Screening and Identification of Protease-Producing Microorganisms in the Gut of Gryllotalpa orientalis (Orthoptera: Gryllotalpidae)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects’ Collection and Dissection
2.2. Screening of Proteolytic Bacteria
2.3. Morphological, Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Identification of Bacteria
2.4. Whole-Genome Analysis of Proteolytic Bacteria
3. Results
3.1. Screening and Identification of Proteolytic Bacteria
3.2. Analysis of Proteolytic Bacteria through Whole-Genome Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Douglas, A.E. Multiorganismal insects: Diversity and function of resident microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatefi, A.; Makhdoumi, A.; Asoodeh, A.; Mirshamsi, O. Characterization of a bi-functional cellulase produced by a gut bacterial resident of rosaceae branch borer beetle, Osphranteria coerulescens (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Ding, S.-Y.; Yuan, J.S. Comparison of insect gut cellulase and xylanase activity across different insect species with distinct food sources. Bioenergy Res. 2010, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankrah, N.Y.D.; Douglas, A.E. Nutrient factories: Metabolic function of beneficial microorganisms associated with insects. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2002–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, M.; Bharathiraja, C.; Pandiarajan, J.; Prasanna, V.A.; Rajendhran, J.; Gunasekaran, P. Insect gut microbiome—An unexploited reserve for biotechnological application. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, S16–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solanki, P.; Putatunda, C.; Kumar, A.; Bhatia, R.; Walia, A. Microbial proteases: Ubiquitous enzymes with innumerable uses. 3 Biotech. 2021, 11, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Maiti, T.K.; Roy, R.N. Enzyme producing insect gut microbes: An unexplored biotechnological aspect. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 384–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Gao, P.; Geng, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Shu, C. Lignocellulose degradation in Protaetia brevitarsis larvae digestive tract: Refining on a tightly designed microbial fermentation production line. Microbiome 2022, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, C.; Song, R.; Matsumoto, K.; Matsumoto, R.; Minkoff, B.B.; Oita, S.; Hara, H.; Takasuka, T.E. Proteomic characterization of lignocellulolytic enzymes secreted by the insect-associated fungus Daldinia decipiens oita, isolated from a forest in northern japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02350-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przemieniecki, S.W.; Kosewska, A.; Ciesielski, S.; Kosewska, O. Changes in the gut microbiome and enzymatic profile of Tenebrio molitor larvae biodegrading cellulose, polyethylene and polystyrene waste. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Ju, F. Polyvinyl chloride degradation by a bacterium isolated from the gut of insect larvae. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hivrale, V.K.; Chougule, N.P.; Chhabda, P.J.; Giri, A.P.; Kachole, M.S. Unraveling biochemical properties of cockroach (Periplaneta americana) proteinases with a gel X-ray film contact print method. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 2005, 141, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hivrale, V.K.; Lomate, P.R.; Kalve, N.D.; Kachole, M.S. Periplaneta americana midgut proteases differentially expressed against dietary components from different plant seeds. Physiol. Entomol. 2011, 36, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.H.; Stat, M.; Bunce, M.; Simmons, L.W. The influence of diet and environment on the gut microbial community of field crickets. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 4704–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavy, O.; Gophna, U.; Gefen, E.; Ayali, A. Dynamics of bacterial composition in the locust reproductive tract are affected by the density-dependent phase. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, M.; Ramya, T.; Anbalagan, S.; Suriya, J.; Krishnan, M. Proteomic analysis of pupal gut serine protease of silkworm, Bombyx mori: Partial purification and biochemical characterization. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 12, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughi, F.; Keshavarz, T.; Evans, C.S. Specificities of proteases for use in leather manufacture. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2006, 81, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Maiti, T.K.; Roy, R.N. Protease production by thermo-alkaliphilic novel gut isolate Kitasatospora cheerisanensis gap 12.4 from Gryllotalpa africana. Biocatal. Bioransform. 2017, 35, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcinskas, A.; Schwabe, M.; Brinkrolf, K.; Plarre, R.; Wielsch, N.; Vogel, H. Larvae of the clothing moth Tineola bisselliella maintain gut bacteria that secrete enzyme cocktails to facilitate the digestion of keratin. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Song, N.; Li, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; Fang, J.; Chen, J. Purification and characterization of four key enzymes from a feather-degrading Bacillus subtilis from the gut of tarantula Chilobrachys guangxiensis. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 96, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Su, T.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z. Isolation, identification, and characterization of polystyrene-degrading bacteria from the gut of Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) larvae. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 736062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suman, S.K.; Dhawaria, M.; Tripathi, D.; Raturi, V.; Adhikari, D.K.; Kanaujia, P.K. Investigation of lignin biodegradation by Trabulsiella sp. Isolated from termite gut. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 112, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, R.; Ahmed, M.; Siddique, A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Jamal, A. Catalytic role of thermostable metalloproteases from Bacillus subtilis kt004404 as dehairing and destaining agent. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 434–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Pan, L.; Zhang, M.; Huang, F.; Zhang, M.; He, Z. Screening of bacterial strains from the gut of pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) and their efficiencies in improving the fermentation of soybean meal. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2020, 367, fnaa017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.L.; Peng, S.; Chen, L.L.; Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhu, F. Identification and characterization of a serine protease from Bacillus licheniformis w10: A potential antifungal agent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Huang, Q.Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.H.; Tango, X.F.; Tang, B. Maturation process and characterization of a novel thermostable and halotolerant subtilisin-like protease with high collagenolytic activity but low gelatinolytic activity. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2022, 88, e02184-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, J.V.; Mathukiya, R.P.; Singh, S.P.; Gohel, S.D. Two steps purification, biochemical characterization, thermodynamics and structure elucidation of thermostable alkaline serine protease from Nocardiopsis alba strain om-5. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holger, H.; Martin, K.; Paul, B.; Kornelia, S.; Elizabeth, M.H.W. Analysis of actinomycete communities by specific amplification of genes encoding 16s rrna and gel-electrophoretic separation in denaturing gradients. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1997, 63, 3233–3241. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Xie, Y.; Gao, X.; Shan, M.; Sun, C.; Niu, Y.D.; Shan, A. Screening of cellulose degradation bacteria from min pigs and optimization of its cellulase production. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marynowska, M.; Goux, X.; Sillam-Dusses, D.; Rouland-Lefevre, C.; Halder, R.; Wilmes, P.; Gawron, P.; Roisin, Y.; Delfosse, P.; Calusinska, M. Compositional and functional characterisation of biomass-degrading microbial communities in guts of plant fibre- and soil-feeding higher termites. Microbiome 2020, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one fastq preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. Spades: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boetzer, M.; Pirovano, W. Toward almost closed genomes with gapfiller. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpiano, C.G.; Sant’Anna, F.H.; Ambrosini, A.; de São José, J.F.B.; Beneduzi, A.; Whitman, W.B.; de Souza, E.M.; Lisboa, B.B.; Vargas, L.K.; Passaglia, L.M.P. Genomic metrics applied to Rhizobiales (Hyphomicrobiales): Species reclassification, identification of unauthentic genomes and false type strains. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 614957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez, L.S.; Aburjaile, F.F.; Farias, A.R.G.; Baia, A.D.B.; Oliveira, W.J.; Silva, A.M.F.; Benko-Iseppon, A.M.; Azevedo, V.; Brenig, B.; Ham, J.H.; et al. Burkholderia semiarida sp. Nov. and burkholderia sola sp. Nov., two novel B. cepacia complex species causing onion sour skin. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 46, 126415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, R.L.; Gladney, L.M.; Huang, A.D.; Griswold, T.; Katz, L.S.; Dinsmore, B.A.; Im, M.S.; Kucerova, Z.; Smith, P.A.; Lane, C.; et al. Rapid identification of enteric bacteria from whole genome sequences using average nucleotide identity metrics. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1225207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, M.; Mubarakali, D.; Thiyonila, B.; Krishnan, M.; Padmanaban, B.; Shantkriti, S. Insect gut as a bioresource for potential enzymes—An unexploited area for industrial biotechnology. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 101010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, X.; Gong, K.; Zhong, L.; Hao, J.; Islam, M.M.; Islam, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Isolation, complete genome sequencing and in silico genome mining of Burkholderia for secondary metabolites. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, J.D.; Klingeman, W.E.; Oppert, C.; Oppert, B.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L. Characterization of cellulolytic activity from digestive fluids of Dissosteira carolina (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 157, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson-Trick, E.C.L.; Getz, L.J.; Slaine, P.D.; Thornbury, M.; Lamoureux, E.; Cook, J.; Langille, M.G.I.; Murray, L.E.; McCormick, C.; Rohde, J.R.; et al. Taxonomic differences of gut microbiomes drive cellulolytic enzymatic potential within hind-gut fermenting mammals. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh Ha, D.T.; Kim Thoa, L.T.; Phuong Thao, T.T.; Dung, T.T.; Minh Ha, T.T.; Phuong Lan, T.T.; Khoo, K.S.; Show, P.L.; Huy, N.D. Production of extracellular agarase from Priestia megaterium at7 and evaluation on marine algae hydrolysis. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2024, 172, 110339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, A.; Colom, J.; Mazhar, S.; Khokhlova, E.; Deaton, J.; Rea, K. Bacillus megaterium renuspore® as a potential probiotic for gut health and detoxification of unwanted dietary contaminants. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1125616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yang, L.-R.; Xu, G.; Wu, J.-P. Identification of organic solvent-tolerant lipases from organic solvent-sensitive microorganisms. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014, 99, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.G.d.; Hurtado, R.; Rodrigues, D.L.N.; Lima, A.; dos Anjos, W.F.; Rifici, C.; Attili, A.R.; Tiwari, S.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Spier, S.J.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis of the Dietzia genus: An insight into genomic diversity, and adaptation. Res. Microbiol. 2023, 174, 103998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, L.H.; Dargis, R.; Højholt, K.; Christensen, J.J.; Skovgaard, O.; Justesen, U.S.; Rosenvinge, F.S.; Moser, C.; Lukjancenko, O.; Rasmussen, S.; et al. Whole genome sequencing as a tool for phylogenetic analysis of clinical strains of mitis group streptococci. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 35, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legein, M.; Wittouck, S.; Lebeer, S. Latilactobacillus fragifolii sp. Nov., isolated from leaves of a strawberry plant (Fragaria x ananassa). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Tohya, M.; Aibibula, Z.; Baba, T.; Daida, H.; Kirikae, T. Re-identification of strains deposited as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas fluorescens and Pseudomonas putida in genbank based on whole genome sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5958–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

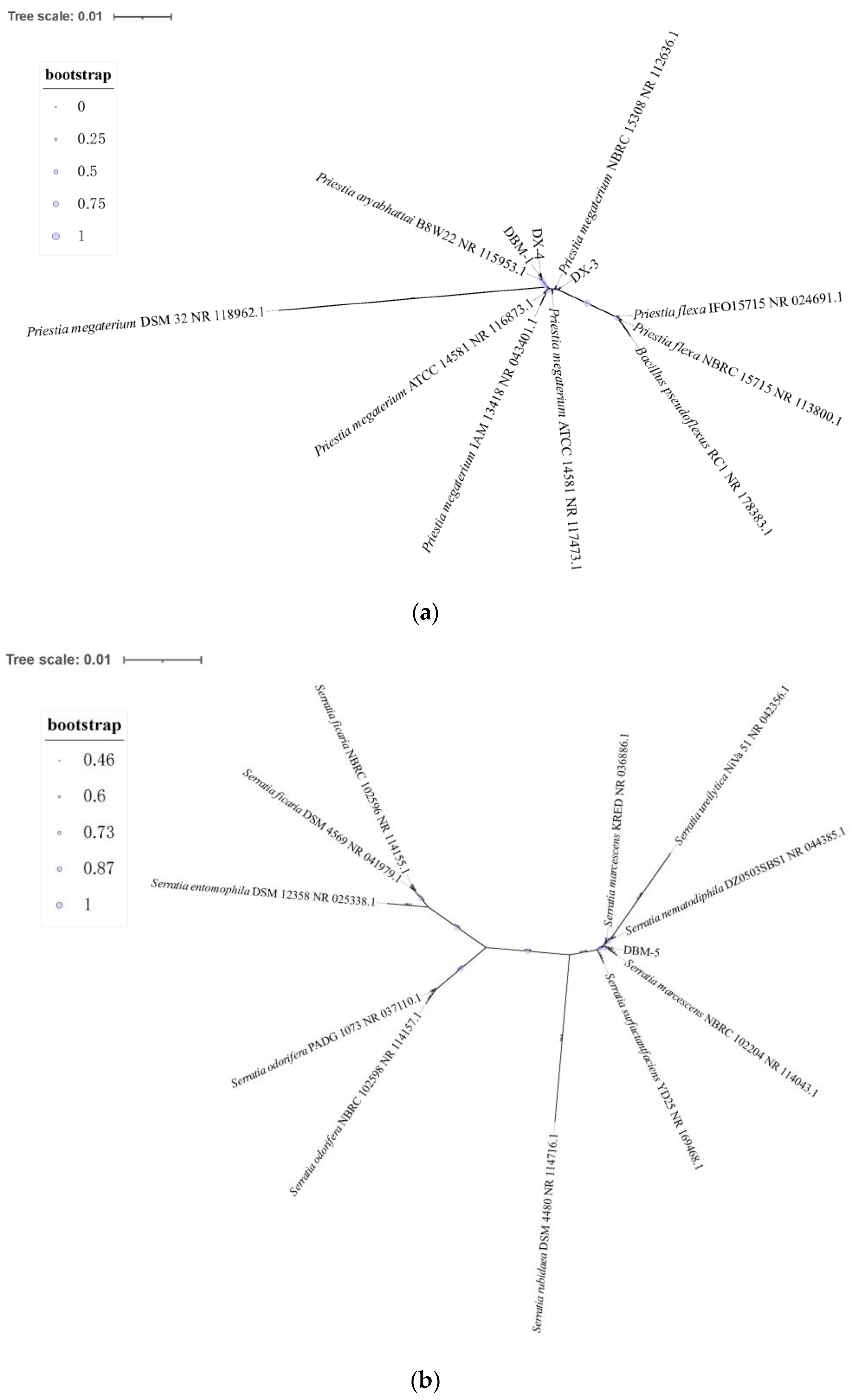
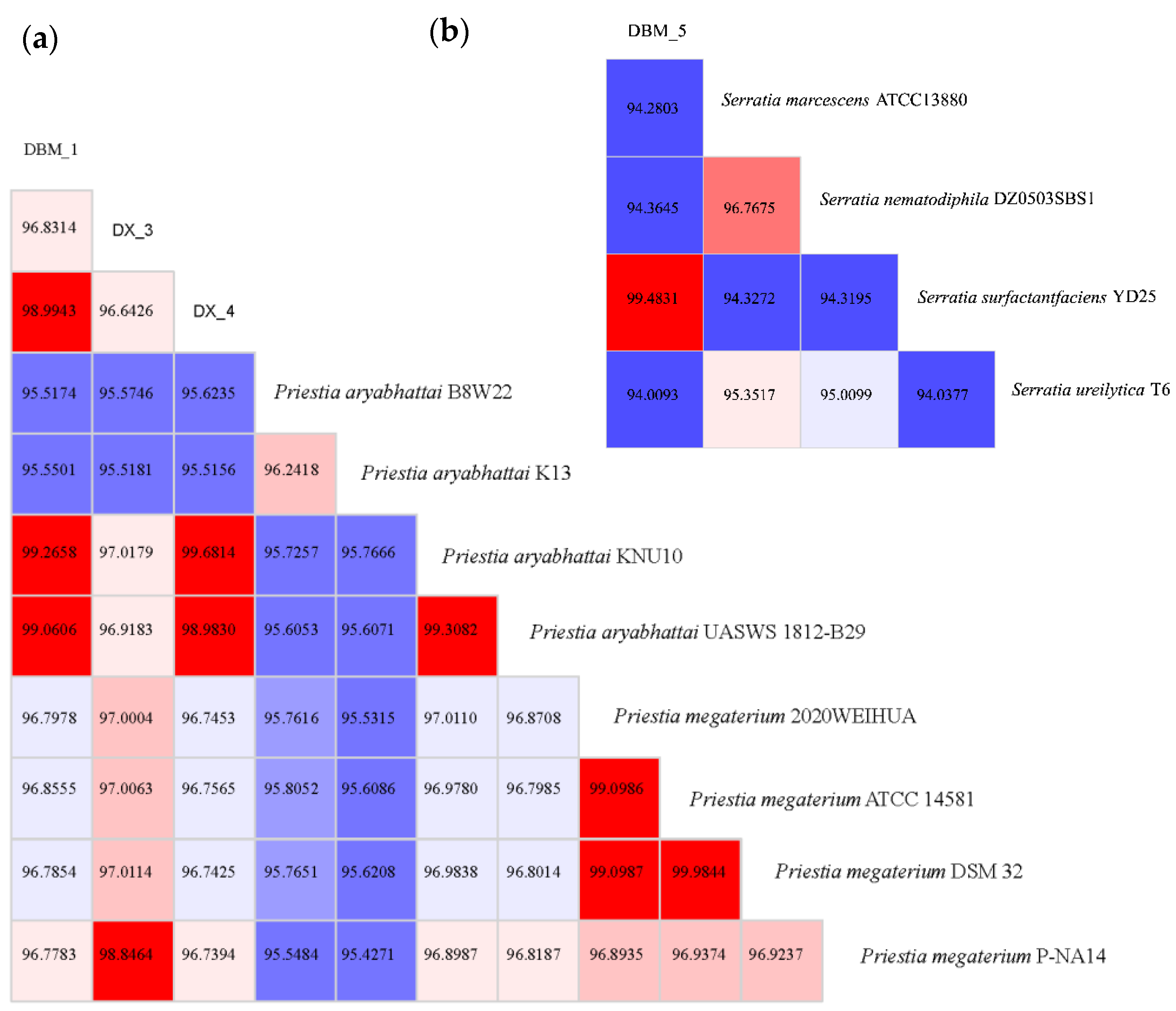

| Strains | Priestia aryabhattai B8W22 | Priestia aryabhattai UASWS 1812-B29 | Priestia megaterium ATCC 14581 | Priestia megaterium P-NA14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBM-1 | 64.1 | 91.9 | 72.8 | 72.6 |
| DX-3 | 64.2 | 73.4 | 74.7 | 90.2 |
| DX-4 | 63.9 | 91.4 | 72.9 | 72.4 |
| Strain | Serratia surfactantfaciens YD25 | Serratia ureilytica T6 | Serratia marcescens ATCC13880 | Serratia nematodiphila DZ0503SBS1 |
| DBM-5 | 96.3 | 25.5 | 56.5 | 56.9 |
| Genome Information | DBM-1 | DX-3 | DX-4 | DBM-5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genome size/bp | 4,894,934 | 5,042,448 | 5,135,523 | 5,036,594 |
| GC/% | 37.79 | 38.04 | 37.66 | 59.72 |
| CDS/ratio (%) | 4963/83.2 | 5130/83.67 | 5222/82.17 | 4667/88.54 |
| rRNA | 12 | 23 | 7 | 12 |
| tRNA | 45 | 107 | 35 | 80 |
| ncRNA | 7 | 7 | 7 | 19 |
| Secondary Metabolite Gene Clusters | Strains/Similarity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolite Type | Nucleotide Length/bp | Similar Gene Clusters/Type | DBM-1 | DX-3 | DX-4 | DBM-5 |
