Molecular Insights into Diapause Mechanisms in Telenomus remus for Improved Biological Control
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Insects
2.2. Diapause Induction
2.3. Total RNA Extraction and Detection
2.4. Transcriptome Assembly and Annotation
2.5. Screening of Diapause-Associated Genes and KEGG Pathway Analysis
2.6. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Light Signal Transduction Genes
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Validation of Light Signal Transduction Gene Expression
3. Results
3.1. Transcriptome Sequencing and Data Assembly of T. remus
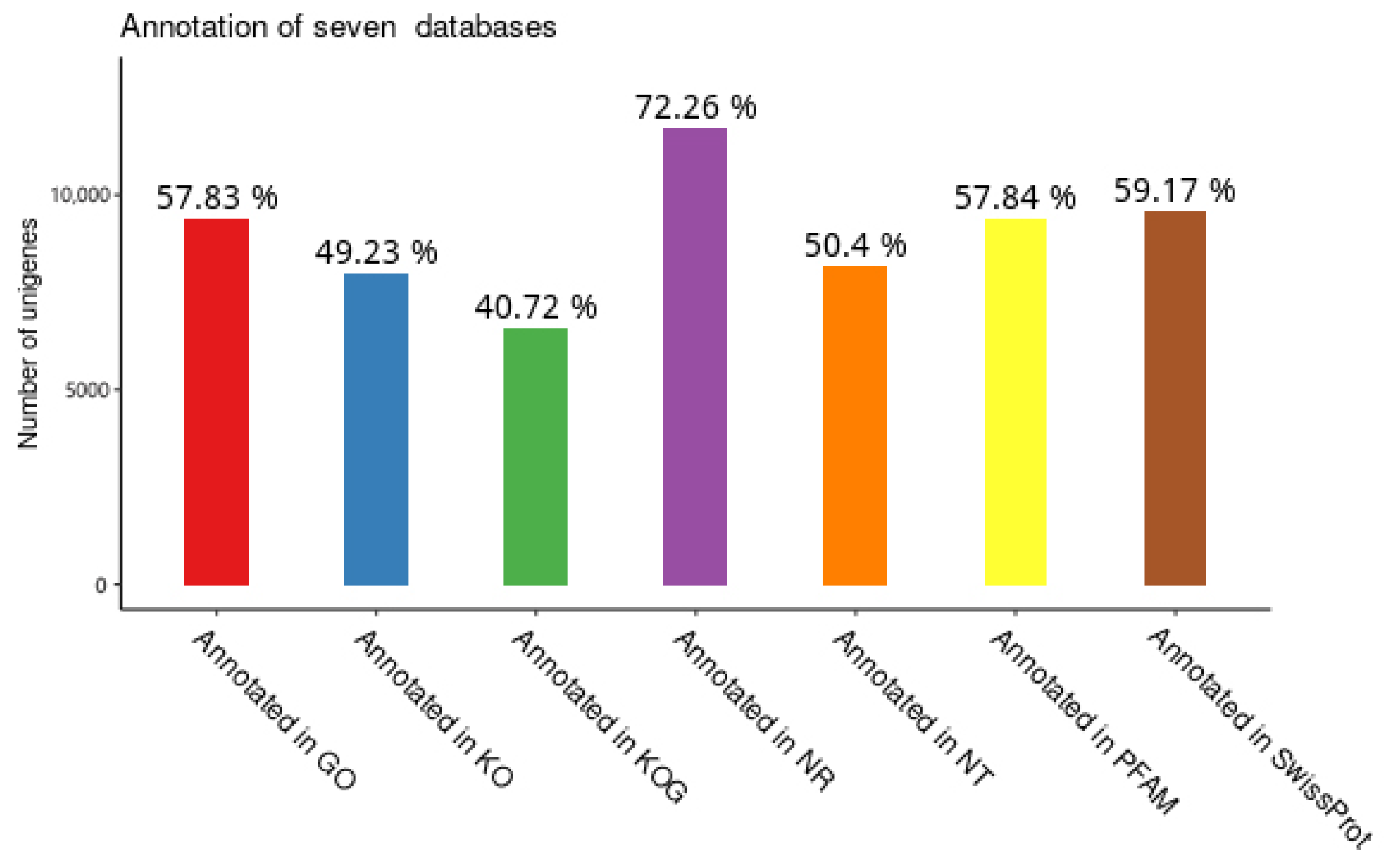
3.2. Functional Annotation of Unigenes in T. remus
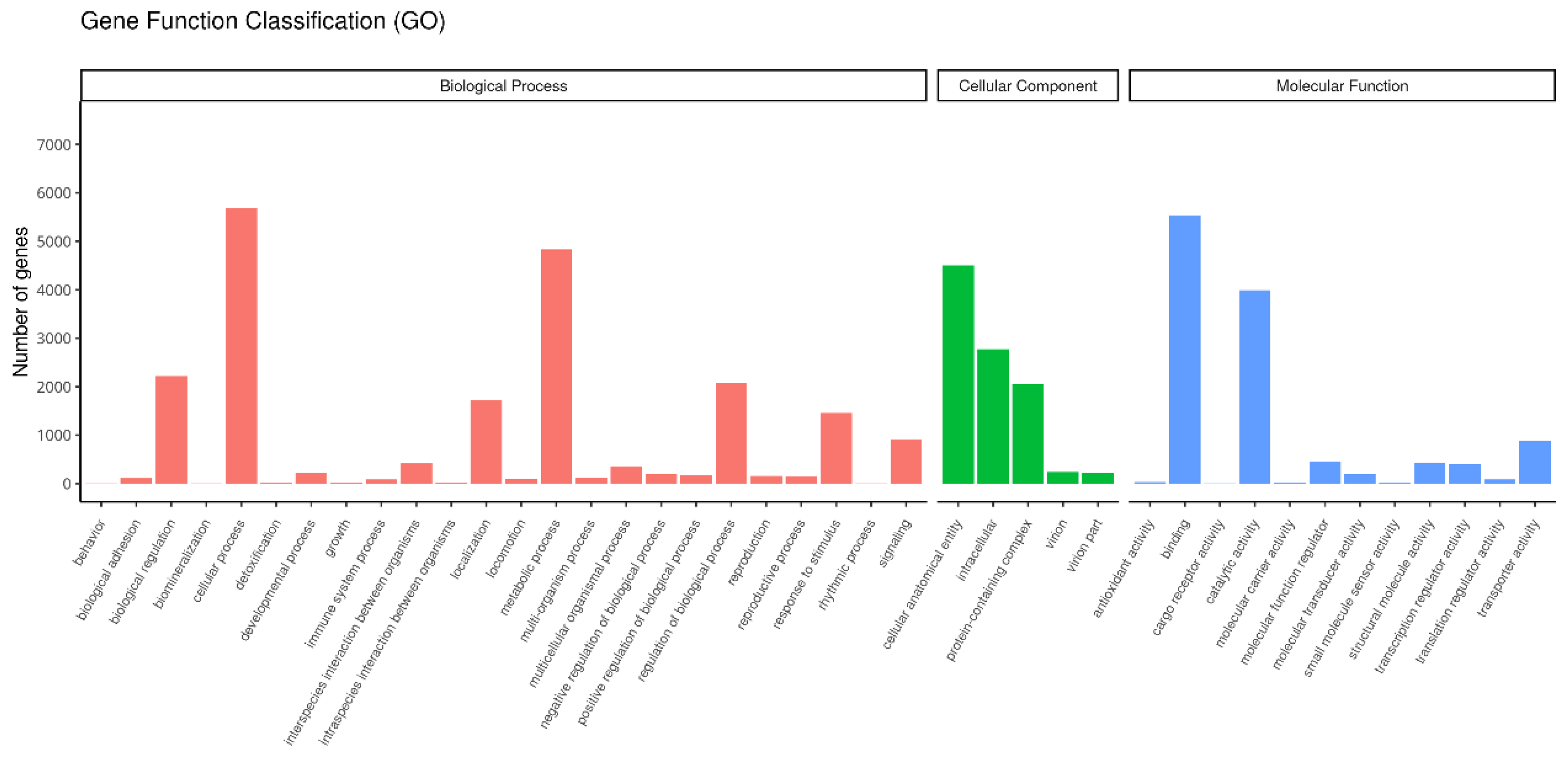
3.3. Functional Classification of Unigenes in T. remus
3.4. Functional Annotation of T. remus in KEGG Database
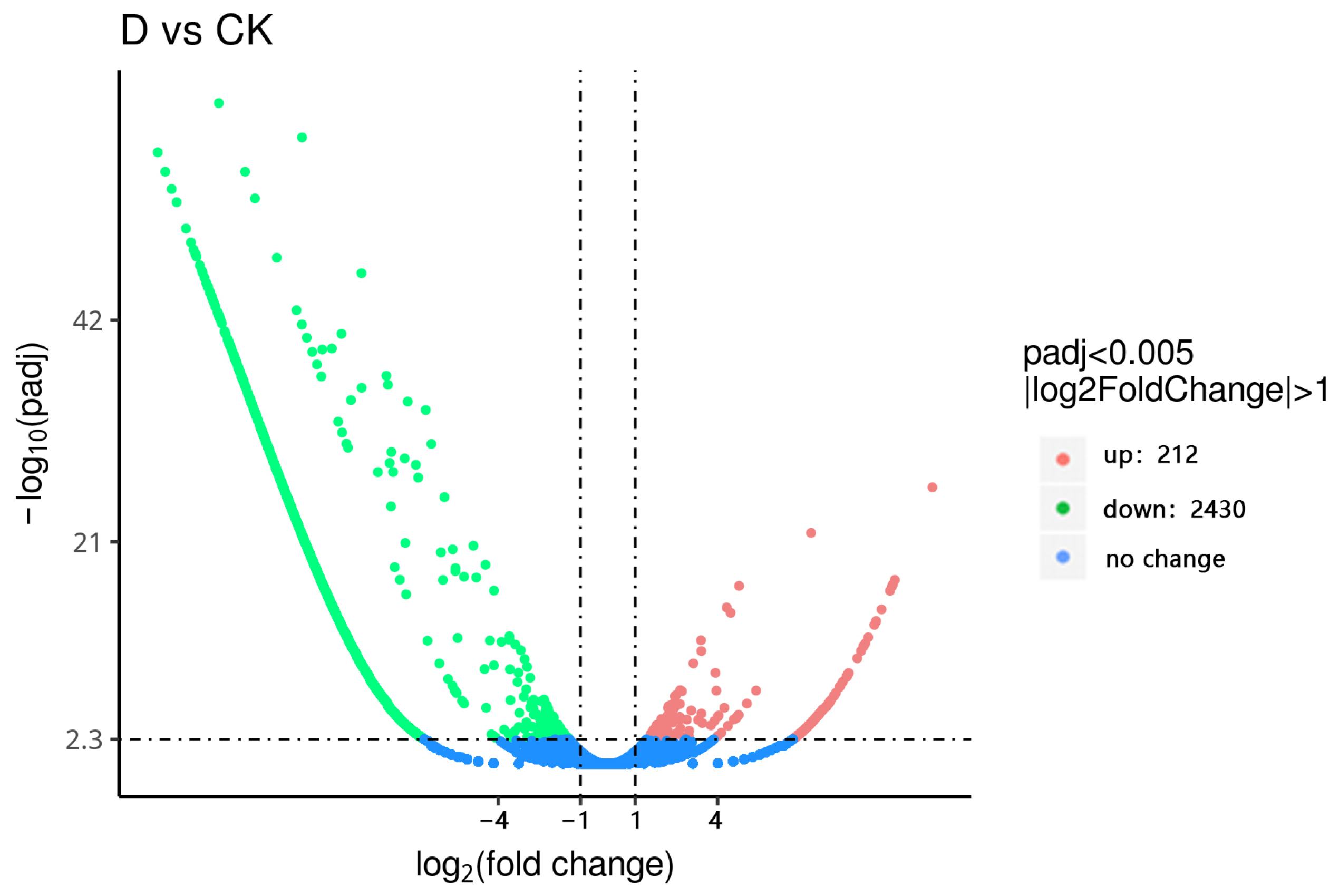
3.5. Screening of Differentially Expressed Genes
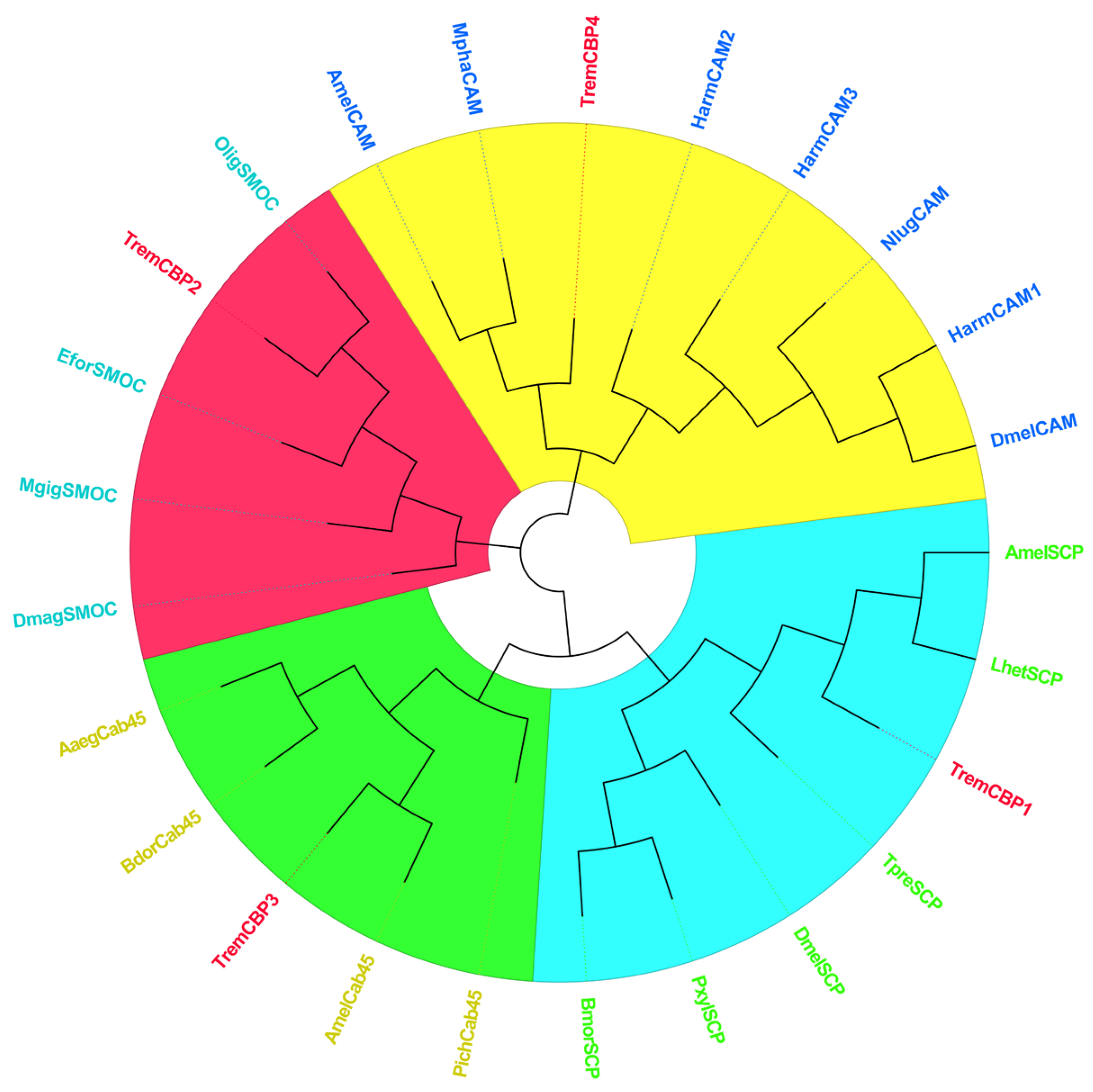
3.6. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Light Signal Transduction Genes in T. remus
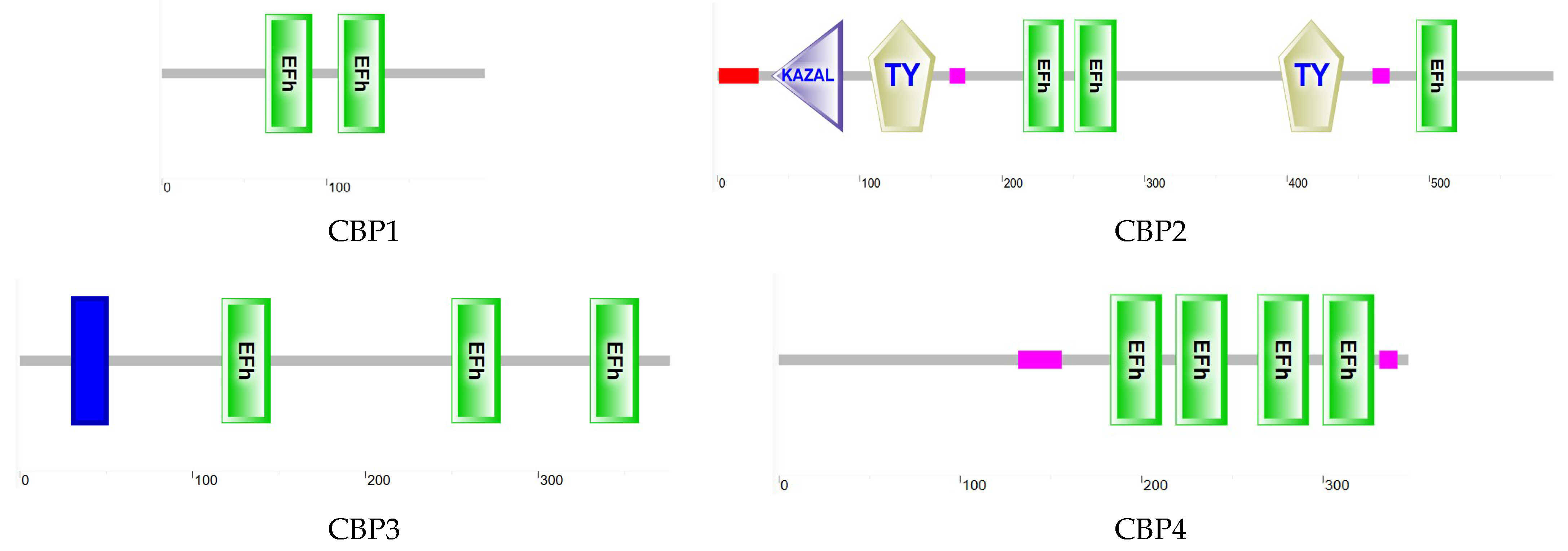
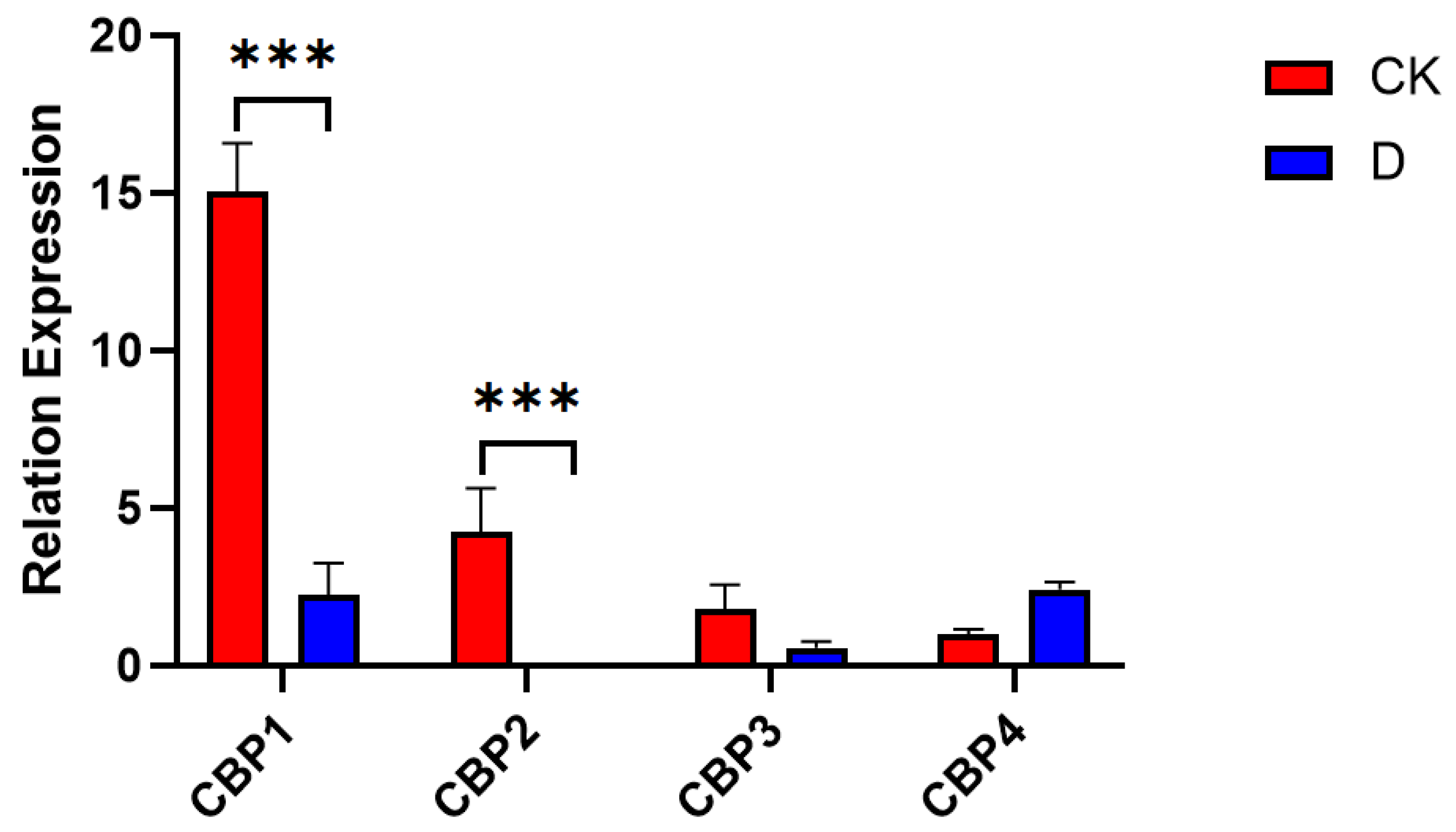
3.6.1. CBP Sequence Analysis
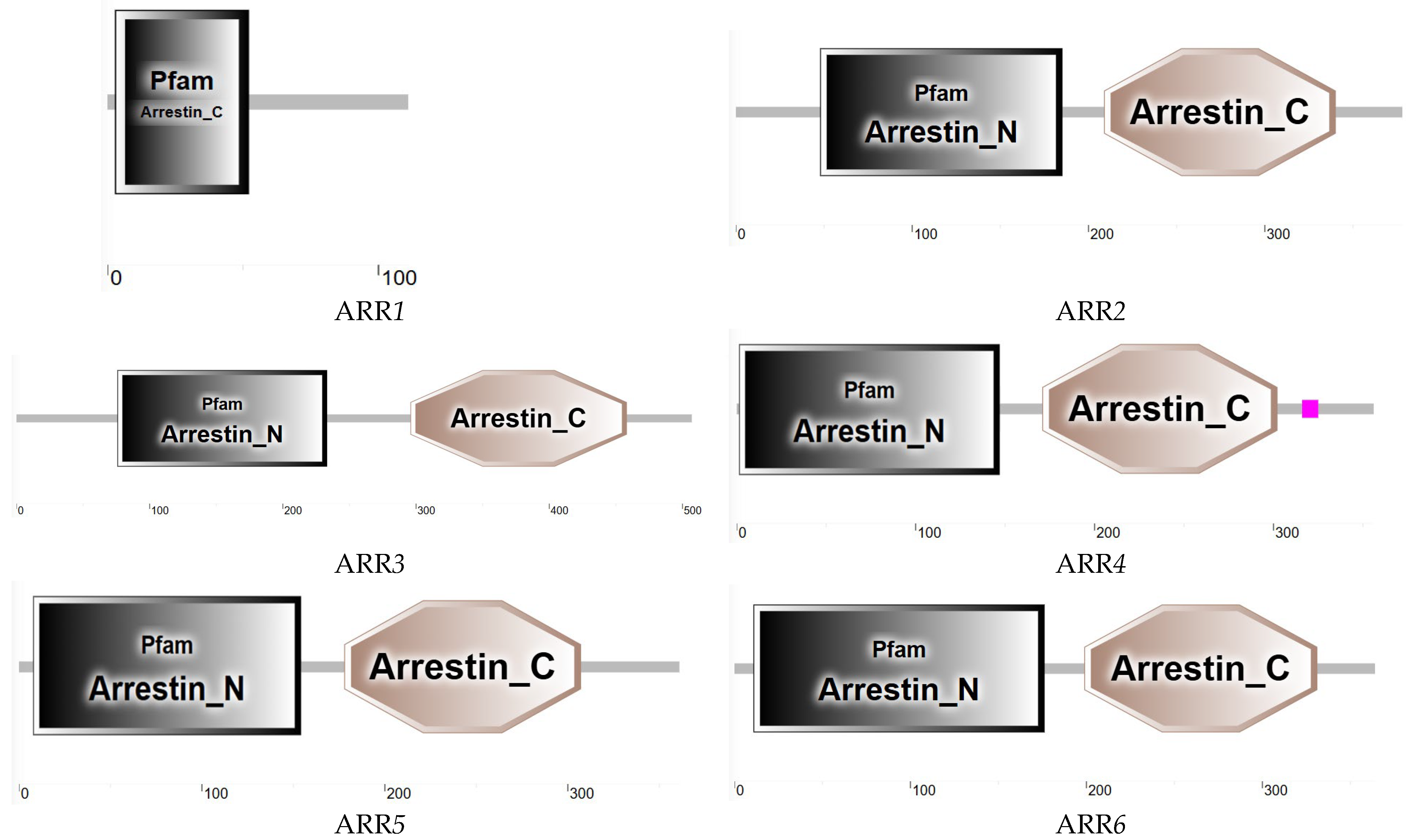
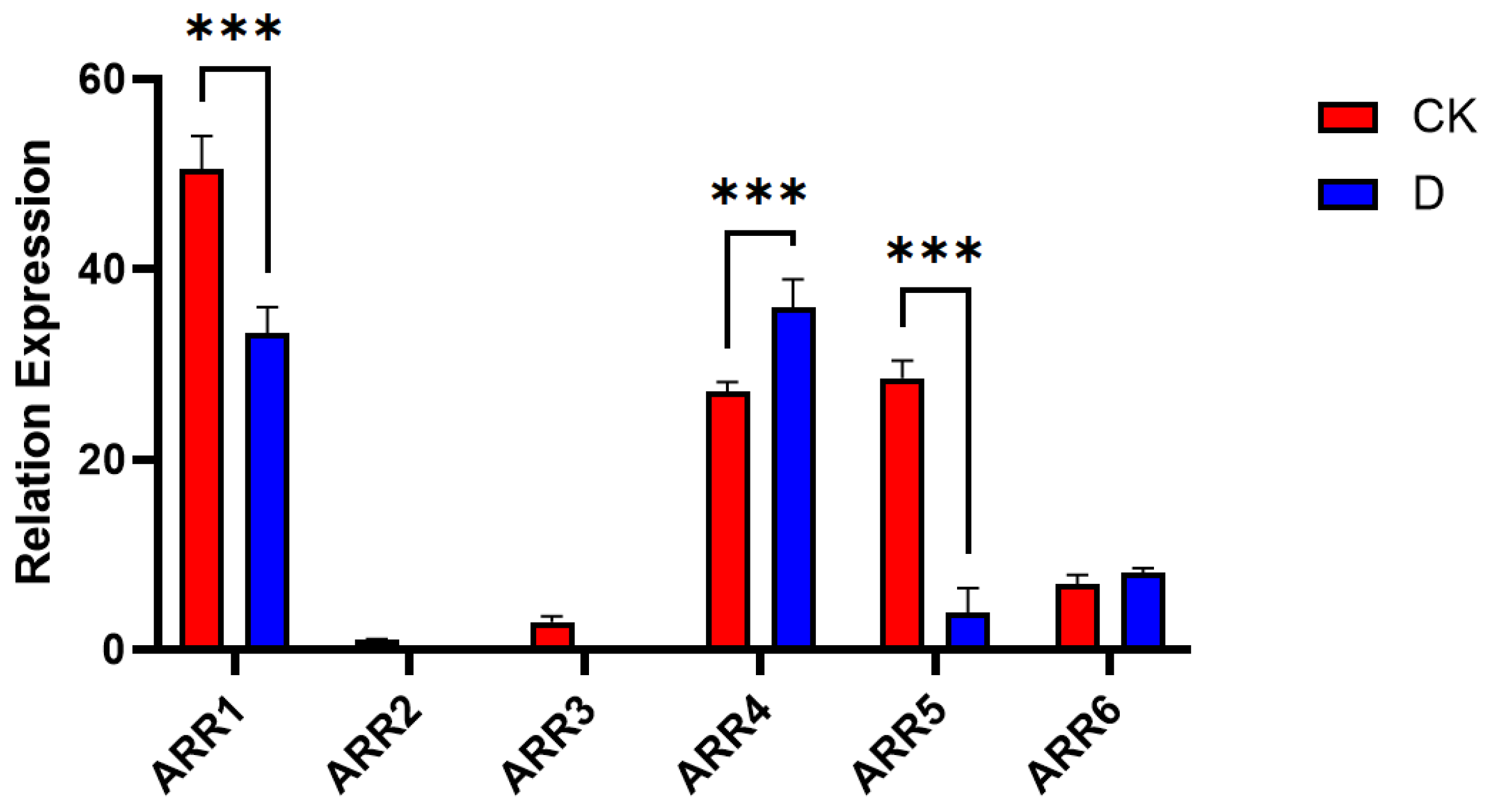
3.6.2. ARR Sequence Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tay, W.T.; Meagher, R.L., Jr.; Czepak, C.; Groot, A.T. Spodoptera frugiperda Ecology, evolution, and management options of an invasive species. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2023, 68, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, R.C.O.D.F.; Carneiro, T.R.; Bueno, A.D.F.; Pratissoli, D.; Fernandes, O.A.; Vieira, S.S. Parasitism capacity of Telenomus remus Nixon (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) on Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) eggs. