Centrifugation-Based Purification Protocol Optimization Enhances Structural Preservation of Nucleopolyhedrovirus Budded Virion Envelopes
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
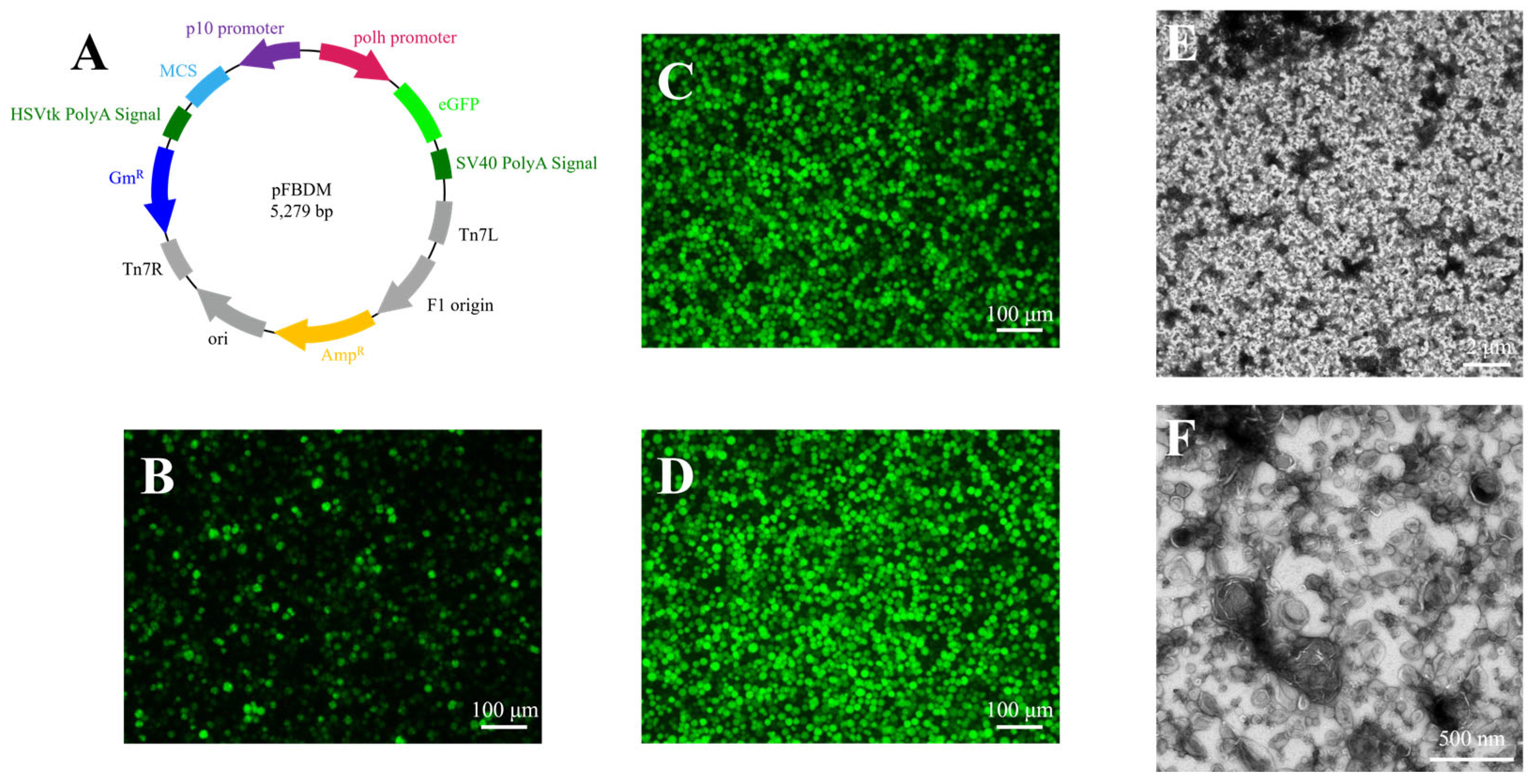
2.2. Construction, Passage, and Amplification of Recombinant Baculovirus
2.3. Differential Centrifugation
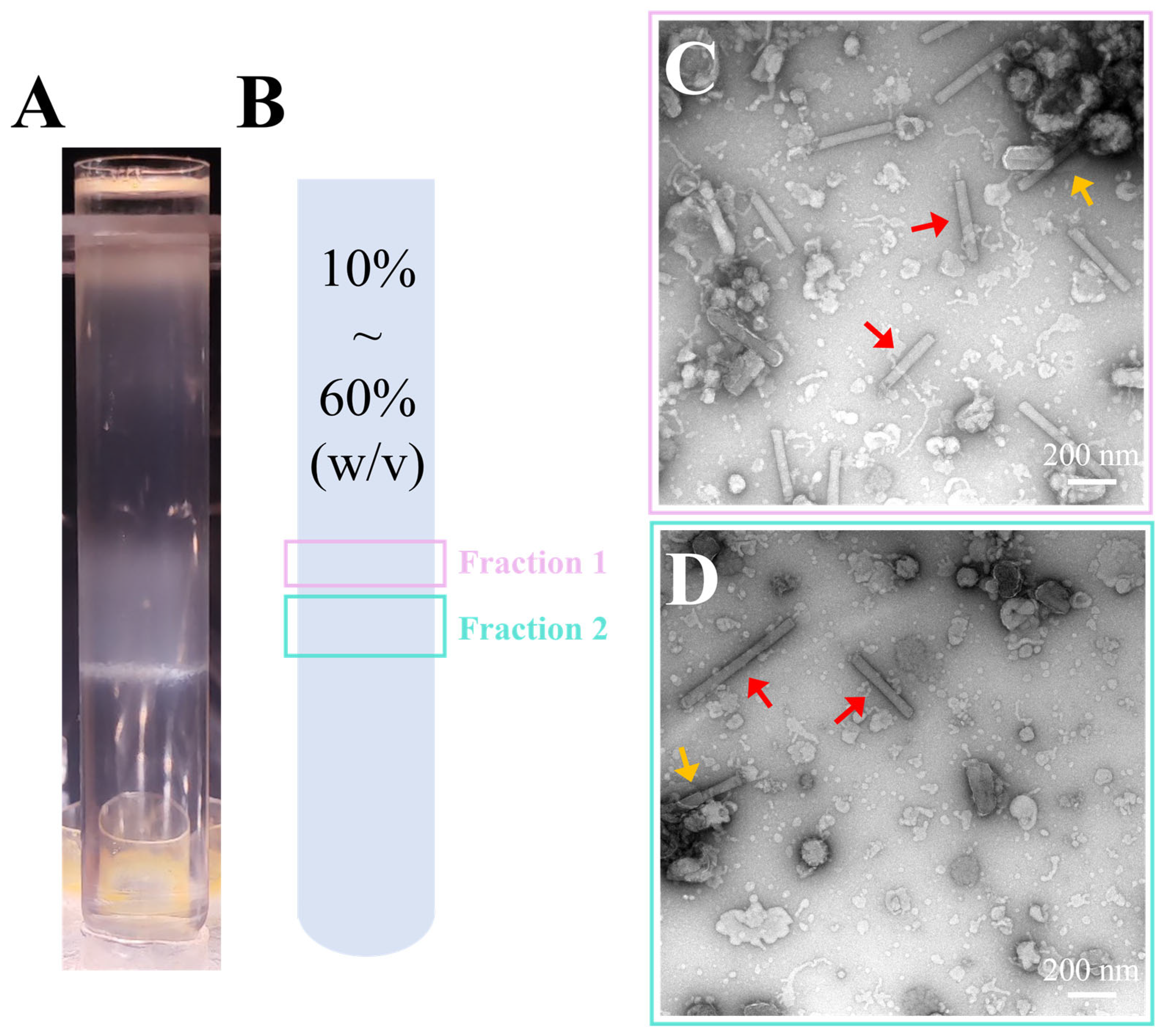
2.4. Sucrose Density Gradient Centrifugation
2.5. Negative-Staining Sample Preparation
2.6. Cryo-Electron Microscopy Sample Preparation and Examination
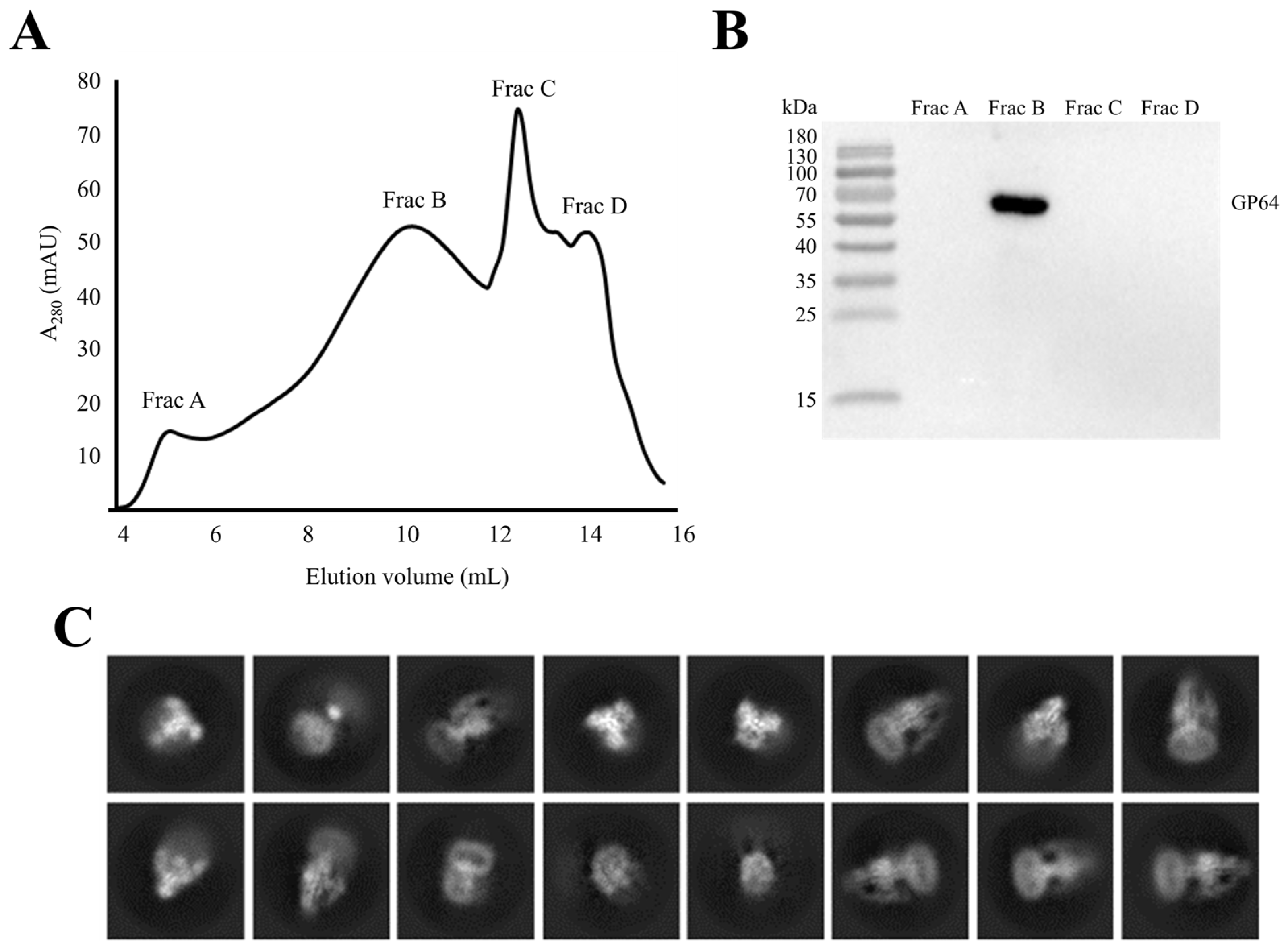
2.7. GP64 Protein Purification
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Cryo-EM Data Collection and Processing
3. Results
3.1. Generation of Recombinant AcMNPV
3.2. Purification of Recombinant AcMNPV via Discontinuous Sucrose Gradient Centrifugation
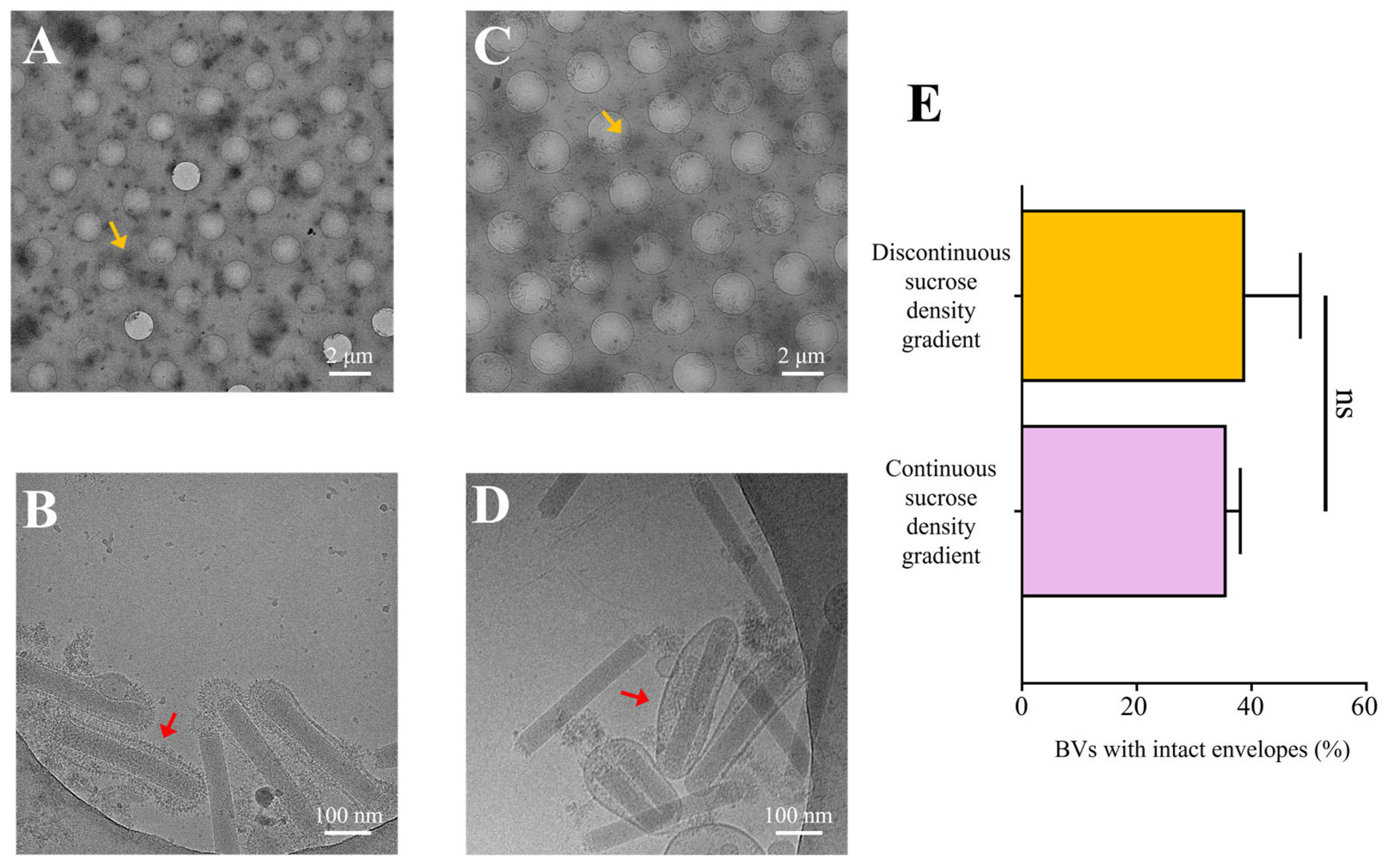
3.3. Purification of Recombinant AcMNPV via Continuous Sucrose Gradient Centrifugation
