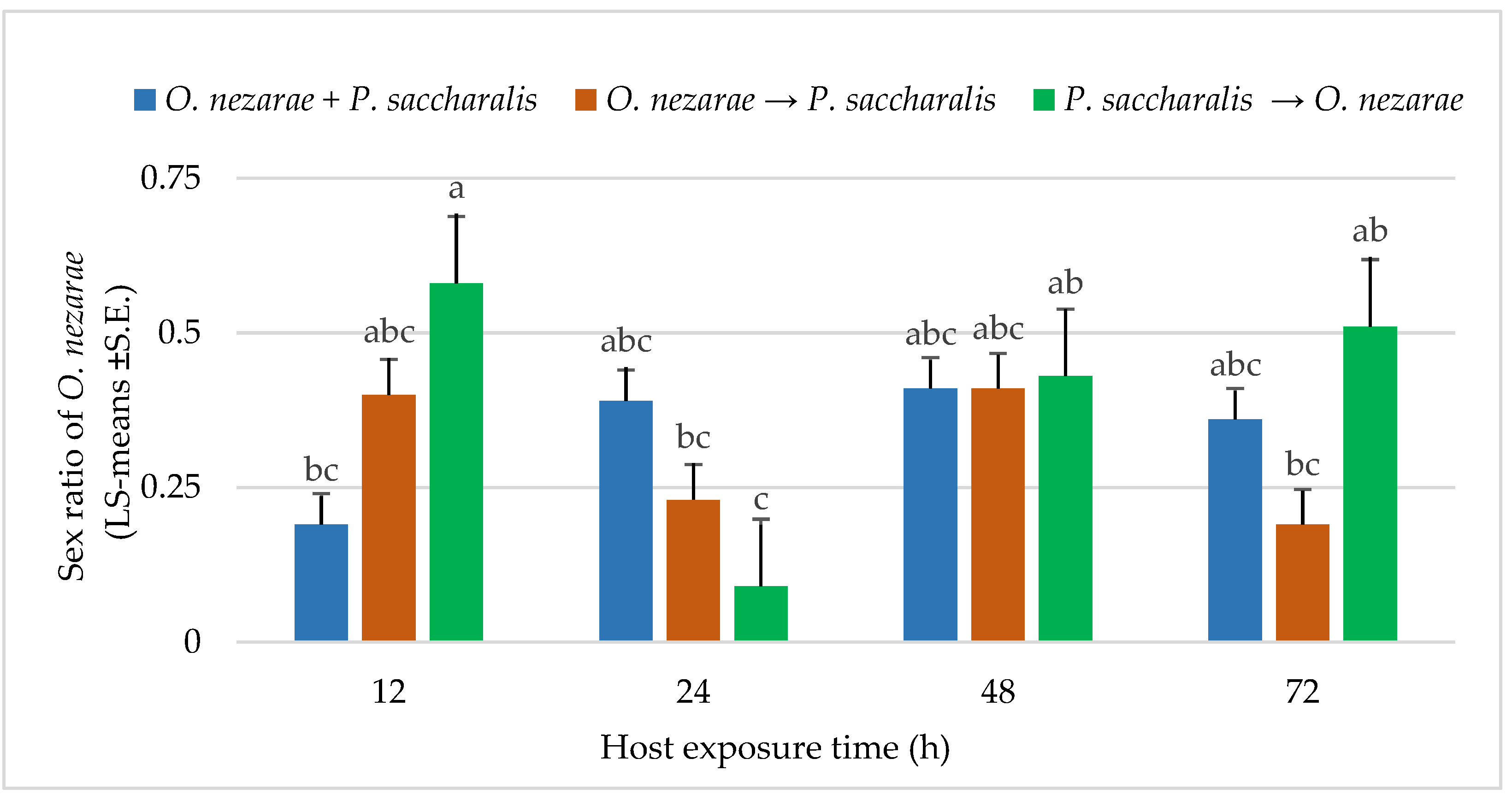Simple Summary
This article studied the interaction between two egg parasitoids, Paratelenomus saccharalis and Ooencyrtus nezarae, of the kudzu bug (Megacopta cribraria). In the laboratory, we focused on how the timing of arrival to host eggs influences egg parasitism, competition, aggressive behaviors of wasps, and intraguild predation of wasp larvae in host eggs. Results showed that interspecific interactions reduced P. saccharalis emergence in the presence of O. nezarae; however, the degree of this effect altered when wasps were released sequentially versus simultaneously and over time. Adults P. saccharalis competed aggressively for the shared host, although O. nezarae larvae outcompeted in multiparasitized eggs. Our results suggest that O. nezarae has the potential to negatively impact the population dynamics of P. saccharalis, which could influence the success of biological control programs targeting the kudzu bug.
Abstract
The present study investigated egg parasitoid interspecific interactions between a generalist, Ooencyrtus nezarae Ishii (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) and a specialist, Paratelenomus saccharalis Dodd (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae) in a laboratory setting using kudzu bug (Megacopta cribraria Fabricius, (Hemiptera: Plataspidae)) eggs as their shared host. Three experiments were conducted to evaluate the emergence of wasps from parasitized hosts after the simultaneous and sequential release of wasps, monitor aggressive behavior of P. saccharalis, and quantify intraguild predation of O. nezarae larvae on heterospecific P. saccharalis larvae. Results showed that total host egg parasitism was higher when both wasps were released simultaneously than if wasps were released sequentially. Ooencyrtus nezarae produced more total offspring than P. saccharalis in all sequential/simultaneous treatments but produced male offspring in most cases. In the aggressive behavioral experiment, specialist, P. saccharalis used head butting to fight O. nezarae, but no other aggressions were observed. In an experiment examining intraguild predation, O. nezarae was able to develop in host eggs parasitized by P. saccharalis four days earlier, acting as a superior larval competitor. These findings shed light on the potential interspecific interactions between O. nezarae and P. saccharalis, which may determine their relative abundance and influence their compatibility in kudzu bug biological control programs.
1. Introduction
Adult female parasitoid wasps deposit their eggs in or on the body surface of other arthropods, which act as the host for developing larvae [1]. In general, parasitoids oviposit on an immature stage of the host, e.g., egg(s), larva(e), or pupa(e). The host is then consumed by the developing parasitoid larva(e) [1]. Parasitoid species may rely on shared common resources (e.g., host species); thus, interactions among these parasitoid species can occur frequently [2,3,4,5,6]. Researchers have debated whether the occurrence of multiple parasitoids has a beneficial or antagonistic effect on pest suppression in agricultural systems. According to some studies, multiple parasitoids might work in tandem to greatly reduce pest populations through direct competition [7,8]. Other research has shown that competition among parasitoids may impair pest suppression and disrupt biological control through indirect competition or intraguild predation of larvae [9,10]. Understanding the interspecific competition between multiple parasitoids in relation to their shared host(s) is critical to determining the efficacy of biological control programs [11,12].
Parasitoids do not immediately remove prey from the habitat like predators, and intact hosts can still be exploited by conspecific or interspecific competitors which may result in indirect competition [13]. The outcome of parasitoid competition can be characterized as direct or indirect [14]. Direct competition involves interaction between two or more individuals that utilize the same resource. Direct competition can occur when adult parasitoids search and compete for the same host resource or among immatures that develop on/in the same host (i.e. superparasitism or multiparasitism) [1,13,14,15,16]. An adult female’s direct competition with a conspecific/heterospecific female can be lethal if she engages in fighting behaviors for egg mass (patch) ownership [17]. The intensity of agonistic behaviors has been shown to escalate in specialist parasitoids because resources are limited as compared to generalists [18]. For immature parasitoids, the presence of more than one larva in a host may alter host quality, quantity, and modify the successful emergence rate of the wasp by leading to the death of the weaker competitor, or increase variability in body size among competitors [13]. As a result, the deposition of eggs in or on a parasitized host generally reduces the fecundity of ensuing adults. Dorn and Beckage [19] reported that the number of emerging adults decreases as the number of immature individuals in the host increases. This phenomenon occurs commonly in solitary parasitoids where only one larva can develop inside the host [20]. Despite this, it has been observed that parasitoids with a broad host range (i.e., generalist species) are typically more likely to exploit already parasitized hosts [21,22]. Host quality can also impact sex ratios. According to local mate competition (LMC) theory, when high-quality hosts are limited, female wasps prefer to oviposit male eggs on poor-quality hosts. In the haplodiploid mating system of parasitoids, female parasitoids produce more males if poor-quality hosts predominate, so multiparasitism and the prospects of poor host quality may result in male-biased sex ratios.
Adult parasitoid competitive success depends on patch allocation time and the decision to invest in the defense of an exploited patch or seek out an unparasitized patch [17]. Many studies have shown that the first parasitoid that oviposits generally outcompetes later individuals of competitor species [16,23]. There are two possible explanations in this case: the established larvae would have (i) consumed most of the nutrition of the host, or (ii) killed eggs or larvae and monopolized the host [1]. Parasitoid larvae may eliminate competitors through physical attack or physiological suppression [16,24]. The first instar larvae of many parasitoids possess large mandibles which may provide them with a competitive advantage over first instars that possess small mandibles [25,26]. Physiological suppression includes toxin secretion, asphyxiation, deprivation of nutrients, and hormonal interference [27]. The order of oviposition and time lag between oviposition events can also influence the competition’s outcome [16,23].
