Assessing the Influence of Stimulatory Feeding of Bee Colonies on Mineral Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Bee Venom
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples of Bee Venom
2.2. Determination of Humidity
2.3. Determination of Dry Matter
2.4. Determination of pH
2.5. Determination of Impurities
- I—represents the quantity of impurities (%);
- m1—represents the mass of the sample taken for analysis (g);
- m2—represents the mass of residue left on the filter paper after drying (g).
2.6. Determination of Ash
- Cash = total ash content
- m—the mass of the crucible with ash after the calcination process, in grams;
- m1—the mass of the empty crucible, in grams;
- m2—the mass of the crucible with the bee products, before the calcination process, in grams.
2.7. Determination of Total Amino Acids
2.8. Mineral Content
2.8.1. Determination of Total Metal Content
2.8.2. Determination of Total Phosphorus Content
2.9. Determination of the Antioxidant Capacity
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of Bee Venom
3.1.1. Moisture, Dry Matter, Ash, Impurities, and pH
3.1.2. Total Amino Acid Content
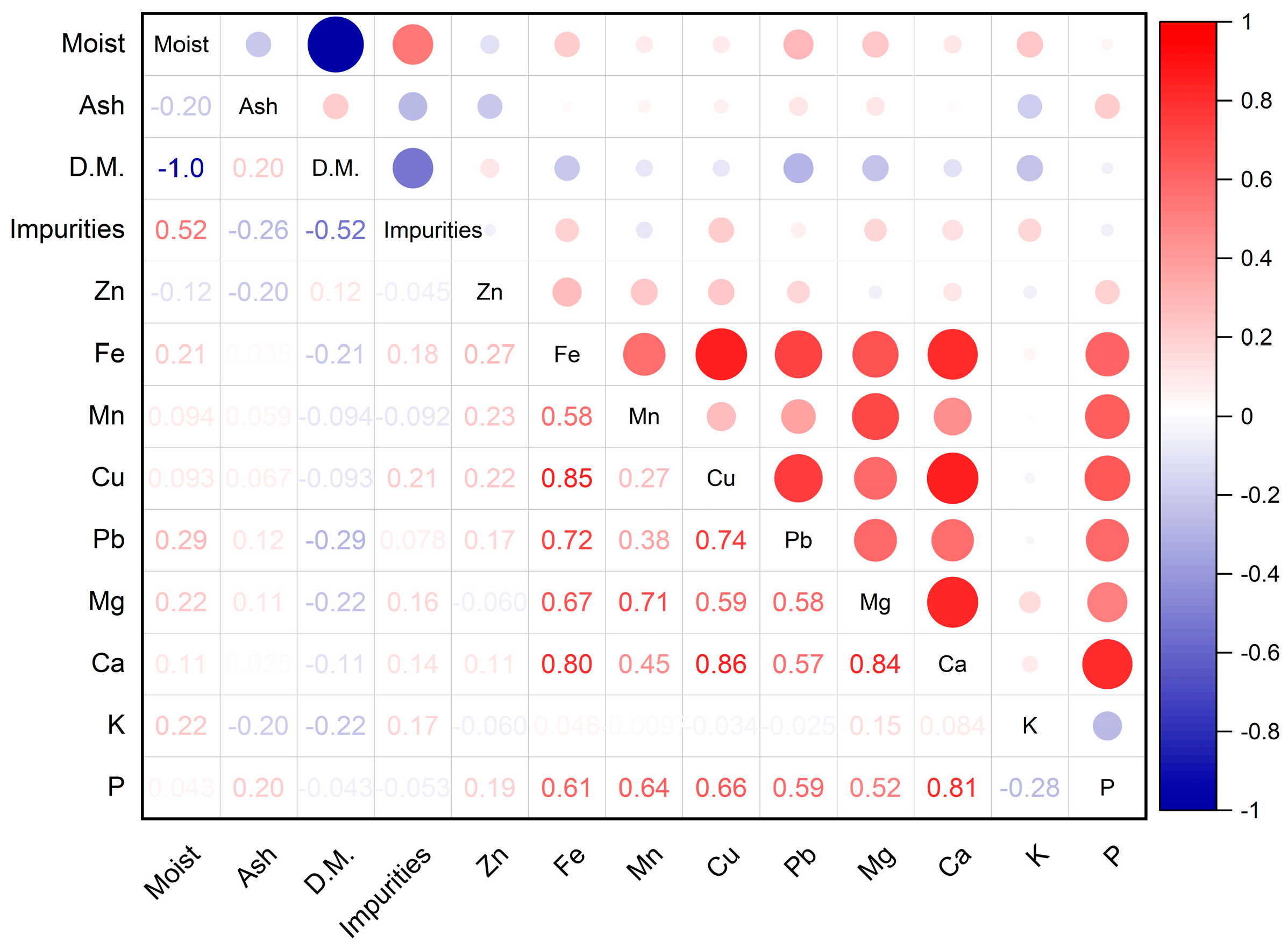
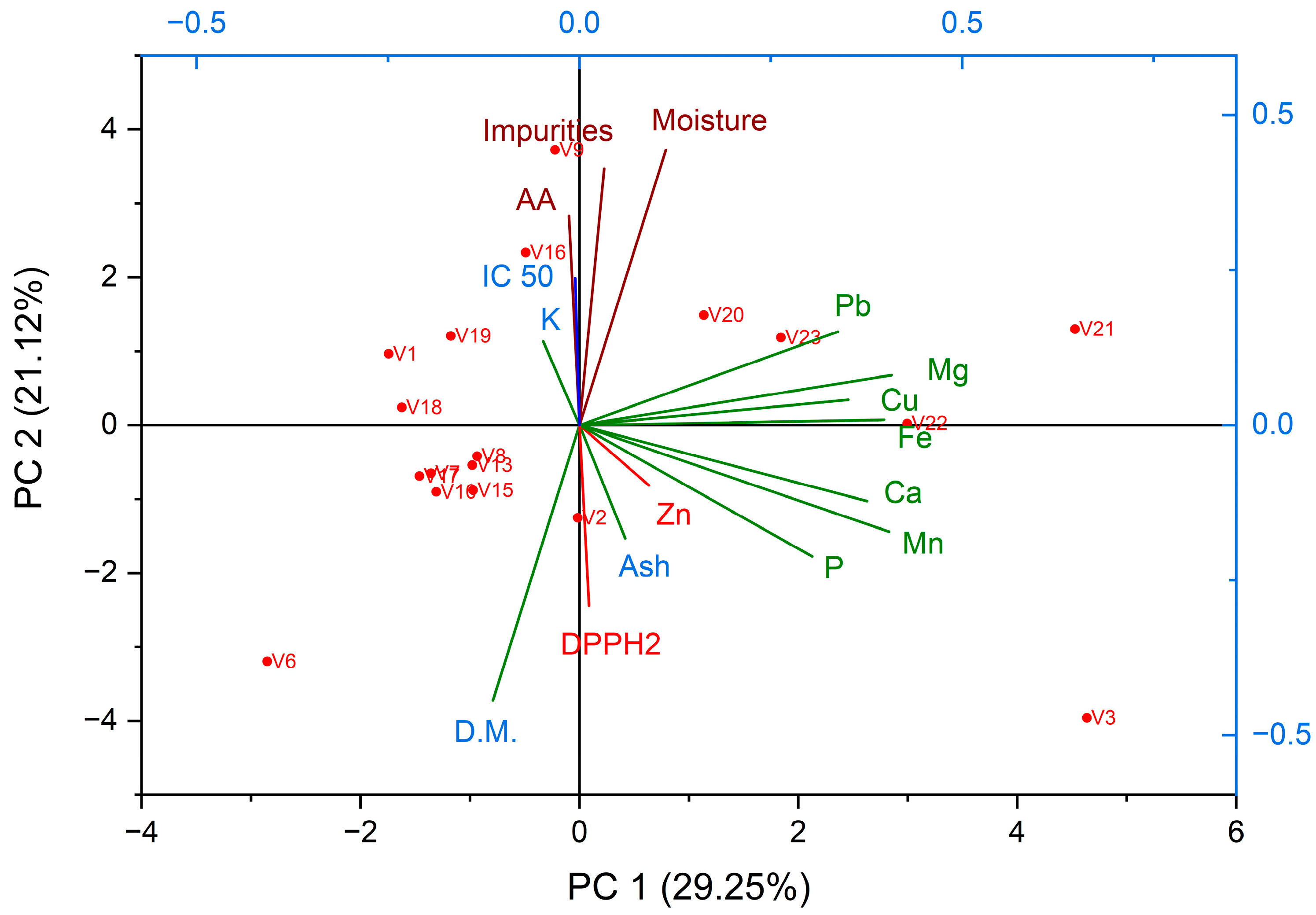
3.1.3. Mineral Content
3.2. Antioxidant Activity by DPPH Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, M. Studies on Bee Venom and Its Medical Uses. Int. J. Adv. Res. Technol. 2012, 1, 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Fratellone, P.M.; Tsimis, F.; Fratellone, G. Apitherapy Products for Medicinal Use. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2016, 22, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isidorov, V.; Zalewski, A.; Zambrowski, G.; Swiecicka, I. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Properties of Honey Bee Venom. Molecules 2023, 28, 4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellner, M.; Winter, D.; von Georgi, R.; Münstedt, K. Apitherapy: Usage and experience in german beekeepers. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2008, 5, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Monge-Fuentes, V.; Gomes, F.; Lopes, K.; dos Anjos, L.; Campos, G.; Arenas, C.; Biolchi, A.; Gonçalves, J.; Galante, P.; et al. Pharmacological Alternatives for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders: Wasp and Bee Venoms and Their Components as New Neuroactive Tools. Toxins 2015, 7, 3179–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.N.K.; Ahmed, M.N.; Biswas, S.; Ara, N.; Rahman, D.M.M.; Hirashima, A.; Hasan, D.M.N. A Review on Bioactivities of Honey Bee Venom. Curr. Res. Trends Biol. Sci. 2019, 30, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanuğur-Samanc, A.E.; Kekeçoğlu, M. An evaluation of the chemical content and microbiological contamination of Anatolian bee venom. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Aldakheel, F.M.; Anjum, S.I.; Raza, G.; Khan, S.A.; Tlak Gajger, I. Pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential of honey bee venom. Saudi Pharm. J. 2023, 31, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.M.; El-Ssayad, M.F.; Yousef, S.Y.A.; Salem, S.H. Bee venom: A potential natural alternative to conventional preservatives for prolonging the shelf-life of soft cheese ‘Talaga’. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehbe, R.; Frangieh, J.; Rima, M.; El Obeid, D.; Sabatier, J.M.; Fajloun, Z. Bee Venom: Overview of Main Compounds and Bioactivities for Therapeutic Interests. Molecules 2019, 24, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Iqbal Qazi, J.; Tabssum, F.; Hussain, A. Increased bee venom production in Apis mellifera workers on the provision of probiotics and organic acids. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 48, 102616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, K.M.; Shib, N.A.; Taher, E.S.; Rashed, F.; Shukry, M.; Atia, G.A.; Taymour, N.; El-Nablaway, M.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Ramadan, M.M.; et al. Harnessing the power of bee venom for therapeutic and regenerative medical applications: An updated review. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1412245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.G.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Yoon, H.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Wan, H.; Li, J.; Jin, B.R. Honeybee (Apis cerana) vitellogenin acts as an antimicrobial and antioxidant agent in the body and venom. