Influences of Salt Stress on Cotton Metabolism and Its Consequential Effects on the Development and Fecundity of Aphis gossypii Glover
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plants Culture and Salt Stress
2.2. Effects of Salt Stress on Cotton Metabolomics
2.2.1. Sampling
2.2.2. Analysis of Cotton Metabolomics
2.3. Aphis gossypii
2.4. Effects of Salt-Stressed Cotton Plants on Growth, Development and Fecundity of A. gossypii
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quality Control and PCA Analysis of Total Samples
3.2. Metabolite Type and Quantity Analysis
3.3. Analysis of Cotton Metabolites
3.4. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Differential Metabolites
3.5. K-Means Cluster Analysis of Differential Metabolites
3.6. Effects of Salt-Stressed Cotton Plants on A. gossypii
3.7. The Correlation Analysis between Fitness and Differential Metabolites
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdelraheem, A.; Esmaeili, N.; O’Connell, M.; Zhang, J.F. Progress and perspective on drought and salt stress tolerance in cotton. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 130, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizipour, M.H.G.; Rajabpour, A.; Jafari, S.; Tahmasebi, A. Host-targeted salt stress affects fitness and vector performance of bird cherry-oat aphid (Rhopalosiphum padi L.) on wheat. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2021, 15, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Analysis and countermeasure research on saline-alkali land change in Xinjiang irrigation area in recent 20 years. Water Resour. Dev. Manag. 2020, 6, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Sharma, P.K. Soil salinity and food security in India. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 533781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusca, M.; Gadea, S.; Vidican, R.; Stoian, V.; Vatca, A.; Balint, C.; Stoian, V.A.; Horvat, M.; Vatca, S. Exploring the research challenges and rerspectives in ecophysiology of plants affected by salinity stress. Agriculture 2023, 13, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chele, K.H.; Tinte, M.M.; Piater, L.A.; Dubery, I.A.; Tugizimana, F. Soil salinity, a serious environmental issue and plant responses: A metabolomics perspective. Metabolites 2021, 11, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global predictions of primary soil salinization under changing climate in the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.B.; Wang, Z.H.; Guo, L.; Li, H.Q.; Tan, M.D.; Zou, J.; Zong, R.; Dhital, Y.P. The impact of long-term mulched drip irrigation on soil particle composition and salinity in arid northwest China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C.H.; Rasool, B.; Davey, J.W.; Hancock, R.D. Cross-tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses in plants: A focus on resistance to aphid infestation. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 2025–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; Hu, X.; Pan, B.; Zeng, B.; Wu, N.; Fang, G.; Cao, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; et al. Draft genome of the cotton aphid Aphis gossypii. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 105, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, N.; Vitek, C.; Kariyat, R. The known and unknowns of aphid biotypes, and their role in mediating host plant defenses. Diversity 2023, 15, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, L.M.; Stiller, W.N. The past, present, and future of host plant resistance in cotton: An Australian perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 895877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoblich, M.; Al Ktash, M.; Wackenhut, F.; Jehle, V.; Ostertag, E.; Brecht, M. Applying UV hyperspectral imaging for the quantification of honeydew content on raw cotton via PCA and PLS-R models. Textiles 2023, 3, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, L.S.; Tena, A.; Idier, M.; Amiens-Desneux, E.; Desneux, N. Quality of aphid honeydew for a parasitoid varies as a function of both aphid species and host plant. Biol. Control 2021, 152, 104099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejat, N.; Mantri, N. Plant immune system: Crosstalk between responses to biotic and abiotic stresses the missing link in understanding plant defence. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2017, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryum, Z.; Luqman, T.; Nadeem, S.; Khan, S.; Wang, B.H.; Ditta, A.; Khan, M.K.R. An overview of salinity stress, mechanism of salinity tolerance and strategies for its management in cotton. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 907937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, N.; Al Hinai, M.S.; Hafeez, M.B.; Rehman, A.; Wahid, A.; Siddique, K.H.; Farooq, M. Regulation of photosynthesis under salt stress and associated tolerance mechanisms. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 178, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.J.; Huang, Z.J.; Li, M.Q.; Hou, Z.N. Growth, ionic homeostasis, and physiological responses of cotton under different salt and alkali stresses. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Wei, Z.H.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.Z.; Liu, F.L. Growth and physiological responses of cotton plants to salt stress. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2021, 207, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Cui, R.; Wang, D.; Huang, H.; Rui, C.; Malik, W.A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, N.; Liu, X.; et al. Combined transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses elucidate key salt-responsive biomarkers to regulate salt tolerance in cotton. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydogdu, M.; Aydogdu, M.H.; Cullu, M.A. The determination of the cotton productivity and losses under the effect of salinity by using Geographical Information System (GIS) and Remote Sensing (RS) Gap region, Akcakale Sampling, Turkey. J. Acad. Soc. Sci. Stud. 2014, 24, 617–630. [Google Scholar]