Kudzu bugs, Megacopta cribraria Fabricius (Hemiptera: Plataspidae), and their egg parasitoids can be used as a model host-parasitoid system to evaluate the outcome of interspecific competition. Two parasitoids, a generalist Ooencyrtus nezarae Ishii (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae), and a specialist Paratelenomus saccharalis Dodd (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae), co-occur and parasitize kudzu bug eggs in Southeast Asia and the southeastern United States [28,29,30,31]. Immatures of both parasitoids feed and develop inside of the host eggs [32,33]. Paratelenomus saccharalis is a primary and solitary endoparasitoid of the Plastaspid family [34]. To date, host data of P. saccharalis in the United States has only been reported from M. cribraria eggs. Another potential host of P. saccharalis is Brachyplatys subaeneuus Westwood (Hemiptera: Plataspidae), which was reported in Miami, Florida in 2020 [35]. Ooencyrtus nezarae is a generalist egg parasitoid reported to attack M. cribraria, and pentatomids that occur in Asia, Africa, Australia, and Europe [28,36,37], and in 2016 was first reported in Alabama [38]. Ooencyrtus nezarae is a gregarious parasitoid in eggs of larger hosts, but in eggs of Megacopta spp., it is usually a solitary parasitoid [39]. In their native range of southeast Asia, P. saccharalis and O. nezarae have been reported to parasitize M. cribraria eggs at rates of 100% and 76.9%, respectively [28,29]. In Alabama, P. saccharalis and O. nezarae have been observed parasitizing kudzu bug eggs in the same soybean field with rates ranging from 42–95% and 82.8–100%, respectively [38], but competition between O. nezarae and P. saccharalis has not been studied in this region. During a three-year field study (2018–2020) in central Alabama, the number of P. saccharalis fell sharply. The population of P. saccharalis reached its lowest level near zero throughout the collection period since population monitoring began in 2013 [40]. A decline of P. saccharalis (specialist species) is concerning because this may disrupt the biocontrol of M. cribraria. One potential explanation is the arrival of O. nezarae in 2016 in Alabama [38]. Research is needed to understand how competitive interaction between these two parasitoid species impacts host suppression, and whether competitive interference may disrupt biocontrol.
The present study investigates competitive interaction through a series of experiments. Experiments were conducted to evaluate (i) the outcome of multiparasitism when O. nezarae and P. saccharalis are released simultaneously or sequentially (i.e., emerged wasp vs. host nymph), (ii) larval competition between O. nezarae and P. saccharalis, (iii) behavior of P. saccharalis adults when they directly interact with adult O. nezarae on host patches, and (iv) the outcome and consequences of intraguild predation of larvae. It is hypothesized that multiparasitism will increase larval mortality because the quality of host tissues is reduced in parasitized hosts, and will result in a decrease in fitness of surviving larvae [41]. We also hypothesized that the specialist P. saccharalis adults will win direct competitions against O. nezarae as either the prior owner of the host or the intruder because specialists are more efficient in resource utilization [42] and more likely to be aggressive over limited and valuable resources [43,44,45]. Paratelenomus saccharalis was also expected to outcompete O. nezarae during larval competition due to first instar O. nezarae larvae possessing small mandibles and remaining attached to their respiratory stalks within a host egg, which limits their mobility and ability to defend themselves against Platygastrid larvae that usually have large and sickle-shaped mandibles [8,46,47].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plants
Soybean seeds (var. Pioneer P49T97R-SA2P) were planted into pots (15.24 cm diameter and 14.22 cm depth) in Sunshine potting mixture #8 (SunGro Horticulture, Bellevue, WA, USA) and grown in an incubator free of pests and pesticides at (26 ± 2 °C and 55 ± 5% RH) [30]. Plants were watered daily (~200 mL per pot) and fertilized according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Scotts-Sierra Horticultural Product Company, Marysville, OH, USA) once a week until use for M. cribraria rearing.
2.2. Insect Rearing
A colony of adult kudzu bugs was established by collecting insects from kudzu, Pueraria montana (Lour) Merr., in Auburn, AL (32.5934° N, 85.4952° W) from late March to May 2021. They were reared in ventilated plastic cages (30 cm × 30 cm × 30 cm) (BugDorm-2, Megaview Science Education Services Co., Ltd., Taichung, Taiwan) at 25 ± 1°C, 14:10 h (L:D), and 75 ± 5% RH [30] in a growth chamber (Percival, Perry, IA, USA.) and provided organic green beans and a vegetative-stage (V2-V3) soybean plant, approximately 18 to 27 cm tall, that could easily fit into the cage. New soybean plants were provided every week [30]. Cages were checked every day for fresh eggs (≤24 h) that appeared milky white in appearance as compared to aged eggs (>24 h) that were darker in color. Each experiment used ≤24 h old kudzu bug eggs (24–30 eggs).
Parasitoid species used in these experiments originated from the same kudzu patches in Auburn, AL, as described above. Collected egg masses with parasitized kudzu bug eggs (grey color) [48] were kept in a 59.1 mL portion cup (Dart container corporation, Mason, MI, USA) at 25 ± 1 °C, 14:10 (L:D) h and 75 ± 5% RH [30] until emergence. Parasitoids were identified as O. nezarae or P. saccharalis, based on details given in [38,49]. Both species were separated into different rearing cups (59.1 mL), and colonies were reared by providing adults with a honey solution (70% v/v) and allowing them to oviposit into fresh kudzu bug eggs (≤24 h old). The honey solution was held in a 0.5 mL Eppendorf microcentrifuge tube with a hole in the bottom through which a cotton string was threaded. Another microcentrifuge tube filled with water was placed to control relative humidity in each cup. This tube was perforated above the water line to dissipate moisture vapor throughout the tube to prevent insect desiccation. Approximately 20 holes were made on the cup wall with a pin for aeration and to prevent condensation. Parasitoid rearing cups were maintained at 25 ± 1°C, 14L:10D h, and 75 ± 5% RH in an incubator (Percival, Perry, IA, USA). These same conditions were used for experiments described below.
2.3. Physiological Condition of Insects
In all experiments, one- and four-day-old P. saccharalis and O. nezarae adult, respectively, were used [50,51]. This differential age range was chosen to coincide with each wasp’s reproductive peaks so that optimum reproduction is represented in these experiments. Within one day of emergence (egression of wasps from host eggs), individual O. nezarae wasp females and males were held together for 96 h to ensure mating occurred quickly after emergence [52]. Only female P. saccharalis have emerged from field-collected M. cribraria eggs. We also observed that these emerged P. saccharalis females were able to make offspring without mating. Therefore, in all experiments, we used unmated P. saccharalis females. Both species were fed 70% honey solution and were naïve (never had oviposition experience) before use in the experiments.
2.4. Experiment I: Timing of Adult Arrival at the Competition
This objective investigated the role of species oviposition order, and the time interval between oviposition of heterospecific females, on the outcome of parasitoid emergence. The following three combinations of wasp species introductions were tested at four-time intervals (12, 24, 48, or 72 h) each: (1) Simultaneous release: a P. saccharalis female and an O. nezarae female were released together for the total time interval (P. saccharalis + O. nezarae); (2) Sequential release i: one female P. saccharalis was released first for half of the total time trial, then it was removed and an O. nezarae female was introduced for the remaining half of the time (P. saccharalis → O. nezarae); and (3) Sequential release ii: one female O. nezarae was released first for half of the total time trial, then it was removed, and a P. saccharalis female was introduced for the remaining half of the time (O. nezarae → P. saccharalis). Wasps from all treatments were removed from the experimental arenas (59.1 mL cup with dimensions of top diameter: 6 cm, bottom diameter: 4.4 cm, and height: 2.8 cm) after the time interval was completed. Host eggs exposed to wasps were incubated until offspring emerged as adults. The total number of live offspring was counted for each species, and unhatched or unparasitized eggs of M. cribraria were counted as ‘unascribed’.
For each treatment (order of oviposition × time interval), 20 replications were performed. The minimum exposure (12 h) and host egg density (24–30 kudzu bug eggs per replicate) were chosen based on the previous studies for P. saccharalis [51] and preliminary studies for O. nezarae (unpublished data) that demonstrated both species alone can parasitize at least one egg/h. Increasing host-limitation over extended periods (e.g., 72 h and 24 eggs) would increase the likelihood of interspecific competition.
2.5. Experiment II: Characterizing Aggressive Behavior of Parasitoids
The purpose of this experiment was to record any aggressive behavior of P. saccharalis or O. nezarae when encountering a heterospecific on the same host patch of kudzu bug eggs. One female P. saccharalis and O. nezarae were simultaneously released into a Petri dish (60 mm × 15 mm) with kudzu bug eggs. A total of 20 replications were conducted for this experiment. Their behavior was recorded for 1 h after their release in the experimental arena. This is the time (1 h) necessary for oviposition. However, these behaviors typically begin within the first 4 min (personal observation), and a female was discarded from the trial if she did not show oviposition behavior within 4 min. A handheld video camera mounted on a tripod stand was used to record the parasitoid behavior through a microscope eyepiece (Model no. SZ2-ILST, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan, magnification 5.6×). The number of confrontations were recorded and included wing waving, chasing, head butting, and boxing with forelegs [53].
2.6. Experiment III: Intraguild Predation of Parasitoid Larvae
Intraguild predation of O. nezarae on P. saccharalis was assessed. It was a unidirectional experiment in which O. nezarae was released after P. saccharalis because the former is a generalist species, and it has been observed that species with a broad host range generally act as hyperparasitoids that feed and oviposit on hosts and primary parasitoids [54]. A naïve female P. saccharalis was offered kudzu bug eggs for 24 h, and then removed. After removing P. saccharalis, host eggs were held for 0, 24, 48, 72, or 96 h before exposing them to a mated, naïve female O. nezarae for 24 h to determine larval and pupal predation on P. saccharalis. Eggs exposed to P. saccharalis were held for a maximum of 96 h because it takes 168–192 h for kudzu bug eggs to hatch, the eggs were approximately 168 h old after exposure to O. nezarae. After exposing O. nezarae, host eggs were incubated until the emergence of P. saccharalis and O. nezarae offspring. Twenty replicates were conducted for this experiment.