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 85, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hanoun, A.; El-Komy, A.; El-Sabrout, K.; Abdella, M. Effect of bee venom on reproductive performance and immune response of male rabbits. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 223, 112987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocyigit, A.; Guler, E.M.; Kaleli, S. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidative properties of honey bee venom on Freund’s Complete Adjuvant-induced arthritis model in rats. Toxicon 2019, 161, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, W.A.; Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Ismail, S.A.A. Involvement of the anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and anti-secretory activity of bee venom in its therapeutic effects on acetylsalicylic acid-induced gastric ulceration in rats. Toxicology 2019, 419, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacoub, C.; Wehbe, R.; Roufayel, R.; Fajloun, Z.; Coutard, B. Bee Venom and Its Two Main Components-Melittin and Phospholipase A2-As Promising Antiviral Drug Candidates. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainu, F.; Masyita, A.; Bahar, M.A.; Raihan, M.; Prova, S.R.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B.; Simal-Gandara, J. Pharmaceutical Prospects of Bee Products: Special Focus on Anticancer, Antibacterial, Antiviral, and Antiparasitic Properties. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mehdi, I.; Falcão, S.I.; Boujraf, S.; Mustapha, H.; Campos, M.G.; Vilas-Boas, M. Analytical methods for honeybee venom characterization. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2022, 13, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazdunski, M.; Fosset, M.; Hughes, M.; Mourre, C.; Romey, G.; Schmid-Antomarchi, H. The apamin-sensitive Ca2+-dependent K+ channel molecular properties, differentiation and endogenous ligands in mammalian brain. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 1985, 50, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, T.M.; Maylie, J.; Adelman, J.P. Determinants of apamin and d-tubocurarine block in SK potassium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 23195–23200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moga, M.A.; Dimienescu, O.G.; Arvătescu, C.A.; Ifteni, P.; Pleş, L. Anticancer Activity of Toxins from Bee and Snake Venom—An Overview on Ovarian Cancer. Molecules 2018, 23, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, N.W.; Rosenstein, R.K.; Yu, S.; Schenten, D.D.; Florsheim, E.; Medzhitov, R. Bee venom phospholipase A2 induces a primary type 2 response that is dependent on the receptor ST2 and confers protective immunity. Immunity 2013, 39, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haktanir, I.; Masoura, M.; Mantzouridou, F.T.; Gkatzionis, K. Mechanism of antimicrobial activity of honeybee (Apis mellifera) venom on Gram-negative bacteria: Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas spp. AMB Express 2021, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawi, J.K. Bee Venom Components as Therapeutic Tools against Prostate Cancer. Toxins 2021, 13, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elswaby, S.; Sadik, M.; Azouz, A.; Emam, N.; Ali, M. In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of honeybee venom and propolis collected from various regions in Egypt. Egypt. Pharm. J. 2022, 21, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Monsef, M.M.; Darwish, D.A.; Zidan, H.A.; Hamed, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.A. Characterization, antimicrobial and antitumor activity of superoxide dismutase extracted from Egyptian honeybee venom (Apis mellifera lamarckii). J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2023, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques Pereira, A.F.; Albano, M.; Bérgamo Alves, F.C.; Murbach Teles Andrade, B.F.; Furlanetto, A.; Mores Rall, V.L.; Delazari Dos Santos, L.; de Oliveira Orsi, R.; Fernandes Júnior, A. Influence of apitoxin and melittin from Apis mellifera bee on Staphylococcus aureus strains. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 141, 104011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choinska, M.; Hrdlička, V.; Šestáková, I.; Navrátil, T. Voltammetric determination of heavy metals in honey bee venom using hanging mercury drop electrode and PLA/carbon conductive filament for 3D printer. Monatshefte Chem. Chem. Mon. 2021, 152, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pătruică, S.; Mot, D. The effect of using prebiotic and probiotic products on intestinal micro-flora of the honeybee (Apis mellifera carpatica). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2012, 102, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazăr, R.N.; Alexa, E.; Obiștioiu, D.; Cocan, I.; Pătruică, S. The Effect of the Use of Essential Oils in the Feed of Bee Families on Honey Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rășinar, A.-D.; Grozea, A.; Boldea, M.; Polen, T.; Pătruică, S. Use Supplementary Feedings on Bee Colony Development and Venom Production. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 57, 251. [Google Scholar]
- Zidan, H.; Mostafa, Z.; Ibrahim, M.; Haggag, S.; Darwish, D.; Elfiky, A. Venom Composition of Egyptian and Carniolan Honeybee, Apis mellifera L. Affected by Collection Methods. Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. A Entomol. 2018, 11, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.E.; El-Ansari, M.K.; Zahra, A.A. Effect of the Honeybee Hybrid and Geographic Region on the Honey Bee Venom Production. J. Plant Prot. Pathol. 2019, 10, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, M.D.; Pfaff, L.A.; Reisman, R.E.; Wypych, J. Phospholipase A2 in venom extracts from honey bees (Apis mellifera L.) of different ages. Toxicon 1990, 28, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowar, E. Venom Glands Parameters, Venom Production and Composition of Honeybee Apis mellifera L. Affected by Substitute Feeding. Middle East. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 5, 596–603. [Google Scholar]
- Zaharia, R.; Trotuș, E.; Trașcă, G.; Georgescu, E.; Șapcaliu, A.; Fătu, V.; Petrișor, C.; Mincea, C. Impact of Seed Treatment with Imidacloprid, Clothianidin and Thiamethoxam on Soil, Plants, Bees and Hive Products. Agriculture 2023, 13, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, M.D.; Sloley, B.D. 5-Hydroxytryptamine in the venom of the honey bee (Apis mellifera L.): Variation with season and with insect age. Toxicon 1988, 26, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-I.; Roh, J.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, H.-S.; Ahn, Y.-J. Insecticidal activities of aromatic plant extracts and essential oils against Sitophilus oryzae and Callosobruchus chinensis. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2003, 39, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabuseenivasan, S.; Jayakumar, M.; Ignacimuthu, S. In vitro antibacterial activity of some plant essential oils. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2006, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyldgaard, M.; Mygind, T.; Meyer, R.L. Essential oils in food preservation: Mode of action, synergies, and interactions with food matrix components. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imtara, H.; Elamine, Y.; Lyoussi, B. Honey Antibacterial Effect Boosting Using Origanum vulgare L. Essential Oil. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 7842583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazăr, R.N.; Moţ, D.; Simiz, E.; Pătruică, S. Research on the use of essential oils on the health of bee families. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 54, 161. [Google Scholar]
- Martin Ewert, A.; Simone-Finstrom, M.; Read, Q.; Husseneder, C.; Ricigliano, V. Effects of ingested essential oils and propolis extracts on honey bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae) health and gut microbiota. J. Insect Sci. 2023, 23, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, D.; Guzman-Novoa, E.; Goodwin, P.H. Effects of Prebiotics and Probiotics on Honey Bees (Apis mellifera) Infected with the Microsporidian Parasite Nosema ceranae. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pătruică, S.; Dumitrescu, G.; Popescu, R.; Filimon, N.M. The effect of prebiotic and probiotic products used in feed to stimulate the bee colony (Apis mellifera) on intestines of working bees. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2013, 11, 2461–2464. [Google Scholar]
- Corcionivoschi, N.; Drinceanu, D.; Pop, I.; Stack, D.; Stef, L.; Julean, C.; Bourke, B. The Effect of Probiotics on Animal Health. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 43, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Gergen, I. Agri-Food Products Analysis; EUROSTAMP Publishing House: Timisoara, Romania, 2004; p. 316. ISBN 973-687-271-8. [Google Scholar]
