Analysis of Intestinal Microbial Diversity of Four Species of Grasshoppers and Determination of Cellulose Digestibility
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Collection
2.2. Sample Treatment
2.3. Extraction of Total DNA from the Intestinal Contents
2.4. Microbial Diversity Analysis
2.5. Digestibility of Cellulose and Hemicellulose
2.6. Correlation between Digestibility and Intestinal Microbial Diversity
3. Results
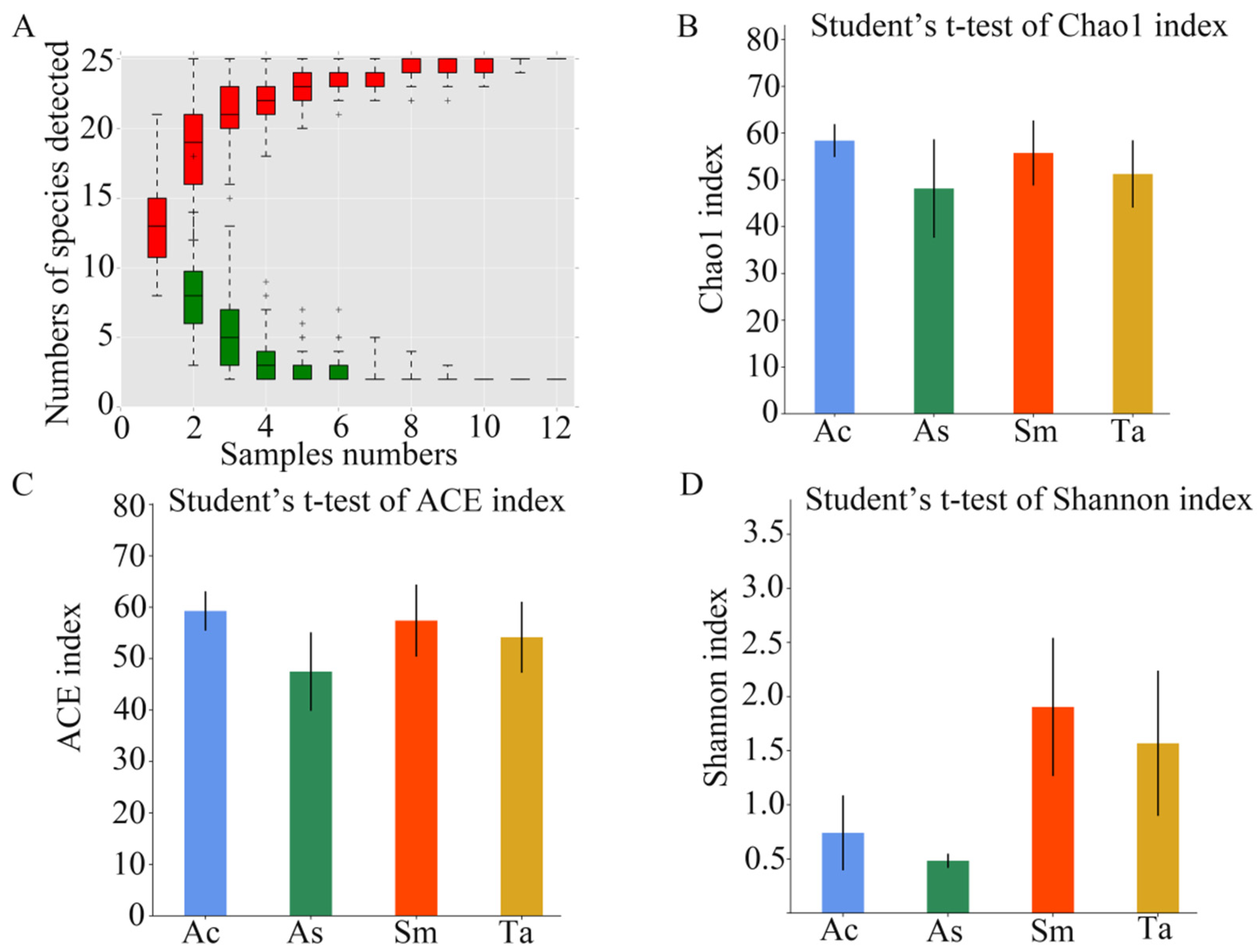
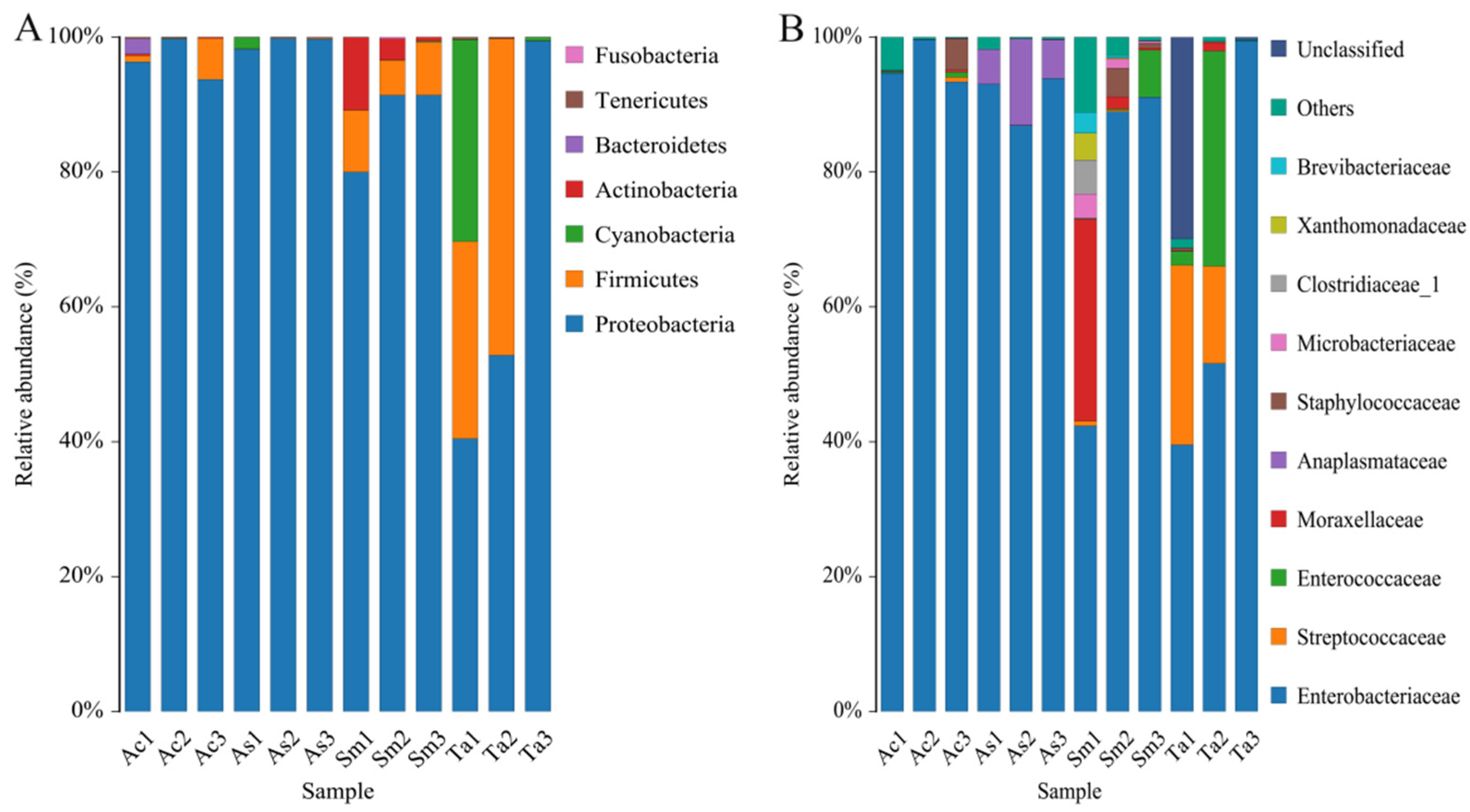
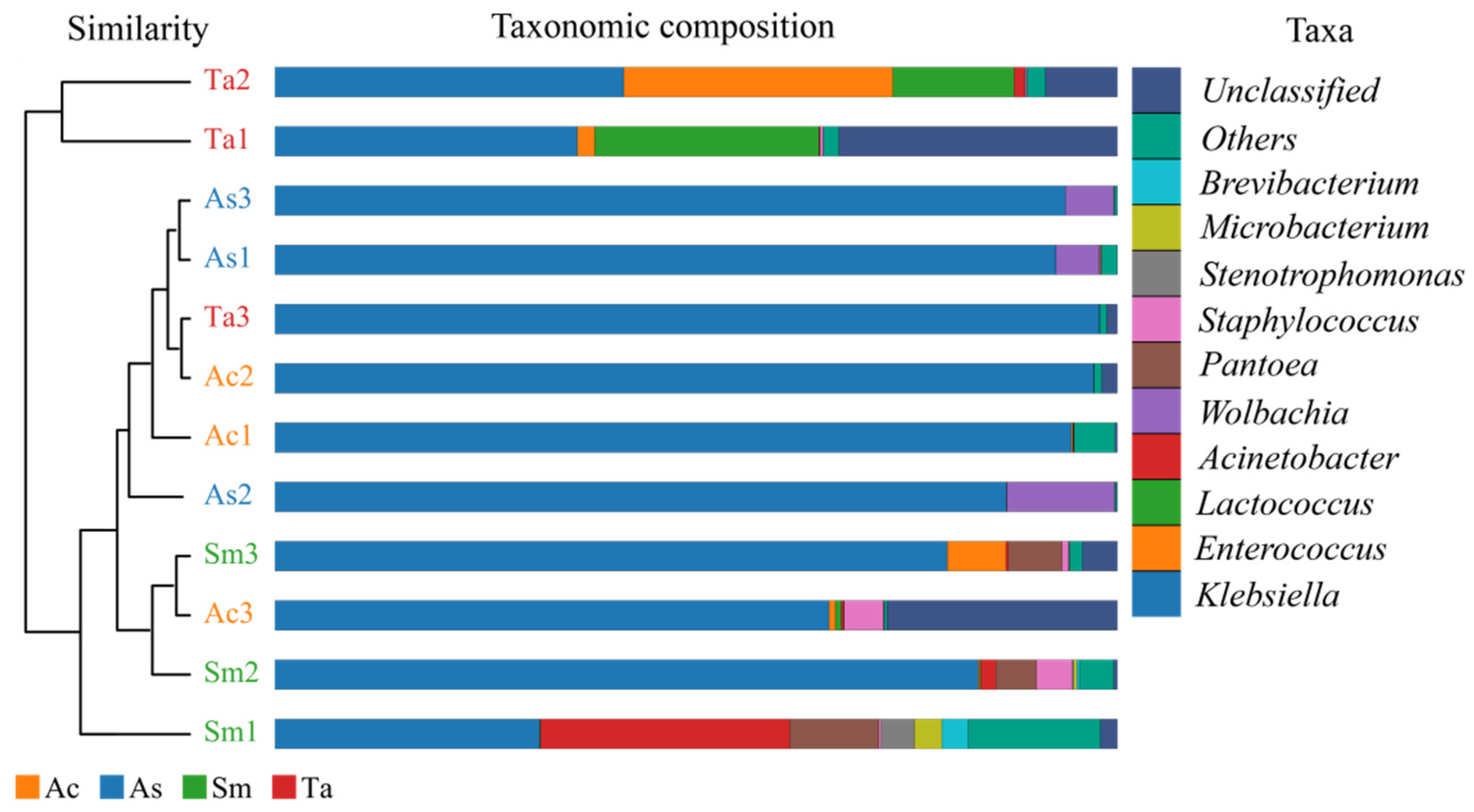
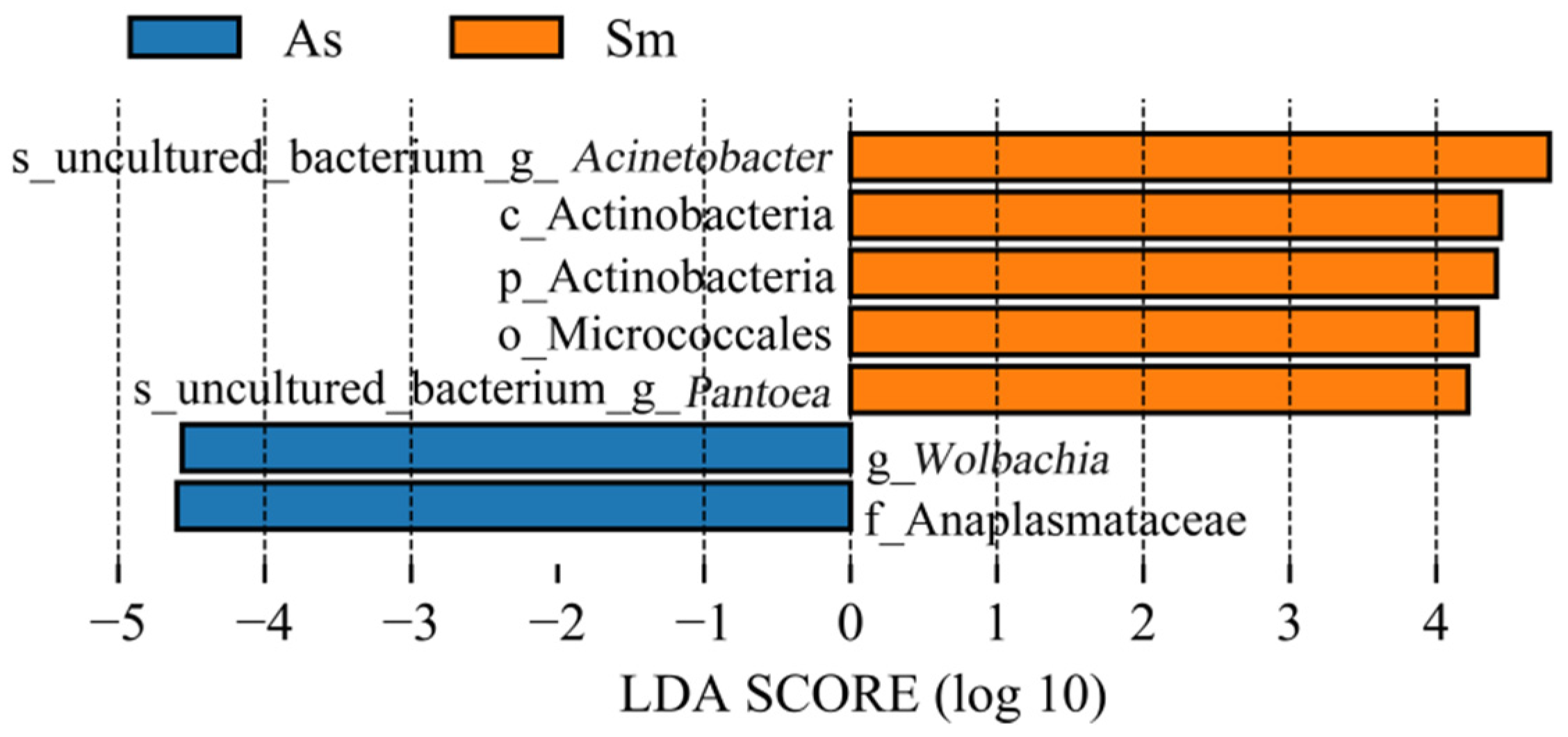
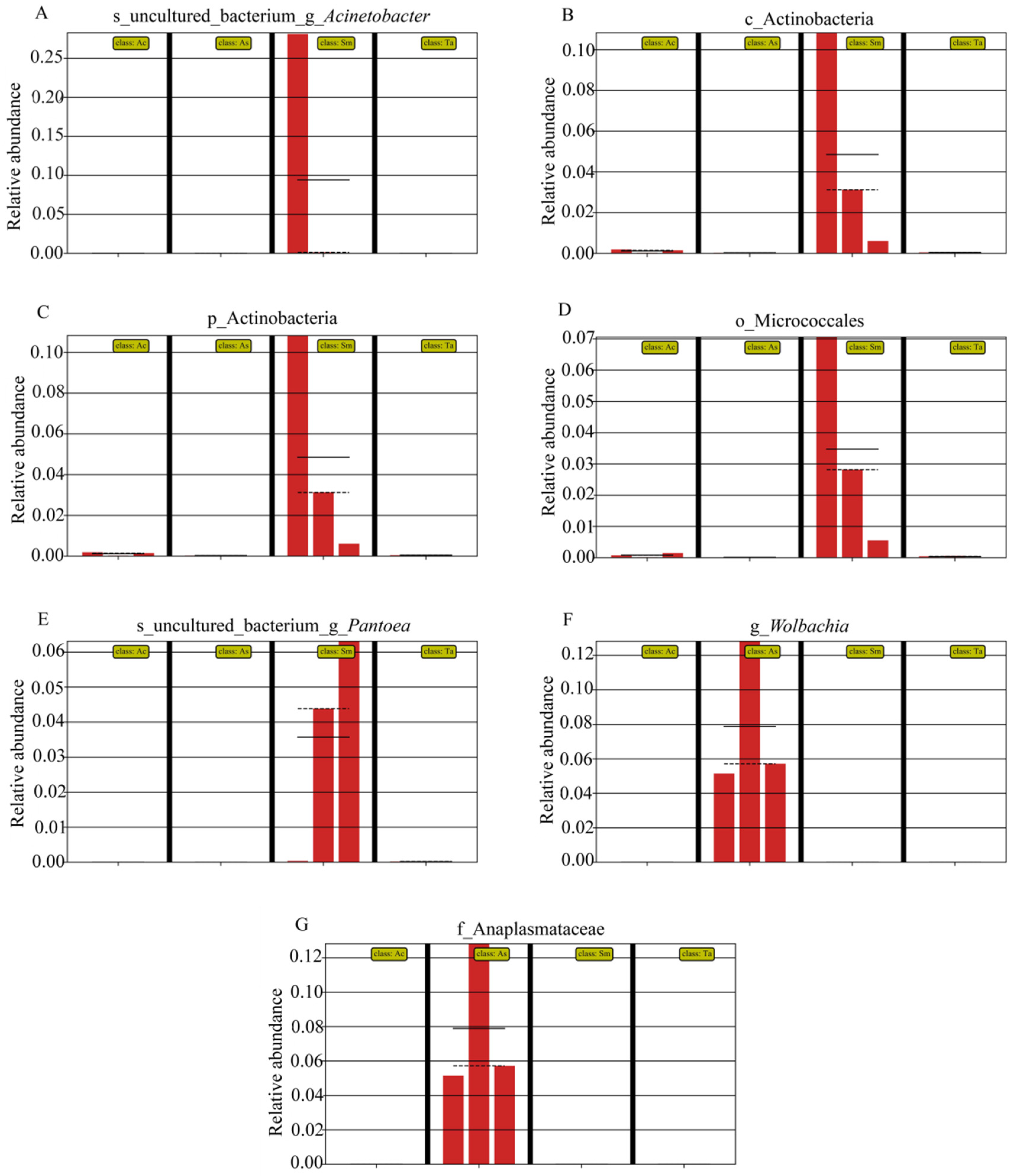
3.1. Analysis of the Gut Microbiota Diversity and Bacterial Composition between Four Species of Grasshoppers
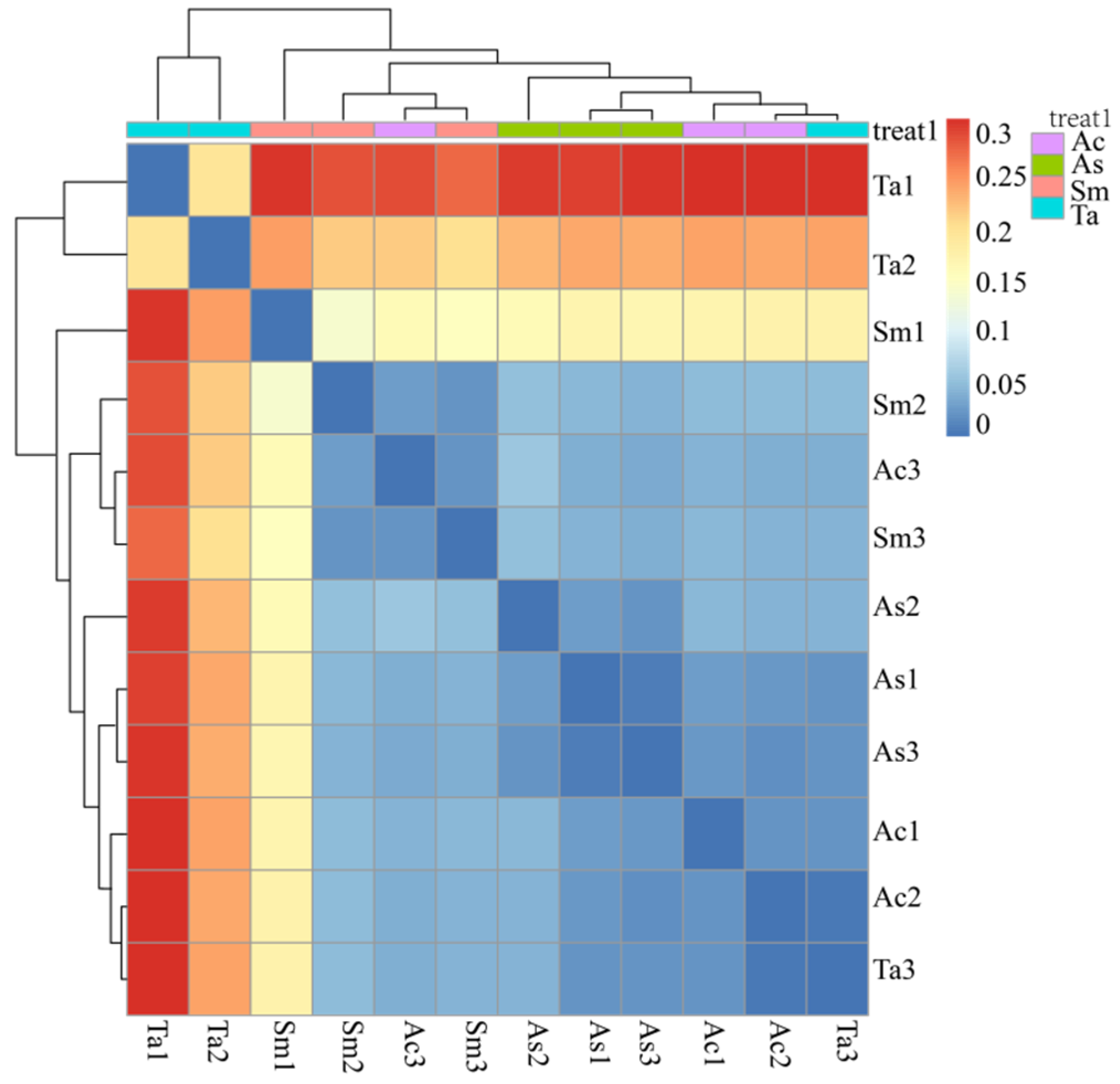
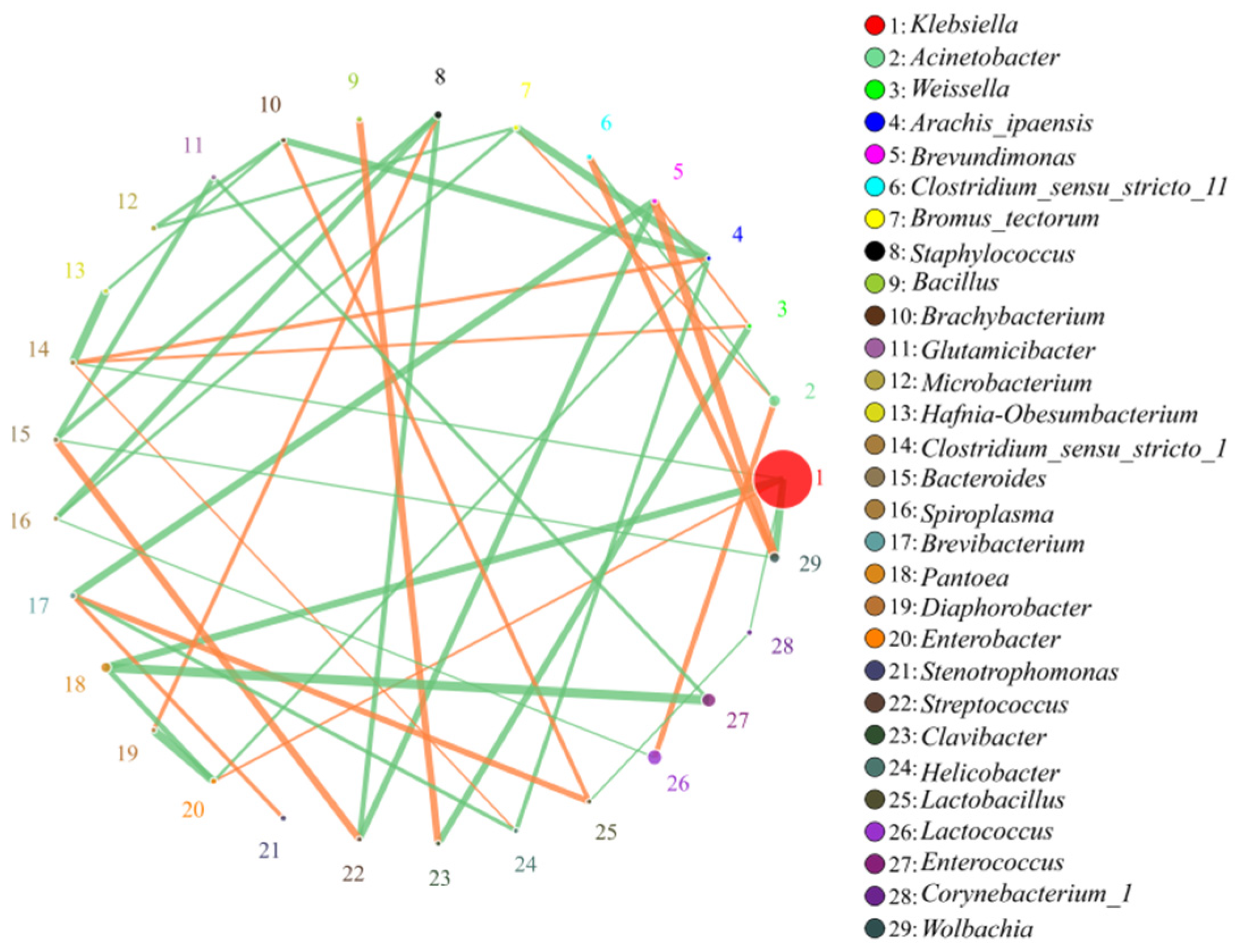
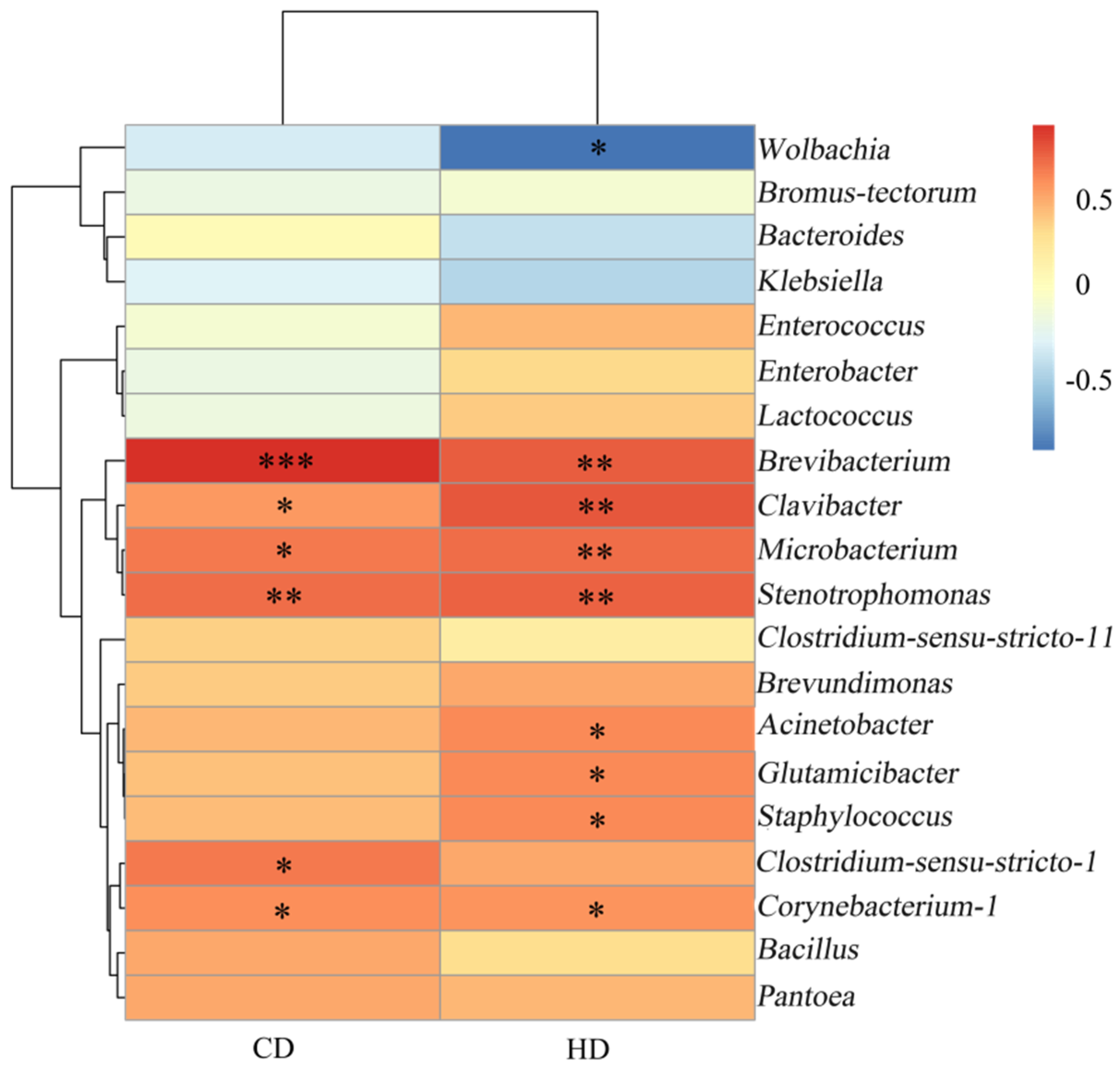
3.2. Correlation Analysis of Bacteria
3.3. Digestibility of Cellulose and Hemicellulose
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Intestinal Microorganism of Grasshopper with Digestibility of Cellulose and Hemicellulose
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basset, Y.; Cizek, L.; Cuénoud, P.; Didham, R.K.; Guilhaumon, F.; Missa, O.; Novotny, V.; Ødegaard, F.; Roslin, T.; Schmidl, J.; et al. Arthropod Diversity in a Tropical Forest. Science 2012, 338, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongoh, Y.; Deevong, P.; Inoue, T.; Moriya, S.; Trakulnaleamsai, S.; Ohkuma, M.; Vongkaluang, C.; Noparatnaraporn, N.; Kudo, T. Intra- and Interspecific Comparisons of Bacterial Diversity and Community Structure Support Coevolution of Gut Microbiota and Termite Host. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6590–6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Ning, K. Metagenomics of insect gut: New borders of microbial big data. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2018, 58, 964–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, Z.; Nabil, R.; Said, E.; Houria, N.; Khadija, T.; Abderrahim, L.; Lahsen, E.G. Preliminary Study of the Intestinal Microbial Diversity of Three Acridoidae: Oedipoda fuscocincta, Dociostaurus moroccanus, and Calliptamus barbarus (Acrididae: Orthoptera), in the Moroccan Middle Atlas. Indian J. Microbiol. 