3. Data and Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted with SAS (Ver. 9.4, SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). Interspecific competitive interaction results from Experiment I were analyzed using a generalized linear mixed model (GLIMMIX) with a normal distribution. The mean proportion of parasitism (parasitized eggs/total eggs), the proportion of kudzu bug nymphs (nymphs/total host eggs), the proportion of wasp offspring (total wasp offspring/total host eggs), and the sex ratio of wasps that emerged from eggs (females/total wasps) were compared among treatments. A two-way ANOVA using a simulated test for mean comparisons was used to analyze the independent variables host exposure time (12, 24, 48, and 72 h) and order of oviposition (O. nezarae + P. saccharalis, O. nezarae → P. saccharalis, and P. saccharalis → O. nezarae).
In Experiment II, the frequency of confrontation was calculated as the number of encounters divided by the length of the period (1 h) per replicate. All frequencies were summed together and then divided by sample size (n = 20) to calculate the average confrontation frequency. We also reported characterized aggressive behaviors including wing waving, chasing, head butting, and boxing with forelegs.
The same parasitism metrics were collected for Experiment III as defined for Experiment I. The independent variables of this experiment were time intervals (0, 24, 48, 72, or 96 h), wasp species (O. nezarae and P. saccharalis), and their interaction. Data were analyzed using a one way-ANOVA in Proc GLIMMIX with a normal distribution and a post hoc mean comparison was performed using the simulated test.
4. Results
4.1. Experiment I: The Timing of Adult Arrival at the Competition
Summary statistics by release order of parasitoids are provided in Table 1. Order of release influenced the host parasitism and strength of interspecific competition, represented by the wasp emergence. The proportion of parasitized eggs was the highest when P. saccharalis arrived earlier or together with O. nezarae. However, the proportion of emerged wasps from parasitized eggs was significantly higher when both competitors arrived simultaneously at the host patch, intermediate when P. saccharalis arrived first, and lowest when O. nezarae arrived before P. saccharalis (for statistics, see Table 1).

Table 1.
The proportion of parasitized host eggs and emerged wasps averaged across treatments in experiments conducted to examine how the order of Ooencyrtus nezarae and/or Paratelenomus saccharalis adult arrival at a Megacopta cribraria egg patch influences competition.
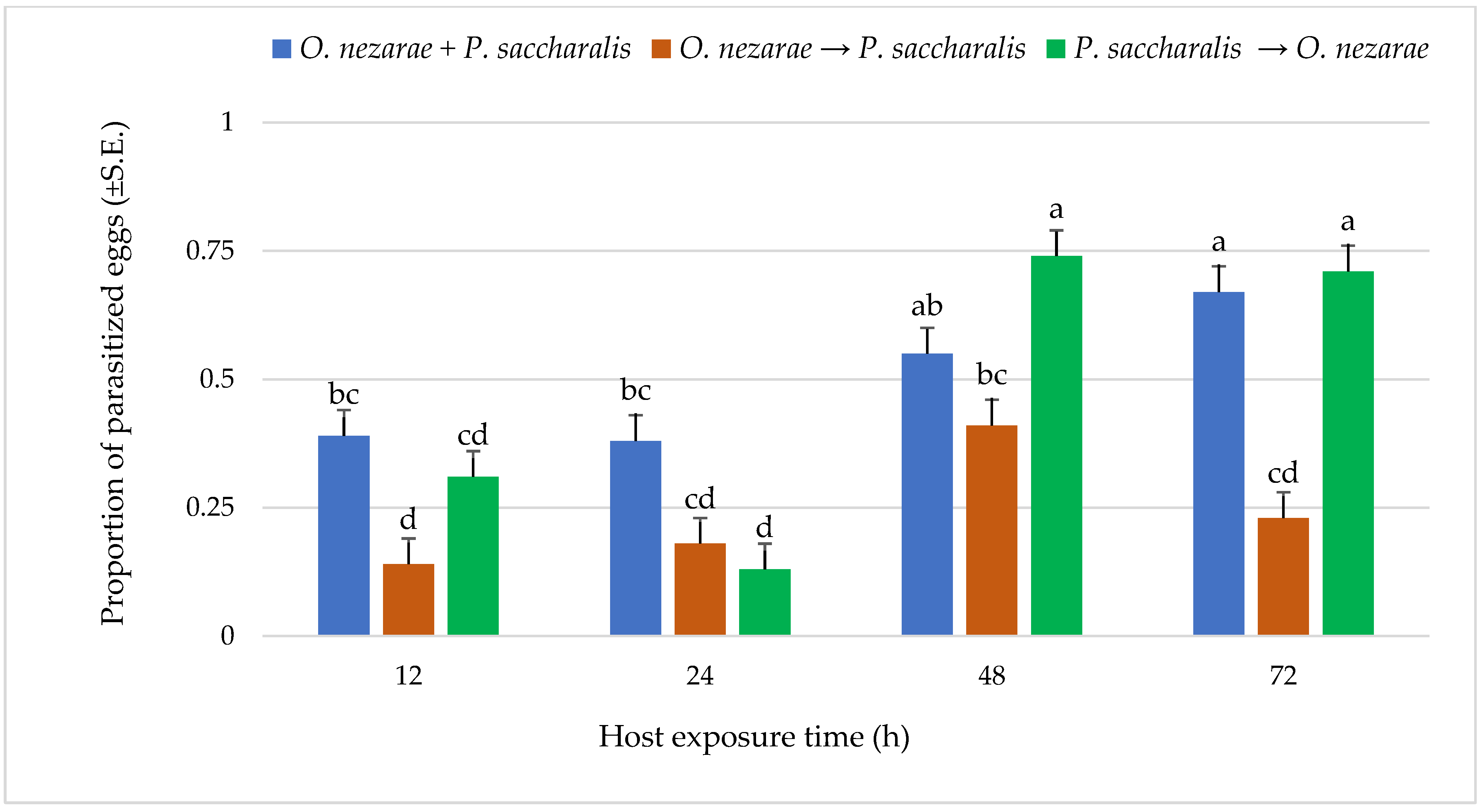
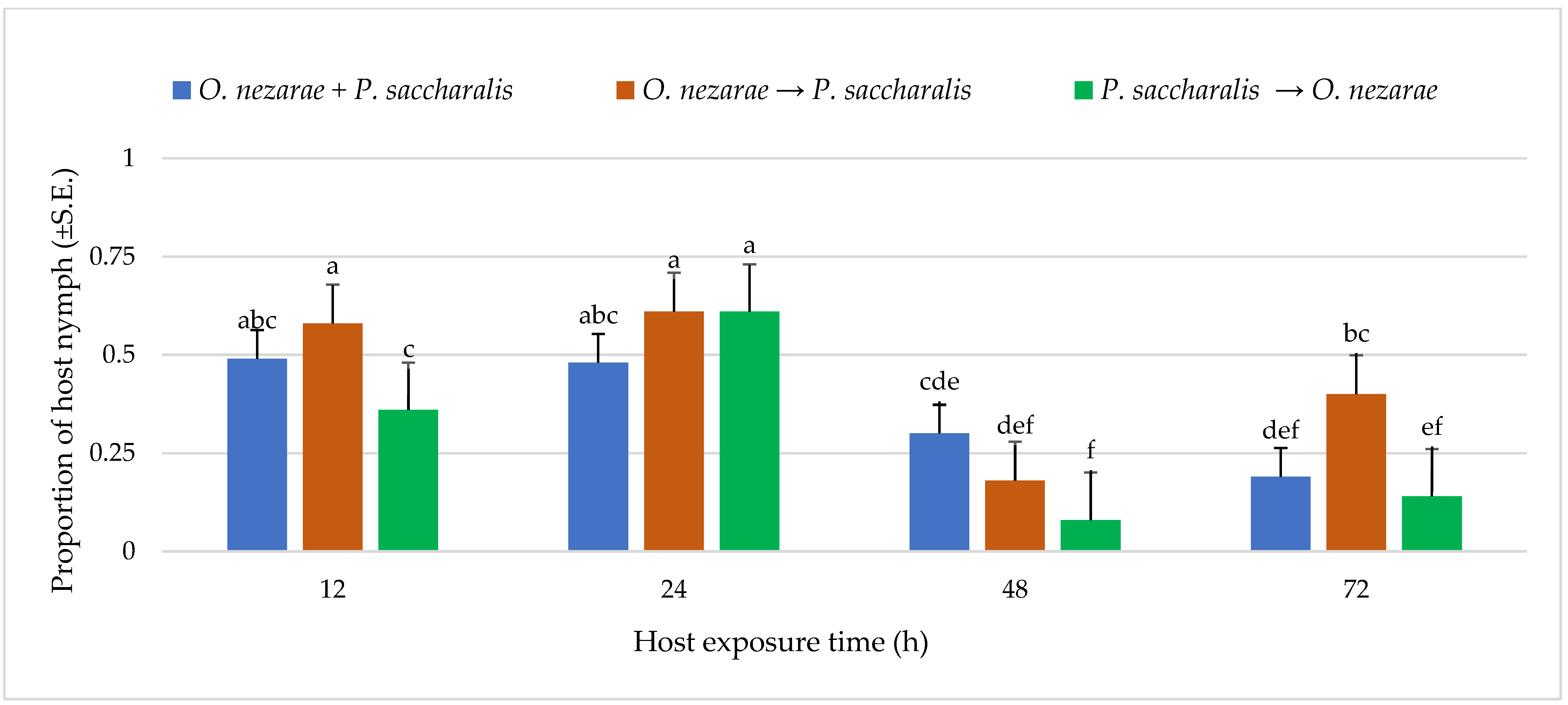
Out of 6147 M. cribraria eggs, a total of 2501 were parasitized. The proportion of parasitized host eggs was affected by the order of the two competitors’ release and the period after they first oviposited (Figure 1). Over the entire experiment, the distribution of parasitoid attack was generally higher with increasing host exposure time, with the exception of O. nezarae to P. saccharalis, indicating that prolonged exposure time provides parasitoids an advantage in parasitizing more host eggs (Figure 1). The increase in parasitism also resulted in a decrease in kudzu bug nymph survival (Figure 2). Interestingly, the host eggs where P. saccharalis first oviposited and were followed by O. nezarae showed higher mortality with longer exposure times (Figure 1).