- Moraru, D.; Alexa, E.; Cocan, I.; Obiștioiu, D.; Radulov, I.; Simiz, E.; Berbecea, A.; Grozea, A.; Dragomirescu, M.; Vintilă, T.; et al. Chemical Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Apilarnil, Royal Jelly, and Propolis Collected in Banat Region, Romania. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekecoglu, M.; Çaprazli, T.; Samanci, T.; Elif, A.; Tanuğur Samancı, A.; Yorulmaz Önder, E. Determination and Comparison of Apitherapeutic Value of Turkish and Chinese Bee Venom Through Chemical Content Analysis. In Proceedings Book of 5th International Eurasian Congress on Natural Nutrition, Healthy Life & Sport, Ankara, Turkey, 2–6 October 2019; Malatya Turgut Ozal University: Battalgazi, Turkey, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, A.; Bhalotia, S.; Kumar, N.R.; Kaur, J. Honey BEE Venom and ITS Composition: Focusing on Different Apis Species—A Review. J. Basic. Appl. Eng. Res. 2016, 3, 2350–2377. [Google Scholar]
- Szabat, P.; Poleszak, J.; Szabat, M.; Boreński, G.; Wójcik, M.; Milanowska, J. Apitherapy—The medical use of bee products. J. Educ. Health Sport 2019, 9, 384–396. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, A.; Elesawy, B.H.; Ali, T.M.; Ahmed, O.M. Bee Venom: From Venom to Drug. Molecules 2021, 26, 4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Mehdi, I.; Falcão, S.I.; Harandou, M.; Boujraf, S.; Calhelha, R.C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Anjos, O.; Campos, M.G.; Vilas-Boas, M. Chemical, Cytotoxic, and Anti-Inflammatory Assessment of Honey Bee Venom from Apis mellifera intermissa. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soekarno, S.; Hernanto, S.; Purbasari, D.; Melani, D. Study of Distillation Method and Time on the Quality of Basil (Ocimum sanctum L.) Essential Oil. J. Tek. Pertan. Lampung J. Agric. Eng. 2024, 13, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zduńczyk, W.; Tkacz, K.; Modzelewska-Kapituła, M. The Effect of Superficial Oregano Essential Oil Application on the Quality of Modified Atmosphere-Packed Pork Loin. Foods 2023, 12, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klupczynska, A.; Plewa, S.; Dereziński, P.; Garrett, T.J.; Rubio, V.Y.; Kokot, Z.J.; Matysiak, J. Identification and quantification of honeybee venom constituents by multiplatform metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabo, R.; Staroň, M.; Sabová, L.; Jančo, I.; Tomka, M.; Árvay, J. Toxic and essential elements in honeybee venom from Slovakia: Potential health risk to humans. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaccabarozzi, D.; Dods, K.; Le, T.T.; Gummer, J.P.A.; Lussu, M.; Milne, L.; Campbell, T.; Wafujian, B.P.; Priddis, C. Factors driving the compositional diversity of Apis mellifera bee venom from a Corymbia calophylla (marri) ecosystem, Southwestern Australia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gîlcescu Florescu, C.A.; Stanciulescu, E.C.; Berbecaru-Iovan, A.; Balasoiu, R.M.; Pisoschi, C.G. In vitro Assessment of Free Radical Scavenging Effect and Thermal Protein Denaturation Inhibition of Bee Venom for an Anti-Inflammatory Use. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2024, 50, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinello, M.; Mutinelli, F. Antioxidant Activity in Bee Products: A Review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobiș, O.; Bonta, V.; Varadi, A.; Strant, M.; Dezmirean, D. Bee Products and Oxidative Stress: Bioavailability of Their Functional Constituents. Mod. Appl. Bioequiv. Availab. 2017, 1, 555565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Venom Sample | Harvest Period | Food Source | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | April | Sugar syrup 1 L | V1 |
| 2 | April | Sugar syrup 1 L + basil essential oil 30 µL | V2 |
| 3 | April | Sugar syrup 1 L + thyme essential oil 30 µL | V3 |
| 4 | April | Sugar syrup 1 L + oregano essential oil 30 µL | V4 |
| 5 | April | Sugar syrup 1 L + Lacium 1 capsule | V5 |
| 6 | April | Sugar syrup 1 L + Colobiotic 1 capsule | V6 |
| 7 | April | Sugar syrup 1 L + Enterolactis Plus 1 capsule | V7 |
| 8 | April | Sugar syrup 1 L + Lacium 1 capsule + oregano essential oil 30 µL | V8 |
| 9 | May | Rapeseed nectar and pollen | V9 |
| 10 | May | Rapeseed nectar and pollen | V10 |
