Bacteria-Mediated RNA Interference for Management of Plagiodera versicolora (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plagiodera Versicolora (Laicharting) Rearing
2.2. Plagiodera Versicolora RNA Extraction and Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Analysis
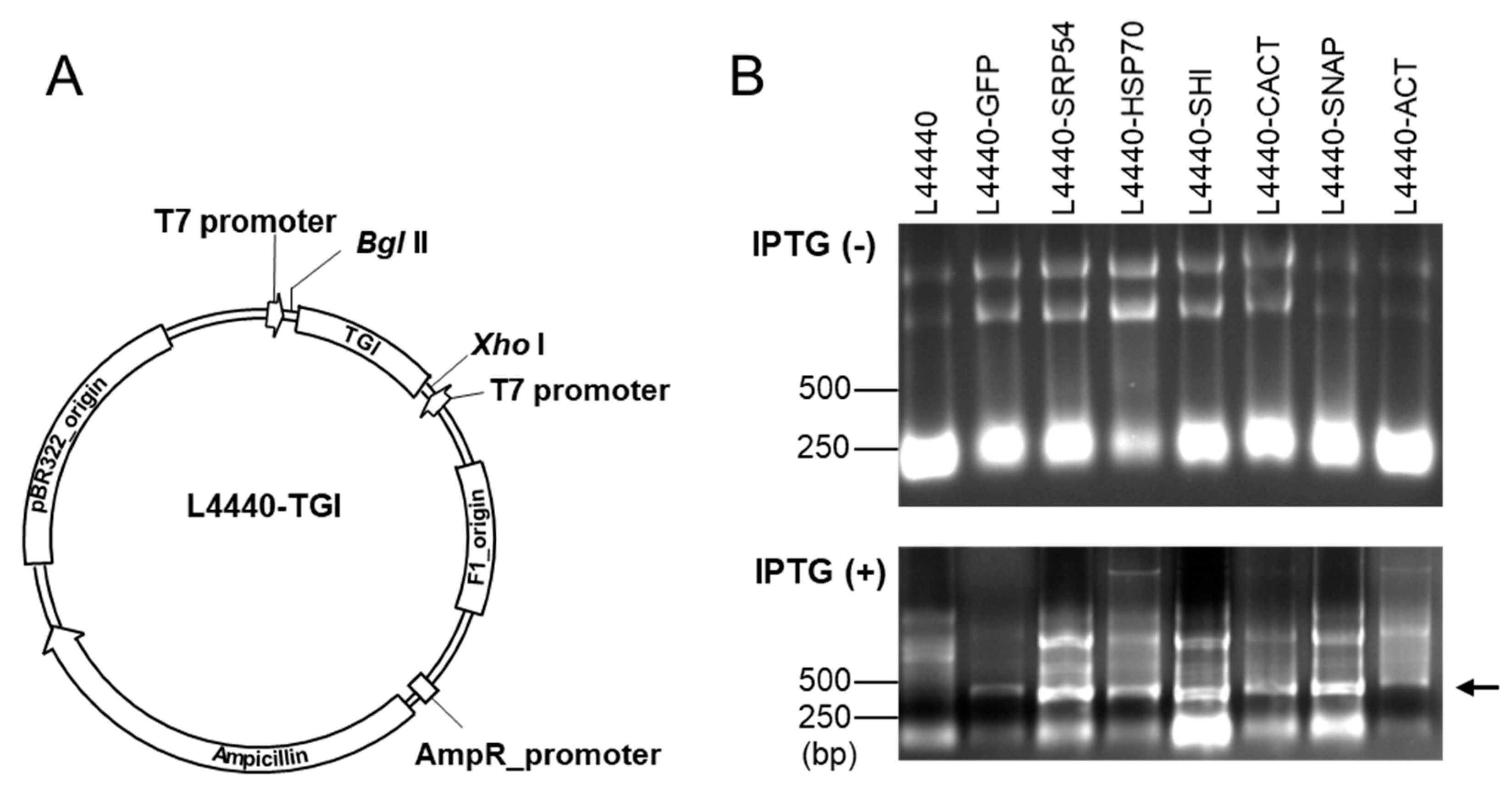
2.3. Construction of Bacterial Expression Vectors for dsRNA Production
2.4. Expression of dsRNA and Larval Feeding Bioassay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of dsRNA Induced in Bacteria
3.2. Insecticidal Activity of dsRNA-Expressing E. coli against Plagiodera versicolora Larvae
3.3. Target Gene Silencing of Plagiodera versicolora Larvae after Feeding Bacteria-Expressed dsRNA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urban, J. Contribution to the knowledge of development and harmfulness of imported willow leaf beetle (Plagiodera versicolora) (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae). J. For. Sci. 2005, 51, 481–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneya, K.; Kugimiya, S.; Takabayashi, J. Leaf beetle larvae, Plagiodera versicolora (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), show decreased performance on uninfested host plants exposed to airborne factors from plants infested by conspecific larvae. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2014, 49, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, M.; Sevim, E.; Demir, İ.; Sevim, A. Culturable bacterial microbiota of Plagiodera versicolora (L.) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) and virulence of the isolated strains. Folia Microbiol. 2013, 58, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Du, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, J. Differential expression of dual Bt genes in transgene poplar Juba (Populus deltoides cv. ‘Juba’) transformed by two different transformation vectors. Can. J. Forest Res. 2015, 45, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; Gao, B. Genetic transformation and expression of Cry1Ac–Cry3A–NTHK1 genes in Populus × euramericana “Neva”. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.L.; Wang, A.X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Yang, M.S.; Wang, J.M. Genetic transformation and expression of transgenic lines of Populus × euramericana with insect-resistance and salt-tolerance genes. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, gmr.15028635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; An, S. The progress in insect cross-resistance among Bacillus thuringiensis toxins. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 102, e21547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Brevault, T.; Carriere, Y. Insect resistance to Bt crops: Lessons from the first billion acres. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carthew, R.W.; Sontheimer, E.J. Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.C.; Doudna, J.A. Molecular mechanisms of RNA interference. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2013, 42, 217–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.; Kostas, S.; Driver, S.; Mello, C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Nunes, M.A.; Espana, M.U.; Namin, H.H.; Jin, P.; Bensoussan, N.; Zhurov, V.; Rahman, T.; De Clercq, R.; Hilson, P.; et al. RNAi-based reverse genetics in the chelicerate model Tetranychus urticae: A comparative analysis of five methods for gene silencing. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandety, R.S.; Kuo, Y.-W.; Nouri, S.; Falk, B.W. Emerging strategies for RNA interference (RNAi) applications in insects. Bioengineered 2014, 6, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Khan, S.A.; Heckel, D.G.; Bock, R. Next-generation insect-resistant plants: RNAi-mediated crop protection. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.R.; Gatehouse, J.A. RNAi-mediated crop protection against insects. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.B.; Cai, W.J.; Wang, J.W.; Hong, G.J.; Tao, X.Y.; Wang, L.J.; Huang, Y.P.; Chen, X.Y. Silencing a cotton bollworm P450 monooxygenase gene by plant-mediated RNAi impairs larval tolerance of gossypol. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, J.A.; Bogaert, T.; Clinton, W.; Heck, G.R.; Feldmann, P.; Ilagan, O.; Johnson, S.; Plaetinck, G.; Munyikwa, T.; Pleau, M.; et al. Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyard, S.; Singh, A.D.; Wong, S. Ingested double-stranded RNAs can act as species-specific insecticides. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Palli, S.R. Mechanisms, applications, and challenges of insect RNA interference. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, J.; Dao, V.A.; Majumdar, U.; Schmitt-Engel, C.; Schwirz, J.; Schultheis, D.; Strohlein, N.; Troelenberg, N.; Grossmann, D.; Richter, T.; et al. Large scale RNAi screen in Tribolium reveals novel target genes for pest control and the proteasome as prime target. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingsohn, L.; Knorr, E.; Billion, A.; Narva, K.E.; Vilcinskas, A. Knockdown of genes in the Toll pathway reveals new lethal RNA interference targets for insect pest control. Insect Mol. Biol. 2017, 26, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liang, X.H.; Uliel, S.; Unger, R.; Ullu, E.; Michaeli, S. RNA interference of signal peptide-binding protein SRP54 elicits deleterious effects and protein sorting defects in trypanosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 47348–47357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenbeck, G. Soluble NSF-attachment proteins. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 1998, 30, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seugnet, L.; Simpson, P.; Haenlin, M. Requirement for dynamin during Notch signaling in Drosophila neurogenesis. Dev. Biol. 1997, 192, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Khan, S.A.; Hasse, C.; Ruf, S.; Heckel, D.G.; Bock, R. Full crop protection from an insect pest by expression of long double-stranded RNAs in plastids. Science 2015, 347, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennerdell, J.; Carthew, R. Use of dsRNA-mediated genetic interference to demonstrate that frizzled and frizzled 2 act in the wingless pathway. Cell 1998, 95, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Christiaens, O.; Liu, J.; Niu, J.; Cappelle, K.; Caccia, S.; Huvenne, H.; Smagghe, G. Delivery of dsRNA for RNAi in insects: An overview and future directions. Insect Sci. 2013, 20, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Xu, J.; Palli, R.; Ferguson, J.; Palli, S.R. Ingested RNA interference for managing the populations of the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajuria, C.; Velez, A.M.; Rangasamy, M.; Wang, H.; Fishilevich, E.; Frey, M.L.; Carneiro, N.P.; Gandra, P.; Narva, K.E.; Siegfried, B.D. Parental RNA interference of genes involved in embryonic development of the western corn rootworm, Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 63, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangasamy, M.; Siegfried, B.D. Validation of RNA interference in western corn rootworm Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) adults. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostylev, M.; Otwell, A.E.; Richardson, R.E.; Suzuki, Y. Cloning should be simple: Escherichia coli DH5α-mediated assembly of multiple DNA fragments with short end homologies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Motohashi, K. Evaluation of the efficiency and utility of recombinant enzyme-free seamless DNA cloning methods. Biochem. Biophy. Rep. 2017, 9, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, T.B.; Duan, J.J.; Palli, S.R.; Rieske, L.K. Identification of highly effective target genes for RNAi-mediated control of emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Lu, M. Gut commensal bacteria in biological invasions. Int. Zool. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taracena, M.L.; Oliveira, P.L.; Almendares, O.; Umana, C.; Lowenberger, C.; Dotson, E.M.; Paiva-Silva, G.O.; Pennington, P.M. Genetically modifying the insect gut microbiota to control Chagas disease vectors through systemic RNAi. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, C.S.; Waniek, P.J.; Mattos, D.P.; Castro, D.P.; Mello, C.B.; Ratcliffe, N.A.; Garcia, E.S.; Azambuja, P. Humoral responses in Rhodnius prolixus: bacterial feeding induces differential patterns of antibacterial activity and enhances mRNA levels of antimicrobial peptides in the midgut. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Shuai, J.; Chen, X.; Ling, E. Expression of antimicrobial peptide genes in Bombyx mori gut modulated by oral bacterial infection and development. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitten, M.M.; Facey, P.D.; Del Sol, R.; Fernandez-Martinez, L.T.; Evans, M.C.; Mitchell, J.J.; Bodger, O.G.; Dyson, P.J. Symbiont-mediated RNA interference in insects. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paim, R.M.; Araujo, R.N.; Lehane, M.J.; Gontijo, N.F.; Pereira, M.H. Application of RNA interference in triatomine (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) studies. Insect Sci. 2013, 20, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzin, V.; Yang, X.; Jing, X.; Zhang, K.; Jander, G.; Douglas, A.E. RNA interference against gut osmoregulatory genes in phloem-feeding insects. J. Insect. Physiol. 2015, 79, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Sui, X.; Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Lu, L.; You, M.; Xie, C.; Li, B.; Ni, Z.; Liang, R. Plant-mediated RNAi of grain aphid CHS1 gene confers common wheat resistance against aphids. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2754–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishilevich, E.; Velez, A.M.; Storer, N.P.; Li, H.; Bowling, A.J.; Rangasamy, M.; Worden, S.E.; Narva, K.E.; Siegfried, B.D. RNAi as a management tool for the western corn rootworm, Diabrotica virgifera virgifera. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 1652–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussain, T.; Aksoy, E.; Caliskan, M.E.; Bakhsh, A. Transgenic potato lines expressing hairpin RNAi construct of molting-associated EcR gene exhibit enhanced resistance against Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata, Say). Transgenic Res. 2019, 28, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Bai, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Fan, Q.; Mi, X.; Wang, L.; He, J.; Pang, J.; Luo, X.; et al. Double-stranded RNAs high-efficiently protect transgenic potato from Leptinotarsa decemlineata by disrupting juvenile hormone biosynthesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11990–11999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.B.; Tao, T.X.; Xue, X.Y.; Wang, L.J.; Chen, X.Y. Cotton plants expressing CYP6AE14 double-stranded RNA show enhanced resistance to bollworms. Transgenic Res. 2011, 20, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.Q.; Liu, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.Q.; Qi, H.S.; Wei, Z.J.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, W.Q.; Li, S. Improvement of pest resistance in transgenic tobacco plants expressing dsRNA of an insect-associated gene EcR. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bock, R. Engineering plastid genomes: Methods, tools, and applications in basic research and biotechnology. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2015, 66, 211–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, L.; Chang, L.; Ma, M.; You, L.; Jiang, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, J. Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) cry1C expression from the plastid genome of poplar leads to high mortality of leaf eating caterpillars. Tree Physiol. 2019, 39, 1525–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Ma, W.; Wang, X.; Gao, M.; Dai, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y.; Chen, S.; Ding, L.; et al. Next-generation transgenic cotton: Pyramiding RNAi and Bt counters insect resistance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, J. Bacteria-Mediated RNA Interference for Management of Plagiodera versicolora (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Insects 2019, 10, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10120415
Zhang Y, Xu L, Li S, Zhang J. Bacteria-Mediated RNA Interference for Management of Plagiodera versicolora (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Insects. 2019; 10(12):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10120415
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yiqiu, Letian Xu, Shengchun Li, and Jiang Zhang. 2019. "Bacteria-Mediated RNA Interference for Management of Plagiodera versicolora (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae)" Insects 10, no. 12: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10120415
APA StyleZhang, Y., Xu, L., Li, S., & Zhang, J. (2019). Bacteria-Mediated RNA Interference for Management of Plagiodera versicolora (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Insects, 10(12), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10120415




