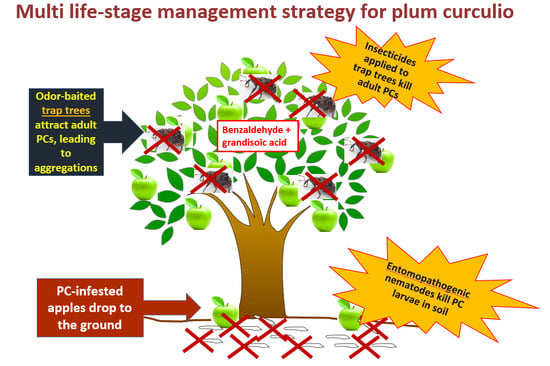
Toward the Integration of an Attract-and-Kill Approach with Entomopathogenic Nematodes to Control Multiple Life Stages of Plum Curculio (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Study 1: Attract-and-Kill of C. Nenuphar Using Odor-Baited Trap Trees
2.3. Study 2: EPN Application against Ground-Dwelling Stages of C. Nenuphar
2.4. Weather
2.5. Characterization of Soil Types
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study 1: Attract-and-Kill of C. Nenuphar Using Odor-Baited Trap Trees
3.2. Study 2: EPN Application against Ground-Dwelling Stages of C. Nenuphar
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Racette, G.; Chouinard, G.; Vincent, C.; Hill, S.B. Ecology and management of plum curculio in apple orchards. Phytoprotection 1992, 73, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leskey, T.C.; Chouinard, G.; Vincent, C. Monitoring and management of the apple maggot fly and the plum curculio: Honouring the legacy of R.J. Prokopy. In Biorational Tree-Fruit Pest Management; Aluja, M., Leskey, T.C., Vincent, C., Eds.; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2009; pp. 110–144. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, C.; Chouinard, G.; Hill, S.B. Progress in plum curculio management: A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1999, 73, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopy, R.J.; Mason, J.L.; Christie, M.; Wright, S.E. Arthropod pest and natural enemy abundance under second-level versus first-level integrated pest management practices in apple orchards: A 4-year study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1996, 57, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reissig, W.H.; Nyrop, J.P.; Straub, R. Oviposition model for timing insecticide sprays against plum curculio in New York State. Environ. Entomol. 1998, 27, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piñero, J.C.; Agnello, A.M.; Tuttle, A.; Leskey, T.C.; Faubert, H.; Koehler, G.; Los, L.; Morin, G.; Leahy, K.; Cooley, D.R.; et al. Effectiveness of odor-baited trap trees for plum curculio (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) monitoring in commercial apple orchards in the Northeast. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leskey, T.C.; Wright, S.E.; Saguez, J.; Vincent, C. Impact of insecticide and fungicide residue contact on plum curculio, Conotrachelus nenuphar (Herbst), mobility and mortality: Implications for pest management. Pest Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leskey, T.C.; Piñero, J.C.; Prokopy, R.J. Odor-baited trap trees: A novel management tool for the plum curculio, Conotrachelus nenuphar (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Mizell, R.F.; Campbell, J.F. Susceptibility of the plum curculio, Conotrachelus nenuphar, to entomopathogenic nematodes. J. Nematol. 2002, 34, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Mizell, R.F.; Cottrell, T.E.; Horton, D.L. Measuring field efficacy of Steinernema feltiae and Steinernema riobrave for suppression of plum curculio, Conotrachelus nenuphar, larvae. Biol. Control 2004, 30, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Leskey, T.C.; Wright, S.E. Virulence of entomopathogenic nematodes to plum curculio, Conotrachelus nenuphar: Effects of strain, temperature, and soil type. J. Nematol. 2011, 43, 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Wright, S.E.; Tuttle, A.F.; Cooley, D.R.; Leskey, T.C. Using entomopathogenic nematodes for biological control of plum curculio, Conotrachelus nenuphar: Effects of irrigation and species in apple orchards. Biol. Control 2013, 67, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopy, R.J.; Chandler, B.W.; Dynok, S.A.; Piñero, J.C. Odor-baited trap trees: A new approach to monitoring plum curculio (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2003, 96, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopy, R.J.; Jácome, I.; Gray, E.; Trujillo, G.; Ricci, M.; Piñero, J.C. Using odor-baited trap trees as sentinels to monitor plum curculio (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in apple orchards. J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 97, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñero, J.C.; Wright, S.E.; Prokopy, R.J. Response of plum curculio (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) to odor-baited traps near woods. J. Econ. Entomol. 