Insecticide Efficacy of Green Synthesis Silver Nanoparticles on Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Liviidae)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Location
2.2. Insect Rearing
2.3. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
2.4. Laboratory Evaluation of Insecticidal Effect on Diaphorina citri
2.5. Evaluation of the Insecticidal Effect on Diaphorina citri in Greenhouse
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of AgNPs by Green Synthesis
3.2. Mortality of 2nd Instar D. citri Nymphs in the Laboratory
3.3. Mortality of 2nd Instar Nymphs of D. citri in Greenhouse
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ollitrault, P.; Navarro, L. Citrus. In Fruit Breeding. Handbook of Plant Breeding; Badenes, M.L., Byrne, D.H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 8, pp. 623–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, S.; Singh, A.; Nema, P.K. Current applications of citrus fruit processing waste: A scientific outlook. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SENASICA (Servicio Nacional de Sanidad, Inocuidad y Calidad Agroalimentaria). Análisis de Impacto Económico Ante un Posible Establecimiento y Dispersión del Cancro de los Cítricos en México en Áreas Comerciales; SENASICA: Mexico City, Mexico, 2022; Available online: https://dj.senasica.gob.mx/Contenido/files/2022/agosto/AnálisisdeimpactoeconómicoanteunposibleestablecimientoydispersióndelCancrodeloscítricosenMéxicoenáreascomerciales_107e4f44-49be-4b9a-8058-df20da906b1a.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- SIAP (Servicio de Información Agroalimentaria y Pesquera). Anuario Estadistico de la Producción Agrícola. 2022. Available online: https://nube.siap.gob.mx/cierreagricola/ (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Bové, J.M. Huanglongbing: A destructive, newly-emerging, century-old disease of citrus. J. Plant. Pathol. 2006, 88, 7–37. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/41998278 (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Cifuentes-Arenas, J.C.; de Goes, A.; de Miranda, M.P.; Beattie, G.A.C.; Lopes, S.A. Citrus flush shoot ontogeny modulates biotic potential of Diaphorina citri. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavala-Zapata, V.; Rangel-Lucio, J.A.; Vargas-Tovar, J.A.; Álvarez-Ramos, R.; Azuara-Domínguez, A. Asociación de la abundancia de huevos y ninfas de primer instar de Diaphorina citri con el tamaño de brote vegetativo del cultivo de naranja valencia (Citrus sinensis (l.) osbeck). Trop. Subtrop. Agroecosyst. 2024, 27, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassanezi, R.B.; Montesino, L.H.; Stuchi, E.S. Effects of huanglongbing on fruit quality of sweet orange cultivars in Brazil. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2009, 125, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassanezi, R.B.; Lopes, S.A.; de Miranda, M.P.; Wulff, N.A.; Volpe, H.X.L.; Ayres, A.J. Overview of citrus huanglongbing spread and management strategies in Brazil. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2020, 45, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, G.; Baldwin, E. Huanglongbing: Devastating disease of citrus. Hortic. Rev. 2016, 44, 315–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N. The citrus Huanglongbing crisis and potential solutions. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molki, B.; Call, D.R.; Ha, P.T.; Omsland, A.; Gang, D.R.; Lindemann, S.R.; Killiny, N.; Beyenal, H. Growth of ‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’ in a host-free microbial culture is associated with microbial community composition. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2020, 142, 109691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-Contreras YG, Z.; Osorio-Hernández, E.; Silva-Espinosa, J.H.; Delgado-Martínez, R.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Álvarez-Ramos, R. Situación Actual, Impacto Económico y Control del Huanglongbing en Tamaulipas. Cienc. Lat. Rev. Cient. Multidiscip. 2022, 6, 4242–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemán, J.; Baños, H.; Ravelo, J. Diaphorina citri y la enfermedad huanglongbing: Una combinación destructiva para la producción citrícola. Rev. Protección Veg. 2007, 22, 154–165. [Google Scholar]
- Grafton-Cardwell, E.E.; Stelinski, L.L.; Stansly, P.A. Biology and management of asian citrus psyllid, vector of the Huanglongbing Pathogens. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 413–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Mann, R.S.; Rogers, M.E.; Stelinski, L.L. Insecticide resistance in field populations of Asian citrus psyllid in Florida. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasquez-Garcia, M.; Velasquez-Monreal, J.; Manuel Medina-Urrutia, V.; de Jesus Cruz-Vargas, C.; Sandoval-Salaza, M.; Virgin-Calleros, G.; Pablo Torres-Moran, J. Insecticide resistance in adult Diaphorina citri Kuwayama from lime orchards in central west Mexico. Southwest. Entomol. 2013, 38, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D.; Gill, T.A.; Pelz-Stelinski, K.S.; Stelinski, L.L. Risk assessment of various insecticides used for management of Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri in Florida citrus, against honey bee, Apis mellifera. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala-Zermeño, M.A.; Gallou, A.; Berlanga-Padilla, A.M.; Serna-Domínguez, M.G.; Arredondo-Bernal, H.C.; Montesinos-Matías, R. Characterisation of entomopathogenic fungi used in the biological control programme of Diaphorina citri in Mexico. Biocontrol Sci. Tech. 2015, 25, 1192–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Afzal, M.; Qureshi, J.A.; Khan, A.M.; Raza, A.M. Botanicals, selective insecticides, and predators to control Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae) in citrus orchards. Insect Sci. 2014, 21, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhns, E.H.; Martini, X.; Hoyte, A.; Stelinski, L.L. Repellent Activity of Botanical Oils against Asian Citrus Psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae). Insects 2016, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, A.; Sétamou, M. Parasitism of Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae) by Tamarixia radiata (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) on residential citrus in Texas: Importance of colony size and instar composition. Biol. Control 2022, 165, 104796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Farooq, M.; Wakeel, A.; Nawaz, A.; Cheema, S.A.; ur Rehman, H.; Ashraf, I.; Sanaullah, M. Nanotechnology in agriculture: Current status, challenges and future opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestovsky, Y.S.; Martínez-Antonio, A. The use of nanoparticles and nanoformulations in agriculture. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 8699–8730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhipa, H. Applications of Nanotechnology in Agriculture, 1st ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 46, ISBN 9780128149928. [Google Scholar]
- Kitherian, S. Nano and Bio-nanoparticles for Insect Control. Res. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G. Mode of action of nanoparticles against insects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 12329–12341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gour, A.; Jain, N.K. Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, S.; Guan, Z.; Ofoegbu, P.C.; Clubb, P.; Rico, C.; He, F.; Hong, J. Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles: Current Developments and Limitations. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnani, R.; Chowdhary, A. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticle by eco-friendly method. Indian J. Nanosci. 2013, 1, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, I.; Singh, N.B.; Singh, A.; Singh, H.; Singh, S.C. Green synthesis of nanoparticles and its potential application. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, H.u.; Majeed, B.; Farooqi, M.A.; Rasul, A.; Sagheer, M.; Ali, Q.; Akhtar, Z.R. Green Synthesis of Silver Nitrate Nanoparticles from Camelina Sativa (L.) and Its Effect to Control Insect Pests of Stored Grains. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, G.D.; Murugan, K.; Selvam, C.P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Euphorbia hirta (Euphorbiaceae) leaf extract against crop pest of cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Biopestic. 2014, 7, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Sedighi, A.; Imani, S.; Moshtaghi Kashanian, G.R.; Najafi, H.; Fathipour, Y. Efficiency of green synthesized silver nanoparticles with sweet orange, Citrus sinensis (L.) (Rutaceae, Sapindales) against Tribolium confusum Duval.(Coleoptera, Tenebrionidae). J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Neira-Vielma, A.A.; Meléndez-Ortiz, H.I.; García-López, J.I.; Sanchez-Valdes, S.; Cruz-Hernández, M.A.; Rodríguez-González, J.G.; Ramírez-Barrón, S.N. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using pecan nut (Carya illinoinensis) shell extracts and evaluation of their antimicrobial activity. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, W.S. A method for computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, M.V.; Abideen, S. Pesticidal effect of green synthesized silver and lead nanoparticles using Avicennia marina against grain storage pest Sitophilus oryzae. Int. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2015, 5, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kamil, D.; Prameeladevi, T.; Ganesh, S.; Prabakharan, N.; Nareshkumar, R.; Thomas, S.P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana and their bioefficacy against mustard aphid (Lipaphis erysimi Kalt.). Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 55, 555–561. [Google Scholar]
