3.2.1. Blepharicera beishanica sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:2D8E7B7C-ED6B-45F9-B4DB-5D8CE81273BE
Type material. Holotype: male (CAU), China: Qinghai Province, Huzhu County, Beishan Forest Farm (36°50’56’’ N 101°56’47’’ E, 2100 m), 2015.VII.27, Liang Wang; Paratypes: 10 males & 3 females (QAU), same data as holotype; 1 female (QAU), China: Qinghai Province, Huzhu County, Beishan Forest Farm (36°50′56″ N 101°56′47″ E, 2100 m), 2015.VII.26, Liang Wang (light trap).
Diagnosis. Compound eye with dorsal division 1/15 of ventral division in male. Mesonotum brown with a yellow median stripe at the posterior half. Mesopleuron is mostly light brown except for anepimeron light yellow. Rs 1.5 times as long as r-m. Gonostylus is slightly swollen and notched apically. Dorsal paramere with tip arrowhead-shaped; dorsal carina clearly visible, tip round and blunt. Medial depression of 8th sternite flat in female. Genital fork X-shaped in female.
Description. Male. Body length 4.00–5.00 mm; wing length 5.25–6.00 mm, width 2.00–2.25 mm.
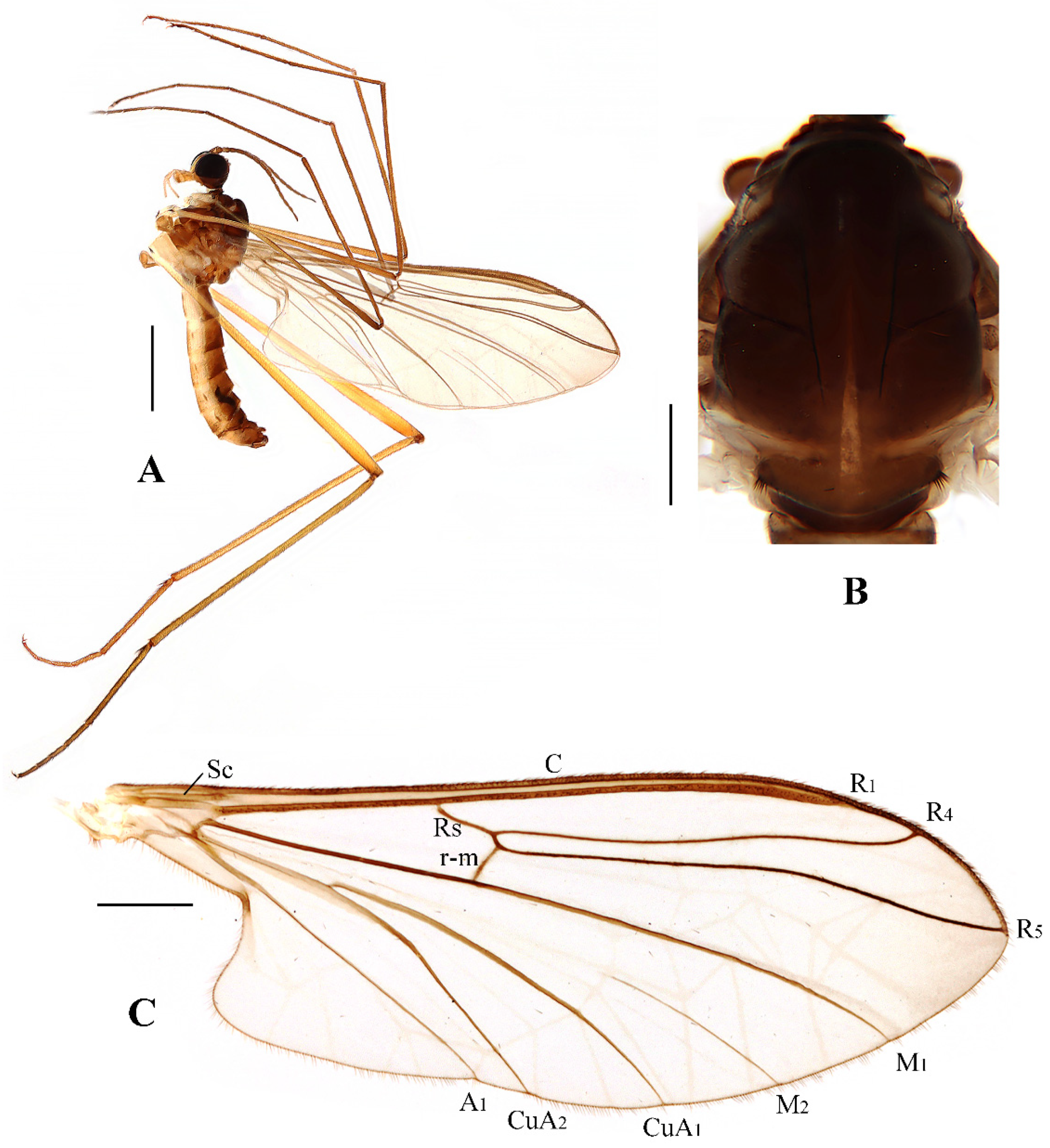
Head (
Figure 2A and
Figure 3A) uniformly brown with brownish black hairs. Compound eyes dichoptic, interocular ridge absent; each compound eye divided, callis oculi absent; dorsal division contiguous with ventral division, 1/15 of ventral division; dorsal division with 11–12 rows of ommatidia, ommatidia red-orange, larger in diameter, with ommatrichia; ventral division black with ommatrichia. Ocelli brownish yellow. Scape and pedicel oval, brown with brownish black hairs; first flagellomere constricted at base, widening at apex, basal 1/2 brownish yellow, apical 1/2 brown, with brownish-black hairs; other flagellomeres cylindrical, brown with brownish black hairs; ultimate flagellomere 1.3 times length of penultimate flagellomere. Clypeus nearly rectangular, brownish yellow, as long as wide; labrum yellow; labellum yellow with brownish black hairs; proboscis about 0.47 times the length of head width. Palpus with five segments, 1st segment almost invisible; 2nd and 3rd segments cylindrical, yellow with brown hairs; 4th segment cylindrical, slightly swollen apically, yellow with brown hairs; 5th segment slender, brownish yellow with brown hairs; relative length of distal four segments as 1.0:1.0:1.5:3.4.