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2010, 53, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Lyu, B.; Lu, H.; Ji, X.; Yang, P.; Su, H.; Cai, B. Investigation and preliminary study of biological characteristic of parasitic wasps of Spodoptera frugiperda in Hainan. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2020, 41, 1189. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, S.F.; Zhou, J.C.; Zhang, Z.T.; Dong, Q.J.; Bai, X.P.; Zhang, L.S.; Dong, H. Five parasitic natural enemies of Spodoptera frugiperda and two hyperparasitoids of Cotesia glomerata were found in southeast of Guizhou province. Plant Prot. 2019, 45, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Colmenarez, Y.C.; Babendreier, D.; Ferrer Wurst, F.R.; Vásquez-Freytez, C.L.; Freitas Bueno, A. The use of Telenomus remus (Nixon, 1937) (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) in the management of Spodoptera spp. Potential, challenges and major benefits. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2022, 3, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Agboyi, L.K.; Layodé, B.F.R.; Fening, K.O.; Beseh, P.; Clottey, V.A.; Day, R.; Kenis, M.; Babendreier, D. Assessing the potential of inoculative field releases of Telenomus remus to control Spodoptera frugiperda in Ghana. Insects 2021, 12, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerster, L.A.; Doetzer, A.K.; Castro, L.C.F.D. Emergence, longevity and fecundity of Trissolcus basalis and Telenomus podisi after cold storage in the pupal stage. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2004, 39, 841–845. [Google Scholar]
