Effects of Aphid Density and Plant Taxa on Predatory Ladybeetle Abundance at Field and Landscape Scales
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Relationship between Aphid and Ladybeetle Abundance at the Field Scale
2.2. Relationship between Aphid and Ladybeetle Abundancein Paired Cotton and Maize Fields at the Regional Landscape Scale
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Field Scale
2.3.2. Regional Landscape Scale
3. Results
3.1. Species Composition of Aphidophagous Ladybeetles
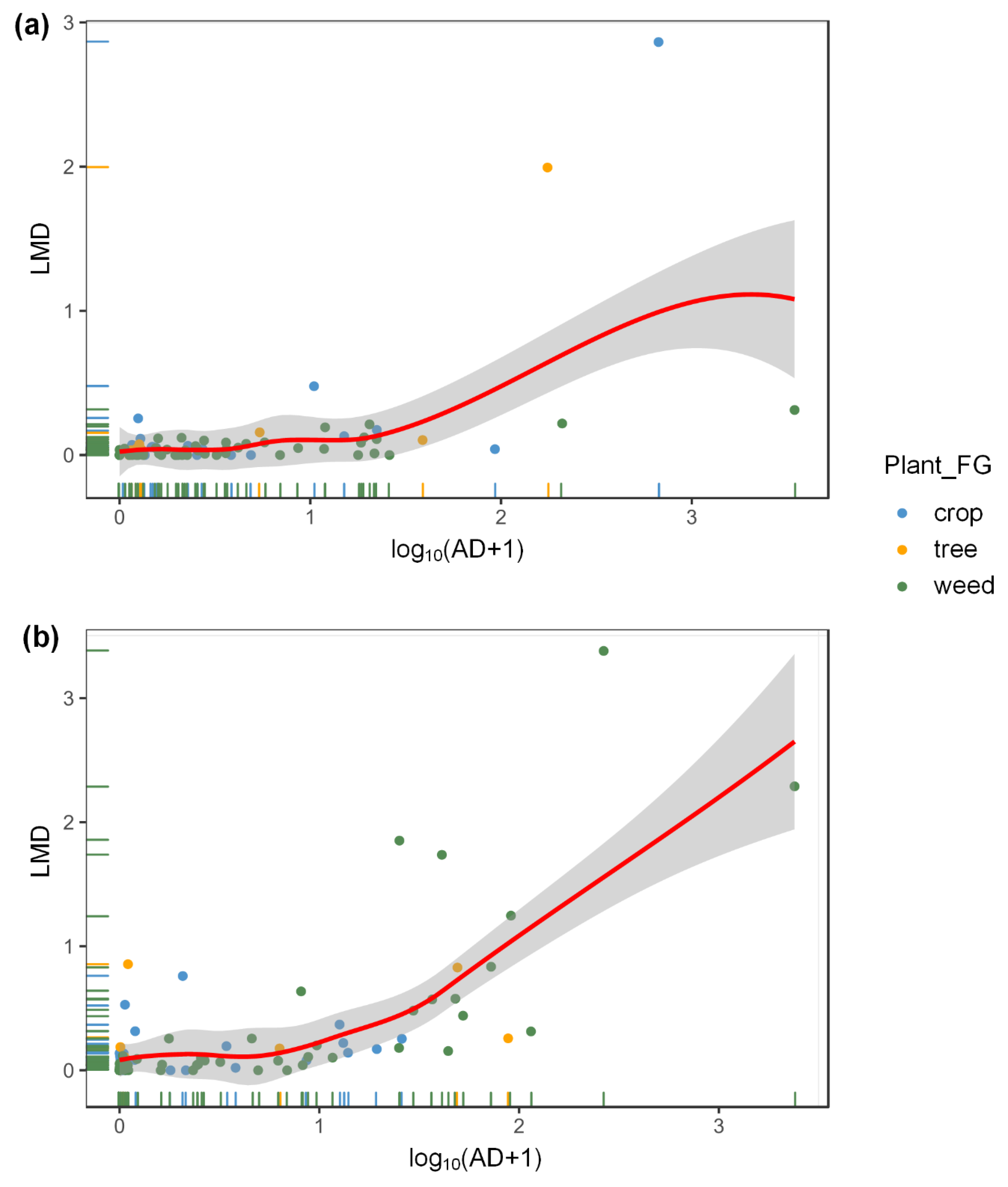
3.2. Effects of Aphids and Plant Taxa on Ladybeetles at the Field Scale
3.3. Effects of Aphids on Ladybeetles at the Regional Landscape Scale
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodek, I.; Honĕk, A.; van Emden, H.F. Ecology and Behaviour of the Ladybeetle Beetles (Coccinellidae); John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, A.F.G. Insect Predator-Prey Dynamics: Ladybeetle Beetles and Biological Control; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Obrycki, J.J.; Harwood, J.D.; Kring, T.J.; O’Neil, R.J. Aphidophagy by Coccinellidae: Application of biological control in agroecosystems. Biol. Control 2009, 51, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, T.B.; Landis, D.A.; Cardoso, F.F.; Difonzo, C.D. Predators suppress Aphis glycines Matsumura population growth in soybean. Environ. Entomol. 2004, 33, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.; Desneux, N.; Lu, Y.H.; Wu, K.M. Key aphid natural enemies showing positive effects on wheat yield through biocontrol services in northern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 226, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, D.S.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Meehan, T.D.; Martin, E.A.; DeClerck, F.; Grab, H.; Gratton, C.; Hunt, L.; Larsen, A.E.; Martínez-Salinas, A.; et al. Crop pests and predators exhibit inconsistent responses to surrounding landscape composition. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E7863–E7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costamagna, A.C.; Landis, D.A.; Difonzo, C.D. Suppression of soybean aphid by generalist predators results in a trophic cascade in soybeans. Ecol. Appl. 2007, 17, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrycki, J.J.; Kring, T.J. Predaceous Coccinellidae in biological control. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 295–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schellhorn, N.A.; Bianchi, F.J.J.A.; Hsu, C.L. Movement of entomophagous arthropods in agricultural landscapes: Links to pest suppression. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 559–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, N.M.; Crutsinger, G.M.; Gross, K.; Haarstad, J.; Knops, J.M.H.; Tilman, D. Plant species loss decreases arthropod diversity and shifts trophic structure. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, J.G.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Desneux, N. Population responses by Oriusinsidiosus to vegetational diversity. Biocontrol 2009, 54, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherber, C.; Eisenhauer, N.; Weisser, W.W.; Schmid, B.; Voigt, W.; Fischer, M.; Schulze, E.D.; Roscher, C.; Weigelt, A.; Allan, E.; et al. Bottom-up effects of plant diversity on multitrophic interactions in a biodiversity experiment. Nature 2010, 468, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomine, E.; Jeavons, E.; Rusch, A.; Bearez, P.; Desneux, N. Effect of crop diversity on predation activity and population dynamics of the mirid predator Nesidiocoris tenuis. J. Pest Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wäckers, F.L. Suitability of Extra-Floral Nectar, Pollen, and Honeydew as Insect Food Sources. In Plant-Provided