Resource Sharing between the Invasive Sirex noctilio and Native Woodborers and Beetles in Pinus Plantations
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
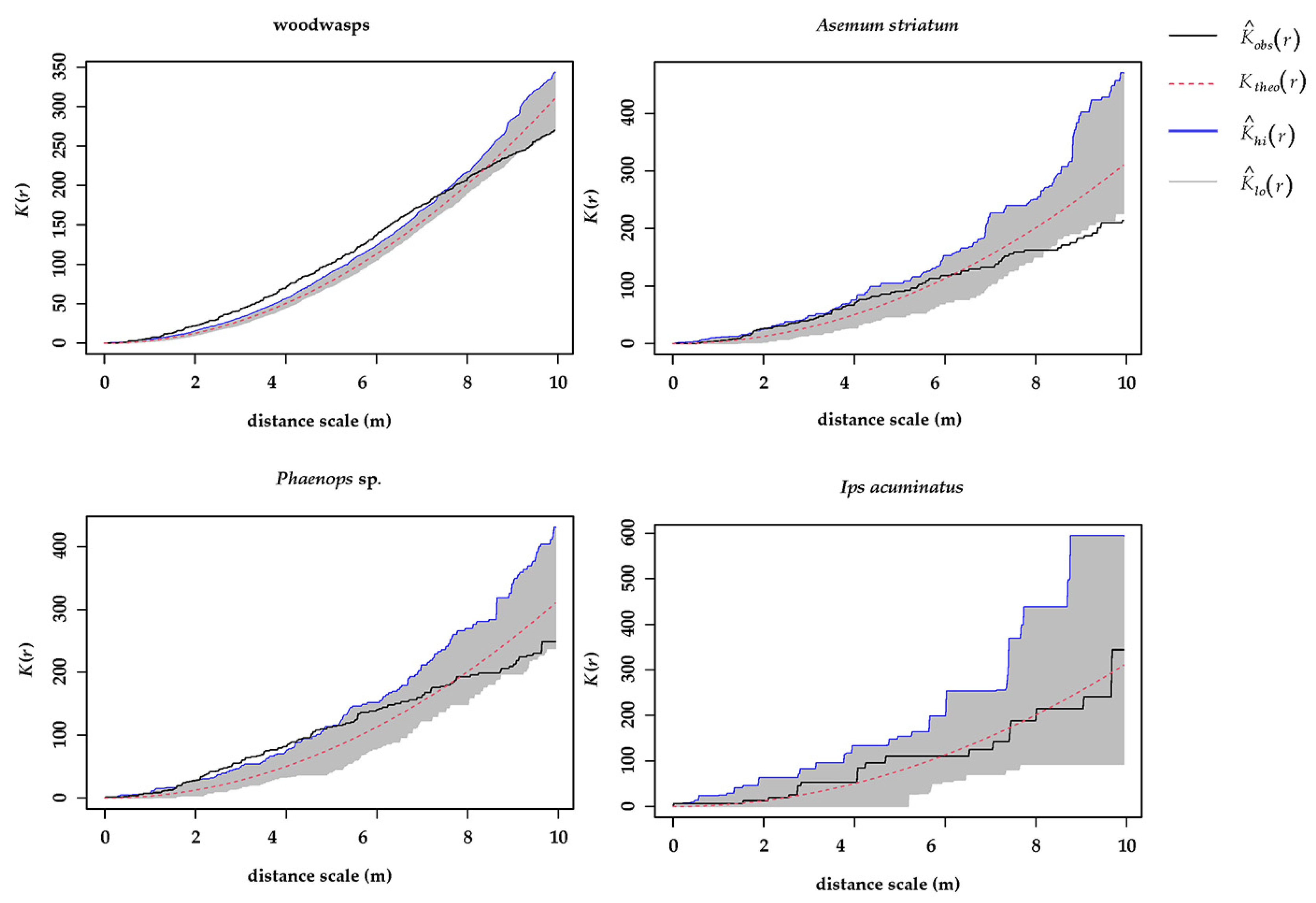
2.2. Degree of Co-Occurrence among Colonizers at the Stand Level
2.3. Effect of Co-Occurrence on Woodwasps in Wood Segments
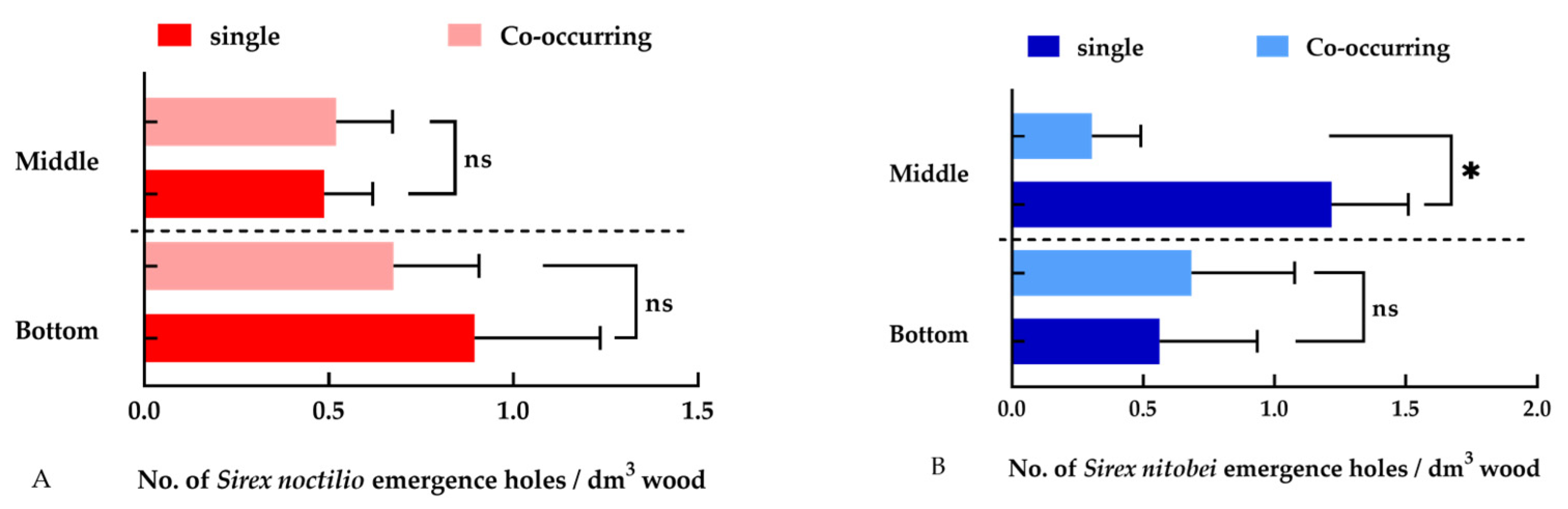
2.3.1. Density of Woodwasps
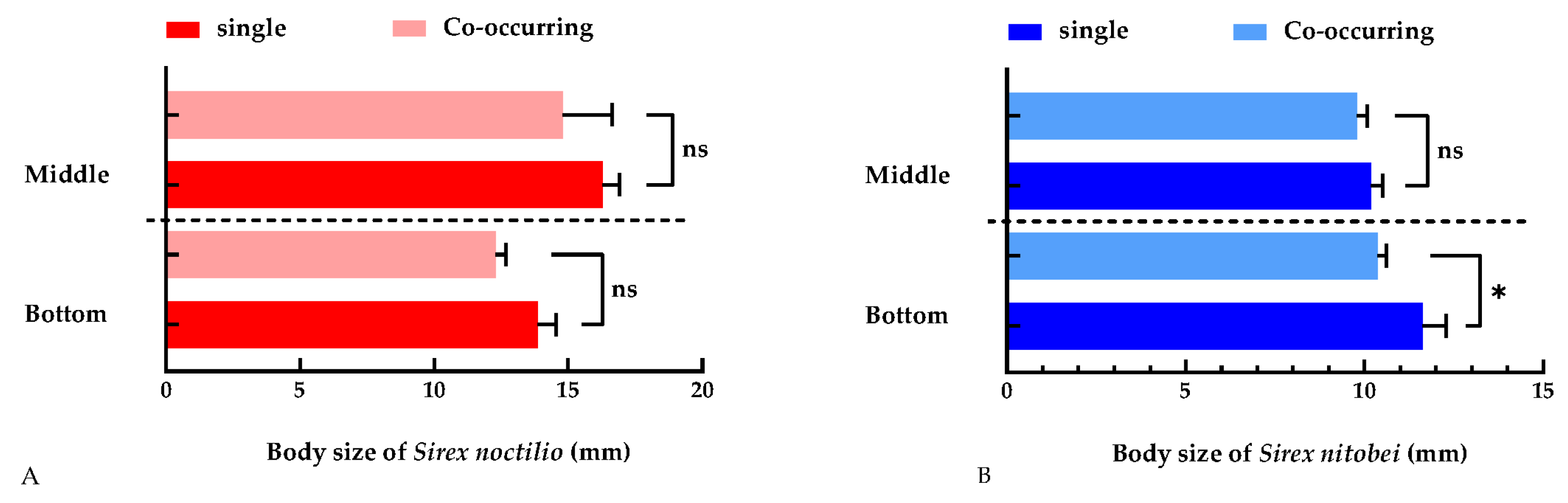
2.3.2. Body Size of Woodwasps
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Colonizer Damage at the Stand Scale
3.2. Within-Tree Associations at the Tree Scale
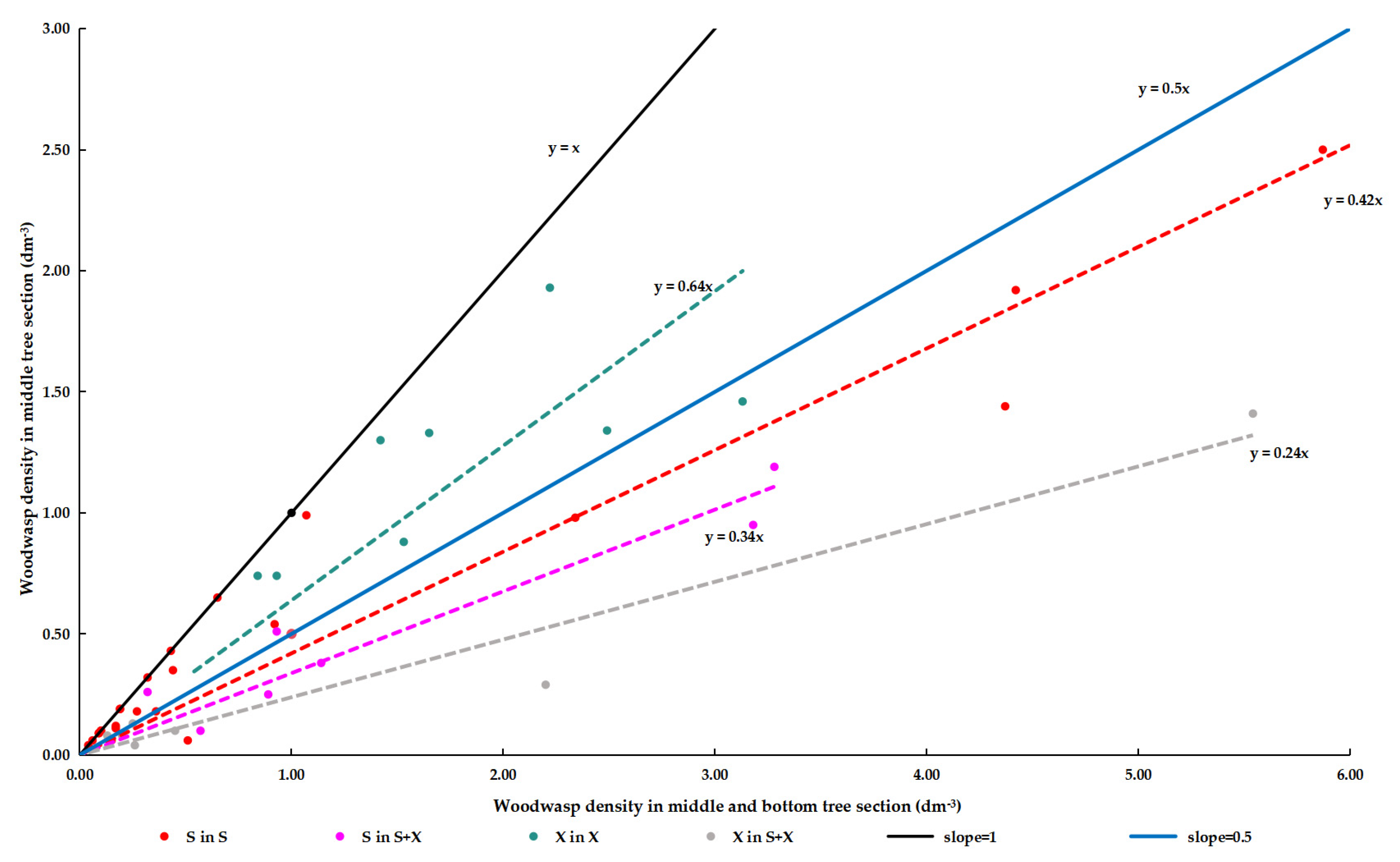
3.3. Effect of Co-Occurrence on Woodwasps in the Wood Segment
3.3.1. Density of Woodwasps
3.3.2. Body Size of Woodwasps
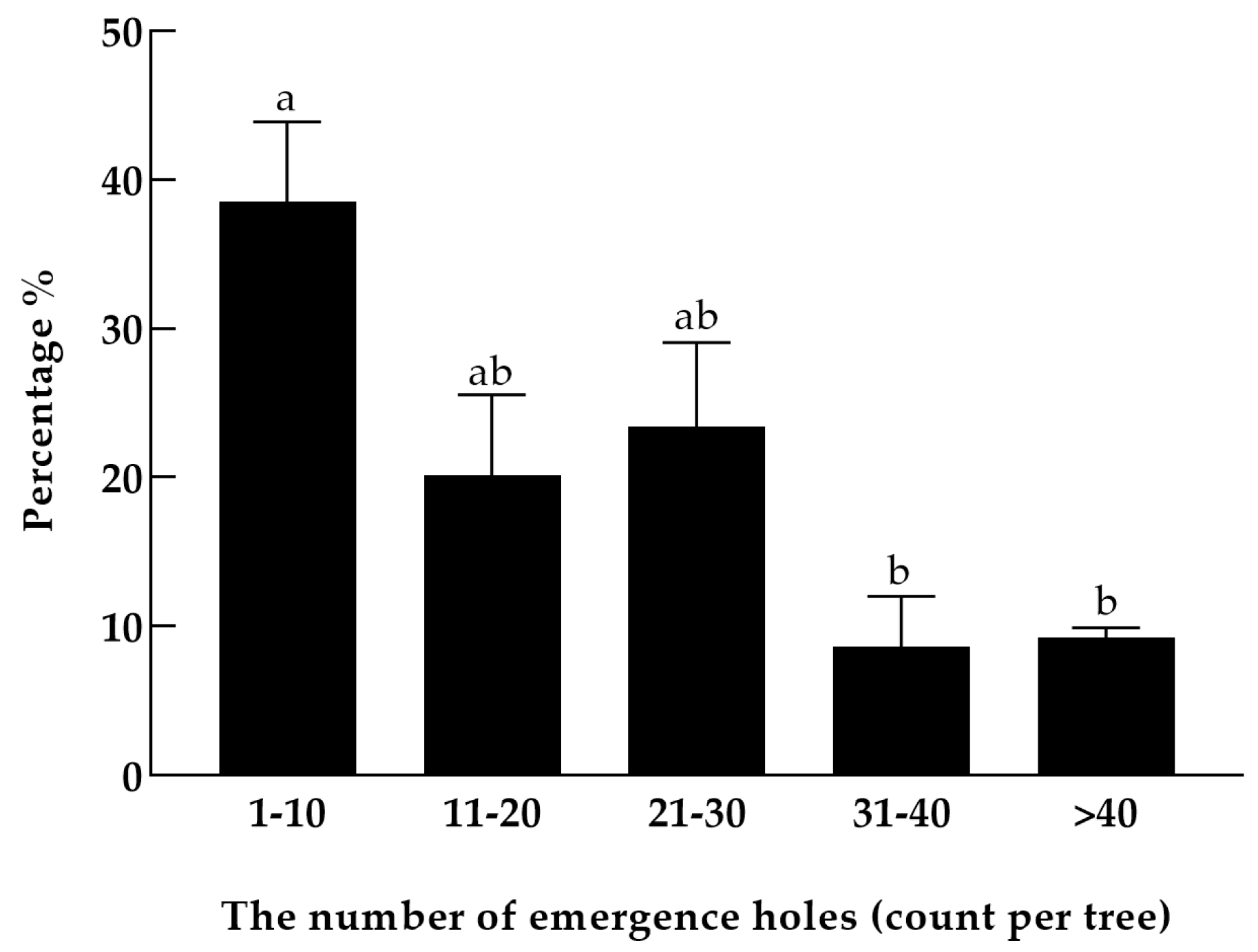
3.4. Within-Tree Distribution of Woodwasps in Different Infestation Types
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simberloff, D. How Common Are Invasion-Induced Ecosystem Impacts? Biol. Invasions 2011, 13, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, O.E.; Stuart Chapin, F., III; Armesto, J.J.; Berlow, E.; Bloomfield, J.; Dirzo, R.; Huber-Sanwald, E.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jackson, R.B.; Kinzig, A.; et al. Global Biodiversity Scenarios for the Year 2100. Science 2000, 287, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnas, J.; Hurley, B.; Slippers, B.; Wingfield, M.J.; Roux, J. Insects and Diseases of Mediterranean Forests: A South African Perspective. In Insects and Diseases of Mediterranean Forest Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 397–430. [Google Scholar]
- Wingfield, M.J.; Garnas, J.R.; Hajek, A.; Hurley, B.P.; de Beer, Z.W.; Taerum, S.J. Novel and Co-Evolved Associations between Insects and Microorganisms as Drivers of Forest Pestilence. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denno, R.F.; McClure, M.S.; Ott, J.R. Interspecific Interactions in Phytophagous Insects: Competition Reexamined and Resurrected. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1995, 40, 297–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, J.E.; Ciesla, W.M.; Meyer, H.E. Insect Defoliation as a Predisposing Agent to a Bark Beetle Outbreak in Eastern Montana. Environ. Entomol. 