Small Laser-Textured Dimples for Improved Tribological Performance of CoCrMo in Artificial Hip Joints
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Sample Fabrication
2.2. Surface Topography Characterization
2.3. Water Contact Angle Measurements
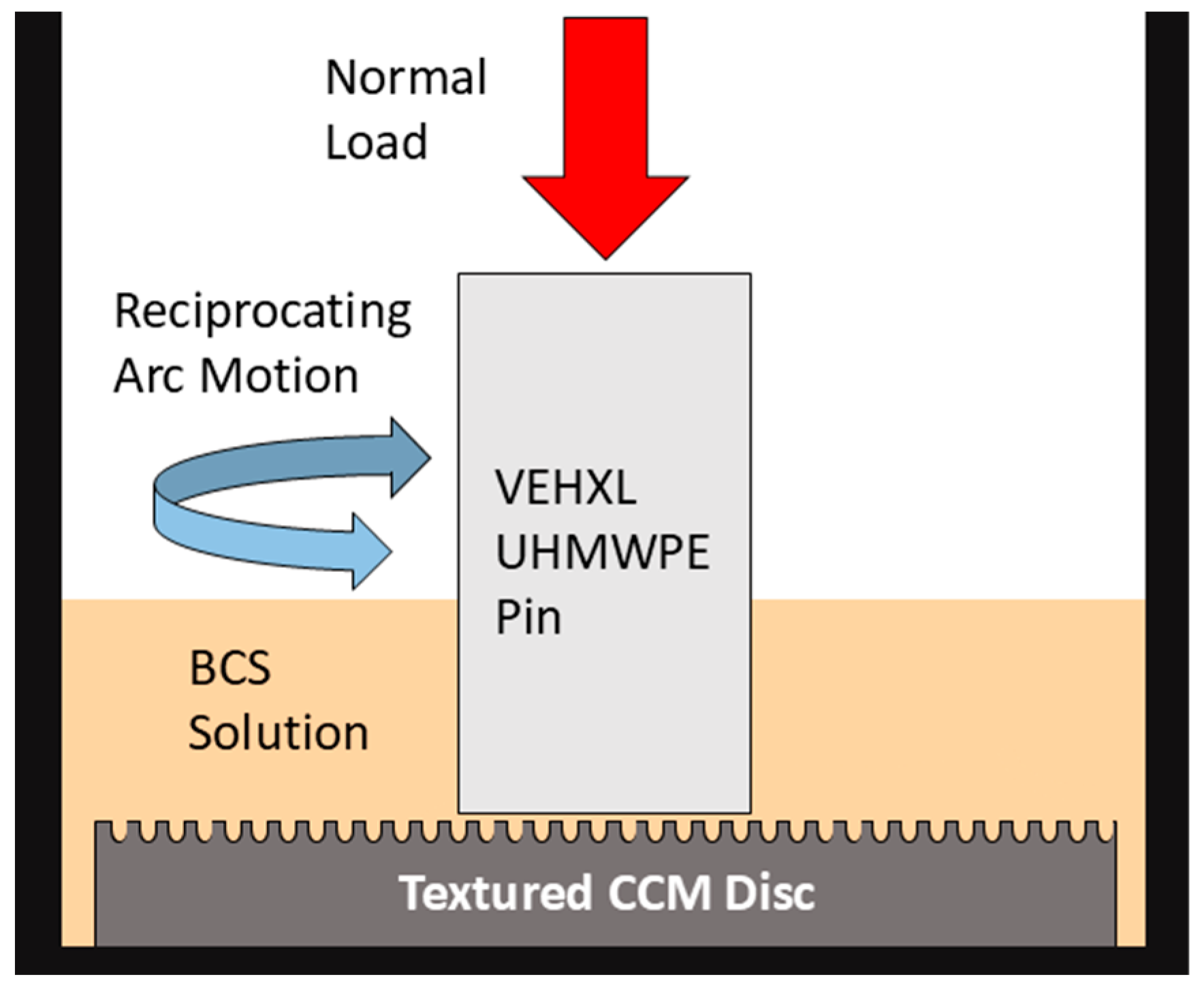
2.4. Pin-on-Disc Tribological Testing
2.5. Wear Analysis
3. Results
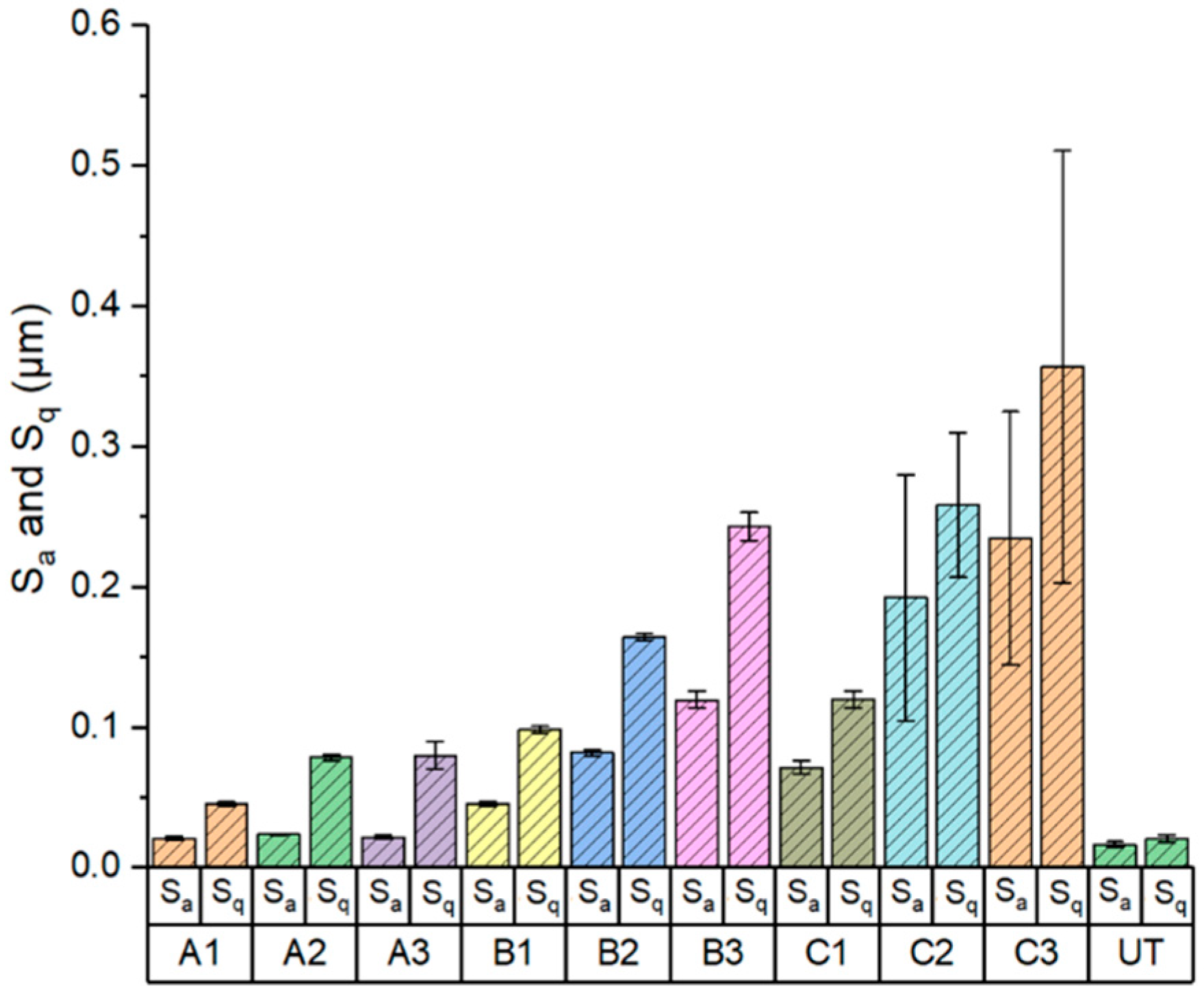
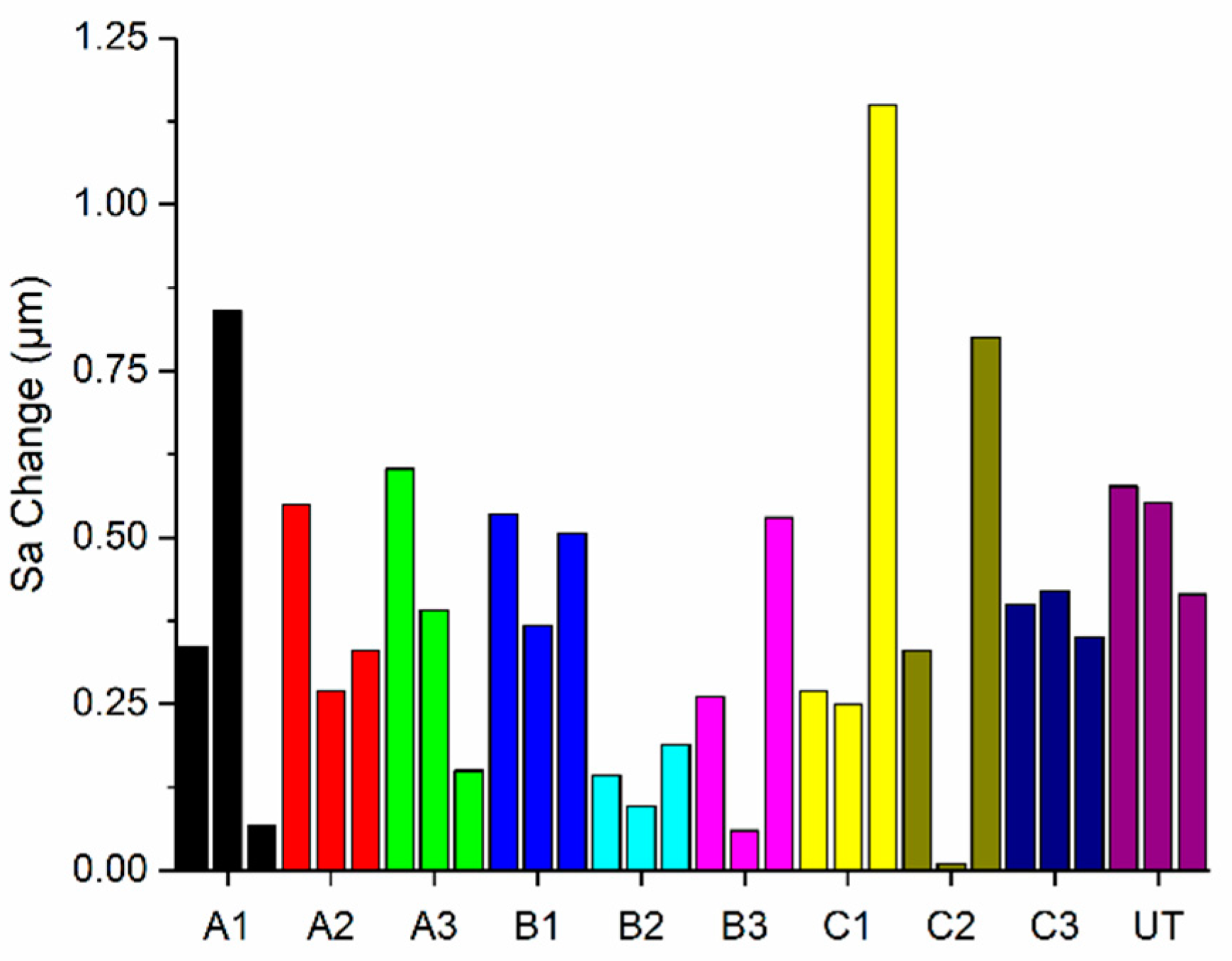
3.1. Surface Topography of Fabricated CCM Disc and UHMWPE Pin
3.2. Surface Wettability
3.3. Friction and Wear Performance
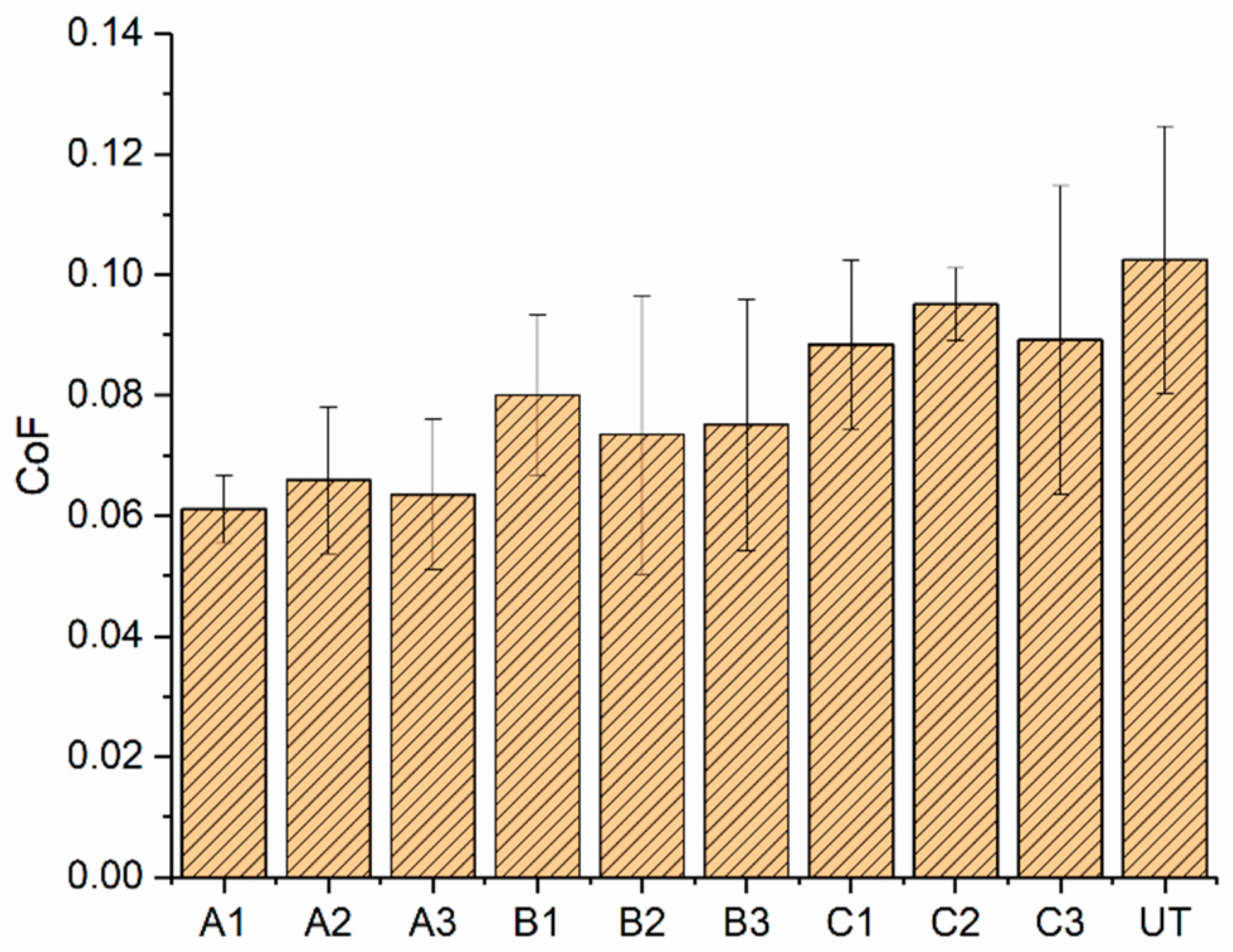
3.3.1. Coefficient of Friction
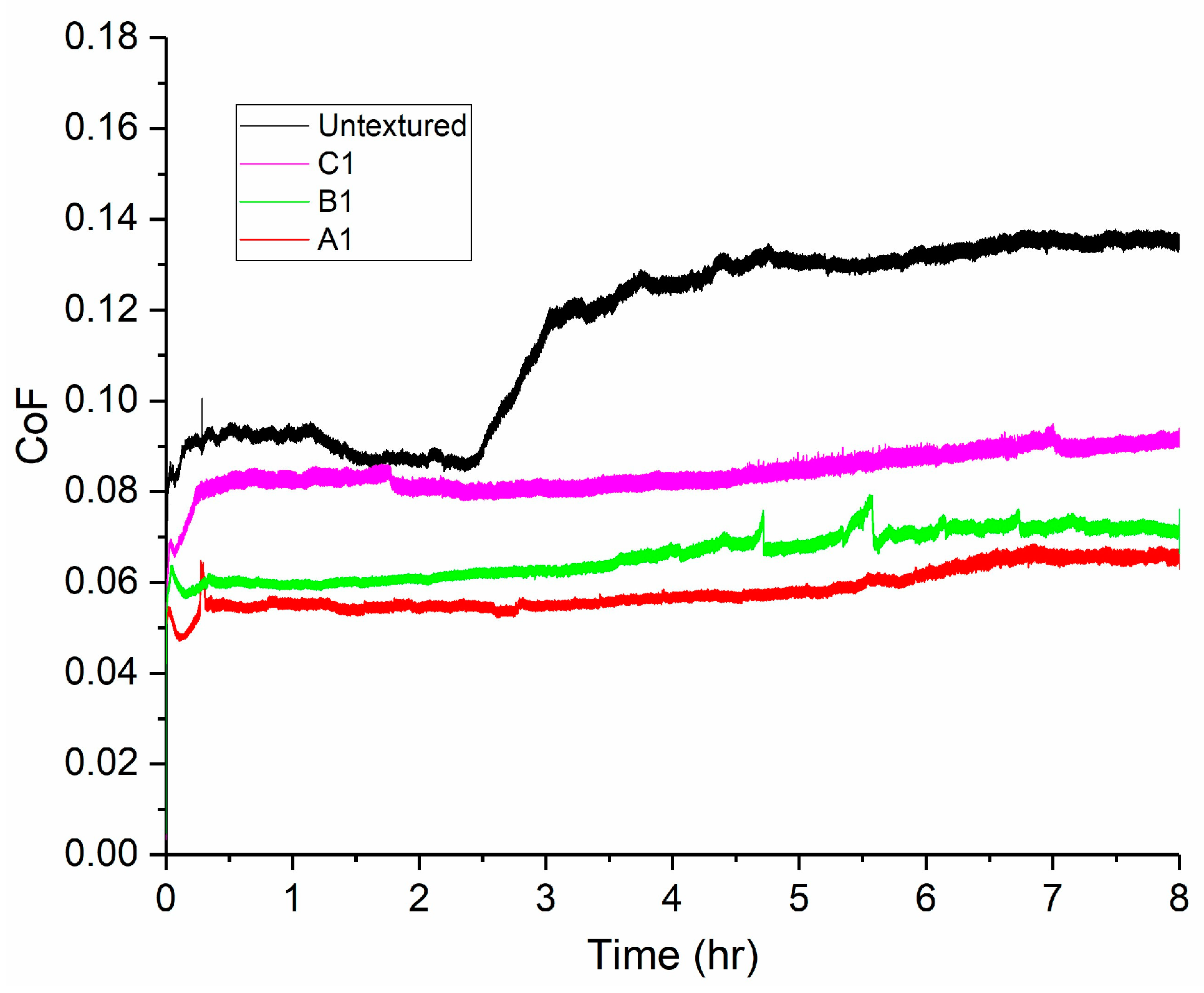
3.3.2. Frictional Behavior
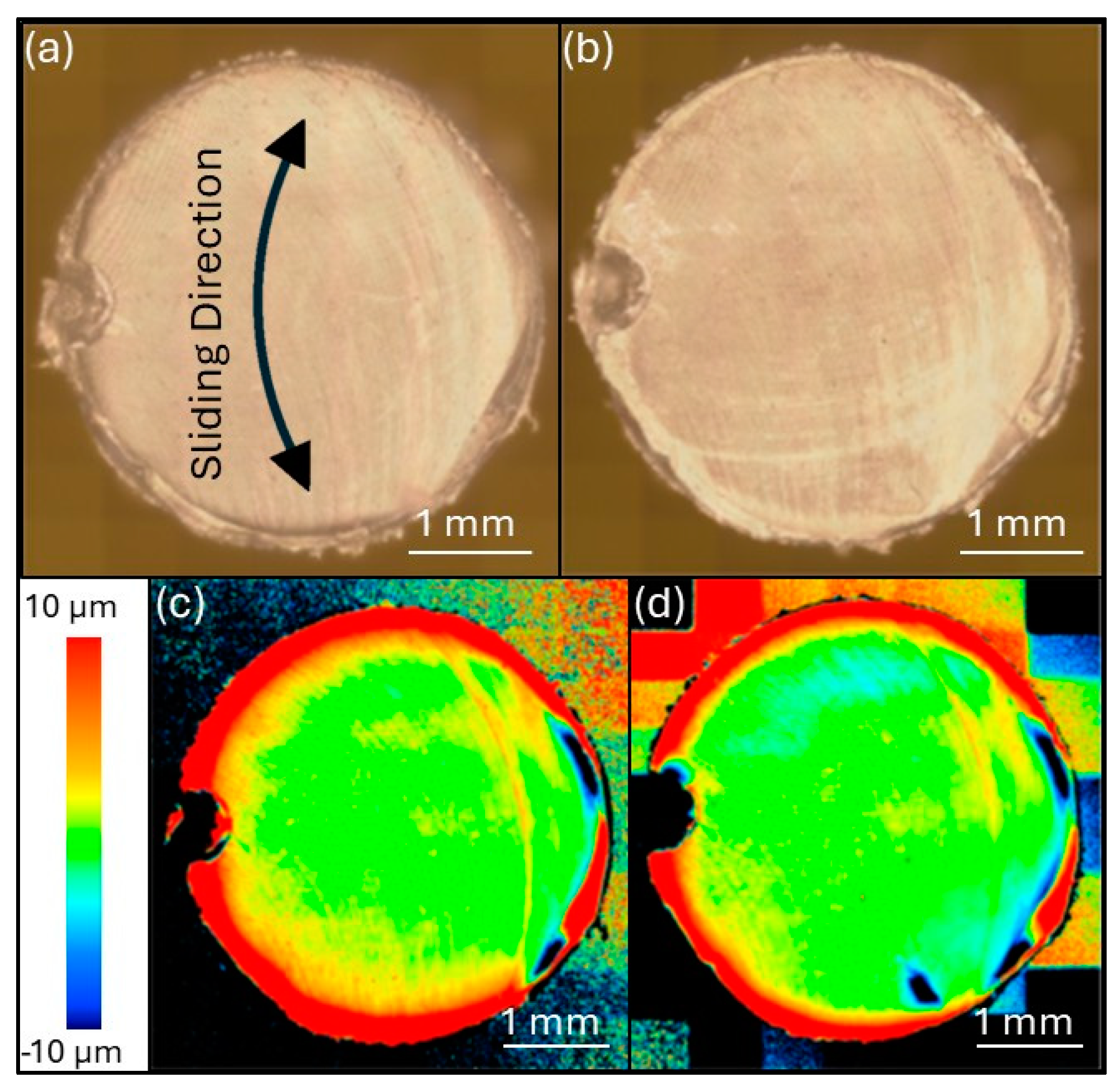
3.3.3. Wear Performance and Mechanisms
4. Discussion
4.1. Wear
4.2. Effect of Protrusions on Texture Performance
4.3. Effect of WCA and Roughness on Tribological Performance
4.4. Mechanisms Governing Tribological Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCM | CoCrMo |
| UHMWPE | Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene |
| CoF | Coefficient of friction |
| THR | Total hip replacement |
| LST | Laser surface texturing |
| MoP | Metal-on-polyethylene |
| VEHXL | Vitamin E-stabilized highly cross-linked |
| IPA | Isopropyl alcohol |
| DI water | Deionized water |
| LSCM | Laser scanning confocal microscopy |
| WCA | Water contact angle |
| BCS | Bovine calf serum |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
References
