Genetic Relationship of Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) Populations That Invaded Africa and Asia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection
2.2. DNA Preparation
2.3. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification
2.4. DNA Sequence Analysis
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. Characterization of the Tpi and COI Gene Segments
2.7. Genetic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Tpi Gene Sequence
3.2. Analysis of the COI Gene Sequence
3.3. Genetic Diversity of Tpi and COI Genes of FAW
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Specimens | Highest Sequence Identity with GenBank Database | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tpi | COI | |||||
| % Identity | Accession Numbers | Countries | % Identity | Accession Numbers | Countries | |
| Con-11 | 99.77 | KT336237 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Con-12 | 99.54 | KT336239 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Con-21 | 100 | KT336239 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Con-31 | 100 | KT336239 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Con-41 | 99.54 | KT336239 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Con-42 | 100 | KT336236 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Tan-1 | 99.54 | KT336236 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Tan-2 | 99.86 | KT336239 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Tan-3 | 100 | KT336237 | USA | 99.85 | MN541574 | India |
| Tan-4 | 99.54 | KT336239 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Uga-1 | 99.77 | KT336236 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Uga-2 | 99.54 | KT336229 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Uga-3 | 100 | KT336239 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Uga-4 | 99.77 | KT336237 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Zim-1 | 100 | KT336236 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Zim-2 | 100 | KT336237 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Ban-1 | 100 | KT336229 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Kor-1 | 97.3 | FO681385 | France | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Kor-2 | 99.54 | KT336236 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Kor-3 | 99.77 | KT336239 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Kor-4 | 100 | KT336236 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Nep-1 | 100 | KT336236 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Nep-2 | 100 | KT336236 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Nep-3 | 100 | KT336236 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Vie-1 | 100 | KT336236 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Vie-2 | 100 | KT336239 | USA | 100 | MT605970 | India |
| Vie-3 | 100 | KT336236 | USA | 100 | MN541574 | India |
| SN | Specimens | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ban-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Kor-1 | 97.07 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | Kor-2 | 97.30 | 97.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | Kor-3 | 99.10 | 97.30 | 97.30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | Kor-4 | 97.30 | 97.07 | 99.55 | 97.30 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | Nep-1 | 97.30 | 97.07 | 99.55 | 97.30 | 100.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | Nep-2 | 97.30 | 97.07 | 99.55 | 97.30 | 100.00 | 100.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | Nep-3 | 97.30 | 97.07 | 99.55 | 97.30 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | Vie-1 | 97.30 | 97.07 | 99.55 | 97.30 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | Vie-2 | 99.32 | 97.30 | 97.52 | 99.77 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| 11 | Vie-3 | 97.30 | 97.07 | 99.55 | 97.30 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 97.07 | ||||||||||||||||
| 12 | Con-11 | 97.30 | 97.30 | 99.55 | 97.75 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 97.52 | 99.55 | |||||||||||||||
| 13 | Con-12 | 99.32 | 97.07 | 97.52 | 99.32 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 99.55 | 97.07 | 97.52 | ||||||||||||||
