Simulation Study on Bearing Lubrication Mechanism and Friction Characteristics of the Biomimetic Non-Smooth Surface of a Cross-Scale, Second-Order Compound Microstructure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Models and Methods
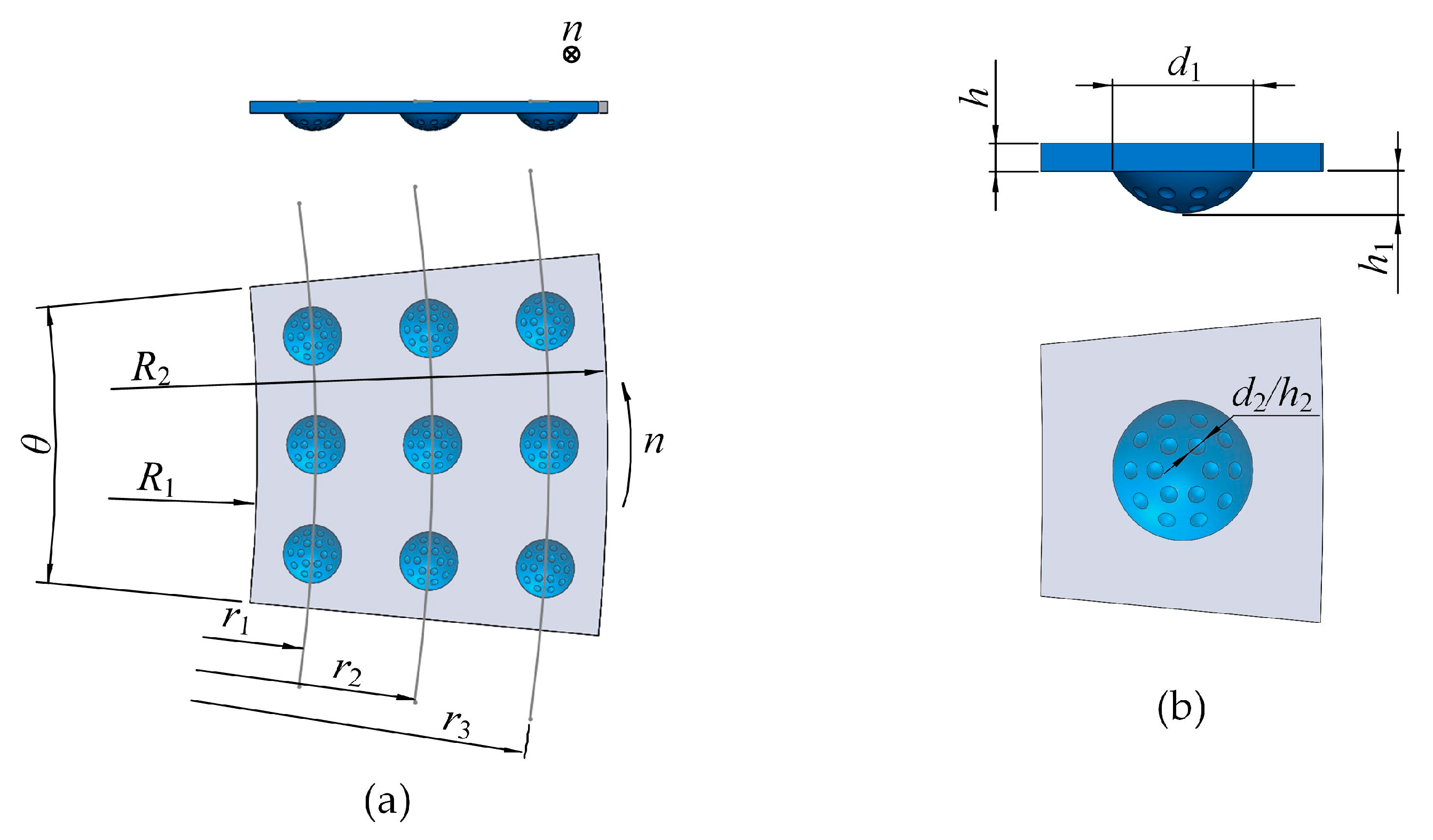
2.1. Model Description
2.2. Governing Equation
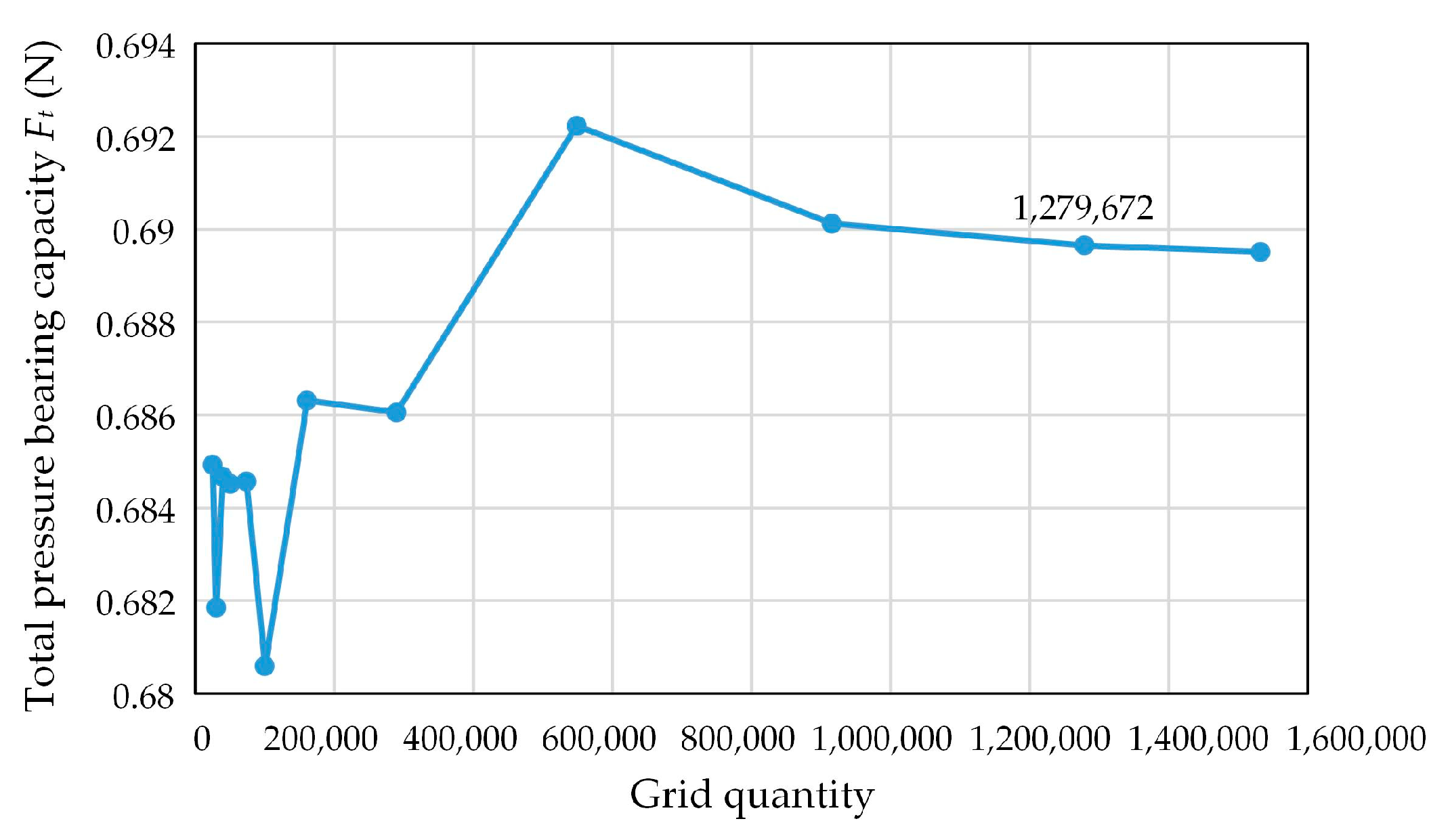
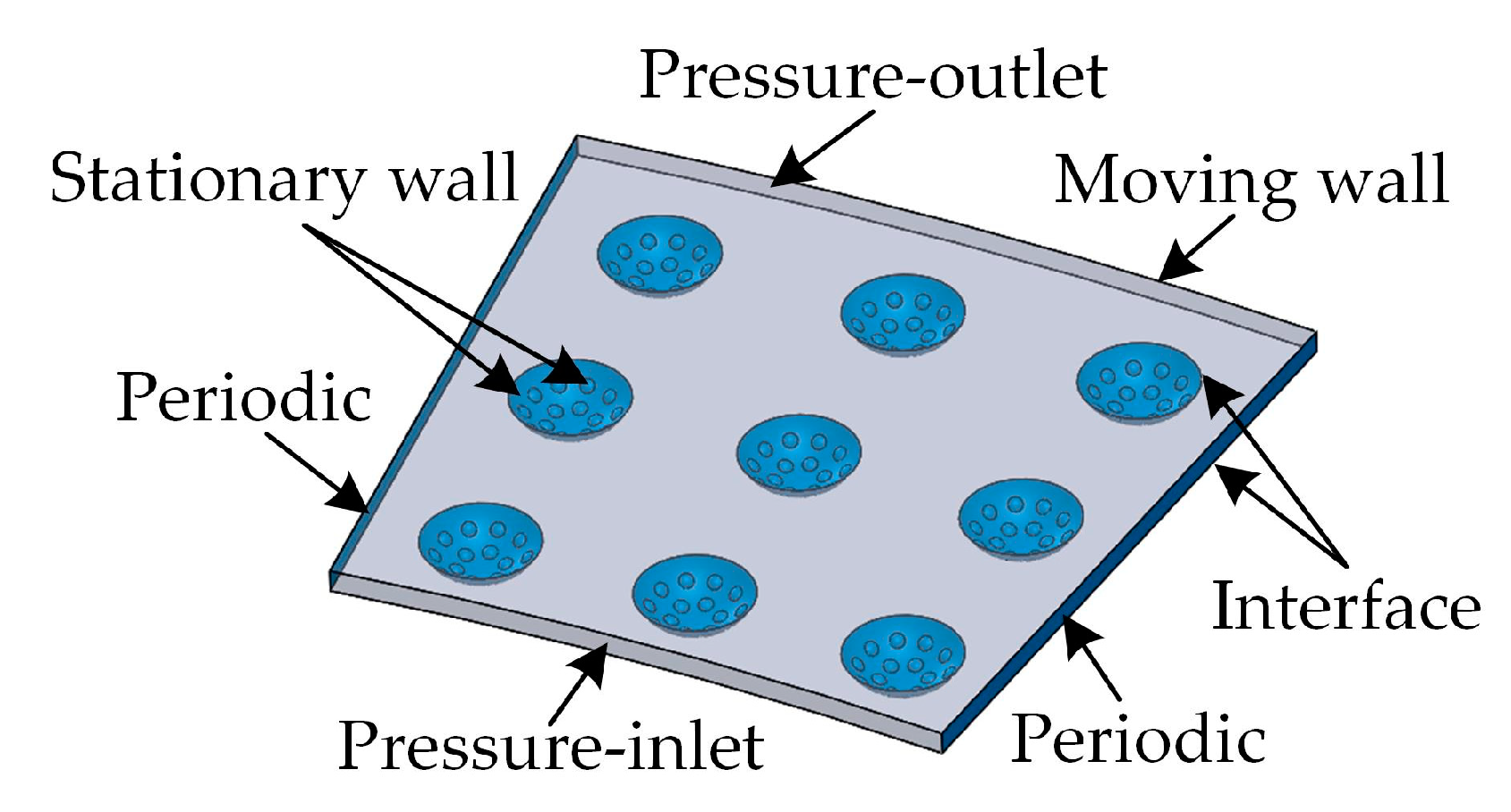
2.3. Simulation Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
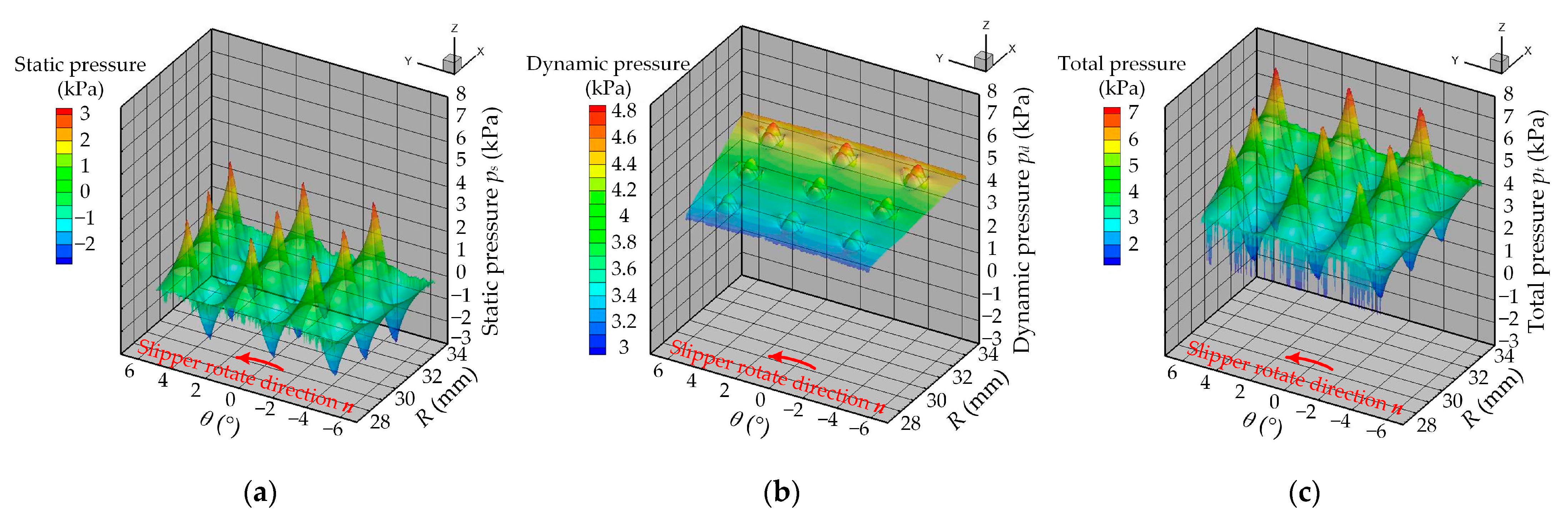
3.1. Analysis of Single Group Test Simulation Results
3.2. Range Analysis of Multi-Index Orthogonal Test Results
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Bearing Capacity and Lubrication Characteristics of Different Surfaces
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, L.Q.; Yang, Z.J.; Han, Z.W. Non-smooth wearable surface of living creatures and their bionic application. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2005, 36, 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.F.; Guo, Z.W.; Huang, Q.R.; Yuan, C.Q. Application of bionic tribology in water-lubricated bearing: A review. J. Bionic Eng. 2022, 19, 902–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.Z.; Zhang, Y.S.; Feng, X.M.; Hu, Y.S. Focus on bioinspired textured surfaces toward fluid drag reduction: Recent progresses and challenges. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2100696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachot, C.; Rosenkranz, A.; Hsu, S.M.; Costa, H.L. A critical assessment of surface texturing for friction and wear improvement. Wear 2017, 372–373, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, B.; Chao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, X.C. Effect of surface texture on wear reduction of the tilting cylinder and the valve plate for a high-speed electro-hydrostatic