Functional Characterization of Outer Membrane Proteins (OMPs) in Xenorhabdus nematophila and Photorhabdus luminescens through Insect Immune Defense Reactions
Abstract
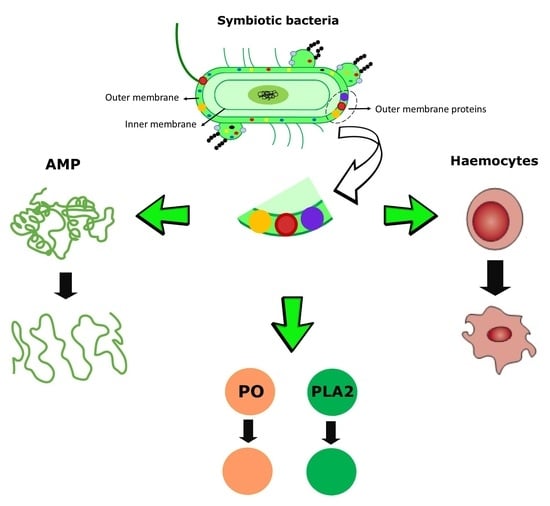
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Culture
2.2. Purification of Outer Membrane Proteins (OMPs)
2.2.1. Bacteria Growth
2.2.2. Preparation of OMPs from Symbiotic Bacteria
2.3. Injection of Bacterial OMPs
2.4. Total Haemocyte Counts and Differential Haemocyte Counts (THC and DHC)
2.5. Protease Assay
2.6. Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) Assay
2.7. Phenoloxidase (PO) Assay
2.8. Gene Expression
2.8.1. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.8.2. Design and Synthesis of Primers
2.8.3. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Outer Membrane Protein Profiles
3.2. Total Haemocyte Count
3.3. Granulocyte Counts
3.4. General Protease Activity
3.5. Phospholipase A2 Assay
3.6. Phenoloxidase Assay
3.7. Attacin Gene Expression
3.8. Cecropin Gene Expression
3.9. Spodoptericin Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaugler, R. Matching Nematode and Insect to Achieve Optimal Field Performance, in Optimal Use of Insecticidal Nematodes in Pest Management; Polavarapu, S., Ed.; Rutgers University: New Brundwick, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Akhurst, R.J.; Dunphy, G.B. Tripartite Interactions Between Symbiotically Associated Entomopathogenic Bacteria, Nematodes, and Their Insect Hosts, in Parasites and Pathogens of Insects; Beckage, N.E., Thompson, S.N., Federich, B.A., Eds.; Académie Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.E.; Cao, A.T.; Dobson, P.; Hines, E.R.; Akhurst, R.J.; East, P.D. Txp40, a ubiquitous insecticidal toxin protein from Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, P.; Kant, S.; Zaman, S.; Kumar Mahaparto, G.; Banerjee, N.; Bhalla Sarin, N. A novel insecticidal GroEL protein from Xenorhabdus nematophila confers insect resistance in tobacco. Transgenic. Res. 2014, 23, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftherianos, I.; Boundy, S.; Joyce, S.A.; Aslam, S.; Marshall, J.W.; Cox, R.J.; Simpson, T.J.; Clarke, D.J.; ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Reynolds, S.E. An antibiotic produced by an insect-pathogenic bacterium suppresses host defenses through phenoloxidase inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2419–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beveridge, T.J. Structures of Gram-negative cell walls and their derived membrane vesicles. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 4725–4733. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rollauer, A.E.; Sooreshjani, M.A.; Noinaj, N.; Buchanan, S.K. Outer membrane protein biogenesis in Gram-negative bacteria. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2015, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forst, S.; Nealson, K. Molecular Biology of the Symbiotic-Pathogenic Bacteria Xenorhabdus spp. and Photorhabdus spp. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 60, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruisheng, A.; Sreevatsan, S.; Grewal, P. Comparative in vivo gene expression of the closely related bacteria Photorhabdus temperata and Xenorhabdus koppenhoeferi upon infection of the same insect host, Rhizotrogus majalis. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 433. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.; Choi, Y.; Kim, Y. An entomopathogenic bacterium, Xenorhabdus nematophila, causes hemocyte apoptosis of beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2005, 8, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kim, Y. Xenorhabdus nematophilus inhibits p-bromophenacyl bromide (BPB)-sensitive PLA2 of Spodoptera exigua. Arch. Insect. Biochem. Physiol. 2003, 54, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.; Chen, C.; Ratcliffe, N.A. Innate immunity in insects: The role of multiple, endogenous serum lectins in the recognition of foreign invaders in the cockroach, Blaberus discoidalis. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen, T.; Nurmiaho, E.L.; RanTan, H.; Eden, C.S. New method for isolation of immunologically pure pili from Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1980, 27, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.C. Changes in the hemocyte picture of Galleria mellonella L. Biol. Bull. 1967, 132, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altuntas, H.; Kilic, A.Y.; Uckan, F.; Ergin, E. Effects of gibberellic acid on haemocytes of Galleria mellonella L. (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Environ. Entomol. 