- El-Desouky, I.I.; Helal, A.H.; Mansour, A.M.R. Ten-Year Survival of Ceramic-on-Ceramic Total Hip Arthroplasty in Patients Younger than 60 Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebergall, A.K.; Greene, M.E.; Laursen, M.B.; Nielsen, P.T.; Malchau, H.; Troelsen, A. 2017, Vitamin E Diffused Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Total Hip Arthroplasty at Five Years. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 99, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Nakashima, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Komohara, Y.; Takeya, M.; Miura, H.; Higaki, H. Influence of Surface Profile of Co-28Cr-6Mo Alloy on Wear Behaviour of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene Used in Artificial Joint. Tribol. Int. 2018, 118, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, K.J.; Thongtrangan, I.; Schwarz, E.M. Osteolysis: Medical and surgical approaches. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2004, 427, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ching, H.A.; Choudhury, D.; Nine, M.J.; Abu Osman, N.A. Effects of Surface Coating on Reducing Friction and Wear of Orthopaedic Implants. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2014, 15, 014402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayarasan, M.; Prabhu Raja, V.; Nithin, V.; Vivinkumar, S.; Vishwaanth, M. Comparative Study of Wear Behavior of Multilayer Coatings for Human Hip Prosthesis. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 787, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, T.; Kawaguchi, H.; Ishihara, K.; Kyomoto, M.; Karita, T.; Ito, H.; Nakamura, K.; Takatori, Y. Wear Resistance of Artificial Hip Joints with Poly(2-Methacryloyloxyethyl Phosphorylcholine) Grafted Polyethylene: Comparisons with the Effect of Polyethylene Cross-Linking and Ceramic Femoral Heads. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2995–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, W.D.; Nugroho, A.; Ismail, R.; Jamari, J.; Bayuseno, A.P. Study of Wear Performance of Crosslinking UHMWPE Acetabular Liner for Artificial Hip Joint Made from CNC Milling. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1078, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cervantes, A.; Domínguez-López, I.; Barceinas-Sánchez, J.D.O.; García-García, A.L. Effects of Surface Texturing on the Performance of Biocompatible UHMWPE as a Bearing Material during in Vitro Lubricated Sliding/Rolling Motion. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 20, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jia, X.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Du, W.; Zhang, H. Research Progress on the Effect of Surface Texture on the Friction Properties of CoCrMo Alloys. Compos. Interfaces 2024, 31, 1269–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, T.; Jamari, J.; Bayuseno, A.P.; Ismail, R.; Tauviqirrahman, M.; Wijaya, P.N. Study of Lubrication Fluid Pressure in Artificial Hip Joint