| 11 | May | Rapeseed nectar and pollen | V11 |
| 12 | May | Rapeseed nectar and pollen | V12 |
| 13 | May | Rapeseed nectar and pollen | V13 |
| 14 | May | Rapeseed nectar and pollen | V14 |
| 15 | May | Rapeseed nectar and pollen | V15 |
| 16 | May | Rapeseed nectar and pollen | V16 |
| 17 | June | Acacia nectar and pollen | V17 |
| 18 | June | Acacia nectar and pollen | V18 |
| 19 | June | Acacia nectar and pollen | V19 |
| 20 | June | Acacia nectar and pollen | V20 |
| 21 | June | Acacia nectar and pollen | V21 |
| 22 | June | Acacia nectar and pollen | V22 |
| 23 | June | Acacia nectar and pollen | V23 |
| 24 | June | Acacia nectar and pollen | V24 |
| Metal | λ (nm) | Lamp Current (mA) | Slit Width (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | 232 | 4 | 0.2 |
| Cr | 357.9 | 7 | 0.2 |
| Cu | 324.8 | 4 | 0.5 |
| Cd | 228.8 | 4 | 0.5 |
| Mn | 279.5 | 5 | 0.2 |
| Zn | 213 | 5 | 1 |
| Fe | 248.3 | 5 | 0.2 |
| Ca | 422.7 | 10 | 0.5 |
| Mg | 285.2 | 4 | 0.5 |
| Pb | 283.3 | 10 | 1.2 |
| K | 414 nm | 4 | 0.5 |
| Venom Sample Harvest I | ||||||||||
| V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | V6 | V7 | V8 | p | ||
| Humidity (%) | 18.00 ± 2.00 a,A,B | 13.00 ± 2.65 a,A | 15.00 ± 1.73 a,A | 17.00 ± 1.73 a,A | 14.00 ± 2.00 a,A | 13.00 ± 2.65 a,A,B | 14.00 ± 2.00 a,A,B | 15.00 ± 0.00 a,A | 0.065 | |
| DM (%) | 82.00 ± 2.00 a,A,B | 87.00 ± 2.65 a,A | 85.00 ± 1.73 a,A | 83.00 ± 1.73 a,A,B | 86.00 ± 2.00 a,A | 87.00 ± 2.65 a,A,B | 86.00 ± 2.00 a,A | 85.00 ± 0.00 a,A | 0.065 | |
| pH | 6.41 ± 0.02 a,A | 5.95 ± 0.04 b,l,A | 6.10 ± 0.05 c,f,A | 6.02 ± 0.05 b,c,f,g,h,A | 5.96 ± 0.04 b,g,h,A | 5.84 ± 0.05 g,i,k,l | 5.81 ± 0.04 d,i,j,A,B | 5.96 ± 0.06 e,h,k,l,A,B | 0.000 | |
| Impurities (%) | 13.33 ± 0.15 a,A | 10.00 ± 0.20 b,I,A | 6.67 ± 0.15 c,A | 10.00 ± 0.10 d,i,A | 10.00 ± 0.15 e,i,A | 6.67 ± 0.08 c,f,A | 9.96 ± 0.14 b,g,i,A | 10.00 ± 0.05 h,I,A | 0.000 | |
| Total amino acids (mg/g) | 398.20 ± 1.37 a,A | 368.17 ± 1.67 b,A | 335.95 ± 1.49 c,A | 346.33 ± 1.94 d,A | 351.24 ± 1.25 e,A | 362.16 ± 1.86 f,A | 359.98 ± 1.65 g,A | 350.15 ± 1.75 h,A | 0.000 | |
| Ash (%) | 5.70 ± 0.07 a,A | 3.00 ± 0.11 b,A | 4.50 ± 0.03 c,A | 4.00 ± 0.04 d,A | 4.80 ± 0.08 e,A | 6.70 ± 0.02 f,A | 5.80 ± 0.05 a,A | 4.10 ± 0.05 g,A | 0.000 | |
| Venom Sample Harvest II | ||||||||||
| V9 | V10 | V11 | V12 | V13 | V14 | V15 | V16 | |||
| Humidity (%) | 22.00 ± 2.00 a,A | 16.00 ± 3.00 a,c,A | 14.00 ± 0.00 b,c,A | 16.00 ± 4.00 a,c,A | 14.00 ± 1.73 b,c,A | 10.00 ± 3.61 b,c,A | 17.00 ± 1.00 a,c,A | 18.00 ± 1.73 a,c,B | 0.002 | |
| DM (%) | 78.00 ± 2.00 a,A | 84.00 ± 3.00 a,c,A | 86.00 ± 0.00 b,c,A | 84.00 ± 4.00 a,c,A | 86.00 ± 1.73 b,c,A | 90.00 ± 3.61 b,c,A | 83.00 ± 1.00 a,c,A,B | 82.00 ± 1.73 a,c,B | 0.002 | |
| pH | 6.11 ± 0.04 a,B | 5.94 ± 0.04 b,A | 6.11 ± 0.04 a,A | 5.90 ± 0.05 b,c,A | 5.71 ± 0.04 f,B | 5.54 ± 0.04 f,B | 5.85 ± 0.04 b,c,A | 5.93 ± 0.06 b,c,A | 0.000 | |
| Impurities (%) | 20.00 ± 0.15 A,B | 10.00 ± 0.08 b,i,A | 13.33 ± 0.08 c,B | 6.67 ± 0.10 d,i,B | 6.67 ± 0.09 e,i,B | 10.00 ± 0.13 c,f,B | 6.67 ± 0.08 b,g,i,B | 13.33 ± 0.11 h,i,B | 0.000 | |
| Total amino acids (mg/g) | 373.63 ± 1.91 a,B | 354.52 ± 1.86 b,i,B | 354.52 ± 1.86 c,i,B | 362.16 ± 2.10 d,B | 384.00 ± 2.13 e,B | 363.25 ± 1.75 f,B | 381.27 ± 1.75 g,B | 403.11 ± 1.25 h,B | 0.000 | |
| Ash (%) | 3.31 ± 0.04 a,B | 7.40 ± 0.05 b,B | 3.31 ± 0.08 a,B | 7.90 ± 0.05 c,B | 3.50 ± 0.04 d,B | 6.60 ± 0.04 e,B | 3.60 ± 0.04 d,f,B | 1.50 ± 0.05 g,B | 0.000 | |
| Venom Sample Harvest III | ||||||||||
| V17 | V18 | V19 | V20 | V21 | V22 | V23 | V24 | |||
| Humidity (%) | 15.00 ± 1.73 a,B | 16.00 ± 3.00 a,A | 17.00 ± 2.00 a,A | 17.00 ± 0.00 a,A | 18.00 ± 0.00 a,B | 17.00 ± 1.00 a,B | 18.00 ± 1.00 a,B | 17.00 ± 0.00 a,A,B | 0.308 | |
| DM (%) | 85.00 ± 1.73 a,B | 84.00 ± 3.00 a,A | 83.00 ± 2.00 a,A | 83.00 ± 0.00 a,B | 82.00 ± 0.00 a,B | 83.00 ± 1.00 a,B | 82.00 ± 1.00 a,B | 83.00 ± 0.000 a,A,B | 0.308 | |
| pH | 5.98 ± 0.06 a,C | 6.04 ± 0.04 a,B | 5.87 ± 0.05 b,c,B | 5.94 ± 0.06 a,c,A | 5.95 ± 0.05 a,c,A | 6.03 ± 0.04 a,C | 5.93 ± 0.05 a,c,B | 6.06 ± 0.04 a,B | 0.001 | |
| Impurities (%) | 7.00 ± 0.10 a,C | 6.67 ± 0.12 a,B | 13.33 ± 0.18 b,c,e,B | 13.33 ± 0.13 b,c,e,C | 13.33 ± 0.21 b,c,e,C | 10.00 ± 0.09 d,B | 6.67 ± 0.10 a,B | 13.33 ± 0.18 e,B | 0.000 | |
| Total amino acids (mg/g) | 407.48 ± 1.750 a,C | 396.56 ± 1.752 b,C | 397.65 ± 1.617 c,C | 394.92 ± 1.834 d,C | 396.02 ± 0,436 e,i,C | 396.02 ± 1.601 f,i,C | 400.93 ± 2.265 g,C | 403.66 ± 1.931 h,C | 0.000 | |