2012, 41, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.P. Insect Hemocytes; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, C.; Brehélin, M. Insect haemocytes: What type of cell is that? J. Insect. Physiol. 2006, 52, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholamzadeh Chitgar, M.; Ghadamyari, M.; Sharifi, M. Identification and characterisation of gut proteases in the fig tree skeletoniser moth, Choreutis nemorana Hübner (Lepidoptera: Choreutidae). Plant. Protect. Sci. 2013, 49, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radvanyi, F.; Jordan, L.; Russo-Marie, F.; Bon, C. A sensitive and continuous fluorometric assay for phospholipase A2 using pyrene-labeled phospholipids in the presence of serum albumin. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 77, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitating of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahatkhah, Z.; Karimi, J.; Ghadamyari, M.; Brivio, M.F. Immune defense of Agriotes lineatus larvae against. BioControl 2015, 60, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darsouei, R.; Karimi, J.; Ghadamyari, M.; Hosseini, M. Differential change patterns of main antimicrobial peptide genes during infection of entomophathogenic nematode and their symbiotic bacteria. J. Parasitol. 2017, 103, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using Real Time quantitative PCR and the 2^-ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute. SAS/STAT User’s Guide, Release 6.03; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuzuki, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Furihata, S.; Ryuda, M.; Tanaka, H.; Sung, E.J.; Bird, G.S.; Zhou, Y.; Shears, S.B.; Hayakawa, Y. Switching between humoral and cellular immune responses in Drosophila is guided by the cytokine GBP. Nat. Commun. 2014, 18, 4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunphy, G.B.; Halwani, A.E. Haemolymph proteins of larvae of Galleria mellonella detoxify endotoxins of the insect pathogenic bacteria Xenorhabdus nematophila (Enterobacteriaceae). J. Insect Physiol. 1997, 43, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunphy, G.B.; Webster, J.M. Lipopolysaccharides of Xenorhabdus nematophilus and their haemocyte toxicity in non-immune Galleria mellonella (Insecta: Lepidoptera) larvae. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1998, 134, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Kim, Y. Eicosanoids mediate prophenoloxidase release from oenocytoids in the beet armyworm Spodoptera exigua. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisman, G.B.; Waukau, J.; Forst, S.A. Characterization and environmental regulation of outer membrane proteins in Xenorhabdus nematophilus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 200–204. [Google Scholar]
- Khandelwal, P.; Choudhury, D.; Birah, A.; Reddy, M.L.; Gupta, G.P.; Banerjee, N. Insecticidal pilin subunit from the insect pathogen Xenorhabdus nematophila. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 6465–6476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, P.; Banerjee-Bhatnagar, N. Insecticidal Activity Associated with the Outer Membrane Vesicles of Xenorhabdus nematophilus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2032–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papamichail, D.; Delihas, N. Outer membrane protein genes and their small non-coding RNA regulator genes in Photorhabdus luminescens. Biol. Direct. 2006, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Fujii, H.; Banno, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Aso, Y. Proteomic studies of lipopolysaccharide-induced polypeptides in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 1821–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duperthuy, M.; Binesse, J.; Le Roux, F.; Romestand, B.; Caro, A.; Got, P.; Givaudan, A.; Mazel, D.; Bachere, E.; Delphine, D.G. The major outer membrane protein OmpU of Vibrio splendidus contributes to host antimicrobial peptide resistance and is required for virulence in the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaja, S.K.; Russo, A.J.; Behl, B.; Banerjee, I.; Yankova, M.; Deshmukh, S.D.; Rathinam, V.A.K. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles mediate cytosolic localization of LPS and caspase-11 activation. Cell 2016, 165, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.Y.; Chowdhury, M.; Huang, Y.D.; Yu, X.Q. Insect antimicrobial peptides and their applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5807–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castillo, J.C.; Creasy, T.; Kumari, P.; Shetty, A.; Shokal, U.; Tallon, L.J.; Elertherianos, L. Drosophila anti-nematode and antibacterial immune regulators revealed by RNA-Seq. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Escajadillo, T.; Fang, R.H.; Gao, W.; Nizet, V.; Zhang, L. Broad-Spectrum neutralization of pore-forming toxins with human erythrocyte membrane-coated nanosponges. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.A.; Kafatos, F.; Janawey, C.; Ezekovitz, R.A.B. Phylogenetic perspectives in innate immunity. Science 1999, 284, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, B.; Hoffmann, J. The host defense of Drosophila melanogaster. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 697–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, P.; Chmiel, D.; Gacek, G.J. Antibacterial peptides of the moth Galleria mellonella. Acta. Biochim. Pol. 2001, 48, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Andrejko, M.; Mizerska-Dudka, M. Elastase B of Pseudomonas aeruginosa stimulates the humoral immune response in the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2011, 107, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadurugamuwa, J.; Beveridge, T.J. Virulence factors are released from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in association with membrane vesicles during normal growth and exposure to gentamicin: A novel mechanism of enzyme secretion. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 3998–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, C.M.; Cherqui, A.; Pereira, A.; Simoes, N. Purification and characterization of two distinct metalloproteases secreted by the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus sp. strain Az29. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3831–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, K.G.; LaRock, C.N.; Argenio, D.A.; Berg, C.A.; Collins, C.M. A metalloprotease secreted by the insect pathogen Photorhabdus luminescens induces melanization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7622–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, L.; Russell, V.; Dunn, P.E. A family of bacteria-regulated, cecropin D-like peptides from Manduca sexta. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 19424–19429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji, D.; Kim, Y. An entomopathogenic bacterium, Xenorhabdus nematophila, inhibits the expression of an antibacterial peptide, cecropin, of the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. J. Insect. Physiol. 2004, 50, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldas, C.; Cherqui, A.; Pereria, A.; Simoes, N. Purification and characterization of an extracellular protease from Xenorhabdus nematophila involved in insect immunosuppression. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, D.W.; Goodman, C.; An, S.; Song, Q. Prostaglandin A2 influences gene expression in an established insect cell line (BCIRL-HzAM1) cells. J. Insect. Physiol. 2012, 58, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Park, Y.; Kim, Y. An entomopathogenic bacterium, Xenorhabdus nematophila, suppresses expression of antimicrobial peptides controlled by Toll and IMD pathways by blocking eicosanoid biosynthesis. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 83, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Darsouei, R.; Karimi, J.; Dunphy, G.B. Functional Characterization of Outer Membrane Proteins (OMPs) in Xenorhabdus nematophila and Photorhabdus luminescens through Insect Immune Defense Reactions. Insects 2019, 10, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100352
Darsouei R, Karimi J, Dunphy GB. Functional Characterization of Outer Membrane Proteins (OMPs) in Xenorhabdus nematophila and Photorhabdus luminescens through Insect Immune Defense Reactions. Insects. 2019; 10(10):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100352
Chicago/Turabian StyleDarsouei, Reyhaneh, Javad Karimi, and Gary B. Dunphy. 2019. "Functional Characterization of Outer Membrane Proteins (OMPs) in Xenorhabdus nematophila and Photorhabdus luminescens through Insect Immune Defense Reactions" Insects 10, no. 10: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100352
APA StyleDarsouei, R., Karimi, J., & Dunphy, G. B. (2019). Functional Characterization of Outer Membrane Proteins (OMPs) in Xenorhabdus nematophila and Photorhabdus luminescens through Insect Immune Defense Reactions. Insects, 10(10), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100352