Identification and Expression Profile of Chemosensory Genes in the Small Hive Beetle Aethina tumida
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects and Tissue Collections
2.2. RNA Extraction, cDNA Library Construction, Illumina Sequencing and De Novo Assembly
2.3. Functional Annotation and Chemosensory Gene Identification
2.4. Sequence and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.5. Transcript Abundance of Chemosensory Genes
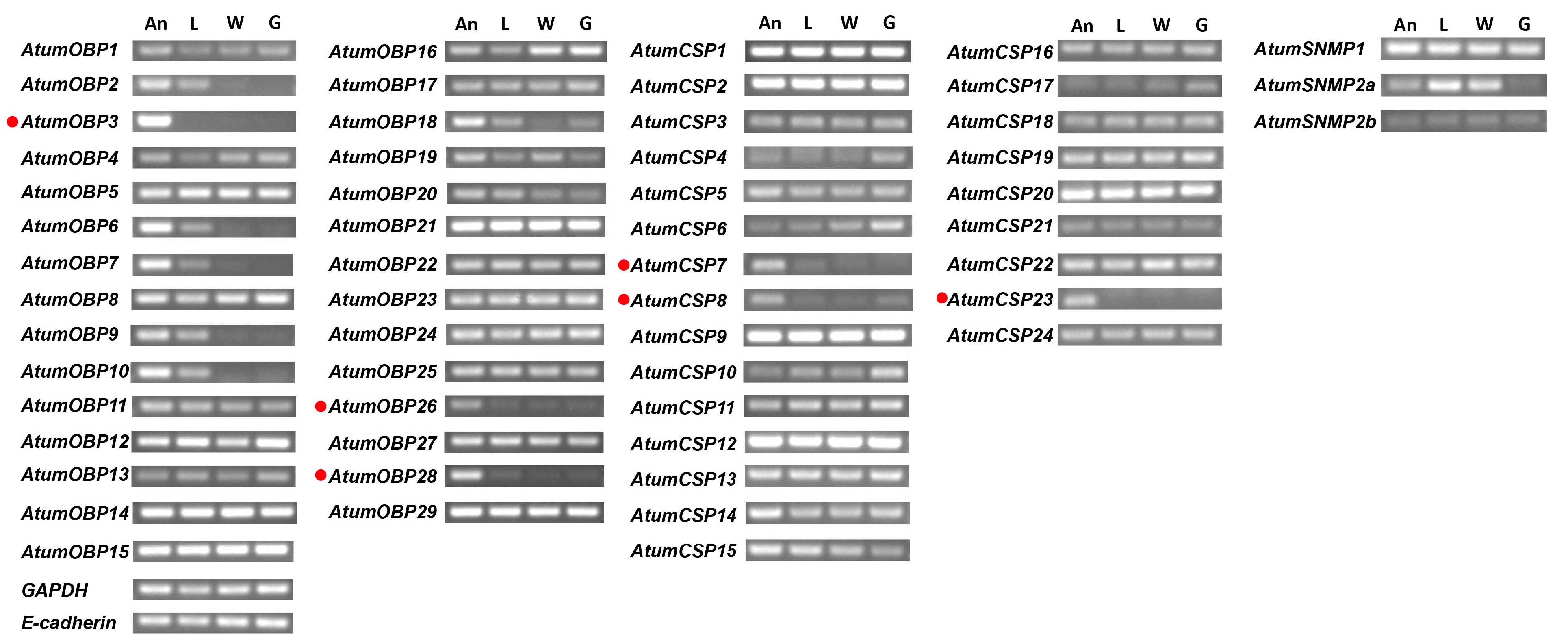
2.6. RT-PCR
3. Results
3.1. Overview of A. tumida Transcriptomes
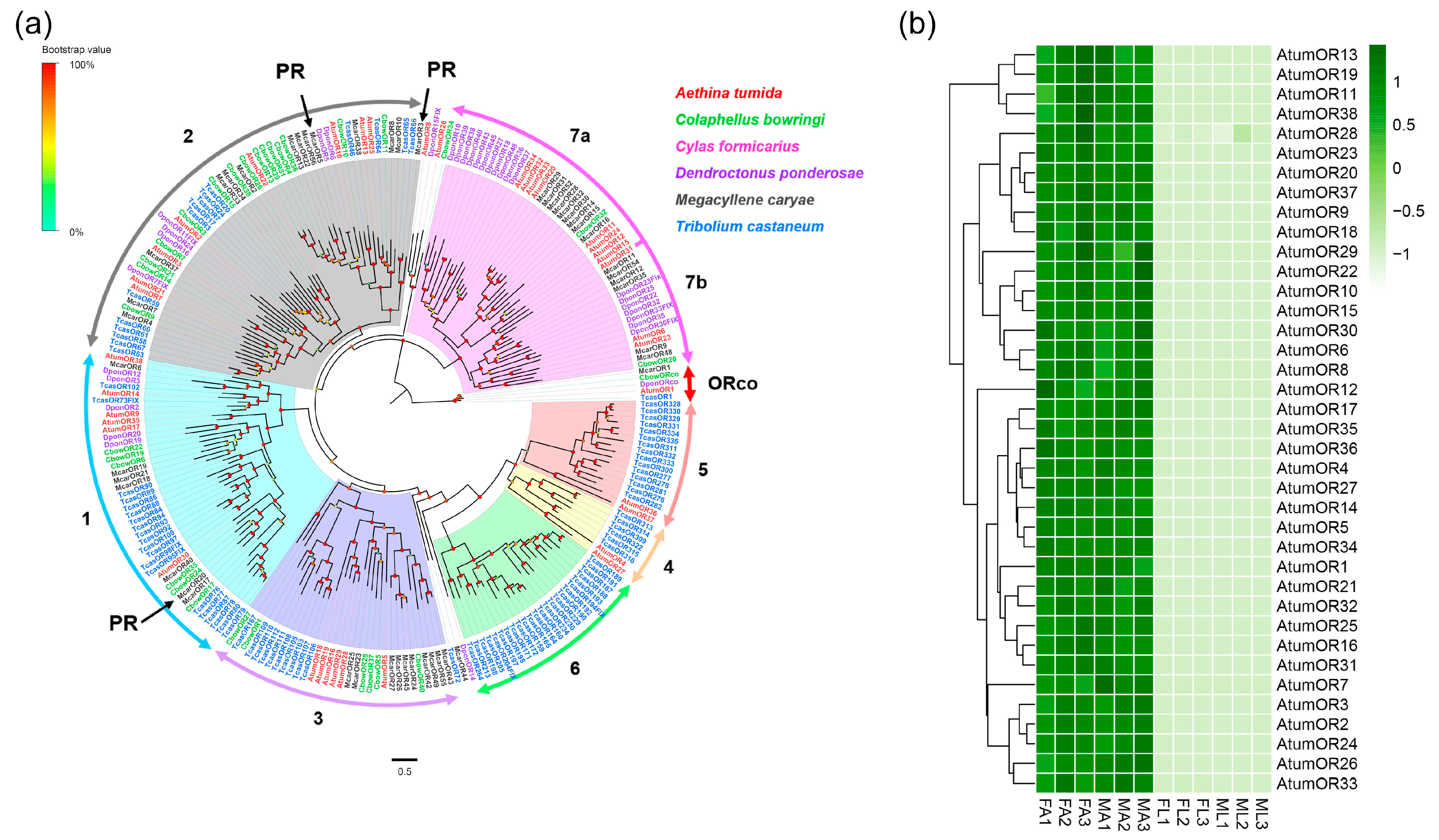
3.2. Candidate Genes Coding for ORs
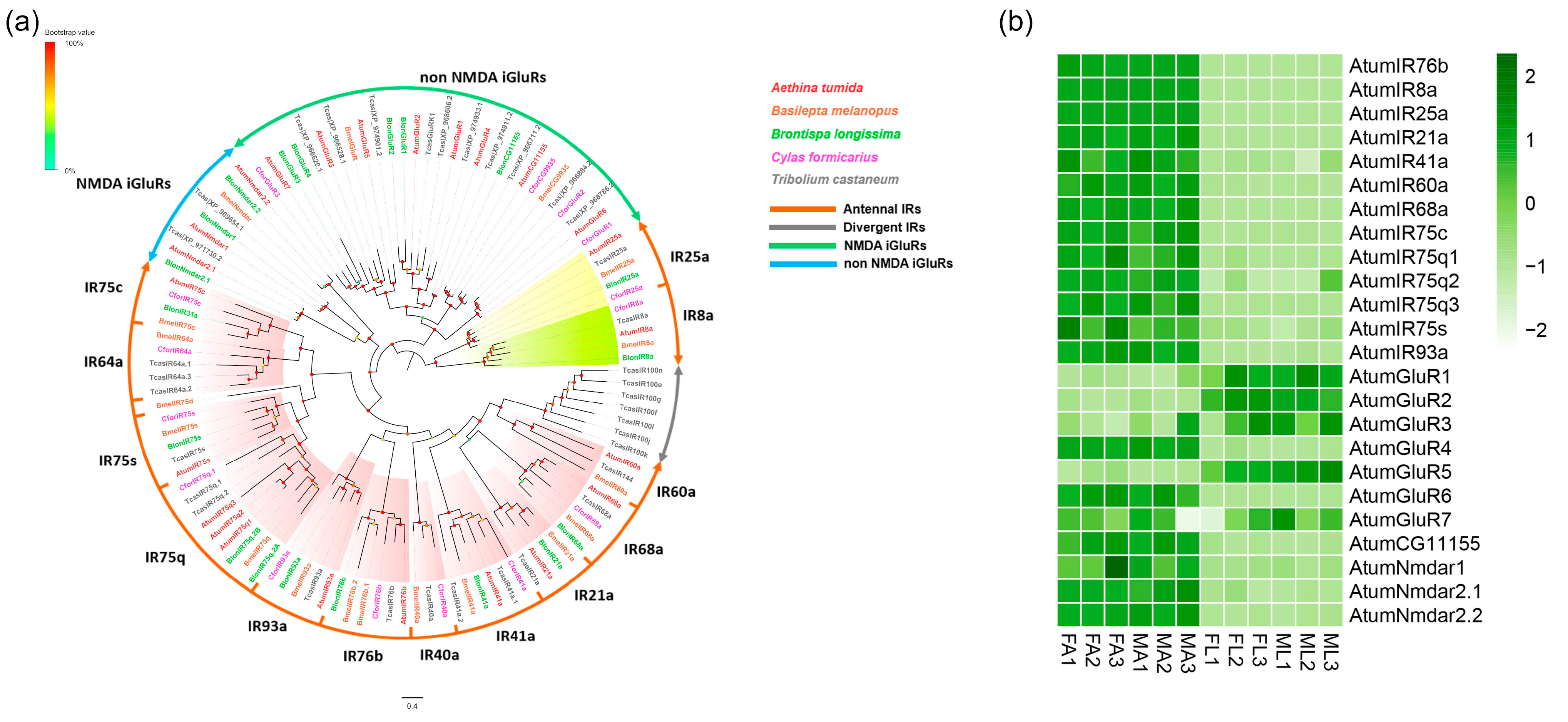
3.3. Candidate Coding Genes for iGluRs/IRs
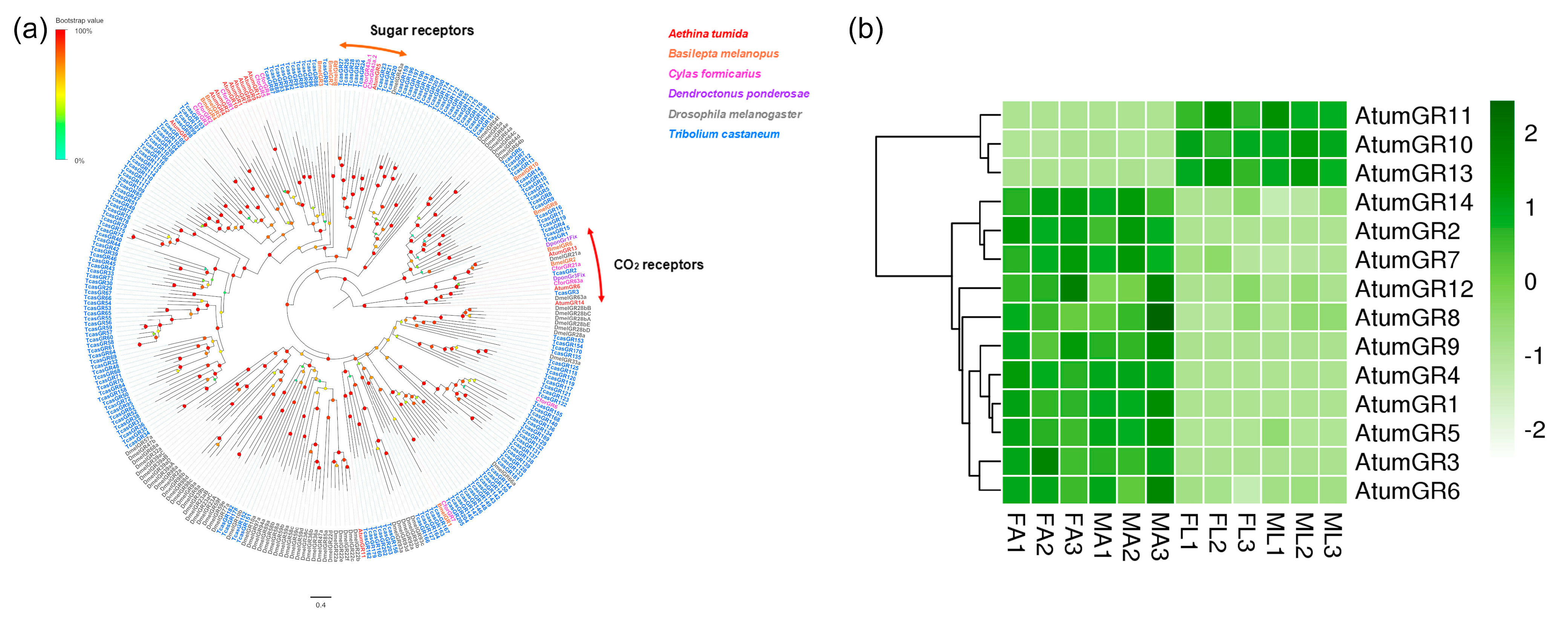
3.4. Candidate Genes Coding for GRs
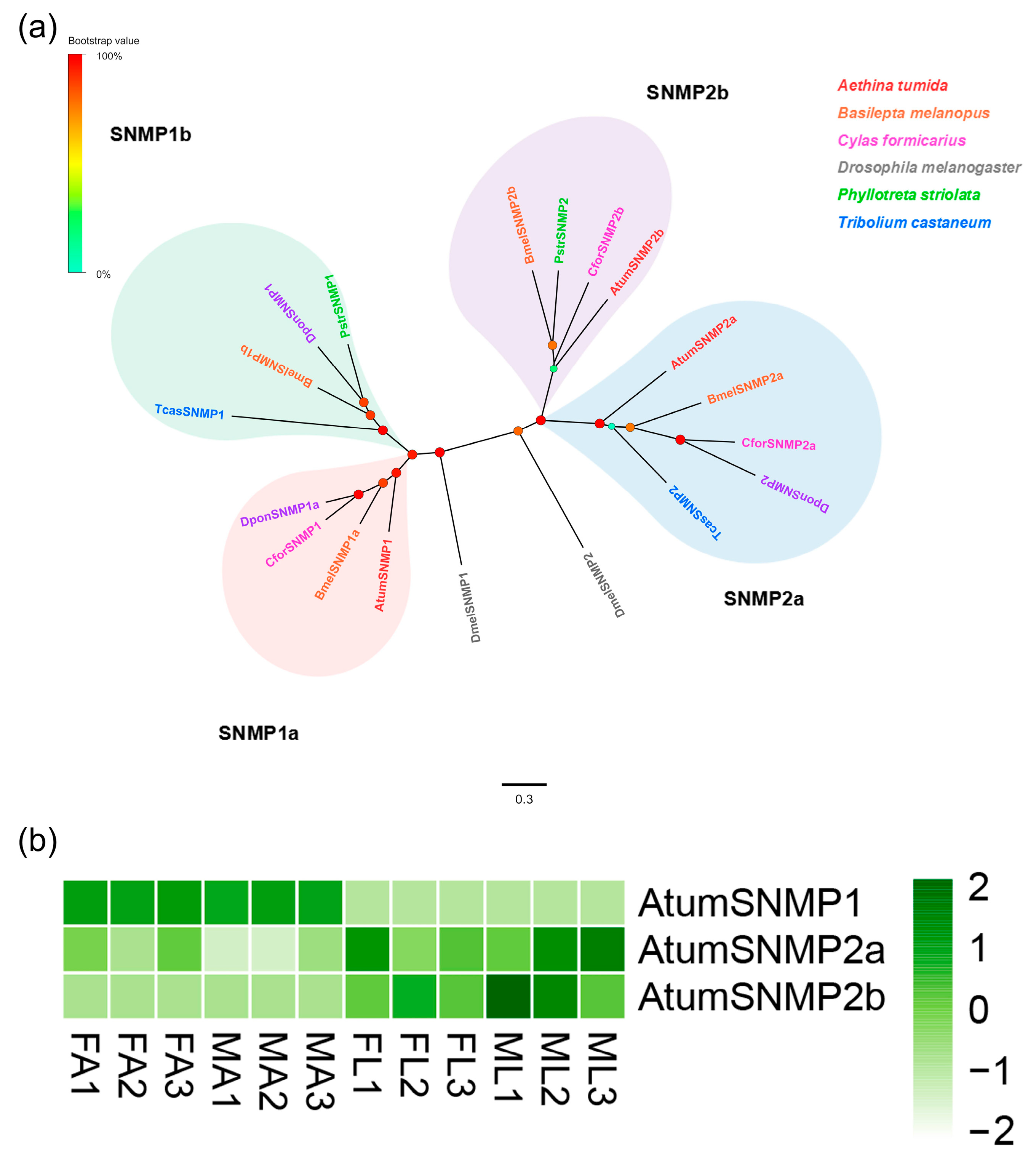
3.5. Candidate Genes Coding for SNMPs
3.6. Candidate Genes Coding for OBPs
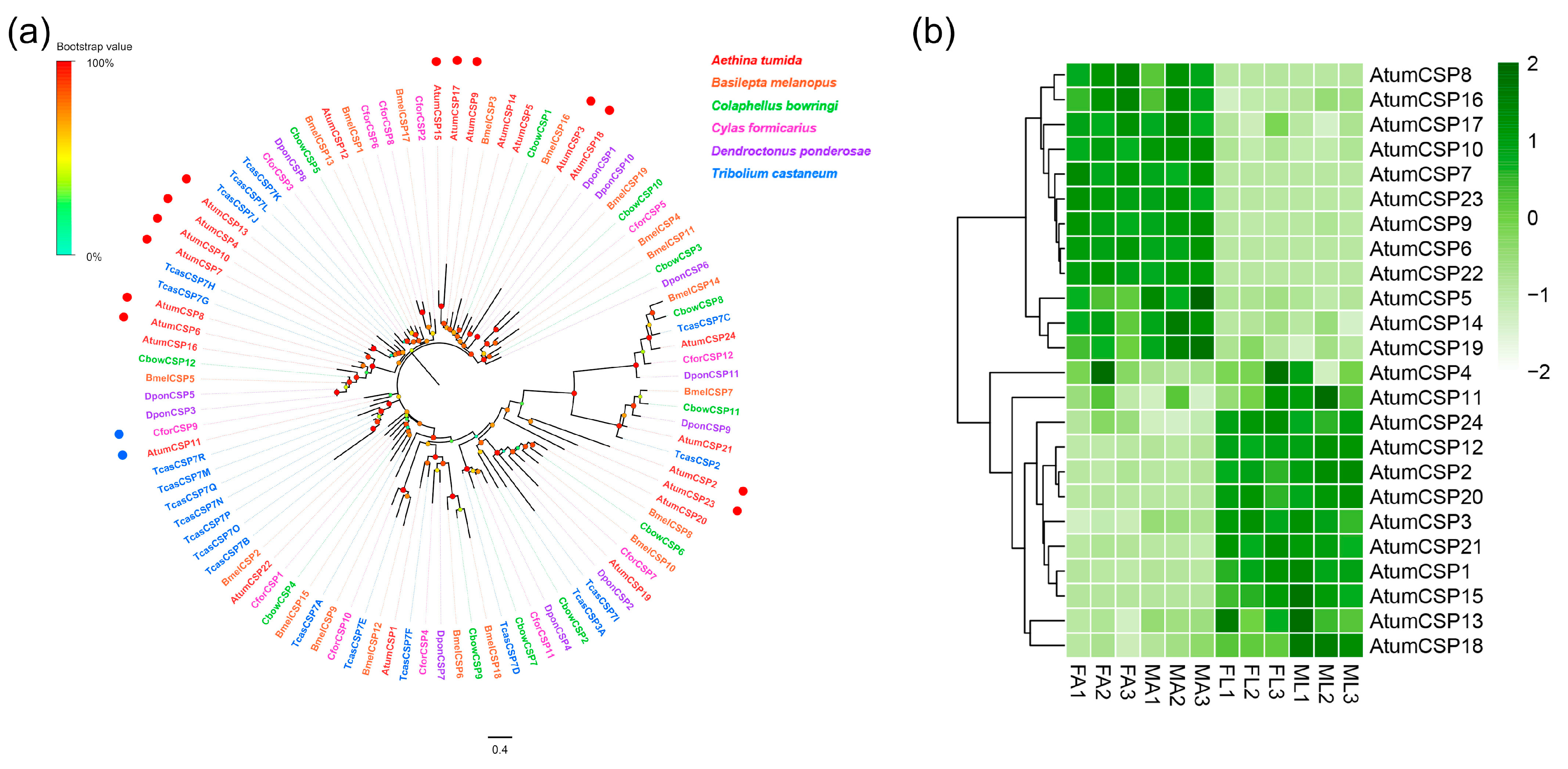
3.7. Candidate Genes Coding for CSPs
3.8. Transcript Levels of SNMPs, OBPs and CSPs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sato, K.; Touhara, K. Insect olfaction: Receptors, signal transduction, and behavior. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2009, 47, 121–138. [Google Scholar]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, R.M.; Carlson, J.R. Drosophila chemoreceptors: A molecular interface between the chemical world and the brain. Trends Genet. 2015, 31, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, R.; Vannice, K.S.; Gomez-Diaz, C.; Vosshall, L.B. Variant ionotropic glutamate receptors as chemosensory receptors in Drosophila. Cell 2009, 136, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touhara, K.; Vosshall, L.B. Sensing odorants and pheromones with chemosensory receptors. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2009, 71, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, R.G.; Riddiford, L.M. Pheromone binding and inactivation by moth antennae. Nature 1981, 293, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Pellegrino, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Vosshall, L.B.; Touhara, K. Insect olfactory receptors are heteromeric ligand-gated ion channels. Nature 2008, 452, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croset, V.; Rytz, R.; Cummins, S.F.; Budd, A.; Brawand, D.; Kaessmann, H.; Gibson, T.J.; Benton, R. Ancient protostome origin of chemosensory ionotropic glutamate receptors and the evolution of insect taste and olfaction. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.Y.; Dahanukar, A.; Weiss, L.A.; Carlson, J.R. The molecular basis of CO2 reception in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3574–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Tanaka, K.; Touhara, K. Sugar-regulated cation channel formed by an insect gustatory receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11680–11685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, R.; Vannice, K.S.; Vosshall, L.B. An essential role for a CD36-related receptor in pheromone detection in Drosophila. Nature 2007, 450, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Ha, T.S.; Smith, D.P. SNMP is a signaling component required for pheromone sensitivity in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10996–11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ni, J.D.; Huang, J.; Montell, C. Requirement for Drosophila SNMP1 for rapid activation and termination of pheromone-induced activity. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Diaz, C.; Bargeton, B.; Abuin, L.; Bukar, N.; Reina, J.H.; Bartoi, T.; Graf, M.; Ong, H.; Ulbrich, M.H.; Masson, J.F.; et al. A CD36 ectodomain mediates insect pheromone detection via a putative tunnelling mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.G.; Miller, N.E.; Litvack, R.; Fandino, R.A.; Sparks, J.; Friedman, R.; Dickens, J.C. The insect SNMP gene family. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Felicioli, A.; Dani, F.R. Soluble proteins of chemical communication: An overview across arthropods. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, L.; Napolitano, E.; Serra, A.; Zhou, X.; Iovinella, I.; Pelosi, P. Identification of pheromone-like compounds in male reproductive organs of the oriental locust Locusta migratoria. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 437, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iovinella, I.; Bozza, F.; Caputo, B.; Della, T.A.; Pelosi, P. Ligand-binding study of Anopheles gambiae chemosensory proteins. Chem. Senses. 2013, 38, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y. Functional characteristics of a novel chemosensory protein in the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner). J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Ye, Z.F.; Yang, K.; Dong, S.L. Antenna-predominant and male-biased CSP19 of Sesamia inferensis able to bind the female sex pheromones and host plant volatiles. Gene 2014, 536, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, P.; Pettis, J.S.; Schäfer, M.O. Quo vadis Aethina tumida? Biology and control of small hive beetles. Apidologie 2016, 47, 427–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toufailia, H.A.; Alves, D.A.; Bená, D.D.C.; Bento, J.M.S.; Iwanicki, N.S.A.; Cline, A.R.; Ellis, J.D.; Ratnieks, F.L.W. First record of small hive beetle, Aethina tumida Murray, in South America. J. Apic. Res. 2017, 56, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrissou, F.O.; Huang, Q.; Yanez, O.; Neumann, P. International beeswax trade facilitates small hive beetle invasions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, P.; Ellis, J.D. The small hive beetle (Aethina tumida Murray, Coleoptera: Nitidulidae): Distribution, biology and control of an invasive species. J. Apic. Res. 2008, 47, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.R.; Ellis, J.D.; Carroll, M.J.; Teal, P.E.A. Aethina tumida (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae) attraction to volatiles produced by Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera: Apidae) and Bombus impatiens (Hymenoptera: Apidae) colonies. Apidologie 2011, 42, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, L.I.D.; Frake, A.M.; Rinderer, T.E.; Arbogast, R.T. Effect of height and color on the efficiency of pole traps for Aethina tumida (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 2011, 104, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suazo, A.; Torto, B.; Teal, P.E.A.; Tumlinson, J.H. Response of the small hive beetle (Aethina tumida) to honey bee (Apis mellifera) and beehive-produced volatiles. Apidologie 2003, 34, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, K.P.; Kempraj, V.; Aurade, R.M.; Roy, T.K.; Shivashankara, K.S.; Verghese, A. Computational reverse chemical ecology: Virtual screening and predicting behaviorally active semiochemicals for Bactrocera dorsalis. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 209. [Google Scholar]
- Choo, Y.M.; Xu, P.; Hwang, J.K.; Zeng, F.; Tan, K.; Bhagavathy, G.; Chauhan, K.R.; Leal, W.S. Reverse chemical ecology approach for the identification of an oviposition attractant for Culex quinquefasciatus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venthur, H.; Zhou, J.J. Odorant receptors and Odorant-Binding proteins as insect pest control targets: A comparative analysis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klijnstra, J.; Roessingh, P. Perception of the oviposition deterring pheromone by tarsal and abdominal contact chemoreceptors in Pieris brassicae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1986, 40, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Dahanukar, A.; Weiss, L.A.; Kwon, J.Y.; Carlson, J.R. The molecular and cellular basis of taste coding in the legs of Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 7148–7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevillon, E.; Silventoinen, V.; Pillai, S.; Harte, N.; Mulder, N.; Apweiler, R.; Lopez, R. InterProScan: Protein domains identifier. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W116–W120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; Mcwilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2-approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3-new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engsontia, P.; Sanderson, A.P.; Cobb, M.; Walden, K.K.; Robertson, H.M.; Brown, S. The red flour beetle’s large nose: An expanded odorant receptor gene family in Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.F.; Hughes, D.T.; Luetje, C.W.; Millar, J.G.; Soriano-Agaton, F.; Hanks, L.M.; Robertson, H.M. Sequencing and characterizing odorant receptors of the cerambycid beetle Megacyllene caryae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, T.; Slone, J.; Song, X.; Amrein, H. A fructose receptor functions as a nutrient sensor in the Drosophila brain. Cell 2012, 151, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanashi, T.; Uechi, N.; Tatsuta, H. Vibrations in hemipteran and coleopteran insects: Behaviors and application in pest management. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2019, 54, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulson, D.; Birch, M.C.; Wyatt, T.D. Mate location in the deathwatch beetle, Xestobium rufovillosum De Geer (Anobiidae): Orientation to substrate vibrations. Anim. Behav. 1994, 47, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kiyotake, H.; Matsumoto, H.; Nakayama, S.; Sakai, M.; Miyatake, T.; Ryuda, M.; Hayakawa, Y. Gain of long tonic immobility behavioral trait causes the red flour beetle to reduce anti-stress capacity. J. Insect Physiol. 2014, 60, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubaki, R.; Hosoda, N.; Kitajima, H.; Takanashi, T. Substrate-borne vibrations induce behavioral responses in the leaf-dwelling cerambycid, Paraglenea fortunei. Zoolog. Sci. 2014, 31, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, A.; Lindeman, A.A.; Carroll, A.L.; Yack, J. Acoustics of the mountain pine