1974, 3, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.; Sapes, G.; Sala, A.; Hood, S. Tree Physiology and Bark Beetles. New Phytol. 2015, 205, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstetter, R.W.; Cronin, J.T.; Klepzig, K.D.; Moser, J.C.; Ayres, M.P. Antagonisms, Mutualisms and Commensalisms Affect Outbreak Dynamics of the Southern Pine Beetle. Oecologia 2006, 147, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klooster, W.S.; Gandhi, K.J.K.; Long, L.C.; Perry, K.I.; Rice, K.B.; Herms, D.A. Ecological Impacts of Emerald Ash Borer in Forests at the Epicenter of the Invasion in North America. Forests 2018, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova-Bienkowskaja, M. Cascading Ecological Effects Caused by the Establishment of the Emerald Ash Borer Agrilus Planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) in European Russia. Eur. J. Entomol. 2015, 112, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shi, J.; Lu, M.; Ren, L.; Zhen, C.; Luo, Y. Detection and Identification of the Invasive Sirex noctilio (Hymenoptera: Siricidae) Fungal Symbiont, Amylostereum areolatum (Russulales: Amylostereacea), in China and the Stimulating Effect of Insect Venom on Laccase Production by A. areolatum YQL03. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fu, N.; Gao, C.; Wang, L.; Ren, L.; Luo, Y. Multilocus Genotyping and Intergenic Spacer Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Amylostereum areolatum (Russulales: Amylostereacea) Symbionts of Native and Non-Native Sirex Species. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermelinger, B.; Thomsen, I.M. The Woodwasp Sirex noctilio and Its Associated Fungus Amylostereum areolatum in Europe. In The Sirex Woodwasp and Its Fungal Symbiont: Research and Management of a Worldwide Invasive Pest; Slippers, B., de Groot, P., Wingfield, M.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 65–80. ISBN 978-94-007-1960-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bordeaux, J.M. Isolation and Structural Characterization of the Active Molecule from Sirex noctilio Woodwasp Venom Inducing Primary Physiological Symptoms in Attacked Pine Species. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gaut, I.P.C. Studies of Siricids and Their Fungal Symbionts. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. Study on Natural Enemies of Sirex noctilio and Biology of Its Dominant Parasitic Wasp. MD. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Bao, M.; Ao, T.; Ren, L.; Luo, Y. Population Distribution Patterns and Ecological Niches of Two Sirex Species Damaging Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 54, 924–932. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Fu, N.; Li, C.; Luo, Y.; Ren, L. Advances in the Study of Mutualism Relationship between Amylostereum areolatum and Sirex noctilio. J. Temp. For. Res. 2020, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Plant Health (PLH); Bragard, C.; Baptista, P.; Chatzivassiliou, E.; Di Serio, F.; Gonthier, P.; Jaques Miret, J.A.; Justesen, A.F.; Magnusson, C.S.; Milonas, P.; et al. Pest Categorisation of Sirex nitobei. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Sasaki, K.; Enda, N. Correlation between Sirex nitobei and Amylostereum areolatum, Associated with the Death of Japanese Pine Trees during Winter Season. J. Jpn. For. Soc. 1978, 60, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitza, K.N.E.; Tabata, M.; Kanzaki, N.; Kimura, K.; Garnas, J.; Slippers, B. Host Specificity and Diversity of Amylostereum Associated with Japanese Siricids. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 24, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.; Hurley, B. Life History and Biology of Sirex noctilio. In The Sirex Woodwasp and Its Fungal Symbiont: Research and Management of A Worldwide Invasive Pest; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 15–30. ISBN 978-94-007-1959-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bordeaux, J.M.; Dean, J.F.D. Susceptibility and Response of Pines to Sirex noctilio. In The Sirex Woodwasp and Its Fungal Symbiont: Research and Management of a Worldwide Invasive Pest; Slippers, B., de Groot, P., Wingfield, M.