Will Peri-Urban Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) Challenge Local Eradication?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Mapping Host Trees
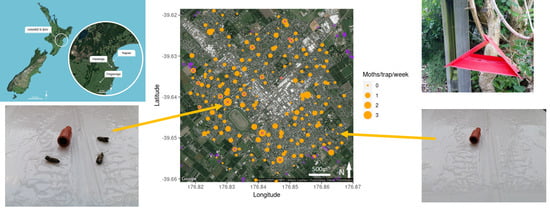
2.2. Traps
2.3. Trapping Locations
2.4. Orchard Trap Catch Data from the Hawke’s Bay Growing District
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hastings Densities and Counts
3.2. Central Hawke’s Bay Densities and Counts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoeckli, S.; Hirschi, M.; Spirig, C.; Calanca, P.; Rotach, M.W.; Samietz, J. Impact of climate change on voltinism and prospective diapause induction of a global pest insect—Cydia pomonella (L.). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CABI. Cydia pomonella; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Witzgall, P.; Stelinski, L.; Gut, L.; Thomson, D. Codling moth management and chemical ecology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2008, 53, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klassen, W. Area-wide approaches to insect pest interventions: History and lessons. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Area-Wide Control of Insect Pests, and the 5th International Symposium on Fruit Flies of Economic Importance, Penang, Malaysia, 28 May–5 June 2000; Tan, K.H., Ed.; Penerbit University: Penang, Malaysia, 2000; pp. 21–38. [Google Scholar]
- Klassen, W. Area-wide integrated pest management and the sterile insect technique. In Sterile Insect Technique; Dyck, V.A., Hendrichs, J., Robinson, A.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 39–68. [Google Scholar]
- Proverbs, M.; Newton, J.; Campbell, C. Codling moth: A pilot program of control by sterile insect release in British Columbia. Can. Entomol. 1982, 114, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proverbs, M.; Newton, J.; Logan, D. Suppression of codling moth, Laspeyresia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Olethreutidae), by release of sterile and partially sterile moths. Can. Entomol. 1978, 110, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proverbs, M. The sterile male technique and its possible use for codling moth eradication. Can. Entomol. 1964, 96, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proverbs, M.; Newton, J. Some effects of gamma radiation on the reproductive potential of the codling moth, Carpocapsa pomonella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Olethreutidae). Can. Entomol. 1962, 94, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.D.; Hutt, R.B.; Butt, B.A. Field dispersal of laboratory-reared fertile female codling moths and population suppression by release of sterile males. Environ. Entomol. 1973, 2, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, B.A.; White, L.D.; Moffitt, H.R.; Hathaway, D.O.; Schoenleber, L.G. Integration of sanitation, insecticides, and sterile moth releases for suppression of populations of codling moths in the Wenas Valley of Washington. Environ. Entomol. 1973, 2, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lance, D.; McInnis, D. Biological basis of the sterile insect technique. In Sterile Insect Technique; Dyck, V.A., Hendrichs, J., Robinson, A.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 69–94. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, G.J.R.; Gardiner, M.G.T. Towards eradication of codling moth in British Columbia by complimentary actions of mating disruption, tree banding and sterile insect technique: Five-year study in organic orchards. Crop Prot. 2005, 24, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloem, S.; Carpenter, J.; McCluskey, A.; Fugger, R.; Arthur, S.; Wood, S. Suppression of the codling moth Cydia pomonella in British Columbia, Canada using an area-wide integrated approach with an SIT components. In Area-Wide Control of Insect Pests; Vreysen, M.J.B., Robinson, A.S., Hendrichs, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 591–601. [Google Scholar]
- Thistlewood, H.; Judd, G.J. Twenty-five years of research experience with the Sterile Insect Technique and area-wide management of codling moth, Cydia pomonella (L.), in Canada. Insects 2019, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trematerra, P.; Gentile, P.; Sciarretta, A. Spatial analysis of pheromone trap catches of codling moth (Cydia pomonella) in two heterogeneous agro-ecosystems, using geostatistical techniques. Phytoparasitica 2004, 32, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.T.; Suckling, D.M.; Wearing, C.H. Past, present, and future of integrated control of apple pests: The New Zealand experience. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2017, 62, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Park, N.; Butcher, M. Apple futures: New Zealands low pesticide residue apple production programme. N. Z. Plant Prot. 2015, 68, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, P.R. The Climate and Weather of Hawke’s Bay; National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research: Wellington, New Zealand, 2013; p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, W.C. Farewell Silent Spring: The New Zealand Apple Story; N. Z. Plant Protection Society: Auckland, New Zealand, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Methyl Bromide Fumigations: Post-Reassessment Guidance for Fumigators; Environmental Protection Authority: Wellington, New Zealand, 2011.
- Horner, R.; Walker, J.; Rogers, D.; Lo, P.; Suckling, D. Use of the sterile insect technique in New Zealand: Benefits and constraints. N. Z. Plant Prot. 2016, 69, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Census Usually Resident Population Counts; Statistics New Zealand: Wellington, New Zealand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, G.; Perry, G.L.; Walker, J.T.; Suckling, D.M. Peri-urban community attitudes towards codling moth trapping and suppression using the sterile insect technique in New Zealand. Insects 2019, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clare, G.; Suckling, D.; Bradley, S.; Walker, J.; Shaw, P.; Daly, J.; McLaren, G.; Wearing, C. Pheromone trap colour determines catch of non-target insects. N. Z. Plant Prot. 2000, 53, 216–220. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 January 2013).