| Ash (%) | 2.00 ± 0.07 a,e,C | 2.30 ± 0.04 a,e,C | 2.40 ± 0.03 a,C | 1.91 ± 0.05 e,C | 5.30 ± 0.05 b,C | 6.20 ± 0.04 c,C | 6.04 ± 0.47 c,A | 4.60 ± 0.04 d,C | 0.000 | |
| p | Humidity | 0.012 | 0.398 | 0.125 | 0.857 | 0.028 | 0.047 | 0.031 | 0.027 | - |
| DM | 0.012 | 0.398 | 0.125 | 0.857 | 0.028 | 0.047 | 0.031 | 0.027 | - | |
| pH | 0.000 | 0.024 | 0.001 | 0.076 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.027 | 0.048 | - | |
| Impurities | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | |
| Total Aa | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | |
| Ash | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | |
| Venom Sample Harvest I | ||||||||||
| V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | V6 | V7 | V8 | p | ||
| Ca (mg/g) | 1.010 ± 0.090 a,A | 3.588 ± 0.190 b,A | 4.650 ± 0.150 c,A | 1.463 ± 0.120 d,A | 1.506 ± 0.110 e,A | 1.076 ± 0.100 f,A | 1.270 ± 0.270 g,A | 1.432 ± 0.230 h,A | 0.000 | |
| K (mg/g) | 8.362 ± 0.360 a,A | 10.275 ± 0.300 b,A | 3.659 ± 0.460 c,A | 2.427 ± 0.170 d,A | 3.588 ± 0.210 e,A | 3.576 ± 0.130 f,A | 5.17 ± 0.310 g,A | 4.828 ± 0.190 h,A | 0.000 | |
| Mg (mg/g) | 0.365 ± 0.023 a,A | 0.523 ± 0.016 b,A | 0.609 ± 0.022 c,A | 0.386 ± 0.014 d,A | 0.427 ± 0.017 e,A | 0.281 ± 0.019 f,A | 0.367 ± 0.026 g,A | 0.412 ± 0.012 h,A | 0.000 | |
| P (mg/g) | 0.994 ± 0.027 a,A | 0.235 ± 0.015 b,A | 0.524 ± 0.024 c,A | - | - | 1.105 ± 0.010 d,A | 0.524 ± 0.026 e,A | 0.354 ± 0.016 f,A | 0.000 | |
| Venom Sample Harvest II | ||||||||||
| V9 | V10 | V11 | V12 | V13 | V14 | V15 | V16 | |||
| Ca (mg/g) | 1.684 ± 0.037 a,B | 0.983 ± 0.058 b,B | 2.205 ± 0.095 c,B | 1.410 ± 0.075 d,B | 1.162 ± 0.102 e,B | 1.353 ± 0.026 f,B | 1.217 ± 0.097 g,B | 1.3817 ± 0.078 h,B | 0.000 | |
| K (mg/g) | 8.289 ± 0.239 a,B | 6.25 ± 0.162 b,B | 3.426 ± 0.116 c,B | 4.536 ± 0.176 d,B | 7.929 ± 0.171 e,B | 3.143 ± 0.143 f,B | 5.032 ± 0.278 g,B | 2.964 ± 0.146 h,B | 0.000 | |
| Mg (mg/g) | 0.477 ± 0.020 a,B | 0.346 ± 0.024 b,B | 0.482 ± 0.018 c,B | 0.477 ± 0.027 d,B | 0.431 ± 0.025 e,B | 0.402 ± 0.045 f,B | 0.343 ± 0.030 g,B | 0.416 ± 0.027 h,B | 0.000 | |
| P (mg/g) | 0.428 ± 0.028 a,B | 0.104 ± 0.015 b,B | - | - | 0.530 ± 0.065 c,B | - | 0.335 ± 0.039 d,B | 0.699 ± 0.022 e,B | 0.000 | |
| Venom Sample Harvest III | ||||||||||
| V17 | V18 | V19 | V20 | V21 | V22 | V23 | V24 | |||
| Ca (mg/g) | 0.900 ± 0.064 a,C | 1.166 ± 0.150 b,C | 1.087 ± 0.123 c,C | 2.676 ± 0.218 d,C | 2.185 ± 0.550 e,C | 3.747 ± 0.297 f,C | 3.231 ± 0.131 g,C | 0.992 ± 0.092 h,C | 0.000 | |
| K (mg/g) | 5.423 ± 0.295 a,C | 7.746 ± 0.314 b,C | 3.142 ± 0.142 c,C | 8.320 ± 0.270 d,C | 6.248 ± 0.248 e,C | 3.931 ± 0.431 f,C | 5.574 ± 0.224 g,C | - | 0.000 | |
| Mg (mg/g) | 0.287 ± 0.036 a,C | 0.292 ± 0.018 b,C | 0.316 ± 0.018 c,C | 0.593 ± 0.027 d,C | 0.604 ± 0.016 e,C | 0.574 ± 0.023 f,C | 0.634 ± 0.034 g,C | - | 0.000 | |
| P (mg/g) | 0.556 ± 0.046 a,C | 0.313 ± 0.023 b,C | 0.289 ± 0.033 c,C | 0.383 ± 0.024 d,C | 1.980 ± 0.280 e,C | 0.273 ± 0.033 f,C | 2.611 ± 0.111 g,C | 5.799 ± 0.239 h,C | 0.000 | |
| p | Ca | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - |
| K | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | |
| Mg | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | |
| P | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | |
| Venom Sample Harvest I | ||||||||||
| V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | V6 | V7 | V8 | p | ||
| Fe (mg/g) | 0.308 ± 0.016 a,A | 0.694 ± 0.038 b,h,A | 0.988 ± 0.078 c,A | 0.458 ± 0.038 d,A | 0.470 ± 0.038 e,i,A | 0.198 ± 0.006 a,A | 0.479 ± 0.048 f,i,A | 0.585 ± 0.046 g,h,i,A | 0.000 | |
| Mn (µg/g) | 36.84 ± 3.28 a,A | 10.14 ± 0.37 b,g,A | 29.651 ± 1.47 c,A | 6.00 ± 0.11 d,h,A | 5.50 ± 0.32 d,e,i,A | 4.40 ± 0.21 a,A | 6.08 ± 0.63 f,h,i,A | 9.72 ± 0.36 g,A | 0.000 | |
| Cu (µg/g) | 4.40 ± 0.18 a,A | 1.10 ± 0.10 b,c,A | 1.11 ± 0.22 c,e,A | 4.90 ± 0.22 d,A | 4.90 ± 0.34 b,e,A | 4.30 ± 0.51 a,A | 9.30 ± 0.53 f,A | 9.00 ± 0.48 f,g,A | 0.000 | |
| Zn (mg/g) | 1.561 ± 0.082 a,A | 0.751 ± 0.056 b,d,g,A | 1.958 ± 0.143 c,A | 0.894 ± 0.065 d,g,A | 1.613 ± 0.108 a,A | 0.707 ± 0.056 b,d,e,A | 1.992 ± 0.228 c,f,A | 1.041 ± 0.030 g,A | 0.000 | |
| Venom Sample Harvest II | ||||||||||
| V9 | V10 | V11 | V12 | V13 | V14 | V15 | V16 | |||
| Fe (mg/g) | 0.508 ± 0.041 a,f,B | 0.467 ± 0.050 a,f,B | 0.691 ± 0.036 b,d,B | 0.627 ± 0.036 c,d,e,B | 0.361 ± 0.028 f,B | 0.450 ± 0.033 a,f,B | 0.521 ± 0.071 a,e,A | 0.495 ± 0.026 a,A | 0.000 | |
