Betelgeuse, the Prototypical Red Supergiant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Stellar Parameters
2.1. Ultraviolet Surface Images
2.2. The Distance Tension
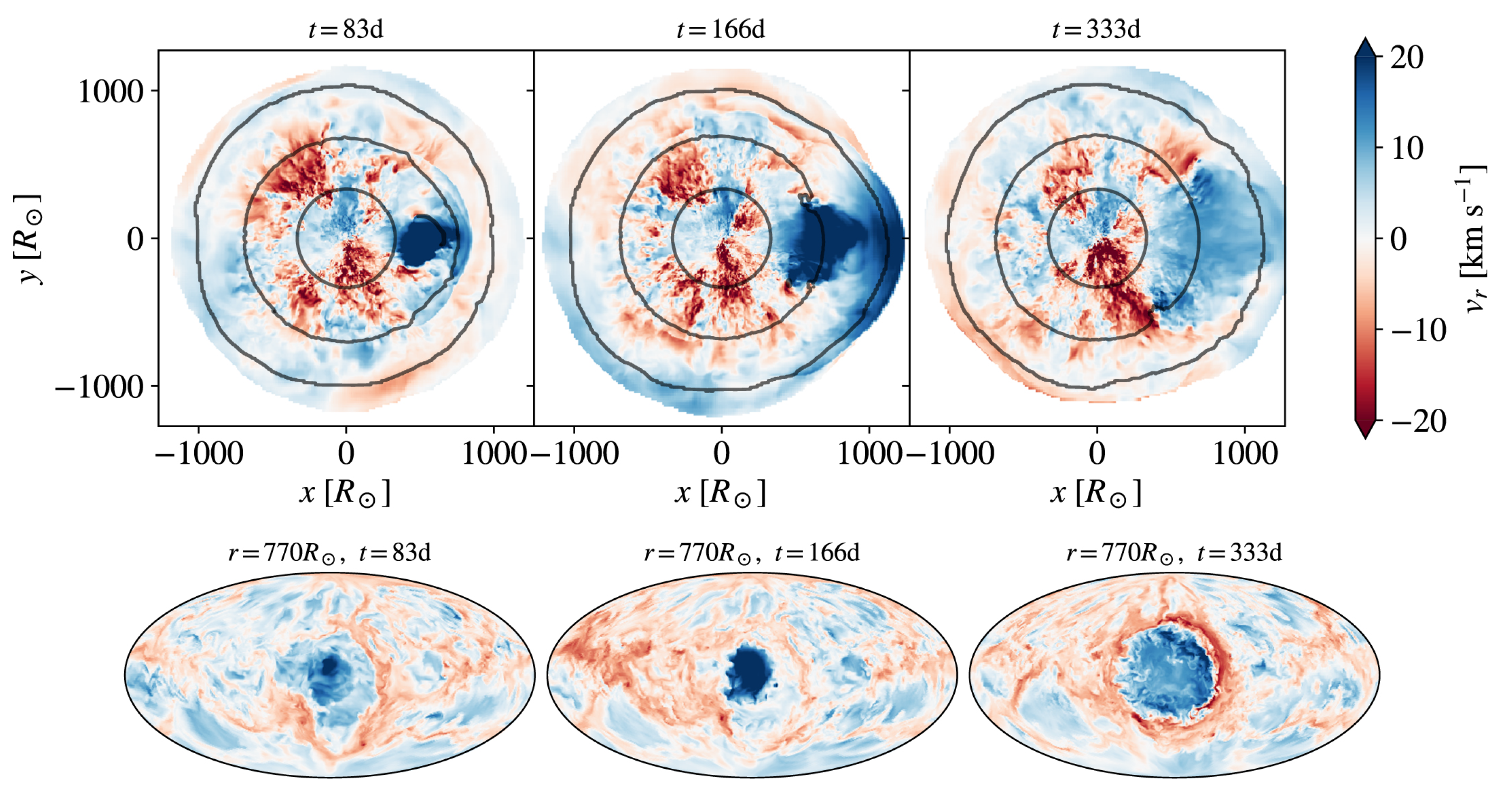
2.3. The Controversial Rotation Velocity
2.4. A Dying Star Hiding Its Age
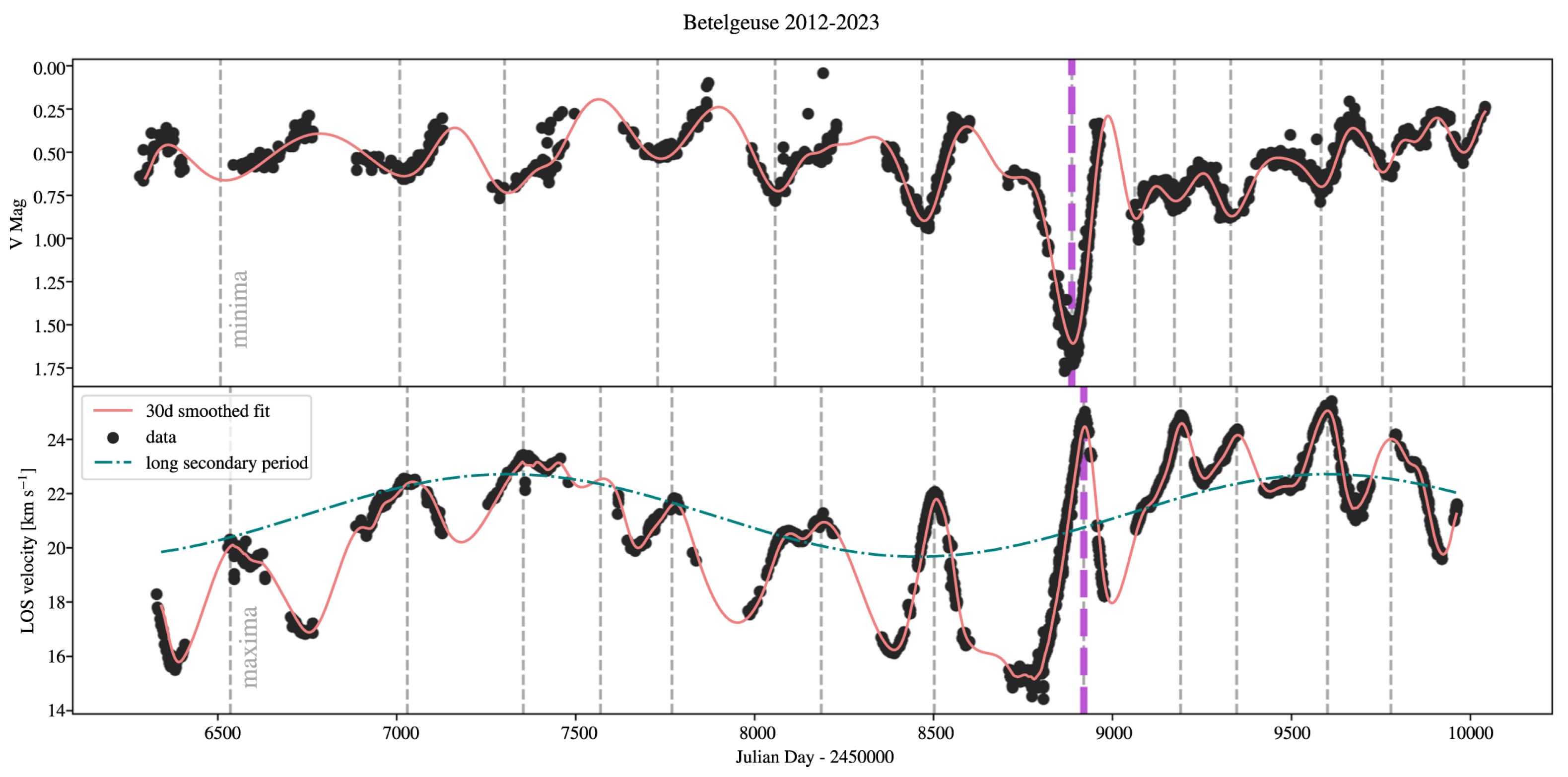
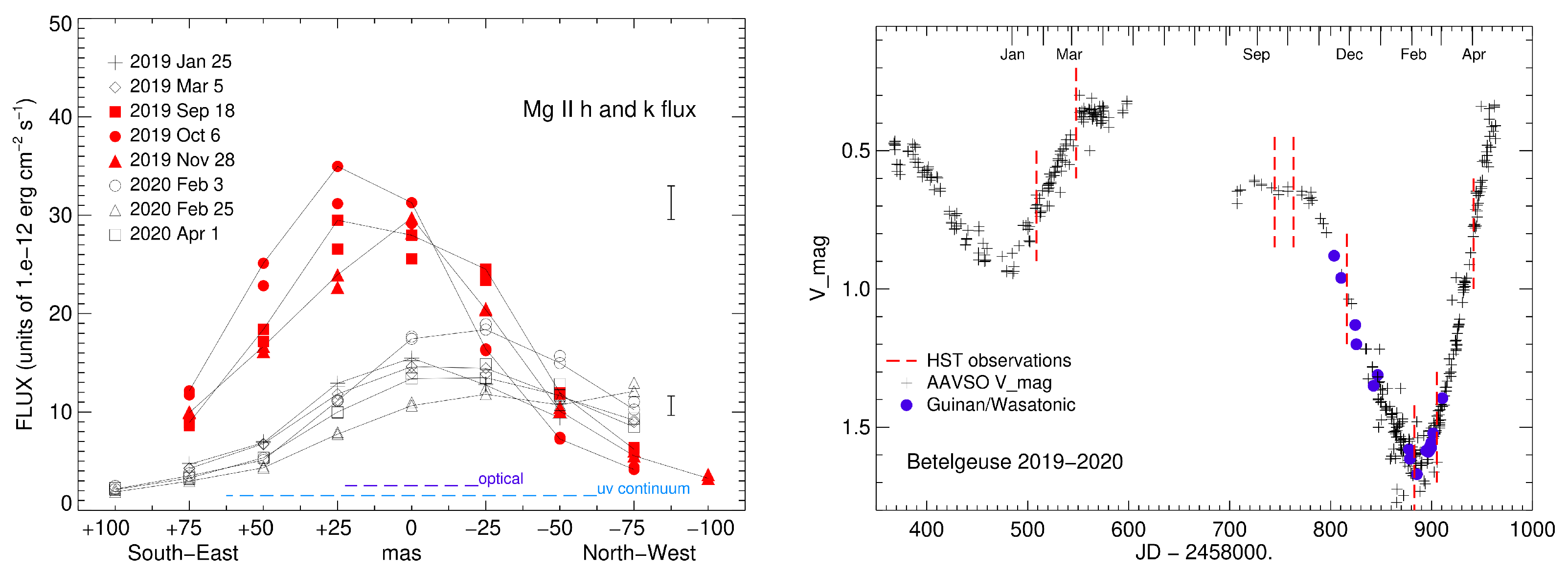
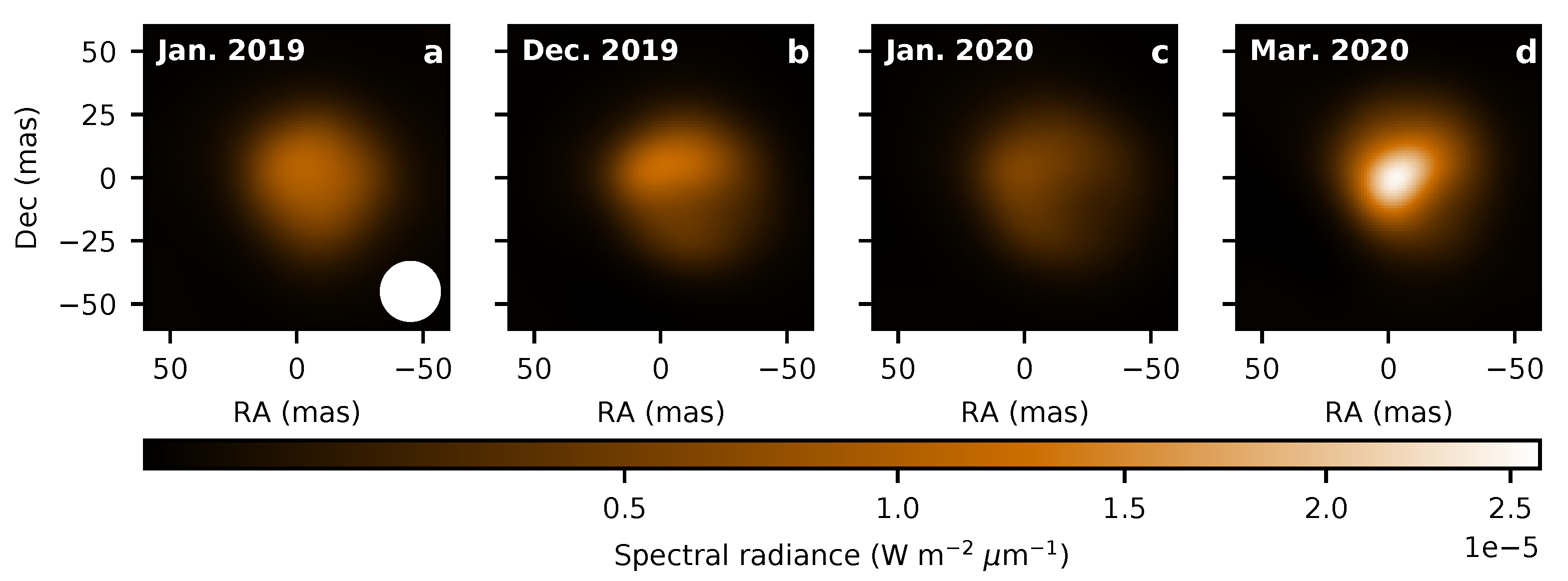
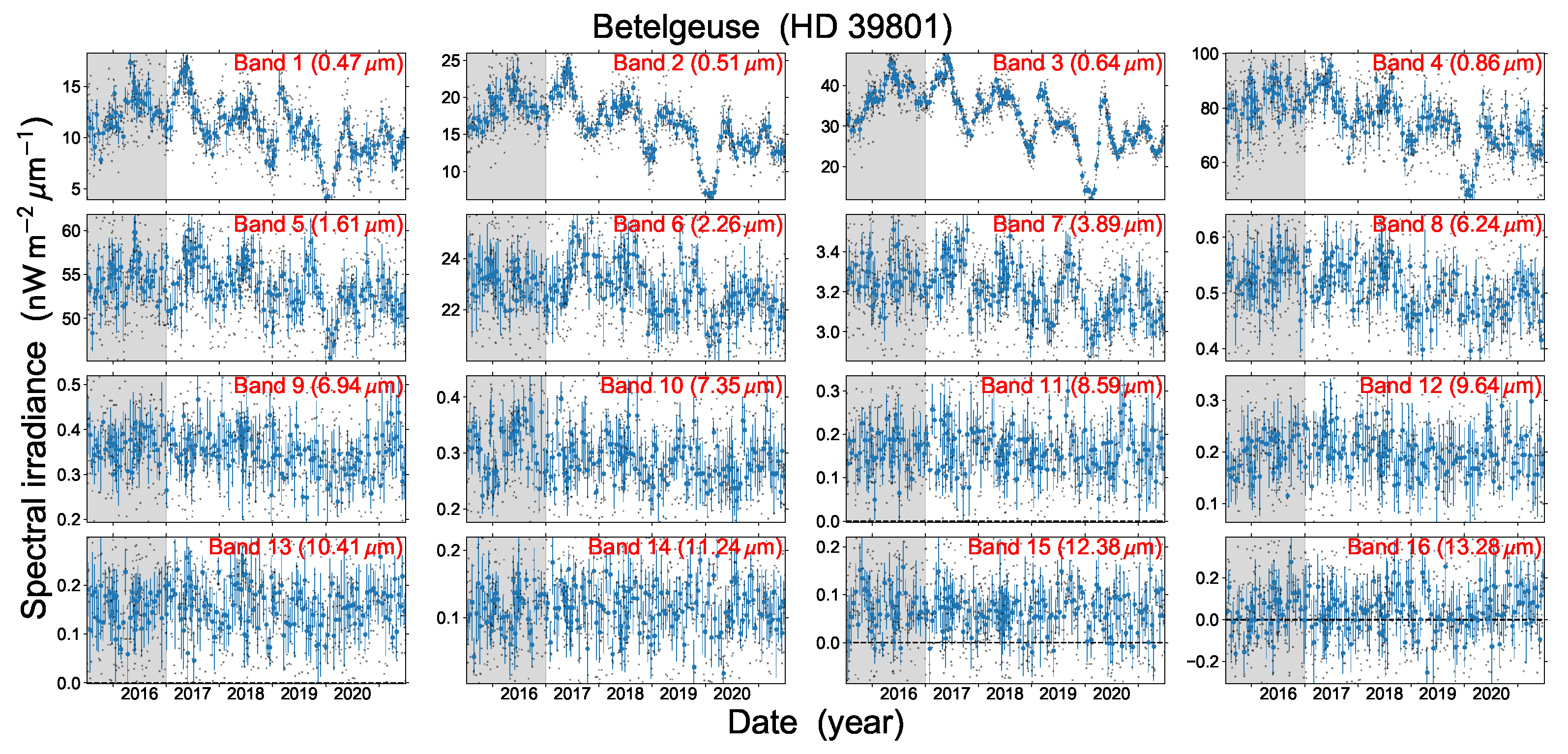
3. The Great Dimming
4. Long Secondary Period
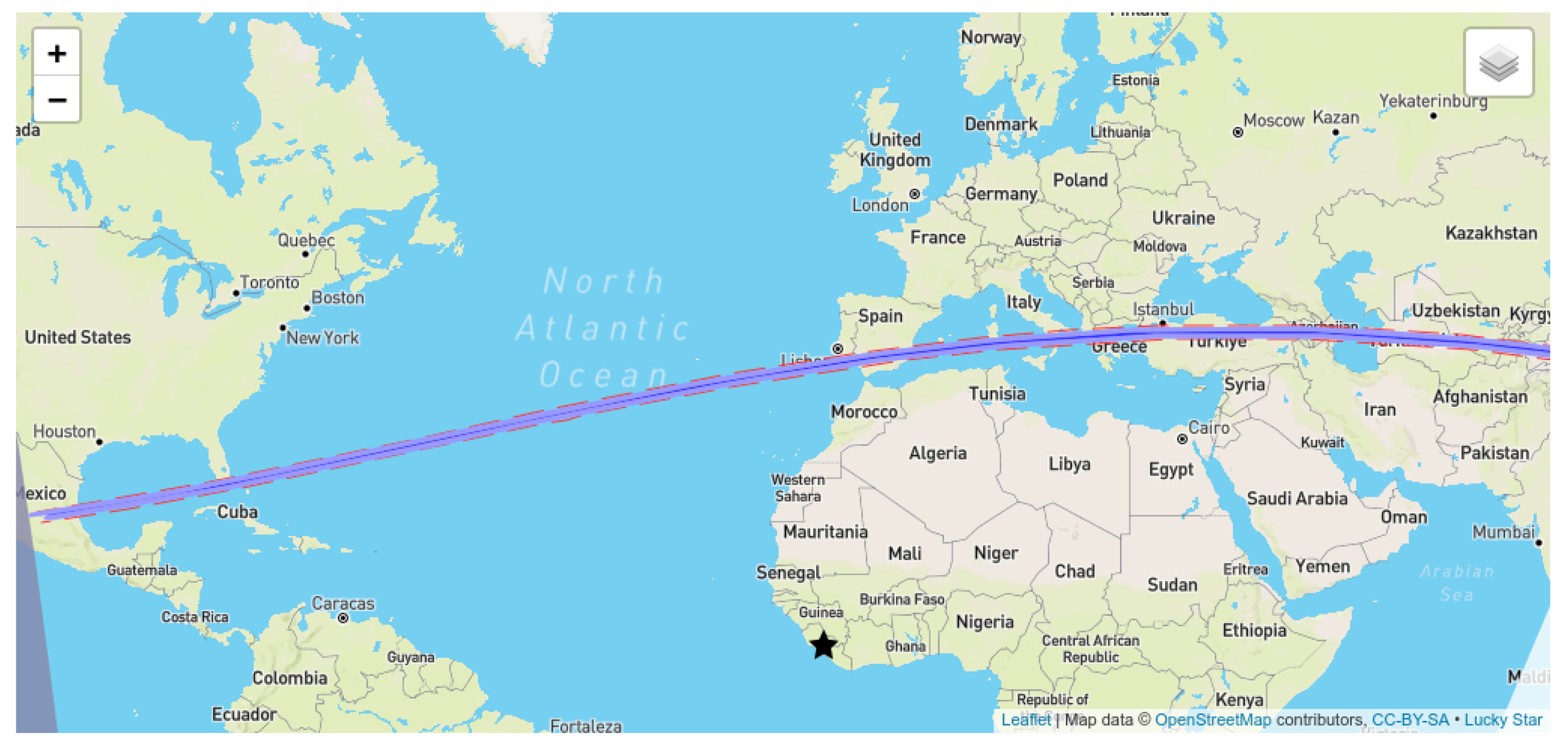
5. The Occultation by Solar System Asteroid 319 Leona in 2023
6. Implications for Other Supergiant Stars
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rappenglück, M. The anthropoid in the sky: Does a 32,000-year old ivory plate show the constellation Orion combined with a pregnancy calendar? Upps. Astron. Obs. Rep. 2003, 59, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Neuhäuser, R.; Torres, G.; Mugrauer, M.; Neuhäuser, D.L.; Chapman, J.; Luge, D.; Cosci, M. Colour evolution of Betelgeuse and Antares over two millennia, derived from historical records, as a new constraint on mass and age. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 516, 693–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelson, A.A.; Pease, F.G. Measurement of the diameter of alpha Orionis with the interferometer. Astrophys. J. 1921, 53, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GIANT STAR EQUAL TO 27,000,000 SUNS LIKE OURS. The New York Times, 30 December 1920.
- Kervella, P.; Le Bertre, T.; Perrin, G. (Eds.) Betelgeuse Workshop 2012; EAS Publications Series; EDP: Les Ulis, France, 2013; Volume 60. [Google Scholar]
- Keenan, P.C.; McNeil, R.C. The Perkins Catalog of Revised MK Types for the Cooler Stars. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1989, 71, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffleit, D.; Warren, W.H., Jr. The Bright Star Catalogue, 5th revised edition. Astron. Data Cent. Bull. 1987, 1, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland, R.L.; Dupree, A.K. First Image of the Surface of a Star with the Hubble Space Telescope. Astrophys. J. 1996, 463, L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnaka, K.; Hofmann, K.H.; Benisty, M.; Chelli, A.; Driebe, T.; Millour, F.; Petrov, R.; Schertl, D.; Stee, P.; Vakili, F.; et al. Spatially resolving the inhomogeneous structure of the dynamical atmosphere of Betelgeuse with VLTI/AMBER. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 503, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Haubois, X.; Perrin, G.; Lacour, S.; Verhoelst, T.; Meimon, S.; Mugnier, L.; Thiébaut, E.; Berger, J.P.; Ridgway, S.T.; Monnier, J.D.; et al. Imaging the spotty surface of <ASTROBJ>Betelgeuse</ASTROBJ> in the H band. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 508, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnaka, K.; Weigelt, G.; Millour, F.; Hofmann, K.H.; Driebe, T.; Schertl, D.; Chelli, A.; Massi, F.; Petrov, R.; Stee, P. Imaging the dynamical atmosphere of the red supergiant Betelgeuse in the CO first overtone lines with VLTI/AMBER. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 529, A163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupree, A.K.; Stefanik, R.P. Direct ultraviolet imaging and spectroscopy of betelgeuse. In Proceedings of the EAS Publications Series; Kervella, P., Le Bertre, T., Perrin, G., Eds.; EAS Publications Series. EDP: Les Ulis, France, 2013; Volume 60, pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Montargès, M.; Kervella, P.; Perrin, G.; Chiavassa, A.; Le Bouquin, J.B.; Aurière, M.; López Ariste, A.; Mathias, P.; Ridgway, S.T.; Lacour, S.; et al. The close circumstellar environment of Betelgeuse. IV. VLTI/PIONIER interferometric monitoring of the photosphere. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 588, A130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, E.; Kervella, P.; Harper, G.M.; Richards, A.M.S.; Decin, L.; Montargès, M.; McDonald, I. The inhomogeneous submillimeter atmosphere of Betelgeuse. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 602, L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- López Ariste, A.; Georgiev, S.; Mathias, P.; Lèbre, A.; Wavasseur, M.; Josselin, E.; Konstantinova-Antova, R.; Roudier, T. Three-dimensional imaging of convective cells in the photosphere of Betelgeuse. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 661, A91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilate, Q.; Ariste, A.L.; Lavail, A.; Mathias, P. The variability of Betelgeuse explained by surface convection. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 691, A297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavassa, A.; Haubois, X.; Young, J.S.; Plez, B.; Josselin, E.; Perrin, G.; Freytag, B. Radiative hydrodynamics simulations of red supergiant stars. II. Simulations of convection on Betelgeuse match interferometric observations. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 515, A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montargès, M.; Cannon, E.; Lagadec, E.; de Koter, A.; Kervella, P.; Sanchez-Bermudez, J.; Paladini, C.; Cantalloube, F.; Decin, L.; Scicluna, P.; et al. A dusty veil shading Betelgeuse during its Great Dimming. Nature 2021, 594, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervella, P.; Verhoelst, T.; Ridgway, S.T.; Perrin, G.; Lacour, S.; Cami, J.; Haubois, X. The close circumstellar environment of Betelgeuse. Adaptive optics spectro-imaging in the near-IR with VLT/NACO. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 504, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decin, L.; Cox, N.L.J.; Royer, P.; Van Marle, A.J.; Vandenbussche, B.; Ladjal, D.; Kerschbaum, F.; Ottensamer, R.; Barlow, M.J.; Blommaert, J.A.D.L.; et al. The enigmatic nature of the circumstellar envelope and bow shock surrounding Betelgeuse as revealed by Herschel. I. Evidence of clumps, multiple arcs, and a linear bar-like structure. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 548, A113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, J.C.; Chatzopoulos, E. Betelgeuse: A review. Astron. Geophys. 2023, 64, 3.11–3.27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitenbroek, H.; Dupree, A.K.; Gilliland, R.L. Spatially Resolved Hubble Space Telescope Spectra of the Chromosphere of alpha Orionis. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 2501–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupree, A.K.; Strassmeier, K.G.; Matthews, L.D.; Uitenbroek, H.; Calderwood, T.; Granzer, T.; Guinan, E.F.; Leike, R.; Montargès, M.; Richards, A.M.S.; et al. Spatially Resolved Ultraviolet Spectroscopy of the Great Dimming of Betelgeuse. Astrophys. J. 2020, 899, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.W.; Dhillon, V.S.; Haniff, C.A. The changing face of Betelgeuse. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1997, 291, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzschild, M. On the scale of photospheric convection in red giants and supergiants. Astrophys. J. 1975, 195, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, K.; Jorissen, A.; Van Eck, S.; Merle, T.; Chiavassa, A.; Paladini, C.; Freytag, B.; Plez, B.; Montargès, M.; Van Winckel, H. Atmosphere of Betelgeuse before and during the Great Dimming event revealed by tomography. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 650, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadlovský, D.; Granzer, T.; Weber, M.; Kravchenko, K.; Krtička, J.; Dupree, A.K.; Chiavassa, A.; Strassmeier, K.G.; Poppenhäger, K. The Great Dimming of Betelgeuse: The photosphere as revealed by tomography over the past 15 yr. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 685, A124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervella, P.; Decin, L.; Richards, A.M.S.; Harper, G.M.; McDonald, I.; O’Gorman, E.; Montargès, M.; Homan, W.; Ohnaka, K. The close circumstellar environment of Betelgeuse. V. Rotation velocity and molecular envelope properties from ALMA. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 609, A67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobel, A.; Dupree, A.K. Spatially Resolved STIS Spectroscopy of α Orionis: Evidence for Nonradial Chromospheric Oscillation from Detailed Modeling. Astrophys. J. 2001, 558, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavassa, A.; Pasquato, E.; Jorissen, A.; Sacuto, S.; Babusiaux, C.; Freytag, B.; Ludwig, H.G.; Cruzalèbes, P.; Rabbia, Y.; Spang, A.; et al. Radiative hydrodynamic simulations of red supergiant stars. III. Spectro-photocentric variability, photometric variability, and consequences on Gaia measurements. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 528, A120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavassa, A.; Kudritzki, R.; Davies, B.; Freytag, B.; de Mink, S.E. Probing red supergiant dynamics through photo-center displacements measured by Gaia. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 661, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA (Ed.) The HIPPARCOS and TYCHO Catalogues. Astrometric and Photometric Star Catalogues Derived from the ESA HIPPARCOS Space Astrometry Mission; ESA Special Publication; ESA: Paris, France, 1997; Volume 1200. [Google Scholar]
- Perryman, M.A.C.; Lindegren, L.; Kovalevsky, J.; Hoeg, E.; Bastian, U.; Bernacca, P.L.; Crézé, M.; Donati, F.; Grenon, M.; Grewing, M.; et al. The HIPPARCOS Catalogue. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 323, L49–L52. [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen, F. Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 474, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, G.M.; Brown, A.; Guinan, E.F.; O’Gorman, E.; Richards, A.M.S.; Kervella, P.; Decin, L. An Updated 2017 Astrometric Solution for Betelgeuse. Astron. J. 2017, 154, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, G.M.; Brown, A.; Guinan, E.F. A New VLA-Hipparcos Distance to Betelgeuse and its Implications. Astron. J. 2008, 135, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, M.; Leung, S.C.; Molnár, L.; Ireland, M.; Kobayashi, C.; Nomoto, K. Standing on the Shoulders of Giants: New Mass and Distance Estimates for Betelgeuse through Combined Evolutionary, Asteroseismic, and Hydrodynamic Simulations with MESA. Astrophys. J. 2020, 902, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupree, A.K.; Strassmeier, K.G.; Calderwood, T.; Granzer, T.; Weber, M.; Kravchenko, K.; Matthews, L.D.; Montargès, M.; Tappin, J.; Thompson, W.T. The Great Dimming of Betelgeuse: A Surface Mass Ejection and Its Consequences. Astrophys. J. 2022, 936, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, E.M.; Massey, P.; Olsen, K.A.G.; Plez, B.; Josselin, E.; Maeder, A.; Meynet, G. The Effective Temperature Scale of Galactic Red Supergiants: Cool, but Not As Cool As We Thought. Astrophys. J. 2005, 628, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famaey, B.; Jorissen, A.; Luri, X.; Mayor, M.; Udry, S.; Dejonghe, H.; Turon, C. Local kinematics of K and M giants from CORAVEL-Hipparco-Tycho-2 data. Revisiting the concept of superclusters. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 430, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Z.; Chiavassa, A.; de Mink, S.E.; Valli, R.; Justham, S.; Freytag, B. Is Betelgeuse Really Rotating? Synthetic ALMA Observations of Large-scale Convection in 3D Simulations of Red Supergiants. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 962, L36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beck, E.; Decin, L.; de Koter, A.; Justtanont, K.; Verhoelst, T.; Kemper, F.; Menten, K.M. Probing the mass-loss history of AGB and red supergiant stars from CO rotational line profiles. II. CO line survey of evolved stars: Derivation of mass-loss rate formulae. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 523, A18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, M.M.; Mathews, G.J.; Lam, D.D.; Quynh Lan, N.; Herczeg, G.J.; Dearborn, D.S.P. Evolutionary Tracks for Betelgeuse. Astrophys. J. 2016, 819, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saio, H.; Nandal, D.; Meynet, G.; Ekström, S. The evolutionary stage of Betelgeuse inferred from its pulsation periods. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 526, 2765–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, J.C.; Nance, S.; Diaz, M.; Smith, S.G.; Hickey, J.; Zhou, L.; Koutoulaki, M.; Sullivan, J.M.; Fowler, J.M. The Betelgeuse Project: Constraints from rotation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 465, 2654–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chatzopoulos, E.; Frank, J.; Marcello, D.C.; Clayton, G.C. Is Betelgeuse the Outcome of a Past Merger? Astrophys. J. 2020, 896, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.M.; Nance, S.; Wheeler, J.C. The Betelgeuse Project. III. Merger Characteristics. Astrophys. J. 2020, 905, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, H.; de Mink, S.E.; de Koter, A.; Langer, N.; Evans, C.J.; Gieles, M.; Gosset, E.; Izzard, R.G.; Le Bouquin, J.B.; Schneider, F.R.N. Binary Interaction Dominates the Evolution of Massive Stars. Science 2012, 337, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordier, E.; Frost, A.J.; Sana, H.; Reggiani, M.; Mérand, A.; Rainot, A.; Ramírez-Tannus, M.C.; de Wit, W.J. The origin of close massive binaries in the M17 star-forming region. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 663, A26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, J.A.; Bauer, E.B.; Howell, D.A. Apparent Magnitude of Betelgeuse as a Type IIP Supernova. Res. Notes Am. Astron. Soc. 2020, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, L.; Joyce, M.; Leung, S.C. Comment on the Feasibility of Carbon Burning in Betelgeuse. Res. Notes Am. Astron. Soc. 2023, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montargès, M.; Kervella, P.; Perrin, G.; Ohnaka, K.; Chiavassa, A.; Ridgway, S.T.; Lacour, S.M. Properties of the CO and H2O MOLsphere of the red supergiant Betelgeuse from VLTI/AMBER observations. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 572, A17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekström, S.; Georgy, C.; Eggenberger, P.; Meynet, G.; Mowlavi, N.; Wyttenbach, A.; Granada, A.; Decressin, T.; Hirschi, R.; Frischknecht, U.; et al. Grids of stellar models with rotation. I. Models from 0.8 to 120 M&sun; at solar metallicity (Z = 0.014). Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 537, A146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K.; Richards, A.M.S.; Ziurys, L.M.; Jones, T.J.; Ishibashi, K. The Mass-loss History of the Red Hypergiant VY CMa. Astron. J. 2021, 161, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Phillips, T.G.; Knapp, G.R. Circumstellar Shells Resolved in the IRAS Survey Data. I. Data Processing Procedure, Results, and Confidence Tests. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1993, 86, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega-Crespo, A.; van Buren, D.; Cao, Y.; Dgani, R. A Parsec-Size Bow Shock around Betelgeuse. Astron. J. 1997, 114, 837–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bertre, T.; Matthews, L.D.; Gérard, E.; Libert, Y. Discovery of a detached H I gas shell surrounding α Orionis. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 422, 3433–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.R.; Olivier, A.E.; Kawaler, S.D. The long secondary periods in semi-regular variables. In Proceedings of the IAU Colloq. 193: Variable Stars in the Local Group; Kurtz, D.W., Pollard, K.R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004; Volume 310, p. 322. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, J.A.; Joyce, M.; Molnár, L. A Buddy for Betelgeuse: Binarity as the Origin of the Long Secondary Period in α Orionis. Astrophys. J. 2024, 977, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granzer, T.; Weber, M.; Strassmeier, K.G.; Dupree, A. Betelgeuse: Long Secondary Period, a Fundamental Mode and Overtones. In Proceedings of the 21st Cambridge Workshop on Cool Stars, Stellar Systems, and the Sun, Toulouse, France, 4–9 July 2022; p. 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, M.; Antoni, A.; Huang, C.D.; Dupree, A.; Loeb, A. Left Ringing: Betelgeuse Illuminates the Connection between Convective Outbursts, Mode Switching, and Mass Ejection in Red Supergiants. Astrophys. J. 2023, 956, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granzer, T.; Weber, M.; Strassmeier, K.G.; Dupree, A. The Curious Case of Betelgeuse. In Proceedings of the 20.5th Cambridge Workshop on Cool Stars, Stellar Systems, and the Sun (CS20.5), Virtually, 2–4 March 2021; p. 