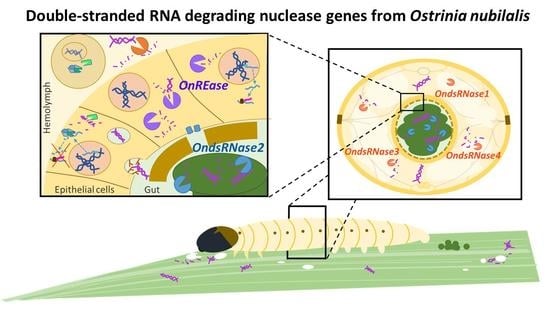
Molecular Characterizations of Double-Stranded RNA Degrading Nuclease Genes from Ostrinia nubilalis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing
2.2. Sequencing of dsRNase and REase cDNAs
2.3. Phylogenetic, Domain, and Peptide Analyses of Predicted Proteins
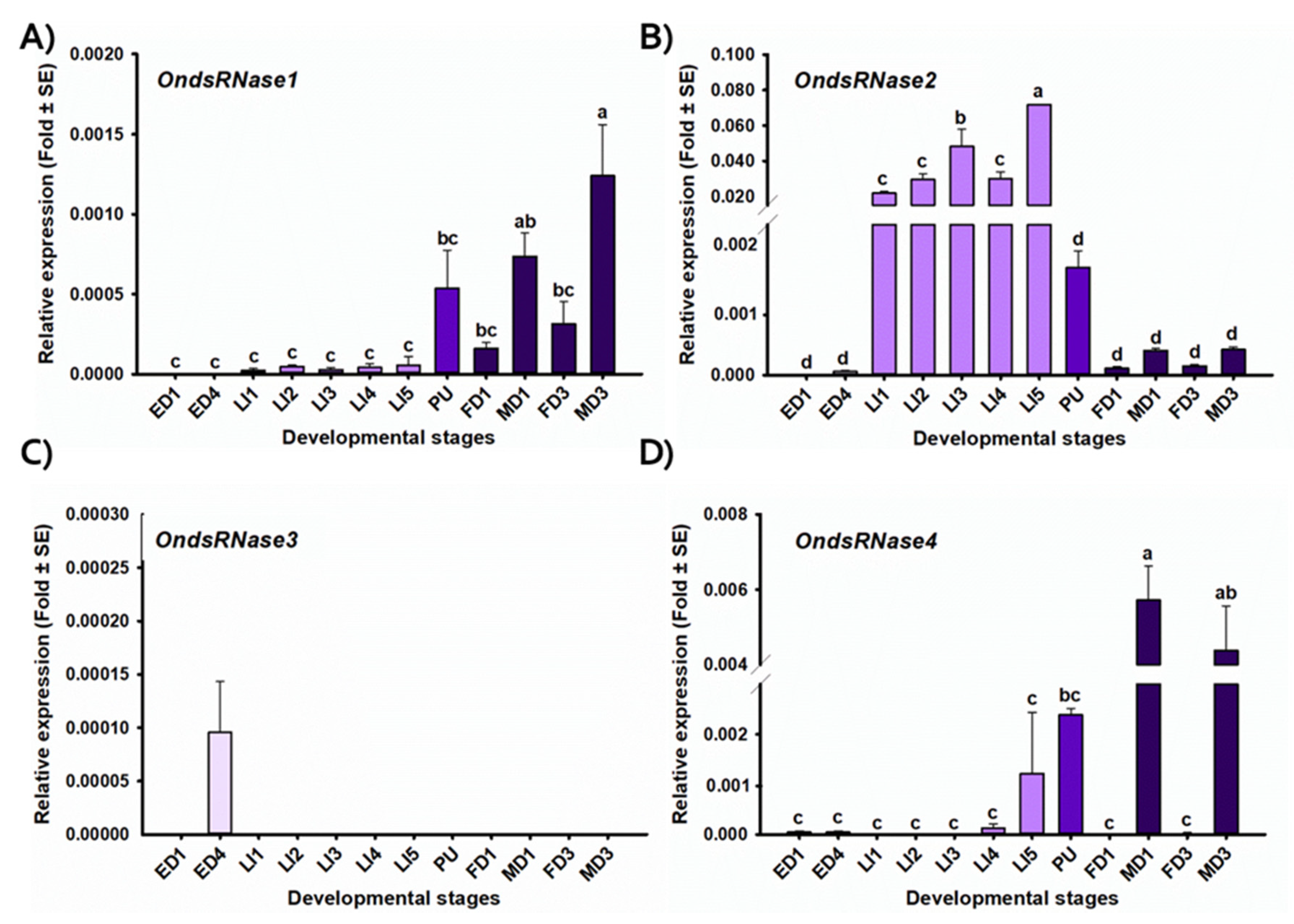
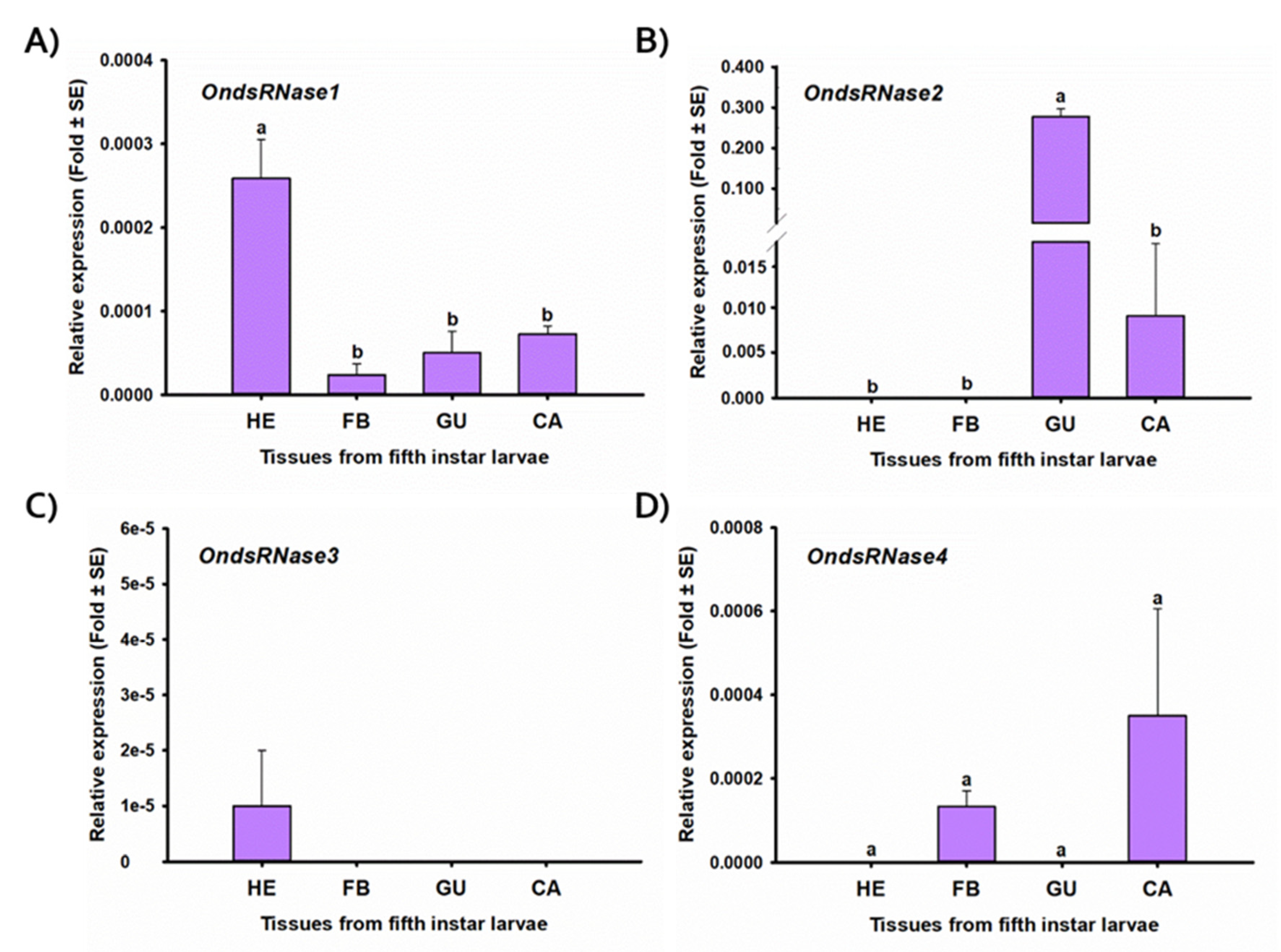
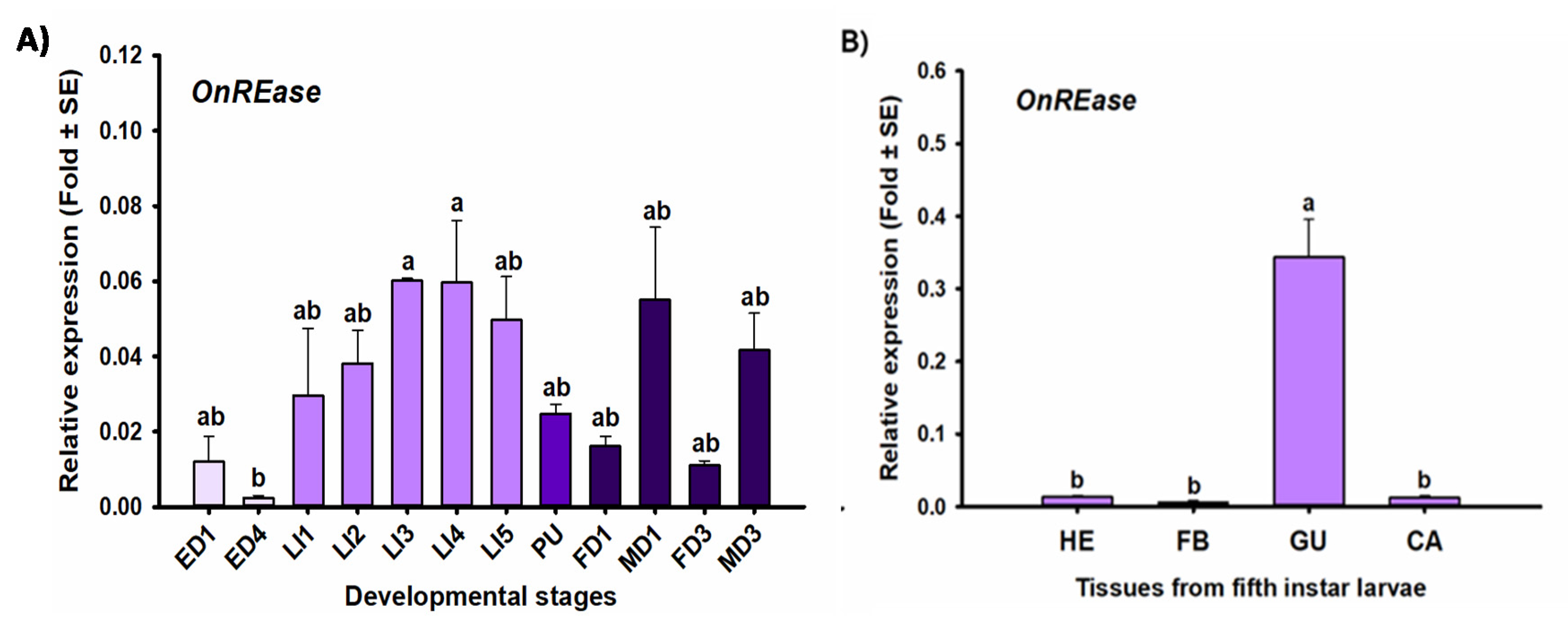
2.4. Stage- and Tissue-Specific Expression Profiles
2.5. RT-qPCR
2.6. Synthesis of dsRNAs
2.7. Transcriptional Responses of Nuclease Genes to dsRNA Exposure
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing and Characterization
3.2. Transcriptional Responses to dsRNA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dowling, D.; Pauli, T.; Donath, A.; Meusemann, K.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Petersen, M.; Peters, R.S.; Mayer, C.; Liu, S.; Zhou, X.; et al. Phylogenetic origin and diversification of RNAi pathway genes in insects. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 3784–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borel, B. When the pesticides run out. Nature 2017, 543, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Head, G.; Carroll, M.; Evans, S.; Rule, D.M.; Willse, A.; Clark, T.; Storer, N.P.; Flannagan, R.D.; Samuel, L.W.; Meinke, L.J. Evaluation of SmartStax and SmartStax Pro maize against western corn rootworm and northern corn rootworm: Effacacy and resistance management evaluation of SmartStax and SmartStax PRO against WCR and NCR. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 1883–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terenius, O.; Papanicolaou, A.; Garbutt, J.S.; Eleftherianos, I.; Huvenne, H.; Kanginakudru, S.; Albrechtsen, M.; An, C.; Aymeric, J.-L.; Barthel, A.; et al. RNA interference in Lepidoptera: An overview of successful and unsucessful studies and implications for experimental design. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolliopoulou, A.; Swevers, L. Recent progress in RNAi research in Lepidoptera: Intracellular machinery, antiviral immune response and prospects for insect pest control. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2014, 6, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, T.G.M.; Buuk, C.; Gloyna, K.; Ortego, F.; Farinós, G.P. Ten years of MON 810 resistance monitoring of field populations of Ostrinia nubilalis in Europe. J. App. Entomol. 2018, 142, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegwart, M.; Thibord, J.B.; Olivares, J.; Hirn, C.; Elias, J.; Maugin, S.; Claire, L. Biochemical and molecular mechanisms associated with the resistance of the European corn borer (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) to Lambda-Cyuhalothrin and first monitoring tool. J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Li, X.; Coates, B.S.; Zhang, Q.; Siegfried, B.D.; Zhou, X. microRNA profiling between Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab-suceptile and resistant European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Hubner). Insect Mol. Biol. 2018, 27, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajuria, C.; Buschman, L.L.; Chen, M.-S.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Zhu, K.Y. A gut-specific chitinase gene essential for regulation of chitin content of peritrophic matrix and growth of Ostrinia nubilalis larvae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajuria, C.; Buschman, L.L.; Chen, M.-S.; Siegfried, B.D.; Zhu, K.Y. Identification of a novel aminopeptidase P-like gene (OnAPP) possibly involved in Bt toxicity and resistance in a major corn pest (Ostrinia nubilalis). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, A.M.W.; Silver, K.; Zhang, J.; Park, Y.; Zhu, K.Y. Molecular mechanisms influencing efficiency of RNA interference in insects. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, R.-B.; Li, H.-C.; Fan, Y.-J.; Hu, S.-R.; Christiaens, O.; Smagghe, G.; Miao, X.-X. A nuclease specific to lepidopteran insects suppresses RNAi. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 6011–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, R.; Chen, Q.; Li, H.; Hu, S.; Miao, X.; Wang, G.; Yang, B. Knockout of the HaREase gene improves the stability of dsRNA and increases sensitivity of Helicoverpa armigera to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin. Front. Physiol 2019, 10, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, A.M.W.; Yu, Z.; Biondi, M.; Song, H.; Silver, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, K.Y. Stability of double-stranded RNA in gut contents and hemolymph of Ostrinia nubilalis larvae. Pest Biochem. Physiol. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swevers, L.; Huvenne, H.; Menschaert, G.; Kontogiannatos, D.; Kourti, A.; Pauchet, Y.; ffrench-Constant, R.; Smagghe, G. Colorado potato beetle (Coleoptera) gut transcriptome analysis: Expression of RNA interference-related genes. Insect Mol. Biol. 2013, 22, 668–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hall, B.G. Building phylogenetic trees from molecular data with MEGA. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenteros, J.J.A.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sonderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenteros, J.J.A.; Salvatore, M.; Emanuelsson, O.; Winther, O.; von Heijne, G.; Elofsson, A.; Nielsen, H. Detecting sequence signals in targeting peptides using deep learning. Life Sci. Alliance 2019, 2, e201900429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horton, P.; Park, K.-J.; Obayashi, T.; Fujta, N.; Harada, H.; Adams-Collier, C.J.; Nakai, K. WoLF PSORT: Protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, K.-C.; Shen, H.-B. Euk-mPLoc: A fusion classifier for large-scale eukaryotic protein subcellular location prediction by incorporating multiple sites. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-Z.; Fang, J.-A.; Xiao, X.; Chou, K.-C. iLoc-Animal: A multi-label learning classifier for predicting subcellular localization of animal proteins. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.L.; Jensen, J.L.; Ørntoft, T.F. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5245–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Tichopad, A.; Prgomet, C.; Neuvians, T.P. Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper-Excel-based tool using pairwise correlations. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimatsu, Y.; Furuno, T.; Sugimura, Y.; Togoh, M.; Ishihara, R.; Tokizane, M.; Kotani, E.; Hayashi, Y.; Furusawa, T. Purification and properties of double-stranded RNA-degrading nuclease, dsRNase, from the digestive juice of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Insect Biotechnol. Sericol. 