Thorax (
Figure 2B). Pronotum and propleuron brown without hairs. Mesonotum brown with a yellow median stripe at posterior 1/2; scutellum light brown with numerous hairs grouped at the posterolateral corner; metanotum brown; mesopleuron mostly light brown except anepimeron light yellow. The relative length of the femur, tibiae, and 1st to 5th tarsomeres in the fore leg as 11.7:10.3:6:2.8:1.7:0.8:1, in the mid-leg as 13.3:10.8:5.2:2.7:1.5:0.8:1, in the hind leg as 17:15:5.5:1.5:1:0.8:1. Fore coxa light brown with brown hairs; mid coxa with an appendage, pale with brownish black hairs; hind coxa pale with brownish black hairs; trochanters pale, anterior margin with black spot apically, with brownish-black hairs; fore and mid femora brownish yellow basally and gradually darkened to brown apically, with brownish-black hairs; hind femur brownish yellow basally and gradually darkened to light brown apically, with brownish-black hairs; fore and mid tibiae brown with brownish black hairs; hind tibia light brown with brownish black hairs; tarsomeres brown with brownish black hairs; claw brown. Tibial spurs 0–0–0. Wing (
Figure 2C) slightly brown apically, apical 1/3 of sc brown; veins brown. Sc rudimentary, not ending at the base of Rs; Rs slightly curved basally, 1.5 times as long as r-m; R
4 wavy, the length from the end of R
1 to end of R
4 shorter than the length from the end of R
4 to end of R
5; r-m straight, included angle between r-m and Rs less than 90 degrees; the length from the end of M
1 to end of M
2 as long as the length from the end of M
2 to end of CuA
1. The base of the halter is pale, and the apex of the halter is light brown with brownish-black hairs.
Abdomen. First tergum brown with middle area pale, 2nd to 7th terga light brown with brown strips, 8th tergum brownish yellow; 1st sternum light brown, 2nd to 7th sterna light brown with pale stripes laterally; abdomen with brownish black hairs. Male genitalia (
Figure 3B–E) brown with basal 1/2 hypandrium pale. Epandrium trapeziform, posterior margin concave, with several brown hairs. Cercus triangular, inner margin slightly bulge, with several brown hairs; anal cone round with two long hairs apically. Gonostylus slightly swollen and notched apically, outer side with a wide triangular lobe folded ventrally, with hairs. Gonocoxal lobe bifurcated, outer gonocoxal lobe transparent, rod-shaped, curved medially swollen apically; inner gonocoxal lobe transparent, rod-shaped, nearly straight. Hypandrium rectangular, twice as long as wide, slightly narrow basally, posterior margin concave, with several brown hairs. Aedeagus slender, curved backward; dorsal paramere with tip arrowhead-shaped and posterior margin round; dorsal carina clearly visible, tip round and blunt.
Female. Body length 5.50–6.50 mm, wing length 7.25–8.00 mm, wing width 2.50–2.80 mm.
Head (
Figure 4A). Compound eyes subholoptic, interocular ridge present; each compound eye divided, callis oculi present; dorsal division separated from ventral division, as large as ventral division; dorsal division with about 20 rows of ommatidia, ommatidia red-orange, larger in diameter, with ommatrichia; ventral division black with ommatrichia. Scape and pedicel oval, dark brown with brownish black hairs; first flagellomere constricted at base, widening at apex, basal 1/2 brownish yellow, apical 1/2 dark brown, with brownish-black hairs; other flagellomeres cylindrical, tapering apically, dark brown with brownish black hairs; ultimate flagellomere twice length of penultimate flagellomere. Labrum brown; labellum brownish yellow with brownish black hairs; mandible brownish yellow; proboscis about 0.89 times length of head width. Palpus with five segments, 1st segment almost invisible, brownish yellow with brownish black hairs; 2nd to 4th segments cylindrical, brownish yellow with brownish black hairs; 5th segment slender, cylindrical, brownish yellow with apical 1/2 brownish black, with brownish-black hairs; relative length of distal four segments as 1.0:1.5:1.5:2.5. Tibial spurs 0–0–2. Terminalia (
Figure 4B): 8th sternite approximately trapezoidal, bilobate posteriorly, medial depression flat, with several hairs laterally; genital fork X-shaped; hypogynial plate broad basally, with triangular bulge laterally, bilobate posteriorly, each lobe round apically, intervalvular area V-shaped, with short hairs posteriorly; epiproct conical with two prominent hairs apically; spermathecae three in number.
Distribution. Currently known only from China (Qinghai).
Etymology. The specific name refers to the type locality Beishan Forest Farm.
Remarks. This new species is very similar to
B. indica (Brunetti, 1911) from Afghanistan, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and India but can be separated by the dorsal division being contiguous with ventral division and being about 1/15 of ventral division, and the gonostylus being broad and distinctly notched apically. In
B. indica, the dorsal division is separated from ventral division by a distinct suture and is as large as ventral division, and the gonostylus is distinctly slender and not distinctly notched apically [
13]. This new species is also similar to
B. asiatica (Brodsky, 1930) from Russia, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and India, but it can be separated from the latter by the light brown 2nd to 7th sterna with pale stripes laterally, and the round and blunt dorsal carina. In
B. asiatica, the 2nd to 7th sterna are dark brown, and the dorsal carina has a very pointed and downcurved tip which is almost parallel to the plate sometimes [
13].
3.2.2. Blepharicera dushanzica sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:7FA1EAD7-A1C9-486C-90A3-89B2BD7A3308
Type material. Holotype: male (CAU), China: Xinjiang Autonomous Region, Dushanzi district, Duku Highway (44°5′36″ N 84°44′59″ E, 1397 m), 2017.VII.25, Jinlong Ren. Paratypes: 4 males & 4 females (QAU), same data as holotype.