| 14 | Con-21 | 99.32 | 97.30 | 97.52 | 99.77 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 100.00 | 97.07 | 97.52 | 99.55 | |||||||||||||
| 15 | Con-31 | 99.32 | 97.30 | 97.52 | 99.77 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 100.00 | 97.07 | 97.52 | 99.55 | 100.00 | ||||||||||||
| 16 | Con-41 | 99.32 | 97.07 | 97.52 | 99.32 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 99.55 | 97.07 | 97.52 | 100.00 | 99.55 | 99.55 | |||||||||||
| 17 | Con-42 | 97.30 | 97.07 | 99.55 | 97.30 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 97.07 | 100.00 | 99.55 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | ||||||||||
| 18 | Tan-1 | 97.30 | 97.07 | 100.00 | 97.30 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 97.52 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 97.52 | 97.52 | 97.52 | 97.52 | 99.55 | |||||||||
| 19 | Tan-2 | 99.55 | 96.62 | 96.85 | 98.65 | 96.85 | 96.85 | 96.85 | 96.85 | 96.85 | 98.87 | 96.85 | 96.85 | 98.87 | 98.87 | 98.87 | 98.87 | 96.85 | 96.85 | ||||||||
| 20 | Tan-3 | 97.52 | 97.30 | 99.32 | 97.52 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 97.30 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 97.30 | 97.30 | 97.30 | 97.30 | 99.77 | 99.32 | 97.07 | |||||||
| 21 | Tan-4 | 99.32 | 97.07 | 97.52 | 99.32 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 99.55 | 97.07 | 97.52 | 100.00 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 100.00 | 97.07 | 97.52 | 98.87 | 97.30 | ||||||
| 22 | Uga-1 | 97.07 | 96.85 | 99.32 | 97.07 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 96.85 | 99.77 | 99.32 | 96.85 | 96.85 | 96.85 | 96.85 | 99.77 | 99.32 | 96.62 | 99.55 | 96.85 | |||||
| 23 | Uga-2 | 99.55 | 97.30 | 97.75 | 99.10 | 97.75 | 97.75 | 97.75 | 97.75 | 97.75 | 99.32 | 97.75 | 97.75 | 99.32 | 99.32 | 99.32 | 99.32 | 97.75 | 97.75 | 99.10 | 97.97 | 99.32 | 97.52 | ||||
| 24 | Uga-3 | 99.32 | 97.30 | 97.52 | 99.77 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 100.00 | 97.07 | 97.52 | 99.55 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.55 | 97.07 | 97.52 | 98.87 | 97.30 | 99.55 | 96.85 | 99.32 | |||
| 25 | Uga-4 | 97.30 | 97.07 | 99.10 | 97.30 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 97.07 | 99.55 | 99.55 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 99.55 | 99.10 | 96.85 | 99.77 | 97.07 | 99.77 | 97.75 | 97.07 | ||
| 26 | Zim-1 | 97.30 | 97.07 | 99.55 | 97.30 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 97.07 | 100.00 | 99.55 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 97.07 | 100.00 | 99.55 | 96.85 | 99.77 | 97.07 | 99.77 | 97.75 | 97.07 | 99.55 | |
| 27 | Zim-2 | 97.52 | 97.30 | 99.32 | 97.52 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 97.30 | 99.77 | 99.77 | 97.30 | 97.30 | 97.30 | 97.30 | 99.77 | 99.32 | 97.07 | 100.00 | 97.30 | 99.55 | 97.97 | 97.30 | 99.77 | 99.77 |
| SN | Specimens | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ban-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Kor-1 | 100 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | Kor-2 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | Kor-3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | Kor-4 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | Nep-1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | Nep-2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | Nep-3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | Vie-1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | Vie-2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||||||||||||||||
| 11 | Vie-3 | 98.33 | 98.33 | 98.33 | 98.33 | 98.33 | 98.33 | 98.33 | 98.33 | 98.33 | 98.33 | ||||||||||||||||
| 12 | Con-11 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | |||||||||||||||
| 13 | Con-12 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | ||||||||||||||
| 14 | Con-21 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | 100 | |||||||||||||
| 15 | Con-31 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||||
| 16 | Con-41 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||||||||||
| 17 | Con-42 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||