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 31–50. ISBN 978-94-007-1960-6. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, H.; Hijii, N. Host-Tree Conditions Affecting the Oviposition Activities of the Woodwasp, Sirex nitobei Matsumura (Hymenoptera: Siricidae). J. For. Res. 1996, 1, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbilgin, N.; Nordheim, E.V.; Aukema, B.H.; Raffa, K.F. Population Dynamics of Ips pini and Ips grandicollis in Red Pine Plantations in Wisconsin: Within- and between-Year Associations with Predators, Competitors, and Habitat Quality. Environ. Entomol. 2002, 31, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, K.; Groot, P. Sirex, Surveys and Management: Challenges of Having Sirex noctilio in North America; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, B.P.; Hatting, H.J.; Wingfield, M.J.; Klepzig, K.D.; Slippers, B. The Influence of Amylostereum areolatum Diversity and Competitive Interactions on the Fitness of the Sirex Parasitic Nematode Deladenus siricidicola. Biol. Control 2012, 61, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.; de Groot, P.; Davis, C.; Smith, S.M. Effect of Two Bark Beetle-Vectored Fungi on the On-Host Search and Oviposition Behavior of the Introduced Woodwasp Sirex noctilio (Hymenoptera: Siricidae) on Pinus sylvestris Trees and Logs. J. Insect Behav. 2012, 25, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, F.; Carnegie, A.; Bashford, R.; Bedding, R.; Nicol, H.; Gurr, G. Bark Beetle (Ips Grandicollis) Disruption of Woodwasp (Sirex noctilio) Biocontrol: Direct and Indirect Mechanisms. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 323, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.S.; Hofstetter, R.W. Effects of Gallery Density and Species Ratio on the Fitness and Fecundity of Two Sympatric Bark Beetles (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, L.J.; Borden, J.H. Competitive Interactions between the Mountain Pine Beetle and the Pine Engraver in Lodgepole Pine. Can. J. For. Res. 1991, 21, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foelker, C.J. Beneath the bark: Associations among Sirex noctilio development, bluestain fungi, and pine host species in North America. Ecol Entomol 2016, 41, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foelker, C.J.; Parry, D.; Fierke, M. Biotic Resistance and the Spatiotemporal Distribution of an Invading Woodwasp, Sirex noctilio. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 1991–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, L.M.; Weslien, J. Reduced Offspring Production in Bark Beetle Tomicus piniperda in Pine Bolts Baited with Ethanol and α-Pinene, Which Attract Antagonistic Insects. J. Chem. Ecol. 1994, 20, 1429–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlyter, F.; Anderbrant, O. Competition and Niche Separation between Two Bark Beetles: Existence and Mechanisms. Oikos 1993, 68, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, R.N.; Mayyasi, A.M.; Foltz, J.L.; Hain, F.P. Interspecific Competition between Monochamus titillator and Dendroctonus frontalis. Environ. Entomol. 1976, 5, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Gao, T.; Shui, S.; Shi, H.; Ren, L.-L.; Shi, J. Biological Characteristics of Sirex nitobei (Hymenoptera: Siricidae) on the Hasi Mountain Natural Pinus tabuliformis Forest in Gansu Province. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2018, 33, 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Ao, T.; Liu, D.; Ren, L.-L.; Sun, X.; Yu, N.; Luo, Y.; Shi, J. Investigation on the Damage Characteristics and Control Measures of Sirex nitobei in Daqinggou, Inner Mongolia. Plant Quar. 2018, 32, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Gouws, E.J.; Gaston, K.J.; Chown, S.L. Intraspecific Body Size Frequency Distributions of Insects. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripley, B.D. Modelling Spatial Patterns. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1977, 39, 172–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.X.; Ren, L.L.; Liu, X.B.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.Z.; Luo, Y.Q. Effects of endophytic fungi in Mongolian pine on the selection behavior of woodwasp (Sirex noctilio) and the growth of its fungal symbiont. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chi, G.; Gao, W.; Huang, G.; LV, Q. Progress in Study on the Ophiostomatoid Fungi Associated with the Bark Beetle. For. Pest Dis. 2009, 28, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wondafrash, M.; Slippers, B.; Hurley, B.; Garnas, J. Local Antagonism and Resource Partitioning between Two Invasive Pine Plantation Pests. Agric. For. Entomol. 2019, 21, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, M.P.; Pena, R.; Lombardo, J.A.; Lombardero, M.J. Host Use Patterns by the European Woodwasp, Sirex noctilio, in Its Native and Invaded Range. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.; de Groot, P.; Smith, S.M. Evidence of Interaction between Sirex noctilio and Other Species Inhabiting the Bole of Pinus. Agric. For. Entomol. 2012, 14, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, D.A. Control Procedures for Sirex noctilio in the Green Triangle: Review from Detection to Severe Outbreak. Aust. For. 1990, 53, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantschner, M.V.; Corley, J.C. Spatial Pattern of Attacks of the Invasive Woodwasp Sirex noctilio, at Landscape and Stand Scales. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spradbery, J.P. A Comparative Study of the Phytotoxic Effects of Siricid Woodwasps on Conifers. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1973, 75, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartshorn, J.A.; Galligan, L.; Stephen, F. Sirex nigricornis (Hymenoptera: Siricidae) Larval Development Correlated with Tree Characteristics and Ophiostomoid Fungal Infection. Great Lakes Entomol 2021, 53, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, S.; Obermajer, A. Moisture and Blue Stain Distribution in Mountain Pine Beetle Infested Lodgepole Pine Trees and Industrial Implications. Wood Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, M.P.; Dolezal, J.E. Emplacement of Fungal Spores by the Woodwasp, Sirex noctilio, during Oviposition. For. Sci. 1969, 15, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamm, R.O.; Wagner, T.L.; Cook, S.P.; Pulley, P.E.; Coulson, R.N.; Mcardle, T.M. Host Colonization by Cohabiting Dendroctonus frontalis, Ips avulsus, and I. calligraphus (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Environ. Entomol. 