Wing Planform Effect on the Aerodynamics of Insect Wings
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
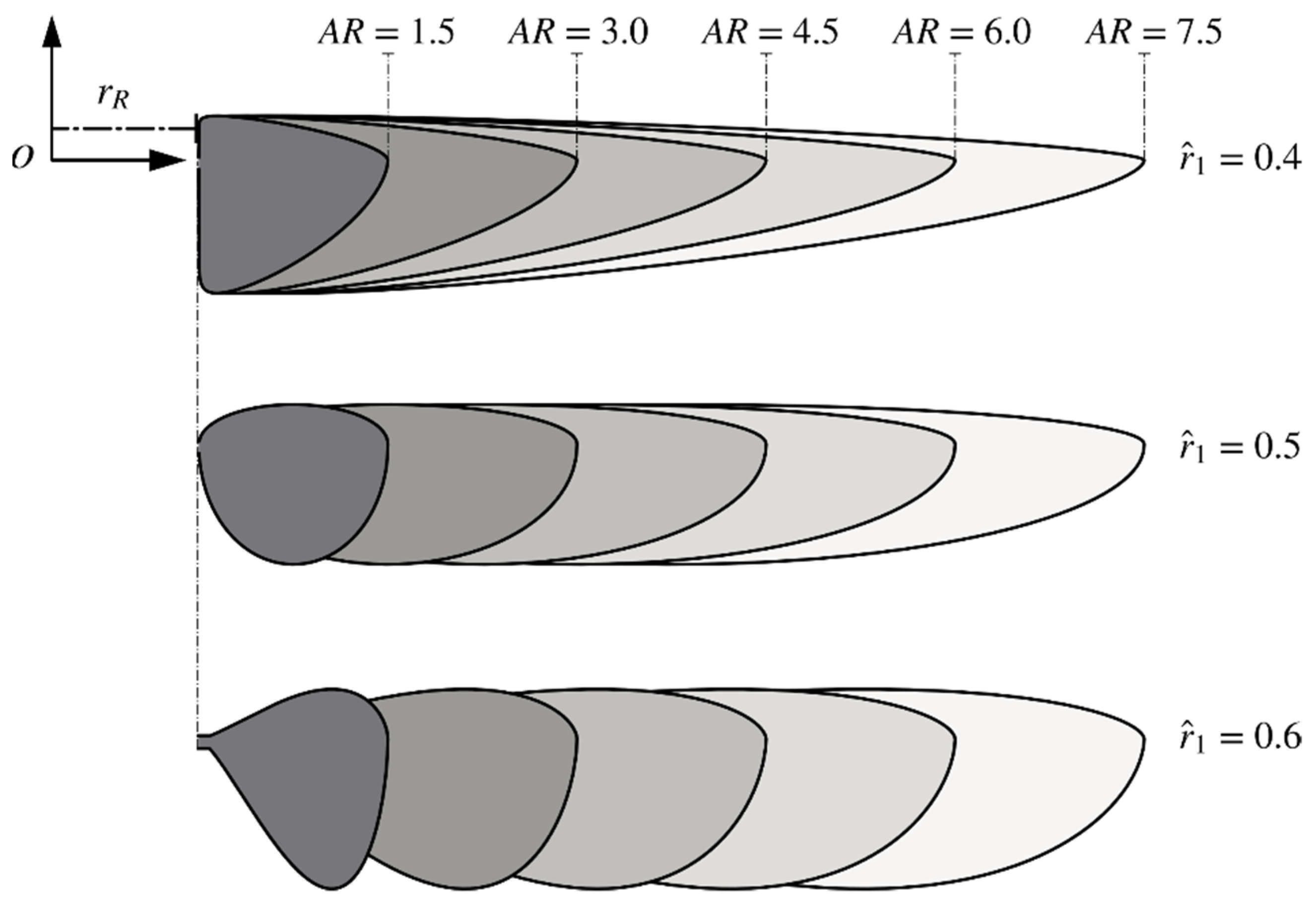
2.1. Wing Planforms and Kinematics
2.2. Numerical Simulation
2.3. Convergence Assessment
2.4. Validation of the Numerical Set-Up
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Aspect Ratio
3.2. Effect of Radial Centroid Location
3.3. Effect of Root Offset
3.4. Average Force Production and Aerodynamic Efficiency
3.4.1. Average Coefficients for Different Aspect Ratio and Radial Centroid Locations
3.4.2. Average Coefficients for Different Aspect Ratio and Wing Root Offset
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ellington, C.P.; van den Berg, C.; Willmott, A.P.; Thomas, A.L.R. Leading-Edge Vortices in Insect Flight. Nature 1996, 384, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, D.D.; Lentink, D. Flapping Wing Aerodynamics: From Insects to Vertebrates. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nabawy, M.R.A.; Crowther, W.J. The Role of the Leading Edge Vortex in Lift Augmentation of Steadily Revolving Wings: A Change in Perspective. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20170159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabawy, M.R.A.; Villamor, G.J.; Li, H. Aerodynamic Modelling of Insect Wings Using Joukowski Transformation. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2021 FORUM, Virtual, 2–6 August 2021; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2021; p. 2938. [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson, M.H.; Lehmann, F.O.; Sane, S.P. Wing Rotation and the Aerodynamic Basis of Insect Flight. Science 1999, 284, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.A.; Zbikowski, R.; Knowles, K. Aerodynamic Modelling of Insect-like Flapping Flight for Micro Air Vehicles. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2006, 42, 129–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxworthy, T. Experiments on the Weis-Fogh Mechanism of Lift Generation by Insects in Hovering Flight. Part 1. Dynamics of the ‘Fling’. J. Fluid Mech. 1979, 93, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usherwood, J.R.; Ellington, C.P. The Aerodynamics of Revolving Wings—II. Propeller Force Coefficients from Mayfly to Quail. J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Sun, M. Effects of Corrugation and Wing Planform on the Aerodynamic Force Production of Sweeping Model Insect Wings. Acta Mech. Sin. Lixue Xuebao 2005, 21, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Tian, F.-B.; Young, J.; Lai, J.C.S. Effects of Wing Shape, Aspect Ratio and Deviation Angle on Aerodynamic Performance of Flapping Wings in Hover. Phys. Fluids 2016, 28, 111901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellington, C.P. The Aerodynamics of Hovering Insect Flight. 2. Morphological Parameters. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1984, 305, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.A.; Kevin Knowles, B.; Zbikowski, R. Insectlike Flapping Wings in the Hover Part 2: Effect of Wing Geometry. J. Aircr. 2008, 45, 1976–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabawy, M.R.A.; Crowther, W.J. A Quasi-Steady Lifting Line Theory for Insect-Like Hovering Flight. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nabawy, M.R.A.; Crowther, W.J. On the Quasi-Steady Aerodynamics of Normal Hovering Flight Part I: The Induced Power Factor. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20131196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nabawy, M.R.A.; Crowther, W.J. Is Flapping Flight Aerodynamically Efficient? In Proceedings of the 32nd AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–20 June 2014; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2014; p. 2277. [Google Scholar]