2022, 62, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavy, O.; Gophna, U.; Gefen, E.; Ayali, A. Locust Bacterial Symbionts: An Update. Insects 2020, 11, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, R.J.; Dillon, V.M. The gut bacteria of insects: Nonpathogenic interactions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2004, 49, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, W.K.; Engel, P.; Koch, H.; Moran, N.A. Genomics and host specialization of honey bee and bumble bee gut symbionts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11509–11514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.Y.; Kho, H.P.; Riedel, S.L.; Kim, S.W.; Gan, C.Y.; Taylor, T.D.; Sudesh, K. An integrative study on biologically re-covered polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and simultaneous assessment of gut microbiome in yellow mealworm. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 265, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.J.; Rusch, D.B.; Stewart, F.J.; Mattila, H.R.; Newton, I.L.G. Saccharide breakdown and fermentation by the honey bee gut microbiome. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 17, 796–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltenpoth, M.; Göttler, W.; Herzner, G.; Strohm, E. Symbiotic Bacteria Protect Wasp Larvae from Fungal Infestation. Curr. Biol. CB 2005, 15, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.F.; Hou, L.; Wei, J.N.; Guo, S.; Cui, W.C.; Yang, P.C.; Kang, L.; Wang, X.H. Aggregation pheromone 4-vinylanisole promotes the synchrony of sexual maturation in female locusts. eLife 2022, 11, e74581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arredondo-Santoyo, M.; Herrera-Camacho, J.; Vázquez-Garcidueñas, M.S.; Vázquez-Marrufo, G. Corn stover induces extracellular laccase activity in Didymosphaeria sp. (syn. = Paraconiothyrium sp.) and exhibits increased in vitro ruminal digestibility when treated with this fungal species. Folia Microbiol. 2020, 65, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Song, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Mao, C.; Li, X. Enhanced Biogas Production by Ligninolytic Strain Enterobacter hormaechei KA3 for Anaerobic Digestion of Corn Straw. Energies 2021, 14, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.-J.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.-F.; Chen, M.; Gao, X.-H.; Wang, F.-Q.; Song, A.-D. Cellulolytic activity and structure of symbiotic bacteria in locust guts. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 7926–7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fu, C.; Long, W.; Xiao, X.; Liao, H.; Yang, Y. Bamboo lignocellulose degradation by gut symbiotic microbiota of the bamboo snout beetle Cyrtotrachelus buqueti. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Maruyama, F.; Kato, H.; Toyoda, A.; Dozono, A.; Ohtsubo, Y.; Nagata, Y.; Fujiyama, A.; Tsuda, M.; Kurokawa, K. Design and Experimental Application of a Novel Non-Degenerate Universal Primer Set that Amplifies Prokaryotic 16S rRNA Genes with a Low Possibility to Amplify Eukaryotic rRNA Genes. DNA Res. 2014, 21, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-M.; Bai, J.; Zheng, F.-Y.; Ling, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhi, Y.-C.; Li, X.-J. Diversity of the gut microbiome in three grasshopper species using 16S rRNA and determination of cellulose digestibility. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostic, A.; Gevers, D.; Siljander, H.; Vatanen, T.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Hämäläinen, A.-M.; Peet, A.; Tillmann, V.; Pöhö, P.; Mattila, I.; et al. The Dynamics of the Human Infant Gut Microbiome in Development and in Progression toward Type 1 Diabetes. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.Y.; Huang, H.; Fu, H.Q.; Chen, H.Q. Advances in cellulose chemistry. CIESC J. 2006, 57, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Fu, Q.; Liao, Q.; Xia, A.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, X.Q.; Zhu, X. Study on degradation kinetics of hemicellulose in wheat straw hydrothermal pretreatment. CIESC J. 2020, 71, 3098–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriani, A.; Bayuningsih, M.; Kusnadi, J.; Rahmani, N.; Juanssilfero, A.; Sari, L.; Ermayanti, T.; Yopi. Hydrolysis of Local Genotype Taro (Colocasia esculenta) Starch by Crude Amylase from Brevibacterium Sp. for Maltooligosaccharides Production. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 439, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipriyadi; Darwis, W.; Wibowo, R.H.; Farestiani, E. Characterization and Identification of Xylanolytic Bacteria Stenotrophomonas sp. EL-8 Isolated from Seagrass Substrates in Enggano Island. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 457, 012068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahr, H.; Bahro, R.; Burger, A.; Ahlemeyer, J.; Eichenlaub, R. Interactions between Clavibacter michiganensis and its host plants. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 1, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shil, R.K.; Mojumder, S.; Sadida, F.F.; Uddin, M.; Sikdar, D. Isolation and Identification of Cellulolytic Bacteria from the Gut of Three Phytophagus Insect Species. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2014, 57, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, R.B.; Lehman, R.M.; Brözel, V.S.; Lundgren, J.G. Gut Bacterial Symbiont Diversity within Beneficial Insects Linked to Reductions in Local Biodiversity. Ann. Èntomol. Soc. Am. 2015, 108, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Donkersley, P.; Rhodes, G.; Pickup, R.W.; Jones, K.C.; Wilson, K. Bacterial communities associated with honeybee food stores are correlated with land use. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 4743–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y.; Yan, Z.; Lv, D.; Wang, P.; Li, Y. Comparison of Gut Bacterial Communities of Grapholita molesta (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) Reared on Different Host Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, M.S.; Wu, X.; Wei, W.; Mendes, L.W.; Allen, K.C.; Pinheiro, J.B.; Clough, S.J.; Zucchi, M.I. Characterization and Comparison of Intestinal Bacterial Microbiomes of Euschistus heros and Piezodorus guildinii Collected in Brazil and the United States. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 769965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín-Miret, J.; González-Serrano, F.; Rosas, T.; Baixeras, J.; Latorre, A.; Pérez-Cobas, A.E.; Moya, A. Temporal variations shape the gut microbiome ecology of the moth Brithys crini. Environ. Microbiol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Vogler, A.P.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X. Host Phylogeny and Diet Shape Gut Microbial Communities within Bamboo-Feeding Insects. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 633075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, M.; Prather, C.; Sun, Y. The gut bacterial communities across six grasshopper species from a coastal tallgrass prairie. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, L.J.; Khachatourians, G.G.; Jones, G.A. Microbial Ecology of the Gut in Laboratory Stocks of the Migratory Grasshopper, Melanoplus sanguinipes (Fab.) (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Delalibera, J.I.; Handelsman, J.; Raffa, K.F. Bacteria Associated with the Guts of Two Wood-Boring Beetles: Anoplophora glabripennis and Saperda vestita (Cerambycidae). Environ. Èntomol. 2006, 35, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, A.; Yuval, B.; Jurkevitch, E. Gut bacterial communities in the Mediterranean fruit fly (Ceratitis capitata) and their impact on host longevity. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.G.; Yang, Y.J.; Liao, Q.J.; Xu, H.X.; Liu, Y.H.; Lv, Z.X. Analysis of the bacterial community structure and diversity in the intestine of Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2016, 59, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Hosokawa, T.; Fukatsu, T. Insect-Microbe Mutualism without Vertical Transmission: A Stinkbug Acquires a Beneficial Gut Symbiont from the Environment Every Generation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4308–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, K.L.; Malta, V.R.D.S.; Machado, S.S.; Junior, G.A.L.; da Silva, A.P.V.; Almeida, R.M.R.G.; da Luz, J.M.R. Bacterial cellulase from the intestinal tract of the sugarcane borer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, P.A.; Sinkins, S.P.; Godfray, H.C.J. Strategies for Introducing Wolbachia to Reduce Transmission of Mosquito-Borne Diseases. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, T.; Deng, X.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; He, S.; Li, J.; Wan, H. Antibiotics increased host insecticide susceptibility via collapsed bacterial symbionts reducing detoxification metabolism in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. J. Pest Sci. 2020, 94, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones-Roblero, C.I.; Rodríguez-Díaz, R.; Santiago-Cruz, J.A.; Zúñiga, G.; Rivera-Orduña, F.N. Degradation capacities of bacteria and yeasts isolated from the gut of Dendroctonus rhizophagus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Folia Microbiol. 2017, 62, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, P.; Moran, N.A. The gut microbiota of insects—Diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 699–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MsangoSoko, K.; Bhattacharya, R.