- Bayram, A.; Ozcan, H.; Kornosor, S. Effect of cold storage on the performance of Telenomus busseolae Gahan (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae), an egg parasitoid of Sesamia nonagrioides (Lefebvre) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Biol. Control. 2005, 35, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Z.; Gao, F.; Liu, M.Y.; Wang, M.Z.; Han, Y.H.; Kong, L.; Chen, H.Y.; Liu, C.X.; Wang, M.Q.; Zhang, L.S. Research advances in diapause in small parasitic wasps in all the world in the last ten years. J. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 40, 82–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.S.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.Y. Maternal effect of diapause in Aphidius gifuensis Ashmead. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2014, 51, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Li YuYan, L.Y.; Zhang LiSheng, Z.L.; Chen HongYin, C.H.; Wang Wei, W.W.; Zhang Jie, Z.J. Temperature and photoperiodic response of diapause induction in Aphidius gifuensis. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2013, 50, 718–726. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Koštál, V.; Simek, P.; Moos, M.; Denlinger, D.L. Shifts in metabolomic profiles of the parasitoid Nasonia vitripennis associated with elevated cold tolerance induced by the parasitoid’s diapause, host diapause and host diet augme. Inset Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 63, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, A.; Goto, S.G. The clock gene period is essential for the photoperiodic response in the jewel wasp Nasonia vitripennis (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2016, 51, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legault, S.; Hébert, C.; Blais, J.; Berthiaume, R.; Bauce, E.; Brodeur, J. Seasonal ecology and thermal constraints of Telenomus spp. (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae), egg parasitoids of the Hemlock Looper (Lepidoptera: Geometridae). Environ. Entomol. 