- Parthiban, E.; Ramachandran, M.; Jayakumar, M.; Ramanibai, R. Biocompatible green synthesized silver nanoparticles impact on insecticides resistant developing enzymes of dengue transmitted mosquito vector. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Samad, L.M.; Bakr, N.R.; El-Ashram, S.; Radwan, E.H.; Abdul Aziz, K.K.; Hussein, H.K.; El Wakil, A.; Hassan, M.A. Silver nanoparticles instigate physiological, genotoxicity, and ultrastructural anomalies in midgut tissues of beetles. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2022, 367, 110166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Prasad, R.; Buhroo, A.A.; Duraisamy, P.; Yousuf, I.; Umadevi, M.; Bindhu, M.R.; Govindarajan, M.; Khanday, A.L. One-pot fabrication and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Solanum lycopersicum: An eco-friendly and potent control tool against rose aphid, Macrosiphum rosae. J. Nanosci. 2016, 2016, 4679410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.; Naeem-Ullah, U.; Khan, W.S.; Saeed, S.; Qayyum, M.A.; Khan, M.A. Characterization of Azadirachta indica synthesized silver nanoparticles and its toxicity against Dusky cotton bug, Oxycarenus hyalinipennis Costa (Hemiptera: Lygaeidae). Int. J. Trop. Insect. Sci. 2023, 43, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Naeem-Ullah, U.; Khan, W.S.; Saeed, S.; Razzaq, K. Biocidal activity of green synthesized silver nanoformulation by Azadirachta indica extract a biorational approach against notorious cotton pest whitefly, Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera; Aleyrodidae). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2022, 42, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manimegalai, T.; Raguvaran, K.; Kalpana, M.; Maheswaran, R. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle using Leonotis nepetifolia and their toxicity against vector mosquitoes of Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus and agricultural pests of Spodoptera litura and Helicoverpa armigera. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 43103–43116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, T.; Afsheen, S.; Iqbal, T. Nanocidal Effect of Rice Husk–Based Silver Nanoparticles on Antioxidant Enzymes of Aphid. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 4855–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikshit, P.; Kumar, J.; Das, A.; Sadhu, S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, S.; Gupta, P.; Kim, B. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles: Applications and Limitations. Catalysts 2021, 11, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, M.; Vishwakarma, S.; Panigrahi, C.; Kumar, J. Nanotechnology: Current applications and future scope in food. Food Front. 