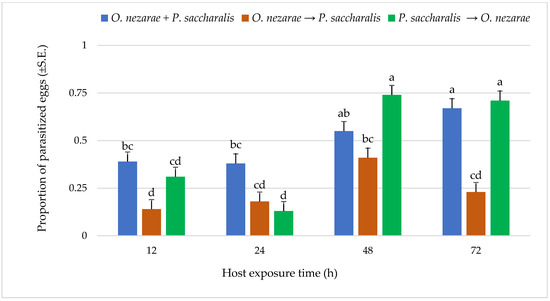
Figure 1.
LS-mean (±S.E) proportion of parasitized Megacopta cribraria eggs under different parasitoid timing x host exposure time conditions. Scenarios examined included simultaneous release of Ooencyrtus nezarae and Paratelenomus saccharalis (O. nezarae + P. saccharalis), sequential release in which O. nezarae was allowed to exploit the host patch first (O. nezarae → P. saccharalis), or sequential release in which P. saccharalis was released first (P. saccharalis → O. nezarae). Data were graphed with two-way ANOVA using simulated multiple comparison test: Release order (F = 31.45, df = 2, 228, p < 0.0001), host exposure time (F = 35.06, df = 3, 228, p < 0.0001) and their interaction (F = 6.86, df = 6, 228, p < 0.0001). Different letters indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05 for the interaction term. (Sample size, n = 20).
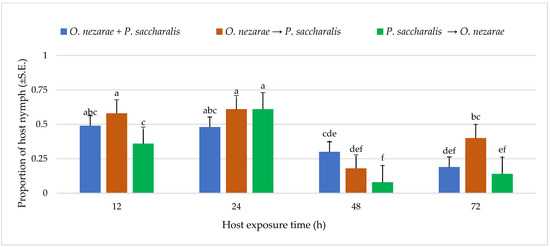
Figure 2.
LS-mean (±S.E) proportion of Megacopta cribraria nymph hatching from eggs in the timing of adult arrival at the competition experiment. Scenarios examined included simultaneous release of Ooencyrtus nezarae and Paratelenomus saccharalis (O. nezarae + P. saccharalis), sequential release in which O. nezarae was allowed to exploit the host patch first (O. nezarae → P. saccharalis), or sequential release in which P. saccharalis was released first (P. saccharalis → O. nezarae). Data were graphed with two-way ANOVA using simulated multiple comparison test: host exposure time (F = 51.35, df = 3, 228, p < 0.0001), release order (F = 11.24, df = 2, 228, p < 0.0001), and their interaction (F = 4.96, df = 6, 228, p < 0.0001). Different letters indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05 for the interaction term. (Sample size, n = 20).
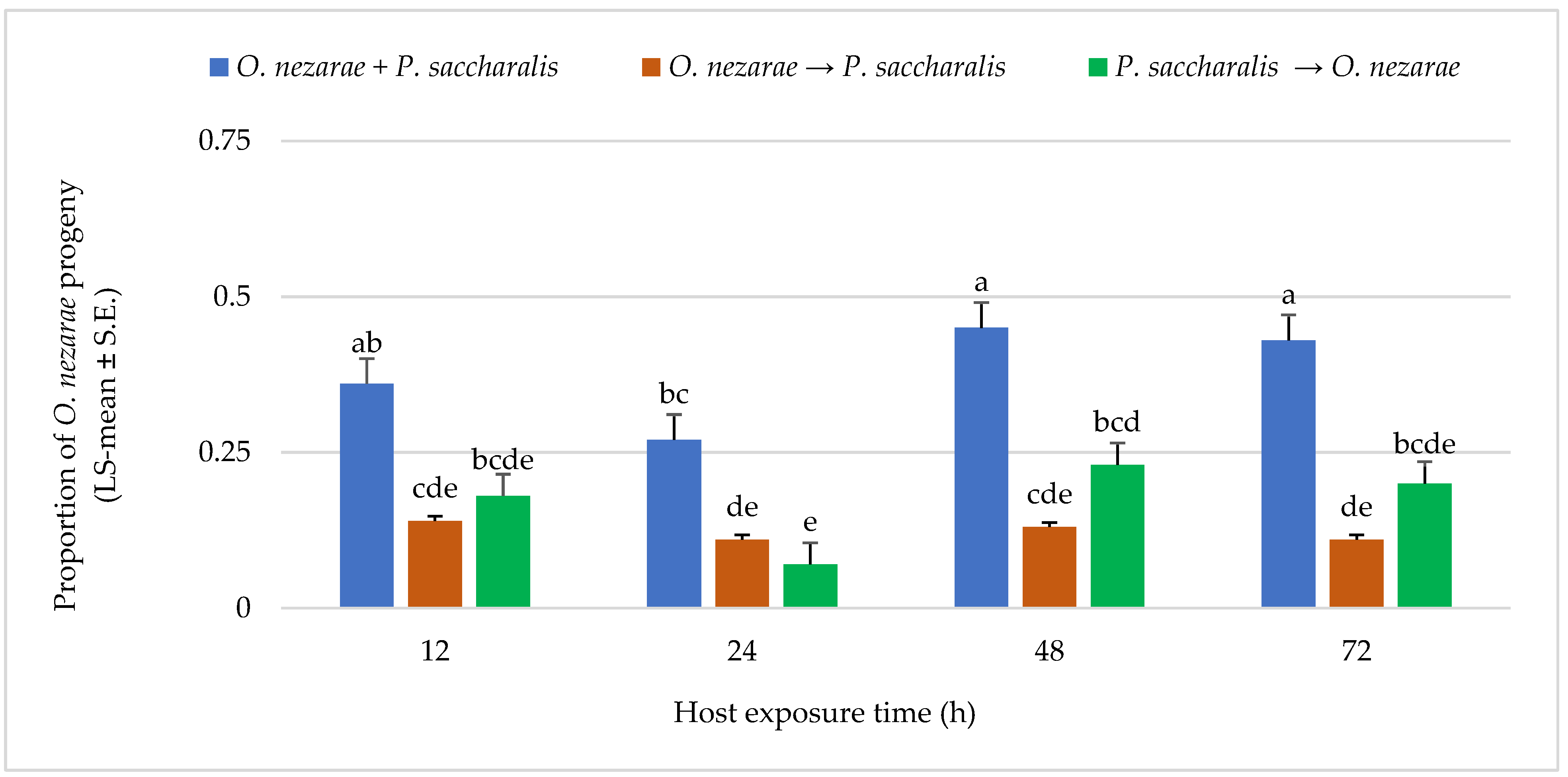
Ooencyrtus nezarae showed differences in its emergence when competing against P. saccharalis. From a total of 1893 parasitoids, O. nezarae yielded an average of 0.74 offspring. The emergence of O. nezarae offspring was higher when their oviposition was simultaneous with P. saccharalis (Figure 3). It is noteworthy that O. nezarae emergence was relatively higher when the host eggs were exposed to both parasitoids for a prolonged period of 48–72 h (Figure 3). In addition, the proportion of O. nezarae offspring was around one-fold higher when O. nezarae arrived second to the host and when there was a delay of more than 12 h between oviposition of P. saccharalis and O. nezarae. It indicated that O. nezarae won almost all competitive events in the parasitized hosts.
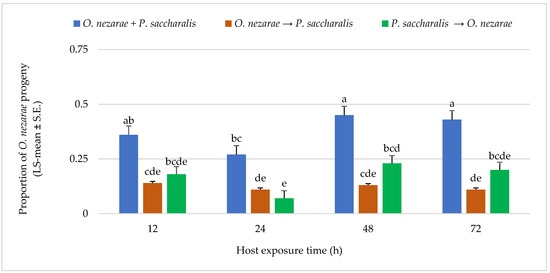
Figure 3.
LS-mean (±S.E) of Ooencyrtus nezarae progeny that emerged from Megacopta cribraria eggs (Sample size, n = 20) in the timing of adult arrival at the competition experiment. Scenarios examined included simultaneous release of O. nezarae and Paratelenomus saccharalis (O. nezarae + P. saccharalis), sequential release in which O. nezarae was allowed to exploit the host patch first (O. nezarae → P. saccharalis), or sequential release in which P. saccharalis was released first (P. saccharalis → O. nezarae). Data were graphed with two-way ANOVA using simulated multiple comparison test: Release order (F = 63.78, df = 2, 228, p < 0.0001), host exposure time (F = 7.51, df = 3, 228, p < 0.0001) and their interaction (F = 1.77, df = 6, 228, p < 0.0001). Different letters indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05 for the interaction term.
