Abstract
A new class of low-power compact radio sources with limited jet structures, named FR 0, is emerging from recent radio-optical surveys. This abundant population of radio galaxies, five times more numerous than FR Is in the local Universe (z < 0.05), represent a potentially interesting target at high and very-high energies (greater than 100 GeV), as demonstrated by a single case of Fermi detection. Furthermore, these radio galaxies have been recently claimed to contribute non-negligibly to the extra-galactic γ-ray background and to be possible cosmic neutrino emitters. Here, we review the radio through X-ray properties of FR 0s to predict their high-energy emission (from MeV to TeV), in light of the near-future facilities operating in this band.
1. Introduction
Radio galaxies (RGs) associated with the most massive black holes (BHs) in the Universe, are important laboratories to study the jet launching mechanism and the production of high and very high energy (HE > 100 MeV; VHE > 100 GeV) radiation by Compton scattering due to the presence of relativistic particles.
Although compact RGs were already known to be associated with massive early-type galaxies (ETGs) since the early 1970s (e.g., [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]), studies of much brighter extended RGs prevailed because of their more interesting and richer jetted structures. These RGs are classified based on their radio morphology, distinguishing between edge-darkened (FR I type) and edge-brightened (FR II type) sources [8] (Figure 1). Nevertheless, in the last decade, a renewed interest towards low-luminosity RGs (e.g., [9]) is driven by the advent of large-area high-sensitivity optical and radio surveys: the cross-correlation of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS, [10]), the Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty centimetres survey (FIRST, [11]) and the National Radio Astronomy Observatory Very Large Array (VLA) Sky Survey (NVSS, [12]) allowed unbiased statistical studies of the radio-AGN activity at low luminosities. With this technique, the authors in [13,14] selected a sample of low-power ∼18,000 RGs up to z ∼ 0.3 with radio fluxes higher than 5 mJy at 1.4 GHz, covering the range of radio luminosity – W Hz. All radio morphologies are represented, including twin-jets and core-jet FR Is, narrow and wide angle tails, and FR IIs. However, most of them (∼80%) appear unresolved or barely resolved at the 5″ FIRST resolution, corresponding to a size limit of ∼10 kpc. This enormous population of low-luminosity compact RGs, different from FR I/IIs, are still virtually unexplored. Recently, the authors in [15,16] concluded (confirmed later by other independent radio studies [17,18,19]) that this new population of RGs, characterized by a paucity of extended radio emission, dominates over FR Is and FR IIs in the local Universe. For their radio morphological peculiarity, this class of sources has been named as FR 0 in contrast to the classical Fanaroff–Riley classes [20,21,22]. This new class represents a radical change in our view of the radio sky because our past knowledge about RGs was biased towards powerful extended (from hundreds of kpc to Mpc) radio sources, as selected by low-frequency high-flux surveys (see e.g., the Third Cambridge (3C) catalogue1 [23]). However, up to now, the paucity of detailed multi-band information on FR 0s limits our comprehension on the origin of this class and the cause of their confined jet structures.
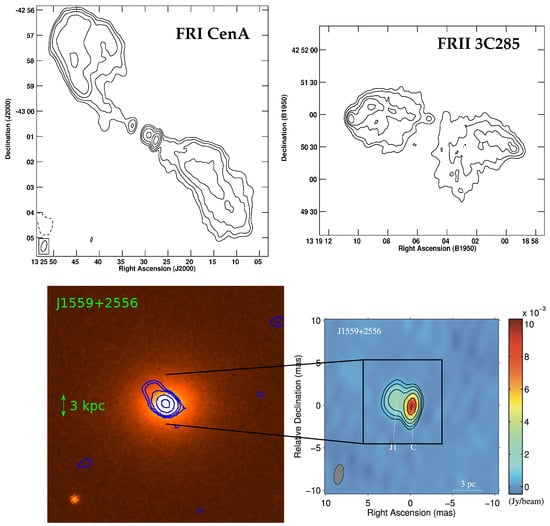
Figure 1.
Multi-band composite panel of radio galaxies. On the top are two examples of radio morphologies of a core-brightened FR I (Centaurus A [24] at 1.4 GHz) and an edge-brightened FR II (3C 285, [25] at 1.4 GHz). On the bottom, we show an example of FR 0, J1559 + 2556. The left panel displays the r-band SDSS image of the elliptical galaxy which hosts the FR 0 with the blue 4.5-GHz radio contours from VLA taken from [26] (3 kpc scale set by the green arrow). The right panel represents the high-resolution zoom on the radio core (on the scale of 3 pc) provided by the VLBI image from [27].
In this review, we summarize the state-of-the-art of multi-wavelength studies of FR 0s, lingering on their emission at high energies from keV to TeV. In particular, we will focus on the FR 0 population as possible -ray emitters based on one case of HE detection (Tol 1326-379, [28]), current models and facilities, and how their limited jets could accelerate particles that up-scatter low-energy photons or collide to eventually produce HE electromagnetic cascades.
2. Broadband Properties: From Radio to X-rays
These compact radio sources have been carefully selected and later included in a catalogue, named FR0CAT [29]. The selected 104 FR 0s with z , live in red massive ( M) ETGs with large BH masses (∼10– M), and are spectroscopically classified as Low Excitation Galaxies (LEG) [16]: these host properties are similar to those seen for the hosts of 3C/FR Is, but they are on average a factor ∼1.6 less massive [19,29]. The radio, optical line, X-ray luminosities of FR 0s generally match those of the 3C/FR Is [21,26,30]. The only feature distinguishing the two classes is the paucity of extended radio emission of FR 0s, which turns in a core dominance2 higher than classical FR Is by a factor ∼30. They show a strong deficit of total radio emission with respect to the 3C sources, being 100 times fainter at the same level of (O III) line luminosity, a proxy of the bolometric AGN power [16] (Figure 2). A similar high core dominance has been also observed in nearby giant ETGs that harbour low-power radio-loud AGN (10 erg s [15,22]), named Core Galaxies (CoreG [31]). These CoreG are basically miniature RGs with nuclei that are the scaled-down version of those of FR Is in terms of AGN bolometric luminosity, jet power and accretion rates [32,33].
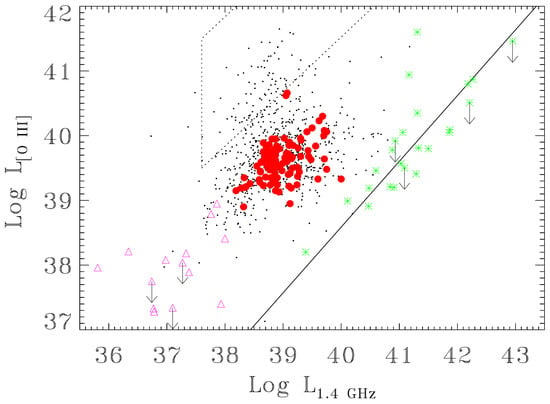
Figure 2.
FIRST 1.4-GHz radio vs. [O III] line luminosity (erg s). The small points correspond to the low-luminosity RG sample selected by [14]. The solid line represents the correlation between line and radio-luminosity derived for the 3CR/FR I sample (green stars). The dotted lines include the region where radio-quiet Seyfert galaxies are found. The red points are the FR 0 included in the FR0CAT [29] and the violet triangles are the CoreG.
However, the available multi-band data for FR 0s to study their nuclear activity are extremely limited. In the radio band, generally only 1.4 GHz FIRST and NVSS images with shallow angular resolution (5″ and 45″, respectively) were available. Hence, in the last five years, several campaigns with the VLA have been performed to zoom in the GHz-band emission at higher resolution, reaching 0.2″ [21,26]. At the kpc scale, the VLA analysis reveals that FR 0s remain compact below ≲1 kpc, with only ∼25% of the sample able to emanate twin or one-sided jets extended for at most a few kpc (Figure 1 as an example). At the parsec scale, higher-resolution radio observations with the Very Large Baseline Interferometer (VLBI) [27] show resolved radio jets for 80% of the sample. The VLBI multi-epoch data and the symmetry of the radio structures indicate that the jet bulk speed is mildly relativistic (between 0.23 c and 0.49 c) with Doppler-boosting factors ranging from 1.7 to 6.
Including low-frequency radio data-points from the Low-Frequency Array (LOFAR) and the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) surveys, the FR 0 radio spectra from hundreds of MHz to several GHz are typically flat ([21,26,34]). However, their SEDs can be generally described as a gentle spectral curvature towards higher radio frequencies, broader than what is seen in young radio sources. The flat-spectrum radio core powers tightly correlate with the AGN bolometric luminosities, following the relation of FR Is and CoreG [21,26]: this clearly indicates a common central engine, where the jet is the main contributor to the whole bolometric power. At higher radio frequencies, a survey at 15 GHz has been planned with the Arcminute Microkelvin Imager (AMI) array.
