1987A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 532, 3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotts, A.P.; Heathcote, S.R. Velocity structure of the ring nebula around supernova 1987A. Nature 1991, 350, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chita, S.M.; Langer, N.; van Marle, A.J.; García-Segura, G.; Heger, A. Multiple ring nebulae around blue supergiants. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 488, L37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akashi, M.; Sabach, E.; Yogev, O.; Soker, N. Forming equatorial rings around dying stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 453, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Podsiadlowski, P. The Progenitor of SN 1987A. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1992, 104, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, T. Red and Yellow Hypergiants. Galaxies 2025, 13, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13020043
Jones T. Red and Yellow Hypergiants. Galaxies. 2025; 13(2):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13020043
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Terry. 2025. "Red and Yellow Hypergiants" Galaxies 13, no. 2: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13020043
APA StyleJones, T. (2025). Red and Yellow Hypergiants. Galaxies, 13(2), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13020043