- Nabawy, M.R.A.; Crowther, W.J. Optimum Hovering Wing Planform. J. Theor. Biol. 2016, 406, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krishna, S.; Cho, M.; Wehmann, H.N.; Engels, T.; Lehmann, F.O. Wing Design in Flies: Properties and Aerodynamic Function. Insects 2020, 11, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandtl, L.; Tragflügeltheorie, I. Mitteilung. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen Math. -Phys. Kl. 1918, 1918, 451–477. [Google Scholar]
- Betz, A. Schraubenpropeller Mit Geringstem Energieverlust. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen Math. -Phys. Kl. 1919, 1919, 193–217. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, N.; Knowles, K.; Bomphrey, R.J. The Effect of Aspect Ratio on the Leading-Edge Vortex over an Insect-like Flapping Wing. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 056020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, N.; Knowles, K.; Bomphrey, R.J. Petiolate Wings: Effects on the Leadingedge Vortex in Flapping Flight. Interface Focus 2017, 7, 20160084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.S.; Chang, J.W.; Cho, H.K. Vortices Behavior Depending on the Aspect Ratio of an Insect-like Flapping Wing in Hover. Exp. Fluids 2015, 56, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbig, R.R.; Sheridan, J.; Thompson, M.C. Reynolds Number and Aspect Ratio Effects on the Leading-Edge Vortex for Rotating Insect Wing Planforms. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 717, 166–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruyt, J.W.; van Heijst, G.J.F.; Altshuler, D.L.; Lentink, D. Power Reduction and the Radial Limit of Stall Delay in Revolving Wings of Different Aspect Ratio. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lentink, D.; Dickinson, M.H. Rotational Accelerations Stabilize Leading Edge Vortices on Revolving Fly Wings. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 2705–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lua, K.B.; Lim, T.T. Aspect Ratio Effects on Revolving Wings with Rossby Number Consideration. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2016, 11, 056013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardin, T.; Colonius, T. On the Lift-Optimal Aspect Ratio of a Revolving Wing at Low Reynolds Number. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20170933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.S.; Zhao, J.; Sheridan, J.; Hourigan, K.; Thompson, M.C. Uncoupling the Effects of Aspect Ratio, Reynolds Number and Rossby Number on a Rotating Insect-Wing Planform. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 859, 921–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Tang, J. Unsteady Aerodynamic Force Generation by a Model Fruit Fly Wing in Flapping Motion. J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabawy, M.R.A.; Crowther, W.J. Aero-Optimum Hovering Kinematics. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 44002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellington, C.P. The Aerodynamics of Hovering Insect Flight. 3. Kinematics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1984, 305, 41–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.R.; Babinsky, H. Reynolds Number Effects on Leading Edge Vortex Development on a Waving Wing. Exp. Fluids 2011, 51, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Sun, M. Unsteady Aerodynamic Forces of a Flapping Wing. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birch, J.M.; Dickson, W.B.; Dickinson, M.H. Force Production and Flow Structure of the Leading Edge Vortex on Flapping Wings at High and Low Reynolds Numbers. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, G.; Sun, M. Effects of Wing Deformation on Aerodynamic Forces in Hovering Hoverflies. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 2273–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakata, T.; Liu, H. Aerodynamic Performance of a Hovering Hawkmoth with Flexible Wings: A Computational Approach. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Huang, Q.; Deng, X.; Sane, S.P. Aerodynamic Effects of Flexibility in Flapping Wings. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patankar, S.V.; Spalding, D.B. A Calculation Procedure for Heat, Mass and Momentum Transfer in Three-Dimensional Parabolic Flows. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1972, 15, 1787–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, R.I. Solution of the Implicitly Discretised Fluid Flow Equations by Operator-Splitting. J. Comput. Phys. 1986, 62, 40–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Gang, D.U.; Sun, M.; Du, G. Lift and Power Requirements of Hovering Insect Flight. Acta Mech. Sin. 2003, 19, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J. Aerodynamic Efficiency of Flapping Flight: Analysis of a Two-Stroke Model. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunt, J.C.R.; Wray, A.A.; Moin, P. Eddies, Streams, and Convergence Zones in Turbulent Flows. In Proceedings of the 1988 Summer Program; Center for Turbulence Research: Stanford, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kweon, J.; Choi, H. Sectional Lift Coefficient of a Flapping Wing in Hovering Motion. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 071703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erzincanli, B.; Sahin, M. The Numerical Simulation of the Wing Kinematics Effects on near Wake Topology and Aerodynamic Performance in Hovering Drosophila Flight. Comput. Fluids 2015, 122, 90–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, J.M.; Dickinson, M.H. The Influence of Wing-Wake Interactions on the Production of Aerodynamic Forces in Flapping Flight. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 2257–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rival, D.E.; Kriegseis, J.; Schaub, P.; Widmann, A.; Tropea, C. Characteristic Length Scales for Vortex Detachment on Plunging Profiles with Varying Leading-Edge Geometry. Exp. Fluids 2014, 55, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmann, A.; Tropea, C. Parameters Influencing Vortex Growth and Detachment on Unsteady Aerodynamic Profiles. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 773, 432–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabawy, M.R.A.; Marcinkeviciute, R. Scalability of Resonant Motor-Driven Flapping Wing Propulsion Systems. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 210452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Morphological Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| 1.5, 3, 4.5, 6, 7.5 | |
| 0.4, 0.5, 0.6 | |
| 0, 1, 2, 3 |
| Mesh Cells, Time Step | ||
|---|---|---|
| = 1 × 10−3 | 1.460 | 2.046 |
| = 1 × 10−3 | 1.471 | 2.052 |
| = 5 × 10−4 | 1.460 | 2.046 |
| = 5 × 10−4 | 1.470 | 2.052 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Nabawy, M.R.A. Wing Planform Effect on the Aerodynamics of Insect Wings. Insects 2022, 13, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050459
Li H, Nabawy MRA. Wing Planform Effect on the Aerodynamics of Insect Wings. Insects. 2022; 13(5):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050459
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hao, and Mostafa R. A. Nabawy. 2022. "Wing Planform Effect on the Aerodynamics of Insect Wings" Insects 13, no. 5: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050459
APA StyleLi, H., & Nabawy, M. R. A. (2022). Wing Planform Effect on the Aerodynamics of Insect Wings. Insects, 13(5), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050459