2021, 2, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadlapudi, V.; Kaladhar, D.S.V.G.K. Review: Green Synthesis of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 2014, 19, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, K.; Banse, V.; Ledwani, L. Green synthesis of nanoparticles: Their advantages and disadvantages. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1724, 020048. [Google Scholar]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Che. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadaroğlu, H.; Alayli Güngör, A.; İnce, S. Synthesis of Nanoparticles by Green Synthesis Method. Int. J. Innov. Res. Rev. 2017, 1, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Zahoor, M.; Khan, R.S.; Ikram, M.; Islam, N.U. The impact of silver nanoparticles on the growth of plants: The agriculture applications. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, G.; Rai, P.; Pandey, A. Chapter 1—Green synthesis of nanoparticles: A greener approach for a cleaner future. In Micro and Nano Technologies; Shukla, A.K., Iravani, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–26. ISBN 978-0-08-102579-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Raja, N.I.; Iqbal, M.; Ejaz, M.; Aslam, S. Green synthesis and evaluation of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial and biochemical profiling in Kinnow (Citrus reticulata L.) to enhance fruit quality and productivity under biotic stress. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 13, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosa, W.F.A.; Mackled, M.I.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; Behiry, S.I.; Al-Askar, A.A.; Basile, A.; Abdelkhalek, A.; Elsharkawy, M.M.; Salem, M.Z.M. Impact of silver nanoparticles on lemon growth performance: Insecticidal and antifungal activities of essential oils from peels and leaves. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 898846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruyer, N.; Dorais, M.; Bastien, C.; Dassylva, N.; Triffault-Bouchet, G. Interaction between silver nanoparticles and plant growth. Acta Hortic. 2014, 1037, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Raja, N.I.; Iqbal, M.; Ejaz, M.; Aslam, S.; Rehman, A.-U.; Javaid, U. Seed germination and biochemical profile of Citrus reticulata (Kinnow) exposed to green synthesised silver nanoparticles. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.K.; Misra, P.; Kole, C. Chapter 8-Uptake, Translocation, Accumulation, Transformation, and Generational Transmission of Nanoparticles in Plants. In Plant Nanotechnology; Kole, C., Kumar, D., Khodakovskaya, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 183–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
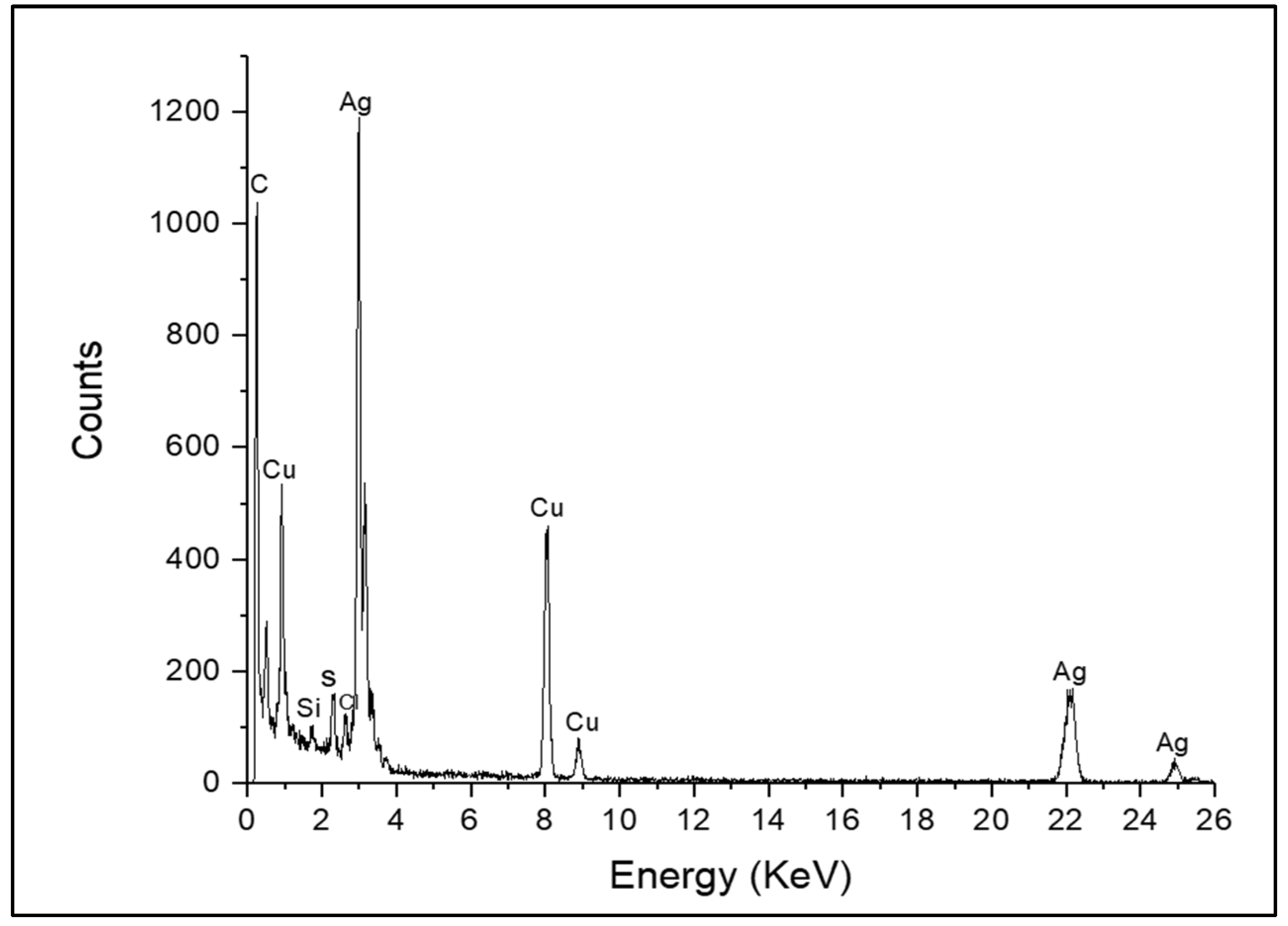
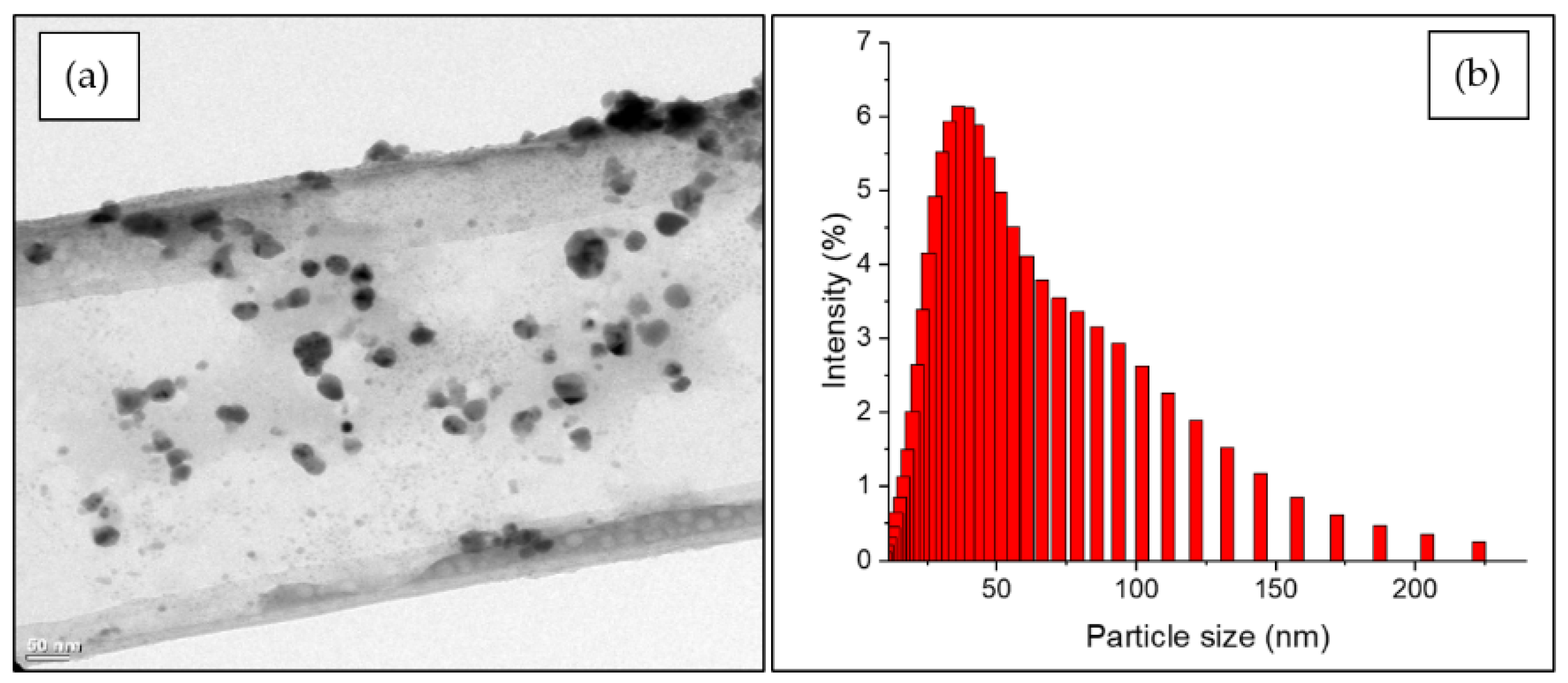
| % Mortality (mean ± S.E) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
| 0 ppm | 2.32 ± 1.23 a | 4.28 ± 1.22 a | 6.43 ± 1.24 a |
| 2 ppm | 21.65 ± 2.62 b | 66.70 ± 3.99 b | 92.35 ± 1.36 b |
| 4 ppm | 24.32 ± 4.05 bc | 77.81 ± 4.07 bc | 94.58 ± 1.83 bc |