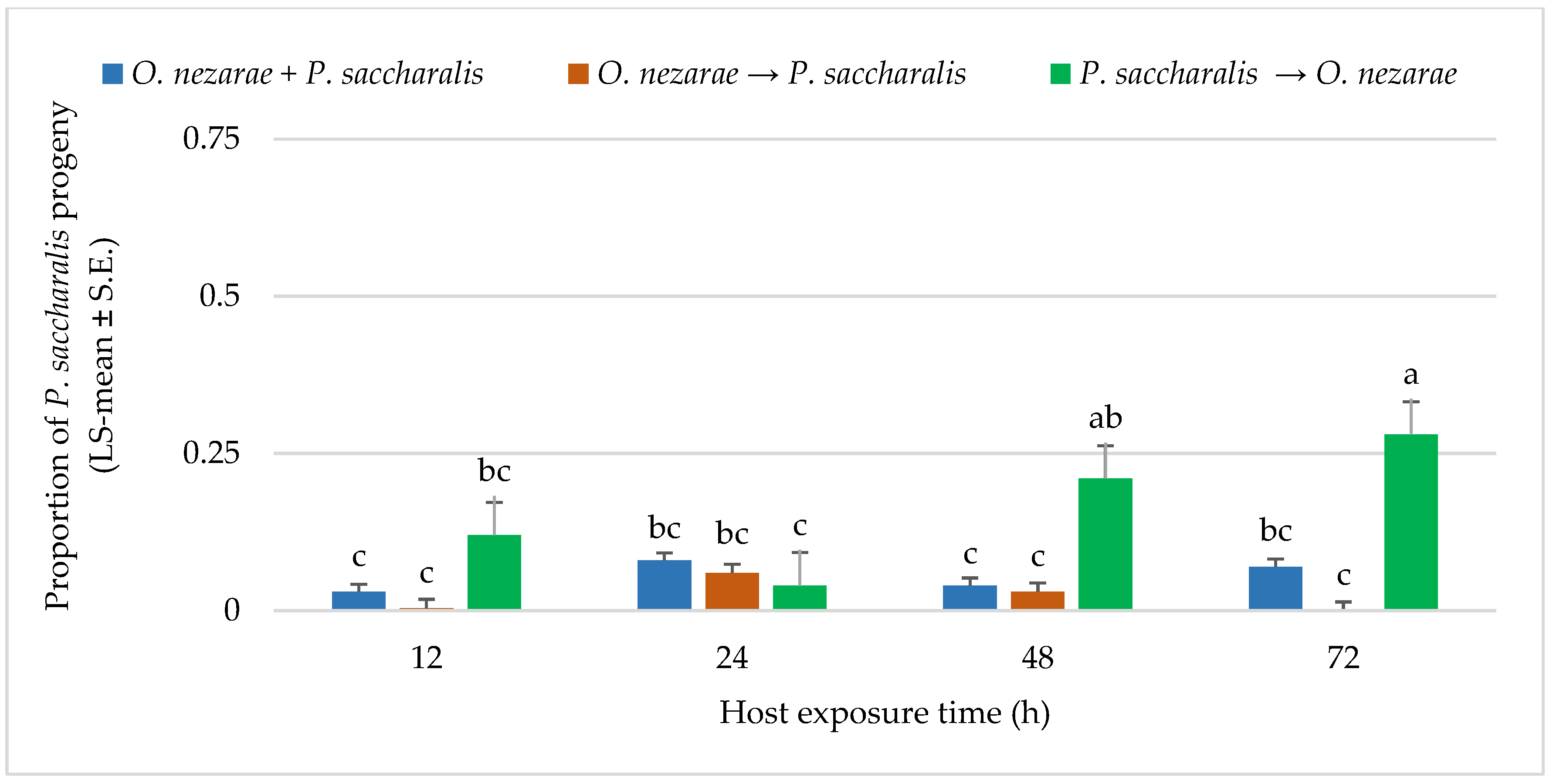
The adult emergence for P. saccharalis was different from O. nezarae. A proportion of 0.26 P. saccharalis emerged from 1893 parasitized host eggs. The interaction between O. nezarae and P. saccharalis was not favorable for P. saccharalis offspring when P. saccharalis arrived at the host patch later or simultaneous with O. nezarae. In most cases, P. saccharalis emergence was highly affected by interference competition when it was introduced later, resulting in P. saccharalis having fewer offspring emergence. It indicates that P. saccharalis accepted a lower number of host eggs previously exposed to O. nezarae at all time points (Figure 4). Emergence of fewer P. saccharalis offspring suggested that P. saccharalis has a competitive disadvantage when it does not have an opportunity to develop to the first instar larva prior to multiparasitism by O. nezarae. A proportion of 0.20 kudzu bug eggs remained unhatched when P. saccharalis and O. nezarae arrived at the host patch together. However, a higher proportion of eggs remained unhatched when competitors arrived in sequence. Ooencyrtus nezarae’s arrival at the host patch first resulted in proportions of unhatched eggs exceeding 0.40 (Supplementary Materials; Table S2), indicating potential feeding behavior on the host.
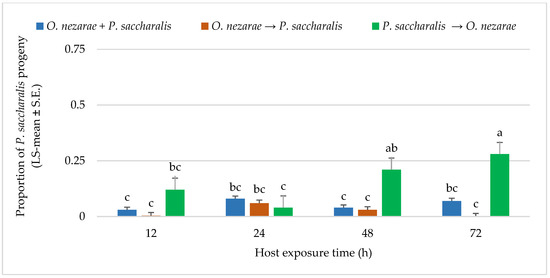
Figure 4.
LS-mean (±SE) of Paratelenomus saccharalis progeny that emerged from Megacopta cribraria eggs (Sample size, n = 20) in the timing of adult arrival at the competition experiment. Scenarios examined included simultaneous release of Ooencyrtus nezarae and P. saccharalis (O. nezarae + P. saccharalis), sequential release in which O. nezarae was allowed to exploit the host patch first (O. nezarae → P. saccharalis), or sequential release in which P. saccharalis was released first (P. saccharalis → O. nezarae). Data were graphed with two-way ANOVA using simulated multiple comparison test: Release order (F = 20.23, df = 2, 228, p < 0.0001), host exposure time (F = 2.68, df = 3, 228, p = 0.047) and their interaction (F = 1.77, df = 6, 228, p = 0.0002). Different letters indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05. for the interaction term.
The proportion of females in O. nezarae offspring emerging from parasitized eggs was correlated with the interaction of the order of parasitism and time interval (for statistics, see below Figure 5). Ooencyrtus nezarae females appeared to adjust the sex allocation of their progeny in response to competition. In most cases, multiparasitism corresponded to the O. nezarae population having a male-biased sex ratio (Figure 5). Even though P. saccharalis only produced female offspring from the field, the number of females in P. saccharalis offspring was higher when P. saccharalis had the opportunity to arrive at the host patch earlier than their competitors (Figure 4).
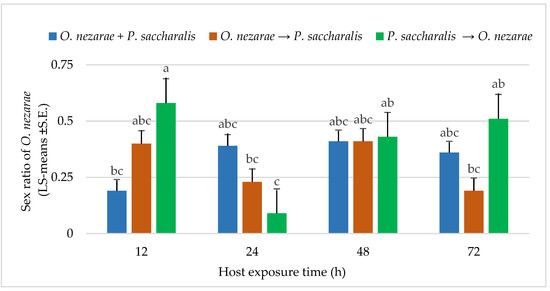
Figure 5.
LS-mean (±S.E.) sex ratio (females/total progeny) of Ooencyrtus nezarae (Sample size, n = 20) on Megacopta cribraria eggs in the timing of adult arrival at the competition experiment. Scenarios examined included simultaneous release of O. nezarae and Paratelenomus saccharalis (O. nezarae + P. saccharalis), sequential release in which O. nezarae was allowed to exploit the host patch first (O. nezarae → P. saccharalis), or sequential release in which P. saccharalis was released first (P. saccharalis → O. nezarae). Data were graphed with two-way ANOVA using simulated multiple comparison test: Release order (F = 1.82, df = 2, 228, p = 0.16), host exposure time (F = 3.61, df = 3, 228, p = 0.01) and their interaction (F = 4.86, df = 6, 228, p = 0.0001). Different letters indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05 for the interaction term.
4.2. Experiment II: Characterizing Aggressive Behavior
Ooencyrtus nezarae and P. saccharalis showed differences in their behavior when competing against each other. When both wasp species were using the host egg patch at the same time, interspecific aggressive behavior occurred between the two species. As soon as P. saccharalis encountered or noticed O. nezarae on the egg mass, they displayed aggressive behaviors, which occurred at a frequency of 1.85 ± 0.25 h−1. The P. saccharalis employed head butting (37 times in 20 replications) to fight the O. nezarae in all their confrontations, and it occasionally flapped its wings (2 times in 20 replications), appearing ready to strike, then charged its competitor, causing it to leave the egg mass. No aggressive behavior was observed by O. nezarae. Female O. nezarae displayed two behaviors on approaching or encountering P. saccharalis: running, in which the O. nezarae female walked away from the P. saccharalis, and left the host patch, and avoiding, in which the O. nezarae avoided physical contact with the approaching P. saccharalis by changing her searching direction.
4.3. Experiment III: Intraguild Predation of Parasitoid Larvae
The summary statistics of intraguild interactions between O. nezarae and P. saccharalis are summarized in Table 2. Intraguild predation of O. nezarae larvae often did not result in a decrease in the host population. A higher impact on the host was mostly achieved when O. nezarae was released right after the P. saccharalis were released. However, the proportion of host parasitism dropped from 0.23 to 0.19 in eggs that were exposed to P. saccharalis prior to being exposed to O. nezarae, 72 h or more before (Table 2).

Table 2.
The proportion of parasitized host eggs and emerged wasps averaged across treatments in an experiment examining intraguild predation of larvae experiment. Host exposure time (h) indicates the interval between the removal of a Paratelenomus saccharalis female and the introduction of a Ooencyrtus nezarae female.
