Dynamics of an Ongoing Wolbachia Spread in the European Cherry Fruit Fly, Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera: Tephritidae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and DNA Extraction
2.2. Wolbachia Screening
2.3. Mitochondrial Genotyping of R. cerasi
2.4. Comparison of Our Results with Historic Data
3. Results
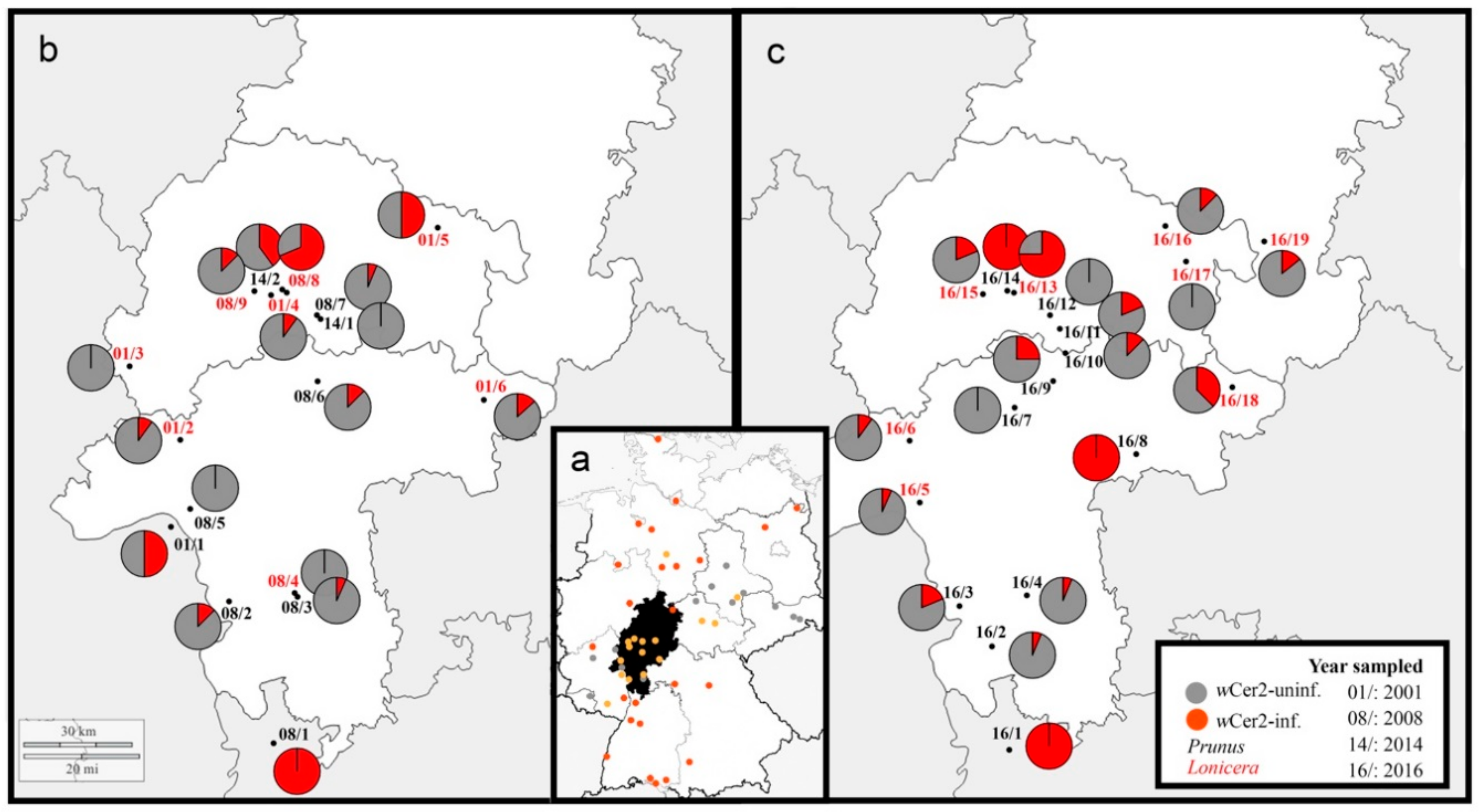
3.1. Wolbachia Infection Frequencies
3.2. Mitochondrial Genotyping of R. cerasi and Haplotype-Wolbachia Associations
3.3. Wolbachia Dynamics and Haplotype Associations in Time and Space
4. Discussion
4.1. Wolbachia Infection Frequencies in Time and Space
4.2. Wolbachia Infection and Mitochondrial Haplotype of the Host
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weinert, L.A.; Araujo-Jnr, E.V.; Ahmed, M.Z.; Welch, J.J. The incidence of bacterial endosymbionts in terrestrial arthropods. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Biol. 2015, 282, 20150249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFall-Ngai, M.; Hadfield, M.G.; Bosch, T.C.G.; Carey, H.V.; Domazet-Loso, T.; Douglas, A.E.; Dubilier, N.; Eberl, G.; Fukami, T.; Gilbert, S.F.; et al. Animals in a bacterial world, a new imperative for the life sciences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moran, N.A.; McCutcheon, J.P.; Nakabachi, A. Genomics and evolution of heritable bacterial symbionts. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 165–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelstadter, J.; Hurst, G.D.D. The ecology and evolution of microbes that manipulate host reproduction. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.; Ferreira, A.; Ashburner, M. The bacterial symbiont Wolbachia induces resistance to RNA viral infections in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, 2753–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaenike, J.; Unckless, R.; Cockburn, S.N.; Boelio, L.M.; Perlman, S.J. Adaptation via symbiosis: Recent spread of a Drosophila defensive symbiont. Science 2010, 329, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, S.L.; Giordano, R.; Colbert, A.M.E.; Karr, T.L.; Robertson, H.M. 16S ribosomal-RNA phylogenetic analysis of the bacterial endosymbionts associated with cytoplasmic incompatibility in insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2699–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspi-Fluger, A.; Inbar, M.; Mozes-Daube, N.; Katzir, N.; Portnoy, V.; Belausov, E.; Hunter, M.S.; Zchori-Fein, E. Horizontal transmission of the insect symbiont Rickettsia is plant-mediated. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Biol. 2012, 279, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, H.; Bertheau, C.; Egan, S.P.; Feder, J.L.; Riegler, M.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Steiner, F.M.; Johannesen, J.; Kern, P.; Tuba, K.; et al. Evidence for a recent horizontal transmission and spatial spread of Wolbachia from endemic Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera: Tephritidae) to invasive Rhagoletis cingulata in Europe. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 4101–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonella, E.; Pajoro, M.; Marzorati, M.; Crotti, E.; Mandrioli, M.; Pontini, M.; Bulgari, D.; Negri, I.; Sacchi, L.; Chouaia, B.; et al. Plant-mediated interspecific horizontal transmission of an intracellular symbiont in insects. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werren, J.H.; Baldo, L.; Clark, M.E. Wolbachia: Master manipulators of invertebrate biology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.A.; Turelli, M. Cytoplasmic incompatibility in insects. In Influential Passengers: Inherited Microorganisms and Arthropod Reproduction; O’Neill, S., Hoffmann, A.A., Werren, J.H., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997; pp. 42–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, G.D.D.; Jiggins, F.M. Problems with mitochondrial DNA as a marker in population, phylogeographic and phylogenetic studies: The effects of inherited symbionts. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Biol. 2005, 272, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turelli, M.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Mckechnie, S.W. Dynamics of cytoplasmic incompatibility and mtDNA variation in natural Drosophila simulans populations. Genetics 1992, 132, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Narita, S.; Nomura, M.; Kato, Y.; Fukatsu, T. Genetic structure of sibling butterfly species affected by Wolbachia infection sweep: Evolutionary and biogeographical implications. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuler, H.; Koppler, K.; Daxbock-Horvath, S.; Rasool, B.; Krumbock, S.; Schwarz, D.; Hoffmeister, T.S.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Steiner, F.M.; Telschow, A.; et al. The hitchhiker’s guide to Europe: The infection dynamics of an ongoing Wolbachia invasion and mitochondrial selective sweep in Rhagoletis cerasi. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 1595–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cariou, M.; Duret, L.; Charlat, S. The global impact of Wolbachia on mitochondrial diversity and evolution. J. Evolut. Biol. 2017, 30, 2204–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boller, E.F.; Bush, G.L. Evidence for genetic variation in populations of European cherry fruit fly, Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera: Tephritidae) based on physiological parameters and hybridization experiments. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1974, 17, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boller, E.F.; Russ, K.; Vallo, V.; Bush, G.L. Incompatible races of European cherry fruit fly, Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera:Tephritidae), their origin and potential use in biological control. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1976, 20, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, D.; McPheron, B.A.; Hartl, G.B.; Boller, E.F.; Hoffmeister, T.S. A second case of genetic host races in Rhagoletis? A population genetic comparison of sympatric host populations in the European cherry fruit fly, Rhagoletis cerasi. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2003, 108, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boller, E.F.; Prokopy, R.J. Bionomics and management of Rhagoletis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1976, 21, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boller, E.F.; Haisch, A.; Russ, K.; Vallo, V. Economic importance of Rhagoletis cerasi L., the feasibility of genetic control and resulting research problems. Entomophaga 1970, 15, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, C.; Grunder, J. Integrated management of European cherry fruit fly Rhagoletis cerasi (L.): Situation in Switzerland and Europe. Insects 2012, 3, 956–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluja, M.; Boller, E.F. Host marking pheromone of Rhagoletis cerasi: Field deployment of synthetic pheromone as a novel cherry fruit fly management strategy. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1992, 65, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluja, M.; Boller, E.F. Host marking pheromone of Rhagoletis cerasi: Foraging behavior in response to synthetic pheromonal isomers. J. Chem. Ecol. 1992, 18, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boller, E.F.; Aluja, M. Oviposition deterring pheromone in Rhagoletis cerasi L. Biological activity of 4 synthetic isomers and HMP discrimination of two host races as measured by an improved laboratory bioassay. J. Appl. Entomol. 1992, 113, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastasiou, S.A.; Papadopoulos, N.T. Description of Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera: Tephritidae) pupal developmental stages: Indications of prolonged diapause. J. Insect Sci. 2014, 14, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blümel, S.; Keck, M.; Nowotny, N.; Fiedler, W.; Russ, K. Detection and therapy of Rickettsia-like-organisms (RLOs) in ovaries of the European cherry fruit fly (Rhagoletis cerasi L.; Trypetidae): An evaluation of their influence on the unidirectional crossing sterility. Pflanzenschutzberichte 1991, 52, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Riegler, M.; Stauffer, C. Wolbachia infections and superinfections in cytoplasmically incompatible populations of the European cherry fruit fly Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera, Tephritidae). Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakovic, V.; Schebeck, M.; Telschow, A.; Stauffer, C.; Schuler, H. Spatial spread of Wolbachia in Rhagoletis cerasi populations. Biol. Lett. 2018, 14, 20180161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turelli, M.; Hoffmann, A.A. Rapid spread of an inherited incompatibility factor in California Drosophila. Nature 1991, 353, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turelli, M.; Cooper, B.S.; Richardson, K.M.; Ginsberg, P.S.; Peckenpaugh, B.; Antelope, C.X.; Kim, K.J.; May, M.R.; Abrieux, A.; Wilson, D.A.; et al. Rapid global spread of wRi-like Wolbachia across multiple Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriesner, P.; Conner, W.R.; Weeks, A.R.; Turelli, M.; Hoffmann, A.A. Persistence of a Wolbachia infection frequency cline in Drosophila melanogaster and the possible role of reproductive dormancy. Evolution 2016, 70, 979–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braig, H.R.; Zhou, W.G.; Dobson, S.L.; O’Neill, S.L. Cloning and characterization of a gene encoding the major surface protein of the bacterial endosymbiont Wolbachia pipientis. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 2373–2378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arthofer, W.; Riegler, M.; Schneider, D.; Krammer, M.; Miller, W.J.; Stauffer, C. Hidden Wolbachia diversity in field populations of the European cherry fruit fly, Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera, Tephritidae). Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 3816–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, C.; Frati, F.; Beckenbach, A.; Crespi, B.; Liu, H.; Flook, P. Evolution, weighting, and phylogenetic utility of mitochondrial gene sequences and a compilation of conserved polymerase chain reaction primers. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1994, 87, 651–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriesner, P.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Lee, S.F.; Turelli, M.; Weeks, A.R. Rapid sequential spread of two Wolbachia variants in Drosophila simulans. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atyame, C.M.; Labbe, P.; Rousset, F.; Beji, M.; Makoundou, P.; Duron, O.; Dumas, E.; Pasteur, N.; Bouattour, A.; Fort, P.; et al. Stable coexistence of incompatible Wolbachia along a narrow contact zone in mosquito field populations. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turelli, M.; Hoffmann, A.A. Cytoplasmic incompatibility in Drosophila simulans—Dynamics and parameter estimates from natural populations. Genetics 1995, 140, 1319–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, N.H.; Turelli, M. Spatial waves of advance with bistable dynamics: Cytoplasmic and genetic analogues of Allee effects. Am. Nat. 2011, 178, E48–E75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.L.; Barton, N.H.; Rasic, G.; Turley, A.P.; Montgomery, B.L.; Iturbe-Ormaetxe, I.; Cook, P.E.; Ryan, P.A.; Ritchie, S.A.; Hoffmann, A.A.; et al. Local introduction and heterogeneous spatial spread of dengue-suppressing Wolbachia through an urban population of Aedes aegypti. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2001894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.A.; Montgomery, B.L.; Popovici, J.; Iturbe-Ormaetxe, I.; Johnson, P.H.; Muzzi, F.; Greenfield, M.; Durkan, M.; Leong, Y.S.; Dong, Y.; et al. Successful establishment of Wolbachia in Aedes populations to suppress dengue transmission. Nature 2011, 476, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.L.; Filipovic, I.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Rasic, G. Fine-scale landscape genomics helps explain the slow spatial spread of Wolbachia through the Aedes aegypti population in Cairns, Australia. Heredity 2018, 120, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakovic, V.; Stauffer, C.; Schuler, H. Allochronic isolation as a potential factor for prezygotic isolation in Rhagoletis cerasi (L.) (Diptera, Tephritidae). Mitt. Dtsch. Ges. Allg. Angew. Entomol. 2018, 21, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Schuler, H.; Kern, P.; Arthofer, W.; Vogt, H.; Fischer, M.; Stauffer, C.; Riegler, M. Wolbachia in parasitoids attacking native European and introduced Eastern cherry fruit flies in Europe. Environ. Entomol. 2016, 45, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, B.D.; Butcher, R.D.J.; Whitfield, W.G.F.; Hubbard, S.F. Horizontal transfer of Wolbachia between phylogenetically distant insect species by a naturally occurring mechanism. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huigens, M.E.; De Almeida, R.P.; Boons, P.A.H.; Luck, R.F.; Stouthamer, R. Natural interspecific and intraspecific horizontal transfer of parthenogenesis-inducing Wolbachia in Trichogramma wasps. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Biol. 2004, 271, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.Z.; Li, S.J.; Xue, X.; Yin, X.J.; Ren, S.X.; Jiggins, F.M.; Greeff, J.M.; Qiu, B.L. The intracellular bacterium Wolbachia uses parasitoid wasps as phoretic vectors for efficient horizontal transmission. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, 1004672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Population # | Location | % wCer2 | % wCer2/HT2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16/1 | Dossenheim | 100 | 100 |