During Bowing (Ruku’). In Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference and Exhibition on Sustainable Energy and Advanced Materials (ICE-SEAM 2021), Melaka, Malaysia, 1 July 2022; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yang, P.; Dymond, I.; Fisher, J.; Jin, Z. Effect of Surface Texturing on the Electrohydrodynamic Lubrication Analysis of Metal-on-Metal Hip Implants. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranuša, M.; Odehnal, L.; Kučera, O.; Nečas, D.; Hartl, M.; Křupka, I.; Vrbka, M. Effect of Surface Texturing on Friction and Lubrication of Ti6Al4V Biomaterials for Joint Implants. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 73, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkarenko, A.; Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I. The Effect of Surface Texturing in Soft Elasto-Hydrodynamic Lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.S.; Ibatan, T.; Shankar, S. Influence of Surface Texture Shape, Geometry and Orientation on Hydrodynamic Lubrication Performance of Plane-to-Plane Slider Surfaces. Lubr. Sci. 2016, 29, 153–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drescher, P.; Oldorf, P.; Dreier, T.; Schnell, G.; Peters, R.; Seitz, H. Ring-Shaped Surface Microstructures for Improved Lubrication Performance of Joint Prostheses. Lubricants 2020, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabolsi, M.; Klassen, T.; Mantwill, F.; Gärtner, F.; Siegel, F.; Schulz, A. Patterned CoCrMo and Al2O3 Surfaces for Reduced Free Wear Debris in Artificial Joint Arthroplasty. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2013, 101, 3447–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Siddaiah, A.; Liao, Y.; Menezes, P.L. Laser Surface Texturing and Related Techniques for Enhancing Tribological Performance of Engineering Materials: A Review. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 53, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, J. Tribological Behavior of CoCrMo Artificial Knee Joint with Symmetrically Biomimetic Textured Surfaces on PEEK. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 157, 108774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyr, A.; Qiu, M.; Speltz, J.W.; Jacobsen, R.L.; Sanders, A.P.; Raeymaekers, B. A Patterned Microtexture to Reduce Friction and Increase Longevity of Prosthetic Hip Joints. Wear 2014, 315, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Tang, Y. Research Progress on the Design of Surface Texture in Tribological Applications: A Mini-Review. Symmetry 2024, 16, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhorn, J.; Borjali, A.; Hippensteel, E.; Nelson, W.; Raeymaekers, B. Microtextured CoCrMo Alloy for Use in Metal-on-Polyethylene Prosthetic Joint Bearings: Multi-Directional Wear and Corrosion Measurements. Tribol. Int. 2018, 124, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, Q.; Raeymaekers, B. Surface Texturing of Prosthetic Hip Implant Bearing Surfaces: A Review. J. Tribol. 2020, 143, 040801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmore, R.B.; Gardner, D.L. The surface structure of ageing human articular cartilage: A study by reflected light interference microscopy (RLIM). J. Anat. 1978, 126 Pt 2, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hidayat, T.; Ammarullah, M.I.; Saputra, E.; Lamura, M.D.P.; KN, C.; Ismail, R.; Bayuseno, A.P.; Jamari, J. A Method for Estimating the Contact Area of a Dual-Mobility Total Hip Prosthesis. AIP Adv. 2024, 14, 015317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccio, F.D. Biotribology of Artificial Hip Joints. World J. Orthop. 2015, 6, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, D.; Ranuša, M.; Fleming, R.A.; Vrbka, M.; Křupka, I.; Teeter, M.G.; Goss, J.; Zou, M. Mechanical Wear and Oxidative Degradation Analysis of Retrieved Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene Acetabular Cups. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 79, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of Solid Surfaces to Wetting by Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of Porous Surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Zhang, J.; Fang, F. Study on the Effect of Hydrodynamic Pressure on the Tribological Performance of Textured Bioimplants. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2021, 236, 3135–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Vera, M.; Ortega, J.A.; Ortega-Ramos, I.A.; Hdz-García, H.M.; Muñoz-Arroyo, R.; Díaz-Guillén, J.C.; Acevedo-Dávila, J.L.; Hernández-Rodriguez, M.A.L. Tribological and Microstructural Characterization of Laser Microtextured CoCr Alloy Tested against UHMWPE for Biomedical Applications. Wear 2021, 477, 203819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Lin, N.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Wu, Y. Correlation between surface textural parameter and tribological behaviour of four metal materials with laser surface texturing (LST). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 583, 152410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borjali, A.; Langhorn, J.; Monson, K.; Raeymaekers, B. Using a Patterned Microtexture to Reduce Polyethylene Wear in Metal-on-Polyethylene Prosthetic Bearing Couples. Wear 2017, 392–393, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, K.; Huang, Q.; Guo, X.; Wang, C. A Study on Tribological Properties of Textured Co-Cr-Mo Alloy for Artificial Hip Joints. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 95, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
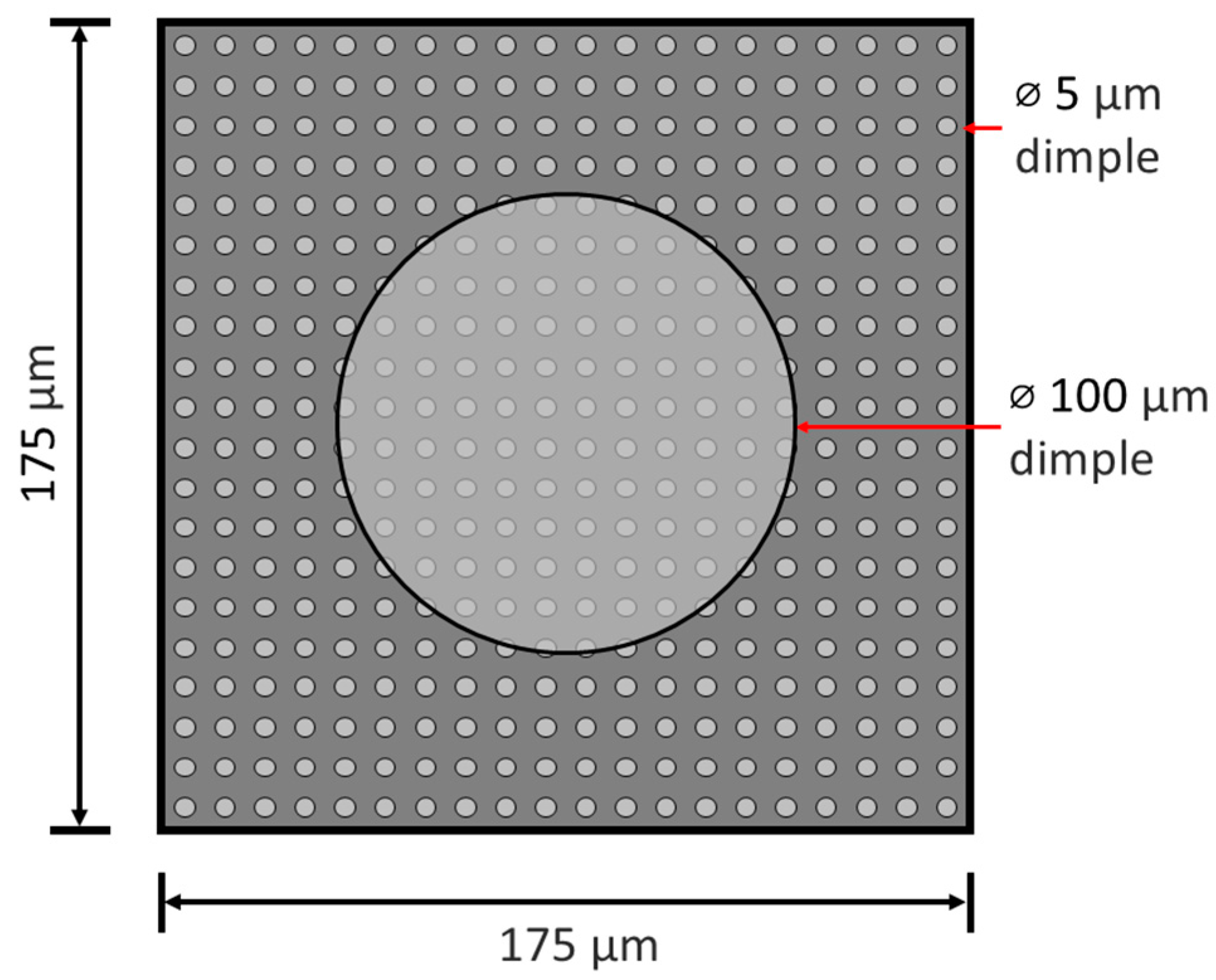
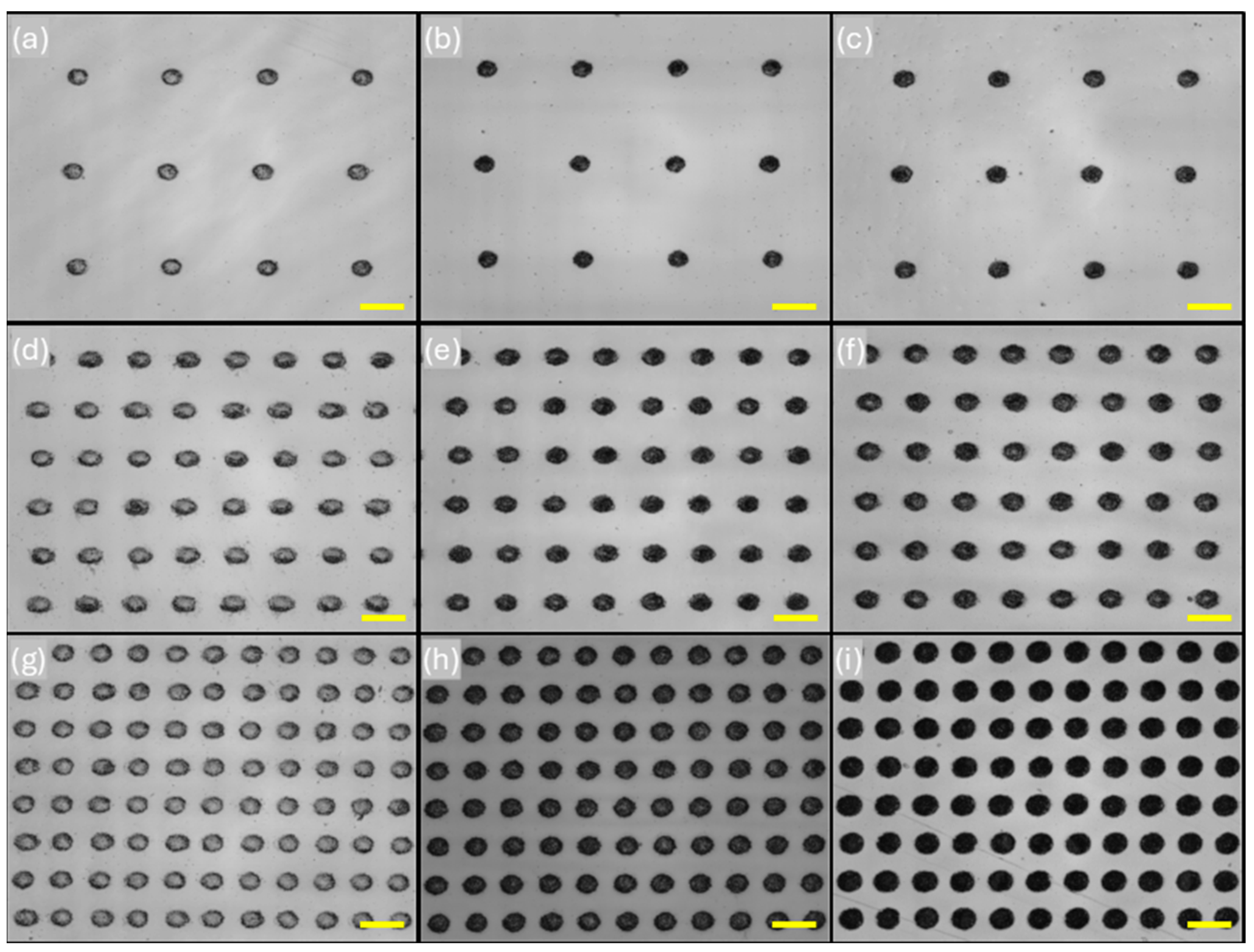
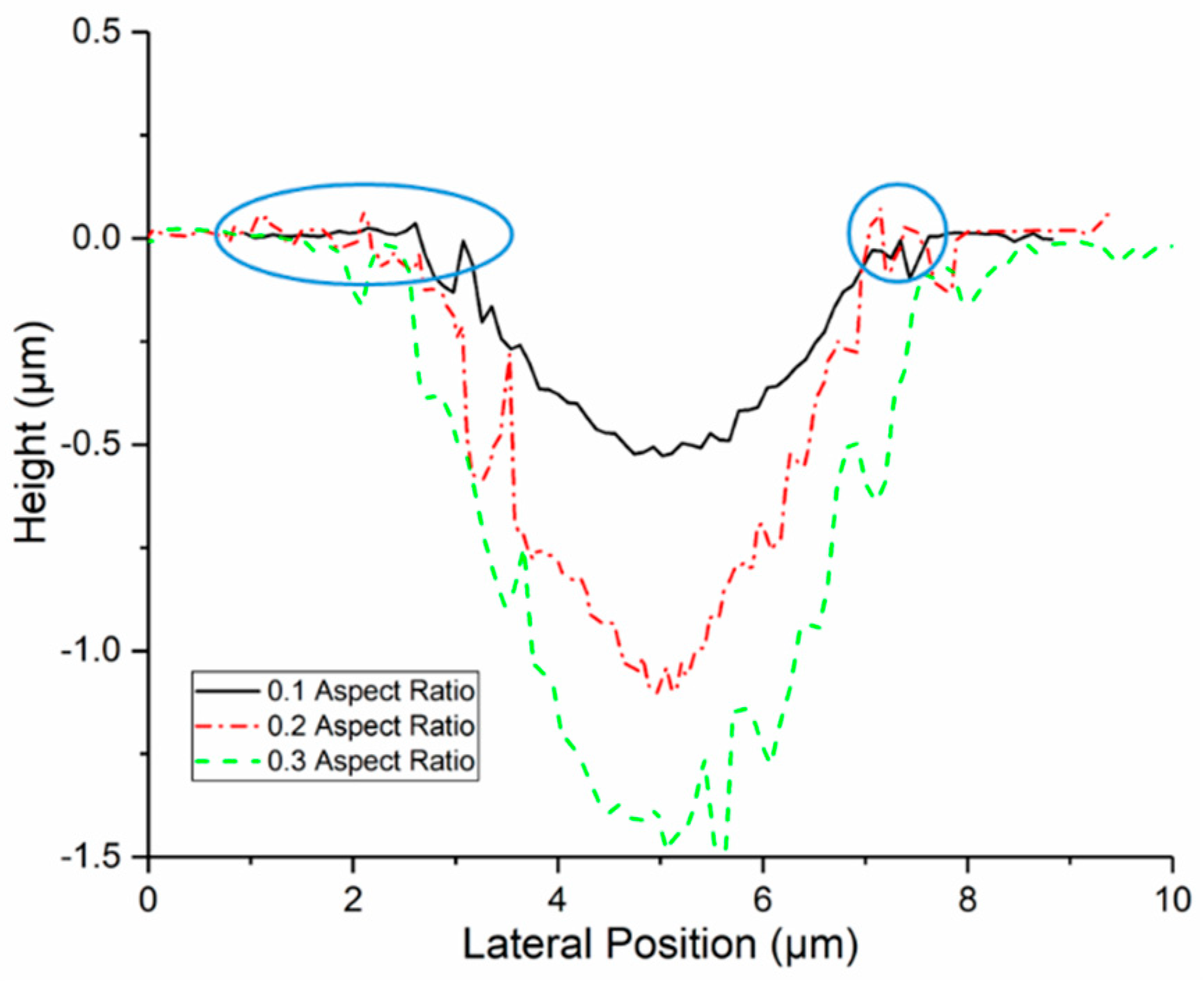




| Texture Type | Diameter (μm) | Depth (μm) | Aspect Ratio | Surface Density (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 5 |
| A2 | 5 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 5 |
| A3 | 5 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 5 |
| B1 | 5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 15 |
| B2 | 5 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 15 |
| B3 | 5 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 15 |
| C1 | 5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 25 |
| C2 | 5 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 25 |
| C3 | 5 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 25 |
| Aspect Ratio | Power (%) | Drill Time (s) | RA Divider | Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 15 | 0.08 | 800 | 700 |
| 0.2 | 20 | 0.10 | 800 | 700 |
| 0.3 | 22 | 0.15 | 800 | 700 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bennett, W.B.; Zou, M. Small Laser-Textured Dimples for Improved Tribological Performance of CoCrMo in Artificial Hip Joints. Lubricants 2025, 13, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13040158
Bennett WB, Zou M. Small Laser-Textured Dimples for Improved Tribological Performance of CoCrMo in Artificial Hip Joints. Lubricants. 2025; 13(4):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13040158
Chicago/Turabian StyleBennett, William B., and Min Zou. 2025. "Small Laser-Textured Dimples for Improved Tribological Performance of CoCrMo in Artificial Hip Joints" Lubricants 13, no. 4: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13040158
APA StyleBennett, W. B., & Zou, M. (2025). Small Laser-Textured Dimples for Improved Tribological Performance of CoCrMo in Artificial Hip Joints. Lubricants, 13(4), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13040158







