Characteristics and Comparative Analysis of Mitochondrial Genomes of the Aphid Genus Hyalopterus Koch (Hemiptera: Aphididae: Aphidinae)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.2. Mitogenome Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
2.3. Sequence Analyses
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
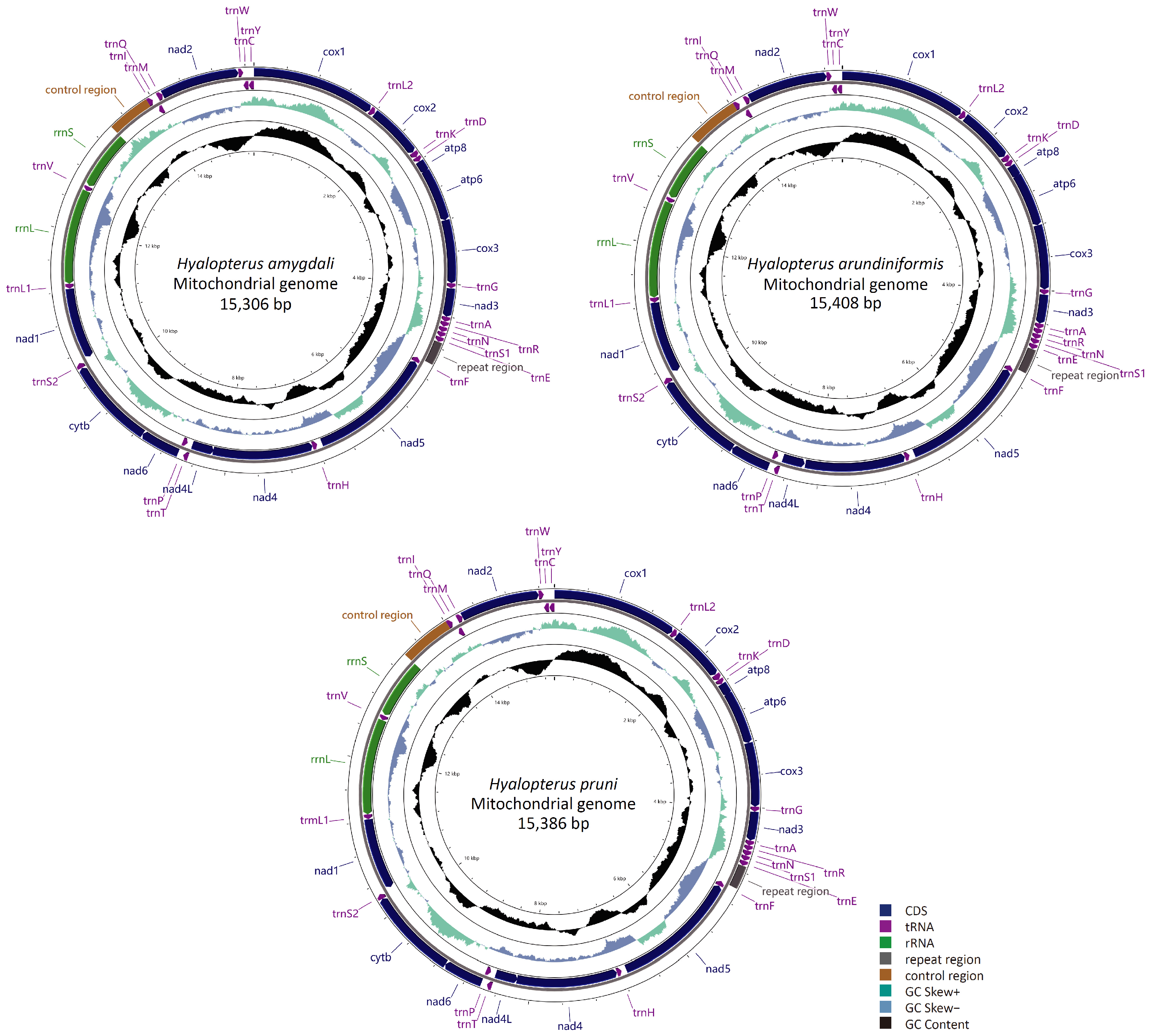