actuator pump. Wear 2018, 414–415, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Fu, Q.; Wood, R.J.K.; Wu, J.; Wang, S.C. Influence of bionic non-smooth surface texture on tribological characteristics of carbon-fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone under seawater lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2020, 144, 106100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Kodama, E.; Sakakibara, K.; Sasaki, S.; Tsujii, Y. Effect of surface texturing on the durability of concentrated polymer brushes. Tribol. Int. 2021, 155, 106668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Yang, X.F.; Dong, W.L.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wu, M. Research and prospect of textured sliding bearing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.M.; Yang, X.F.; Cheng, J.; Wang, S.R.; Duan, D.R.; Xiao, J.P.; Li, W.Y. Optimization of performance parameters and mechanism of bionic texture on friction surface. Coatings 2020, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Resendiz, J.; Tomkowski, R.; Liu, X. An experimental study of micro-dimpled texture in friction control under dry and lubricated conditions. Micromachines 2022, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.N.; Gao, D.R.; Chen, B.; Zhao, J.H. Friction and wear study on friction pairs with a biomimetic non-smooth surface of 316L relative to CF/PEEK under a seawater lubricated condition. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2019, 32, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y.N.; Gao, D.R.; Zhao, J.H. Tribological properties of friction pair between 316L stainless steel and CF/PEEK with nonsmooth surface under seawater lubrication. Tribol. Trans. 2020, 63, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.N.; Gao, J.X.; Gao, D.R.; Sun, Y.N.