Diagnosis. Compound eye with dorsal division 1/3 of ventral division in male. Mesonotum brownish black with a brownish yellow median stripe at posterior 1/2. Scutellum brown. Episternum brown; epimeron yellow. Rs slightly shorter than r-m. Gonostylus slightly swollen and notched apically. Dorsal paramere with tip bilobed; dorsal carina with tip very point, spike-like. Medial depression of 8th sternite M-shaped in female. Genital fork X-shaped in female.
Description. Male. Body length 4.00–5.50 mm; wing length 4.50–6.00 mm, width 1.50–2.00 mm.
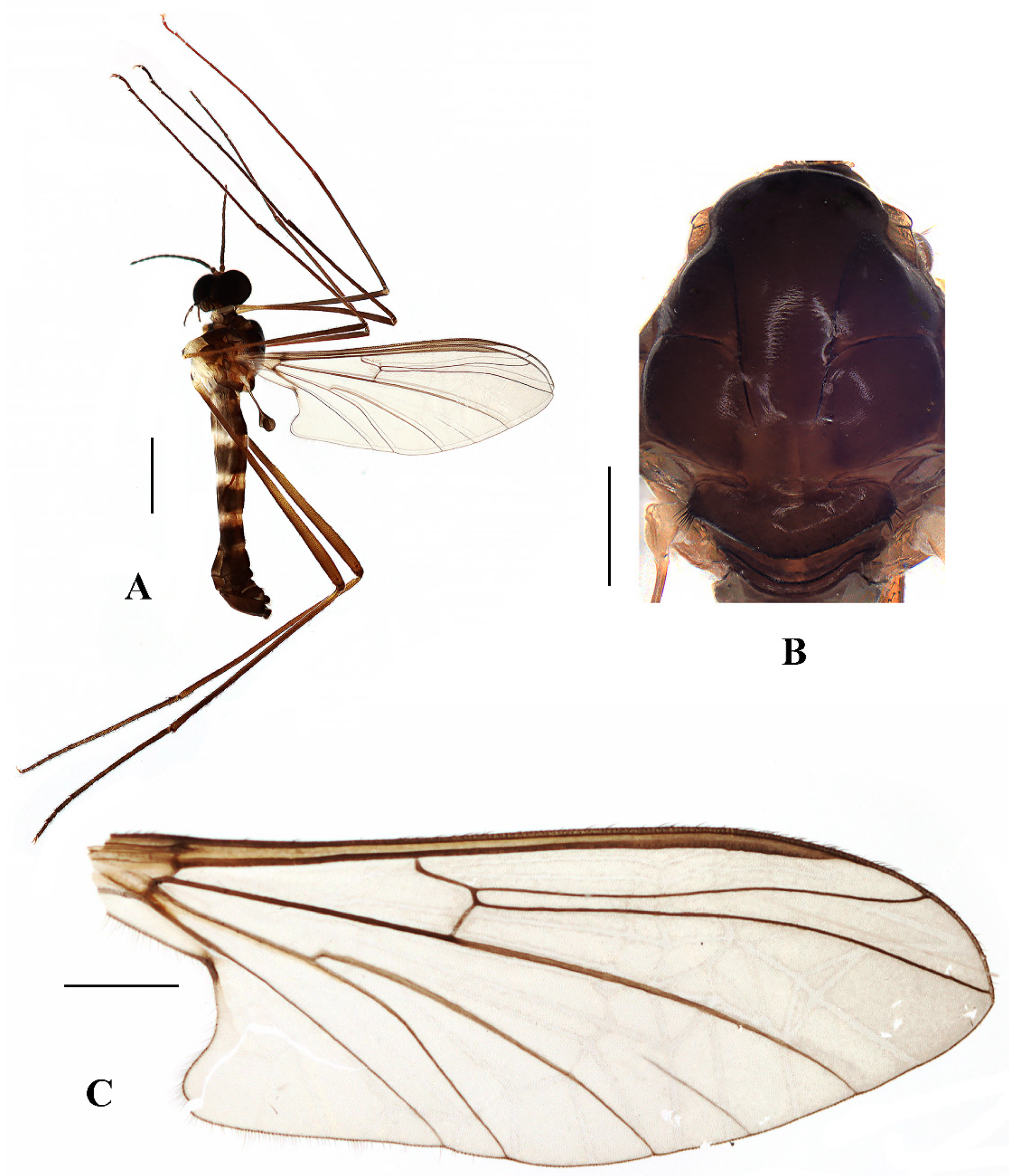
Head (
Figure 5A and
Figure 6A) uniformly brownish black with black hairs. Compound eyes dichoptic, interocular ridge absent; each compound eye divided, callis oculi absent; dorsal division contiguous with ventral division, 1/3 of ventral division; dorsal division with 18–20 rows of ommatidia, ommatidia red-orange, larger in diameter, with ommatrichia; ventral division black with ommatrichia. Ocelli brownish black. Scape and pedicel oval, brown with brownish black hairs; first flagellomere constricted at base, widening at apex, basal 1/2 pale, apical 1/2 brownish black, with brownish-black hairs; other flagellomeres cylindrical, dark brown with brownish black hairs; ultimate flagellomere 1.3 times length of penultimate flagellomere. Clypeus rectangular, dark brown, as long as wide; labrum brownish yellow; labellum brownish yellow with brownish black hairs; proboscis about 0.65 times the length of head width. Palpus with five segments, 1st segment almost invisible; 2nd to 4th segments cylindrical, yellow with brownish black hairs; 5th segment slender, brownish yellow with brownish black hairs; relative length of distal four segments as 1.1:1.0:1.1:1.8.