- Ribeiro, P.J., Jr.; Diggle, P.J. geoR: Package for geostatistical data analysis an illustrative session. Artif. Intell. 2006, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wikle, C.K.; Zammit-Mangion, A.; Cressie, N. Spatio-Temporal Statistics with R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Suckling, D.M.; Gibb, A.R.; Dentener, P.R.; Seldon, D.S.; Clare, G.K.; Jamieson, L.; Baird, D.; Kriticos, D.J.; El-Sayed, A.M. Uraba lugens (Lepidoptera: Nolidae) in New Zealand: Pheromone trapping for delimitation and phenology. J. Econ. Entomol. 2005, 98, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.T.; Jonusas, G. The influence of tree species and edge effects on pheromone trap catches of oak processionary moth Thaumetopoea processionea (L.) in the U.K. Agric. For. Entomol. 2019, 21, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trona, F.; Anfora, G.; Bengtsson, M.; Witzgall, P.; Ignell, R. Coding and interaction of sex pheromone and plant volatile signals in the antennal lobe of the codling moth Cydia pomonella. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 4291–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolt, P.J.; Phillips, T.W. Host plant influences on sex pheromone behavior of phytophagous insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1997, 42, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Turlings, T.C.J. Plant volatiles as mate-finding cues for insects. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolt, P.; Suckling, D.; Judd, G. Positive interaction of a feeding attractant and a host kairomone for trapping the codling moth, Cydia pomonella (L.). J. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 33, 2236–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, A.M.; Cole, L.; Revell, J.; Manning, L.-A.; Twidle, A.; Knight, A.L.; Bus, V.G.; Suckling, D.M. Apple volatiles synergize the response of codling moth to pear ester. J. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 39, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaleski, A.; Mumford, J. Pulling out the evil by the root: The codling moth Cydia pomonella eradication programme in Brazil. In Area-Wide Control of Insect Pests: From Research to Field Implementation; Vreysen, M.J.B., Robinson, A.S., Hendrichs, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 581–590. [Google Scholar]
- Mani, E.; Wildbolz, T. The dispersal of male codling moths (Laspeyresia pomonella L.) in the upper Rhine Valley. Zeit. Ang. Ent. 1977, 83, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, P.; Weyeneth, A.; Weber, D.C.; Dorn, S. Long flights in Cydia pomonella L. (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) measured by a flight mill: Influence of sex, mated status and age. Physiol. Entomol. 1997, 22, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, R.; Thistlewood, H.; Judd, G.J.R. Modelling dispersal of sterile male codling moths, Cydia pomonella, across orchard boundaries. Ecol. Model. 2007, 205, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, D.M.; Knight, A.L.; Henrick, C.A.; Rajapaska, D.; Lingren, B.; Dickens, J.C.; Reynolds, K.M.; Buttery, R.G.; Merrill, G.; Roitman, J. A pear-derived kairomone with pheromonal potency that attracts male and female codling moth, Cydia pomonella (L.). Naturwissenschaften 2001, 88, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, B.D.; Landolt, P.J. Field experiment of a three-chemical controlled-release dispensers to attract codling coth (Cydia pomonella) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, C.G.; Schenker, J.; McGhee, P.; Gut, L.; Brunner, J.; Miller, J. Maximizing information yield from pheromone-baited monitoring traps: Estimating plume reach, trapping radius, and absolute density of Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in Michigan apple. J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockerhoff, E.B.; Liebhold, A.; Richardson, B.; Suckling, D.M. Eradication of invasive forest insects: Concept, methods, costs and benefits. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 2010, 40, S117–S135. [Google Scholar]
- Suckling, D.M.; Barrington, A.M.; Chhagan, A.; Stephens, A.E.A.; Burnip, G.M.; Charles, J.G.; Wee, S.L. Eradication of the Australian painted apple moth Teia anartoides in New Zealand: Trapping, inherited sterility, and male competitiveness. In Area-Wide Control of Insect Pests: From Research to Field Implementation; Vreysen, M.J.B., Robinson, A.S., Hendrichs, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 603–615. [Google Scholar]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horner, R.; Paterson, G.; Walker, J.T.S.; Perry, G.L.W.; Jaksons, R.; Suckling, D.M. Will Peri-Urban Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) Challenge Local Eradication? Insects 2020, 11, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11040207
Horner R, Paterson G, Walker JTS, Perry GLW, Jaksons R, Suckling DM. Will Peri-Urban Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) Challenge Local Eradication? Insects. 2020; 11(4):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11040207
Chicago/Turabian StyleHorner, Rachael, Georgia Paterson, James T.S. Walker, George L.W. Perry, Rodelyn Jaksons, and David Maxwell Suckling. 2020. "Will Peri-Urban Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) Challenge Local Eradication?" Insects 11, no. 4: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11040207
APA StyleHorner, R., Paterson, G., Walker, J. T. S., Perry, G. L. W., Jaksons, R., & Suckling, D. M. (2020). Will Peri-Urban Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) Challenge Local Eradication? Insects, 11(4), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11040207