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhao, J.H. Effect of micro-textured surfaces and sliding speed on the lubrication mechanism and friction-wear characteristics of CF/PEEK rubbing against 316L stainless steel under seawater lubrication. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.S.; Liu, Y.W. Design and optimization of a new geometric texture shape for the enhancement of hydrodynamic lubrication performance of parallel slider surfaces. Biosurface Biotribology 2016, 2, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.L.; Wu, H.C.; Zhao, L.M.; Yang, L. Effect of surface micro-pit on oil film performance of slipper pair in axial piston pump under high pressure. Lubr. Eng. 2018, 43, 30–34, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, S.L.; Wu, H.C.; Zhao, L.M.; Yang, L. Study on the effect of material matching to the performance of dry friction of the slipper pair in axial piston pump under high pressure. Mach. Des. Manuf. 2019, 3, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sugihara, T.; Enomoto, T. Performance of cutting tools with dimple textured surfaces: A comparative study of different texture patterns. Precis. Eng. 2017, 49, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.K.; Kinoshita, S.; Sugihara, T.; Enomoto, T. Exploring the role of the interface adhesion phenomena focusing on surface expansion distribution. Tribol. Int. 2023, 179, 108160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Sai, Q.Y.; Wang, S.W.; Williams, J. Effects of laser surface texturing and lubrication on the vibrational and tribological performance of sliding contact. Lubricants 2022, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naduvinamani, N.; Angadi, A. Static and dynamic characteristics of rough porous Rayleigh step bearing lubricated with couple stress fluid. Lubricants 2022, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B. Studies