In the optical band, the continuum and spectral information of the nuclei are limited to the SDSS data, which yield to a low luminosity of the central source and a prominent radio loudness3.
2.1. X-ray Properties of FR 0s
At higher energies, the properties of FR 0s are almost unexplored. The authors in [30] performed the first systematic study in the X-ray (2–10 keV) band of a sample of 19 FR 0 galaxies selected from [14] on the basis of: (i) redshift z ≤ 0.15, (ii) radio size ≤10 kpc (in FIRST images); (iii) FIRST flux >30 mJy; (iv) LEG optical classification; (v) having available X-ray data in the public archives of the XMM-Newton, Chandra and Swift satellites. The aforementioned criteria guaranteed that the considered objects are classified as FR 0s, although at higher radio flux densities than the FR0CAT sources. Finally, Tol 1326-379, the first FR 0 radio galaxy detected in -rays (see Section 4), was added to the sample. The principal results of this study are:
- 1.
- The X-ray spectra of FR 0s are generally well represented by a power-law absorbed by a Galactic column density. An additional intrinsic absorber is not required by the data suggesting that, in these sources, the circum-nuclear environment is depleted of cold matter (e.g., the dusty torus is missing). In some cases, the addition of a thermal component is required by the data: this soft X-ray emission could be related to extended intergalactic medium or to the hot corona typical of ETGs [36]. The spectral slope of the power-law is generally steep, = 1.9 ± 0.3. Only in two cases, which includes Tol 1326-379, is the photon index flatter, ∼1.2;
- 2.
- FR 0s span a range in X-ray luminosity L = 10–10 erg s, similar to FR Is. When the X-ray luminosity is compared to the radio core one, a clear correlation is attested. This points towards a non-thermal origin (i.e., the jet) of the X-ray emission in FR 0s as commonly believed in FR Is (e.g., [32,37,38]) (Figure 3);
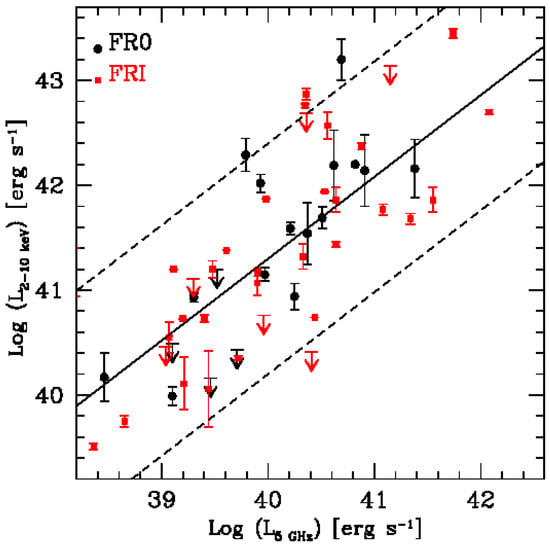 Figure 3. X-ray (2–10 keV) luminosity versus radio core (5 GHz) luminosity (in erg s) for FR 0s (black circles) and FR Is (red squares). Upper limits are represented by arrows. The black solid line is the linear regression for FR 0s FR Is: log = (7.8 ± 0.6) + (0.8 ± 0.1)log L. Black dashed lines are uncertainties on the slope, taken from [30].
Figure 3. X-ray (2–10 keV) luminosity versus radio core (5 GHz) luminosity (in erg s) for FR 0s (black circles) and FR Is (red squares). Upper limits are represented by arrows. The black solid line is the linear regression for FR 0s FR Is: log = (7.8 ± 0.6) + (0.8 ± 0.1)log L. Black dashed lines are uncertainties on the slope, taken from [30]. - 3.
- The central engine of FR 0s is probably powered by radiatively-inefficient accretion disc (i.e., Advection Dominated Accretion Flow [ADAF] model, [39]), as suggested by the small values of the Eddington-scaled luminosities, = L/L∼10-.
2.2. The Uniqueness of the FR 0 Class
What makes FR 0 class important is their large abundance, being five times more numerous than 3C/FR Is at z <0.05. Even at low radio frequencies where optically-thin radio jet emission is expected to dominate over the flat-spectrum core emission, in the LOFAR survey (the Low-Frequency Array Two-Metre Sky Survey LoTSS, [40]), ∼70% of RGs appears to be low-luminosity unresolved sources [41,42] at the same angular resolution of FIRST images (5″): about a few thousand of these compact RGs are potentially FR 0 candidates with respect to a comparable number of extended FR Is and FR IIs [43].
What makes this class of RGs unique is their lack of substantial extended radio emission and consequent high core dominance although they harbour an FR I-like nucleus. Are they low-power blazars? No, the more-preferentially symmetric jet structures of the FR 0s on a kpc scale rule out a significant projection effect [21,26]. The similar radio core-bolometric luminosity correlations, derived from [O III], X-ray, of FR 0s and FR Is yield to their common radio misalignment, since emission line and HE emission are typically considered independent of orientation. Another proof of the misaligned nature of FR 0s comes from the distribution of the ratio between [O III] and X-ray luminosities (R). While FR 0s and FR Is show similar values of R−1.7 (e.g., [38,44]), low-luminosity blazars have R−3.3 (e.g., [30,45]) as expected if the X-ray emission is beamed. Are they small fading FR Is? A past FR I radio activity is ruled out by the non-detection of extended diffuse emission at low radio frequencies and low angular resolutions (LOFAR and GMRT [34]. The FR 0 nuclear affinity with FR Is is, furthermore, downsized by the the mildly relativistic jet speed measured from VLBI with respect to the still relativistic speeds at parsec scales of FR Is [46,47,48]. Are they young FR Is? An age scenario, for which FR 0s are young RGs that will all eventually evolve into extended radio sources cannot be generally reconciled with the larger space density of FR 0s than FR Is [26]. Nevertheless, a possible contribution of ∼10% of genuinely young radio sources cannot be excluded among FR 0s (see [17]), based on the fraction of sources with inverted radio spectra [34]. Unlike FR 0s, genuinely young radio sources show different multi-band characteristics: (i) GHz-peaked radio spectra due to strong synchrotron self-absorption [49]; (ii) typically brighter in radio and optical line due to the enhanced emission caused by an expanding radio cocoon in a dense gas-rich environment [50]; (iii) FR II-like bolometric and HE powers associated with a radiatively efficient accretion disc (e.g., [51,52,53,54,55,56]); (iv) often show signatures of intrinsic H I and X-ray absorption [56,57], which suggest that these sources are typically embedded in a rich interstellar medium.
All these characteristics and differences with respect to the other FR classes, blazars, young sources and radio-quiet AGNs point to FR0s as a stand-alone class, which does not fully fit in a orientation-dependent AGN unification scheme [58] a priori, but does in a possible evolutionary AGN scheme [59]. Furthermore, no clear incongruity in the nuclear and host properties of the FR 0s with respect to the other RGs can account for the different radio properties.
A similar class of low-luminosity compact RGs (LLC) have been recently addressed by [60], as kpc-scale radio sources with possibly fading steep-spectrum disrupted jets and short-lived activity because of a lack of significant fuelling onto the BH [61,62]. These sources appear more consistent with an interpretation of FR I/FR II short-lived progenitors, rather than an intrinsically different radio class as it emerges from the multi-band studies of LCC. Nevertheless, a large overlap between the FR 0 and LLC populations cannot be excluded.
3. What Causes the Deficit of Extended Radio Emission in FR 0s?
While VLBI observations [27] and forthcoming enhanced Multi-Element Radio Linked Interferometer Network (eMERLIN) [63] observations show a larger fraction of asymmetric pc-scale radio structures, in JVLA maps [21,26], the jets appear more symmetric at larger scales. In addition, the nuclear luminosities of FR 0s reconcile with those of FR Is, suggesting similar AGN energetics. Hence, these results concur on the picture that FR 0 jets are probably launched relativistic at pc scale, while, at a larger scale, they decelerate showing smaller Lorentz factors 4.