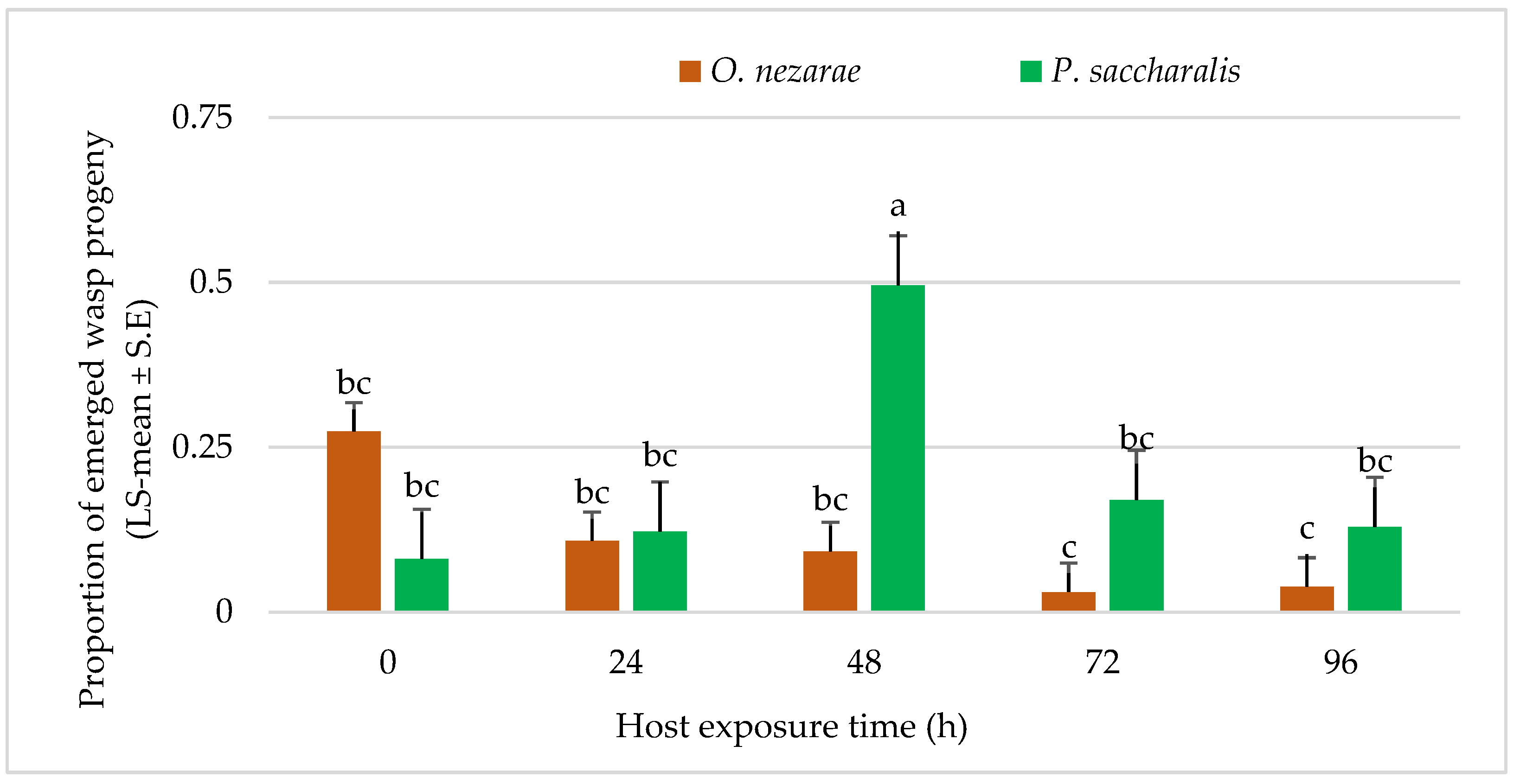
The proportion of wasp emergence was also affected by intraguild predation of O. nezarae larvae (Table 2). The wasp emergence decreased from the parasitized eggs as the differences in the timing of oviposition between both parasitoids increased except for the time delay of 24 h. Ooencyrtus nezarae accepted all host eggs that had been exposed to P. saccharalis from 0–96 h before. The offspring of O. nezarae was even able to develop in host eggs parasitized by P. saccharalis 96 h earlier (Figure 6).
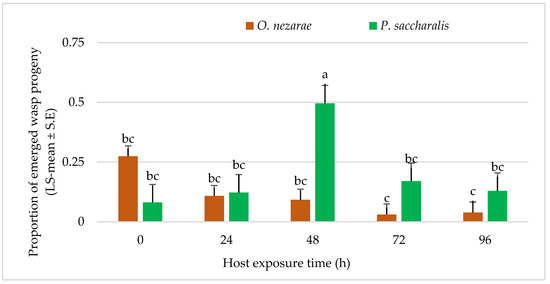
Figure 6.
LS-mean (±SE) of Ooencyrtus nezarae and Paratelenomus saccharalis progeny that emerged from host eggs among treatments. Data were graphed with one-way ANOVA using simulated multiple comparison test (F =10.91, df =4, 95, p < 0.0001 for the main effect i.e., host exposure time). Different letters indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05. (Sample size, n = 20).
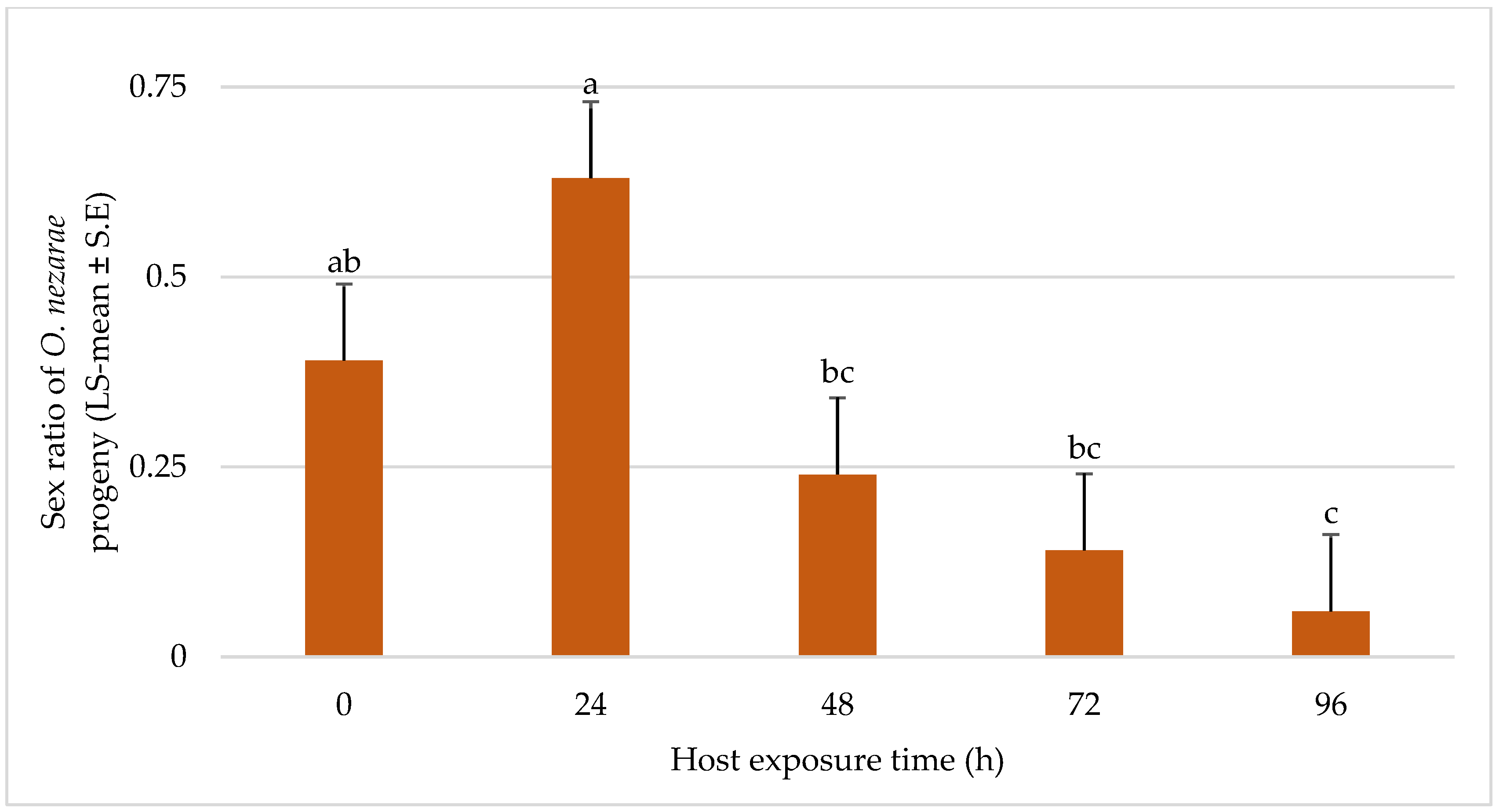
In most of the situations, the sex ratio of O. nezarae was male-biased and there was a trend towards longer duration experiments showing less favorable effects on female emergence of O. nezarae (Figure 7).
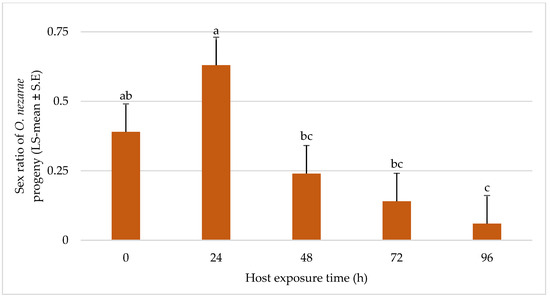
Figure 7.
