The Plastic Larval Body Color of the Pale Grass Blue Butterfly Zizeeria maha (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) in Response to the Host Plant Color: The Maternal Effect on Crypsis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
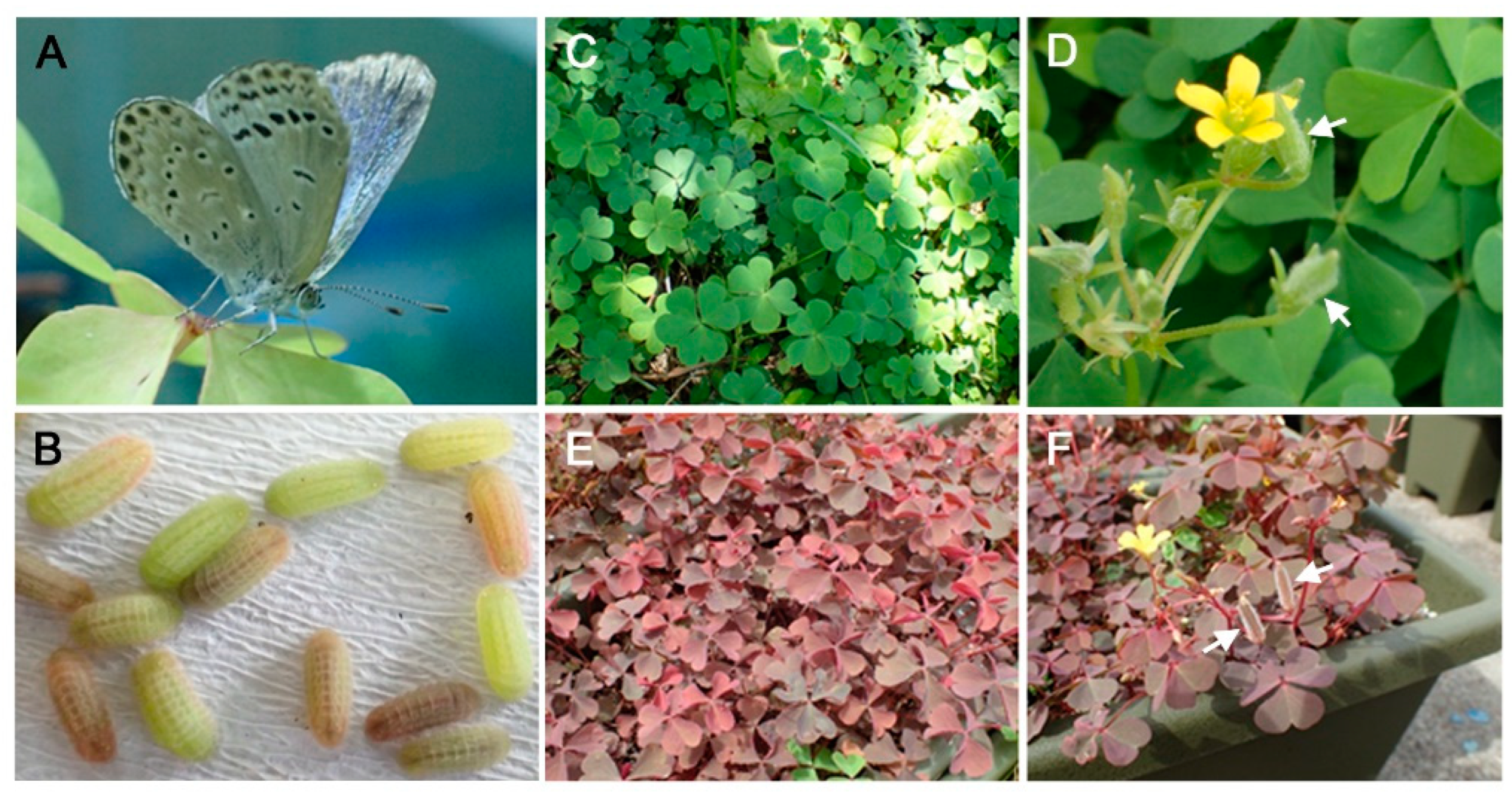
2.1. Butterfly and Its Host Plant
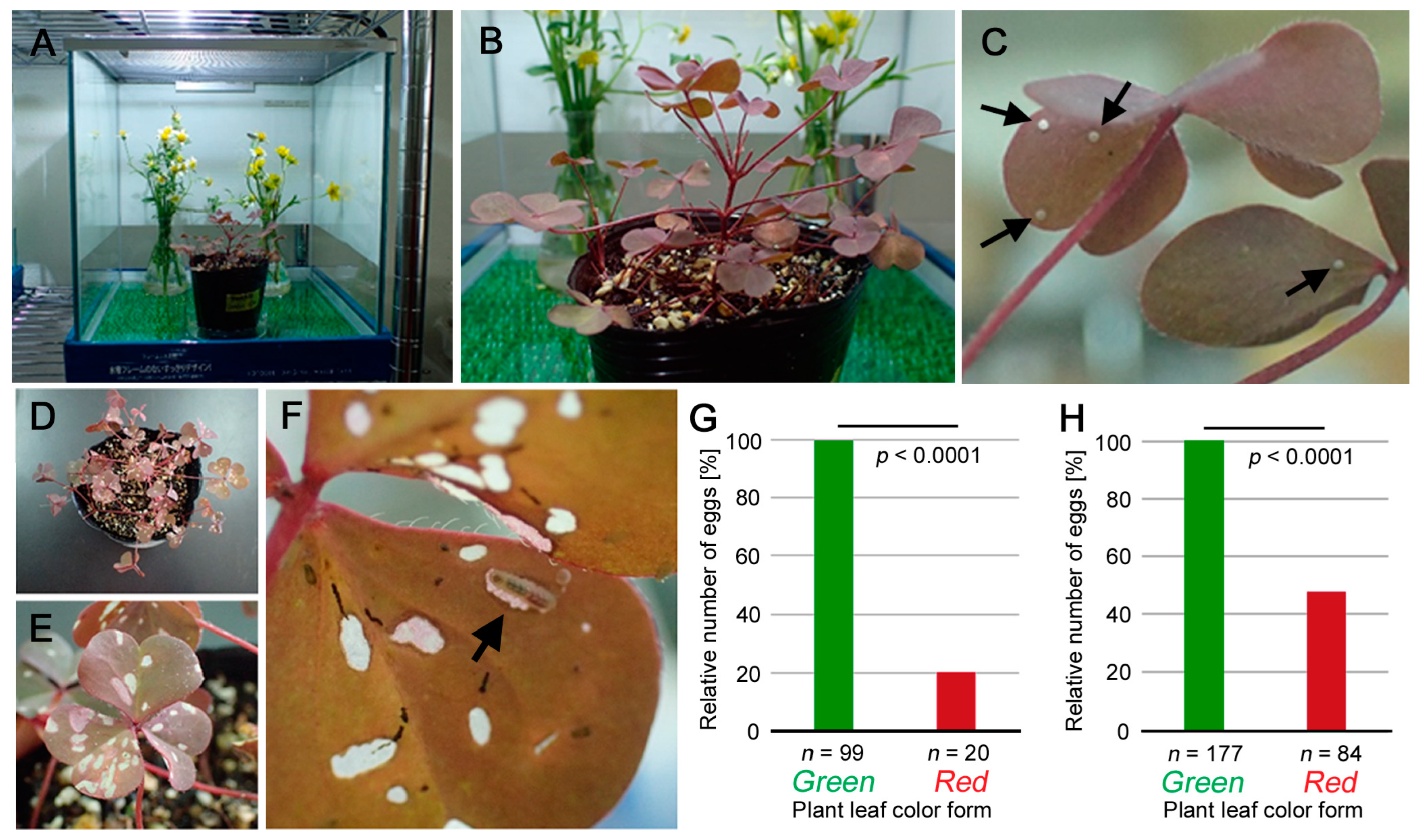
2.2. Plant Cultivation
2.3. Butterfly Rearing
2.4. Behavioral Tests
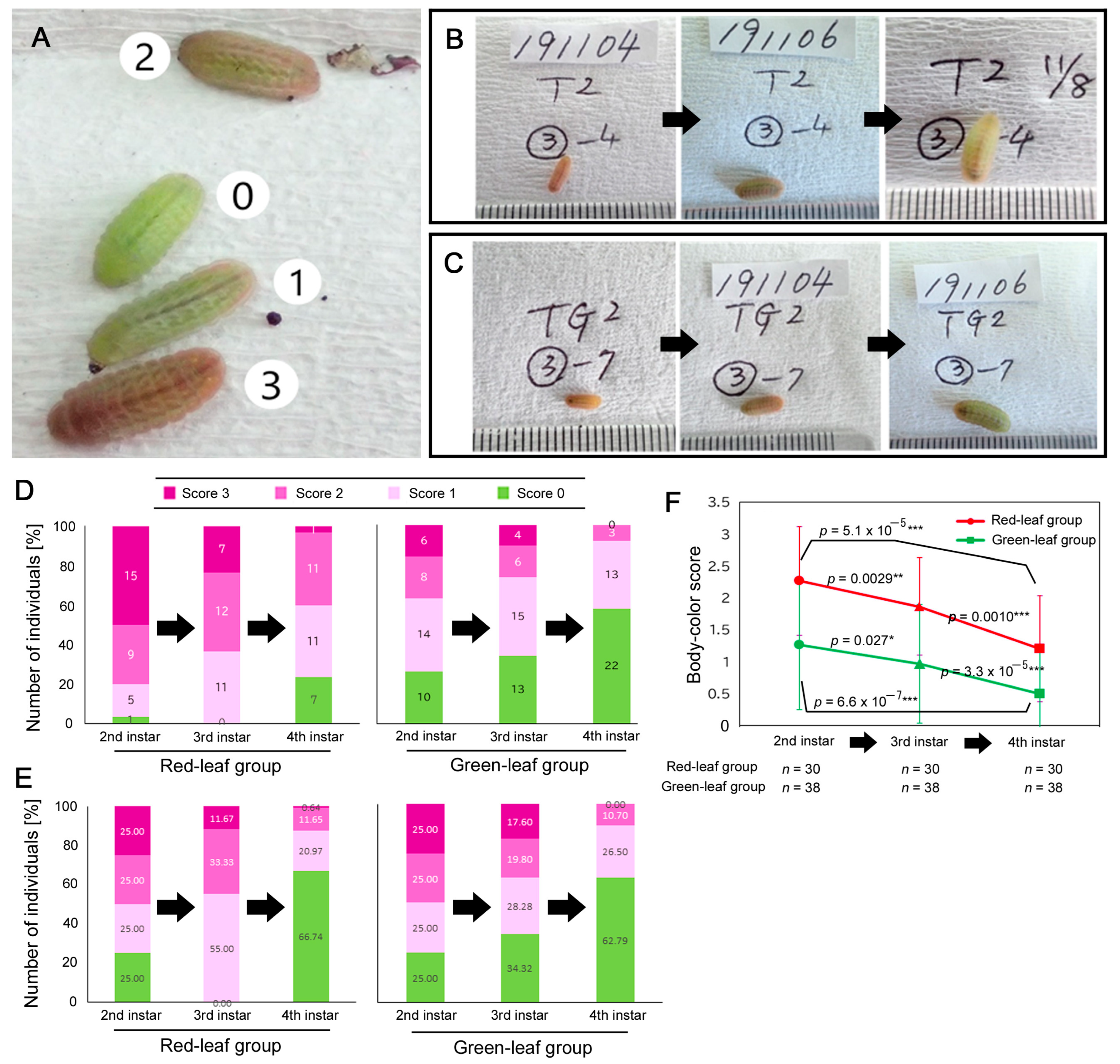
2.5. Body Color Scores and Single-Individual Tracking
2.6. Lineages and Lines
2.7. Definitions of Operational Effects
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Suitability of the Red Form Plant: Oviposition Preference and Larval Growth
3.2. Single-Individual Tracking
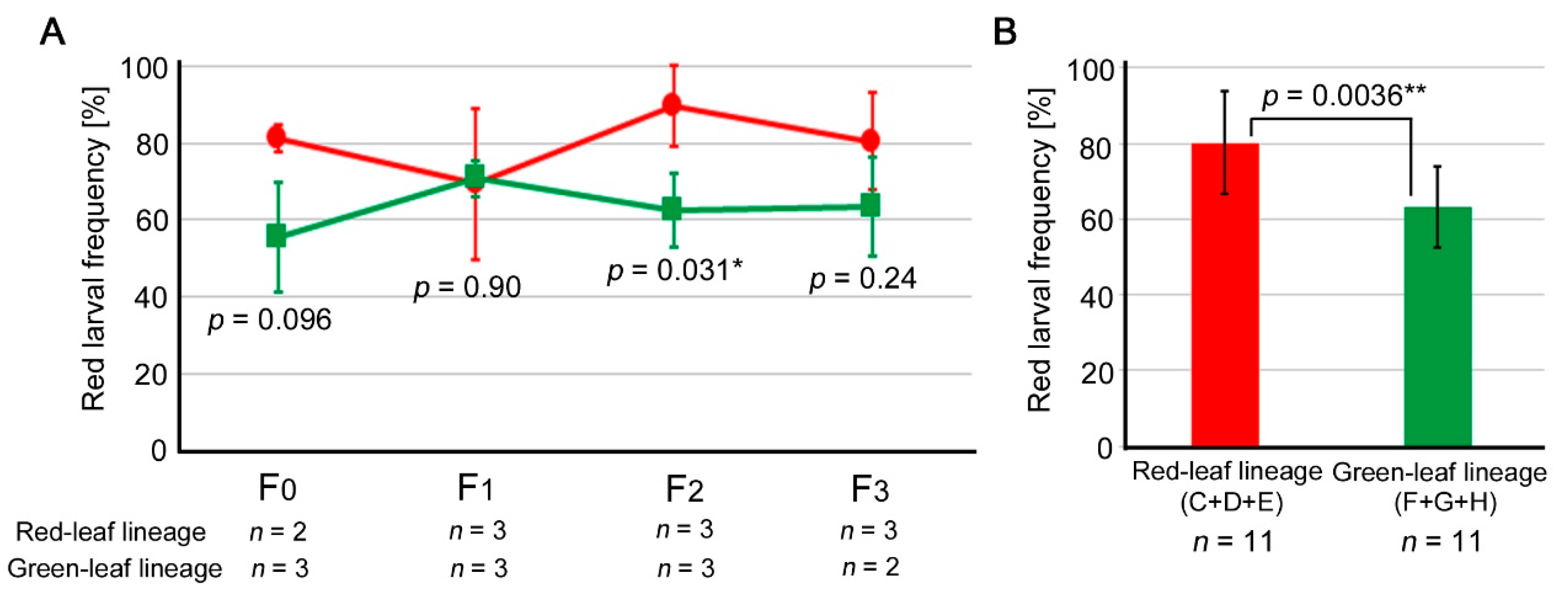
3.3. Comparison between the Red Leaf and Green Leaf Lineages
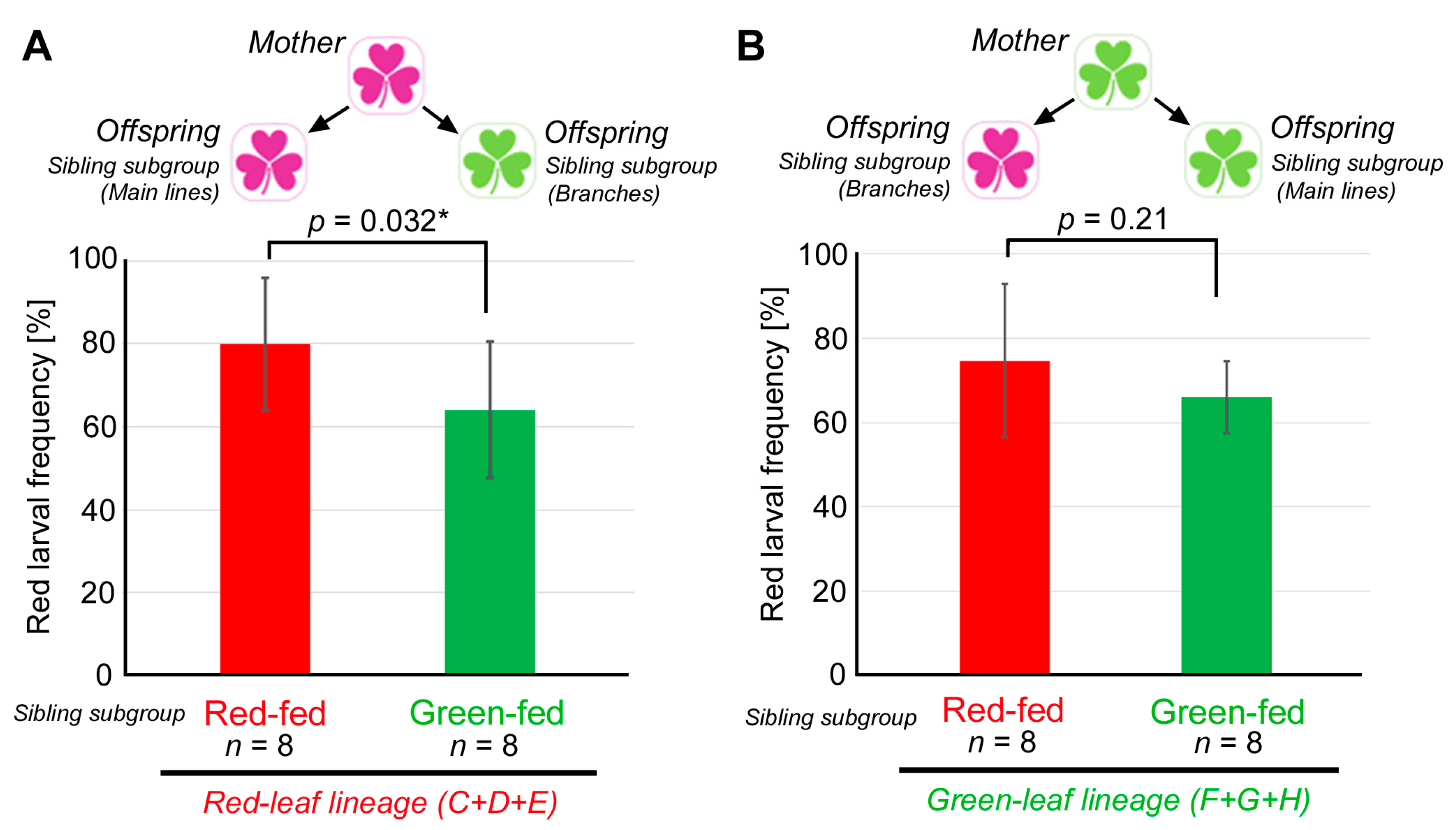
3.4. Comparison between the Red-Fed and Green-Fed Siblings
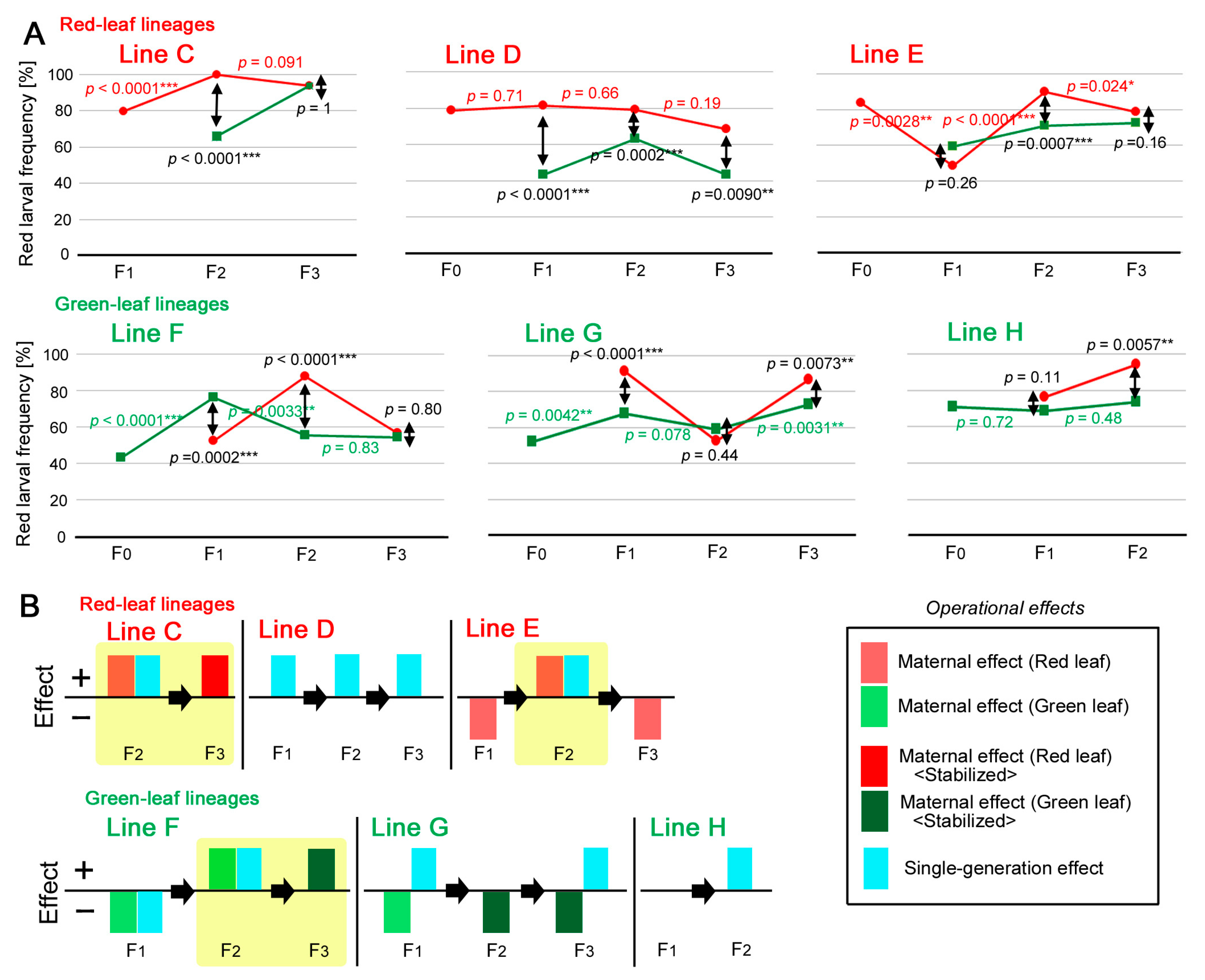
3.5. Dynamics of the Individual Lines: Red Leaf Lineage
3.6. Dynamics of the Individual Lines: Green Leaf Lineage
4. Discussion
4.1. Oviposition Preference and Larval Growth
4.2. Decrease in Red Larval Frequencies during Larval Growth
4.3. Lineage and Sibling Comparisons
4.4. Dynamics of the Independent Lines
4.5. Possible Mechanisms of Maternal Effects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Losey, J.E.; Ives, A.J.; Harmon, J.; Ballantyne, H.; Brown, C. A polymorphism maintained by opposite patterns of parasitism and predation. Nature 1997, 388, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolnick, D.I.; Fitzpatrick, B.M. Sympatric speciation: Models and empirical evidence. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2007, 38, 459–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.M.; Mckinnon, J.S. Linking color polymorphism maintenance and speciation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, B.M.; Fordyce, J.A.; Gavrilets, S. Pattern, process and geographic models of speciation. J. Evol. Biol. 2009, 22, 