2001, 94, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñero, J.C.; Prokopy, R.J. Field evaluation of plant odor and pheromonal combinations for attracting plum curculios. J. Chem. Ecol. 2003, 12, 2735–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eller, F.J.; Bartelt, R.J. Grandisoic acid, a male-produced aggregation pheromone from the plum curculio, Conotrachelus nenuphar. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Hazir, S.; Glazer, I. Basic and applied research: Entomopathogenic nematodes. In Microbial Agents for Control of Insect Pests: From Discovery to Commercial Development and Use; Lacey, L.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, C.; Chouinard, C.; Bostanian, N.J.; Morin, Y. Peripheral zone treatments for plum curculio management: Validation in commercial apple orchards. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1997, 84, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopy, R.J.; Harp, M.; Hamilton, A.; Chandler, B.; Jacome, I. Comparison of Avaunt versus Guthion in every-row versus perimeter-row sprays against key apple insect pests: 2002 results and project summary. Fruit Notes 2003, 68, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Leskey, T.C.; Zhang, A. Impact of temperature on plum curculio, Conotrachelus nenuphar Herbst (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) responses to odor-baited traps. J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Bigurra, E.; Jácome, I.; Trujillo, G.; Prokopy, R.J. Are adult plum curculios capable of overwintering within apple orchards? Fruit Notes 2004, 69, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Decagon Inc. Decagon’s 5TE Water Content, Temperature, and Electrical Conductivity (EC) Sensor. Available online: http://manuals.decagon.com/Retired%20and%20Discontinued/Manuals/13509_5TE_Web.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- USDA-NRCS. Official Series Descriptions. Available online: https://soilseries.sc.egov.usda.gov (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Piñero, J.C.; Prokopy, R.J. Temporal dynamics of plum curculio, Conotrachelus nenuphar (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) immigration into an apple orchard in Massachusetts. Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chouinard, G.; Hill, S.B.; Vincent, C.; Barthakur, N.N. Border-row sprays against the plum curculio (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in apple orchards: A behavioral study. J. Econ. Entomol. 1992, 85, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskey, T.C.; Hock, V.; Chouinard, G.; Cormier, D.; Leahy, K.; Cooley, D.; Tuttle, A.; Eaton, A.; Zhang, A. Evaluating electrophysiological and behavioral responses to volatiles for improvement of odor-baited trap tree management of Conotrachelus nenuphar (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environ. Entomol. 2014, 43, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Saona, C.; Nielsen, A.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.; Tewari, S.; Kyryczenko-Roth, V.; Firbas, N.; Leskey, T. Exploring an odor-baited “Trap Bush” approach to aggregate plum curculio (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) injury in blueberries. Insects 2019, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Orchard/Year | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2018 | 2019 | 3-Year Avg. Volumetric Water Content | 3-Year Avg. Soil Temp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple Hill (NH) | Air temp PCPN | 17.2 26.1 | 16.9 16.3 | 17.7 15.1 | 18.2 8.6 | 17.1 9.6 | 16.6 21.6 | 0.18 | 19.21 |