Assuming a stationary jet scenario, the idea of a jet stratification with different velocity patterns [64] seems to better reproduce the general properties of the FR 0 class. The similarity of the nuclear properties of FR Is and FR 0s suggests that, within a few parsecs, the jet physics of the two FR classes need to be analogous. Therefore, as valid for FR Is, we speculate that a inner relativistic spine is likely to be responsible to produce the multi-band properties of the unresolved radio core and observed pc-scale jet asymmetry. However, to account for the confined jet capabilities of the FR 0s, the inner spine should be limited in length along the jet (≲1 kpc). The outer layer travelling with a mild relativistic speed (∼0.3 c) will dominate on a kpc scale and will account for the observed extended jet morphologies. The mild relativistic jet bulk speed and a possible intrinsic spine weakness together with entrainment of the galaxy medium could concur to a possible loss of jet stability. In this scenario, the jets would suffer from deceleration and premature disruption before escaping the host core radius, slowly burrowing their way into the external medium. Nevertheless, the optical host magnitudes of the FR 0s, a proxy for local density, comparable with those of FR Is, do not concur with the idea of a dense galaxy-scale environment which could cause the jet frustration through the interaction with interstellar density [65,66]. Alternatively, the scarcity of sites of plasma accelerations along the jet could also account for their restrained jet capabilities.
In a time-dependent jet scenario, an intermittent nuclear activity injects sporadically relativistic plasma in the jet and hence does not provide sufficient bulk flow to sustain the jet along large distances from the BH. This lack of plasma injection might reduce the jet momentum and cause significant jet deceleration within the galaxy. To infer the duty cycles of FR 0s by comparing the space densities of FR 0s with respect to the extended FR Is, short active phases of a few thousands years are strongly favoured with respect to longer ones [29]. Analogously to FR 0s, LLC have also been interpreted as powered by a short-lived outburst of the central activity, which may turn in compact radio jets [61]. Deep Low-frequency radio observations with LOFAR could reveal past radio activities of FR 0s and measure their activity recurrence. Nevertheless, a preliminary analysis on a small number of sources in the LoTSS survey seems to reject this hypothesis.
A further scenario proposes that FR 0s have low, prograde BH spin, which would limit the extracting energy to launch the jet and eventually evolve into full-fledged FR Is thanks to the increasing angular momentum of the accreting material [59]. Assuming a BH spin- dependence (e.g., [67,68]), the low BH spin would be the ultimate reason for the lower bulk Lorentz factor, reducing the ability of the FR 0s’ jets to penetrate the galaxy medium. The low BH spin could be caused by a possibly poorer large-scale environment than that of FR Is [69], which sets (i) a less intense accretion history than FR Is, or (ii) a less frequent merger history [70] to favor BH–BH coalescence, which spins up the central BH, a condition required to produce extended relativistic jets.
4. High Energy (Gev-Tev) View of FR 0s
While the previous -ray mission, EGRET, detected a few RGs (e.g., [71,72]), the Fermi -ray space telescope [73] has revolutionised our knowledge of the sky above 100 MeV. Among the outstanding results reached in ten years of survey, there is certainly the discovery of RGs as an whole class of GeV emitters [74]. Contrarily to blazars, where relativistic effects boost and blue-shift the emission of the jet that is closely aligned to the observer’s line of sight, in RGs, where the viewing angle of the jet is large (>1/), the detection of such sources at high energies is disfavoured. However, misaligned RGs were also detected by Fermi-LAT in only 15 months of survey [74] and their number continues to increase [75,76]. A few of them are also known as VHE emitters including M87 (d ∼ 16 Mpc), the first extra-galactic source detected at VHE energies, and Centaurus A (CenA), the nearest (d ∼ 4 Mpc) AGN to us5. Although misaligned RGs represent 2% of the entire extra-galactic -ray population that is dominated by blazars [77,78], they are extremely relevant in addressing problems related to the jet structure, the particle acceleration mechanism and the location of the acceleration sites. Moreover, RGs have been known to significantly contribute to the extra-galactic diffuse -ray background [79,80] and, interestingly, they are often invoked as possible sources of high-energy neutrinos and ultra-high energy cosmic-rays [81,82].
Being an emerging class of low-luminosity RGs, so far, only a few studies have focused on FR 0s in the GeV domain. Currently, only one FR 0 has been associated with a -ray counterpart by Fermi, i.e., Tol 1326-379 [28]. The source is characterized by a GeV luminosity (L = 2 × 10 erg s) lower than blazars, consistent with FR Is but with a slightly steeper photon index ( = 2.8) than classical FR Is. The radio-GeV spectral energy distribution (SED) of the core is double-humped (see Figure 4a) similar to other jet-dominated radio-loud AGN. Despite the similar radio luminosity, M 87 is less luminous than Tol 1326-379 by a factor of 30 at 1 GeV and has a flatter SED in the -ray domain. In contrast, the SEDs of CenA and Tol 1326-379 are quite similar in shape with a steep -ray trend, but the former source is about two orders of magnitude fainter.
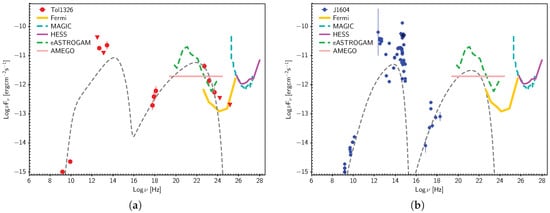
Figure 4.
(a) the SED of Tol 1326-379 (red points), the only FR 0 observed by Fermi so far, is modelled with a one-zone synchrotron–SSC model (grey dashed line). Following the modelling presented in [83], a moderate viewing angle (∼30) and bulk motion ( 2) have been assumed. (b) the SED of another FR 0, J160426.51 + 17 (blue points) with a model similar to that applied to Tol 1326-379 is shown (data from [28]). The expected sensitivity curves of current and future instruments in the MeV to TeV window are plotted (see the legend). While, in the framework of standard, one-zone leptonic models, a detection in the VHE range seems unlikely, both sources could be detected at MeV energies by future missions such as AMEGO [88] and e-ASTROGAM [89] (see Section 4.1).
At low energies, the non-thermal synchrotron component of Tol 1326-379 dominates over any accretion-related contribution, further supporting the case of an ADAF disc suggested by the X-ray study (see [30] and Section 2.1). The peak at the high-energies (so-called Compton peak) appears to be relatively prominent, comparable with or even higher than the synchrotron one, differently from BL Lac sources. The whole SED can be consistently reproduced by a synchrotron and synchrotron-self-Compton (SSC) model assuming either an aligned () or a misaligned ( 30 [83]) jet, with a total jet energy flux of the order of few 10 erg s [83].
Is Tol 1326-379 a unique γ-ray case? It has been estimated that core-dominated RGs nearby, i.e., FR0s and Core Galaxies [31], can account for ∼4–18% of the unresolved -ray background below 50 GeV observed by the LAT instrument on-board Fermi [84]. Unfortunately, no FR 0 is listed among the ∼37 non-blazar AGN in the recently released Fourth LAT AGN Catalog (4LAC, [76]). Nevertheless, one should note that Tol 1326-379 was initially classified as a blazar and a careful analysis of its multi-wavelength properties revealed its FR 0 nature [28]. Furthermore, the 4LAC includes a large number (∼1090) of sources defined as blazar candidates of uncertain type (BCUs), which could hide new -ray FR 0s. The range of -ray fluxes and photon indexes of BCUs ( = 1.5–3.0) are also compatible with those of Tol 1326-379, which can be taken as a reference for FR 0s at high energies. The cross-correlation of the BCUs from the 4LAC with the FR0CAT did not return any match. However, the FR0CAT selected only sources in the northern hemisphere, while more than 50% of the BCUs are in the less explored southern sky, where Tol 1326-379 itself has been found. Thus, future efforts must be devoted to extend the search for -ray FR 0 sources to this part of the sky (see [17]).
Interestingly, spectral fitting of the synchrotron peak of the SED of the BCUs in the 4LAC reveals an emerging population of faint, BL Lac-like sources characterized by a low synchrotron peak ( Hz, [76]). A fraction of these sources could be truly faint low-power BL Lacs (rather than located at high redshift) and possibly represent the aligned counterparts of FR 0s. The joint study of the two classes can be an effective way to explore the jet formation and the emission processes at the lowest levels of accretion onto the supermassive BH (see [45]).
Finally, it is important to stress that the Fermi catalogues place a 5 threshold to the detection of a source, which might leave out inherently faint -ray emitters (see [85] for an example). Therefore, progress in the characterization of the FR 0 class in the -ray window requires ad hoc analysis of the individual targets, exploiting the whole Fermi dataset, the most up-to-date calibrations and data selection, to look for sub-threshold emission. Besides the likelihood analysis of individual sources, the -ray properties of FR 0s can also be studied collectively by means of techniques searching for a signal in excess over the background in stacked data of a large sample (see [86] as example). These procedures could unearth a non-negligible population of low-luminosity RGs and FR 0s emitting at HE [87].