Food for Carnivorous Insects; Wäckers, F.L., van Rijn, P.C.J., Bruin, J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wäckers, F.L.; van Rijn, P.C.J. Pick and Mix: Selecting Flowering Plants to Meet the Requirements of Target Biological Control Insects. In Biodiversity and Insect Pests: Key Issues for Sustainable Management; Gurr, S.D., Snyder, W.E., Read, D.M.Y., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Thomine, E.; Rusch, A.; Supplisson, C.; Monticelli, L.S.; Amiens-Desneux, E.; Lavoir, A.V.; Desneux, N. Highly diversified crop systems can promote the dispersal and foraging activity of the generalist predator Harmonia axyridis. Entomol. Gen. 2020, 40, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, S.; Romeis, J.; Collatz, J. Utilization of plant-derived food sources from annual flower strips by the invasive harlequin ladybird Harmonia axyridis. Biol. Control 2018, 122, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leather, S.R.; Cooke, R.C.A.; Fellowes, M.D.E.; Rombe, R. Distribution and density of ladybeetles (Coleoptera: Coccinelldiae) in non-crop habitats. Eur. J. Entomol. 1999, 96, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Prasifka, J.R.; Heinz, K.M.; Minzenmayer, R.R. Timing, magnitude, rates, and putative causes of predator movement between cotton and grain sorghum fields. Environ. Entomol. 2004, 33, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elliott, N.C.; Kieckhefer, R.W.; Phoofolo, M.W. Prey foraging movements by Hippodamia convergens 1 in wheat are influenced by hunger and aphids. Southwest Entomol. 2013, 38, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, C.M.; Verdugo, J.A.; Grez, A.A.; Tapia, J.; Lavandero, B. Movement between crops and weeds: Temporal refuges for aphidophagous insects in Central Chile. Cienc. Investig. Agrar. 2013, 40, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, E.W.; Dixon, A.F.G. Cues for oviposition by ladybeetle beetles (Coccinellidae): Response to aphids. J. Anim. Ecol. 1986, 55, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoretti, N.; Weisser, W.W. The impact of individual ladybeetles (Coccinellaseptempunctata, Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on aphids colonies. Eur. J. Entomol. 2000, 97, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Werf, W.; Evans, E.W.; Powell, J. Measuring and modelling the dispersal of Coccinellaseptempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in alfalfa fields. Eur. J. Entomol. 2000, 97, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, E.W. Searching and reproductive behaviour of female aphidophagous ladybeetles (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): A review. Eur. J. Entomol. 2003, 100, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.J.J.A.; van der Werf, W. Model evaluation of the function of prey in non-crop habitats for biological control by ladybeetles in agricultural landscapes. Ecol. Model 2004, 171, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, M.M.; Landis, D.A.; Gratton, C.; Schmidt, N.; O’Neal, M.; Mueller, E.; Chacon, J.; Heimpel, G.E.; DiFonzo, C.D. Landscape composition influences patterns of native and exotic lady beetle abundance. Divers. Distrib. 2009, 15, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woltz, M.J.; Landis, D.A. Coccinellid response to landscape composition and configuration. Agric. For. Entomol. 2014, 16, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellhorn, N.A.; Parry, H.R.; Macfadyen, S.; Wang, Y.; Zalucki, M.P. Connecting scales: Achieving in-field pest control from areawide and landscape ecology studies. Insect Sci. 2015, 22, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrec, R.; Badenhausser, I.; Bretagnolle, V.; Börger, L.; Roncoroni, M.; Guillon, N.; Gauffre, B. Crop succession and habitat preferences drive the distribution and abundance of carabid beetles in an agricultural landscape. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 199, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djoudi, E.A.; Plantegenest, M.; Aviron, S.; Pétillon, J. Local vs. landscape characteristics differentially shape emerging and circulating assemblages of carabid beetles in agroecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 270, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, M.; Landis, D.; Gratton, C.; DiFonzo, C.; O’neal, M.; Chacon, J.; Wayo, M.; Schmidt, N.; Mueller, E.; Heimpel, G. Landscape diversity enhances biological control of an introduced crop pest in the north-central USA. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Kremen, C. Pest control experiments show benefits of complexity at landscape and local scales. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 1936–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, P.H.; Colunga-Garcia, M.; Gage, S.H. Establishing pathways of energy flow for insect predators using stable isotope ratios: Field and laboratory evidence. Oecologia 1997, 109, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelbermann, K.; Scheu, S. Stable isotope enrichment (delta N-15 and delta C-13) in a generalist predator (Pardosalugubris, Araneae: Lycosidae): Effects of prey quality. Oecologia 2002, 130, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallhart, N.; Wallinger, C.; Juen, A.; Traugott, M. Dispersal abilities of adult click beetles in arable land revealed by analysis of carbon stable isotopes. Agric. For. Entomol. 2009, 11, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, K.J.; Gratton, C. Stable isotopes reveal different patterns of inter-crop dispersal in two ladybeetle species. Ecol. Entomol. 2011, 36, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, F.; Men, X.Y.; Yang, B.; Su, J.W.; Zhang, Y.S.; Zhao, Z.H.; Ge, F. Maize benefits the predatory beetle, Propylea japonica (Thunberg), to provide potential to enhance biological control for aphids in cotton. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, F.; di Lascio, A.; Carlino, P.; Costantini, M.L.; Rossi, L.; Pons, X. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope signatures to determine predatordispersal between alfalfa and maize. Biol. Control 2014, 77, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.H.; Wu, K.M.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Guo, Y.Y.; Desneux, N. Widespread adoption of Bt cotton and insecticide decrease promotes biocontrol services. Nature 2012, 487, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Desneux, N.; Lu, Y.H.; Liu, B.; Wu, K.M. Characterization of the natural enemy community attacking cotton aphid in the Bt cotton ecosystem in northern China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Niu, C.Y.; Desneux, N. Identification of top-down forces regulating cotton aphid population growth in transgenic Bt cotton in central China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.R. Farmland Weeds in China: A Collection of Colored Illustrative Plates; Agricultural Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.S.; Lu, Y.H.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G. Early-Season host switching in Adelphocoris spp. (Hemiptera: Miridae) of differing host breadth. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, S.X.; Wang, X.M.; Pang, H.; Peng, Z.Q.; Zeng, T. Colored Pictorial Handbook of Ladybeetle Beetles in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Desneux, N.; Decourtye, A.; Delpuech, J.M. The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolker, B.M.; Brooks, M.E.; Clark, C.J.; Geange, S.W.; Poulsen, J.R.; Stevens, M.H.H.; White, J.S.S. Generalized linear mixed models: A practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S. Fourth Edition; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Soft. 2015, 67, 133–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareiva, P.; Odell, G. Swarms of predators exhibit “preytatxis” if individual predators use area-restricted search. Am. Nat. 1987, 130, 233–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellhorn, N.A.; Andow, D.A. Response of coccinellids to their aphid prey at different spatial scales. Popul. Ecol. 2005, 47, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seagraves, M.P. Lady beetle oviposition behavior in response to the trophic environment. Biol. Control 2009, 51, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honĕk, A.; Martinkova, Z.; Štrobach, J. Effect of aphid abundance and urbanization on the abundance of Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2018, 115, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassou, A.G.; Tixier, P. Response of pest control by generalist predators to local-scale plant diversity: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertrand, C.; Eckerter, P.W.; Ammann, L.; Entling, M.H.; Gobet, E.; Herzog, F.; Mestre, L.; Tinner, W.; Albrecht, M. Seasonal shifts and complementary use of pollen sources by two bees, a lacewing and a ladybeetle species in European agricultural landscapes. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 2431–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuldiner-Harpaz, T.; Coll, M. Estimating the effect of plant-provided food supplements on pest consumption by omnivorous predators: Lessons from two coccinellid beetles. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, M.M.; Lima, E.; Lemos, F.; Venzon, M.; Janssen, A. Non-crop plant to attract and conserve an aphid predator (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in tomato. Biol. Control 2017, 115, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareiva, P.; Sahakian, R. Tritrophic effects of a simple architectural mutation in pea plants. Nature 1990, 345, 433–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grevstad, F.S.; Klepetka, B.W. The influence of plant architecture on the foraging efficiencies of a suite of ladybird beetles feeding on aphids. Oecologia 1992, 92, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, P.G.; Cuddington, K. Effects of plant gross morphology on predator searching behaviour. Environ. Entomol. 2012, 41, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honĕk, A.; Martinkova, Z.; Dixon, A.F.G.; Skuhrovec, J.; Roy, H.E.; Brabec, M.; Pekar, S. Life cycle of Harmonia axyridis in central Europe. BioControl 2018, 63, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honĕk, A.; Martinkova, Z.; Roy, H.E.; Dixon, A.F.G.; Skuhrovec, J.; Pekár, S.; Brabec, M. Differences in thephenology of Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) and nativecoccinellids in Central Europe. Environ. Entomol. 2019, 48, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Honĕk, A.; Brabec, M.; Martinkova, Z.; Dixon, A.F.G.; Pekár, S.; Skuhrovec, J. Factors determining local and seasonal variation in abundance of Harmonia axyridis in Central Europe. Eur. J. Entomol. 2019, 116, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Park, K.C. Methyl salicylate, a soybean aphid-induced plant volatile attractive to the predator CoccinellaSeptempunctata. J. Chem. Ecol. 2005, 31, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girling, R.D.; Hassal, M. Behavioural responses of the seven-spot ladybeetle Coccinellaseptempunctata to plant headspace chemicals collected from four crop Brassicas and Arabidopsis thaliana, infested with Myzuspersicae. Agric. For. Entomol. 