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, D.; Matsunaga, N.; Jian, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Fukue, K.; Hamano, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Kawakita, H.; Kondo, S.; Otsubo, S.; et al. Effective temperatures of red supergiants estimated from line-depth ratios of iron lines in the YJ bands, 0.97–1.32 μm. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 502, 4210–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, D.; Yamazaki, K.; Uno, S. The Great Dimming of Betelgeuse seen by the Himawari-8 meteorological satellite. Nat. Astron. 2022, 6, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, L.D.; Dupree, A.K. Spatially Resolved Observations of Betelgeuse at λ7 mm and λ1.3 cm Just prior to the Great Dimming. Astrophys. J. 2022, 934, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexeeva, S.; Zhao, G.; Gao, D.Y.; Du, J.; Li, A.; Li, K.; Hu, S. Spectroscopic evidence for a large spot on the dimming Betelgeuse. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinan, E.F.; Wasatonic, R.J.; Calderwood, T.J. The Fainting of the Nearby Red Supergiant Betelgeuse. Astron. Telegr. 2019, 13341, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Levesque, E.M.; Massey, P. Betelgeuse Just Is Not That Cool: Effective Temperature Alone Cannot Explain the Recent Dimming of Betelgeuse. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 891, L37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, D.V.; Bailey, J.; De Horta, A.Y.; Norris, B.R.M.; Lomax, J.R. Multi-band Aperture Polarimetry of Betelgeuse during the 2019-20 Dimming. Res. Notes Am. Astron. Soc. 2020, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonov, B.; Dodin, A.; Burlak, M.; Goliguzova, M.; Fedoteva, A.; Zheltoukhov, S.; Lamzin, S.; Strakhov, I.; Voziakova, O. Differential Speckle Polarimetry of Betelgeuse in 2019–2020: The rise is different from the fall. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.05215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lançon, A.; Hauschildt, P.H.; Ladjal, D.; Mouhcine, M. Near-IR spectra of red supergiants and giants. I. Models with solar and with mixing-induced surface abundance ratios. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 468, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dullemond, C.P.; Juhasz, A.; Pohl, A.; Sereshti, F.; Shetty, R.; Peters, T.; Commercon, B.; Flock, M. RADMC-3D: A Multi-Purpose Radiative Transfer Tool; ASCL: Leicester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kashyap, V.L.; Drake, J.J.; Patnaude, D. Non-detection of Betelgeuse in X-rays. Astron. Telegr. 2020, 13501, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Freytag, B.; Höfner, S.; Aringer, B.; Chiavassa, A. Dimming events of evolved stars due to clouds of molecular gas: Scenarios based on 3D radiation-hydrodynamics simulations with CO5BOLD. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 692, A223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappin, S.J.; Eyles, C.J.; Davies, J.A. Determination of the Photometric Calibration and Large-Scale Flatfield of the STEREO Heliospheric Imagers: II. HI-2. Sol. Phys. 2015, 290, 2143–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupree, A.; Guinan, E.; Thompson, W.T.; STEREO/SECCHI/HI Consortium. Photometry of Betelgeuse with the STEREO Mission While in the Glare of the Sun from Earth. Astron. Telegr. 