2012, 41, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, W. Progress in research on diapause of chalcidoids. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2013, 50, 1706–1718. [Google Scholar]
- An, T.; Zhang, H.; Han, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L. Transcriptome Analysis of Diapause-associated Genes of Aphidius gifuensis Ashmaed. Chin. J. Biol. Control. 2017, 33, 604–611. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, J.; Huang, J. Using transcriptome sequencing to analyze the diapause-related genes of female adults of whitefly predatory lady beetle Delphastus catalinae. J. Plant Prot. 2023, 50, 468–478. [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denlinger, D.L. Regulation of diapause. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2002, 47, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Fu, S.; Xue, F.S. Characters of Insect Diapause Stage and Photoperiod Sensitive Stage. Biol. Disaster Sci. 2013, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Poelchau, M.F.; Reynolds, J.A.; Denlinger, D.L.; Elsik, C.G.; Armbruster, P.A. A de novo transcriptome of the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus, to identify candidate transcripts for diapause preparation. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Desneux, N.; Lei, C.; Niu, C. Transcriptome characterization analysis of Bactrocera minax and new insights into its pupal diapause development with gene expression analysis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Congiu, L.; Lindström, L.; Piiroinen, S.; Vidotto, M.; Grapputo, A. Sequencing, de novo assembly and annotation of the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata, transcriptome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86012. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H.; Zhu, H.; Yu, P.; Luo, G.; Zhang, R.; Yue, Q.; Fang, J. Time-Series Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Molecular Profiles of Diapause Termination Induced by Long Photoperiods and High Temperature in Chilo suppressalis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, D.S.; Lewis, R.D.; Warman, G.R. Photoperiodic induction of diapause Opening the black box. Physiol. Entomol. 2004, 29, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, H.; Pan, Y.; Lyu, M.; Yang, Z.; Kou, X.; Deng, X.W.; Zhong, S. Sensory circuitry controls cytosolic calcium-mediated phytochrome B phototransduction. Cell 2023, 186, 1230–1243.e14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quail, P.H.; Boylan, M.T.; Parks, B.M.; Short, T.W.; Xu, Y.; Wagner, D. Phytochromes Photosensory perception and signal transduction. Science 1995, 268, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montell, C. Drosophila visual transduction. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 356–363. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, K.Y.; Lü, F.G.; Guo, W.C.; Li, G.Q. Characterization and functional study of a putative juvenile hormone diol kinase in the Colorado potato beetle Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 90, 154–167. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, Y.X.; Xu, W.H. Integrated proteomic and metabolomic analysis of larval brain associated with diapause induction and preparation in the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, K.; Sun, Y.; Beckingham, K.; Zuker, C.S. CAM regulation of Drosophila light-activated channels and receptor function mediates termination of the light response in vivo. Cell 1997, 91, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alloway, P.G.; Dolph, P.J. A role for the light-dependent phosphorylation of visual arrestin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6072–6077. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stavenga, D.G.; Hardie, R.C. Metarhodopsin control by arrestin, light-filtering screening pigments, and visual pigment turnover in invertebrate microvillar photoreceptors. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2011, 197, 227–241. [Google Scholar]
- Hardie, R.; Raghu, P. Visual transduction in Drosophila. Nature 2001, 413, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Hanson, S.M.; Francis, D.J.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Thibonnier, M.; Klug, C.S.; Shoham, M.; Gurevich, V.V. Arrestin Binding to CAM: A Direct Interaction Between Two Ubiquitous Signaling Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 364, 955–963. [Google Scholar]

| Primer | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| RPL12 | GAGGTGTGTTGGTGGAGAA | TAAGAGAGGCAGCAGAAGG |
| RPS2 | GGGGAAACAAAATCGGTAA | CGGTGTGAGGTAGGCATAA |
| CBP1 | ACGATTATGGAGGGTAAAGGA | ATGTCGATCAGCCTGAAATG |
| CBP2 | GGAATGGGCTGCTTGTCTATC | CTTTCGTCGTTGGTTTCTGGT |
| CBP3 | ATCAGTCAAGCCATCAAAGAAA | GAACGCTAGAAACTCGTCCAA |
| CBP4 | CGCTAGTAACGAGCAGGAGA | CAGTTGTGAGAACGGACGAA |
| ARR1 | CGCAGCGTGAGAACCTTGGC | CGTTTGAATAGCATTGGACCTTGT |
| ARR2 | CACAAACATGACCAGGAAGC | CCAAGAAAGGTTGACGGAAG |
| ARR3 | AACAACAGCACCAAGACCATC | TAACGAGTTTCACCCTGACATA |