| 18 | Tan-1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||||||||
| 19 | Tan-2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||
| 20 | Tan-3 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 99.85 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | 98.48 | |||||||
| 21 | Tan-4 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.48 | ||||||
| 22 | Uga-1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.48 | 100 | |||||
| 23 | Uga-2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.48 | 100 | 100 | ||||
| 24 | Uga-3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.48 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
| 25 | Uga-4 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.48 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| 26 | Zim-1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.48 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| 27 | Zim-2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.48 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
References
- Sparks, A.N. A review of the biology of the fall armyworm. Fla. Entomol. 1979, 62, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luginbill, P. The fall armyworm. Us Dept. Agric. Tech. Bull. 1928, 34, 1–91. [Google Scholar]
- Goergen, G.; Kumar, P.L.; Sankung, S.B.; Togola, A.; Tamò, M. First report of outbreaks of the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (J E Smith) (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae), a new alien invasive pest in West and Central Africa. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cock, M.J.W.; Beseh, P.K.; Buddie, A.G.; Cafá, G.; Crozier, J. Molecular methods to detect Spodoptera frugiperda in Ghana, and implications for monitoring the spread of invasive species in developing countries. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, A.; Van Vuuren, A.; Rong, I.H. Characterisation of the fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda J.E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) from South Africa. Afr. Entomol. 2018, 26, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoshi, R.N.; Goergen, G.; Tounou, K.A.; Agboka, K.; Koffi, D.; Meagher, R.L. Analysis of strain distribution, migratory potential, and invasion history of fall armyworm populations in northern Sub-Saharan Africa. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiger, P.C.; Yeshwanth, H.M.; Muralimohan, K.; Vinay, N.; Kumar, A.R.V.; Chandrashekara, K. Occurrence of the new invasive pest, fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), in the maize fields of Karnataka, India. Curr. Sci. 2018, 115, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharanabasappa; Chandrashekara, K.; Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Asokan, R.; Maruthi, M.S.; Pavithra, H.B.; Hegbe, K.; Navi, S.; Prabhu, S.T.; Goergen, G.E. First report of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), an alien invasive pest on maize in India. Pest Manag. Hortic. Ecosyst. 2018, 24, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Shylesha, A.N.; Jalali, S.K.; Gupta, A.; Varshney, R.; Venkatesan, T.; Shetty, P.; Ojha, R.; Ganiger, P.C.; Navik, O.; Subaharan, K.; et al. Studies on new invasive pest Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and its natural enemies. J. Biol. Control 2018, 32, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, H.M.M.; Asokan, R.; Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Sharanabasappa; Prasad, Y.G.; Maruthi, M.S.; Shashank, P.R.; Devi, N.I.; Surakasula, A.; Adarsha, S.; et al. Prevalence of “R” strain and molecular diversity of fall army worm Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in India. Indian J. Entomol. 2018, 80, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Seo, B.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Song, J.H.; Lee, W. First report of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith, 1797) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), a new migratory pest in Korea. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2020, 59, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vennila, S.; Wang, Z.; Young, K.; Khurana, J.; Cruz, I.; Chen, J.; Reynaud, B.; Delatte, H.; Baufeld, P.; Rajan, R.P.; et al. G20 discussion group on fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E.Smith) [Lepidoptera: Noctuidae]. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Facilitatng International Research Collaboration on Transboundary Plant Pests, Tsukuba, Japan, 27–29 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization Global Action for Fall Armyworm Control. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fall-armyworm/global-action/en/ (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- EPPO Spodoptera Frugiperda (LAPHER). Available online: https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/LAPHFR/distribution (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- Nagoshi, R.N.; Dhanani, I.; Asokan, R.; Mahadevaswamy, H.M.; Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Sharanabasappa; Meagher, R.L. Genetic characterization of fall armyworm infesting South Africa and India indicate recent introduction from a common source population. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoshi, R.N.; Nagoshi, B.Y.; Cañarte, E.; Navarrete, B.; Solórzano, R.; Garcés-Carrera, S. Genetic characterization of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) in Ecuador and comparisons with regional populations identify likely migratory relationships. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoshi, R.N.; Goergen, G.; Du Plessis, H.; van den Berg, J.; Meagher, R. Genetic comparisons of fall armyworm populations from 11 countries spanning sub-Saharan Africa provide insights into strain composition and migratory behaviors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashley, D.P. Host-associated genetic differentiation in fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): A sibling species complex? Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1986, 79, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montezano, D.G.; Specht, A.; Sosa-Gómez, D.R.; Roque-Specht, V.F.; Sousa-Silva, J.C.; Paula-Moraes, S.V.; Peterson, J.A.; Hunt, T.E. Host plants of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in the Americas. Afr. Entomol. 2018, 26, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashley, D.P.; Johnson, S.J.; Sparks, A.N. Genetic population structure of migratory moths: The fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashley, D.P. Quantitative genetics, development, and physiological adaptation in host strains of fall armyworm. Evolution 1988, 42, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoshi, R.N.; Meagher, R.L. Behavior and distribution of the two fall armyworm host strains in Florida. Fla. Entomol. 2004, 87, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, P.; Legeai, F.; Lemaitre, C.; Scaon, E.; Orsucci, M.; Labadie, K.; Gimenez, S.; Clamens, A.L.; Henri, H.; Vavre, F.; et al. Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) host-plant variants: Two host strains or two distinct species? Genetica 2015, 143, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashley, D.P.; Martin, J.A. Reproductive incompatibility between host strains of the fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1987, 80, 731–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, A.T.; Marr, M.; Heckel, D.G.; SchÖfl, G. The roles and interactions of reproductive isolation mechanisms in fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) host strains. Ecol. Entomol. 2010, 35, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, A.T.; Marr, M.; Schöfl, G.; Lorenz, S.; Svatos, A.; Heckel, D.G. Host strain specific sex pheromone variation in Spodoptera frugiperda. Front. Zool. 2008, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay-Roe, M.M.; Meagher, R.L.; Nagoshi, R.N. Effects of cyanogenic plants on fitness in two host strains of the fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda). J. Chem. Ecol. 2011, 37, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prowell, D.P. Sex linkage and speciation in Lepidoptera. In Endless Forms: Species and Speciation; Howard, D.J., Berlocher, S.H., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Prowell, D.P.; McMichael, M.; Silvain, J.F. Multilocus genetic analysis of host use, introgression, and speciation in host strains of fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2004, 97, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoshi, R.N. Improvements in the identification of strains facilitate population studies of fall armyworm subgroups. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2012, 105, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murúa, M.G.; Nagoshi, R.N.; Santos, D.A.D.; Hay-Roe, M.M.; Meagher, R.L.; Vilardi, J.C. Demonstration using field collections that Argentina fall armyworm populations exhibit strain-specific host plant preferences. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 2305–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoshi, R.N. The fall armyworm triose phosphate isomerase (Tpi) gene as a marker of strain identity and interstrain mating. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2010, 103, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoshi, R.N.; Meagher, R.L. Using intron sequence comparisons in the triose phosphate isomerase gene to study the divergence of the fall armyworm host strains. Insect Mol. Biol. 2016, 25, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoshi, R.N. Evidence that a major subpopulation of fall armyworm found in the Western Hemisphere is rare or absent in Africa, which may limit the range of crops at risk of infestation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0208966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäffer, A.A.; Aravind, L.; Madden, T.L.; Shavirin, S.; Spouge, J.L.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V.; Altschul, S.F. Improving the accuracy of PSI-BLAST protein database searches with composition-based statistics and other refinements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 2994–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W (improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice). Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, F. Evolutionary relationship of DNA sequences in finite populations. Genetics 1983, 105, 437–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, M.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. TCS: A computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol. Ecol. 2000, 9, 1657–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, N.; Gracy, R.G.; Ashika, T.R.; Mohan, G.; Swathi, R.S.; Mohan, M.; Chaudhary, M.; Bakthavatsalam, N.; Venkatesan, T. Population structure and genetic diversity of invasive fall armyworm after 2 years of introduction in India. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoshi, R.N.; Htain, N.N.; Boughton, D.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Nagoshi, B.Y.; Mota-Sanchez, D. Southeastern Asia fall armyworms are closely related to populations in Africa and India, consistent with common origin and recent migration. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albery, W.; Knowles, J. Evolution of enzyme function and the development of catalytic efficiency. Biochemistry 1976, 15, 5631–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
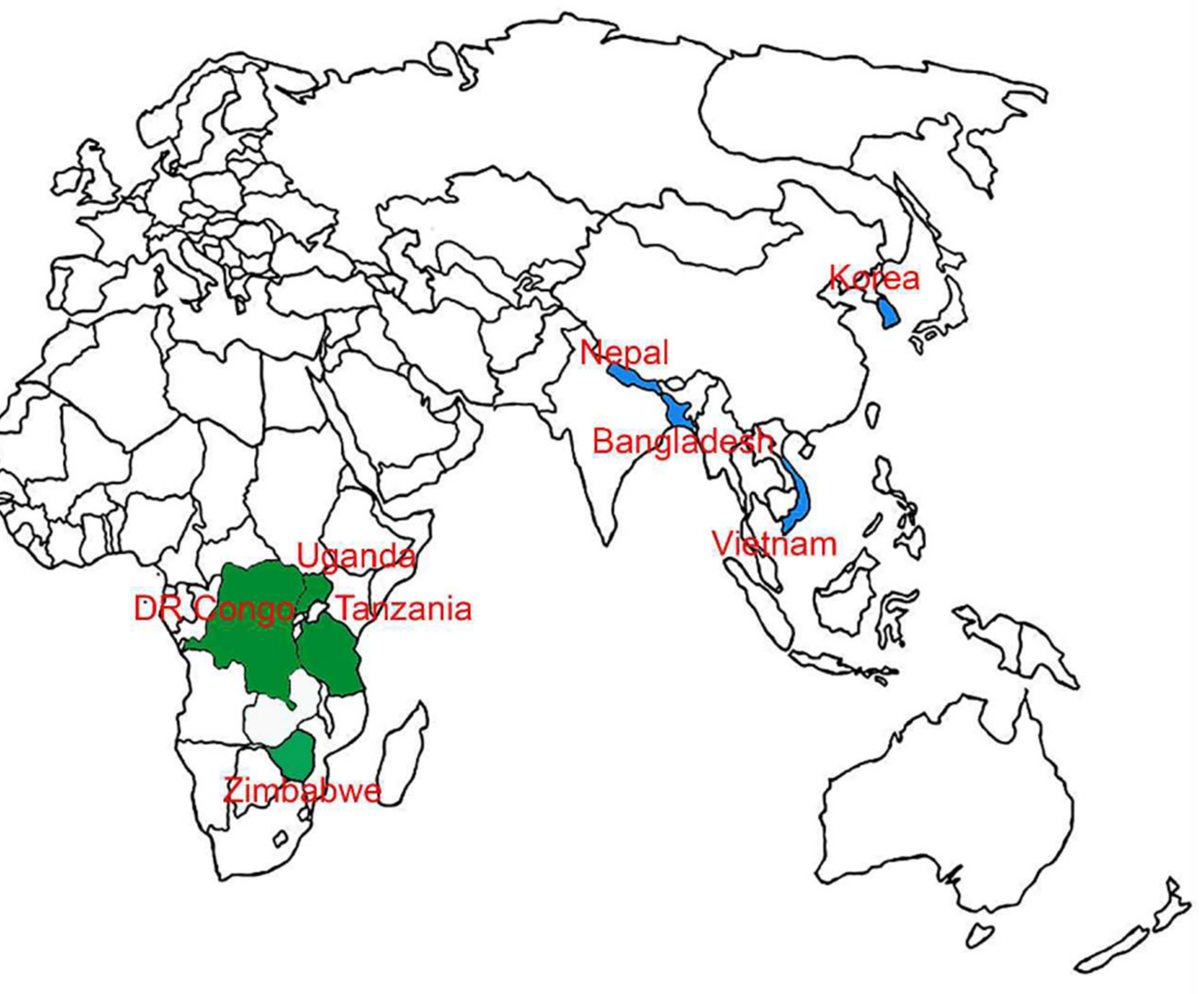




| Regions/ Countries | Locations | Specimen Names | Collection Dates | Insect Stages | Accession Numbers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tpi | COI | |||||
| Africa | ||||||
| DR Congo | Katana, Kabare | Con-11 | 11/29/2018 | Larva | MT894220 | MT103350 |
| Miti, Kabare | Con-12 | 11/29/2018 | Larva | MT894221 | MT933052 | |
| Minova, Kalehe | Con-21 | 11/29/2018 | Larva | MT894222 | MT933053 | |
| Luvungi, Uvira | Con-31 | 12/15/2018 | Larva | MT894223 | MT933054 | |
| Sange, Uvira | Con-41 | 12/15/2018 | Larva | MT894224 | MT933055 | |
| Nduba, Walungu | Con-42 | 12/15/2018 | Larva | MT894225 | MT103349 | |
| Tanzania | Arusha, Tengeru | Tan-1 | 1/10/2019 | Larva | MT894226 | MT103348 |
| Mlali, Morogoro | Tan-2 | 1/17/2019 | Larva | MT894227 | MT933056 | |
| Sri, Pwani | Tan-3 | 1/10/2019 | Larva | MT894228 | MT933057 | |
| Sua, Morogoro | Tan-4 | 1/14/2019 | Larva | MT894229 | MT933058 | |