on the Morphological Dimensions of the Riblet Surface of Fast-Swimming Sharks. Master Degree Thesis, Qingdao University of Science & Technology, Qingdao, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, C.J.; Peakall, J.; Burns, A.D.; Keevil, G.M.; Dorrell, R.M.; Wignall, P.B.; Fletcher, T.M. Hydrodynamic efficiency in sharks: The combined role of riblets and denticles. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2021, 16, 046008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. Superior lubrication properties of biomimetic surfaces with hierarchical structure. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.R.; Cheng, H.; Cong, Q.; Li, J.Q.; Chen, B.C.; Ren, L.Q. Bionic study on the dung beetle (Copris ochus Motschulsky) for reduction of soil adhesion. Acta Biophys. Sin. 2001, 17, 785–793. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Sun, J.R.; Li, J.Q.; Ren, L.Q. Structure of the integumentary surface of the dung beetle Copris ochus Motschulsky and its relation to non-adherence of substrate particles. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2002, 45, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.S.; Wu, D.F.; Li, D.L.; Deng, Y.P. Applications and research progress of hydraulic technology in deep sea. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 54, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.P.; Bai, X.Q.; Yuan, C.Q. Discussion on connotation and research scopes of ocean tribology and its research progress. J. Mech. Eng. 2013, 49, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wen, H.X.; Chen, W. Research status on tribological behaviors of materials under seawater environment. Mater. Rep. 2017, 31, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, S.L.; Yin, F.L. Progress and prospect of water hydraulic piston pump. Chin. Hydraul. Pneum. 