3.1. General Features of the Mitogenomes of Hyalopterus
3.2. Nucleotide Composition
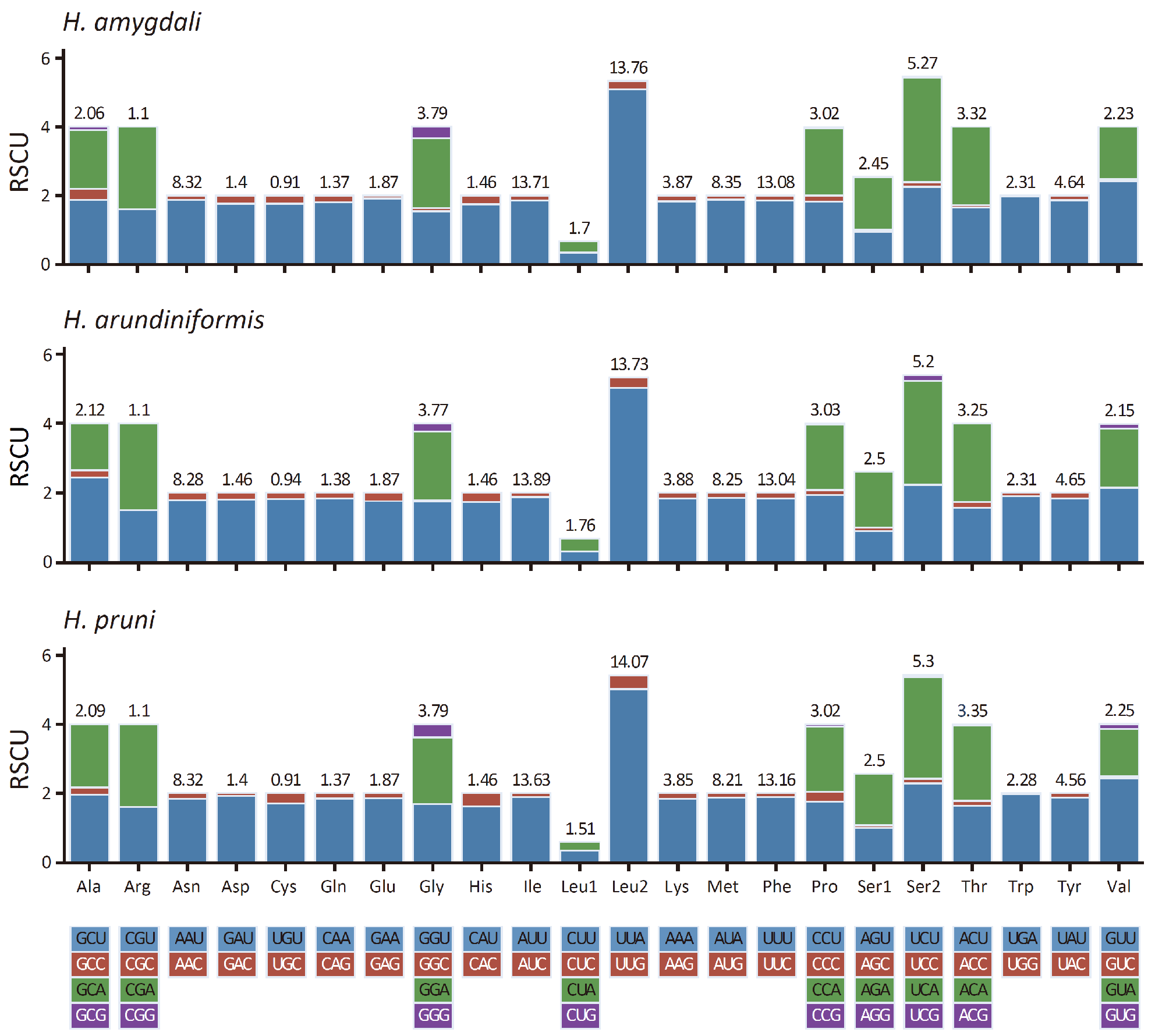
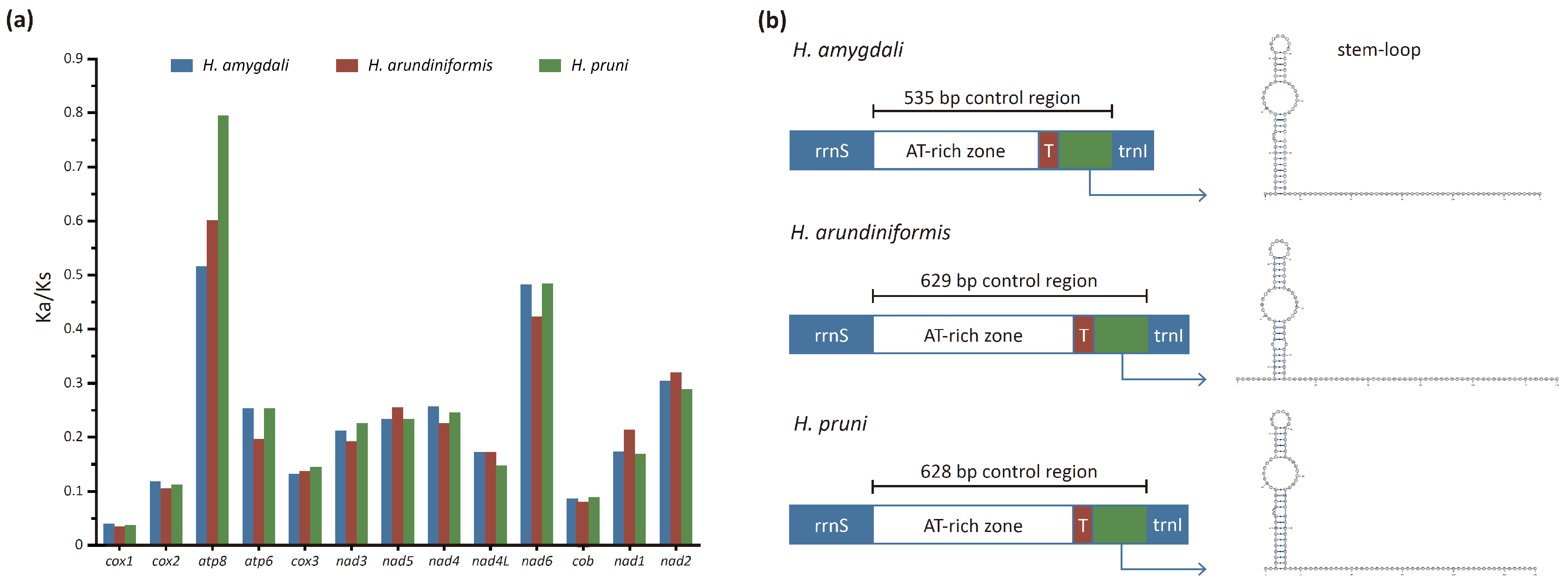
3.3. Protein-Coding Genes