| ARR4 | ATATCCACCAGGCAACTCGG | GGCATTACCAACGCCATCAA |
| ARR5 | AGACCCTTTAGCCAATACTCCA | TCGGCATTACCAATACCATCA |
| ARR6 | GGCTTTAAGGAGCTGGAGAT | CTTGGTGCTTTGAGTTGTGC |
| Length Range | Transcript | Unigene |
|---|---|---|
| 300–500 bp | 6226 (21.64%) | 4074 (25.09%) |
| 500–1000 bp | 5176 (17.99%) | 3876 (23.88%) |
| 1000–2000 bp | 5265 (18.30%) | 3209 (19.77%) |
| >2000 bp | 12,102 (42.07%) | 5073 (31.25%) |
| Total Number | 28,769 | 16,232 |
| Total Length | 72,003,323 | 31,186,643 |
| N50 Length | 4596 | 3540 |
| Mean Length | 2503 | 1921 |
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Unigen Number |
|---|---|---|
| Ribosome | ko03010 | 273 |
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | ko04141 | 178 |
| Oxidative phosphorylation | ko00190 | 177 |
| Endocytosis | ko04144 | 153 |
| PI3K–Akt signaling pathway | ko04151 | 150 |
| Lysosome | ko04142 | 149 |
| Spliceosome | ko03040 | 144 |
| cAMP signaling pathway | ko04024 | 135 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | ko04010 | 120 |
| Nucleocytoplasmic transport | ko03013 | 115 |
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | ko04120 | 115 |
| Pancreatic secretion | ko04972 | 114 |
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | ko04723 | 113 |
| mTOR signaling pathway | ko04150 | 111 |
| AMPK signaling pathway | ko04152 | 111 |
| Insulin signaling pathway | ko04910 | 111 |
| Focal adhesion | ko04510 | 105 |
| MAPK signaling pathway-fly | ko04013 | 103 |
| Wnt signaling pathway | ko04310 | 101 |
| Purine metabolism | ko00230 | 100 |
| Unigene Reference | ORF | Gene Name | BLAST Best Hi (Accession Number; Name; Species) | E Value | Identity | Full Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster-4246.4268 | 588 | TremCBP1 | sarcoplasmic calcium-binding protein 1 isoform X2 [Cephus cinctus] | 2 × 10−119 | 81.87% | Yes |