LS-mean (±S.E.) sex ratio (females/total progeny) of Ooencyrtus nezarae (Sample size, n = 20) on Megacopta cribraria eggs intraguild predation experiment. Data were graphed with one-way ANOVA using simulated multiple comparison test (F = 10.91, df = 4, 95, p < 0.0001 for the main effect i.e., host exposure time). Different letters indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05.
5. Discussion
We investigated both the direct and indirect interspecific interference competition between P. saccharalis and O. nezarae by comparing the proportion of parasitized host eggs, host nymphs, and emerged parasitoids in a sequential or simultaneous release of both species. Both wasp species showed differences in host parasitism and emergence when competing against each other. Ooencyrtus nezarae acted as a superior larval competitor in almost all competitive events. Paratelenomus saccharalis adults showed agonistic behavior against its heterospecific female to defend the host patch. The outcomes of such competitive situations are discussed below.
5.1. Experiment I: The Timing of Adult Arrival at the Competition
The direct interference results showed that competition occurs between both parasitoid species for the common host, and the order of release, i.e., the timing of the wasp’s arrival at the host patch, also influenced the outcome. When specialist P. saccharalis arrived earlier or together with generalist O. nezarae, egg parasitism rates were the highest. However, when O. nezarae exploited the host patch first, the overall parasitism was lower. Our results are consistent with those of [55] showing that specialist (Microplitis mediator Haliday) had more impact on the parasitism of Helicoverpa armigera Hübner larvae when it was released prior to a generalist (Campoletis chlorideae Uchida) [55]. The possible explanation for these results is that the specialist species has better host handling strategies due to specificity, and is much more efficient in host utilization compared to a generalist [56]. The host handling time of female P. saccharalis is much shorter (an average of 10.48 min) [51] than O. nezarae (an average of 19.32 min) [39].
The seasonal arrival time of P. saccharalis is quite different in nature. In the native range (Japan), P. saccharalis arrives in May and O. nezarae in June [31]. In the United States, O. nezarae arrives earlier in May, whereas P. saccharalis first appears in July, and both species overlap from July to October in soybean fields (personal observation). Ooencyrtus nezarae host feeding behavior may also influence parasitism. When O. nezarae was released first, regardless of host exposure time, the highest proportion of kudzu bug eggs were neither hatched nor parasitized (i.e., unascribed eggs) by wasps. The proportion of unascribed eggs was equal to or more than that of parasitized eggs.
Parasitism and emergence were highest when O. nezarae and P. saccharalis arrived at the host patch simultaneously, and only a small fraction of parasitized eggs did not produce wasps in this treatment. When O. nezarae arrived later than P. saccharalis, the proportion of parasitized host eggs was higher, but fewer wasps emerged from parasitized eggs. More than half of the parasitized eggs did not yield parasitoids and were non-viable (Supplementary Materials; Table S1). A similar result was found when O. nezarae arrived earlier than P. saccharalis at the host patch; the highest proportion of parasitized eggs that did not produce wasps was observed when the wasp was given a longer time to exploit the host (Supplementary Materials; Table S2). These results might be related to the preference of O. nezarae for parasitized eggs over unparasitized eggs. Ooencyrtus nezarae female prefers parasitized host eggs to save their energy and time in host drilling [39]. In fact, the handling time of O. nezarae on a parasitized host is an average of 17.23 min, which is considerably shorter than an unparasitized host, taking only 19.32 min in handling [39]. It also suggests that O. nezarae is superior in interspecific larval competition (intrinsic competition).
5.2. Experiment II: Characterizing Aggressive Behavior
When P. saccharalis and O. nezarae arrive at the host patch together, P. saccharalis exhibits aggressive behavior; O. nezarae did not show any distinct behavior toward P. saccharalis to defend the kudzu bug egg patch. It was observed that O. nezarae reached the host eggs earlier than P. saccharalis and took possession of the eggs. Then, P. saccharalis females that arrived later would fight with O. nezarae to access the host. Paratelenomus saccharalis exhibited continuous head striking of O. nezarae that generally caused O. nezarae to leave the host patch. Such aggressive tactics were also observed in other Platygastrid egg parasitoids such as Trissolcus basalis Wollaston against O. telenomicida Vassiliev to utilize Nezara viridula Linnaeus eggs [47]. In Japan, P. saccharalis females were also observed to aggressively exclude females of O. nezarae from utilizing the host patch [31]. Since O. nezarae can utilize both unparasitized and parasitized hosts, aggressive behavior from O. nezarae towards P. saccharalis is not advantageous, therefore leaving the host patch and searching out additional patches without a P. saccharalis female present would be expedient for them. The lack of aggressive behavior in O. nezarae females may also be related to their broad host range in the United States [38], or due to its smaller size (max. overall body length = 0.77 mm) in comparison to P. saccharalis females (max. overall body length 0.83 mm) [30,34].
5.3. Experiment III: Intraguild Predation of Larvae
Intraguild predation data reaffirms the vulnerability of P. saccharalis immatures (72–96 h), as O. nezarae successfully emerges from multiparasitized eggs, speculating the adaptive outcome of the temporal trophic shift from M. cribraria eggs to its primary parasitoid, P. saccharalis. It increased the window of opportunity to exploit host eggs and allowed them to evade exclusion by the more fecund wasp species. However, this trophic shift ended with a detrimental outcome for both species, as non-reproductive mortality increased significantly (0.84 at 96 h). Our result was consistent with Cusumano and Peri [47], who observed high levels of dead host and parasitoid mortality with later-stage multiparasitism by O. telenomicida.
It has been observed that Ooencyrtus spp. with a broad host range generally shift their trophic position when hosts become scarce [21,22,57]. Mohammadpour et al. [8] investigated competition between O. pityocampi Mercet and Trissolcus agriope Kozlov and Le on the host eggs of Brachynema signatum Jakovlev. Ooencyrtus pityocampi was able to develop as a superior larval competitor or could be as a facultative hyperparasitoid on the latter species [8]. This is presumably through direct physical attack between larvae [58]. Studies also show that embryological differences between the species can be one possible reason to outcompete the competitor by hatching earlier [1]. However, the developmental biology of P. saccharalis and O. nezarae have yet to be investigated.
6. Conclusions
Both parasitoid species differed in terms of their host utilization and competitive interference strength. Paratelenomus saccharalis was the species that had the greatest ability to exploit the resource, while O. nezarae was the strongest species in the direct and indirect competition. Our work has shown that O. nezarae has the potential to impact the population dynamics of P. saccharalis, which could be detrimental to biological control programs of M. cribraria. Additional field studies, however, are needed to determine interspecific competition under natural conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/insects14010035/s1, Table S1: The proportion of unascribed eggs (unhatched or unparasitized) averaged across treatments in experiments conducted to examine how the order of Ooencyrtus nezarae and/or Paratelenomus saccharalis adult arrival at a Megacopta cribraria egg patch influences competition; Table S2: The proportion of unascribed eggs (unhatched or unparasitized) averaged across treatments in experiments conducted to examine how the order of Ooencyrtus nezarae and/or Paratelenomus saccharalis adult arrival at a Megacopta cribraria egg patch influences competition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Y.F., R.R.B. and S.W.; experimental design, R.R.B., A.M.C.-M. and S.W.; Data curation, A.L.J. and S.W.; formal analysis, A.L.J. and S.W.; funding acquisition, H.Y.F. and A.L.J.; writing—original draft, S.W.; writing—review and editing, H.Y.F., A.L.J., R.R.B., A.M.C.-M. and S.W. All co-authors contributed to this manuscript and approved it. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for this study was provided by the Alabama Agricultural Experiment Stations, and Hatch projects ALA015-4-19062.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be provided upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Bernardo for his assistance in the data analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Harvey, J.A.; Poelman, E.H.; Tanaka, T. Intrinsic inter-and intraspecific competition in parasitoid wasps. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, P.W. Parasitiods utilizing the same host: Adaptive nature of differences in size and form. Ecology 1972, 53, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bográn, C.E.; Heinz, K.M.; Ciomperlik, M.A. Interspecific competition among insect parasitoids: Field experiments with whiteflies as hosts in cotton. Ecology 2002, 83, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polis, G.A.; Strong, D.R. Food web complexity and community dynamics. Am. Nat. 1996, 147, 813–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.A.; Wagenaar, R.; Martijn Bezemer, T. Life-history traits in closely related secondary parasitoids sharing the same primary parasitoid host: Evolutionary opportunities and constraints. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2009, 132, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodeur, J.; Rosenheim, J.A. Intraguild interactions in aphid parasitoids. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2000, 97, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusumano, A.; Peri, E.; Bradleigh, V.S.; Colazza, S. Interspecific extrinsic and intrinsic competitive interactions in egg parasitoids. BioControl 2012, 57, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, M.; Jalali, M.A.; Michaud, J.P.; Ziaaddini, M.; Hashemirad, H. Multiparasitism of stink bug eggs: Competitive interactions between Ooencyrtus pityocampae and Trissolcus agriope. BioControl 2014, 59, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frago, E. Interactions between parasitoids and higher order natural enemies: Intraguild predation and hyperparasitoids. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2016, 14, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veen, F.J.; Rajkumar, A.; Muller, C.B.; Godfray, H.C. Increased reproduction by pea aphids in the presence of secondary parasitoids. Ecol. Entomol. 