3.4. Optimized Purification Methodology for AcMNPV
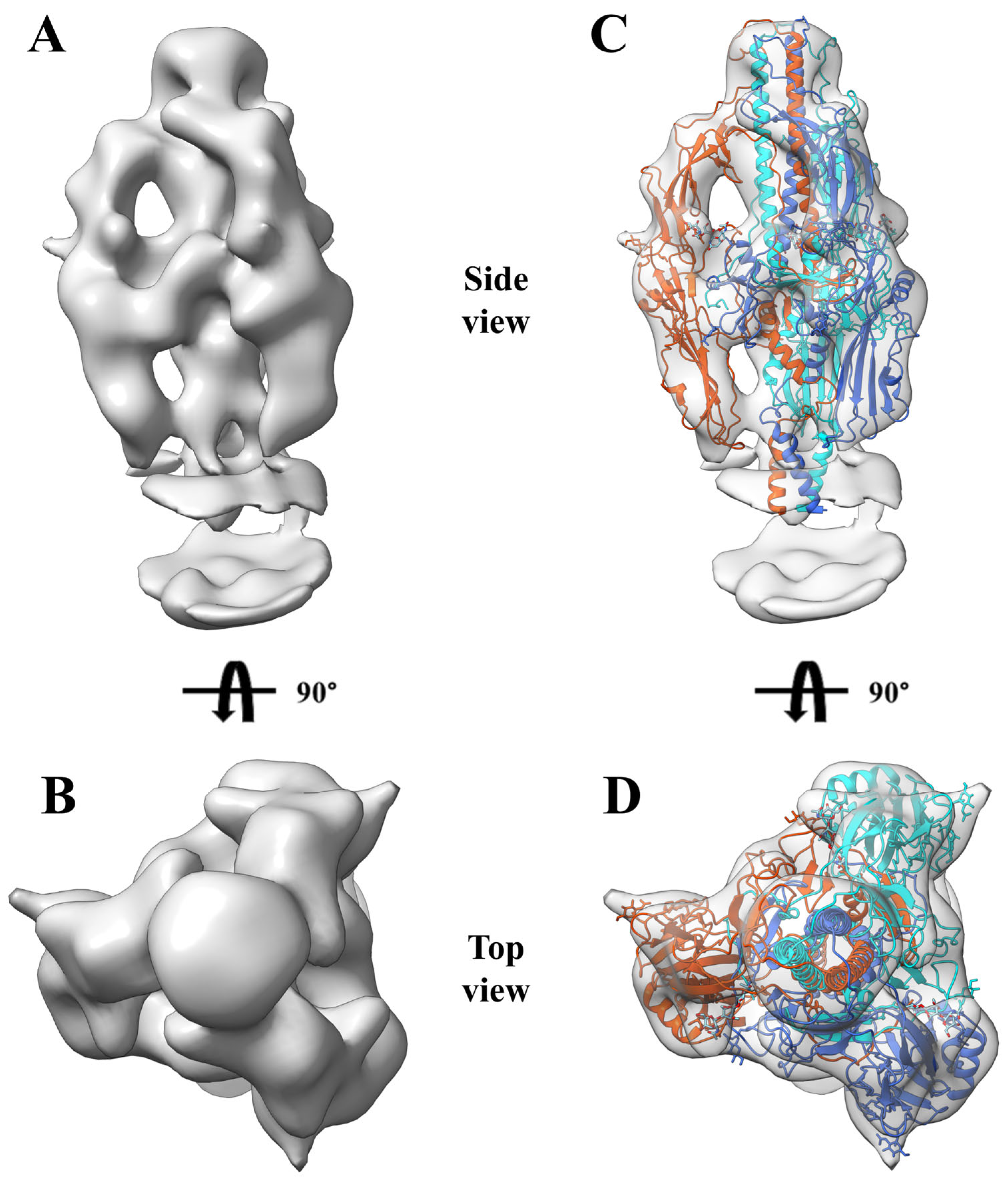
3.5. Near-Native State of Metastable Prefusion GP64
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AcMNPV | Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus |
| Cryo-EM | Cryo-electron microscopy |
| NPV | Nucleopolyhedrovirus |
| BEVS | Baculovirus expression vector system |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| Sf9 | Spodoptera frugiperda 9 cells |
| eGFP | Enhanced green fluorescent protein |
| rAcMNPV | Recombinant Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| W/V | Weight/Volume |
| W/W | Weight/Weight |
| polh | Polyhedrin promoter |
| DDM | Dodecyl maltoside |
| CHS | Cholesteryl hemi-succinate |
| SEC | Size-exclusion chromatography |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
References