Thorax (
Figure 5B). Pronotum and propleuron brown without hairs. Mesonotum brownish black with a brownish yellow median stripe at posterior 1/2; scutellum brown with numerous hairs grouped at the posterolateral corner; metanotum brown; episternum brown; epimeron yellow. The relative length of the femur, tibiae, and 1st to 5th tarsomeres in the fore leg as 15:10.5:7.8:3.6:2.2:1:1, in the mid-leg as 13.8:10.5:6.2:2.7:1.8:1:1, in the hind leg as 15.5:12.7:5:1.2:1:0.8:1. Fore coxa pale with basal 1/2 light brown, with light brown hairs; mid coxa with an appendage, pale with brownish black hairs; hind coxa pale with brownish black hairs; trochanters pale, anterior margin with black spot apically, with brownish-black hairs; femora pale basally and gradually darkened to brown apically, with brownish-black hairs; tibiae brown with brownish black hairs; tarsomeres brown yellow with brownish black hairs; claw brownish yellow. Tibial spurs 0–0–0. Wing (
Figure 5C) slightly brown apically, sc light brown; veins brown. Sc rudimentary, not ending at the base of Rs; Rs slightly shorter than r-m; R
4 wavy, the length from the end of R
1 to end of R
4 shorter than the length from the end of R
4 to end of R
5; r-m slightly curved apically, included angle between r-m and Rs less than 90 degrees; the length from the end of M
1 to end of M
2 as long as the length from the end of M
2 to end of CuA
1. The base of halter is pale, the apex of halter light brown with brownish black hairs.
Abdomen. First and 2nd terga brown, 3rd to 7th terga dark brown with basal 1/3 brown, 8th tergum dark brown; sterna pale; abdomen with brownish black hairs. Male genitalia (
Figure 6B–E) brown with basal 2/3 hypandrium pale. Epandrium trapeziform, posterior margin concave, with several brown hairs. Cercus triangular, inner margin straight, with several brown hairs; anal cone straight. Gonostylus slightly swollen and notched apically, outer side with a wide triangular lobe folded ventrally, with hairs. Gonocoxal lobe bifurcated, outer gonocoxal lobe transparent, rod-shaped, slightly curved; inner gonocoxal lobe transparent, fusiform, nearly straight, broader than outer gonocoxal lobe. Hypandrium rectangular, twice as long as wide, slightly narrow basally, posterior margin concave, with several brown hairs. Aedeagus slender, curved backward; dorsal paramere with tip bilobed, posterior margin round; dorsal carina clearly visible, tip very point, spike-like.
Female. Body length 6.50–7.50 mm, wing length 7.00–8.00 mm, wing width 2.20–2.50 mm.
Head (
Figure 7A). Compound eyes subholoptic, interocular ridge present; each compound eye divided, callis oculi present; dorsal division separated from ventral division, as large as ventral division; dorsal division with about 20 rows of ommatidia, ommatidia red-orange, larger in diameter, with ommatrichia; ventral division black with ommatrichia. Scape and pedicel oval, light brown with brownish black hairs; first flagellomere constricted at base, widening at apex, basal 1/2 pale, apical 1/2 brownish black, with brownish-black hairs; other flagellomeres cylindrical, tapering apically, brownish black with brownish black hairs; ultimate flagellomere 1.72 times length of penultimate flagellomere. Labrum dark brown; labellum brownish yellow with brownish black hairs; mandible brownish yellow; proboscis about 0.81 times length of head width. Palpus with five segments, 1st segment almost invisible, yellow with brownish black hairs; 2nd to 4th segments cylindrical, yellow with brownish black hairs; 5th segment slender, cylindrical, yellow with brownish black hairs; relative length of distal four segments as 1.1:1.0:1.3:2.6. Tibial spurs 0–0–2. Terminalia (
Figure 7B): 8th sternite approximately trapezoidal, bilobate posteriorly, medial depression M-shaped, with six hairs laterally; genital fork X-shaped; hypogynial plate broad basally, bilobate posteriorly, with round bulge laterally, each lobe round apically, intervalvular area V-shaped, with short hairs posteriorly; epiproct conical with two prominent hairs apically; spermathecae three in number.
Distribution. Currently known only from China (Xinjiang).
Etymology. The specific name refers to the type locality Dushanzi.
Remarks. This new species is very similar to
B. indica from Afghanistan, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and India but can be separated by the dorsal division being contiguous with ventral division and being about 1/3 of ventral division, the gonostylus being broad and distinctly notched apically, the dorsal paramere with tip bilobed, and the dorsal carina with tip very point, spike-like. In
B. indica, the dorsal division is separated from ventral division by a distinct suture and is as large as ventral division, the gonostylus is distinctly slender and not distinctly notched apically, the tip of the dorsal paramere is not bilobed, and the dorsal carina is simple finger-like [
13]. This new species is also similar to
B. asiatica from Russia, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and India, but it can be separated from the latter by the brown scutellum, the pale sterna of the abdomen, and the dorsal paramere with tip bilobed. In
B. asiatica, the scutellum is dark brown, the sterna of the abdomen are dark brown, and the dorsal paramere is not bilobed [
13].
3.2.3. Blepharicera nigra sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:D15D6F7C-8381-4EFF-93FE-B5F5F857F2DC
Type material. Holotype: male (CAU), China: Yunnan Province, Gejiu County, Lvshuihe Forest Park (505m), 2019.III.30, Liang Wang. Paratypes: 8 males & 10 females (QAU), same data as holotype; 5 males & 6 females (QAU), China: Yunnan Province, Gejiu County, Lvshuihe Forest Park (505m), 2019. III.30, Xin Li.
Diagnosis. Compound eye with dorsal division 1/20 of ventral division in male. Mesonotum brownish black. Scutellum brownish black. Mesopleuron mostly dark brown, except katepimeron light brown. Rs 1.2 times as long as r-m. Gonostylus slightly swollen and notched deeply at tip. Dorsal paramere with tip U-shaped; dorsal carina with tip round and blunt. Medial depression of 8th sternite U-shaped in female. Genital fork X-shaped in female.
Description. Male. Body length 4.25–4.50 mm; wing length 4.00–4.30 mm, width 1.50–1.60 mm.