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Sharma, K.; Subramanian, S. Cellulolytic activity of gut bacteria isolated from the eri silkworm larvae, Samia ricini, (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 2785–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.C.; Srygley, R.B.; Healy, F.; Swaminath, K.; Mueller, U.G. Spatial Structure of the Mormon Cricket Gut Microbiome and its Predicted Contribution to Nutrition and Immune Function. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinioti, P.; Ras, E.; Augustinos, A.A.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Mathiopoulos, K.D.; Caceres, C.; Bourtzis, K. Manipulation of insect gut microbiota towards the improvement of Bactrocera oleae artificial rearing. Èntomol. Exp. Appl. 2020, 168, 523–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinioti, P.; Ras, E.; Augustinos, A.A.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Mathiopoulos, K.D.; Caceres, C.; Bourtzis, K. The impact of fruit fly gut bacteria on the rearing of the parasitic wasp Diachasmimorpha longicaudata. Èntomol. Exp. Appl. 2020, 168, 541–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.H.; Qin, D.Y.; Dai, X.Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y. Effects of intestinal bacteria Citrobacter freundi and Klebsiella oxytoca on the development and substance metabolism of Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2020, 63, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, F.E.; Peiffer, M.; Tan, C.-W.; Stanley, B.A.; Stanley, A.; Wang, J.; Jones, A.G.; Hoover, K.; Rosa, C.; Luthe, D.; et al. Fall Armyworm-Associated Gut Bacteria Modulate Plant Defense Responses. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2017, 30, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.H.; Zhou, K.Y.; Xiong, Z. Screening and Identification of Lipase-producing Bacteria from Intestinal Canal of Dendrolimus kikuchii and Preliminary Studies on Its Enzyme Properties. J. Microbiol. 2012, 32, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, K.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A critical review of analytical methods in pretreatment of lignocelluloses: Composition, imaging, and crystallinity. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.Y.; Ping, B.A. Research on Cellulose-decomposing and Methanogenesis in Vitro within Rumen Fluid of Tibetan Sheep by Added Hydrolyzed Casein. Chin. J. Vet. Med. 2017, 53, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.J.; Meng, L.; Luo, Q.J.; An, S.Z.; Chen, A.L.; Wang, J.Y. Effects of Different Utilization Methods of Corn Stalks on Digestion and Metabolism of Sheep. Grass-Feed. Livest. 2000, S1, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Ren, C.W.; Zhang, C.W. The effect of dry matter intake, milk production and digestibility of different wheat stalk chopped lengths and processing for dairy cows. China Feed 2019, 6, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi-Shotorkhoft, A.; Mohammadabadi, T.; Motamedi, H.; Chaji, M.; Fazaeli, H. Isolation and identification of termite gut symbiotic bacteria with lignocellulose-degrading potential, and their effects on the nutritive value for ruminants of some by-products. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 221, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.; Manna, B.; Majumder, S.; Ghosh, A. Species-wide Metabolic Interaction Network for Understanding Natural Lignocellulose Digestion in Termite Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.Q.; Shi, D.D.; Cai, H.Y.; Yu, D.L.; Meng, K.; Yang, P.L. Identification and Genome Analysis of a Cellulose Degrading Strain from the Intestinal Tract of Protaetia brevitarsis Larva. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Sample Code | Collection Date | Locality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acrida cinerea | Ac1 | July 2018 | Baoding, China |
| Ac2 | July 2018 | ||
| Ac3 | October 2018 | ||
| Trilophidia annulate | Ta1 | October 2018 | Baoding, China |
| Ta2 | October 2018 | ||
| Ta3 | July 2018 | ||
| Sphingonotus mongolicus | Sm1 | October 2018 | Baoding, China |
| Sm2 | July 2018 | ||
| Sm3 | July 2018 | ||
| Atractomorpha sinensis | As1 | July 2018 | Baoding, China |
| As2 | July 2018 | ||
| As3 | July 2018 |
| Sample | Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Genus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ac1 | 1 | 6 | 10 | 17 | 34 | 36 |
| Ac2 | 1 | 6 | 10 | 15 | 28 | 32 |
| Ac3 | 1 | 6 | 9 | 13 | 24 | 28 |
| As1 | 1 | 5 | 9 | 14 | 23 | 26 |
| As2 | 1 | 5 | 9 | 15 | 28 | 29 |
| As3 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 14 | 24 | 28 |
| Sm1 | 1 | 6 | 10 | 18 | 33 | 41 |
| Sm2 | 1 | 6 | 10 | 18 | 32 | 37 |
| Sm3 | 1 | 5 | 8 | 15 | 24 | 28 |