| Mn (µg/g) | 9.20 ± 0.31 a,B | 6.90 ± 0.31 b,f,g,B | 9.70 ± 0.42 c,B | 8.60 ± 0.28 d,B | 5.00 ± 0.56 e,h,B | 6.60 ± 0.46 f,B | 7.10 ± 0.54 g,B | 5.10 ± 0.22 h,B | 0.000 | |
| Cu (µg/g) | 7.00 ± 0.47 a,B | 9.20 ± 0.84 b,f,B | 1.03 ± 0.14 c,e,B | 1.19 ± 0.32 d,B | 1.05 ± 0.16 e,B | 9.00 ± 0.83 f,g,B | 8.70 ± 0.40 g,B | 9.21 ± 0.29 b,f,h,A | 0.000 | |
| Zn (mg/g) | 0.897 ± 0.051 a,B | 1.114 ± 0.073 a,f,B | 1.356 ± 0.093 b,e,f,B | 1.010 ± 0.080 a,A | 1.371 ± 0.103 c,f,g,A | 1.365 ± 0.090 d,f,B | 1.586 ± 0.129 e,g,B | 1.064 ± 0.106 a,A | 0.000 | |
| Venom Sample Harvest III | ||||||||||
| V17 | V18 | V19 | V20 | V21 | V22 | V23 | V24 | |||
| Fe (mg/g) | 0.479 ± 0.026 a,B | 0.718 ± 0.062 b,e,A | 0.368 ± 0.033 a,C | 0.737 ± 0.057 b,B | 1.405 ± 0.044 c,C | 1.290 ± 0.046 c,C | 0.513 ± 0.033 a,e,A | 1.739 ± 0.119 d,B | 0.000 | |
| Mn (µg/g) | 7.70 ± 0.32 a,C | 7.50 ± 0.38 a,C | 4.00 ± 0.20 b,C | 10.50 ± 0.48 c,C | 18.30 ± 0.32 d,C | 11.70 ± 0.64 e,C | 12.70 ± 0.47 f,C | 10.20 ± 0.47 g,C | 0.000 | |
| Cu (µg/g) | 9.10 ± 0.22 a,C | 5.60 ± 0.40 b,C | 10.01 ± 0.32 c,B | 9.40 ± 0.61 d,C | 18.60 ± 0.67 e,C | 14.90 ± 0.94 f,C | 8.40 ± 0.41 g,C | 3.74 ± 0.27 h,B | 0.000 | |
| Zn (mg/g) | 1.899 ± 0.078 a,C | 1.480 ± 0.041 b,f,C | 1.483 ± 0.160 c,f,B | 1.701 ± 0.067 a,f,B | 1.469 ± 0.204 d,f,A | 1.540 ± 0.215 a,f,B | 0.656 ± 0.075 e,C | 1.549 ± 0.126 a,f,B | 0.000 | |
| p | Fe | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.618 | 0.000 | - |
| Mn | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | |
| Cu | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | |
| Zn | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.206 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 | - | |
| Venom Sample Harvest I | |||||||||
| V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | V6 | V7 | V8 | p | |
| Ni (µg/g) | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | - |
| Cd (µg/g) | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | - |
| Pb (µg/g) | 23.90 ± 1.10 a,A | 18.19 ± 0.91 b,f,A | 32.17 ± 0.92 c,A | 15.34 ± 0.43 d,A | 21.09 ± 0.64 e,A | 18.27 ± 0.72 f,A | 18.77 ± 0.77 g,A | 20.48 ± 0.51 h,A | 0.000 |
| Venom Sample Harvest II | |||||||||
| V9 | V10 | V11 | V12 | V13 | V14 | V15 | V16 | ||
| Ni (µg/g) | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | - |
| Cd (µg/g) | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | - |
| Pb (µg/g) | 20.21 ± 1.26 a,B | 24.36 ± 0.51 b,f,B | 28.72 ± 1.77 c,B | 44.75 ± 1.25 d,B | 35.12 ± 1.27 e,B | 24.45 ± 1.20 f,B | 27.16 ± 0.99 g,B | 33.94 ± 1.94 h,B | 0.000 |
| Venom Sample Harvest III | |||||||||
| V17 | V18 | V19 | V20 | V21 | V22 | V23 | V24 | ||
| Ni (µg/g) | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | - |
| Cd (µg/g) | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | Undetectable | - |
| Pb (µg/g) | 25.80 ± 1.20 a,B | 23.50 ± 1.11 b,B | 32.48 ± 1.63 c,B | 36.24 ± 1.04 d,B | 53.22 ± 1.11 e,B | 38.43 ± 1.23 f,B | 38.83 ± 1.73 g,B | 56.05 ± 0.75 h,B | 0.000 |
| p | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - |
| Concentration (mg/mL) | Venom Sample Harvest I | Ascorbic Acid | ||||||||
| V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 (% Inhibition) | V5 | V6 | V7 | V8 | Concentration (mg/mL) | (% Inhibition) | |
| 2.00 | 73.91 ± 2.11 b | 67.14 ± 2.06 c,d | 82.62 ± 1.57 a | 69.24 ± 4.45 b,c | 79.40 ± 6.23 a | 87.05 ± 1.07 a | 43.31 ± 1.31 i | 50.07 ± 1.82 g,h | 0.10 | 91.75 |
| 1.25 | 49.89 ± 0.9 e–g | 45.84 ± 1.23 h,i | 56.39 ± 1.39 b,c | 43.52 ± 1.65 i,j | 54.58 ± 1.11 c,d | 59.36 ± 1.48 b,c | 36.59 ± 1.34 m,n | 40.08 ± 1.67 k,l | 0.08 | 71.59 |
| 1.00 | 41.47 ± 0.88 a–f | 31.75 ± 1.07 d–g | 42.75 ± 1.59 a–e | 34.13 ± 1.78 c–g | 41.95 ± 0.71 a–f | 46.65 ± 1.37 a–c | 24.14 ± 1.69 g | 28.05 ± 1.36 f,g | 0.06 | 56.02 |
| 0.625 | 25.78 ± 15.57 a–c | 23.55 ± 0.68 bc | 19.09 ± 1.08 | 23.94 ± 1.62 bc | 28.24 ± 1.11 bc | 28.51 ± 1.27 bc | 18.56 ± 0.76 bc | 18.75 ± 1.10 c | 0.04 | 44.94 |
| 0.313 | 13.97 ± 1.13 b–e | 11.61 ± 0.73 f–i | 14.62 ± 0.93 a–c | 11.94 ± 1.07 e–h | 13.89 ± 1.14 b–e | 14.43 ± 0.69 b–d | 6.74 ± 0.62 m | 8.93 ± 0.72 k–m | 0.02 | 27.02 |
| Venom Sample Harvest II | ||||||||||
| V9 | V10 | V11 | V12 | V13 | V14 | V15 | V16 | |||
| 2.00 | 60.15 ± 1.04 e | 71.46 ± 1.21 b,c | 59.89 ± 0.65 e,f | 70.39 ± 0.64 b,c | 62.04 ± 0.72 d,e | 66.98 ± 1.87 c,d | 86.53 ± 1.06 a | 53.88 ± 0.93 f,g | 0.10 | 91.75 |