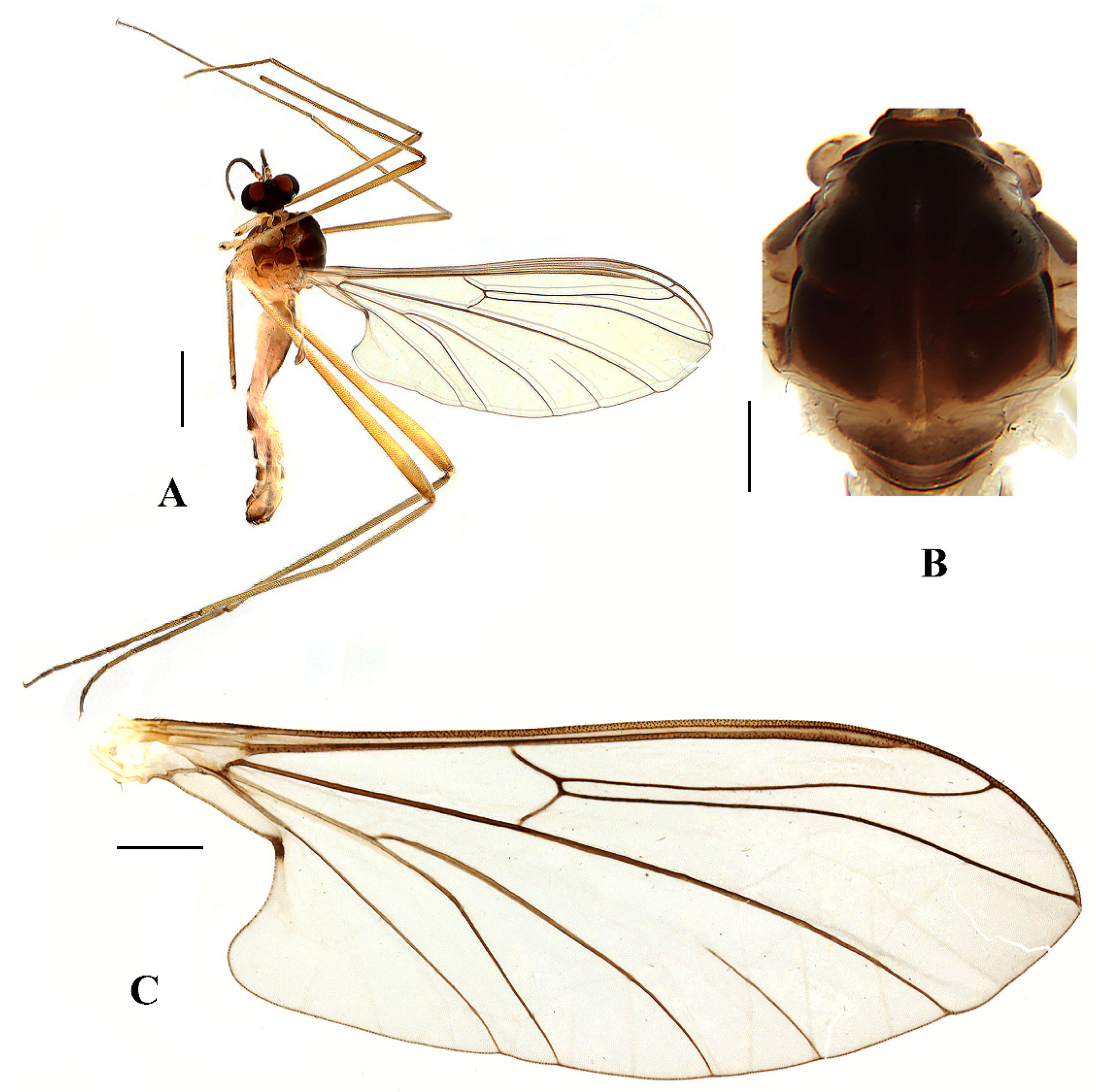
Head (
Figure 8A and
Figure 9A) uniformly black with black hairs. Compound eyes dichoptic, interocular ridge absent; each compound eye divided, callis oculi absent; dorsal division contiguous with ventral division, 1/20 of ventral division; dorsal division with 6–7 rows of ommatidia, ommatidia brownish yellow, larger in diameter, with ommatrichia; ventral division black with ommatrichia. Ocelli brownish yellow. Scape and pedicel oval, black with black hairs; first flagellomere constricted at base, widening at apex, basal 1/2 brownish yellow, apical 1/2 brownish black, with black hairs; other flagellomeres cylindrical, brownish black with brownish black hairs; ultimate flagellomere 1.5 times length of penultimate flagellomere. Clypeus nearly rectangular, brownish black, twice as long as wide; labrum brownish yellow; labellum brownish yellow with brownish black hairs; proboscis about 0.52 times the length of head width. Palpus with five segments, 1st segment almost invisible; 2nd and 3rd segments cylindrical, brownish black with black hairs; 4th segment cylindrical, slightly swollen apically, brownish black with black hairs; 5th segment slender, brownish yellow with brownish black hairs; relative length of distal four segments as 1.0: 0.8: 1.0: 2.3.
Thorax (
Figure 8B). Pronotum and propleuron brownish black without hairs. Mesonotum brownish black; scutellum brownish black with numerous hairs grouped at the posterolateral corner; metanotum brownish black; mesopleuron mostly brownish black, except katepimeron light brown. The relative length of the femur, tibiae, and 1st to 5th tarsomeres in the fore leg as 11:9.2:6.7:2.9:2:0.8:1, in mid leg as 12.5:9.5:6.5:2.3:2:0.8:1, in hind leg as 16.7:14.6:6.1:2:1.4:0.9:1. Fore coxa dark brown with brownish black hairs; mid coxa with an appendage, pale with brownish black hairs; hind coxa pale with brownish black hairs; trochanters pale, anterior margin with black spot apically, with brownish-black hairs; fore and mid femora brownish yellow basally and gradually darkened apically, with brownish-black hairs; hind femur yellowish brown basally, the middle area gradually darkened to dark brown and gradually lightened to brown apically, with brownish-black hairs; fore and mid tibiae dark brown with brownish black hairs; hind tibia brown with brownish black hairs; tarsomeres dark brown with brownish black hairs, hind tarsomere with a black long hair basally; claw brown. Tibial spurs 0–0–0. Wing (
Figure 8C) slightly brown apically, sc brown; veins brown. Sc rudimentary, not ending at the base of Rs; Rs slightly curved basally, 1.2 times as long as r-m; R
4 wavy, the length from the end of R
1 to end of R
4 shorter than the length from the end of R
4 to end of R
5; r-m straight, included angle between r-m and Rs less than 90 degrees; the length from the end of M