- Quijano-Medina, T.; Turlings, T.C.J.; Sosenski, P.; Grandi, L.; Cervera, J.C.; Moreira, X.; Abdala-Roberts, L. Effects of soil salinity on the expression of direct and indirect defences in wild cotton Gossypium hirsutum. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xin, C.Y.; Xu, Y.Y.; Wang, D.; Lin, X.Q.; Chen, Z.Z. Effect of salt stress on secondary metabolites of cotton and biological characteristics and detoxification enzyme activity of cotton spider mites. Crop Prot. 2021, 141, 105498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.P.; Wang, C.; Li, H.T.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.Z.; Lu, Y.H. Bottom-up effects of drought-stressed cotton plants on performance and feeding behavior of Aphis gossypii. Plants 2023, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Eneji, A.E.; Kong, X.; Wang, K.; Dong, H. Salt stress effects on secondary metabolites of cotton in relation to gene expression responsible for aphid development. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ge, S.; Xu, X.; Xing, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, X.; Lv, M.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, Y. Multiomics analysis reveals new insights into the apple fruit quality decline under high nitrogen conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 5559–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Moon, Y.S.; Pack, I.S.; Kim, C.G. Salinity affects metabolomic profiles of different trophic levels in a food chain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.P.; Rahman, M.S.; Nowrin, F.; Haque, S.S.; Qin, X.H.; Haque, M.A.; Uddin, M.M.; Landis, D.A.; Howlader, M.T.H. Salinity influences plant-pest-predator tritrophic interactions. J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.X.; Lu, X.Y.; Tao, Y.F.; Guo, H.J.; Min, W. Comparative ionomics and metabolic responses and adaptive strategies of cotton to salt and alkali stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 871387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.M.F.; Salama, K.H.; Allam, H.Y. Role of the plasma membrane in saline conditions: Lipids and proteins. Bot. Rev. 2015, 81, 416–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, M.; Divyanshu, K.; Kumar, S.; Swapnil, P.; Zehra, A.; Shukla, V.; Yadav, M.; Upadhyay, R.S. Regulation of L-proline biosynthesis, signal transduction, transport, accumulation and its vital role in plants during variable environmental conditions. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.Y.; Shi, G.Y.; Guo, X.Y.; Zhang, L.W.; Xu, W.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Su, Z.; Hua, J.P. Transcriptome analysis reveals that distinct metabolic pathways operate in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive upland cotton varieties subjected to salinity stress. Plant Sci. 2015, 238, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widodo; Patterson, J.H.; Newbigin, E.; Tester, M.; Bacic, A.; Roessner, U. Metabolic responses to salt stress of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cultivars, Sahara and Clipper, which differ in salinity tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 4089–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, S.; Chong, K. Comparative metabolomic analysis reveals a reactive oxygen species-dominated dynamic model underlying chilling environment adaptation and tolerance in rice. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 1295–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirma, M.; Araújo, W.L.; Fernie, A.R.; Galili, G. The multifaceted role of aspartate-family amino acids in plant metabolism. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 4995–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misyura, M.; Guevara, D.; Subedi, S.; Hudson, D.; McNicholas, P.D.; Colasanti, J.; Rothstein, S.J. Nitrogen limitation and high density responses in rice suggest a role for ethylene under high density stress. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Beier, M.P.; Tabuchi-Kobayashi, M.; Hayatsu, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Umetsu-Ohashi, T.; Sasaki, K.; Ishiyama, K.; Murozuka, E.; Kojima, M.; et al. Cytosolic glutamine synthetase GS1;3 is involved in rice grain ripening and germination. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 835835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, W.J., Jr. Herbivory in relation to plant nitrogen content. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1980, 11, 119–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, M.J. Environmental pressures on top-down and bottom-up forces in coastal ecosystems. Diversity 2021, 13, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masisi, K.; Beta, T.; Moghadasian, M.H. Antioxidant properties of diverse cereal grains: A review on in vitro and in vivo studies. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Li, Q.; Bi, K.S. Bioactive flavonoids in medicinal plants: Structure, activity and biological fate. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handa, N.; Kohli, S.K.; Sharma, A.; Thukral, A.K.; Bhardwaj, R.; Abd Allah, E.F.; Alqarawi, A.A.; Ahmad, P. Selenium modulates dynamics of antioxidative defence expression, photosynthetic attributes and secondary metabolites to mitigate chromium toxicity in Brassica juncea L. plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 161, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagoskina, N.V.; Zubova, M.Y.; Nechaeva, T.L.; Kazantseva, V.V.; Goncharuk, E.A.; Katanskaya, V.M.; Baranova, E.N.; Aksenova, M.A. Polyphenols in plants: Structure, biosynthesis, abiotic stress regulation, and practical applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shende, V.V.; Bauman, K.D.; Moore, B.S. The shikimate pathway: Gateway to metabolic diversity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2024, 41, 604–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, S.; Singh, S.; Sohal, S.K. Inhibitory effect of chrysin on growth, development and oviposition behaviour of melon fruit fly, Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Coquillett) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Phytoparasitica 2022, 50, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Han, P.; Yan, W.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Shi, X.Y.; Zhou, X.G.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X.W. Uptake of quercetin reduces larval sensitivity to lambda-cyhalothrin in Helicoverpa armigera. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Zhou, Z.X.; Zhang, J.M.; Shi, C.H.; Zhang, G.H.; Jin, Z.Y.; Wang, W.K.; Li, C.R. Effect of plant secondary metabolites on common cutworm, Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Entomol. Res. 2018, 48, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golawska, S.; Sprawka, I.; Lukasik, I.; Golawski, A. Are naringenin and quercetin useful chemicals in pest-management strategies? J. Pest Sci. 2014, 87, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Luo, J.; Zhu, X.; Gao, X.; Hua, H.; Cui, J. Transcriptomic