4.1. Perspectives with Upcoming MeV–TeV Observatories
Here, we test whether FR 0s could be detected by current and future generations of HE and VHE telescopes. We use two FR 0s as reference (Figure 4): while one is Tol 1326-379, detected by Fermi, the other source is a nearby (z = 0.04) FR 0 radio galaxy, J160426.51+17. It shows a flat X-ray spectral index (1.1 ± 0.3) and X-ray luminosity similar to Tol 1326-379 (see [30]) that make it a potential candidate for a -ray detection. As an exercise, we adjusted the model adopted for Tol 1326-379 to reproduce the SED of J160426.51+17 (Figure 4b): the output in the GeV window could be just at the Fermi detection limit.
Of equal importance for the characterization of the HE output of these sources will be the synergies between the VHE and the rest of the HE window. In particular, the Fermi observations have shown that, in RGs, the 0.1–100 GeV band probes the Compton component beyond the peak, i.e., the decaying tail, while the peak likely falls in the MeV energy range. Therefore, missions such as AMEGO [88] and e-ASTROGAM [89], proposed with the goal of exploring the MeV sky, will be crucial to make progress in our knowledge of the processes producing the most energetic radiation. As an example, in Figure 4, we plotted the expected sensitivity curves for the two instruments on the SEDs of Tol 1326-379 and J160426.51+17. In both cases, the two telescopes would detect the two FR 0s at MeV energies. By filling the gap between the X-ray and GeV–TeV band, MeV measurements will also play an important role to discriminate between leptonic and hadronic models (see, e.g., [90]).
In a TeV regime, we compare the flux sensitivity curves of current Cherenkov telescopes (MAGIC [91], VERITAS [92], H.E.S.S. [93]) with the SEDs of the two FR 0s cases (Figure 4). The Inverse Compton bump is modelled with a power-law component [28] that fits the measured points in the Fermi band; above 10 Hz the source is undetected. The predicted SED in the VHE regime is well below the sensitivity of all the Cherenkov telescopes in 50 h of observation (see Figure 5 for a zoom of the SED of Tol 1326-379 at VHE). A major step further will be possible thanks to the forthcoming Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA) [94]. Thanks to the improvement in sensitivity by a factor 5–20 (depending on the energy range 10 GeV–300 TeV) with respect to current Cherenkov telescopes, CTA will enable population studies and allow us to verify whether or not FR 0s are VHE emitters. Moreover, CTA will work as an observatory in synergy with other HE facilities, providing simultaneous data from a few MeV up to hundreds of TeV. This will guarantee the opportunity to test different mechanisms of VHE photon production in RGs in general [95,96] and FR 0s in particular, as outlined in the next section.
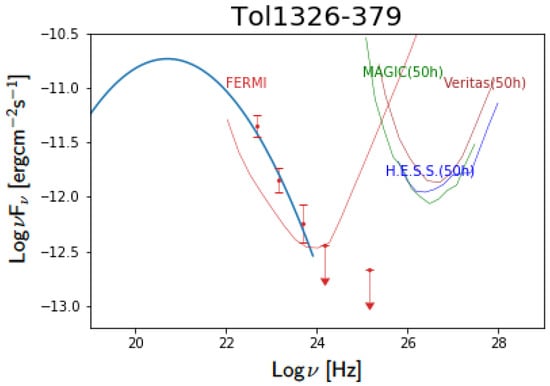
Figure 5.
SED of Tol 1326-379 in the high energy band. The red points are Fermi-LAT measurements (with the corresponding sensitivity curve) fitted by a power-law component that reproduces the inverse Compton bump. We plot the expected differential sensitivity curves for 50 h of exposure of MAGIC (in green) [91], VERITAS (in brown) [92] and H.E.S.S telescopes (in blue) [93].
5. Are FR 0s VHE Candidate Sources?
The lack of evident FR 0s in the Fermi/LAT catalogues and in the TeV catalogues (e.g., TevCat and TeGeV catalogues6) is not surprising. However, it is worth noting that the current Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescopes (IACT) operate in pointing mode, generally triggered by external alerts (e.g., the observation of an optical, X-ray or -ray flare). Consequently, their TeV catalogues might include a bias towards blazars.
The question is therefore whether these sources may or may not be considered candidate TeV emitters, and which scenarios would imply their detection. In the case of Tol 1326-379, a detection >100 GeV would indicate the presence of a distinct radiative component, with respect to the SSC one, which should remain sub-dominant in the 0.1–10 GeV band. Thus far, indications that such components could actually exist have been only found in the SED of the core of the radio galaxy Centaurus A [97,98]. Interestingly, its emission deviates from the simple extrapolation of the <3 GeV spectrum observed by Fermi, displaying a clear hardening at <250 GeV ([99] and references therein). A comprehensive discussion concerning the processes that could explain the origin of a TeV component is presented in [96]. Here, we review the different models of VHE photon production in AGN in relation to the FR 0 class.
The conventional leptonic jet (one-zone) SSC models predicts that X-ray-to--ray part of the SED originates from inverse Compton (IC) scattering of low energy photons by relativistic electrons in a single emitting region within the inner jet. The scattered photons may have an internal origin, produced by the synchrotron mechanism (SSC [100]), or external origin, i.e., seed photons coming from the accretion disc, the broad line region, or the dusty torus (external Compton, EC, e.g., [101,102]). Still in the framework of leptonic models, a jet with a stratified kinematic structure opens to multi-zone emission models. In its simplest realisation, this could be a two-zone model with a inner fast spine ( 1) nested in a outer slower sheath () [64]. Depending on the observer’s line of sight, the emission of one of the two zones prevails, with the spine dominating at small angles (i.e., in blazars) and the layer at larger angles (in misaligned AGN). The two emitting regions may radiatively interact, by providing each other additional target synchrotron photons to be Compton scattered. Because of the velocity gradient between the two emitting regions, the synchrotron emission coming from one region is boosted in the other, making this an efficient way to produce HE emission.
Hadronic models, in which relativistic protons within the jet are ultimately responsible for the observed emission, have been also proposed (e.g., [103,104]). These relativistic protons can interact with the soft synchrotron radiation and produce electromagnetic cascades above several tens of TeV and be responsible for the neutrino production. FR 0s have been recently proposed as cosmic neutrino emitters because of their -ray emission [83,105].
In the BH proximity, the BH gap model predicts that particles streaming along the magnetic field lines in the magnetosphere can be accelerated to very high energies due to the formation of (partially) unscreened electric field regions (gaps) [106,107]. The width of the gap h and the BH mass set the maximum -ray luminosity that can be emitted with Compton peaks in the range 10–100 TeV. In this gap model (stationary or time-dependent), very low accretion rates, or the presence of a radiatively-inefficient disc, represent a necessary condition for the detectability of magnetospheric VHE emission. This requires the accretion rate to be below a critical value, typically ∼0.01 (e.g., [108]) and in turn leads to a constraint on the average jet power. Assuming a rapidly spinning BH, the constraints on the gap size and accretion rate thus translate into a characteristic upper limit on the extractable VHE power of [109] where is the accretion rate scaled at the rate at the Eddington limit and r is the gravitational radius. Assuming that the gap width in FR 0s is consistent with the gravitational radius as found from the VHE variability of M 87 (e.g., [110]) and assuming similar accretion rates to M 87 as supported by the results for CoreG [33] and for FR 0s [30], the expected VHE luminosities for FR 0s from the gap models are erg s. For M87, the VHE luminosity is 3–10 × 10 erg s (e.g., [111]), which is three orders below the expected VHE gap luminosity. Therefore, since FR 0s and M 87 have similar bolometric AGN power, we could expect TeV luminosities for the FR 0s to be an order of magnitude lower because of their on average one-magnitude lower BH masses (∼) than M 87.
Relativistic jets are generally expected to be initially magnetically supported and models of collisionless magnetic reconnection are known to accelerate non-thermal electrons and produce HE photons by IC scattering (e.g., [112,113]) in the jets. Magnetic reconnection energy, when released, may provide an additional relativistic velocity component of the ejected plasma relative to the mean bulk flow of the jet, in any direction. This Doppler-boosted effect may lead to VHE emission even in misaligned AGN, including FR 0s. If the released magnetic power is responsible for the acceleration of the radiating relativistic particles, then the radio synchrotron radiation sets the minimum value to this power. Figure 6 compares the magnetic reconnection power driven by turbulence derived by [114] with the observed core radio luminosities of FR 0s taken from the FR0CAT [29]. We find that the magnetic reconnection power extracted from reconnection of the magnetic lines in the inner coronal region around the BHs of FR0s could be energetically sufficient to explain the core synchrotron radio emission from them, as also found valid for low-luminosity AGN [114,115]. Figure 6 also includes the -ray luminosity of Tol 1326-379, indicating that the magnetic reconnection produces enough power to emit HE -ray radiation.