1 to end of M
2 as long as the length from the end of M
2 to end of CuA
1. The base of halter is pale, the apex of halter brownish black, with brownish-black hairs.
Abdomen. First tergum brownish black with middle area pale, 2nd tergum brownish black, 3rd to 5th terga brownish black with basal 1/3 pale, 6th to 8th terga brownish black; 1st to 5th sterna brownish black with basal 1/3 pale, 6th and 7th terga brownish black; abdomen with brownish black hairs. Male genitalia (
Figure 9B–E) brownish black. Epandrium trapeziform, posterior margin concave, with several brownish-black hairs. Cercus triangular, inner margin bulge, with several brownish-black hairs; anal cone round. Gonostylus slightly swollen and notched deeply at the tip, outer side with a wide triangular lobe folded ventrally, with hairs. Gonocoxal lobe bifurcated, outer gonocoxal lobe transparent, rod-shaped and curved, round apically; inner gonocoxal lobe transparent, rod-shaped, slightly curved, point apically. Hypandrium rectangular, twice as long as wide, slightly narrow basally, posterior margin concave, with several brownish-black hairs. Aedeagus slender, curved backward; dorsal paramere with tip U-shaped, posterior margin round; dorsal carina clearly visible, tip round and blunt.
Female. Body length 4.50–6.00 mm, wing length 5.00–7.50 mm, wing width 1.80–2.20 mm.
Head (
Figure 10A). Compound eyes subholoptic, interocular ridge present; each compound eye divided, callis oculi present; dorsal division separated from ventral division, as large as ventral division; dorsal division with about 14 rows of ommatidia, ommatidia red-orange, larger in diameter, with ommatrichia; ventral division black with ommatrichia. Scape oval, black with black hairs; pedicel cylindrical, black with black hairs; first flagellomere cylindrical, constricted at base, brownish black with basal 1/5 brown, with black hairs; other flagellomeres cylindrical, tapering apically, brownish black with black hairs; ultimate flagellomere twice length of penultimate flagellomere. Labrum brownish black; labellum pale with brownish black hairs; mandible present, brownish yellow; proboscis about 0.73 times length of head width. Palpus with five segments, 1st segment almost invisible, brown with brownish black hairs; 2nd to 5th segments cylindrical, brownish black with brownish black hairs; relative length of distal four segments as 1.0:1.2:1.2:1.6. Tibial spurs 0–0–2. Terminalia (
Figure 10B): 8th sternite approximately trapezoidal, bilobate posteriorly, medial depression U-shaped, with several hairs laterally; genital fork X-shaped; hypogynial plate broad basally, bilobate posteriorly, each lobe round apically, intervalvular area U-shaped, with short hairs posteriorly; epiproct round with two prominent hairs apically; spermathecae three in number.
Distribution. Currently known only from China (Yunnan).
Etymology. The specific name is from Latin nigia (adjective, feminine, meaning black), referring to the body color mostly being brownish black to black.
Remarks. This new species is very similar to
B. japonica (Kitakami, 1931) from Japan but can be separated by the mandible being present in females, the mid coxa with an appendage, the mid trochanter is not modified, and the dorsal paramere with a tip U-shaped medially. In
B. japonica, the mandible is absent in females, the mid coxa has no appendage, the mid trochanter is modified, and the tip of the dorsal paramere is vestigial arrow-head-pattern [
13,
36]. This new species is also similar to
B. parva Zwick
et Arefina, 2005 from the Russian Far East but can be separated by the cercus being tapered posteriorly, the gonostylus being notched deeply at the tip but not bifurcated, and the rod-shaped inner gonocoxal lobe. In
B. parva, the cercus is round, the gonostylus is deeply bifurcated, and the inner gonocoxal lobe is blade-like [
37].
3.2.4. Blepharicera xinjiangica sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:218C6007-4FAC-4190-AE45-BBF36A78EB00
Type material. Holotype: male (CAU), China: Xinjiang Autonomous Region, Dushanzi district, Duku Highway (44°5’36’’ N 84°44’59’’ E, 1397 m), 2017.VII.25, Jinlong Ren. Paratypes: 5 males (QAU), same data as holotype; 1 male & 2 females (QAU), China: Xinjiang Autonomous Region, Zhaosu County, Qiongbola Forest Park (43°26’3’’ N 81°1’13’’ E, 1976 m), 2017.VII.30, Bing Zhang; 2 females (QAU), China: Xinjiang Autonomous Region, Emin County, Hudie Valley (46°56’38’’ N 84°40’38’’ E, 1457 m), 2017.VIII.2, Bing Zhang.
Diagnosis. Compound eye with dorsal division 1/3 of ventral division in male. Mesonotum dark brown with posterior margin yellow, posterior 1/2 with the extensive light brown middle area, and a brownish yellow narrow median stripe. Scutellum light brown with anterior 1/3 yellow. Episternum light brown; epimeron yellow. Rs longer than r-m. Gonostylus slightly swollen and notched apically. Dorsal paramere with tip arrowhead-shaped; dorsal carina clearly visible, tip point. Medial depression of 8th sternite M-shaped in female. Genital fork X-shaped in female.
Description. Male. Body length 4.50–6.00 mm; wing length 5.00–6.50 mm, width 2.00–2.20 mm.