2342–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallet, J.; Meyer, A.; Nosil, P.; Feder, J.L. Space, sympatry and speciation. J. Evol. Biol. 2009, 22, 2332–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhout, H.F. The Development and Evolution of Butterfly Wing Patterns; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Futahashi, R.; Sato, J.; Meng, Y.; Okamoto, S.; Daimon, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Suetsugu, Y.; Narukawa, J.; Takahashi, H.; Banno, Y.; et al. yellow and ebony are the responsible genes for the larval color mutants of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Genetics 2008, 180, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Qiao, L.; Tong, X.; Cao, C.; Chen, P.; Chen, J.; Lu, C.; Xiang, Z. Mutations of an arylalkylamine-N-acetyltransferase, Bm-iAANAT, are responsible for silkworm melanism mutant. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 19553–19560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Katsuma, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Kadono-Okuda, K.; Mita, K.; Shimada, T. Yellow-e determines the color pattern of larval head and tail spots of the silkworm Bombyx mori. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 5624–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Guo, Q.; Li, M.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Miao, X.; Huang, Y. Disruption of an N-acetyltransferase gene in the silkworm reveals a novel role in pigmentation. Development 2010, 137, 4083–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Duan, J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, S.; Akinkurolere, R.O.; Xu, A.; Qian, H.; et al. A major facilitator superfamily protein participates in the reddish brown pigmentation in Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, M.; Kiuchi, T.; Banno, Y.; Katsuma, S.; Shimada, T. Identification of the silkworm quail gene reveals a crucial role of a receptor guanylyl cyclase in larval pigmentation. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 68, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoda, S.; Yamaguchi, J.; Mita, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Banno, Y.; Ando, T.; Daimon, T.; Fujiwara, H. The transcription factor Apontic-like controls diverse colouration pattern in caterpillars. Nat Commun. 2014, 5, 4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KonDo, Y.; Yoda, S.; Mizoguchi, T.; Ando, T.; Yamaguchi, J.; Yamamoto, K.; Banno, Y.; Fujiwara, H. Toll ligand Spätzle3 controls melanization in the stripe pattern formation in caterpillars. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8336–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Tong, X.; Gai, T.; Li, C.; Qiao, L.; Monteiro, A.; Hu, H.; Han, M.; Ding, X.; Wu, S.; et al. Body shape and color of silkworm larvae are influenced by a novel cuticular protein. Genetics 2017, 207, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.K.; Koshikawa, S.; Kobayashi, I.; Uchino, K.; Sezutsu, H. Modular cis-regularoty logic of yellow gene expression in silkmoth larvae. Insect Mol. Biol. 2019, 28, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirataki, H.; Futahashi, R.; Fujiwara, H. Species-specific coordinated gene expression and trans-regulation of larval color pattern in three swallowtail butterflies. Evol. Dev. 2010, 12, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futahashi, R.; Shirataki, H.; Narita, T.; Mita, K.; Fujiwara, H. Comprehensive microarray-based analysis for stage-specific larval camouflage pattern-associated genes in the swallowtail butterfly, Papilio xuthus. BMC Biol. 2012, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Seki, T.; Yamaguchi, J.; Fujiwara, H. Prepatterning of Papilio xuthus caterpillar camouflage is controlled by three homeobox genes: clawless, abdominal-A and Abdominal-B. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futahashi, R.; Fujiwara, H. Juvenile hormone regulates butterfly larval pattern switches. Science 2008, 319, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futahashi, R.; Fujiwara, H. Regulation of 20-hydroxyecdysone on the larval pigmentation and the expression of melanin synthesis enzymes and yellow gene of the swallowtail butterfly, Papilio xuthus. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruma, K.; Riddiford, L.M.; Hopkins, T.L.; Morgan, T.D. Roles of dopa decarboxylase and phenoloxidase in the melanization of the tobacco hornworm and their control by 20-hydroxyecdysone. J. Comp. Physiol. B 1985, 155, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiruma, K.; Riddiford, L.M. The molecular mechanisms of cuticular melanization: The ecdysone cascade leading to dopa decarboxylase expression in Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazel, W.N. The environmental and genetic control of seasonal polyphenism in larval color and its adaptive significance in a swallowtail butterfly. Evolution 2002, 56, 248–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nice, C.C.; Fordyce, J.A. How caterpillars avoid overheating: Behavioral and phenotypic plasticity of pipevine swallowtail larvae. Oecologia 2006, 146, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, V.E.; Morallo-Rejesus, B. Effects of nutrition on larval color of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner). Philipp. J. Entomol. 1976, 3, 201–224. [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki, A.; Shimizu, K.; Fujisaki, K. Effect of host plant part on larval body color polymorphism in Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2009, 102, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anazonwu, D.L.; Johnson, S.J. Effects of host and density on larval color, size and development of the velvetbean caterpillar, Anticarsia gemmatalis. Environ. Entomol. 1986, 15, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fescemyer, H.W.; Erlandson, C.M. Influence of diet on the density-dependent phase polymorphism of velvetbean caterpillars (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environ. Entomol. 1993, 22, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, J.; Edmunds, M. The causes of colour and colour change in caterpillars of the poplar and eyed hawkmoths (Lathoe poluli and Smerinthus ocellata). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1989, 37, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tojo, S. Variation in phase polymorphism in the common cutworm, Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1991, 26, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirôzu, T.; Hara, A. Early Stages of Japanese Butterflies in Colour; Hoikusha: Osaka, Japan, 1969; Volume II. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, H.; Hama, E.; Kuzuya, T.; Takahashi, A.; Takahashi, M.; Tanaka, B.; Tanaka, H.; Wakabayashi, M.; Watanabe, Y. The Life Histories of Butterflies in Japan; Hoikusha: Osaka, Japan, 1984; Volume III. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Teshirogi, M. An Illustrated Book of the Japanese Lycaenidae; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1997. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Sibatani, A. A remarkable polymorphism of mature larvae of Zizina labradus (Godart), common grass blue butterfly (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) from the Sydney area. Aust. Entomol. Mag. 1984, 11, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gurung, R.D.; Iwata, M.; Hiyama, A.; Taira, W.; Degnan, B.; Degnan, S.; Otaki, J.M. Comparative morphological analysis of the immature stages of the grass blue butterflies Zizeeria and Zizina (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae). Zool. Sci. 2016, 33, 384–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, H. Life history and peculiarities of the cycad-eating Chilades pandava (Horsfield, 1829) (Lycaenidae), a recent regular warm season visitor to Japan. Butterflies (Teinopalpus) 2014, 66, 4–21. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Kato, Y.; Satonaka, M. Larval color and wing morph in the lycaenid butterfly Acytolepis puspa. Yadoriga 2014, 242, 12–15. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Whitman, D.W.; Agrawal, A.A. What is phenotypic plasticity and why it is important. In Phenotypic Plasticity of Insects: Mechanisms and Consequences; Whitman, D., Ananthakrishnan, T.N., Eds.; CRC Press: Enfield, NH, USA, 2009; pp. 1–63. [Google Scholar]