2020, 13901, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Soszyński, I.; Olechowska, A.; Ratajczak, M.; Iwanek, P.; Skowron, D.M.; Mróz, P.; Pietrukowicz, P.; Udalski, A.; Szymański, M.K.; Skowron, J.; et al. Binarity as the Origin of Long Secondary Periods in Red Giant Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 911, L22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, M.; Blunt, S.; De Rosa, R.J.; Dupree, A.K.; Granzer, T.; Harper, G.M.; Huang, C.D.; Leiner, E.M.; Loeb, A.; Nielsen, E.L.; et al. Radial Velocity and Astrometric Evidence for a Close Companion to Betelgeuse. Astrophys. J. 2025, 978, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, J.C.; Heap, S.R.; Beaver, E.A.; Boggess, A.; Carpenter, K.G.; Ebbets, D.C.; Hutchings, J.B.; Jura, M.; Leckrone, D.S.; Linsky, J.L.; et al. An Atlas of Alpha Orionis Obtained with the Goddard High Resolution Spectrograph on the Hubble Space Telescope. Astron. J. 1995, 109, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupree, A.K.; Lobel, A.; Young, P.R.; Ake, T.B.; Linsky, J.L.; Redfield, S. A Far-Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Survey of Luminous Cool Stars. Astrophys. J. 2005, 622, 629–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, J.L.; Santos-Sanz, P.; Sicardy, B.; Benedetti-Rossi, G.; Duffard, R.; Morales, N.; Braga-Ribas, F.; Fernández-Valenzuela, E.; Nascimbeni, V.; Nardiello, D.; et al. The large trans-Neptunian object 2002 TC302 from combined stellar occultation, photometry, and astrometry data. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 639, A134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vara-Lubiano, M.; Benedetti-Rossi, G.; Santos-Sanz, P.; Ortiz, J.L.; Sicardy, B.; Popescu, M.; Morales, N.; Rommel, F.L.; Morgado, B.; Pereira, C.L.; et al. The multichord stellar occultation on 2019 October 22 by the trans-Neptunian object (84922) 2003 VS2. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 663, A121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, B.E.; Bruno, G.; Gomes-Júnior, A.R.; Pagano, I.; Sicardy, B.; Fortier, A.; Desmars, J.; Maxted, P.F.L.; Braga-Ribas, F.; Queloz, D.; et al. A stellar occultation by the transneptunian object (50000) Quaoar observed by CHEOPS. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 664, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, F.; Gomez-Merchan, R.; Pérez, E.; Betancort-Rijo, J.E.; Leñero-Bardallo, J.A.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, Á.; Glez-de-Rivera, G.; Díaz-López, S.; de Elias Cantalapiedra, J. Single-photon gig in Betelgeuse’s occultation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.14704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Ziurys, L.M.; Bernal, J.J.; Gordon, M.S.; Helton, L.A.; Ishibashi, K.; Jones, T.J.; Richards, A.M.S.; Vlemmings, W. The Unexpected Spectrum of the Innermost Ejecta of the Red Hypergiant VY CMa. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 874, L26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Jones, T.J. Episodic Gaseous Outflows and Mass Loss from Red Supergiants. Astron. J. 2022, 163, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jencson, J.E.; Sand, D.J.; Andrews, J.E.; Smith, N.; Pearson, J.; Strader, J.; Valenti, S.; Beasor, E.R.; Rothberg, B. An Exceptional Dimming Event for a Massive, Cool Supergiant in M51. Astrophys. J. 2022, 930, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anugu, N.; Baron, F.; Gies, D.R.; Lanthermann, C.; Schaefer, G.H.; Shepard, K.A.; Brummelaar, T.t.; Monnier, J.D.; Kraus, S.; Le Bouquin, J.B.; et al. The Great Dimming of the Hypergiant Star RW Cephei: CHARA Array Images and Spectral Analysis. Astron. J. 2023, 166, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anugu, N.; Gies, D.R.; Roettenbacher, R.M.; Monnier, J.D.; Montargés, M.; Mérand, A.; Baron, F.; Schaefer, G.H.; Shepard, K.A.; Kraus, S.; et al. Time Evolution Images of the Hypergiant RW Cephei during the Rebrightening Phase Following the Great Dimming. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 973, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Sanchez, G.; de Wit, S.; Bonanos, A.Z.; Antoniadis, K.; Boutsia, K.; Boumis, P.; Christodoulou, E.; Kalitsounaki, M.; Udalski, A. Episodic mass loss in the very luminous red supergiant [W60] B90 in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 690, A99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
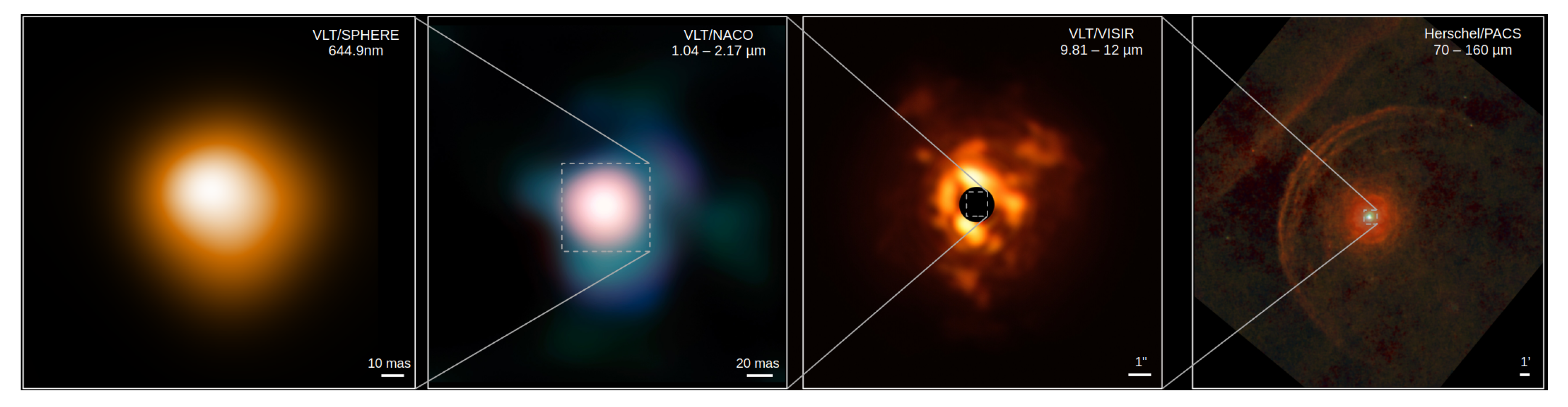

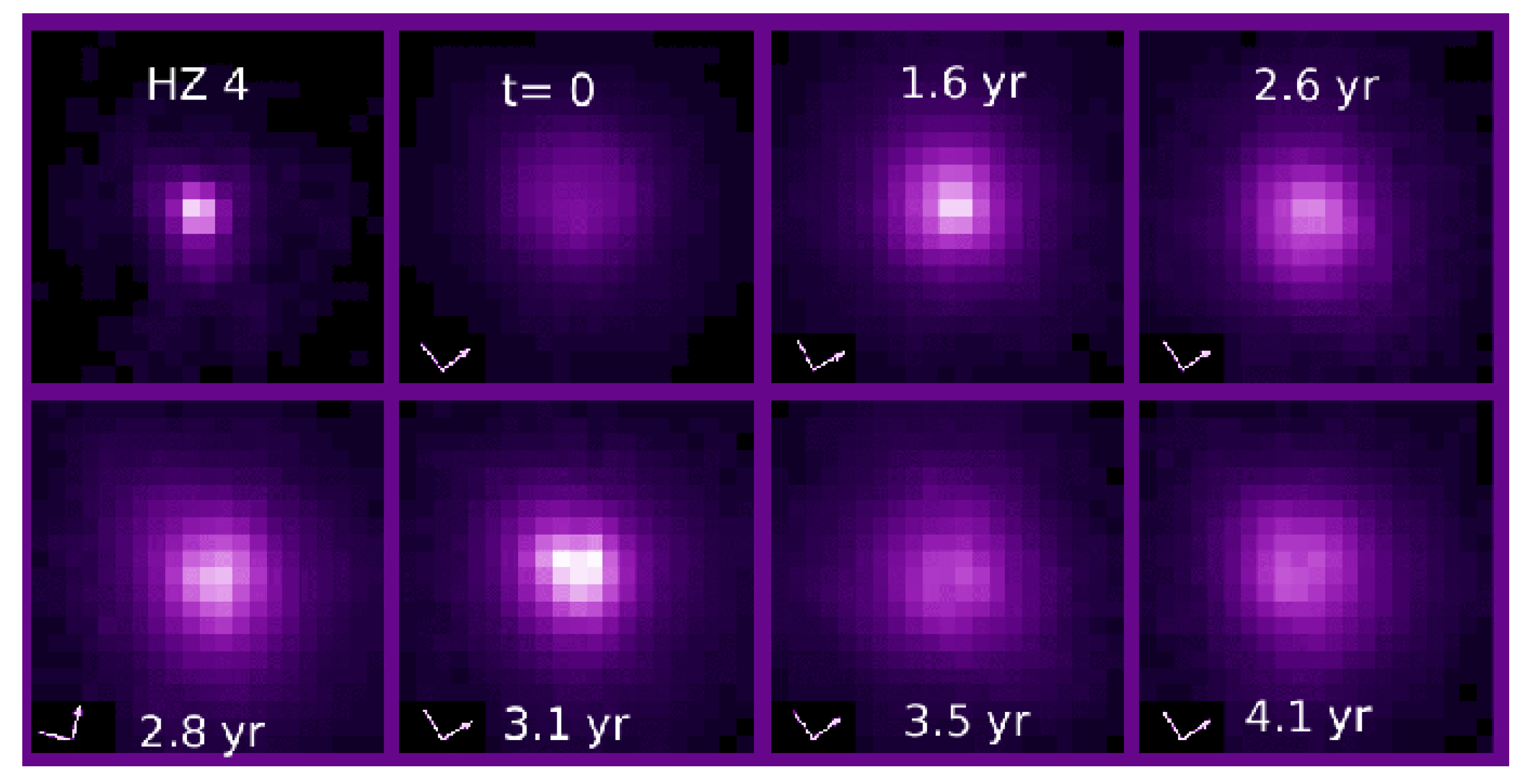

| Property | Value | Reference | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | K | [39] | Spectrometry and MARCS models |
| Spectral type | M1-M2Ia-Iab | [6] | Photographic spectra |
| Radial velocity | km | [40] | Integrated photospheric spectrum |
| Rotation velocity | [28] | Equatorial velocity, 28SiO (, ) | |
| Rotation velocity | None? | [41] | RHD simulations |
| Chromospheric rotation velocity | 14.6 km | [22] | UV spectroscopy |
| Uniform disk angular diameter—Photosphere | mas mas | [18] | K band continuum interferometry January 2019 + February 2020 |
| Uniform disk angular diameter—Chromosphere | mas | [8] | 250 nm continuum imaging |
| Distance | pc | [35] | Hipparcos IAD + VLA + e-MERLIN |
| Distance | pc | [37] | Seismic analysis |
| Photospheric radius | This work | VLTI January 2019 + Hipparcos IAD + VLA + e-MERLIN | |
| Photospheric radius | [37] | Seismic analysis | |
| Mass-loss rate | [42] | d = 131 pc, CO line profile | |
| Initial mass | [43] | d pc | |
| Current mass | [43] | d pc | |
| Age | Myr | [43] | d pc |
| Initial mass | [37] | Seismic analysis | |
| Current mass | [37] | Seismic analysis | |
| Age | Myr | [37] | Seismic analysis |
| Initial mass | 19 | [44] | d = pc Seismic analysis |
| Current mass | [44] | d = pc Seismic analysis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dupree, A.K.; Montargès, M. Betelgeuse, the Prototypical Red Supergiant. Galaxies 2025, 13, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13030050
Dupree AK, Montargès M. Betelgeuse, the Prototypical Red Supergiant. Galaxies. 2025; 13(3):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13030050
Chicago/Turabian StyleDupree, Andrea K., and Miguel Montargès. 2025. "Betelgeuse, the Prototypical Red Supergiant" Galaxies 13, no. 3: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13030050
APA StyleDupree, A. K., & Montargès, M. (2025). Betelgeuse, the Prototypical Red Supergiant. Galaxies, 13(3), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13030050