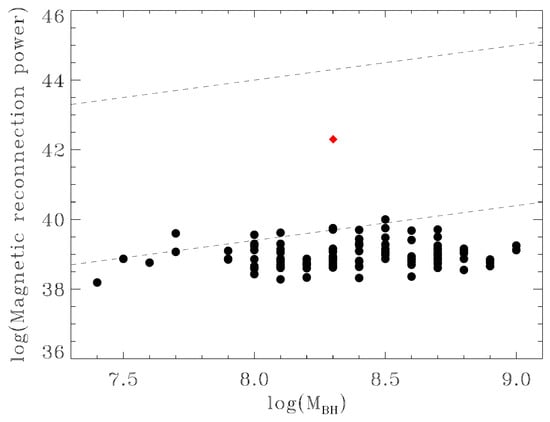
Figure 6.
Turbulent driven magnetic reconnection power (erg s) against BH masses (M) compared to the observed radio emission from FIRST catalogue for the 104 FR 0s from the FR0CAT (black points). For Tol 1326-379, we also plot the high-energy (>1 GeV) luminosity (red diamond). The region enclosed between the two dashed lines represents the maximum range of magnetic reconnection power predicted for RGs for supermassive BHs with different internal conditions (see [114]).
The scenario where -ray emission is produced by isotropically distributed relativistic electrons in the kpc-scale jet [116] has been raised to reconcile with the extended HE detection from the jet lobes of CenA [117] and with the possibility that X-ray jets could emit at VHE [118,119]. Relativistic electrons in the extended jets or lobes could Comptonise soft non-thermal X-ray radiation and CMB photons, which are beamed due to electron relativistic motion. The mild relativistic jet speed at a kpc scale expected for the FR 0s and their limited jet sizes disfavour but do not fully reject the possibility of VHE emission originated on a large jet scale from the FR 0 population.
On the whole, the VHE-emission models predict that FR 0s are TeV emitters with luminosities comparable or within an order of magnitude less than those observed from the core of local FR Is (i.e., M 87 and CenA). Nevertheless, the low brightness and further distance of the FR 0 population than the known TeV-emitting misaligned RGs (at least a factor of 2 in distance) hampers their detection at VHE even with future sensitive instruments. All the more, because it is unexpected, the detection of even a single FR 0 would open up interesting scenarios on the jet physics (radiative processes and jet accelerations) in these peculiar RGs.
6. Summary, Conclusions and Future Perspectives
The ongoing progress over the last few decades with consecutive Fermi catalogues and the upcoming advent of high-sensitivity MeV-TeV facilities make the HE astronomy accessible to a large part of the community and these observatories play a unique scientific role in the comprehension of the jet physics in radio-loud AGN. In such a framework, FR 0s, compact RGs with a substantial deficit of extended radio emission [22], are catching the attention of the community because of their large abundance with respect to the other FR classes and their potentiality of being HE emitters as a new class.
In this work, we reviewed the multi-band properties of this class of RGs, from radio to X-rays. Then, based on the unique Fermi detection of the FR 0 population (i.e., Tol 1326-379 [28]) so far, we explored the possibility of GeV–TeV emission of this abundant class of RGs, considering current (conventional and more exotic) models for -ray emission in AGN. Indeed, the Fermi detection of an FR 0 has opened up several scenarios to interpret its multi-wavelength SED. Whereas the similar broadband spectral nuclear properties of FR 0s and FR Is suggest common jet physics in the proximity to the BH, the indisputable differences of the jet structures at large scales between the two classes might imply intrinsic variations in the particle accelerations and in HE emitting processes. A weak/short fast spine and the scarcity of sites of particle accelerations, limited to several pc along the jet, reconcile with the global multiband properties of FR 0s, the confined jet structures and the kpc-scale jet symmetry. In a time-dependent scenario, a nuclear recurrent activity could lead to a discontinuous plasma injection in the jet and its possible deceleration. In the framework of HE emitting sites, the core region appears to be most plausible scene where -ray radiation can be produced because of the dominant role of the fast spine in the jet, which can relativistically accelerate particles.
Several mechanisms can be proposed to address the particle acceleration in the inner part of the FR0 jets and their -ray production. Relativistic shocks between jet layers moving at different speeds are responsible for accelerating particles along the shock front and could produce significant -ray emission by IC. A magnetospheric gap model followed by a radiatively inefficient accretion flow to avoid -pair production seems to reconcile with the expected HE luminosities of FR 0s. Magnetic reconnection, where magnetic energy is transferred to accelerating particles, predicts non-thermal synchrotron powers that are sufficient to justify the observed radio core luminosities of FR 0s.
Detection of new FR 0s at HE and VHE bands in the next future or stringent upper limits could help to set the jet parameter space of this peculiar class of RGs and constrain models on particle acceleration and HE emission processes. In this framework, to test whether FR 0s could be detected at HE, we compare the broadband SEDs of two cases of FR 0s with the sensitivity curves of MeV–GeV satellites and TeV Cherenkov telescopes. At MeV energies, the possible detection of the FR 0s will cover the gap between the X-ray and the VHE emission, crucial for having a comprehensive view of the jet properties. Below a few GeV, the detection of new FR 0s appears to be feasible with current and future -ray facilities, and more sources could possibly hide among the unknown blazar candidates in the Fermi catalogue. At VHE, the steep GeV spectrum and low brightness of Tol 1326-379 make a detection unlikely. However, our knowledge of this class at high energies is still very limited, hence it will be important to investigate the FR 0s with more sensitive observatories, such as CTA in the near future.
The FR 0 population, which outnumbers the FR Is, is expected to contribute up to ∼18% to the extra-galactic -ray background [84]. Recently, TeV-emitting candidates associated with low-power compact radio sources hosted in red ETGs have been selected by [120]. The authors predict that a few hundred of these candidates will be detectable by new generations of Cherenkov telescopes in 50 h in the entire extra-galactic sky in the local Universe. We speculate that these TeV emitters could be the parent aligned population of the FR 0s.
The optimal already-tested synergy between current radio, X-ray and -ray telescopes in the last decade and the upcoming generations of high-sensitivity and high-resolution facilities in such bands (i.e, SKA, LOFAR, ngVLA, eROSITA, Athena, Lynx, CTA) will offer unique insights into jet physics and particle acceleration mechanisms in the vicinity of the BH. These new observatories will probe the very low and high energy bands of the SEDs of the RGs which populate the low luminosity tail of the local radio AGN luminosity [14]. In this very low-power regime, an enormous population of compact radio sources, which generally includes all nearby giant elliptical galaxies [121,122,123,124,125] consistent with an FR 0 classification, could accelerate jets and potentially be -ray emitters. CTA, which will unearth such a population of low-power HE sources, will provide important progress in our understanding of the AGN phenomena, by providing robust constraints on the BH-jet coupling at a low-luminosity regime.
Author Contributions
R.D.B. has led several reference works on FR 0s, developing Section 1, Section 2.2, Section 3, Section 5 and Section 6, and coordinated this review. E.T. has led the work on the results presented in Section 2.1 and contributed to Section 4, G.M. and B.B. has led the discussion in Section 4. All the authors contributed to the discussion and writing of this work.
Funding
R.D.B. acknowledges the support of STFC under grant ST/R000638/1 and the Italian grant (Progetto di Ateneo/CSP 2016). E.T acknowledges the financial contribution from the agreement ASI-INAF n.2017-14-H.0.