- Pfennig, D.W.; Wund, M.A.; Snell-Rood, E.C.; Cruickshank, T.; Schlichting, C.D.; Moczek, A.P. Phenotypic plasticity’s impacts on diversification and speciation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousseau, T.A.; Dingle, H. Maternal effects in insect life histories. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1991, 36, 511–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousseau, T.; Fox, C.W. The adaptive significance of maternal effects. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uller, T. Developmental plasticity and the evolution of parental effects. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woestmann, L.; Saastamoinen, M. The importance of trans-generational effects in Lepidoptera. Curr. Zool. 2016, 62, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiyama, A.; Otaki, J.M. Dispersibility of the pale grass blue butterfly Zizeeria maha (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) revealed by one-individual tracking in the field: Quantitative comparisons between subspecies and between sexes. Insects 2020, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaki, J.M.; Hiyama, A.; Iwata, M.; Kudo, T. Phenotypic plasticity in the range-margin population of the lycaenid butterfly Zizeeria maha. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, J.; Bridle, J.R.; Pomiankowski, A. Novel variation associated with species range expansion. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiyama, A.; Taira, W.; Otaki, J.M. Color-pattern evolution in response to environmental stress in butterflies. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taira, W.; Hiyama, A.; Nohara, C.; Sakauchi, K.; Otaki, J.M. Ingestional and transgenerational effects of the Fukushima nuclear accident on the pale grass blue butterfly. J. Radiat. Res. 2015, 56 (Suppl. S1), i2–i18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohara, C.; Taira, W.; Hiyama, A.; Tanahara, A.; Takatsuji, T.; Otaki, J.M. Ingestion of radioactively contaminated diets for two generations in the pale grass blue butterfly. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohara, C.; Hiyama, A.; Taira, W.; Otaki, J.M. Robustness and radiation resistance of the pale grass blue butterfly from radioactively contaminated areas: A possible case of adaptive evolution. J. Hered. 2018, 109, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaki, J.M. Understanding low-dose exposure and field effects to resolve the field-laboratory paradox: Multifaceted biological effects from the Fukushima nuclear accident. In New Trends in Nuclear Science; Awwad, N.S., AlFaify, S.A., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, United Kingdom, 2018; pp. 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, M.; Hiyama, A.; Otaki, J.M. System-dependent regulations of colour-pattern development: A mutagenesis study of the pale grass blue butterfly. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, M.; Taira, W.; Hiyama, A.; Otaki, J.M. The lycaenid central symmetry system: Color pattern analysis of the pale grass blue butterfly Zizeeria maha. Zool. Sci. 2015, 32, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, K.; Otaki, J.M. Real-time in vivo imaging of the developing pupal wing tissues in the pale grass blue butterfly Zizeeria maha: Establishing the lycaenid system for multiscale bioimaging. J. Imaging 2019, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirôzu, T. The Standard of Butterflies in Japan; Gakken: Tokyo, Japan, 2006. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Washitani, I.; Yoshioka, A.; Suda, S.; Yasukawa, M.; Kitsuregawa, M. The pale grass blue butterfly in the citizen science Tokyo butterfly monitoring project. Kagaku 2013, 83, 961–966. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Satake, Y.; Ohwi, J.; Kitamura, S.; Watari, S.; Tominari, T. Wild Flowers of Japan. Herbaceous plants [II]; Heibonsha: Tokyo, Japan, 1999. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Yonekura, K.; Kajita, T. Plant Index for Japanese and Academic Names (YList). 2007. Available online: http://ylist.info (accessed on 13 December 2020). (In Japanese).
