Oxalic Acid Treatment: Short-Term Effects on Enzyme Activities, Vitellogenin Content, and Residual Oxalic Acid Content in House Bees, Apis mellifera L.
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Haemolymph Collection
2.2. Oxalic Acid Content
2.3. Enzymatic Assays
2.4. Vitellogenin Content
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Oxalic Acid Content
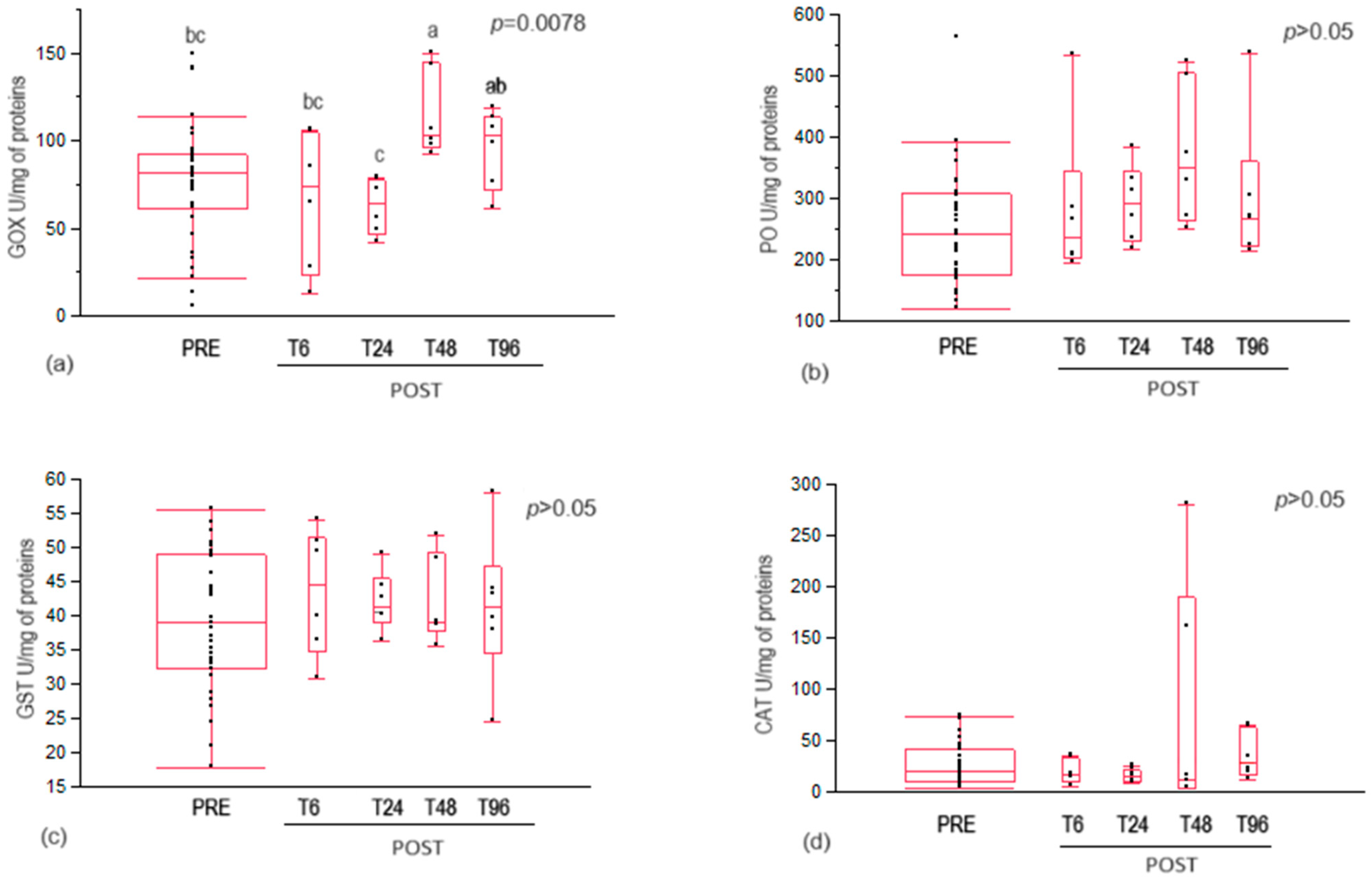
3.2. Enzymatic Assays
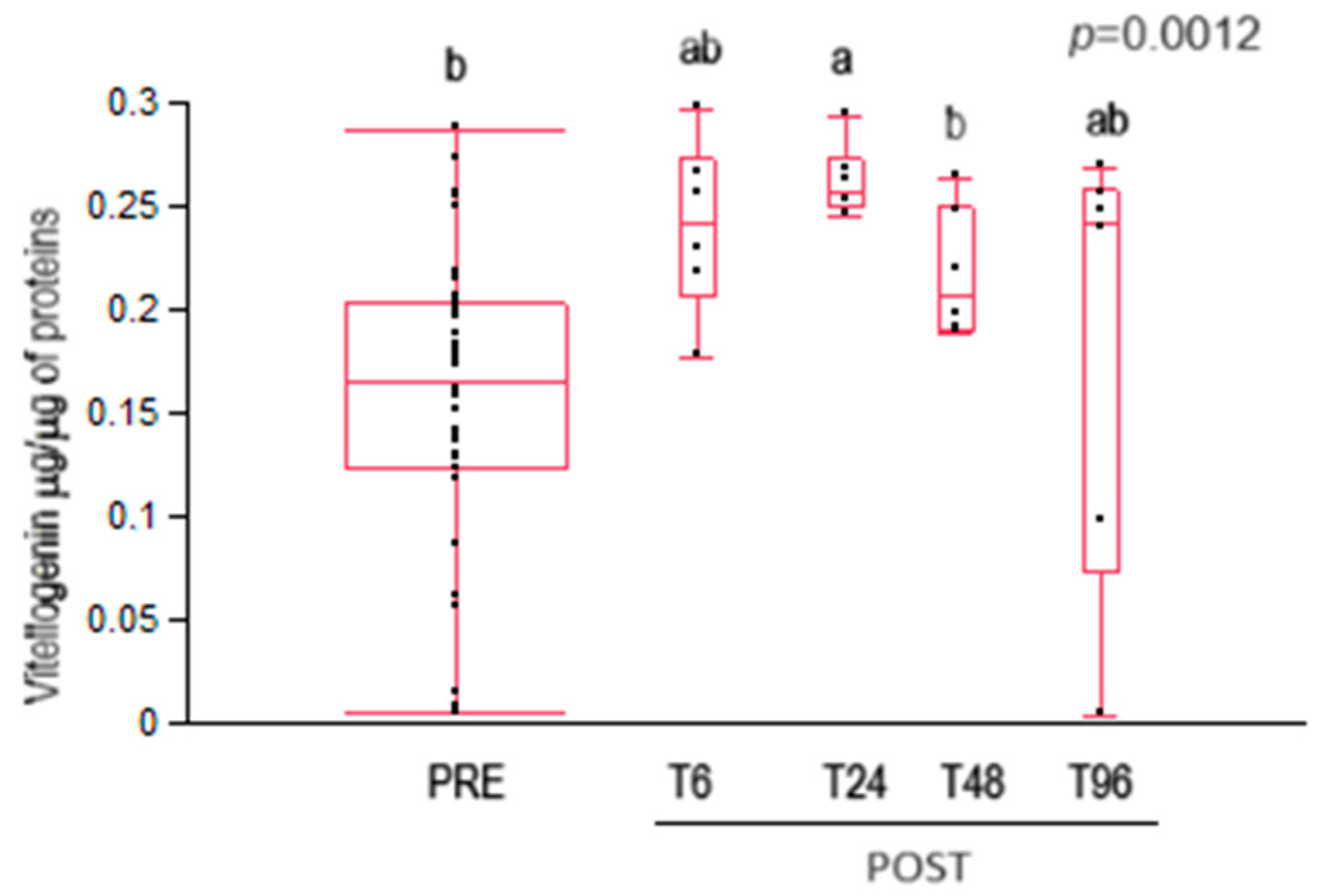
3.3. Vitellogenin Content
4. Discussion
4.1. Oxalic Acid Content
4.2. Immune System Enzymes
4.3. Antioxidant Enzymes
4.4. Vitellogenin
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeGrandi-Hoffman, G.; Graham, H.; Ahumada, F.; Smart, M.; Ziolkowski, N. The economics of honey bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae) management and overwintering strategies for colonies used to pollinate almonds. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 2524–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porrini, C.; Mutinelli, F.; Bortolotti, L.; Granato, A.; Laurenson, L.; Roberts, K.; Gallina, A.; Silvester, N.; Medrzycki, P.; Renzi, T.; et al. The status of honey bee health in Italy: Results from the nationwide bee monitoring network. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhauer, N.; Kulhanek, K.; Antúnez, K.; Human, H.; Chantawannakul, P.; Chauzat, M.P. Drivers of colony losses. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 26, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boncristiani, H.; Ellis, J.D.; Bustamante, T.; Graham, J.; Jack, C.; Kimmel, C.B.; Mortensen, A.; Schmehl, D.R. World honey bee health: The global distribution of western honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) pests and pathogens. Bee World 2020, 98, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, P.; Shumkova, R.; Palova, N.; Neov, B. Factors associated with honey bee colony losses: A mini-review. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.J. The role of Varroa and viral pathogens in the collapse of honeybee colonies: A modelling approach. J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 38, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzi, F.; Le Conte, Y. Ecology of Varroa destructor, the major ectoparasite of the western honey bee, Apis mellifera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkranz, P.; Aumeier, P.; Ziegelmann, B. Biology and control of Varroa destructor. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 103, S96–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen-Walker, P.L.; Gunn, A. The effect of the ectoparasitic mite, Varroa destructor on adult worker honeybee (Apis mellifera) emergence weights, water, protein, carbohydrate, and lipid levels. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2001, 101, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralj, J.; Fuchs, S. Parasitic Varroa destructor mites influence flight duration and homing ability of infested Apis mellifera foragers. Apidologie 2006, 37, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annoscia, D.; Del Piccolo, F.; Nazzi, F. How does the mite Varroa destructor kill the honeybee Apis mellifera? Alteration of cuticular hydrocarbons and water loss in infested honeybees. J. Insect Physiol 2012, 58, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.P.; Siede, R. Honey bee viruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2007, 70, 33–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisder, S.; Aumeier, P.; Genersch, E. Deformed wing virus: Replication and viral load in mites (Varroa destructor). J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Steen, J.; Vejsnæs, F. Varroa control: A brief overview of available methods. Bee World 2021, 98, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cabrera, J.; Bumann, H.; Rodríguez-Vargas, S.; Kennedy, P.J.; Krieger, K.; Altreuther, G.; Hertel, A.; Hertlein, G.; Nauen, R.; Williamson, M.S. A single mutation is driving resistance to pyrethroids in European populations of the parasitic mite, Varroa destructor. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tihelka, E. Effects of synthetic and organic acaricides on honey bee health: A review. Slov. Vet. Res. 2018, 55, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, A.I.; Steinhauer, N.A.; van Engelsdorp, D. Use of chemical and nonchemical methods for the control of Varroa destructor (Acari: Varroidae) and associated winter colony losses in US beekeeping operations. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 1509–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondet, F.; Le Conte, Y. Parasites. In Bee Health and Veterinarians; OIE, World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2014; pp. 131–141. ISBN 9789290449232. [Google Scholar]
- Nanetti, A.; Ghini, S.; Gattavecchia, E.; Bartolomei, P.; Marcazzan, G.L.; Massi, S. Pharmacodynamics of Oxalic Acid and Treatment Residues in Honey, European Group for Integrated Varroa Control, Rauischholzhausen. 2003. Available online: http://www.apis.admin.ch/host/varroa/rauisch.htm (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Rademacher, E.; Harz, M. Oxalic acid for the control of varroosis in honey bee colonies—A review. Apidologie 2006, 37, 98–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charriére, J.D.; Imdorf, A. Oxalic acid treatment by trickling against Varroa destructor: Recommendations for use in central Europe and under temperate climate conditions. Bee World 2002, 83, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanetti, A.; Büchler, R.; Charrière, J.; Friesd, I.; Helland, S.; Imdorf, A. Oxalic acid treatments for varroa control (a review). Apiacta 2003, 38, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Charrière, J.D.; Imdorf, A.; Kuhn, R. Bee tolerance of different winter Varroa treatments. Schweiz. Bienen-Ztg. 2004, 127, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Terpin, B.; Perkins, D.; Richter, S.; Leavey, J.K.; Snell, T.W.; Pierson, J.A. A scientific note on the effect of oxalic acid on honey bee larvae. Apidologie 2019, 50, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toomemaa, K.; Martin, A.J.; Williams, I.H. The effect of different concentrations of oxalic acid in aqueous and sucrose solution on Varroa mites and honey bees. Apidologie 2010, 41, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Toufailia, H.; Scandian, L.; Ratnieks, F.L. Towards integrated control of varroa: (2) comparing application methods and doses of oxalic acid on the mortality of phoretic Varroa destructor mites and their honey bee hosts. J. Apic. Res 2015, 54, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorc, A.; Alburaki, M.; Werle, C.; Knight, P.R.; Adamczyk, J. Brood removal or queen caging combined with oxalic acid treatment to control varroa mites (Varroa destructor) in honey bee colonies (Apis mellifera). Apidologie 2017, 48, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higes, M.; Meana, A.; Suárez, M.; Llorente, J. Negative long-term effects on bee colonies treated with oxalic acid against Varroa jacobsoni Oud. Apidologie 1999, 30, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorc, A.; Škerl, M.I.S. Toxicological and immunohistochemical testing of honeybees after oxalic acid and rotenone treatments. Apidologie 2007, 38, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Hernández, R.; Pascual, M.H.; Pérez, J.L.; del Nozal Nalda, M.J.; Mañés, M.A.M. Short-term negative effect of oxalic acid in “Apis mellifera iberiensis”. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 5, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagona, S.; Coppola, F.; Nanetti, A.; Cardaio, I.; Tafi, E.; Palego, L.; Betti, L.; Giannaccini, G.; Felicioli, A. Queen caging and oxalic acid treatment: Combined effect on vitellogenin content and enzyme activities in the first post-treatment workers and drones, Apis mellifera L. Animals 2022, 12, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.D.; Aronstein, K.; Chen, Y.P.; Hetru, C.; Imler, J.L.; Jiang, H.; Kanost, M.; Thompson, G.J.; Zou, Z.; Hultmark, D. Immune pathways and defence mechanisms in honey bees Apis mellifera. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucekova, M.; Valachova, I.; Kohutova, L.; Prochazka, E.; Klaudiny, J.; Majtan, J. Honeybee glucose oxidase—Its expression in honeybee workers and comparative analyses of its content and H2O2-mediated antibacterial activity in natural honeys. Sci. Nat. 2014, 101, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Santoyo, I.; Córdoba-Aguilar, A. Phenoloxidase: A key component of the insect immune system. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2012, 142, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdam, G.V.; Simões, Z.L.; Hagen, A.; Norberg, K.; Schrøder, K.; Mikkelsen, Ø.; Kirkwood TB, L.; Omholt, S.W. Hormonal control of the yolk precursor vitellogenin regulates immune function and longevity in honeybees. Exp. Gerontol 2004, 39, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmela, H.; Sundström, L. Vitellogenin in inflammation and immunity in social insects. Inflamm. Cell Signal. 2018, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weirich, G.F.; Collins, A.M.; Williams, V.P. Antioxidant enzymes in the honey bee, Apis mellifera. Apidologie 2002, 33, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Sun, R.; Shi, W.; Yan, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, X.; Xu, B. Characterization of a mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase gene from Apis cerana cerana and its role in oxidative stress. J. Insect Physiol. 2014, 60, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagona, S.; Coppola, F.; Nanetti, A.; Tafi, E.; Palego, L.; Betti, L.; Giannaccini, G.; Felicioli, A. effects of two commercial protein diets on the health of two imago ages of Apis mellifera L. reared in laboratory. Animals 2022, 12, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, M.; Fronte, B.; Sagona, S.; Carrozza, M.L.; Forzan, M.; Pizzurro, F.; Bibbiani, C.; Miragliotta, V.; Abramo, F.; Millanta, F.; et al. Effect of 1, 3-1, 6 β-glucan on natural and experimental deformed wing virus infection in newly emerged honeybees (Apis mellifera ligustica). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habig, W.H.; Pabst, M.J.; Jakoby, W.B. Glutathione S-transferases: The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goth, L. A simple method for determination of serum catalase activity and revision of reference range. Clin. Chim. Acta 1991, 196, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Eisenhardt, D.; Rademacher, E. Sublethal effects of oxalic acid on Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera: Apidae): Changes in behaviour and longevity. Apidologie 2012, 43, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanetti, A.; Bartolomei, P.; Bellato, S.; De Salvio, M.; Gattavecchia, E.; Ghini, S. Pharmacodynamics of Oxalic Acid in the Honey Bee Colony. In Proceedings of the 38th Apimondia International Congress, Apimondia, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 24–29 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Çalişkan, M. The metabolism of oxalic acid. Turk. J. Zool. 2000, 24, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanov, S.; Charrière, J.D.; Imdorf, A.; Kilchenmann, V.; Fluri, P. Determination of residues in honey after treatments with formic and oxalic acid under field conditions. Apidologie 2002, 33, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozal, M.J.; Bernal, J.L.; Gómez, L.A.; Higes, M.; Meana, A. Determination of oxalic acid and other organic acids in honey and in some anatomic structures of bees. Apidologie 2003, 34, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjlane, N.; Tarek, E.O.; Haddad, N. Evaluation of oxalic acid treatments against the mite Varroa destructor and secondary effects on honey bees Apis mellifera. J. Arthropod-Borne Dis. 2016, 10, 501. [Google Scholar]