1987, 16, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, T.D.; Birch, M.C.; Švihra, P. Niche Breadth and Resource Partitioning by Four Sympatric Species of Bark Beetles (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Oecologia 1981, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwald, M. Ecological Segregation of Bark Beetles (Coleoptera, Scolytidae) of Spruce. J. Appl. Entomol. 1986, 101, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, F.D.; Stewart, N.C. The Biology and Behaviour of the Woodwasp Sirex noctilio F. in New Zealand. Trans. R. Soc. N. Z. 1966, 7, 195–204. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, F.G.; Harris, J.A.; Kassaby, F.Y.; Minko, G. An Improved Technique for Early Detection and Control of the Sirex Wood Wasp in Radiata Pine Plantations. Aust. For. 1982, 45, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, B.P.; Slippers, B.; Croft, P.K.; Hatting, H.J.; van der Linde, M.; Morris, A.R.; Dyer, C.; Wingfield, M.J. Factors Influencing Parasitism of Sirex noctilio (Hymenoptera: Siricidae) by the Nematode Deladenus siricidicola (Nematoda: Neotylenchidae) in Summer Rainfall Areas of South Africa. Biol. Control 2008, 45, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stillwell, M.A. Woodwasps (Siricidae) in conifers and the associated fungus, Stereum chailletii, in eastern Canada. For. Sci. 1966, 12, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, H.; Hijii, N. Reproductive strategy of a woodwasp with no fungal symbionts, Xeris spectrum (Hymenoptera: Siricidae). Oecologia 1997, 112, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manukyan, A.R.; Smirnova, A.V. New data on the family Siricidae (Hymenoptera, Symphyta) in Baltic amber. Paleontol. J. 2021, 55, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, F.D. Bionomics of siricidae. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1968, 13, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
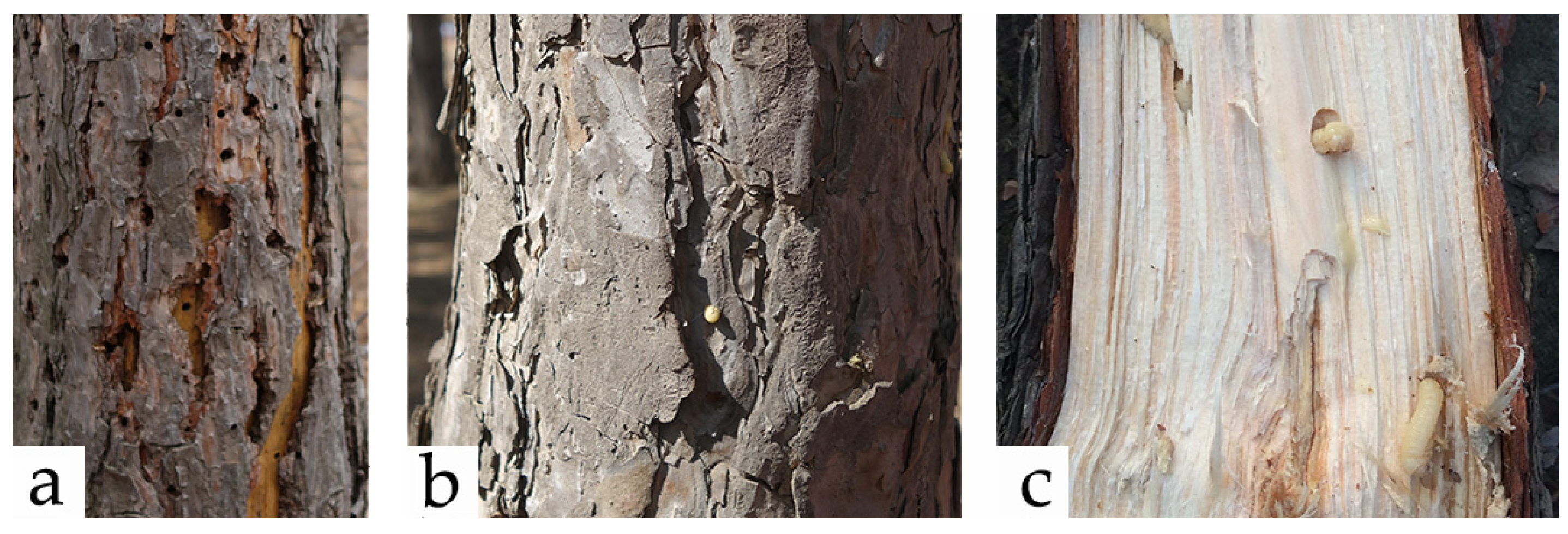