2008, 10, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, P.D.; Schillings, T.; Farmakidis, J.; Heuskin, S.; Lognay, G.; Verheggen, F.J.; Brostaux, Y.; Haubruge, E.; Francis, F. Testing semiochemicals from aphid, plant and conspecific: Attraction of Harmonia axyridis. Insect Sci. 2012, 19, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turlings, T.; Erb, M. Tritrophic interactions mediated by herbivore-induced plant volatiles: Mechanisms, ecological relevance, and application potential. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, C.L.; Xu, B.; Pan, H.S.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.Z.; Lu, Y.H. Volatiles from Sophora japonica flowers attract Harmonia axyridis adults (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J. Integr. Agr. 2019, 18, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Risch, S.J.; Wrubel, R.; Andow, D. Foraging by a predaceous beetle, Coleomegillamaculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), in a polyculture: Effects of plant density and diversity. Env. Entomol. 1982, 11, 949–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andow, D.A.; Risch, S.J. Predation in diversified agroecosystems: Relations between a coccinellid predator Coleomegillamaculata and its food. J. Appl. Ecol. 1985, 2, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermunt, B.; Cuddington, K.; Sobek-Swant, S.; Crosthwaite, J.C.; Lyons, D.B.; Sinclair, B.J. Temperatures experienced by wood-boring beetles in the under-bark microclimate. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2012, 269, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tougeron, K.; van Baaren, J.; Burel, F.; Alford, L. Comparing thermal tolerance across contrasting landscapes: First steps towards understanding how landscape management could modify ectotherm thermal tolerance. Insect Conserv. Diver. 2016, 9, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alford, L.; Tougeron, K.; Pierre, J.S.; Burel, F.; Van Baaren, J. The effect of landscape complexity and microclimate on the thermal tolerance of a pest insect. Insect Sci. 2017, 25, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grez, A.A.; Torres, C.; Zaviezo, T.; Lavander, B.; Ramírez, M. Migration of coccinellids to alfalfa fields with varying adjacent vegetation in Central Chile. Cienc. Investig. Agrar. 2010, 37, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, H.S.; Xiu, C.L.; Liu, B.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Lu, Y.H. Whorl-stage maize provides a microclimate refuge for predatory ladybeetles. Biol. Control 2020, 142, 104162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Lu, Y.H.; Morales, H.; Vazquez, L.L.; Legaspi, J.C.; Eliopoulos, P.A.; Hernandez, L.M. Current status and potential of conservation biological control for agriculture in the developing world. Biol. Control 2013, 65, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayl, R.J.; Shields, M.W.; Tiwari, S.; Wratten, S.D. Conservation biological control of insect pests. Sust. Agric. Rev. 2018, 28, 103–124. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, M.J.; Gordy, J.W.; Kerns, D.L.; Woolley, J.B.; Rooney, W.L.; Bowling, R.D. Sugarcane aphid population growth, plant injury, and natural enemies on selected grain sorghum hybrids in Texas and Louisiana. J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworski, C.C.; Xiao, D.; Xu, Q.X.; Ramirez-Romero, R.; Guo, X.J.; Wang, S.; Desneux, N. Varying the spatial arrangement of synthetic herbivore-induced plant volatiles and companion plants to improve conservation biological control. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, H.; Tagaki, T.; Kogi, K. Effects of conspecific and heterospecific larval tracks on the oviposition behaviour of the predatory ladybeetle, Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2000, 97, 551–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoogendoorn, M.; Heimpel, G.E. Competitive interactions between an exotic and a native ladybeetle: A field cage study. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2004, 111, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, T.H.; Timms, J.E.L.; Taylor, A. Oviposition responses to patch quality in the larch ladybeetle Aphidectaolbiterata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): Effects of aphid density, and con- and heterospecific tracks. B. Entomol. Res. 2006, 96, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ovchinnikov, A.N.; Belyakova, N.A.; Ovchinnikova, A.A.; Reznik, S.Y. Factors determining larval cannibalistic behavior in invasive and native populations of the multicolored Asian ladybird, Harmonia axyridis. Entomol. Gen. 2019, 38, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D.M.; Xu, B.; Xu, J.X.; Lu, Y.H.; Harwood, J.D. Intraguild predation among three common Coccinellids (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in China: Detection using DNA-based gut-content analysis. Environ. Entomol. 2017, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honěk, A.; Dixon, A.F.G.; Soares, A.O.; Skuhrovec, J.; Martinkova, Z. Spatial and temporal changes in the abundance and 16omposition of ladybird (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) communities. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2017, 20, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Fixed Effects | Estimates | S.E. | Wald Z | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 1.85600 | 0.070920 | 26.17 | <0.001 |
| AD | 0.00001 | 0.000003 | 3.93 | < 0.001 |
| Crop_maize | −0.16050 | 0.029880 | −5.37 | <0.001 |
| Month_August | 1.06200 | 0.035830 | 29.65 | <0.001 |
| AD:crop_maize | 0.00035 | 0.000004 | 91.37 | <0.001 |
| AD:month_July | 0.00018 | 0.000031 | 6.01 | <0.001 |
| AD:month_August | −0.00034 | 0.000004 | −87.56 | <0.001 |
| Crops | June | July | August | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Samples | Carbon Isotope Ratioδ13C | C3 Plant | C4 Plant | No. Samples | Carbon Isotope Ratioδ13c | C3 Plant | C4 Plant | No. Samples | Carbon Isotope Ratioδ13c | C3 Plant | C4 Plant | |
| Cotton | 119 | −26.70 ± 1.01 | ~100.00%(119) | ~0.00%(0) | 101 | −25.46 ± 1.78 | ~100.00%(101) | ~0.00%(0) | 458 | −21.11 ± 5.92 | ~86.57%(396) | ~13.43%(62) |
| Maize | 199 | −26.62 ± 1.51 | ~100.00%(199) | ~0.00%(0) | 141 | −23.72 ± 3.91 | ~100.00%(141) | ~0.00%(0) | 852 | −14.12 ± 5.01 | ~28.29%(241) | ~71.71%(611) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, H.; Liu, B.; Jaworski, C.C.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Desneux, N.; Thomine, E.; Lu, Y. Effects of Aphid Density and Plant Taxa on Predatory Ladybeetle Abundance at Field and Landscape Scales. Insects 2020, 11, 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100695
Pan H, Liu B, Jaworski CC, Yang L, Liu Y, Desneux N, Thomine E, Lu Y. Effects of Aphid Density and Plant Taxa on Predatory Ladybeetle Abundance at Field and Landscape Scales. Insects. 2020; 11(10):695. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100695
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Hongsheng, Bing Liu, Coline C. Jaworski, Long Yang, Yongqiang Liu, Nicolas Desneux, Eva Thomine, and Yanhui Lu. 2020. "Effects of Aphid Density and Plant Taxa on Predatory Ladybeetle Abundance at Field and Landscape Scales" Insects 11, no. 10: 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100695
APA StylePan, H., Liu, B., Jaworski, C. C., Yang, L., Liu, Y., Desneux, N., Thomine, E., & Lu, Y. (2020). Effects of Aphid Density and Plant Taxa on Predatory Ladybeetle Abundance at Field and Landscape Scales. Insects, 11(10), 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100695