Acknowledgments
We thank Alessandro Capetti and Paola Grandi for the discussions that have contributed to the ideas that we expose in this review, and for sharing the multi-band data for the SED of Tol 1326-379. We thank the referees for providing useful comments to the original manuscript and X.P. Cheng for giving us permission to add his figure into this publication. Part of this work is based on archival data, software or online services provided by the Space Science Data Center - ASI. This research has made used of TOPCAT7 [126] for the preparation and manipulation of the tabular data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Rogstad, D.H.; Ekers, R.D. Radio sources and elliptical galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1969, 157, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeschen, D.S. Radio observations of E and SO galaxies. Astron. J. 1970, 75, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekers, R.D.; Ekers, J.A. A survey of elliptical galaxies at 6 cm. Astron. Astrophys. 1973, 24, 247. [Google Scholar]
- Sadler, E.M. Radio and optical observations of a complete sample of E and SO galaxies. III. A radio continuum survey at 2.7 and 5.0 GHz. Astron. J. 1984, 89, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellermann, K.I.; Pauliny-Toth, I.I.K. Compact radio sources. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1981, 19, 373–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slee, O.B.; Sadler, E.M.; Reynolds, J.E.; Ekers, R.D. Parsec-scale radio cores in early-type galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1994, 269, 928–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wrobel, J.M.; Heeschen, D.S. Radio continuum sources in nearby and bright E/S0 galaxies: Active nuclei versus star formation. Astron. J. 1991, 101, 148–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanaroff, B.L.; Riley, J.M. The morphology of extragalactic radio sources of high and low luminosity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1974, 167, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyland, K.; Harwood, J.J.; Mukherjee, D.; Jagannathan, P.; Rujopakarn, W.; Emonts, B.; Alatalo, K.; Bicknell, G.V.; Davis, T.A.; Greene, J.E.; et al. Revolutionizing our understanding of AGN feedback and its importance to galaxy evolution in the era of the next generation very large array. Astrophys. J. 2018, 859, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abazajian, K.N.; Adelman-McCarthy, J.K.; Agüeros, M.A.; Allam, S.S.; Allende Prieto, C.; An, D.; Anderson, K.S.J.; Anderson, S.F.; Annis, J.; Bahcall, N.A.; et al. The seventh data release of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2009, 182, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.H.; White, R.L.; Helfand, D.J. The FIRST Survey: Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty Centimeters. Astrophys. J. 1995, 450, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, J.J.; Cotton, W.D.; Greisen, E.W.; Yin, Q.F.; Perley, R.A.; Taylor, G.B.; Broderick, J.J. The NRAO VLA Sky Survey. Astrophys. J. 1998, 115, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, P.N.; Kauffmann, G.; Heckman, T.M.; Ivezić, Ž. A sample of radio-loud active galactic nuclei in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 362, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, P.N.; Heckman, T.M. On the fundamental dichotomy in the local radio-AGN population: Accretion, evolution and host galaxy properties. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 421, 1569–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, R.D.; Capetti, A. Radio and spectroscopic properties of miniature radio galaxies: Revealing the bulk of the radio-loud AGN population. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 508, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, R.D.; Capetti, A. Spectro-photometric properties of the bulk of the radio-loud AGN population. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 519, A48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, E.M.; Ekers, R.D.; Mahony, E.K.; Mauch, T.; Murphy, T. The local radio-galaxy population at 20 GHz. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 438, 796–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittam, I.H.; Riley, J.M.; Green, D.A.; Jarvis, M.J. The faint source population at 15.7 GHz—III. A high-frequency study of HERGs and LERGs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 462, 2122–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraghaei, H.; Best, P.N. The nuclear properties and extended morphologies of powerful radio galaxies: The roles of host galaxy and environment. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 466, 4346–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G. Extragalactic relativistic jets. Am. Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 1381, 180–198. [Google Scholar]
- Baldi, R.D.; Capetti, A.; Giovannini, G. Pilot study of the radio-emitting AGN population: The emerging new class of FR 0 radio-galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 576, A38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, R.D.; Capetti, A.; Giovannini, G. The new class of FR 0 radio galaxies. Astron. Nachr. 2016, 337, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinrad, H.; Djorgovski, S.; Marr, J.; Aguilar, L. A third update of the status of the 3 CR sources: Further new redshifts and new identifications of distant galaxies. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1985, 97, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.O.; Feigelson, E.D.; Schreier, E.J. The inner radio structure of Centaurus A: Clues to the origin of thejet X-ray emission. Astrophys. J. 1983, 273, 128–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, P.; Leahy, J.P. Ageing and speeds in a representative sample of 21 classical double radio sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1987, 225, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, R.D.; Capetti, A.; Giovannini, G. High-resolution VLA observations of FR0 radio galaxies: The properties and nature of compact radio sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 482, 2294–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-P.; An, T. Parsec-scale Radio Structure of 14 Fanaroff–Riley Type 0 Radio Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2018, 863, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, P.; Capetti, A.; Baldi, R.D. Discovery of a Fanaroff-Riley type 0 radio galaxy emitting at γ-ray energies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, R.D.; Capetti, A.; Massaro, F. FR0CAT: A FIRST catalog of FR 0 radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 609, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torresi, E.; Grandi, P.; Capetti, A.; Baldi, R.D.; Giovannini, G. X-ray study of a sample of FR0 radio galaxies: Unveiling the nature of the central engine. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 5535–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmaverde, B.; Capetti, A. The host galaxy/AGN connection in nearby early-type galaxies. Is there a miniature radio-galaxy in every “core” galaxy? Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 447, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Balmaverde, B.; Capetti, A.; Grandi, P. The Chandra view of the 3C/FR I sample of low luminosity radio-galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 451, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmaverde, B.; Baldi, R.D.; Capetti, A. The accretion mechanism in low-power radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 486, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capetti, A.; Baldi, R.D.; Brienza, M.; Morganti, R.; Giovannini, G. The low-frequency properties of FR 0 radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. submitted.
- Kellermann, K.I.; Sramek, R.; Schmidt, M.; Shaffer, D.B.; Green, R. VLA Observations of Objects in the Palomar Bright Quasar Survey. Astron. J. 1989, 98, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbiano, G.; Kim, D.-W.; Trinchieri, G. An X-ray Catalog and Atlas of Galaxies. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1992, 80, 531–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardcastle, M.J.; Worrall, D.M. Radio, optical and X-ray nuclei in nearby 3CRR radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000, 314, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hardcastle, M.J.; Evans, D.A.; Croston, J.H. The active nuclei of z < 1.0 3CRR radio sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 396, 1929–1952. [Google Scholar]
- Narayan, R.; Yi, I. Advection-dominated Accretion: Self-Similarity and Bipolar Outflows. Astrophys. J. 1995, 444, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimwell, T.W.; Tasse, C.; Hardcastle, M.J.; Mechev, A.P.; Williams, W.L.; Best, P.N.; Röttgering, H.J.A.; Callingham, J.R.; Dijkema, T.J.; de Gasperin, F.; et al. The LOFAR Two-metre Sky Survey. II. First, data release. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 622, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardcastle, M.J.; Williams, W.L.; Best, P.N.; Croston, J.H.; Duncan, K.J.; Röttgering, H.J.A.; Sabater, J.; Shimwell, T.W.; Tasse, C.; Callingham, J.R.; et al. Radio-loud AGN in the first LoTSS data release. The lifetimes and environmental impact of jet-driven sources. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 622, A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, J.; Best, P.N.; Hardcastle, M.J.; Shimwell, T.W.; Tasse, C.; Williams, W.L.; Brüggen, M.; Cochrane, R.K.; Croston, J.H.; de Gasperin, F.; et al. The LoTSS view of radio AGN in the local Universe. The most massive galaxies are always switched on. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 622, A17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingo, B.; Croston, J.H.; Hardcastle, M.J.; Best, P.N.; Duncan, K.J.; Morganti, R.; Rottgering, H.J.A.; Sabater, J.; Shimwell, T.W.; Williams, W.L.; et al. Revisiting the Fanaroff-Riley dichotomy and radio-galaxy morphology with the LOFAR Two-Metre Sky Survey (LoTSS). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 488, 2701–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttiglione, S.; Capetti, A.; Celotti, A.; Axon, D.J.; Chiaberge, M.; Macchetto, F.D.; Sparks, W.B. An optical spectroscopic survey of the 3CR sample of radio galaxies with z < 0.3. II. Spectroscopic classes and accretion modes in radio-loud AGN. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 509, A6. [Google Scholar]