- Hiyama, A.; Iwata, M.; Otaki, J.M. Rearing the pale grass blue Zizeeria maha (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae): Toward the establishment of a lycaenid model system for butterfly physiology and genetics. Entomol. Sci. 2010, 13, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, G.D.; Remington, C.L. Color vision in Lycaena butterflies: Spectral tuning of receptor arrays in relation to behavioral ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2783–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Matsuyama, S.; Yamaji, K. Oxalic acid as a larval feeding stimulant for the pale grass blue butterfly Zizeeria maha (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2016, 51, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallow, M.F.A.; Matsumura, M.; Suzuki, Y. Oviposition preference and reproductive performance of Japanese Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2001, 36, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, C.N.K.; Walter, G.H. Polyphagy and primary host plants: Oviposition preference versus larval performance in the lepidopteran pest Helicoverpa armigera. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2007, 1, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladner, D.T.; Altizer, S. Oviposition preference and larval performance of North American monarch butterflies on four Asclepias species. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2005, 116, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forister, M.L. Oviposition preference and larval performance within a diverging lineage of lycaenid butterflies. Ecol. Entomol. 2004, 29, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, C.E.; Nice, C.C.; Fordyce, J.A.; Gompert, Z.; Forister, M.L. Larval performance in the context of ecological diversification and speciation in Lycaeides butterflies. Intl. J. Ecol. 2012, 2012, 242154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.G.; Gompert, Z.; Fordyce, J.A.; Buerkie, C.A.; Grinstead, R.; Jahner, J.P.; Mikel, S.; Nice, C.C.; Santamaria, A.; Forister, M.L. The many dimensions of diet breadth: Phytochemical, genetic, behavioral, and physiological perspectives on the interaction between a native herbivore and an exotic host. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, P. Herbivore host choice and optimal bad motherhood. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Robledo, C.; Horvitz, C.C. Parent-offspring conflicts, “optimal bad motherhood” and the “mother knows best” principles in insect herbivores colonizing novel host plants. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 2, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, K.R.; Yasuda, G.K.; Owens, K.N.; Wakimoto, B.T. Paternal effects in Drosophila: Implications for mechanisms of early development. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 1997, 38, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crean, A.J.; Bonduriansky, R. What is a paternal effect? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, L.W.; Lovegrove, M. Nongenetic paternal effects via seminal fluid. Evol. Lett. 2019, 3, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A. Flavonoid pigments in chalkhill blue (Lysandra coridon Poda) and other lycaenid butterflies. J. Chem. Ecol. 1987, 13, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geuder, M.; Wray, V.; Fiedler, K.; Proksch, P. Sequestration and metabolism of host-plant flavonoids by the lycaenid butterfly Polyommatus bellargus. J. Chem. Ecol. 1997, 23, 1361–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghardt, F.; Proksch, P.; Fiedler, K. Flavonoid sequestration by the common blue butterfly Polyommatus icarus: Quantitative intraspecific variation in relation to larval host plant, sex and body size. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2001, 29, 875–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knüttel, H.; Fiedler, K. Host-plant-derived variation in ultraviolet wing patterns influences mate selection by male butterflies. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 2447–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizokami, H.; Tomita-Yokotani, K.; Yoshitama, K. Flavonoids in the leaves of Oxalis corniculata and sequestration of the flavonoids in the wing scales of the pale grass blue butterfly, Pseudozizeeria maha. J. Plant Res. 2008, 121, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizokami, H.; Yoshitama, K. Sequestration and metabolism of host-plant flavonoids by the pale grass blue, Pseusozizeeria maha (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae). Entomol. Sci. 2009, 12, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Imran, M. Carotenoids, pigments, phenolic composition and antioxidant activity of Oxalis corniculata leaves. Food Biosci. 2019, 32, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakauchi, K.; Taira, W.; Otaki, J.M. Metabolomic response of the creeping wood sorrel Oxalis corniculata to low-dose radiation exposure from Fukushima’s contaminated soil. Life 2021, 11, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakauchi, K.; Taira, W.; Otaki, J.M. Metabolomic profiles of the creeping wood sorrel Oxalis corniculata in radioactively contaminated fields in Fukushima: Dose-dependent changes in key metabolites. Life 2022, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshida, A.; Yabu, S.; Otaki, J.M. The Plastic Larval Body Color of the Pale Grass Blue Butterfly Zizeeria maha (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) in Response to the Host Plant Color: The Maternal Effect on Crypsis. Insects 2023, 14, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020202
Yoshida A, Yabu S, Otaki JM. The Plastic Larval Body Color of the Pale Grass Blue Butterfly Zizeeria maha (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) in Response to the Host Plant Color: The Maternal Effect on Crypsis. Insects. 2023; 14(2):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020202
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshida, Ai, Shintaro Yabu, and Joji M. Otaki. 2023. "The Plastic Larval Body Color of the Pale Grass Blue Butterfly Zizeeria maha (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) in Response to the Host Plant Color: The Maternal Effect on Crypsis" Insects 14, no. 2: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020202
APA StyleYoshida, A., Yabu, S., & Otaki, J. M. (2023). The Plastic Larval Body Color of the Pale Grass Blue Butterfly Zizeeria maha (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) in Response to the Host Plant Color: The Maternal Effect on Crypsis. Insects, 14(2), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020202