| Ta1 | 1 | 6 | 10 | 16 | 30 | 35 |
| Ta2 | 1 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 18 | 22 |
| Ta3 | 1 | 6 | 9 | 16 | 26 | 29 |
| Total | 1 | 7 | 12 | 21 | 42 | 55 |
| Species | Sample ID | ACE | Chao1 | Shannon | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acrida cinerea | Ac | 59.2633 | 58.3929 | 0.7407 | 0.9997 |
| Atractomorpha sinensis | As | 47.4831 | 48.1513 | 0.4829 | 0.9998 |
| Sphingonotus mongolicus | Sm | 57.3990 | 55.7500 | 1.9040 | 0.9999 |
| Trilophidia annulate | Ta | 54.1572 | 51.2593 | 1.5683 | 0.9998 |
| Species of Grasshopper | Sample ID | Cellulose Content in Feces (%) | Cellulose Digestibility (%) | Hemicellulose Content in Feces (%) | Hemicellulose Digestibility (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acrida cinerea | Ac | 33.28 ± 0.02 | 56.97 ± 0.09 | 7.86 ± 0.01 | 39.28 ± 0.12 |
| Atractomorpha sinensis | As | 37.29 ± 0.02 | 54.86 ± 0.06 | 11.37 ± 0.01 | 17.77 ± 0.10 |
| Sphingonotus mongolicus | Sm | 44.36 ± 0.03 | 67.91 ± 0.08 | 12.14 ± 0.01 | 47.51 ± 0.12 |
| Trilophidia annulata | Ta | 41.54 ± 0.04 | 49.87 ± 0.06 | 11.20 ± 0.02 | 19.25 ± 0.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, J.; Ling, Y.; Li, W.-J.; Wang, L.; Xue, X.-B.; Gao, Y.-Y.; Li, F.-F.; Li, X.-J. Analysis of Intestinal Microbial Diversity of Four Species of Grasshoppers and Determination of Cellulose Digestibility. Insects 2022, 13, 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050432
Bai J, Ling Y, Li W-J, Wang L, Xue X-B, Gao Y-Y, Li F-F, Li X-J. Analysis of Intestinal Microbial Diversity of Four Species of Grasshoppers and Determination of Cellulose Digestibility. Insects. 2022; 13(5):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050432
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Jing, Yao Ling, Wen-Jing Li, Li Wang, Xiao-Bao Xue, Yuan-Yi Gao, Fei-Fei Li, and Xin-Jiang Li. 2022. "Analysis of Intestinal Microbial Diversity of Four Species of Grasshoppers and Determination of Cellulose Digestibility" Insects 13, no. 5: 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050432
APA StyleBai, J., Ling, Y., Li, W.-J., Wang, L., Xue, X.-B., Gao, Y.-Y., Li, F.-F., & Li, X.-J. (2022). Analysis of Intestinal Microbial Diversity of Four Species of Grasshoppers and Determination of Cellulose Digestibility. Insects, 13(5), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050432