| Clark Brothers (MA) | Air temp PCPN | 16.9 46.0 | 16.9 3.3 | 17.1 28.5 | 0.25 | 19.48 | |||
| Clarkdale (MA) | Air temp PCPN | 18.1 35.8 | 18.1 20.8 | 17.9 23.1 | 18.4 14.2 | 18.0 13.2 | 0.19 | 20.44 | |
| Cold Spring Orchard (MA) | Air temp PCPN | 18.1 13.7 | 17.8 11.7 | ----- | 21.2 | ||||
| Gould Hill (NH) | Air temp PCPN | 17.4 35.0 | 17.7 13.7 | 14.4 16.7 | 0.20 | 19.34 | |||
| Poverty Lane Orchards (NH) | Air temp PCPN | 15.9 24.4 | 16.3 19.4 | 16.0 22.8 | 18.2 6.2 | 17.0 9.7 | 16.4 21.6 | 0.21 | 18.34 |
| Scott Farms (VT) | Air temp PCPN | 16.8 30.7 | 17.3 18.8 | 17.1 16.8 | 0.19 | 19.40 |
| Year | Treatment | Trap Type | Mean Cumulative Emergence of Adult C. Nenuphar (±SEM) | Outcomes of Analyses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | S. riobrave (n = 18) | PVC enclosure | 0.00 a | Wilcoxon Matched Pairs Test; z = 2.85, p = 0.004. |
| Control (n = 18) | PVC enclosure | 2.22 (±0.6) b | ||
| S. riobrave (n = 15) | Pyramid | 1.06 (±0.6) a | Wilcoxon Matched Pairs Test; z = 3.47, p < 0.001. | |
| Control (n = 15) | Pyramid | 12.87 (±2.6) b | ||
| 2014 | S. riobrave (n = 18) | PVC enclosure | 0.00 a | Wilcoxon Matched Pairs Test; z = 2.27, p = 0.020. |
| Control (n = 18) | PVC enclosure | 0.78 (±0.3) b | ||
| S. riobrave (n = 15) | Pyramid | 15.60 (±4.5) a | Wilcoxon Matched Pairs Test; z = 2.40, p = 0.016. | |
| Control (n = 15) | Pyramid | 28.60 (±5.9) b | ||
| 2015 | S. riobrave (n = 18) | PVC enclosure | 0.50 (±0.6) a | Wilcoxon Matched Pairs Test; z = 3.39, p < 0.001. |
| Control (n = 18) | PVC enclosure | 3.33 (±0.6) b | ||
| S. riobrave (n = 16) | Pyramid | 0.68 (±0.2) a | Wilcoxon Matched Pairs Test; z = 2.02, p = 0.043. | |
| Control (n = 17) | Pyramid | 4.23 (±0.8) b | ||
| 2018 | S. riobrave (n = 19) | Pyramid | 1.05 (±0.5) a | Wilcoxon Matched Pairs Test; z = 3.33, p < 0.001. |
| Control (n = 16) | Pyramid | 6.38 (±1.3) b | ||
| 2019 | S. riobrave (n = 5) | Pyramid | 1.00 (±0.4) a | Kruskal-Wallis H = 10.19; p = 0.017. Kruskal-Wallis |
| S. carpocapsae (n = 5) | Pyramid | 2.60 (±1.6) a | ||
| S. feltiae (n = 5) | Pyramid | 6.40 (±0.7) b | ||
| Control (n = 5) | Pyramid | 6.20 (± 0.7) b |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piñero, J.C.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.; Cooley, D.R.; Tuttle, A.F.; Eaton, A.; Drohan, P.; Leahy, K.; Zhang, A.; Hancock, T.; Wallingford, A.K.; et al. Toward the Integration of an Attract-and-Kill Approach with Entomopathogenic Nematodes to Control Multiple Life Stages of Plum Curculio (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Insects 2020, 11, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060375
Piñero JC, Shapiro-Ilan D, Cooley DR, Tuttle AF, Eaton A, Drohan P, Leahy K, Zhang A, Hancock T, Wallingford AK, et al. Toward the Integration of an Attract-and-Kill Approach with Entomopathogenic Nematodes to Control Multiple Life Stages of Plum Curculio (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Insects. 2020; 11(6):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060375
Chicago/Turabian StylePiñero, Jaime C., David Shapiro-Ilan, Daniel R. Cooley, Arthur F. Tuttle, Alan Eaton, Patrick Drohan, Kathleen Leahy, Aijun Zhang, Torri Hancock, Anna K. Wallingford, and et al. 2020. "Toward the Integration of an Attract-and-Kill Approach with Entomopathogenic Nematodes to Control Multiple Life Stages of Plum Curculio (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)" Insects 11, no. 6: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060375
APA StylePiñero, J. C., Shapiro-Ilan, D., Cooley, D. R., Tuttle, A. F., Eaton, A., Drohan, P., Leahy, K., Zhang, A., Hancock, T., Wallingford, A. K., & Leskey, T. C. (2020). Toward the Integration of an Attract-and-Kill Approach with Entomopathogenic Nematodes to Control Multiple Life Stages of Plum Curculio (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Insects, 11(6), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060375