| 8 ppm | 34.87 ± 4.56 bcd | 82.45 ± 5.35 bc | 96.10 ± 1.95 bc |
| 16 ppm | 41.01 ± 4.46 cde | 86.63 ± 2.21 c | 96.66 ± 1.15 bc |
| 32 ppm | 45.83 ± 2.26 de | 87.40 ± 6.08 c | 97.84 ± 0.76 bc |
| 64 ppm | 55.21 ± 7.64 e | 90.66 ± 2.65 c | 100 ± 0.00 c |
| g.l | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| F | 16.84 | 57.88 | 646.94 |
| Pr < F | <0.0001 *** | <0.0001 *** | <0.0001 *** |
| R2 | 0.83 | 0.95 | 0.96 |
| &LC50 ($LF 95%) | 40.89 (25.84–87.22) | 0.23 (0.01–0.74) | 0.01 (4.26 × 10−8–0.15) |
| &LC95 ($LF 95%) | 18,845 (2926–759,106) | 189.25 (70.26–1864) | 4.97 (1.47–10.89) |
| % Mortality (mean ± S.E) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
| 0 ppm | 2.08 ± 2.08 a | 3.27 ± 2.18 a | 9.01 ± 3.94 a |
| 16 ppm | 5.97 ± 1.45 a | 8.04 ± 1.23 ab | 13.19 ± 1.59 a |
| 32 ppm | 10.6 ± 3.34 a | 27.75 ± 6.98 b | 50.57 ± 9.39 b |
| 64 ppm | 55.08 ± 8.69 b | 64.19 ± 9.54 c | 78.69 ± 6.07 c |
| 128 ppm | 56.99 ± 2.74 b | 70.14 ± 4.38 c | 80.14 ± 4.59 c |
| g.l | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| F | 34.89 | 27.64 | 34.42 |
| Pr < F | <0.0001 *** | <0.0001 *** | <0.0001 *** |
| Pr < F Bloque | 0.07 | 0.124 | 0.185 |
| R2 | 0.72 | 0.78 | 0.65 |
| &LC50 ($LF 95%) | 85.45 (72.87–104.16) | 58.90 (51.03–68.86) | 37.93 (32.53–43.72) |
| &LC95 ($LF 95%) | 496.53 (331.14–916.35) | 334.65 (238.03–550.28) | 212.66 (159.10–322.39) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zavala-Zapata, V.; Ramírez-Barrón, S.N.; Sánchez-Borja, M.; Aguirre-Uribe, L.A.; Delgado-Ortiz, J.C.; Sánchez-Peña, S.R.; Mayo-Hernández, J.; García-López, J.I.; Vargas-Tovar, J.A.; Hernández-Juárez, A. Insecticide Efficacy of Green Synthesis Silver Nanoparticles on Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Liviidae). Insects 2024, 15, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15070469
Zavala-Zapata V, Ramírez-Barrón SN, Sánchez-Borja M, Aguirre-Uribe LA, Delgado-Ortiz JC, Sánchez-Peña SR, Mayo-Hernández J, García-López JI, Vargas-Tovar JA, Hernández-Juárez A. Insecticide Efficacy of Green Synthesis Silver Nanoparticles on Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Liviidae). Insects. 2024; 15(7):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15070469
Chicago/Turabian StyleZavala-Zapata, Vidal, Sonia N. Ramírez-Barrón, Maricarmen Sánchez-Borja, Luis A. Aguirre-Uribe, Juan Carlos Delgado-Ortiz, Sergio R. Sánchez-Peña, Juan Mayo-Hernández, Josué I. García-López, Jesus A. Vargas-Tovar, and Agustín Hernández-Juárez. 2024. "Insecticide Efficacy of Green Synthesis Silver Nanoparticles on Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Liviidae)" Insects 15, no. 7: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15070469
APA StyleZavala-Zapata, V., Ramírez-Barrón, S. N., Sánchez-Borja, M., Aguirre-Uribe, L. A., Delgado-Ortiz, J. C., Sánchez-Peña, S. R., Mayo-Hernández, J., García-López, J. I., Vargas-Tovar, J. A., & Hernández-Juárez, A. (2024). Insecticide Efficacy of Green Synthesis Silver Nanoparticles on Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Liviidae). Insects, 15(7), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15070469