2015, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.Z.; Huang, P.; Tian, Y.; Ma, L.R. Principles of Tribology, 5th ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2018; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.R.; Wang, H.J.; Liu, Q.Z.; Cai, W.H. Engineering Fluid Mechanics, 3rd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.A.; Tang, X.Q.; Wang, W.B.; Ying, R.; Zhang, T. Reliability verification method of numerical simulation based on grid independence and time independence. J. Shihezi Univ. Nat. Sci. 2017, 35, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lachner, H. Hydrostatic lagerungen in axialkolbenmachine. Hydraul. Pneum. 1974, 18, 605–611. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J. Study on the Lubrication and Friction Properties of Macroscale and Microscale Surface Texture. Doctor Degree Thesis, China University of Mining & Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Jacobs, G.; König, F.; Zhang, S.; Goeldel, V.S. Investigation of microflow effects in textures on hydrodynamic performance of journal bearings using CFD simulations. Lubricants 2023, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhou, Y.K.; Zhu, H.; Yang, H.F. The effect of surface texturing on reducing the friction and wear of steel under lubricated sliding contact. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 273, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Xue, W.D.; Tang, B. Optimize Experimental Design Method and Data Analysis; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]




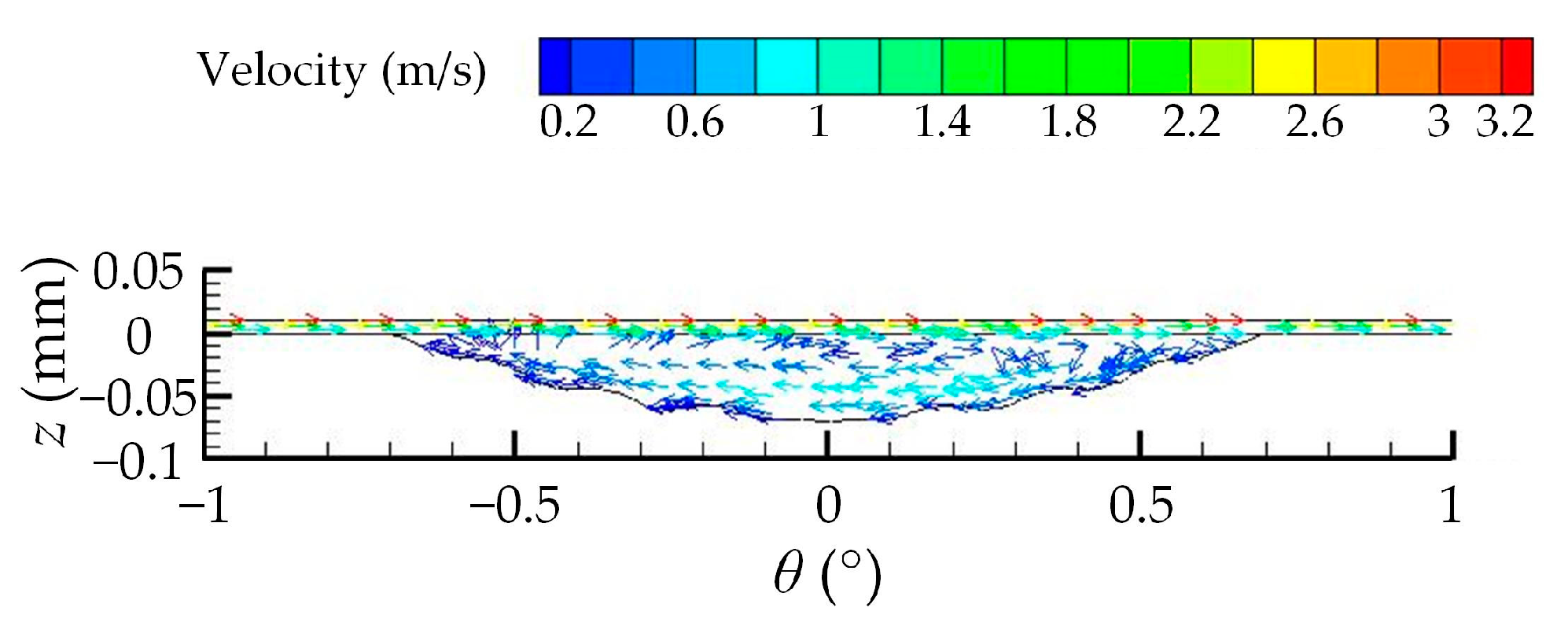
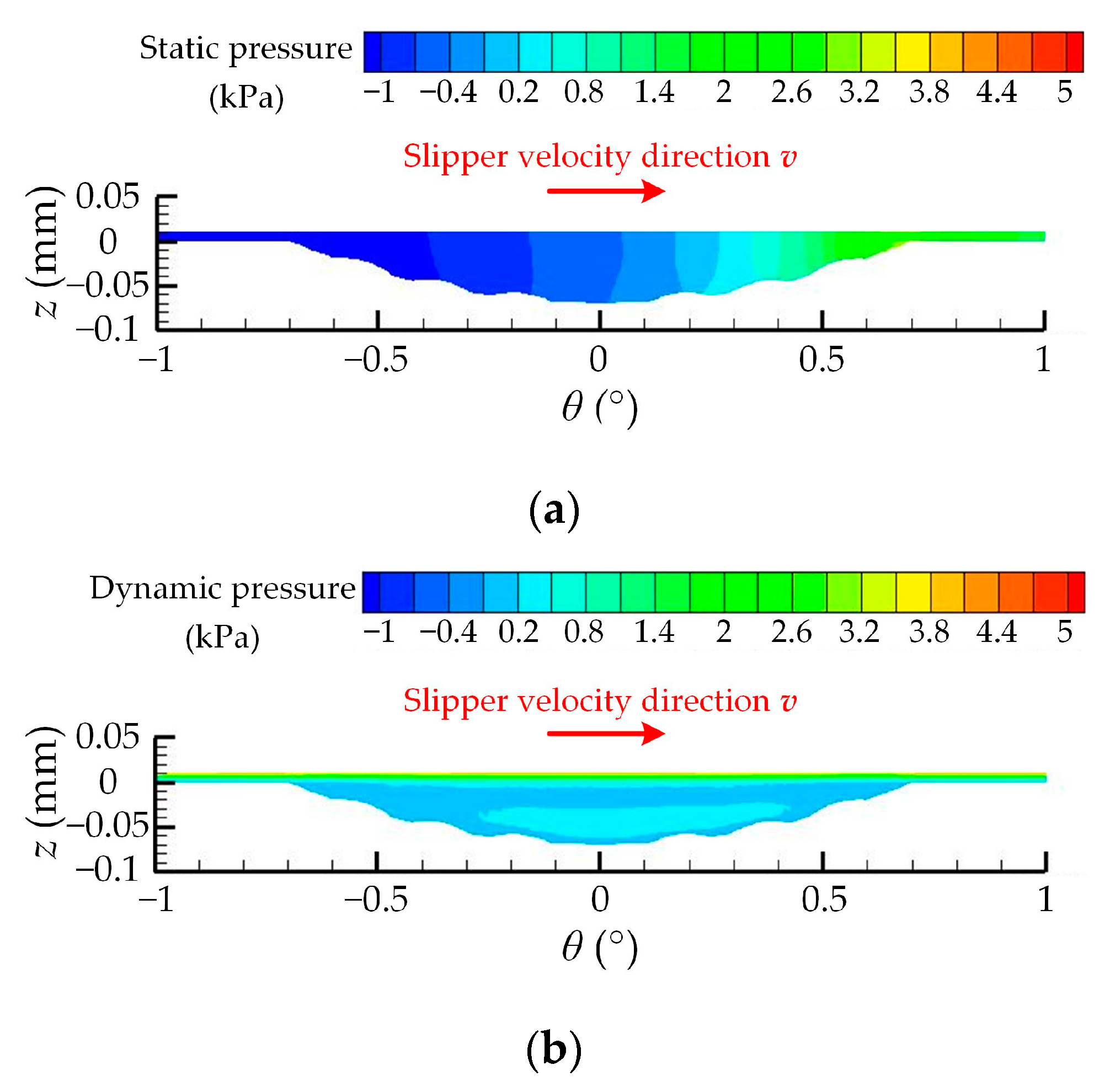
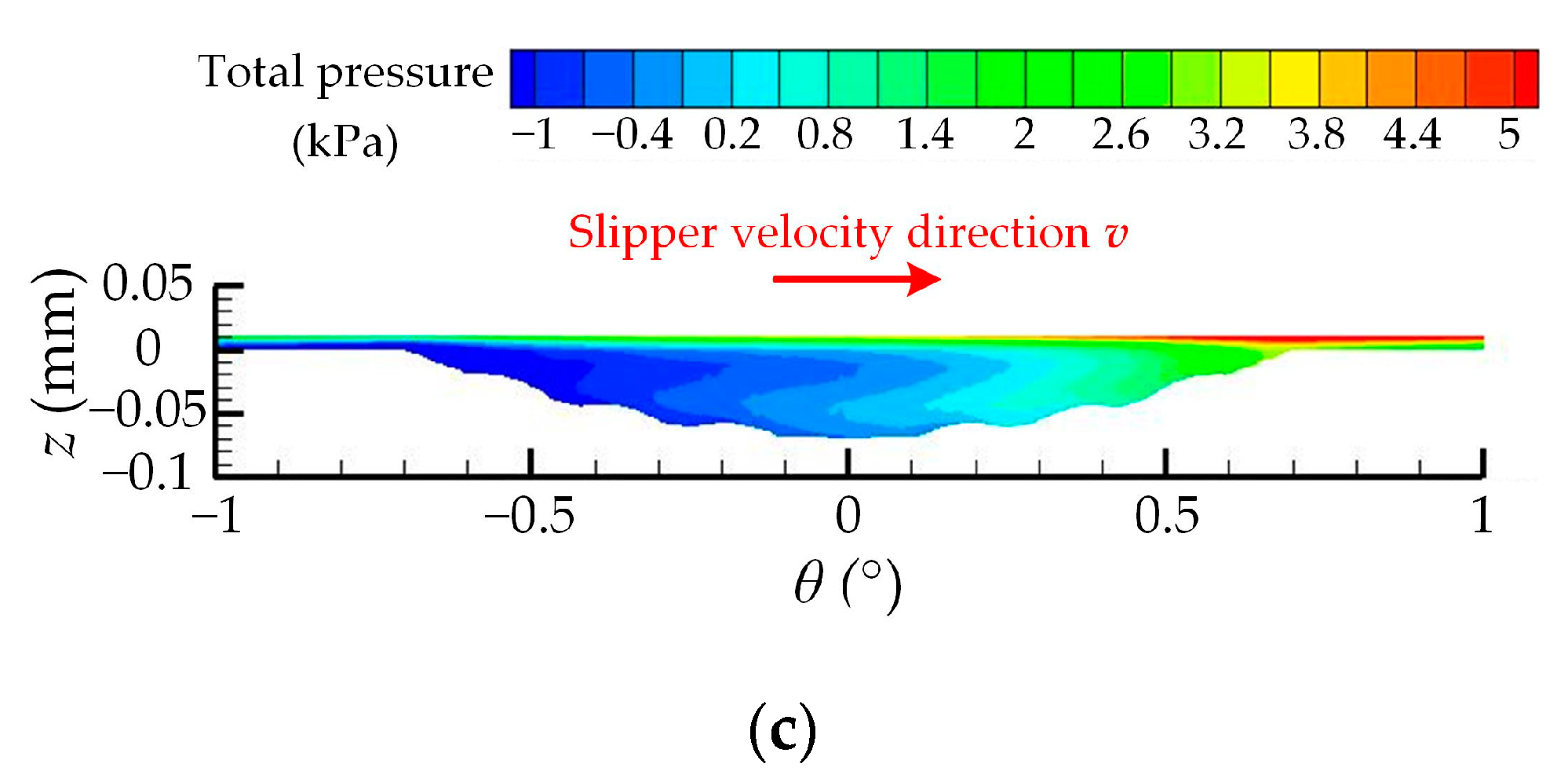
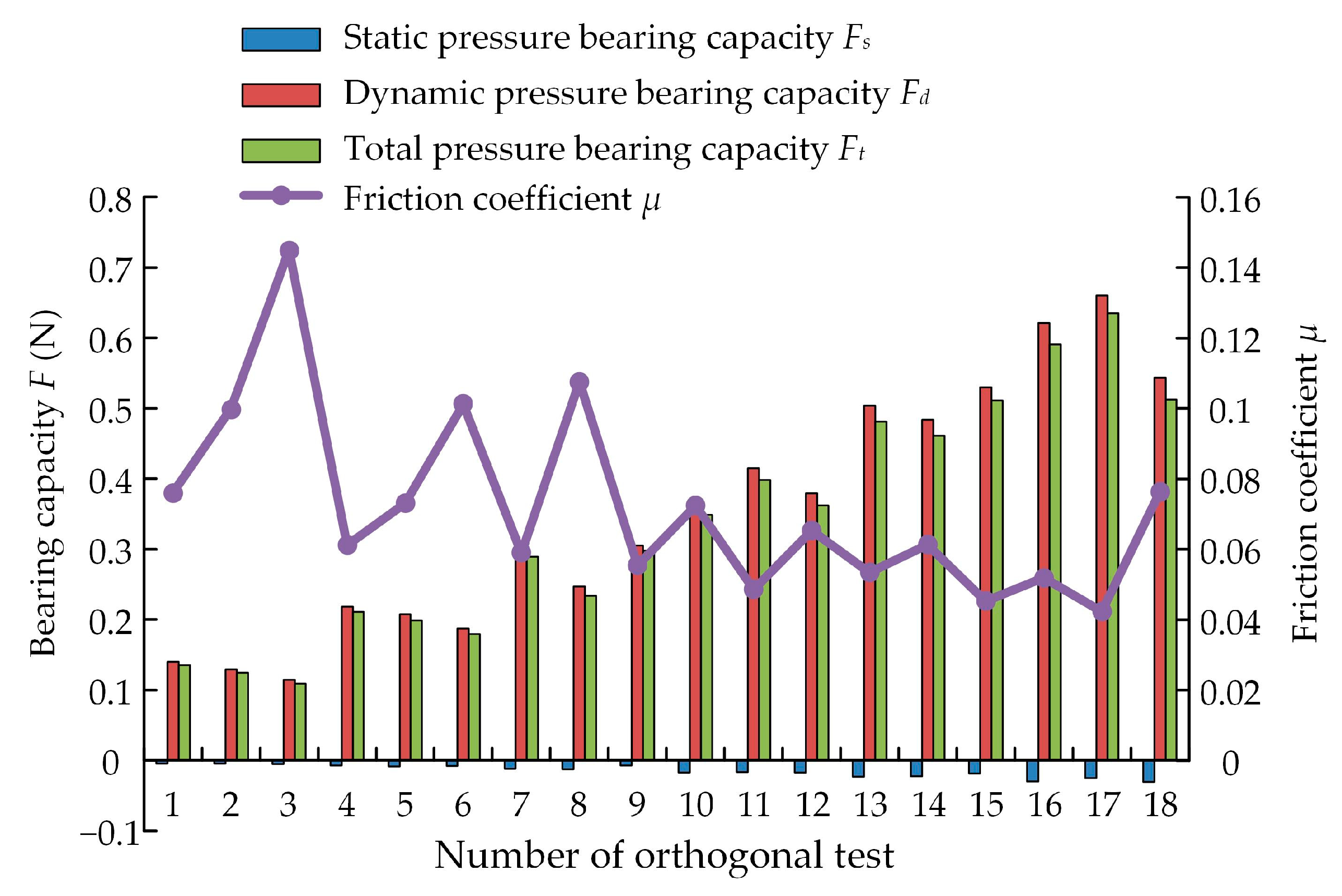
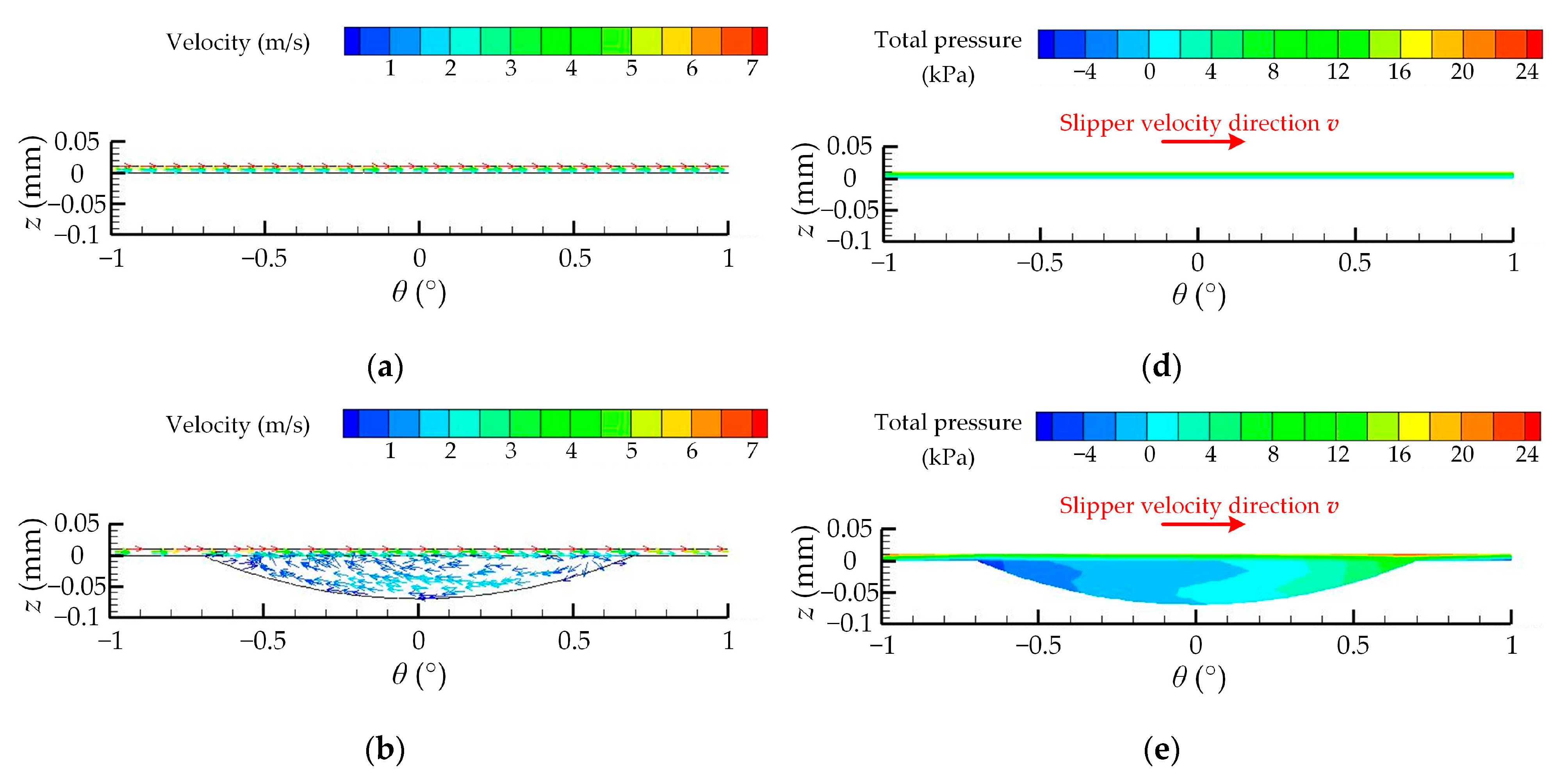
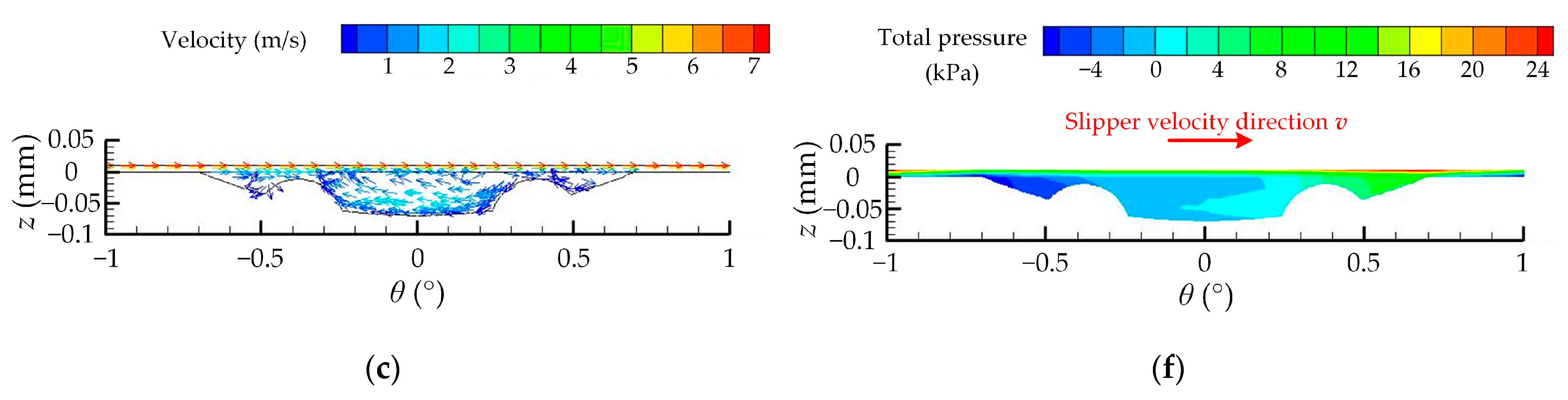
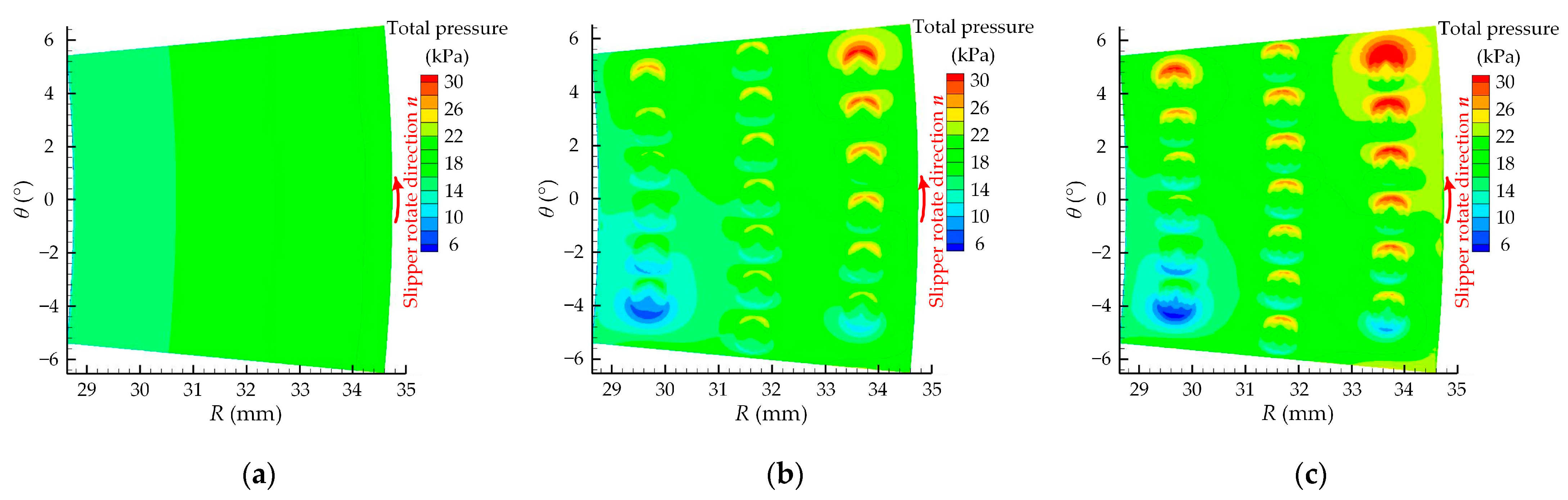