| Uganda | Mbale | Uga-1 | 1/10/2018 | Larva | MT894230 | MT933059 |
| Masindi | Uga-2 | 10/17/2017 | Larva | MT894231 | MT933060 | |
| Kole | Uga-3 | 10/18/2018 | Larva | MT894232 | MT933061 | |
| Luwero | Uga-4 | 10/15/2018 | Larva | MT894233 | MT933062 | |
| Zimbabwe | Harare research station, Harare | Zim-1 | 2/8/2019 | Larva | MT894234 | MT103346 |
| Chipinge, Manicaland | Zim-2 | 2/22/2019 | Larva | MT894235 | MT103347 | |
| Asia | ||||||
| Bangladesh | Dhaka | Ban-1 | 8/14/2019 | Larva | MT894236 | MT933063 |
| Korea | Jeju | Kor-1 | 9/19/2019 | Adult | MT894237 | MT933064 |
| Gyeongsan | Kor-2 | 8/29/2019 | Larva | MT894238 | MT103342 | |
| Gyeongsan | Kor-3 | 6/10/2020 | Larva | MT894239 | MT933065 | |
| Jeju | Kor-4 | 6/9/2020 | Adult | MT894240 | MT933066 | |
| Nepal | Bhakundebesi, Kavre | Nep-1 | 9/24/2019 | Larva | MT894241 | MT103345 |
| Khumaltar, Lalitpur | Nep-2 | 7/30/2019 | Larva | MT894242 | MT933067 | |
| Khaira, Pyathan | Nep-3 | 8/6/2019 | Larva | MT894243 | MT933068 | |
| Vietnam | Ninh Binh | Vie-1 | 9/30/2019 | Adult | MT894244 | MT103334 |
| Vinh Phuc | Vie-2 | 9/30/2019 | Adult | MT894245 | MT103335 | |
| Hanoi | Vie-3 | 9/30/2019 | Larva | MT894246 | MT103336 | |
| Genes | Regions | Number of Sequences | Segregating Sites | Haplotypes | Haplotype Diversity | Nucleotide Diversity | Theta/Site | Tajima’s D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tpi | Africa | 16 | 18 | 10 | 0.933 | 0.016911 | 0.012 | 1.531362 |
| Asia | 10 | 14 | 5 | 0.667 | 0.011671 | 0.011 | 1.11681 | |
| COI | Africa | 16 | 10 | 2 | 0.125 | 0.0019 | 0.005 | −2.182611 ** |
| Asia | 11 | 11 | 2 | 0.182 | 0.00304 | 0.006 | −2.011459 * |
| Sn | Speamens | Haplotypes | Strains |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Con-11 | h2 | Tpi-Ca1 |
| 2 | Con-42, Kor-4, Nep-1, Nep-2, Nep-3, Vie-1, Vie-3, Zim-1 | h5 | |
| 3 | Kor-2, Tan-1 | h6 | |
| 4 | Tan-3, Zim-2 | h9 | |
| 5 | Uga-1 | h10 | |
| 6 | Uga-4 | h12 | |
| 7 | Con-21, Con-31, Uga-3, Vie-2 | h4 | Tpi-Ca2a |
| 8 | Kor-3 | h7 | |
| 9 | Ban-1 | h1 | Tpi-Ca2b |
| 10 | Con-12, Con-14, Tan-4 | h3 | |
| 11 | Tan-2 | h8 | |
| 12 | Uga-2 | h11 |
| Sn | Speamens | Haplotypes | Strains |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ban-1, Kor-1, Kor-2, Kor-3, Kor-4, Nep-1, Nep-2, Nep-3, Vie-1, Vie-2, Con-11, Con-12, Con-21, Con-31, Con-41, Con-42, Tan-1, Tan-2, Tan-4, Uga-1, Uga-2, Uga-3, Uga-4, Zim-1, Zim-2 | h1 | COI-R |
| 2 | Vie-3 | h2 | COI-C |
| 3 | Tan-3 | h3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acharya, R.; Akintola, A.A.; Malekera, M.J.; Kamulegeya, P.; Nyakunga, K.B.; Mutimbu, M.K.; Shrestha, Y.K.; Hemayet, J.S.M.; Hoat, T.X.; Dao, H.T.; et al. Genetic Relationship of Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) Populations That Invaded Africa and Asia. Insects 2021, 12, 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12050439
Acharya R, Akintola AA, Malekera MJ, Kamulegeya P, Nyakunga KB, Mutimbu MK, Shrestha YK, Hemayet JSM, Hoat TX, Dao HT, et al. Genetic Relationship of Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) Populations That Invaded Africa and Asia. Insects. 2021; 12(5):439. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12050439
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcharya, Rajendra, Ashraf Akintayo Akintola, Matabaro Joseph Malekera, Patrick Kamulegeya, Keneth Benedictor Nyakunga, Munyaradzi Kennedy Mutimbu, Yam Kumar Shrestha, Jahan S. M. Hemayet, Trinh Xuan Hoat, Hang Thi Dao, and et al. 2021. "Genetic Relationship of Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) Populations That Invaded Africa and Asia" Insects 12, no. 5: 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12050439
APA StyleAcharya, R., Akintola, A. A., Malekera, M. J., Kamulegeya, P., Nyakunga, K. B., Mutimbu, M. K., Shrestha, Y. K., Hemayet, J. S. M., Hoat, T. X., Dao, H. T., Park, J.-H., Kim, I., Nam, M., Lee, S.-J., Kim, S.-M., Hwang, H.-S., & Lee, K.-Y. (2021). Genetic Relationship of Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) Populations That Invaded Africa and Asia. Insects, 12(5), 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12050439