2007, 62, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Arimatsu, Y.; Kotani, E.; Sugimura, Y.; Furusawa, T. Molecular characterization of a cDNA encoding extracellular dsRNase and its expression in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Smagghe, G.; Swevers, L. Transcriptional response of BmToll9-1 and RNAi machinery genes to exogenous dsRNA in the midgut of Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynant, N.; Santos, D.; Verdonck, R.; Spit, J.; Van Wielendaele, P.; Vanden Broeck, J. Identification, functional characterization and phylogenetic analysis of double stranded RNA degrading enzymes present in the gut of the desert locust. Schistocerca gregaria. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spit, J.; Philips, A.; Wynant, N.; Santos, D.; Plaetinck, G.; Vanden Broeck, J. Knockdown of nuclease activity in the gut enhances RNAi efficiency in the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata, but not in the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Insect Biochem Mol. Biol. 2017, 81, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Cooper, A.M.W.; Silver, K.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Ma, E.; Zhu, K.Y.; Zhang, J. A double-stranded RNA degrading enzyme reduces the efficiency of oral RNA interference in migratory locust. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 8, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Cooper, A.M.W.; Silver, K.; Li, T.; Ma, E.; Zhu, K.Y.; Zhang, J. Contributions of dsRNases to differential RNAi efficiencies between the injection and oral delivery of dsRNA in Locusta migratoria. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1707–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesbrecht, D.; Heschuk, D.; Wiens, I.; Boguski, D.; LaChance, P.; Whyard, S. RNA interference is enhanced by knockdown of double-stranded RNases in the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insects 2020, 11, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.K.; Singh, S.; Mogilicherla, K.; Shukla, J.N.; Palli, S.R. Comparative analysis of double-stranded RNA degradation and processing in insects. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lunin, V.Y.; Levdikov, V.M.; Shlyapnikov, S.V.; Blagova, E.V.; Lunin, V.V.; Wilson, K.S.; Mikhailov, A.M. Three-dimensional structure of Serratia marcescens nuclease at 1.7 A resolution and mechanism of its action. FEBS Lett. 1997, 412, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Swevers, L.; Iatrou, K.; Huvenne, H.; Smagghe, G. Bombyx mori DNA/RNA non-specific nuclease: Expression of isoforms in insect culture cells, subcellular localization and functional assays. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Gatehouse, J.A.; Fitches, E.C. A systematic study of RNAi effects and dsRNA stability in Tribolium castaneum and Acyrthosiphon pisum, following injection and ingestion of analogous dsRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lomate, P.R.; Bonning, B.C. Distinct properties of proteases and nucleases in the gut, salivary gland and saliva of southern green stink bug, Nezara viridula. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Miao, X. Second-generation sequencing supply an effective way to screen RNAi targets in large scale for potential application in pest insect control. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18644. [Google Scholar]
- Garbutt, J.S.; Bellés, X.; Richards, E.H.; Reynolds, S.E. Persistence of double-stranded RNA in insect hemolymph as a potential determiner of RNA interference success: Evidence from Manduca sexta and Blattella germanica. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castellanos, N.L.; Smagghe, G.; Sharma, R.; Oliveira, E.E.; Christiaens, O. Liposome encapsulation and EDTA formulation of dsRNA targeting essential genes increase oral RNAi-caused mortality in the Neotropical stink bug Euschistus heros. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.H.; Huang, J.H.; Liu, Y.; Belles, X.; Lee, H.J. Oral delivery of dsRNA lipoplexes to German cockroach protects dsRNA from degradation and induces RNAi response. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christiaens, O.; Tardajos, M.G.; Reyna, Z.L.M.; Dash, M.; Dubruel, P.; Smagghe, G. Increased RNAi efficacy in Spodoptera exigua via the formulation of dsRNA with guanylated polymers. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Han, Z. Efficiency of different methods for dsRNA delivery in cotton bollworm (Helicoverpa armigera). J. Integr Agric. 2014, 13, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Gillet, F.; Garcia, R.A.; Macedo, L.L.P. Investigating engineered ribonucleoprotein particles to improve oral RNAi delivery in crop insect pests. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar]