Head (
Figure 11A and
Figure 12A) uniformly brownish black with black hairs. Compound eyes dichoptic, interocular ridge absent; each compound eye divided, callis oculi absent; dorsal division contiguous with ventral division, 1/3 of ventral division; dorsal division with 18–20 rows of ommatidia, ommatidia red-orange, larger in diameter, with ommatrichia; ventral division black with ommatrichia. Ocelli brownish black. Scape and pedicel oval, light brown with brownish black hairs; first flagellomere constricted at base, widening at apex, basal 1/2 pale, apical 1/2 dark brown, with brownish-black hairs; other flagellomeres cylindrical, dark brown with brownish black hairs; ultimate flagellomere 1.3 times length of penultimate flagellomere. Clypeus rectangular, dark brown, as long as wide; labrum brownish yellow; labellum brownish yellow with brown hairs; proboscis about 0.57 times the length of head width. Palpus with five segments, 1st segment almost invisible; 2nd and 3rd segments cylindrical, yellow with brownish black hairs; 4th segment cylindrical, slightly swollen apically, brownish yellow with brownish black hairs; 5th segment slender, brownish yellow with brownish black hairs; relative length of distal four segments as 1.0:1.0:1.1:2.6.
Thorax (
Figure 11B). Pronotum and propleuron brown without hairs. Mesonotum dark brown with posterior margin yellow, posterior 1/2 with the extensive light brown middle area and a brownish yellow narrow median stripe; scutellum light brown with anterior 1/3 yellow, numerous hairs grouped at posterolateral corner of scutellum; metanotum light brown; episternum light brown; epimeron yellow. The relative length of the femur, tibiae, and 1st to 5th tarsomeres in fore leg as 16:11:8:4:2.5:1:1, in mid leg as 14:10.8:6.5:3:1.8:1:1, in hind leg as 15.7:12.7:5:1.3:1:0.7:1. Fore coxa pale with basal 1/2 light brown, with light brown hairs; mid coxa with an appendage, pale with brownish black hairs; hind coxa pale with brownish black hairs; trochanters pale, anterior margin with black spot apically, with brownish-black hairs; femora brownish yellow with light brown ring apically, with brownish-black hairs; tibiae brownish yellow with brownish black hairs; tarsomeres brownish yellow with brownish black hairs; claw brownish yellow. Tibial spurs 0–0–0. Wing (
Figure 11C) slightly brown apically, sc light brown; veins brown. Sc rudimentary, not ending at the base of Rs; Rs slightly curved basally, longer than r-m; R
4 wavy, the length from the end of R
1 to end of R
4 shorter than the length from the end of R
4 to end of R
5; r-m straight, included angle between r-m and Rs less than 90 degrees; the length from the end of M
1 to end of M
2 longer than the length from the end of M
2 to end of CuA
1. The base of halter is pale, the apex of halter light brown with brownish black hairs.
Abdomen. First tergum brown with middle area pale, 2nd to 6th terga brown with basal 1/3 light brown, 7th and 8th terga brown; sterna pale; abdomen with brownish black hairs. Male genitalia (
Figure 12B–E) brown with basal 1/3 hypandrium pale. Epandrium rectangular, with several brown hairs. Cercus triangular, inner margin slightly bulge, with several brown hairs; anal cone straight. Gonostylus slightly swollen and notched apically, outer side with a wide triangular lobe folded ventrally, with hairs. Gonocoxal lobe bifurcated, outer gonocoxal lobe transparent, rod-shaped, slightly curved; inner gonocoxal lobe transparent, fusiform, slightly curved, broader than outer gonocoxal lobe. Hypandrium rectangular, twice as long as wide, slightly narrow basally, posterior margin concave, with several brown hairs. Aedeagus slender, curved backward; dorsal paramere with tip arrowhead-shaped and posterior margin round; dorsal carina clearly visible, tip point.
Female. Body length 6.00–7.00 mm, wing length 7.00–7.50 mm, wing width 2.25–2.50 mm.
Head (
Figure 13A). Compound eyes subholoptic, interocular ridge present; each compound eye divided, callis oculi present; dorsal division separated from ventral division, as large as ventral division; dorsal division with about 20 rows of ommatidia, ommatidia red-orange, larger in diameter, with ommatrichia; ventral division black with ommatrichia. Scape and pedicel oval, light brown with brownish black hairs; first flagellomere constricted at base, widening at apex, basal 1/2 pale, apical 1/2 brownish black, with brownish-black hairs; other flagellomeres cylindrical, tapering apically, brownish black with brownish black hairs; ultimate flagellomere 1.54 times length of penultimate flagellomere. Labrum brown; labellum brownish yellow with brownish black hairs; mandible brownish yellow; proboscis about 0.86 times length of head width. Palpus with five segments, 1st segment almost invisible, yellow with brownish black hairs; 2nd to 4th segments cylindrical, yellow with brownish black hairs; 5th segment slender, cylindrical, yellow with brownish black hairs; relative length of distal four segments as 1.0:0.8:1.0:2.2. Tibial spurs 0–0–2. Terminalia (
Figure 13B): 8th sternite approximately trapezoidal, bilobate posteriorly, medial depression M-shaped, with six hairs laterally; genital fork X-shaped; hypogynial plate broad basally, bilobate posteriorly, with triangular bulge laterally, each lobe round apically, intervalvular area V-shaped, with short hairs posteriorly; epiproct conical with two prominent hairs apically; spermathecae three in number.
Distribution. Currently known only from China (Xinjiang).
Etymology. The specific name refers to the type locality Xinjiang.
Remarks. This new species is very similar to
B. asiatica from Russia, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and India, but it can be separated from the latter by the mesonotum being dark brown with a yellow posterior margin, extensive light brown middle area at the posterior 1/2 and a brownish yellow narrow median stripe, the scutellum being light brown with yellow anterior 1/3, the pale sterna of the abdomen, the dorsal paramere with tip arrowhead-shaped, and the dorsal carina being not very pointed and not downcurved. In
B. asiatica, the mesonotum and scutellum are dark brown, the sterna of the abdomen are dark brown, the tip of the dorsal paramere is conical, and the dorsal carina has a very pointed and downcurved tip that is almost parallel to plate sometimes [
13]. This new species is also very similar to
B. balangshana Zhang
et Kang, 2022 from China but can be separated by the dorsal division being 1/3 of ventral division, the inner gonocoxal lobe being fusiform and the dorsal carina being clearly visible with point tip. In
B. balangshana, the dorsal division is as large as the ventral division, the inner gonocoxal lobe is rod-shaped, and the dorsal carina has a perpendicular tip [
13].