| Number | Experimental Factor | Total Pressure-Bearing Capacity Ft (N) | Friction Coefficient μ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A Rotate Speed n (r/min) | B First Order Diameter d1 (mm) | C First Order Depth-to-Diameter Ratio δ1 | D Second Order Diameter d2 (mm) | E Second Order Depth-to-Diameter Ratio δ2 | F Area Rate S (%) | G Arrangement Angle φ (°) | |||
| 1 | 1(1000) | 1(0.7) | 1(0.1) | 1(0.07) | 1(0.1) | 1(10) | 1(0) | 0.1353 | 0.0760 |
| 2 | 1 | 2(1.0) | 2(0.3) | 2(0.1) | 2(0.3) | 2(20) | 2(α/3) | 0.1246 | 0.0999 |
| 3 | 1 | 3(1.3) | 3(0.5) | 3(0.13) | 3(0.5) | 3(30) | 3(α/2) | 0.1093 | 0.1450 |
| 4 | 2(1250) | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 0.2107 | 0.0611 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0.1989 | 0.0731 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0.1797 | 0.1012 |
| 7 | 3(1500) | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 0.2889 | 0.0589 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0.2336 | 0.1075 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.2981 | 0.0554 |
| 10 | 4(1750) | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0.3484 | 0.0723 |
| 11 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0.3981 | 0.0485 |
| 12 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0.3620 | 0.0653 |
| 13 | 5(2000) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0.4808 | 0.0533 |
| 14 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0.4610 | 0.0613 |
| 15 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.5111 | 0.0453 |
| 16 | 6(2250) | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0.5907 | 0.0519 |
| 17 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0.6349 | 0.0423 |
| 18 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0.5123 | 0.0762 |