| Gene Names | OndsRNase1 | OndsRNase2 | OndsRNase3 | OndsRNase4 | OnREase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GenBank accession number | MT524715 | MT524712 | MT524713 | MT524714 | MT524716 |
| ORF (bp) | 1341 | 1347 | 1182 | 1212 | 1866 |
| Protein (aa) | 446 | 448 | 393 | 403 | 621 |
| Mass (kDa) | 50.66 | 50.01 | 44.13 | 46.14 | 71.99 |
| Isoelectric point (pI) | 5.67 | 7.17 | 7.95 | 6.26 | 5.64 |
| Sec/SPI likelihood | 0.9956, 0.999 | 0.9978, 1.000 | 0.9948, 0.997 | 0.7565, 0.9536 | 0.0013, 0.0005 |
| Sec/SPI cleavage site (aa) | 18–19 | 16–17 | 20–21 | 22–23, 23–24 | n/a |
| Localization predictions | Extracellular, NASL | Extracellular, Mitochondria | Extracellular, NASL | Extracellular, NASL, Mitochondria | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cooper, A.M.W.; Song, H.; Shi, X.; Yu, Z.; Lorenzen, M.; Silver, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, K.Y. Molecular Characterizations of Double-Stranded RNA Degrading Nuclease Genes from Ostrinia nubilalis. Insects 2020, 11, 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100652
Cooper AMW, Song H, Shi X, Yu Z, Lorenzen M, Silver K, Zhang J, Zhu KY. Molecular Characterizations of Double-Stranded RNA Degrading Nuclease Genes from Ostrinia nubilalis. Insects. 2020; 11(10):652. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100652
Chicago/Turabian StyleCooper, Anastasia M. W., Huifang Song, Xuekai Shi, Zhitao Yu, Marcé Lorenzen, Kristopher Silver, Jianzhen Zhang, and Kun Yan Zhu. 2020. "Molecular Characterizations of Double-Stranded RNA Degrading Nuclease Genes from Ostrinia nubilalis" Insects 11, no. 10: 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100652
APA StyleCooper, A. M. W., Song, H., Shi, X., Yu, Z., Lorenzen, M., Silver, K., Zhang, J., & Zhu, K. Y. (2020). Molecular Characterizations of Double-Stranded RNA Degrading Nuclease Genes from Ostrinia nubilalis. Insects, 11(10), 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100652