3.2.5. Keys to Chinese Blepharicera Species
1. Dorsal division of compound eye large, at least 1/3 of ventral division (
Figure 6A and
Figure 12A) ... 2
-Dorsal division of compound eye small, at most 1/10 of ventral division (
Figure 3A and
Figure 9A) ... 7
2. Gonostylus bifurcated … 3
3. Ultimate flagellomere shorter than penultimate flagellomere; Rs 1.5 times as long as r-m; ventral branch of gonostylus glabrous [
15] ...
B. taiwanica (Kitakami, 1937)
-Ultimate flagellomere longer than penultimate flagellomere; Rs as long as or slightly longer than r-m; ventral branch of gonostylus with two tufts of short dense setae [
18] ...
B. macropyga Zwick, 1990
4. Epandrium semicircular; cercus semi-elliptical; gonostylus with a semicircular inside lobe near base [
18] ...
B. hainana Kang
et Yang, 2014
-Epandrium trapeziform or rectangular; cercus triangular; gonostylus without a semicircular inside lobe near base … 5
5. Dorsal division of compound eye as large as ventral division; inner gonocoxal lobe rod-shaped ... B. balangshana Zhang et Kang, 2022
-Dorsal division of compound eye 1/3 of ventral division; inner gonocoxal lobe fusiform … 6
6. Wing with Rs slightly shorter than r-m (Figure 5C); mesonotum brownish black with a brownish yellow median stripe at posterior 1/2; scutellum uniformly brown; epandrium trapeziform (Figure 5B); dorsal paramere with tip bilobed (Figure 6D); dorsal carina with tip very point, spike-like (Figure 6E) … B. dushanzica sp. nov.
-Wing with Rs longer than r-m (
Figure 11C); mesonotum dark brown with posterior margin yellow, posterior 1/2 with the extensive light brown middle area and a brownish yellow narrow median stripe; scutellum light brown with anterior 1/3 yellow (
Figure 11B); epandrium rectangular; dorsal paramere with tip arrowhead-shaped (
Figure 12D); dorsal carina with the tip not very pointed (
Figure 12E) …
B. xinjiangica sp. nov.-Cercus semicircular or semi-elliptical ... 13
8. Outer gonocoxal lobe straight ... 9
-Outer gonocoxal lobe S-shaped ... 12
9. Abdomen with second to 7th sterna uniformly dark brown; dorsal carina pointed and downcurved [
13] …
B.
asiatica (Brodsky, 1930)
-Abdomen with second to 7th sterna with the basal or middle pale area; dorsal carina flat or round … 10
10. Body length 3.00–4.00 mm; wing with Rs as long as r-m [
20] …
B. xizangica Kang, Zhang
et Yang, 2022
-Body length 4.00–5.00 mm; wing with Rs longer than r-m … 11
11. Wing with Rs 1.5 times as long as r-m (Figure 2C); dorsal paramere with tip arrowhead-shaped (Figure 3D) … B. beishanica sp. nov.
-Wing with Rs 1.2 times as long as r-m (
Figure 8C); dorsal paramere with tip U-shaped (
Figure 9D) …
B. nigra sp. nov.12. Ultimate flagellomere shorter than penultimate flagellomere; dorsal branch of gonostylus broader than ventral branch; inner gonocoxal lobe fusiform; dorsal carina subtle ... B. kongsica Zhang et Kang, 2022
-Ultimate flagellomere longer than penultimate flagellomere; dorsal branch of gonostylus as broad as ventral branch; inner gonocoxal lobe digitiform; dorsal carina clearly visible ... B. gengdica Zhang et Kang, 2022
13. Mid coxa with a conical projection, conical projection about half as long as trochanter and densely with stiff black bristles towards tip [
16] ...
B. yamasakii (Kitakami, 1950)
-Mid coxa without projection like above ... 14
14. Posterior margin of epandrium not distinctly concaved medially; cercus semicircilar; gonostylus bifurcated and strongly notched apically [
18] ...
B. dimorphops Alexander, 1953
-Posterior margin of epandrium concave medially, V-shaped; cercus semi-elliptical; gonostylus not bifurcated and slightly notched apically [
18] ...
B. hebeiensis Kang
et Yang, 2014
1. Feeler entirely absent; 7th segment without appendage; caudal appendage absent; suckers rather small (Kitakami, 1950: plate V, figure 55) [
16] …
B. yamasakii (Kitakami, 1950)
-A rudimentary posterior feeler present on 4th to 6th abdominal segments; 7th segment with appendage; caudal appendage present; suckers rather large … 2
2. Dorsal integument with densely long and curved whitish hairs (Kitakami, 1937: plate II, figure 18); ventral integument with short setae sparse (Kitakami, 1937: plate II, figure 19); a thoracic spot not fully developed; 1st to 5th abdominal segments with single wart; 7th abdominal segment with a pair of short distally chitinized appendages; caudal appendage short (Kitakami, 1937: plate II, figure 18; Kitakami, 1941: plate I, figure 13) [
15,
38] …
B. taiwanica (Kitakami, 1937)
-Dorsal integument with sparsely setaceous (Kitakami, 1937: plate II, figure 20); ventral integument glabrous (Kitakami, 1937: plate II, figure 21); thoracic spot V-shaped; claws large and elongated; 2nd to 4th abdominal segments with single sharp dorsal thorn; 7th abdominal segment with a pair of elongated strongly chitinized appendages; caudal appendage elongated (Kitakami, 1937: plate II, figure 20) [
15,
38] …
B. uenoi (Kitakami, 1937)