3.4. Transfer and Ribosomal RNA Genes
3.5. Control Region
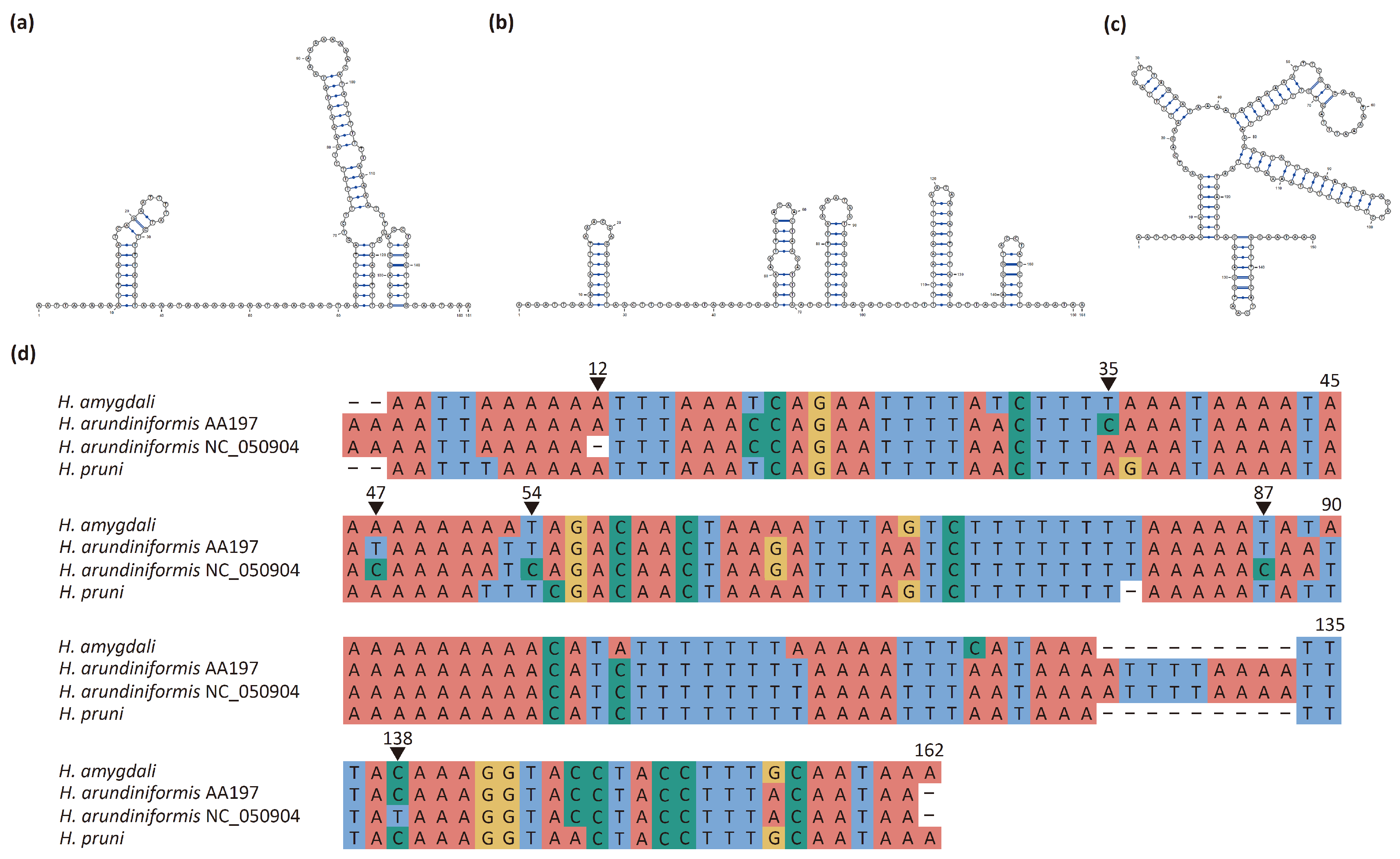
3.6. Repeat Region
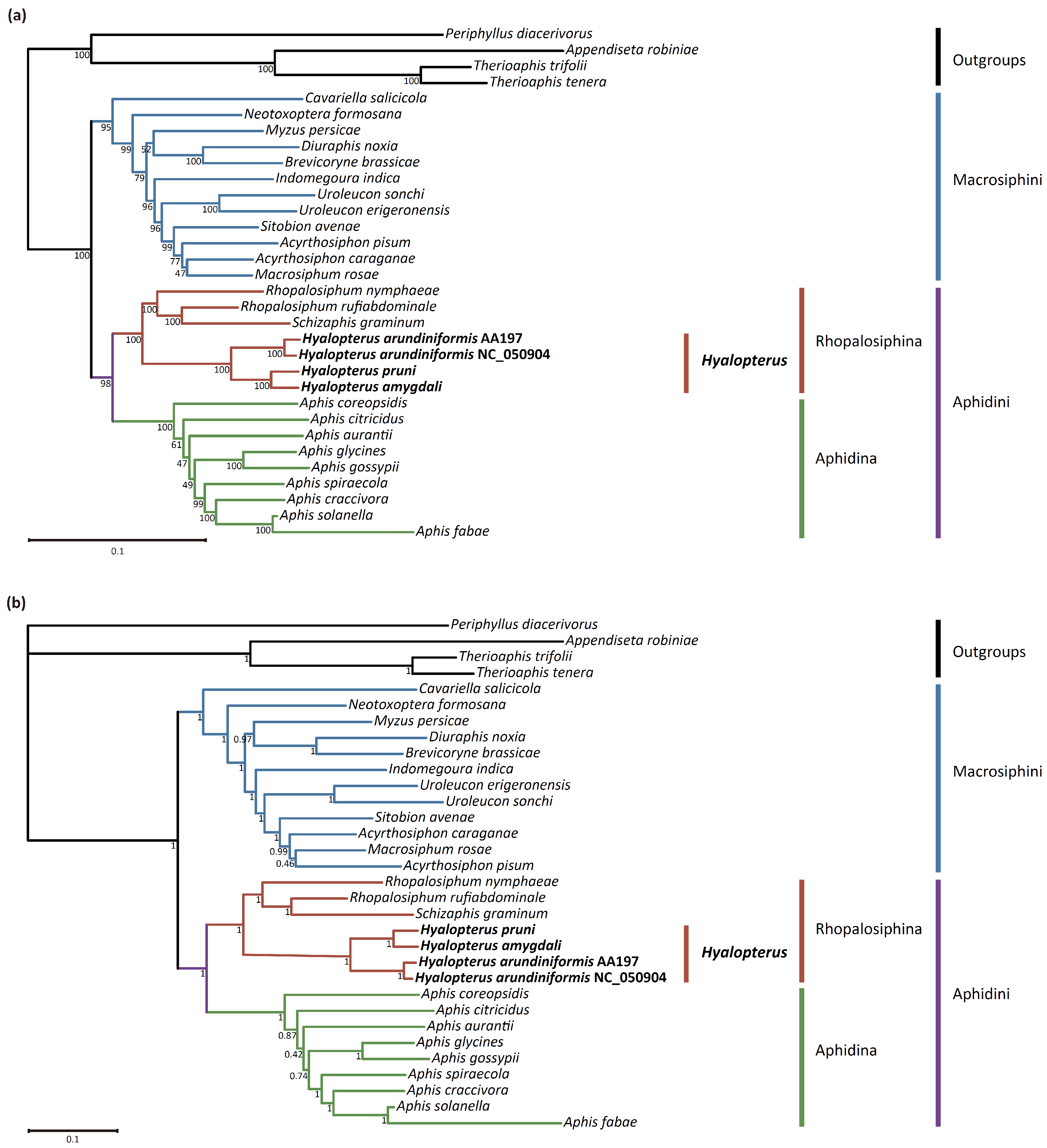
3.7. Phylogenetic Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the world’s Plants: An Online Identification and Information Guide. Available online: https://aphidsonworldsplants.info/ (accessed on 6 April 2024).