| Cluster-4246.6862 | 1761 | TremCBP2 | SPARC-related modular calcium-binding protein 2 [Dufourea novaeangliae] | 0 | 65.93% | Yes |
| Cluster-4246.8699 | 1128 | TremCBP3 | 45 kDa calcium-binding protein [Pogonomyrmex barbatus] | 3 × 10−148 | 63.11% | Yes |
| Cluster-4246.458 | 1044 | TremCBP4 | probable calcium-binding protein CML11 isoform X1 [Frieseomelitta varia] | 3 × 10−98 | 86.29% | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, G.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, Q.; Lai, X.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Yan, H.; Xie, X.; et al. Molecular Insights into Diapause Mechanisms in Telenomus remus for Improved Biological Control. Insects 2025, 16, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040393
Yu G, Sheng L, Zhang Z, Zou Q, Lai X, Tang Y, Li Y, Liu J, Yan H, Xie X, et al. Molecular Insights into Diapause Mechanisms in Telenomus remus for Improved Biological Control. Insects. 2025; 16(4):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040393
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Guojie, Longyu Sheng, Zhongyue Zhang, Qi Zou, Xinxin Lai, Yan Tang, Yuyao Li, Jia Liu, Hao Yan, Xianglin Xie, and et al. 2025. "Molecular Insights into Diapause Mechanisms in Telenomus remus for Improved Biological Control" Insects 16, no. 4: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040393
APA StyleYu, G., Sheng, L., Zhang, Z., Zou, Q., Lai, X., Tang, Y., Li, Y., Liu, J., Yan, H., Xie, X., Hu, F., & Wang, Z. (2025). Molecular Insights into Diapause Mechanisms in Telenomus remus for Improved Biological Control. Insects, 16(4), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040393