analysis of salivary gland and proteomic analysis of oral secretion in Helicoverpa armigera under cotton plant leaves, gossypol, and tannin stresses. Genomics 2022, 114, 110267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, C.G. Effects of persimmon tannin on survival and reproduction of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Entomol. Res. 2015, 45, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Yeo, J.D. Insoluble-bound phenolics in food. Molecules 2016, 21, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debona, D.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Datnoff, L.E. Silicon’s role in abiotic and biotic plant stresses. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 85–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Aswad, A.F.; Aisu, J.; Khalifa, M.H. Biological activity of tannins extracts from processed Camellia sinensis (black and green tea), Vicia faba and Urtica dioica and Allium cepa essential oil on three economic insects. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2023, 130, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.; Daud, M.K.; Zhu, S. Effects of pigment glands and gossypol on growth, development and insecticide-resistance of cotton bollworm (Heliothis armigera (Hübner)). Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krempl, C.; Heidel-Fischer, H.M.; Jimenez-Aleman, G.H.; Reichelt, M.; Menezes, R.C.; Boland, W.; Vogel, H.; Heckel, D.G.; Joussen, N. Gossypol toxicity and detoxification in Helicoverpa armigera and Heliothis virescens. Insect Biochem. Mol. 2016, 78, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Pan, Y.; Gao, X.; Xi, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.; Bi, R.; Yang, S.; Xin, X.; Shang, Q. Cytochrome P450 CYP6DA2 regulated by cap ‘n’ collar isoform C (CncC) is associated with gossypol tolerance in Aphis gossypii Glover. Insect Mol. Biol. 2016, 25, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbehenn, R.V.; Peter Constabel, C. Tannins in plant-herbivore interactions. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Wu, G.; Wan, F.H. Effects of high-gossypol cotton on the development and reproduction of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) MEAM1 cryptic species. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, F.; Siddiqui, H.; Alam, P.; Hayat, S. Glucose-induced response on photosynthetic efficiency, ROS homeostasis, and antioxidative defense system in maintaining carbohydrate and ion metabolism in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) under salt-mediated oxidative stress. Protoplasma 2021, 258, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, K.; Ohri, P.; Bhardwaj, R. Decoding sugar regulation and homeostasis in plants: Cracking functional roles under stresses. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 4797–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, F.; Hayat, S. Effect of glucose on the morpho-physiology, photosynthetic efficiency, antioxidant system, and carbohydrate metabolism in Brassica juncea. Protoplasma 2019, 256, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.W.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Yang, H.X.; Wei, C.X.; Wan, Y.