| 1.25 | 47.67 ± 0.78 g,h | 48.18 ± 0.82 f–h | 38.42 ± 0.96 l,m | 45.93 ± 0.95 hi | 39.03 ± 0.80 l,m | 43.34 ± 0.78 i,j | 67.90 ± 0.94 a | 34.15 ± 0.91 n | 0.08 | 71.59 |
| 1.00 | 37.08 ± 0.95 b–g | 44.14 ± 0.95 a–d | 28.77 ± 0.84 e–g | 36.74 ± 0.87 b–g | 31.30 ± 0.51 d–g | 34.32 ± 0.65 c–g | 55.36 ± 1.13 a | 27.91 ± 0.67 a–c | 0.06 | 56.02 |
| 0.625 | 20.57 ± 10.12 c | 26.11 ± 9.89 a–c | 17.84 ± 5.84 a,b | 22.58 ± 7.45 b,c | 19.91 ± 6.89 a–c | 18.83 ± 9.32 b,c | 34.81 ± 11.25 a–c | 17.57 ± 5.63 a | 0.04 | 44.94 |
| 0.313 | 10.75 ± 0.43 g–k | 14.28 ± 0.32 b–d | 8.39 ± 0.61 l–m | 9.39 ± 0.44 i–l | 9.19 ± 0.70 j–l | 9.20 ± 0.59 i–l | 16.85 ± 0.54 a–c | 9.58 ± 0.58 i–l | 0.02 | 27.02 |
| Venom Sample Harvest III | ||||||||||
| V17 | V18 | V19 | V20 | V21 | V22 | V23 | V24 | |||
| 2.00 | 74.47 ± 1.51 b | 59.78 ± 0.54 e,f | 66.34 ± 0.94 c,d | 61.52 ± 0.58 d,e | 66.84 ± 1.16 c,d | 71.90 ± 0.55 d,e | 47.52 ± 0.67 g–i | 74.97 ± 0.39 b | 0.10 | 91.75 |
| 1.25 | 49.61 ± 0.39 e–g | 41.51 ± 0.48 j–l | 39.82 ± 0.30 k,l | 42.63 ± 0.72 j–l | 42.42 ± 0.56 j–l | 50.91 ± 0.41 e–g | 30.15 ± 0.85 o | 52.66 ± 0.43 d,e | 0.08 | 71.59 |
| 1.00 | 40.03 ± 0.73 b–f | 32.43 ± 0.58 d–g | 31.21 ± 0.77 d–g | 36.71 ± 20.89 d–g | 34.17 ± 5.26 b–f | 41.65 ± 0.43 a–f | 23.63 ± 0.37 g | 41.09 ± 0.48 b–f | 0.06 | 56.02 |
| 0.625 | 26.16 ± 1.29 b,c | 19.50 ± 1.50 b,c | 20.66 ± 0.34 b,c | 19.72 ± 0.82 b,c | 24.00 ± 0.86 b,c | 25.86 ± 0.44 b,c | 16.37 ± 0.63 c | 28.68 ± 0.68 b,c | 0.04 | 44.94 |
| 0.313 | 12.84 ± 0.72 c–g | 12.46 ± 0.53 c–g | 8.93 ± 0.28 k–m | 12.24 ± 0.74 d–h | 11.21 ± 0.79 g–j | 13.59 ± 0.81 b–f | 10.13 ± 0.24 h–l | 15.29 ± 0.97 a,b | 0.02 | 27.02 |
| Venom Sample Harvest I | |||||||||
| V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | V6 | V7 | V8 | Ascorbic Acid | |
| IC50 SD (mg/mL) | 3.62 ± 0.0755 | 4.05 ± 0.1323 | 3.30 ± 0.0300 | 4.00 ± 0.1100 | 3.41 ± 0.1015 | 3.16 ± 0.0819 | 5.65 ± 0.1323 | 5.01 ± 0.0854 | 2.47 ± 0.0458 |
| R2 | 0.9759 | 0.9693 | 0.9782 | 0.9537 | 0.9812 | 0.9814 | 0.9878 | 0.9983 | 0.9916 |
| Hill Slope | 14.399 | 13.335 | 16.330 | 13.418 | 15.736 | 17.609 | 9.117 | 10.361 | 15.610 |
| Venom Sample Harvest II | |||||||||
| V9 | V10 | V11 | V12 | V13 | V14 | V15 | V16 | ||
| IC50 SD (mg/mL) | 4.17 ± 0.0656 | 3.68 ± 0.0557 | 4.56 ± 0.0656 | 3.89 ± 0.0600 | 4.42 ± 0.0721 | 4.10 ± 0.0917 | 2.87 ± 0.0721 | 5.03 ± 0.1572 | 2.47 ± 0.0458 |
| R2 | 0.9948 | 0.9675 | 0.9675 | 0.9758 | 0.9627 | 0.9719 | 0.9956 | 0.9588 | 0.9916 |
| Hill Slope | 12.590 | 13.605 | 12.358 | 14.535 | 12.482 | 14.007 | 17.245 | 10.518 | 15.610 |
| Venom Sample Harvest III | |||||||||
| V17 | V18 | V19 | V20 | V21 | V22 | V23 | V24 | ||
| IC50 SD (mg/mL) | 3.64 ± 0.0656 | 4.45 ± 0.1323 | 4.24 ± 0.0656 | 4.27 ± 0.0656 | 4.10 ± 0.1000 | 3.65 ± 0.1000 | 5.76 ± 0.1015 | 3.52 ± 0.0819 | 2.47 ± 0.0458 |
| R2 | 0.9749 | 0.9762 | 0.9487 | 0.9739 | 0.9589 | 0.9869 | 0.9454 | 0.9827 | 0.9916 |
| Hill Slope | 14.671 | 11.665 | 13.398 | 12.147 | 12.968 | 14.167 | 8.856 | 14.334 | 15.610 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rășinar, A.D.; Radulov, I.; Berbecea, A.; Floares, D.; Vicar, N.; Simiz, E.; Dragomirescu, M.; Pătruică, S. Assessing the Influence of Stimulatory Feeding of Bee Colonies on Mineral Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Bee Venom. Insects 2025, 16, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040423
Rășinar AD, Radulov I, Berbecea A, Floares D, Vicar N, Simiz E, Dragomirescu M, Pătruică S. Assessing the Influence of Stimulatory Feeding of Bee Colonies on Mineral Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Bee Venom. Insects. 2025; 16(4):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040423
Chicago/Turabian StyleRășinar, Adrian Dan, Isidora Radulov, Adina Berbecea, Doris Floares (Oarga), Nicoleta Vicar, Eliza Simiz, Monica Dragomirescu, and Silvia Pătruică. 2025. "Assessing the Influence of Stimulatory Feeding of Bee Colonies on Mineral Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Bee Venom" Insects 16, no. 4: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040423
APA StyleRășinar, A. D., Radulov, I., Berbecea, A., Floares, D., Vicar, N., Simiz, E., Dragomirescu, M., & Pătruică, S. (2025). Assessing the Influence of Stimulatory Feeding of Bee Colonies on Mineral Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Bee Venom. Insects, 16(4), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040423