- Capetti, A.; Raiteri, C.M. Looking for the least luminous BL Lacertae objects. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 580, A73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, T.; Castaldini, C.; Cotton, W.D.; Feretti, L.; Giovannini, G.; Lara, L.; Marcaide, J.M.; Wehrle, A.E. VLBI Observations of a Complete Sample of Radio Galaxies. VI. The Two FR I Radio Galaxies B2 0836 + 29 and 3C 465. Astrophys. J. 1995, 454, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, G.; Cotton, W.D.; Feretti, L.; Lara, L.; Venturi, T. VLBI Observations of a Complete Sample of Radio Galaxies: 10 Years Later. Astrophys. J. 2010, 552, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharb, P.; O’Dea, C.P.; Tilak, A.; Baum, S.A.; Haynes, E.; Noel-Storr, J.; Fallon, C.; Christiansen, K. VLBA and Chandra Observations of Jets in FR I Radio Galaxies: Constraints on Jet Evolution. Astrophys. J. 2012, 754, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, C.P.; Baum, S.A.; Stanghellini, C. What Are the Gigahertz Peaked-Spectrum Radio Sources? Astrophys. J. 1991, 380, 66–77. [Google Scholar]
- O’Dea, C.P. The Compact Steep-Spectrum and Gigahertz Peaked-Spectrum Radio Sources. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1998, 110, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guainazzi, M.; Siemiginowska, A.; Stanghellini, C.; Grandi, P.; Piconcelli, E.; Azubike Ugwoke, C. A hard X-ray view of giga-hertz peaked spectrum radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 446, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labiano, A. Tracing jet-ISM interaction in young AGN: Correlations between [O III] λ 5007 Å, and 5-GHz emission. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 488, L59–L62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliori, G.; Siemiginowska, A.; Kelly, B.C.; Stawarz, Ł.; Celotti, A.; Begelman, M.C. Jet Emission in Young Radio Sources: A Fermi Large Area Telescope Gamma-Ray View. Astrophys. J. 2014, 780, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemiginowska, A.; Sobolewska, M.; Guainazzi, M.; Hardcastle, M.; Migliori, G.; Ostorero, L.; Stawarz, L. X-ray Properties of the Gigahertz Peaked and Compact Steep Spectrum Sources. Astrophys. J. 2008, 684, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tengstrand, O.; Guainazzi, M.; Siemiginowska, A.; Fonseca Bonilla, N.; Labiano, A.; Worrall, D.M.; Grandi, P.; Piconcelli, E. The X-ray view of giga-hertz peaked spectrum radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 501, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vink, J.; Snellen, I.; Mack, K.-H.; Schilizzi, R. The X-ray properties of young radio-loud AGN. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 367, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti, R.; Oosterloo, T. The interstellar and circumnuclear medium of active nuclei traced by H I 21 cm absorption. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2018, 26, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urry, C.M.; Padovani, P. Unified schemes for radio-loud active galactic nuclei. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1995, 107, 803–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, D.; Singh, C.B. FR 0 Radio Galaxies and Their Place in the Radio Morphology Classification. Astrophys. J. 2019, 871, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunert-Bajraszewska, M.; Thomasson, P. A survey of Low Luminosity Compact sources. Astron. Nachr. 2009, 330, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunert-Bajraszewska, M.; Gawroński, M.P.; Labiano, A.; Siemiginowska, A. A survey of low-luminosity compact sources and its implication for the evolution of radio-loud active galactic nuclei—I. Radio data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 408, 2261–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunert-Bajraszewska, M.; Labiano, A.; Siemiginowska, A.; Guainazzi, M. First, X-ray observations of low-power compact steep spectrum sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 437, 3063–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, R.D.; Capetti, A.; Giovannini, G. The eMERLIN view of FR 0 radio galaxies. In preparation.
- Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F.; Chiaberge, M. Structured jets in TeV BL Lac objects and radiogalaxies. Implications for the observed properties. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 432, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledlow, M.J.; Owen, F.N. 20 cm VLA Survey of Abell Clusters of Galaxies. VI. Radio/Optical Luminosity Functions. Astrophys. J. 1996, 112, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, C.R.; Best, P.N. Luminosity function, sizes and FR dichotomy of radio-loud AGN. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 381, 1548–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchekhovskoy, A.; Narayan, R.; McKinney, J.C. Black Hole Spin and The Radio Loud/Quiet Dichotomy of Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2010, 711, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraschi, L.; Colpi, M.; Ghisellini, G.; Perego, A.; Tavecchio, F. On the role of black hole spin and accretion in powering relativistic jets in AGN. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 355, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capetti, A.; Massaro, F.; Baldi, R.D. The large-scale environment of FR 0 radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2019. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, Y.; Volonteri, M.; Silk, J. Black hole evolution—III. Statistical properties of mass growth and spin evolution using large-scale hydrodynamical cosmological simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 440, 1590–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinle, H.; Bennett, K.; Bloemen, H.; Collmar, W.; Diehl, R.; Hermsen, W.; Lichti, G.G.; Morris, D.; Schonfelder, V.; Strong, A.W.; et al. COMPTEL observations of Centaurus A at MeV energies in the years 1991 to 1995. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 330, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, R.; Halpern, J.; Mirabal, N.; Gotthelf, E.V. Is the EGRET Source 3EG J1621+8203 the Radio Galaxy NGC 6251? Astrophys. J. 2002, 574, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, W.B.; Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Althouse, W.; Anderson, B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Band, D.L.; Barbiellini, G.; et al. The Large Area Telescope on the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission. Astrophys. J. 2009, 697, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Bechtol, K.; Bellazzini, R.; Berenji, B.; et al. Fermi Large Area Telescope Observations of Misaligned Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2010, 720, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahakyan, N.; Baghmanyan, V.; Zargaryan, D. Fermi-LAT observation of nonblazar AGNs. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 614, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Fermi-LAT collaboration. Fermi Large Area Telescope Fourth Source Catalog. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.10045. [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Becerra Gonzalez, J.; Bellazzini, R.; Bissaldi, E.; et al. The Third Catalog of Active Galactic Nuclei Detected by the Fermi Large Area Telescope. Astrophys. J. 2015, 810, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acero, F.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Albert, A.; Atwood, W.B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; et al. Fermi Large Area Telescope Third Source Catalog. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2015, 218, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawarz, Ł.; Kneiske, T.M.; Kataoka, J. Kiloparsec-Scale Jets in FR I Radio Galaxies and the γ-Ray Background. Astrophys. J. 2006, 637, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Di Mauro, M.; Manconi, S.; Zechlin, H.-S.; Ajello, M.; Charles, E.; Donato, F. Deriving the Contribution of Blazars to the Fermi-LAT Extragalactic γ-ray Background at E > 10 GeV with Efficiency Corrections and Photon Statistics. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichmann, B.; Rachen, J.P.; Merten, L.; van Vliet, A.; Becker Tjus, J. Ultra-high-energy cosmic rays from radio galaxies. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2018, 2018, 036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, K. High-energy neutrinos from extragalactic jets. Astropart. Phys. 1995, 3, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavecchio, F.; Righi, C.; Capetti, A.; Grandi, P.; Ghisellini, G. High-energy neutrinos from FR 0 radio galaxies? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 475, 5529–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W.; Shrader, C.R.; Malkan, M.A. The Extragalactic Gamma-Ray Background from Core Dominated Radio Galaxies. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 879, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliori, G.; Siemiginowska, A.; Sobolewska, M.; Loh, A.; Corbel, S.; Ostorero, L.; Stawarz, Ł. First, Detection in Gamma-Rays of a Young Radio Galaxy: Fermi-LAT Observations of the Compact Symmetric Object PKS 1718-649. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 821, L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Anderson, B.; Atwood, W.B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Bellazzini, R.; Bhat, P.N.; et al. Fermi LAT Stacking Analysis of Swift Localized GRBs. Astrophys. J. 2016, 822, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, S.; Bazo, J. Search for gamma-ray counterparts of newly discovered radio astrophysical sources. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.01664. [Google Scholar]
- Moiseev, A.; Amego Team. All-Sky Medium Energy Gamma-ray Observatory (AMEGO). In Proceedings of the 35th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2017), Busan, Korea, 10–20 July 2017; p. 798. [Google Scholar]