- Rademacher, E.; Harz, M.; Schneider, S. Effects of oxalic acid on Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Insects 2017, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouibi, A.; Bouchema, W.F.; Loucif-Ayad, W.; Achou, M.; Soltani, N. Risks assessment of two acaricides (fluvalinate and oxalic acid) in Apis mellifera intermissa (Hymenoptera, Apidae): Acetylcholinesterase and glutathione S-transferase activities. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2016, 4, 503–508, E-ISSN: 2320-7078. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolić, T.V.; Purać, J.; Orčić, S.; Kojić, D.; Vujanović, D.; Stanimirović, Z.; Gržetić, I.; Ilijević, K.; Šikoparija, B.; Blagojević, D.P. Environmental effects on superoxide dismutase and catalase activity and expression in honey bee. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 90, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabbri, R.; Ferlizza, E.; Nanetti, A.; Monari, E.; Andreani, G.; Galuppi, R.; Isani, G. Biomarkers of nutritional status in honeybee haemolymph: Effects of different biotechnical approaches for Varroa destructor treatment and wintering phase. Apidologie 2018, 49, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sagona, S.; Tafi, E.; Coppola, F.; Nanetti, A.; Boni, C.B.; Orlando, C.; Palego, L.; Betti, L.; Giannaccini, G.; Felicioli, A. Oxalic Acid Treatment: Short-Term Effects on Enzyme Activities, Vitellogenin Content, and Residual Oxalic Acid Content in House Bees, Apis mellifera L. Insects 2024, 15, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15060409
Sagona S, Tafi E, Coppola F, Nanetti A, Boni CB, Orlando C, Palego L, Betti L, Giannaccini G, Felicioli A. Oxalic Acid Treatment: Short-Term Effects on Enzyme Activities, Vitellogenin Content, and Residual Oxalic Acid Content in House Bees, Apis mellifera L. Insects. 2024; 15(6):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15060409
Chicago/Turabian StyleSagona, Simona, Elena Tafi, Francesca Coppola, Antonio Nanetti, Chiara Benedetta Boni, Caterina Orlando, Lionella Palego, Laura Betti, Gino Giannaccini, and Antonio Felicioli. 2024. "Oxalic Acid Treatment: Short-Term Effects on Enzyme Activities, Vitellogenin Content, and Residual Oxalic Acid Content in House Bees, Apis mellifera L." Insects 15, no. 6: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15060409
APA StyleSagona, S., Tafi, E., Coppola, F., Nanetti, A., Boni, C. B., Orlando, C., Palego, L., Betti, L., Giannaccini, G., & Felicioli, A. (2024). Oxalic Acid Treatment: Short-Term Effects on Enzyme Activities, Vitellogenin Content, and Residual Oxalic Acid Content in House Bees, Apis mellifera L. Insects, 15(6), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15060409