- Mosco, M.C.; Arduino, P.; Bullini, L.; Barbagallo, S. Genetic heterogeneity, reproductive isolation and host preferences in mealy aphids of the Hyalopterus pruni complex (Homoptera, Aphidoidea). Mol. Ecol. 1997, 6, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozier, J.D.; Roderick, G.K.; Mills, N.J. Genetic evidence from mitochondrial, nuclear, and endosymbiont markers for the evolution of host plant associated species in the aphid genus Hyalopterus (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Evolution 2007, 61, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulios, K.D.; Margaritopoulos, J.T.; Tsitsipis, J.A. Morphological separation of host adapted taxa within the Hyalopterus pruni complex (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2007, 104, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozier, J.D.; Foottit, R.G.; Miller, G.L.; Mills, N.J.; Roderick, G.K. Molecular and morphological evaluation of the aphid genus Hyalopterus Koch (Insecta: Hemiptera: Aphididae), with a description of a new species. Zootaxa 2008, 1688, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakauskas, R.; Havelka, J.; Zaremba, A. Mitochondrial COI and morphological specificity of the mealy aphids (Hyalopterus ssp.) collected from different hosts in Europe (Hemiptera, Aphididae). ZooKeys 2013, 319, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.Y.; Qiao, G.X. Phylogeny and species reassessment of Hyalopterus (Aphididae, Aphidinae). Zool. Scr. 2020, 49, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozier, J.D.; Roderick, G.K.; Mills, N.J. Tracing the invasion history of mealy plum aphid, Hyalopterus pruni (Hemiptera: Aphididae), in North America: A population genetics approach. Biol. Invasions 2009, 11, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, J.L. Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curole, J.P.; Kocher, T.D. Mitogenomics: Digging deeper with complete mitochondrial genomes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1999, 14, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Yang, P.; Jiang, F.; Chapuis, M.P.; Shali, Y.; Sword, G.A.; Kang, L. Mitochondrial genomes reveal the global phylogeography and dispersal routes of the migratory locust. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 4344–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Qiao, G. Mitochondrial genome sequences effectively reveal deep branching events in aphids (Insecta: Hemiptera: Aphididae). Zool. Scr. 2017, 46, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condamine, F.L.; Nabholz, B.; Clamens, A.L.; Dupuis, J.R.; Sperling, F.A.H. Mitochondrial phylogenomics, the origin of swallowtail butterflies, and the impact of the number of clocks in Bayesian molecular dating. Syst. Entomol. 2018, 43, 460–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, R.; Feng, K.; Yue, B.; Du, C.; Zhou, C. Characterization of seventeen complete mitochondrial genomes: Structural features and phylogenetic implications of the lepidopteran insects. Insects 2022, 13, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.H.; Sun, P.Y.; Lao, Y.L.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.N.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Q. Mitogenome of a monotypic genus, Oliotius Kottelat, 2013 (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae): Genomic characterization and phylogenetic position. Gene 2023, 851, 147035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, M.L.; Baumann, L.; Baumann, P. Organization of the mitochondrial genomes of whiteflies, aphids, and psyllids (Hemiptera, Sternorrhyncha). BMC Evol. Biol. 2004, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Du, Z.; Song, F.; He, J. The complete mitochondrial genome of the mealy plum aphid, Hyalopterus pruni (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2020, 5, 3667–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, Y.; Xi, H.; Park, J.; Lee, W. The complete mitochondrial genome of Rhopalosiphum nymphaeae (Linnaeus, 1761) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2020, 5, 1613–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. GigaScience 2012, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Al-Arab, M.; Bernhart, S.H.; Reinhardt, F.; Stadler, P.F.; Middendorf, M.; Bernt, M. Improved annotation of protein-coding genes boundaries in metazoan mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 10543–10552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.R.; Stothard, P. The CGView Server: A comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W181–W184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Qin, M.; Jiang, L.Y.; Qiao, G.X. The mitochondrial genome of Greenidea psidii van der Goot (Hemiptera: Aphididae: Greenideinae) and comparisons with other Aphididae aphids. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darty, K.; Denise, A.; Ponty, Y. VARNA: Interactive drawing and editing of the RNA secondary structure. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1974–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothard, P. The sequence manipulation suite: JavaScript programs for analyzing and formatting protein and DNA sequences. BioTechniques 2000, 28, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Rivas, B.; Martínez-Torres, D. Combination of molecular data support the existence of three main lineages in the phylogeny of aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and the basal position of the subfamily Lachninae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 55, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebijith, K.B.; Asokan, R.; Hande, H.R.; Joshi, S.; Surveswaran, S.; Ramamurthy, V.V.; Krishna Kumar, N.K. Reconstructing the macroevolutionary patterns of aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae) using nuclear and mitochondrial DNA sequences. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2017, 121, 796–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, C.L.; Miller, G.L. Phylogenomics of the Aphididae: Deep relationships between subfamilies clouded by gene tree discordance, introgression and the gene tree anomaly zone. Syst. Entomol. 2022, 47, 470–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, F.; Zardoya, R.; Telford, M.J. TranslatorX: Multiple alignment of nucleotide sequences guided by amino acid translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W7–W13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraku, S.; Zmasek, C.M.; Nishimura, O.; Katoh, K. aLeaves facilitates on-demand exploration of metazoan gene family trees on MAFFT sequence alignment server with enhanced interactivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W22–W28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castresana, J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talavera, G.; Castresana, J. Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clary, D.O.; Wolstenholme, D.R. The mitochondrial DNA molecule of Drosophila yakuba: Nucleotide sequence, gene organization, and genetic code. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, X.L.; Qiao, G.X. Comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes of five aphid species (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and phylogenetic implications. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Donthu, R.K.; Hall, R.; Hon, L.; Weber, E.; Badger, J.H.; Giordano, R. Description of soybean aphid (Aphis glycines Matsumura) mitochondrial genome and comparative mitogenomics of Aphididae (Hemiptera: Sternorrhyncha). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 113, 103208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, C.; Liu, Q.; Zou, T.; Qiao, G.; Huang, X. Insights into the evolution of aphid mitogenome features from new data and comparative analysis. Animals 2022, 12, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronova, N.V.; Warner, D.; Shulinski, R.; Levykina, S.; Bandarenka, Y.; Zhorov, D. The largest aphid mitochondrial genome found in invasive species Therioaphis tenera (Aizenberg, 1956). Mitochondrial DNA B 2019, 4, 730–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronova, N.V.; Levykina, S.; Warner, D.; Shulinski, R.; Bandarenka, Y.; Zhorov, D. Characteristic and variability of five complete aphid mitochondrial genomes: Aphis fabae mordvilkoi, Aphis craccivora, Myzus persicae, Therioaphis tenera and Appendiseta robiniae (Hemiptera; Sternorrhyncha; Aphididae). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Qiao, G.; Chen, J. The complete mitochondrial genome of Schizoneuraphis gallarum van der Goot, 1917 (Hemiptera: Aphididae: Hormaphidinae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2021, 6, 2982–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.Y.; Qiao, G.X. Hemipteran mitochondrial genomes: Features, structures and implications for phylogeny. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12382–12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.J.; Shi, M.; Chen, X.X.; Sharkey, M.J.; van Achterberg, C.; Ye, G.Y.; He, J.H. New views on strand asymmetry in insect mitochondrial genomes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, D.; Montoya, J.; Attardi, G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature 1981, 290, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, D.R. Animal mitochondrial DNA: Structure and evolution. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1992, 141, 173–216. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.X.; Hewitt, G.M. Insect mitochondrial control region: A review of its structure, evolution and usefulness in evolutionary studies. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1997, 25, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Lu, C.; Deng, J.; Huang, X. The first complete mitochondrial genome of Lachninae species and comparative genomics provide new insights into the evolution of gene rearrangement and the repeat region. Insects 2021, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Chen, S.; Chen, Q.D.; Pu, D.Q.; Chen, Z.T.; Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, X. The first mitochondrial genomes of the family Haplodiplatyidae (Insecta: Dermaptera) reveal intraspecific variation and extensive gene rearrangement. Biology 2022, 11, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.; Qiao, G. Human-mediated eco-evolutionary processes of the herbivorous insect Hyalopterus arundiniformis during the Holocene. Divers. Distrib. 2022, 28, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Shin, S.; Jung, S.; Clarke, D.J.; Lee, S. Molecular phylogeny of Macrosiphini (Hemiptera: Aphididae): An evolutionary hypothesis for the Pterocomma-group habitat adaptation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 121, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Jang, Y. Macroevolutionary patterns in the Aphidini aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae): Diversification, host association, and biogeographic origins. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| H. amygdali | H. arundiniformis | H. pruni | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A + T% | AT-Skew | GC-Skew | A + T% | AT-Skew | GC-Skew | A + T% | AT-Skew | GC-Skew | |
| Whole genome | 83.90 | 0.08 | −0.25 | 83.80 | 0.08 | −0.27 | 83.88 | 0.07 | −0.27 |
| PCGs | 83.10 | −0.15 | −0.05 | 82.95 | −0.15 | −0.04 | 83.07 | −0.16 | −0.03 |
| First codon | 80.00 | 0 | 0.13 | 79.92 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 80.14 | −0.01 | 0.15 |
| Second codon | 75.90 | −0.40 | −0.13 | 75.79 | −0.39 | −0.12 | 75.66 | −0.40 | −0.13 |
| Third codon | 93.70 | −0.09 | −0.29 | 93.20 | −0.10 | −0.22 | 93.41 | −0.10 | −0.17 |
| PCGs-J | 82.00 | −0.06 | −0.23 | 81.74 | −0.06 | −0.23 | 81.99 | −0.07 | −0.22 |
| PCGs-J-first codon | 79.20 | 0.12 | 0 | 78.66 | 0.12 | −0.01 | 79.11 | 0.11 | 0.01 |
| PCGs-J-second codon | 73.80 | −0.36 | −0.27 | 73.71 | −0.36 | −0.26 | 73.53 | −0.36 | −0.27 |
| PCGs-J-third codon | 93.40 | 0.015 | −0.88 | 92.86 | 0.02 | −0.80 | 93.35 | 0.00 | −0.76 |
| PCGs-N | 85.00 | −0.29 | 0.32 | 84.90 | −0.30 | 0.35 | 84.79 | −0.30 | 0.34 |
| PCGs-N-first codon | 81.40 | −0.18 | 0.38 | 81.50 | −0.18 | 0.40 | 81.79 | −0.19 | 0.40 |
| PCGs-N-second codon | 79.60 | −0.46 | 0.15 | 78.70 | −0.45 | 0.15 | 79.07 | −0.46 | 0.15 |
| PCGs-N-third codon | 94.40 | −0.25 | 0.69 | 93.50 | −0.28 | 0.84 | 93.50 | −0.27 | 0.80 |
| tRNA genes | 85.60 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 85.77 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 85.50 | 0.05 | 0.13 |
| rRNA genes | 84.80 | −0.07 | 0.34 | 84.93 | −0.08 | 0.34 | 84.93 | −0.07 | 0.34 |
| Control region | 84.10 | −0.07 | −0.16 | 85.53 | −0.05 | −0.32 | 86.31 | −0.08 | −0.30 |
| Repeat region | 89.90 | 0.19 | −0.39 | 89.30 | 0.18 | −0.50 | 88.38 | 0.14 | −0.33 |
| Species | Length of Repeat Region (bp) | Length of Repeat Unit (bp) | Copy Number | Sequence Similarity of Repeat Unit (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. amygdali | H. arundiniformis AA197 | H. arundiniformis NC_050904 | H. pruni | ||||
| H. amygdali | 286 | 151 | 1.834 | – | 84.57 | 82.10 | 91.39 |
| H. arundiniformis AA197 | 299 | 161 | 1.832 | 84.57 | – | 96.27 | 84.57 |
| H. arundiniformis NC_050904 | 298 | 160 | 1.838 | 82.10 | 96.27 | – | 82.72 |
| H. pruni | 284 | 150 | 1.860 | 91.39 | 84.57 | 82.72 | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Jiang, L.; Qiao, G.; Chen, J. Characteristics and Comparative Analysis of Mitochondrial Genomes of the Aphid Genus Hyalopterus Koch (Hemiptera: Aphididae: Aphidinae). Insects 2024, 15, 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15060389
Zhang X, Li C, Jiang L, Qiao G, Chen J. Characteristics and Comparative Analysis of Mitochondrial Genomes of the Aphid Genus Hyalopterus Koch (Hemiptera: Aphididae: Aphidinae). Insects. 2024; 15(6):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15060389
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaolu, Cailing Li, Liyun Jiang, Gexia Qiao, and Jing Chen. 2024. "Characteristics and Comparative Analysis of Mitochondrial Genomes of the Aphid Genus Hyalopterus Koch (Hemiptera: Aphididae: Aphidinae)" Insects 15, no. 6: 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15060389
APA StyleZhang, X., Li, C., Jiang, L., Qiao, G., & Chen, J. (2024). Characteristics and Comparative Analysis of Mitochondrial Genomes of the Aphid Genus Hyalopterus Koch (Hemiptera: Aphididae: Aphidinae). Insects, 15(6), 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15060389