| Experimental Factor | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A Rotate Speed n (r/min) | B First Order Diameter d1 (mm) | C First Order Depth-to-Diameter Ratio δ1 | D Second Order Diameter d2 (mm) | E Second Order Depth-to-Diameter Ratio δ2 | F Area Rate S (%) | G Arrangement Angle φ (°) | ||
| Total pressure-bearing capacity Ft (N) | K1 | 0.3692 | 2.0548 | 2.1881 | 1.9753 | 2.0263 | 2.0460 | 1.9396 |
| K2 | 0.5893 | 2.0511 | 1.9676 | 2.0327 | 1.9551 | 2.0875 | 2.0718 | |
| K3 | 0.8206 | 1.9725 | 1.9227 | 2.0703 | 2.0970 | 1.9448 | 2.0669 | |
| K4 | 1.1085 | |||||||
| K5 | 1.4528 | |||||||
| K6 | 1.7379 | |||||||
| k1 | 0.1231 | 0.3425 | 0.3647 | 0.3292 | 0.3377 | 0.3410 | 0.3233 | |
| k2 | 0.1964 | 0.3418 | 0.3279 | 0.3388 | 0.3258 | 0.3479 | 0.3453 | |
| k3 | 0.2735 | 0.3288 | 0.3204 | 0.3451 | 0.3495 | 0.3241 | 0.3445 | |
| k4 | 0.3695 | |||||||
| k5 | 0.4843 | |||||||
| k6 | 0.5793 | |||||||
| Range R | 0.4562 | 0.0137 | 0.0442 | 0.0158 | 0.0237 | 0.0238 | 0.0220 | |
| Adjusted range R’ | 0.2924 | 0.0175 | 0.0564 | 0.0202 | 0.0301 | 0.0303 | 0.0281 | |
| Order | A > C > F > E > G > D > B | |||||||
| Optimal level | A6 | B1 | C1 | D3 | E3 | F2 | G2 | |
| Optimal combination | A6B1C1D3E3F2G2 | |||||||
| Friction coefficient μ | K1 | 0.3209 | 0.3736 | 0.3285 | 0.4221 | 0.4456 | 0.3828 | 0.4504 |
| K2 | 0.2354 | 0.4326 | 0.4267 | 0.4310 | 0.4263 | 0.4199 | 0.4103 | |
| K3 | 0.2218 | 0.4883 | 0.5392 | 0.4414 | 0.4226 | 0.4918 | 0.4339 | |
| K4 | 0.1862 | |||||||
| K5 | 0.1599 | |||||||
| K6 | 0.1703 | |||||||
| k1 | 0.1070 | 0.0623 | 0.0548 | 0.0703 | 0.0743 | 0.0638 | 0.0751 | |
| k2 | 0.0785 | 0.0721 | 0.0711 | 0.0718 | 0.0710 | 0.0610 | 0.0684 | |
| k3 | 0.0739 | 0.0814 | 0.0899 | 0.0736 | 0.0704 | 0.0820 | 0.0723 | |
| k4 | 0.0621 | |||||||
| k5 | 0.0533 | |||||||
| k6 | 0.0568 | |||||||
| Range R | 0.0537 | 0.0191 | 0.0351 | 0.0032 | 0.0038 | 0.0182 | 0.0067 | |
| Adjusted range R’ | 0.0344 | 0.0244 | 0.0447 | 0.0041 | 0.0049 | 0.0231 | 0.0085 | |