beetle (Dendroctonus ponderosae) (Curculionidae, Scolytinae): Sonic, ultrasonic, and vibration characteristics. Can. J. Zool. 2013, 91, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Min, S.; Grosjean, Y.; Leblanc, C.; Bell, R.; Benton, R.; Suh, G.S. Acid sensing by the Drosophila olfactory system. Nature 2010, 468, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silbering, A.F.; Rytz, R.; Grosjean, Y.; Abuin, L.; Ramdya, P.; Jefferis, G.S.X.E.; Benton, R. Complementary function and integrated wiring of the evolutionarily distinct Drosophila olfactory subsystems. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 13357–13375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kain, P.; Boyle, S.M.; Tharadra, S.K.; Guda, T.; Christine, P.; Dahanukar, A.; Ray, A. Odour receptors and neurons for DEET and new insect repellents. Nature. 2013, 502, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, T.W.; He, Z.; Gorur-Shandilya, S.; Menuz, K.; Larter, N.K.; Stewart, S.; Carlson, J.R. The Drosophila IR20a clade of ionotropic receptors are candidate taste and pheromone receptors. Neuron 2014, 83, 850–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Zhang, M.; Ucpunar, H.K.; Svensson, T.; Quillery, E.; Gompel, N.; Ignell, R.; Grunwald, K.I. Ionotropic chemosensory receptors mediate the taste and smell of polyamines. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knecht, Z.A.; Silbering, A.F.; Ni, L.; Klein, M.; Budelli, G.; Bell, R.; Abuin, L.; Ferrer, A.J.; Samuel, A.D.; Benton, R.; et al. Distinct combinations of variant ionotropic glutamate receptors mediate thermosensation and hygrosensation in Drosophila. Elife 2016, 5, e17879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, L.; Klein, M.; Svec, K.V.; Budelli, G.; Chang, E.C.; Ferrer, A.J.; Benton, R.; Samuel, A.D.; Garrity, P.A. The Ionotropic Receptors IR21a and IR25a mediate cool sensing in Drosophila. Elife 2016, 5, e13254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, Z.A.; Silbering, A.F.; Cruz, J.; Yang, L.; Croset, V.; Benton, R.; Garrity, P.A. Ionotropic