| Characteristics | Sirex Woodwasps 1 | Asemum striatum | Phaenops sp. | Ips acuminatus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shape of emergence hole | Circle | Ellipsoid | Similar to the letter “D”/half-moon | Circle |
| Diameter of emergence hole | 3.04–6.91 mm | 4.00–13.00 mm | ≈3 mm | 1–2 mm |
| Treatment of frass | Frass accumulates in the gallery | Frass discharged from the gallery | Frass accumulates in the gallery | Frass fills the gallery |
| Asemum striatum | Phaenops sp. | Ips acuminatus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sirex woodwasps | −0.297 *** | −0.291 *** | −0.116 |
| Asemum striatum | 0.270 *** | 0.076 | |
| Phaenops sp. | 0.214 *** |
| Year | Variable | Coefficient | SE | z-Value | Probability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y − 1 | Sirex woodwasps | 0.993 | 0.006 | 172.67 | *** |
| Asemum striatum | –0.442 | 0.058 | −7.59 | *** | |
| Phaenops sp. | 0.461 | 0.068 | 6.78 | *** | |
| Ips acuminatus | –0.041 | 0.036 | −1.17 | 0.24 | |
| y | Sirex woodwasps | 0.991 | 0.006 | 163.88 | *** |
| Asemum striatum | 0.443 | 0.058 | 7.63 | *** | |
| Phaenops sp. | –0.437 | 0.070 | −6.25 | *** | |
| Ips acuminatus | 0.018 | 0.016 | 1.12 | 0.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Gao, C.; Fu, N.; Ren, L.; Luo, Y. Resource Sharing between the Invasive Sirex noctilio and Native Woodborers and Beetles in Pinus Plantations. Insects 2024, 15, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15070478
Wang M, Gao C, Fu N, Ren L, Luo Y. Resource Sharing between the Invasive Sirex noctilio and Native Woodborers and Beetles in Pinus Plantations. Insects. 2024; 15(7):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15070478
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ming, Chenglong Gao, Ningning Fu, Lili Ren, and Youqing Luo. 2024. "Resource Sharing between the Invasive Sirex noctilio and Native Woodborers and Beetles in Pinus Plantations" Insects 15, no. 7: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15070478
APA StyleWang, M., Gao, C., Fu, N., Ren, L., & Luo, Y. (2024). Resource Sharing between the Invasive Sirex noctilio and Native Woodborers and Beetles in Pinus Plantations. Insects, 15(7), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15070478