- De Angelis, A.; Tatischeff, V.; Tavani, M.; Oberlack, U.; Grenier, I.; Hanlon, L.; Walter, R.; Argan, A.; von Ballmoos, P.; Bulgarelli, A.; et al. The e-ASTROGAM mission. Exploring the extreme Universe with gamma rays in the MeV - GeV range. Exp. Astron. 2017, 44, 25–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, M.; Dimitrakoudis, S.; Padovani, P.; Mastichiadis, A.; Resconi, E. Photohadronic origin of γ-ray BL Lac emission: Implications for IceCube neutrinos. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 448, 2412–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitarek, J.; Carmona, E.; Colin, P.; Mazin, D.; Tescaro, D. Performance of the MAGIC telescopes after the major upgrade. In Proceedings of the 34th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2015), The Hague, The Netherlands, 30 July–6 August 2015; p. 981. [Google Scholar]
- Park, N.; VERITAS Collaboration. Performance of the VERITAS experiment. In Proceedings of the 34th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2015), The Hague, The Netherlands, 30 July–6 August 2015; p. 771. [Google Scholar]
- Holler, M.; de Naurois, M.; Zaborov, D.; Balzer, A.; Chalmé-Calvet, R. Photon Reconstruction for H.E.S.S. Using a Semi-Analytical Model. In Proceedings of the 34th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2015), The Hague, The Netherlands, 30 July–6 August 2015; p. 980. [Google Scholar]
- Actis, M.; Agnetta, G.; Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.; Aleksić, J.; Aliu, E.; Allan, D.; Allekotte, I.; Antico, F.; Antonelli, L.A.; et al. Design concepts for the Cherenkov Telescope Array CTA: An advanced facility for ground-based high-energy gamma-ray astronomy. Exp. Astron. 2011, 32, 193–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioni, R.; Grandi, P.; Torresi, E.; Vignali, C.; Knödlseder, J. Radio galaxies with the Cherenkov Telescope Array. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 92, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, F.; Levinson, A. Radio Galaxies at VHE Energies. Galaxies 2018, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Anton, G.; de Almeida, U.B.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Becherini, Y.; Behera, B.; Benbow, W.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; et al. Discovery of Very High Energy γ-Ray Emission from Centaurus a with H.E.S.S. Astrophys. J. 2009, 695, L40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahakyan, N.; Yang, R.; Aharonian, F.A.; Rieger, F.M. Evidence for a Second Component in the High-energy Core Emission from Centaurus A? Astrophys. J. Lett. 2013, 770, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. E. S. S. Collaboration; Abdalla, H.; Abramowski, A.; Aharonian, F.; Ait Benkhali, F.; Angüner, E.O.; Arakawa, M.; Armand, C.; Arrieta, M.; Backes, M.; et al. The γ-ray spectrum of the core of Centaurus A as observed with H.E.S.S. and Fermi-LAT. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 619, A71. [Google Scholar]
- Maraschi, L.; Ghisellini, G.; Celotti, A. A Jet Model for the Gamma-Ray–emitting Blazar 3C 279. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1992, 397, L5–L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermer, C.D. On the Beaming Statistics of Gamma-Ray Sources. Astrophys. J. 1995, 446, L63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Madau, P. On the origin of the gamma-ray emission in blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1996, 280, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M. Modeling the emission processes in blazars. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2007, 309, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, B.; Petropoulou, M.; Zhang, H.; D’Ammando, F.; Finke, J.; Baring, M.; Boettcher, M.; Dimitrakoudis, S.; Gan, Z.; Giannios, D.; et al. Multi-Physics of AGN Jets in the Multi-Messenger Era. Bull. Am. Astron. Soc. 2019, 51, 92. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, I.B.; Wu, K.; On, A.Y.L.; Saxton, C.J. High-energy neutrino fluxes from AGN populations inferred from X-ray surveys. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 451, 3649–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruderman, M.A.; Sutherland, P.G. Theory of pulsars: Polar gaps, sparks, and coherent microwave radiation. Astrophys. J. 1975, 196, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.; Melikidze, G.I.; Geppert, U. Drifting subpulses and inner acceleration regions in radio pulsars. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 407, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Narayan, R. On the Nature of X-ray-Bright, Optically Normal Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2004, 612, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoulakos, G.; Rieger, F.M. Magnetospheric Gamma-Ray Emission in Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2018, 852, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, J.; Aliu, E.; Anderhub, H.; Antonelli, L.A.; Antoranz, P.; Backes, M.; Baixeras, C.; Barrio, J.A.; Bartko, H.; Bastieri, D.; et al. Very High Energy Gamma-Ray Observations of Strong Flaring Activity in M 87 in 2008 February. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2008, 685, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.; Beilicke, M.; Bernlöhr, K.; Börst, H.-G.; Bojahr, H.; Bolz, O.; Coarasa, T.; Contreras, J.L.; Cortina, J.; et al. Is the giant radio galaxy M 87 a TeV gamma-ray emitter? Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 403, L1–L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalewajko, K.; Giannios, D.; Begelman, M.C.; Uzdensky, D.A.; Sikora, M. Radiative properties of reconnection-powered minijets in blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 413, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.-D.; Yuan, Y.-F.; Li, Y.-R.; Wang, J.-M. A General Relativistic External Compton-Scattering Model for TeV Emission from M 87. Astrophys. J. 2012, 746, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, L.H.S.; de Gouveia Dal Pino, E.M.; Singh, C.B. The Role of Fast Magnetic Reconnection on the Radio and Gamma-ray Emission from the Nuclear Regions of Microquasars and Low Luminosity AGNs. Astrophys. J. 2015, 802, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gouveia Dal Pino, E.M.; Piovezan, P.P.; Kadowaki, L.H.S. The role of magnetic reconnection on jet/accretion disk systems. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 518, A5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarek, W. GeV–TeV γ-rays produced by electrons in the kpc-scale jet as a result of Comptonization of the inner jet emission. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 483, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Baughman, B.M.; Bechtol, K.; et al. Fermi Gamma-Ray Imaging of a Radio Galaxy. Science 2010, 328, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hardcastle, M.J.; Croston, J.H. Modelling TeV γ-ray emission from the kiloparsec-scale jets of Centaurus A and M87. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-Y.; Rieger, F.M.; Aharonian, F.A. Particle Acceleration in Mildly Relativistic Shearing Flows: The Interplay of Systematic and Stochastic Effects, and the Origin of the Extended High-energy Emission in AGN Jets. Astrophys. J. 2017, 842, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmaverde, B.; Caccianiga, A.; Della Ceca, R.; Wolter, A.; Belfiore, A.; Ballo, L.; Berton, M.; Gioia, I.; Maccacaro, T.; Sbarufatti, B. Te-REX: A sample of extragalactic TeV-emitting candidates. Astron. Astrophys. submitted.
- Nagar, N.M.; Falcke, H.; Wilson, A.S.; Ho, L.C. Radio Sources in Low-Luminosity Active Galactic Nuclei. I. VLA Detections of Compact, Flat-Spectrum Cores. Astrophys. J. 2000, 542, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcke, H.; Nagar, N.M.; Wilson, A.S.; Ulvestad, J.S. Radio Sources in Low-Luminosity Active Galactic Nuclei. II. Very Long Baseline Interferometry Detections of Compact Radio Cores and Jets in a Sample of LINERs. Astrophys. J. 2000, 542, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, M.E.; Barthel, P.D.; Ho, L.C. The Radio Properties of Composite LINER/H II Galaxies. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2003, 142, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nyland, K.; Young, L.M.; Wrobel, J.M.; Sarzi, M.; Morganti, R.; Alatalo, K.; Blitz, L.; Bournaud, F.; Bureau, M.; Cappellari, M.; et al. The ATLAS3D Project—XXXI. Nuclear radio emission in nearby early-type galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 458, 2221–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, R.D.; Williams, D.R.A.; McHardy, I.M.; Beswick, R.J.; Argo, M.K.; Dullo, B.T.; Knapen, J.H.; Brinks, E.; Muxlow, T.W.B.; Aalto, S.; et al. LeMMINGs—I. The eMERLIN legacy survey of nearby galaxies. 1.5-GHz parsec-scale radio structures and cores. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 3478–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.B. TOPCAT & STIL: Starlink Table/VOTable Processing Software. Astronomical Data Analysis Software and Systems XIV. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. Conf. Ser. 2005, 347, 29. [Google Scholar]
| 1. | The 3C catalogue selects radio sources with flux densities higher than 9 Jy at 178 MHz. |
| 2. | The core dominance is the ratio between the emission from the unresolved radio core and the total radio emission of the RG. |
| 3. | Radio loudness, R, is defined as ratio between the flux densities in the radio (6 cm, 5 GHz) and in the optical band (4400 Å) [35]; where radio-loud AGN have 10. Assuming the optical galaxy emission as an upper limit on the optical nuclear component and 5 mJy as minimum radio flux, the radio loudness of FR 0s is at least >11. |
| 4. | The Lorentz factor for jets is where v is the jet speed. |
| 5. | In addition to M 87 and CenA, there are other four radio galaxies detected at TeV energies, i.e., NGC 1275 (d ∼ 76.7 Mpc), IC 310 (d ∼ 82.8 Mpc), PKS 0625-35 (d ∼ 245 Mpc) and 3C 264 (d ∼ 95.1 Mpc). |
| 6. | TevCat (http://tevcat.uchicago.edu/) and TGeVCat (https://www.ssdc.asi.it/tgevcat/) are online catalogues for TeV astronomy. |
| 7. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).