2001, 26, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassell, M.P.; Varley, G.C. New inductive population model for insect parasites and its bearing on biological control. Nature 1969, 223, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassell, M.P. Mutual interference between searching insect parasites. J. Anim. Ecol. 1971, 40, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, G.; Brodeur, J. Intra-and interspecific interactions among parasitoids: Mechanisms, outcomes and biological control. In Trophic and Guild in Biological Interactions Control; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwolfer, H. The structure and effect of parasite complexes attacking phytophagous host insects. In Dynamics of Populations, Proceedings of the Advanced Study Institute on ‘Dynamics and Numbers in Populations’, Oosterbeck, The Netherlands, 7–18 September 1970; den Boer, P.J., Gradwell, G.R., Eds.; Centre for Agricultural Publishing and Documentation: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1971; pp. 405–418. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenheim, J.A.; Kaya, H.K.; Ehler, L.E.; Marois, J.J.; Jaffee, B.A. Intraguild predation among biological-control agents: Theory and evidence. Biol. Control 1985, 5, 303–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes, C.M.; Cortesero, A.M.; Stapel, J.O.; Lewis., W.J. Intrinsic and extrinsic competitive interactions between two larval parasitoids of Heliothis virescens. Ecol. Entomol. 1999, 24, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusumano, A.; Peri, E.; Colazza, S. Interspecific competition/facilitation among insect parasitoids. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2016, 14, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overington, S.E.; Dubois, F.; Lefebvre, L. Food unpredictability drives both generalism and social foraging: A game theoretical model. Behav. Ecol. 2008, 19, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, S.; Beckage, N.E. Superparasitism in gregarious hymenopteran parasitoids: Ecological, behavioural and physiological perspectives. Physiol. Entomol. 2007, 32, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandon, S.; Rivero, A.; Varaldi, J. Superparasitism evolution: Adaptation or manipulation? Am. Nat. 2006, 167, E1–E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodeur, J. Host specificity and trophic relationships of hyperparasitoids. In Parasitoid Population Biology; Hochberg, M.E., Ives, A.R., Eds.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 163–183. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, M.S.; Woolley, J.B. Evolution and behavioral ecology of heteronomous aphelinid parasitoids. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2001, 46, 251–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillman, P.G.; Powell, J.E. Interspecific discrimination and larval competition among Microplitis croceipes, Microplitis demolitor, Cotesia kazak (Hym, Braconidae), and Hyposoter didymator (Hym, Ichneumonidae), parasitoids of Heliothis virescens (Lep, Noctuidae). Entomophaga 1992, 37, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uka, D.; Hiraoka, T.; Iwabuchi, K. Physiological suppression of the larval parasitoid Glyptapanteles pallipes by the polyembryonic parasitoid Copidosoma floridanum. J. Insect Physiol. 2006, 52, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, J.E.; Corrigan, J.E. Intrinsic competition between the gregarious parasite, Cotesia glomeratus and the solitary parasite Cotesia rubecula [Hymenoptera: Braconidae] for their host Artogeia rapae [Lepidoptera: Pieridae]. Entomophaga 1987, 32, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfir, R.; Van Hamburg, H. Interspecific competition between Telenomus ullyetti (Hymenoptera:Scelionidae) and Trichogrammatoidea lutea (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) parasitizing eggs of the cotton bollworm Heliothis armiger in the laboratory. Environ. Entomol. 1988, 17, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Messing, R.H. Intra-and interspecific competition by Fopius arisanus and Diachasmimorpha tryoni (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), parasitoids of tephritid fruit flies. Biol. Control 2003, 27, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, K.; Hirose, Y. Seasonal egg parasitism of phytophagous stink bugs in a soybean field in Fukuoka. In Proc. Assoc. Pl. Prot. Kyushu 1985, 31, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Takasu, K.; Hirose, Y. Kudzu-vine community as a breeding site of Ooencyrtus nezarae Ishi (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae), an egg parasitoid of bugs attacking soybean. Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1986, 30, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademokoya, B.; Balusu, R.; Morawo, T.; Fadamiro, H. Attraction of Paratelenomus saccharalis (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae), an egg parasitoid of Megacopta cribraria (Hemiptera: Plataspidae), to host associated olfactory cues. J. Entomol. Sci. 2017, 52, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, K.; Adati, T.; Olson, D.M.; Takasu, K. Seasonal occurrence and interspecific interactions of egg parasitoids of Megacopta cribraria (heteroptera: Plataspidae) in Japan. Environ. Entomol. 2017, 46, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alim, M.A.; Lim, U. Ecotoxicological effect of insecticides on Ooencyrtus nezarae (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) reared from refrigerated and unrefrigerated Riptortus pedestris (Hemiptera: Alydidae) host. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, I.A.; Roberts, P.M.; Gardner, W.A.; Oliver, K.M.; Reay-Jones, F.P.; Reisig, D.D.; Toews, M.D. Spatial distribution of Megacopta cribraria (Hemiptera: Plataspidae) adults, eggs and parasitism by Paratelenomus saccharalis (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae) in soybean. Environ. Entomol. 2017, 46, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.F. Revision of world species of Paratelenomus Dodd (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae). Can. Entomol. 1996, 128, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eger, J.E., Jr.; Pitcher, A.J.; Halbert, S.E.; Penca, C.; Hodges, A.C. First report of Brachyplatys subaeneus (Westwood) (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Plataspidae) in the United States. Insecta Mundi 2020, 0814, 1–6. Available online: https://journals.flvc.org/mundi/article/download/126889/126532 (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Hirose, Y.; Takasu, K.; Takagi, M. Egg parasitoids of phytophagous bugs in soybean: Mobile natural enemies as naturally occurring biological control agents of mobile pests. Biol. Control 1996, 7, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, N.; Wada, T.; Higuchi, H.; Ono, M.; Leal, S.W. A component of a synthetic aggregation pheromone of Riptortus clavatus (Thunberg) (Heteroptera: Alydidae), that attracts an egg parasitoid, Ooencyrtus nezarae Ishii (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1997, 32, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ademokoya, B.; Balusu, R.; Ray, C.; Mottern, J.; Fadamiro, H. The first record of Ooencyrtus nezarae (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) on kudzu bug (Hemiptera: Plataspidae) in North America. J. Insect Sci. 2018, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, K.; Hirose, Y. The parasitoid Ooencyrtus nezarae (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) prefers hosts parasitized by conspecifics over unparasitized hosts. Oecologia 1991, 87, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicas-Mosier, A.M.; Balusu, R.R.; Ajayi, O.S.; Kafle, B.D.; Morawo, T.; Mertoglu, G.; Smith, C.M.; Warsi, S.; Fadamiro, H.Y. Kudzu Bug (Megacopta cribraria) and associated egg parasitoids emergence rates in Alabama are predicted by weather indices. Environ. Entomol. 2022, 51, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potting, R.P.J.; Snellen, H.M.; Vet, L.E.M. Fitness consequences of superparasitism and mechanism of host discrimination in the stemborer parasitoid Cotesia flavipes. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1997, 82, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.S.; Stireman, J., III. O. Does anti-parasitoid defense explain host-plant selection by a polyphagous caterpillar? Oikos 2003, 100, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, F.; Giraldeau, L.A.; Grant, J.W. Resource defense in a group-foraging context. Behav. Ecol. 2003, 14, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G. Should I fight or should I flight? How studying insect aggression can help integrated pest management. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, Y. Agonistic behavior. In Encyclopedia of Animal Cognition and Behavior; Vonk, J., Shackelford, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, K.; Hirose, Y. The number of larval instars in Ooencyrtus species (Hymenoptera, Encyrtidae). Jpn. J. Entomol. 1989, 57, 398–401. [Google Scholar]
- Cusumano, A.; Peri, E.; Vinson, S.B.; Colazza, S. Intraguild interactions between two egg parasitoids exploring host patches. BioControl 2011, 56, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britt, K.E. An Ecological Study of the Kudzu Bug in East Tennessee: Life History, Seasonality, and Phenology. Master’s Thesis, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, W.A.; Blount, J.L.; Golec, J.R.; Jones, W.A.; Hu, X.P.; Talamas, E.J.; Evans, R.M.; Dong, X.; Ray, C.H., Jr.; Buntin, G.D.; et al. Discovery of Paratelenomus saccharalis (Dodd) (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae), an egg parasitoid of Megacopta cribraria F. (Hemiptera: Plataspidae) in its expanded North American range. J. Entomol. Sci. 2013, 48, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, K.S.D.; Takagi, M.; Ueno, T. Effect of female’s age on the progeny production and sex ratio of Ooencyrtus nezarae, an egg parasitoid of the bean bug Riptortus clavatus. J. Fac. Agr. Kyushu Univ. 2010, 55, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, S.I.; Takasu, K. Food deprivation increases reproductive effort in a parasitoid wasp. Biol. Control 2019, 133, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjisaffar, F.; Perring, T.M. Life history evaluation of Ooencyrtus lucidus, a newly described egg parasitoid of Bagrada hilaris. Insects 2020, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G.; Canale, A. Aggressive behavior in olive fruit fly females: Oviposition site guarding against parasitic wasps. J. Insect Behav. 2016, 29, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasylenko, Y.; Těšitel, J.; Ceccantini, G.; Oliveira-da-Silva, M.; Dvořák, V.; Steele, D.; Sosnovsky, Y.; Piwowarczyk, R.; Watson, D.M.; Teixeira-Costa, L. Parasites on parasites: Hyper-, epi-, and autoparasitism among flowering plants. Am. J. Bot. 2021, 108, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.P.; Zhang, J.H.; Yan, Y.H.; Wang, C.Z. Interspecific competition between the ichneumonid Campoletis chlorideae and the braconid Microplitis mediator in their host Helicoverpa armigera. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2008, 127, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernays, E.A. Neural limitations in phytophagous insects: Implications for diet breadth and evolution of host affiliation. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2001, 46, 703–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, D.; Amarasekare, P. The role of transient dynamics in biological pest control: Insights from a host parasitoid community. J. Anim. Ecol. 2012, 81, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinson, S.B. Competition and host discrimination between two species of tobacco budworm parasitoids. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1972, 65, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).