| 16/2 | Bensheim | 6.3 | 6.3 |
| 16/3 | Stockstadt | 18.8 | 18.8 |
| 16/4 | Ober-Ramstadt | 6.3 | 6.3 |
| 16/5 | Erbenheim | 6.7 | 6.7 |
| 16/6 | Idstein | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| 16/7 | Rosbach | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 16/8 | Hailer | 100 | 100 |
| 16/9 | Weckesheim | 25.0 | 25.0 |
| 16/10 | Utphe | 12.5 | 12.5 |
| 16/11 | Langsdorf | 18.8 | 18.8 |
| 16/12 | Lich | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 16/13 | Gießen/Lonicera | 75.0 | 62.5 * |
| 16/14 | Gießen/Prunus | 100 | 68.8 * |
| 16/15 | Lahnau | 18.8 | 0.0 * |
| 16/16 | Alsfeld | 12.5 | 12.5 |
| 16/17 | Wallenrod | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 16/18 | Schlüchtern | 37.5 | 37.5 |
| 16/19 | Grossenmoor | 14.3 | 14.3 |
| Location | Population # | Host | Year | n | % wCer2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dossenheim | 99/1 | Lonicera | 1999 | 10 | 100 |
| 08/1 | Prunus | 2008 | 16 | 100 | |
| 16/1 | Prunus | 2016 | 16 | 100 | |
| Ober-Ramstadt | 08/3 | Lonicera | 2008 | 15 | 0 |
| 08/4 | Prunus | 2008 | 15 | 6.7 | |
| 16/4 | Prunus | 2016 | 16 | 6.3 | |
| Stockstadt | 08/2 | Prunus | 2008 | 16 | 12.5 |
| 16/3 | Prunus | 2016 | 16 | 18.8 | |
| Lich | 08/7 | Prunus | 2008 | 16 | 6.3 |
| 14/1 | Prunus | 2014 | 10 | 0 | |
| 16/12 | Prunus | 2016 | 16 | 0 | |
| Gießen | 01/4 | Lonicera | 2001 | 10 | 10 |
| 08/8 | Lonicera | 2008 | 16 | 68.8 | |
| 16/13 | Lonicera | 2016 | 16 | 75 | |
| 16/14 | Prunus | 2016 | 16 | 100 | |
| Lahnau | 08/9 | Lonicera | 2008 | 16 | 12.5 |
| 16/15 | Prunus | 2016 | 16 | 18.8 | |
| Alsfeld | 01/5 | Lonicera | 2001 | 10 | 50 |
| 16/16 | Lonicera | 2016 | 16 | 12.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schebeck, M.; Feldkirchner, L.; Stauffer, C.; Schuler, H. Dynamics of an Ongoing Wolbachia Spread in the European Cherry Fruit Fly, Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera: Tephritidae). Insects 2019, 10, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10060172
Schebeck M, Feldkirchner L, Stauffer C, Schuler H. Dynamics of an Ongoing Wolbachia Spread in the European Cherry Fruit Fly, Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera: Tephritidae). Insects. 2019; 10(6):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10060172
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchebeck, Martin, Lukas Feldkirchner, Christian Stauffer, and Hannes Schuler. 2019. "Dynamics of an Ongoing Wolbachia Spread in the European Cherry Fruit Fly, Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera: Tephritidae)" Insects 10, no. 6: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10060172
APA StyleSchebeck, M., Feldkirchner, L., Stauffer, C., & Schuler, H. (2019). Dynamics of an Ongoing Wolbachia Spread in the European Cherry Fruit Fly, Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera: Tephritidae). Insects, 10(6), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10060172







