Key Amino Acid Residues Involved in Binding Interactions between Bactrocera minax Odorant-Binding Protein 3 (BminOBP3) and Undecanol
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. 3D Modeling and Molecular Docking
2.3. Cloning and Sequencing of BminOBP3
2.4. Preparation of Mutant cDNA Sequences
2.5. Expression Vectors Construction
2.6. Expression and Purification of BminOBP3 and Mutants
2.7. Fluorescence Binding Assays
2.8. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
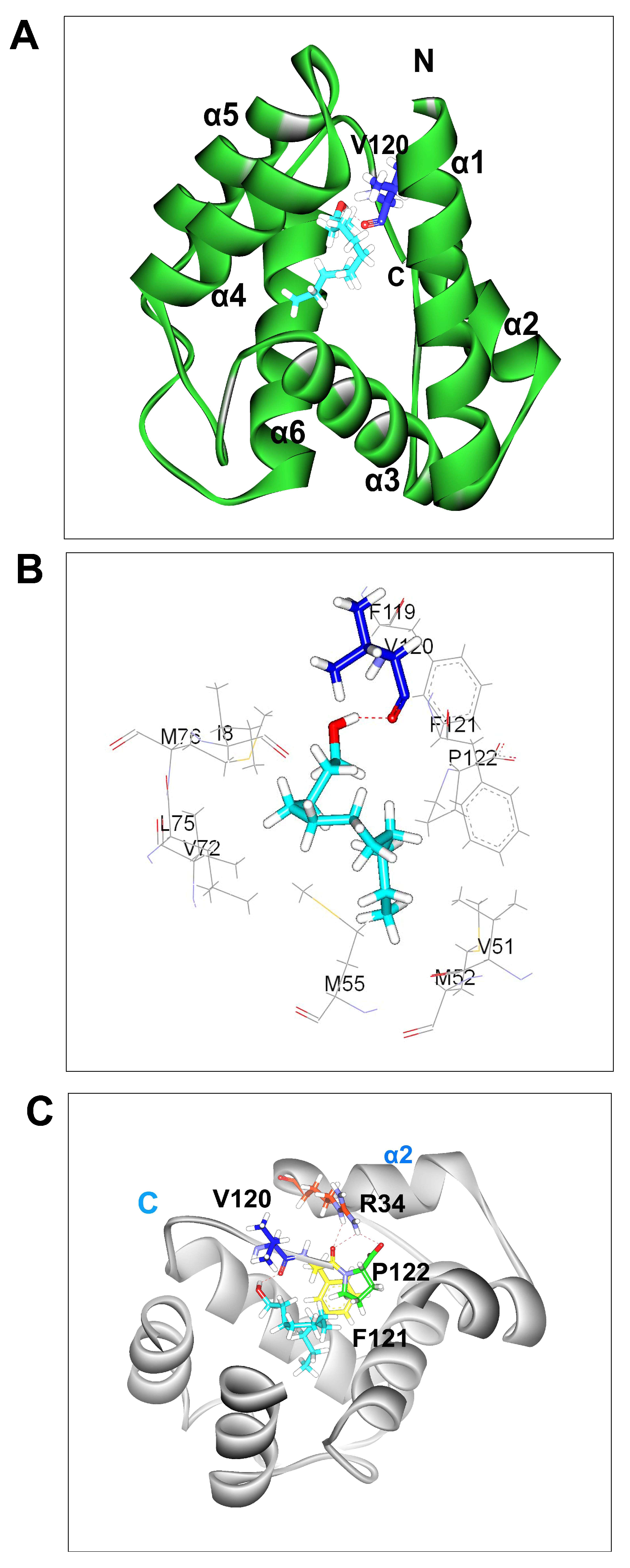
3.1. 3D Model of BminOBP3
3.2. Molecular Docking
3.3. Expression and Purification of BminOBP3 and Mutant Proteins
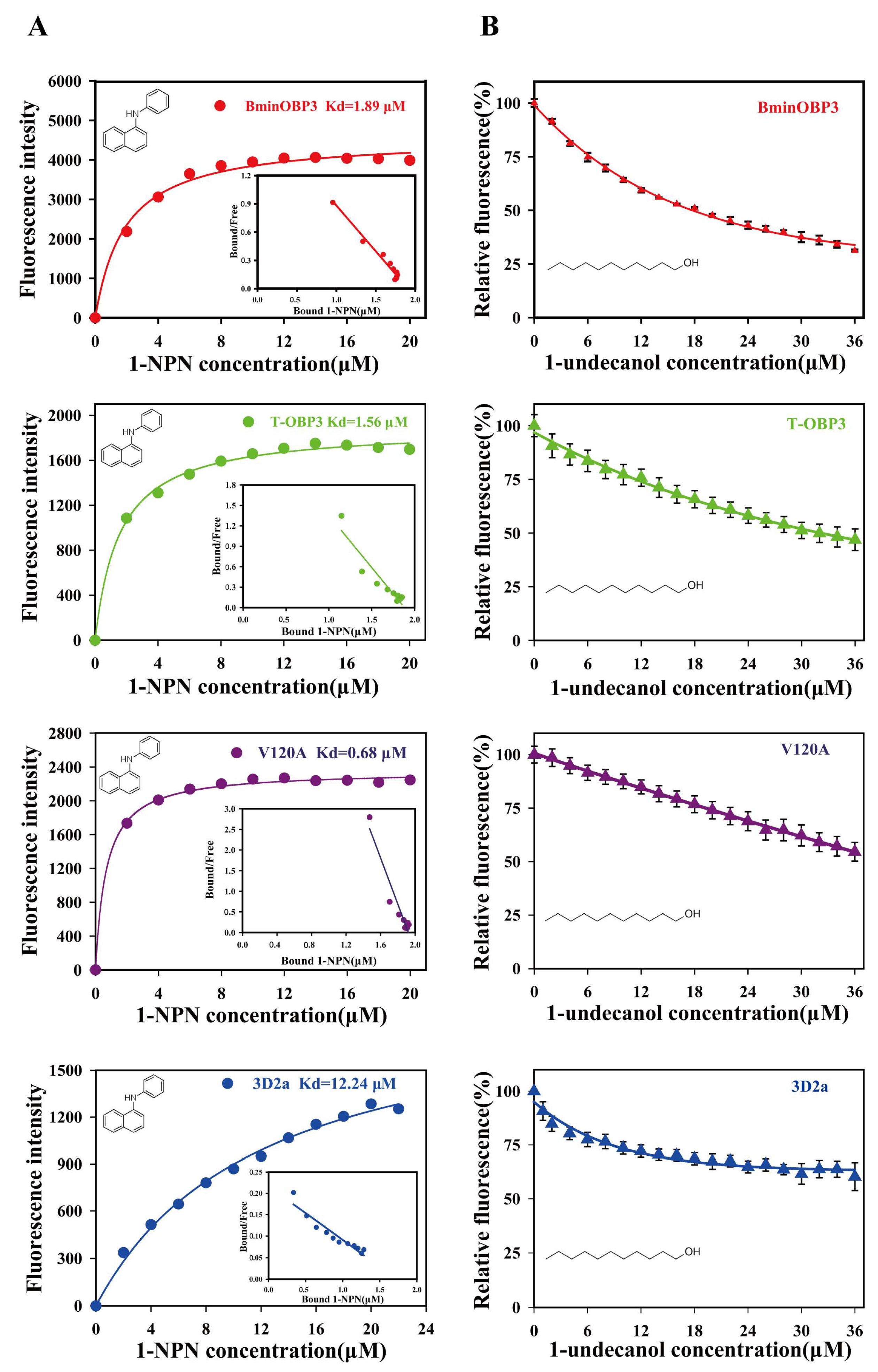
3.4. Binding Affinities of BminOBP3 and Mutants to Undecanol
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leal, W.S. Pheromone reception. Top Curr. Chem. 2005, 240, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrecht, R.A. Odorant-binding proteins: Expression and function. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1998, 855, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, J.; Breer, H. Olfactory reception in invertebrates. Science 1999, 286, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaissling, K.E. Olfactory perireceptor and receptor events in moths: A kinetic model. Chem. Senses 2001, 26, 125–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Pellegrino, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Vosshall, L.B.; Touhara, K. Insect olfactory receptors are heteromeric ligand-gated ion channels. Nature 2008, 452, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicher, D.; Schäfer, R.; Bauernfeind, R.; Stensmyr, M.C.; Heller, R.; Heinemann, S.H.; Hansson, B.S. Drosophila odorant receptors are both ligand-gated and cyclic-nucleotide-activated cation channels. Nature 2008, 452, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, G.R. Research progress of integrated coding of peripheral olfactory signals in the central nervous system of insects. Acta. Entomol. Sin. 2020, 63, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.X.; Atkinson, R.; Jones, D.N.M.; Smith, D.P. Drosophila OBP LUSH is required for activity of pheromone-sensitive neurons. Neuron 2005, 45, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, J.; Guidolin, A.; Sed, Z.; Cornel, A.J.; Leal, W.S. Knockdown of a mosquito odorant-binding protein involved in the sensitive detection of oviposition attractants. J. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 36, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, B.; Grossi, G.; Falabella, P.; Liu, Y.; Yan, S.; Lu, J.; Xi, J.; Wang, G. Molecular basis of alarm pheromone detection in aphids. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liang, X.F.; Xu, L.; Keesey, I.W.; Lei, Z.R.; Smagghe, G.; Wang, J.J. An Antennae-Specific Odorant-Binding Protein Is Involved in Bactrocera dorsalis Olfaction. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, B.H.; Nikonova, L.; Leal, W.S.; Clardy, J. Sexual attraction in the silkworm moth: Structure of the pheromone-binding-protein-bombykol complex. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenschlage, C.; Leal, W.S.; Clardy, J. Bombyx mori pheromone-binding protein binding nonpheromone ligands: Implications for pheromone recognition. Structure 2007, 15, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.J.; Robertson, G.; He, X.L.; Dufour, S.; Hooper, A.M.; Pickett, J.A.; Keep, N.H.; Field, L.M. Characterisation of Bombyx mori odorant-binding proteins reveals that a general odorant-binding protein discriminates between sex pheromone components. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 389, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thode, A.B.; Kruse, S.W.; Nix, J.C.; Jones, D.N.M. The role of multiple hydrogen-bonding groups in specific alcohol binding sites in proteins: Insights from structural studies of LUSH. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 376, 1360–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, C.; Li, K. Three amino acid residues of an odorant-binding protein are involved in binding odours in Loxostege sticticalis L. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2015, 24, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.X.; Li, C.B.; Liu, D.G. Analyses of structural dynamics revealed flexible binding mechanism for the Agrilus mali odorant binding protein 8 towards plant volatiles. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 1642–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenschlager, C.; Leal, W.S.; Clardy, J. Coil-to-helix transition and ligand release of Bombyx mori pheromone-binding protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 335, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damberger, F.F.; Ishida, Y.; Leal, W.S.; Wuethrich, K. Structural basis of ligand binding and release in insect pheromone-binding proteins: NMR structure of Antheraea polyphemus PBP1 at pH 4.5. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 373, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S.; Ishida, Y.; Pelletier, J.; Xu, W.; Rayo, J.; Xu, X.Z.; Ames, J.B. Olfactory Proteins Mediating Chemical Communication in the Navel Orangeworm Moth, Amyelois transitella. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wogulis, M.; Morgan, T.; Ishida, Y.; Leal, W.S.; Wilson, D.K. The crystal structure of an odorant binding protein from Anopheles gambiae: Evidence for a common ligand release mechanism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 339, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Xu, X.Z.; Xu, W.; Inshida, Y.; Leal, W.S.; Ames, J.B.; Clardy, J. Crystal and solution structures of an odorant-binding protein from the southern house mosquito complexed with an oviposition pheromone. Pro. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19102–19107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, N.R.; Krogh, R.; Xu, W.; Ishida, Y.; Iulek, J.; Leal, W.S.; Oliva, G. Structure of an odorant-binding protein from the mosquito Aedes aegypti suggests a binding pocket covered by a pH-sensitive “Lid”. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Tian, X.L.; Gui, L.Y.; Wang, F.L.; Zhang, G.H. Functional characterization of two antenna-enriched odorant-binding proteins from Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 2361–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwede, T.; Kopp, J.; Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL: An automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2003, 31, 3381–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, G.N.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Sasisekharan, V. Stereochemistry of polypeptide chain configurations. J. Mol. Biol. 1963, 7, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüthy, R.; Bowie, J.U.; Eisenberg, D. Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Nature 1992, 356, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.S.; Robertson, D.H.; Brooks, C.L.; Vieth, M. Detailed analysis of grid-based molecular docking: A case study of CDOCKER-A CHARMm-based MD docking algorithm. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, F.L.; Gui, L.Y.; Zhang, G.H. Identification and tissue distribution of odorant binding protein genes in the citrus fruit fly, Bactrocera minax (Enderlein)(Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2019, 22, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Mei, X.D.; Feng, J.N.; Berg, B.G.; Zhang, Y.J.; Guo, Y.Y. Characterization of three pheromone-binding proteins (PBPs) of Helicoverpa armigera(Hübner) and their binding properties. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.H.; Chen, J.; Yu, H.L.; Tian, X.L.; Wu, J.X. Molecular and Functional Characterization of pheromone binding protein 1 from the Oriental Fruit Moth, Grapholita molesta (Busck). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-Pdb Viewer: An environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavasotto, C.N.; Phatak, S.S. Homology modeling in drug discovery: Current trends and applications. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, L.; You, K.X.; Jing, Q. The Extracting Method and Application of a Sex Pheromone of Bactrocera minax. China Patent CN103 766 336, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.Y.; Wang, W.X.; Zhang, Z.D.; Zhang, L. Binding specificity of locust odorant binding protein and its key binding site for initial recognition of alcohols. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Pace, T.C.S.; Castillo, C.; Bohne, C.; O’Neill, M.A.; Plettner, E. Ligand-interaction kinetics of the pheromone-binding protein from the Gypsy moth, L.dispar: Insights into the mechanism of binding and release. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.M.; Tang, H.; Bohne, C.; Plettner, E. Binding conformation and kinetics of two pheromone-binding proteins from the Gypsy moth Lymantria dispar with biological and nonbiological ligands. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegelberger, G. Redox-shift of the pheromone-binding protein in the silkmoth Antheraea polyphemus. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 232, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larter, N.K.; Sun, J.S.; Carlson, J.R. Organization and function of Drosophila odorant binding proteins. eLife 2016, 5, e20242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Sun, J.S.; Carlson, J.R. Robust olfactory responses in the absence of odorant binding proteins. eLife 2019, 8, e51040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Purpose | Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloning/expression for the wild-type BminOBP3 | OBP3E-Forward | CGCGGATCCG(1)GTGCTACGGAAGATC(16) | |
| OBP3E-Reverse | CCCAAGCTTT(369)TAAGGGAAAACAAAC(354) | ||
| Expression for mutants | For the expression of the C-terminus (I116-P122) truncated mutant of BminOBP3 | T-OBP3E-Forward | CGCGGATCCG(1)GTGCTACGGAAGA(14) |
| T-OBP3E-Reverse | CCCAAGCTTTTAA(354)TTATCGCGCAAACA(331) | ||
| For the expression of the mutant that lacks the last two amino acids (F121 and P122) from the C-terminus of BminOBP3 | 3D2aE-Forward | GGATCCG(1)GTGCTACGGAA(12) | |
| 3D2aE-Reverse | AAGCTTTTAA(360)ACAAACTTGGATATATT(343) | ||
| For the expression of the BminOBP3-V120A (valine to alanine at position 120) mutant | V120A-Forward | A(348)TCCAAGTTTGCTTTCCCTTAA(369) | |
| V120A-Reverse | A(347)TATTATCGCGCAAACAAATTAG(323) | ||
| Proteins | Undecanol | |
|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μM) | Ki (μM) | |
| BminOBP3 | 17.72 ± 0.78 | 11.59 ± 0.51 a |
| T-OBP3 | 32.06 ± 0.74 | 19.57 ± 0.45 b |
| V120A | >36 | _ |
| 3D2a | >36 | _ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Tian, X.; Gui, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, G. Key Amino Acid Residues Involved in Binding Interactions between Bactrocera minax Odorant-Binding Protein 3 (BminOBP3) and Undecanol. Insects 2023, 14, 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14090745
Yang L, Tian X, Gui L, Wang F, Zhang G. Key Amino Acid Residues Involved in Binding Interactions between Bactrocera minax Odorant-Binding Protein 3 (BminOBP3) and Undecanol. Insects. 2023; 14(9):745. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14090745
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ling, Xiaoli Tian, Lianyou Gui, Fulian Wang, and Guohui Zhang. 2023. "Key Amino Acid Residues Involved in Binding Interactions between Bactrocera minax Odorant-Binding Protein 3 (BminOBP3) and Undecanol" Insects 14, no. 9: 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14090745
APA StyleYang, L., Tian, X., Gui, L., Wang, F., & Zhang, G. (2023). Key Amino Acid Residues Involved in Binding Interactions between Bactrocera minax Odorant-Binding Protein 3 (BminOBP3) and Undecanol. Insects, 14(9), 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14090745