| terpene | 20,819 | surfactin/NRP:lipopeptide | +/13% | +/13% | +/13% | — |
| terpene | 20,849 | carotenoid/terpene | +/50% | +/50% | +/50% | — |
| NI-siderophore | 16,576 | schizokinen/other | +/100% | +/50% | +/62% | — |
| lassopeptide | 23,919 | paeninodin/RiPP | +/60% | +/60% | +/80% | — |
| T3PKS | 41,086 | — | + | + | + | — |
| terpene | 21,869 | — | + | + | + | — |
| phosphonate | 17,423 | — | + | — | + | — |
| lanthipeptide-class-i | 16,669 | paenicidin A/RiPP:lanthipeptide | +/28% | — | — | — |
| lanthipeptide-class-i | 23,288 | — | — | — | + | — |
| prodigiosin | 35,021 | prodigiosin/polyketide | — | — | — | +/100% |
| thiopeptide | 26,440 | o-antigen/saccharide | — | — | — | +/14% |
| opine-like-metallophore | 22,098 | yersinopine/other | — | — | — | +/100% |
| RRE-containing | 20,279 | synechobactin C9/C11/13/14/16/A/B/C (other) | — | — | — | +/9% |
| NRPS | 47,380 | viobactin/NPR | — | — | — | +/46% |
| NRPS | 45,787 | — | — | — | — | — |
| betalactone | 25,668 | — | — | — | — | — |
| NRP-metallophore | 51,398 | trichrysobactin/cyclic trichrysobactin/chrysobactin/dichrysobactin (NRP) | — | — | — | +/46% |
| NRPS butyrolactone | 59,588 | rhizomide A/B/C (NRP) | — | — | — | +/100% |
| Proteases | DBM-1 | DX-3 | DX-4 | DBM-5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serine protease EC 3.4.21.53 | ctg00001_001478 | ctg00002_001384 | ctg00001_002979 | ctg00001_000175 | |
| Pepsin EC 3.4.23.3 | ctg00001_001049 | ctg00002_001814 | ctg00001_002548 | ctg00002_002628 | |
| Trypsin | EC 3.4.21.1 | ctg00004_004107 | ctg00006_003884 | ctg00003_004439 | ctg00002_00254 |
| EC 3.4.21.2 | ctg00001_001383 | ||||
| Cysteine protease | |||||
| Metalloprotease | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, X.; Zhao, L.; Wu, F.; Zhou, H.; Shi, F. Screening and Identification of Protease-Producing Microorganisms in the Gut of Gryllotalpa orientalis (Orthoptera: Gryllotalpidae). Insects 2024, 15, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15080629
Zheng X, Zhao L, Wu F, Zhou H, Shi F. Screening and Identification of Protease-Producing Microorganisms in the Gut of Gryllotalpa orientalis (Orthoptera: Gryllotalpidae). Insects. 2024; 15(8):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15080629
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Xiang, Lu Zhao, Fangtong Wu, He Zhou, and Fuming Shi. 2024. "Screening and Identification of Protease-Producing Microorganisms in the Gut of Gryllotalpa orientalis (Orthoptera: Gryllotalpidae)" Insects 15, no. 8: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15080629
APA StyleZheng, X., Zhao, L., Wu, F., Zhou, H., & Shi, F. (2024). Screening and Identification of Protease-Producing Microorganisms in the Gut of Gryllotalpa orientalis (Orthoptera: Gryllotalpidae). Insects, 15(8), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15080629