| Order | C > A > B > F > G > E > D | |||||||
| Optimal level | A5 | B1 | C1 | D1 | E3 | F1 | G2 | |
| Optimal combination | A5B1C1D1E3F1G2 | |||||||
| Smooth Surface | Spherical Pit | Spherical Pit Containing Spherical Convex Hulls | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total pressure-bearing capacity Ft (N) | 0.6215 | 0.6335 | 0.6897 |
| Friction coefficient μ | 0.0443 | 0.0424 | 0.0401 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Xing, H.; Guan, T.; Gao, D. Simulation Study on Bearing Lubrication Mechanism and Friction Characteristics of the Biomimetic Non-Smooth Surface of a Cross-Scale, Second-Order Compound Microstructure. Lubricants 2023, 11, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11020077
Liang Y, Wang C, Zhang Z, Zhang Z, Wang W, Xing H, Guan T, Gao D. Simulation Study on Bearing Lubrication Mechanism and Friction Characteristics of the Biomimetic Non-Smooth Surface of a Cross-Scale, Second-Order Compound Microstructure. Lubricants. 2023; 11(2):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11020077
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yingna, Cunyuan Wang, Zongyi Zhang, Zhepeng Zhang, Wei Wang, Hao Xing, Tianyuan Guan, and Dianrong Gao. 2023. "Simulation Study on Bearing Lubrication Mechanism and Friction Characteristics of the Biomimetic Non-Smooth Surface of a Cross-Scale, Second-Order Compound Microstructure" Lubricants 11, no. 2: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11020077
APA StyleLiang, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Z., Wang, W., Xing, H., Guan, T., & Gao, D. (2023). Simulation Study on Bearing Lubrication Mechanism and Friction Characteristics of the Biomimetic Non-Smooth Surface of a Cross-Scale, Second-Order Compound Microstructure. Lubricants, 11(2), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11020077