Receptor-dependent moist and dry cells control hygrosensation in Drosophila. Elife 2017, 6, e26654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Blais, S.; Park, J.Y.; Min, S.; Neubert, T.A.; Suh, G.S. Ionotropic glutamate receptors IR64a and IR8a form a functional odorant receptor complex in vivo in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 10741–10749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Jiang, N.; Ning, C.; Li, G.; Huang, L.; Wang, C. The olfactory reception of acetic acid and ionotropic receptors in the Oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata Walker. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 118, 103312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.X.; Atkinson, R.; Jones, D.; Smith, D.P. Drosophila OBP LUSH is required for activity of pheromone-sensitive neurons. Neuron 2005, 45, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Diaz, C.; Reina, J.H.; Cambillau, C.; Benton, R. Ligands for pheromone-sensing neurons are not conformationally activated odorant binding proteins. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, T.; Pelosi, P.; Dong, S.; Wang, G.R. Pheromone binding proteins enhance the sensitivity of olfactory receptors to sex pheromones in Chilo suppressalis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Lin, J.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, X. BdorOBP83a-2 mediates responses of the oriental fruit fly to semiochemicals. Front. Physisiol. 2018, 9, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Sun, J.S.; Carlson, J.R. Robust olfactory responses in the absence of odorant binding proteins. Elife 2019, 8, e51040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Wang, Q.; Gao, P.; Wen, J. Identification and comparison of chemosensory genes in the antennal transcriptomes of Eucryptorrhynchus scrobiculatus and E. brandti fed on Ailanthus altissima. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuhl, C.J.; Teal, P.E.A. Identification of an aggregation pheromone from the small hive beetle (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae). BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bin, S.; He, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Lin, J. Differential expression analysis of chemoreception genes in the striped flea beetle Phyllotreta striolata using a transcriptomic approach. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e153067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, S.Y.; Qu, M.Q.; Li, K.M.; Peng, Z.Q.; Wu, Z.Z.; Lin, J.T. Antennal and abdominal transcriptomes reveal chemosensory gene families in the coconut hispine beetle. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, S.Y.; Qu, M.Q.; Pu, X.H.; Wu, Z.Z.; Lin, J.T. Antennal transcriptome and expression analyses of olfactory genes in the sweetpotato weevil Cylas formicarius. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Zhai, X.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, F.; Zhao, H. Identification and Expression Profile of Chemosensory Genes in the Small Hive Beetle Aethina tumida. Insects 2021, 12, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12080661
Wu L, Zhai X, Li L, Li Q, Liu F, Zhao H. Identification and Expression Profile of Chemosensory Genes in the Small Hive Beetle Aethina tumida. Insects. 2021; 12(8):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12080661
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Lixian, Xin Zhai, Liangbin Li, Qiang Li, Fang Liu, and Hongxia Zhao. 2021. "Identification and Expression Profile of Chemosensory Genes in the Small Hive Beetle Aethina tumida" Insects 12, no. 8: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12080661
APA StyleWu, L., Zhai, X., Li, L., Li, Q., Liu, F., & Zhao, H. (2021). Identification and Expression Profile of Chemosensory Genes in the Small Hive Beetle Aethina tumida. Insects, 12(8), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12080661