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Bai, J.G. Glucose application protects chloroplast ultrastructure in heat-stressed cucumber leaves through modifying antioxidant enzyme activity. Biol Plant. 2015, 59, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.G.; Guo, S.R.; Chen, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Shu, S. Enhancement of salt-stressed cucumber tolerance by application of glucose for regulating antioxidant capacity and nitrogen metabolism. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2020, 100, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Yang, Q.H. The relationships between the physiological and biochemical mechanisms of aphid resistance of cotton and the population dynamics of the cotton aphid. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. 1993, 20, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Wang, H.; Ji, X.; Dong, H. Effects of abiotic stress on cotton secondary metabolism and cotton aphid population dynamics. Cotton Sci. 2016, 28, 324–330. [Google Scholar]



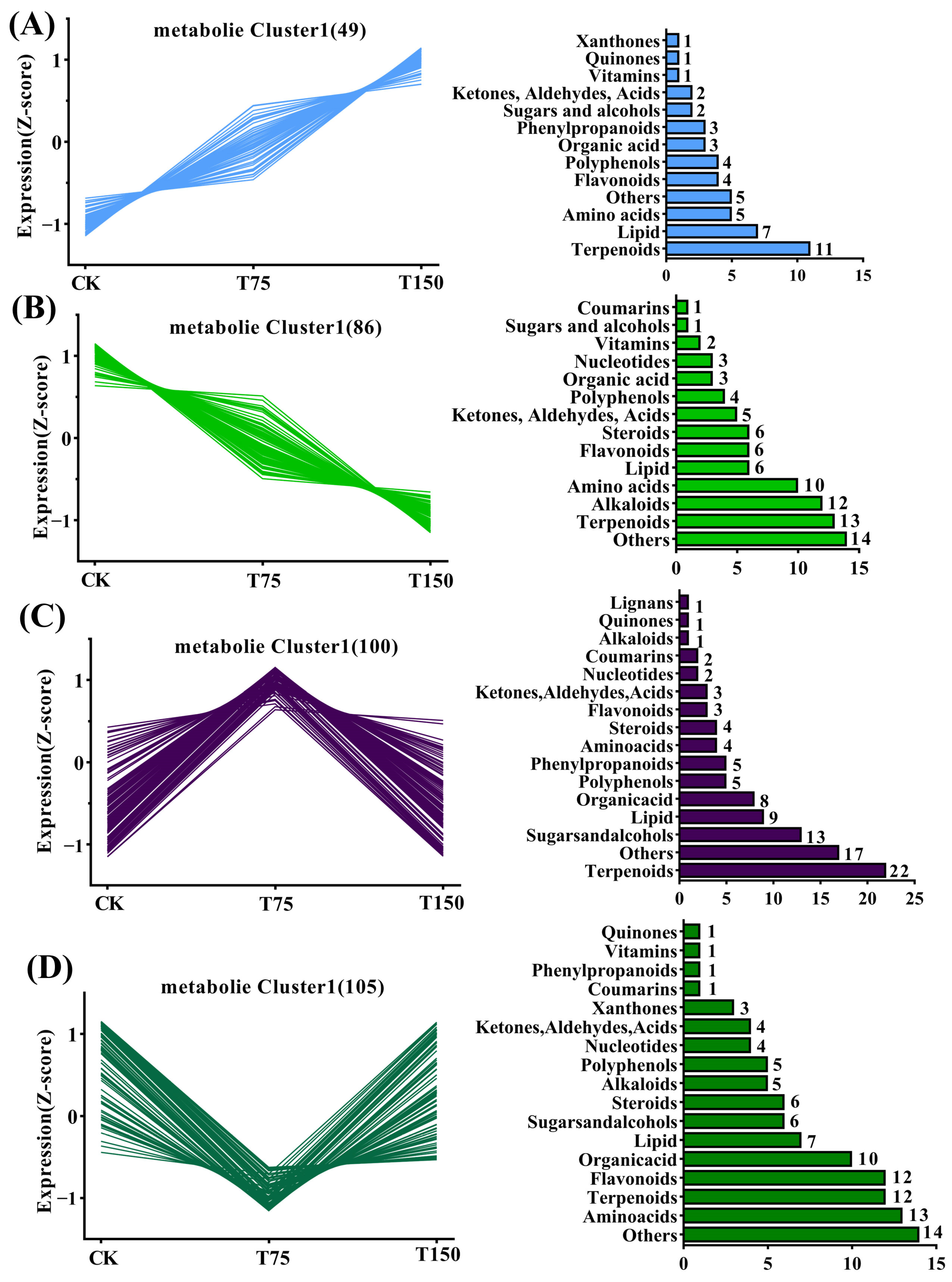
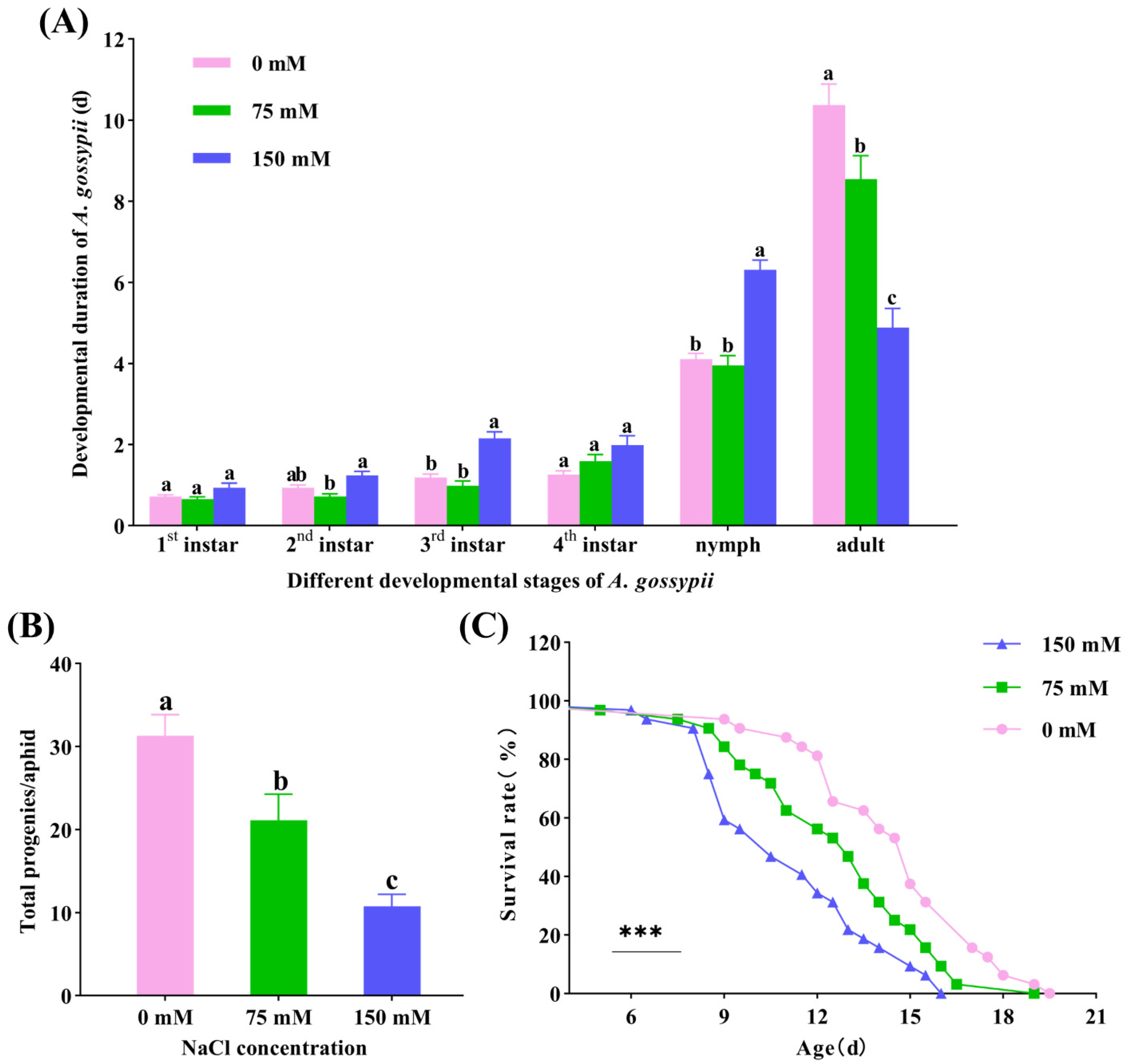
| ID | Differential Metabolites | Correlation Coefficient R | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adult Longevity | Fecundity/Aphid | ||
| NEG_q114 | Dihydromyricetin | −0.969 | −0.915 |
| NEG_q228 | Neoastilbin | −0.944 | −0.985 |
| NEG_q295 | Taxifolin | −0.914 | −0.975 |
| NEG_q156 | Gossypol | −0.903 | −0.946 |
| NEG_q238 | Olivetol | −0.882 | −0.956 |
| NEG_q152 | Glucosyringic Acid | −0.948 | −0.893 |
| NEG_q82 | Chloranthalactone E | −0.852 | −0.967 |
| NEG_q164 | Incensole | −0.903 | −0.977 |
| NEG_q262 | Polpunonic Acid | −0.879 | −0.965 |
| NEG_t44 | Centellasaponin B | −0.963 | −0.95 |
| NEG_t136 | Benzyl glucoside | 0.984 | 0.94 |
| NEG_t42 | Microcystin-LR | 0.966 | 0.981 |
| NEG_t122 | Rauvotetraphylline B | 0.965 | 0.972 |
| NEG_t125 | Eupteleasaponin I | 0.963 | 0.981 |
| POS_t112 | Cis-Jasmone | 0.952 | 0.985 |
| NEG_q78 | Catechin | 0.951 | 0.927 |
| POS_q127 | Histamine (Phosphate) | 0.951 | 0.976 |
| POS_q237 | Sah | 0.949 | 0.915 |
| NEG_q138 | Fraxin | 0.948 | 0.982 |
| POS_q279 | γ-Aminobutyric acid | 0.944 | 0.968 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, W.; Song, B.; Pan, H.; Liu, X. Influences of Salt Stress on Cotton Metabolism and Its Consequential Effects on the Development and Fecundity of Aphis gossypii Glover. Insects 2024, 15, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15090713
Jiao W, Song B, Pan H, Liu X. Influences of Salt Stress on Cotton Metabolism and Its Consequential Effects on the Development and Fecundity of Aphis gossypii Glover. Insects. 2024; 15(9):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15090713
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Wangquan, Bingmei Song, Hongsheng Pan, and Xiaoning Liu. 2024. "Influences of Salt Stress on Cotton Metabolism and Its Consequential Effects on the Development and Fecundity of Aphis gossypii Glover" Insects 15, no. 9: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15090713
APA StyleJiao, W., Song, B., Pan, H., & Liu, X. (2024). Influences of Salt Stress on Cotton Metabolism and Its Consequential Effects on the Development and Fecundity of Aphis gossypii Glover. Insects, 15(9), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15090713