- Knipe, D.M.; Howley, P.M. Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Wolters Kluwer Health—Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4511-0563-6. [Google Scholar]
- Shulla, A.; Randall, G. (+) RNA Virus Replication Compartments: A Safe Home for (Most) Viral Replication. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 32, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grove, J.; Marsh, M. The Cell Biology of Receptor-Mediated Virus Entry. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 195, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateu, M.G. Assembly, Stability and Dynamics of Virus Capsids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 531, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.E.; Le Sage, V.; Lakdawala, S.S. Viral and Host Heterogeneity and Their Effects on the Viral Life Cycle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernomordik, L.V.; Zimmerberg, J.; Kozlov, M.M. Membranes of the World Unite! J. Cell Biol. 2006, 175, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kephart, S.M.; Hom, N.; Lee, K.K. Visualizing Intermediate Stages of Viral Membrane Fusion by Cryo-Electron Tomography. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2024, 49, 916–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.C. Viral Membrane Fusion. Virology 2015, 479–480, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.M.; Ward, A.E.; Odongo, L.; Tamm, L.K. Viral Membrane Fusion: A Dance Between Proteins and Lipids. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2023, 10, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernomordik, L.V.; Kozlov, M.M. Protein-Lipid Interplay in Fusion and Fission of Biological Membranes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 175–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaney, M.-C.; Rey, F.A. Class II Enveloped Viruses: Enveloped Virions with Symmetric Coats. Cell. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backovic, M.; Jardetzky, T.S. Class III Viral Membrane Fusion Proteins. In Cell Fusion in Health and Disease; Dittmar, T., Zänker, K.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 950, pp. 91–101. ISBN 978-94-007-0781-8. [Google Scholar]
- Mas, V.; Melero, J.A. Entry of Enveloped Viruses into Host Cells: Membrane Fusion. In Structure and Physics of Viruses; Mateu, M.G., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 105, pp. 567–592. ISBN 978-3-031-65186-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lozada, C.; Barlow, T.M.A.; Gonzalez, S.; Lubin-Germain, N.; Ballet, S. Identification and Characteristics of Fusion Peptides Derived From Enveloped Viruses. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 689006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielian, M.; Rey, F.A. Virus Membrane-Fusion Proteins: More than One Way to Make a Hairpin. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-H.; Gessler, D.J.; Zhan, W.; Gallagher, T.L.; Gao, G. Adeno-Associated Virus as a Delivery Vector for Gene Therapy of Human Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, W.J.; Laranjeira, B.J.; Pereira, S.A.R.; Florencio, C.M.G.D.; Moreno, E.C.; Miller, M.A.; Giglio, R.; Schuck-Paim, C.; Moura, F.E.A. Comparative Dynamics, Morbidity and Mortality Burden of Pediatric Viral Respiratory Infections in an Equatorial City. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2012, 31, e9–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Samulski, R.J. Engineering Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors for Gene Therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Lui, G.C.Y.; Wong, K.T.; Li, T.C.M.; Tse, E.C.M.; Chan, J.Y.C.; Yu, J.; Wong, S.S.M.; Choi, K.W.; Wong, R.Y.K.; et al. High Morbidity and Mortality in Adults Hospitalized for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Liu, H.-J. Baculovirus as a Vaccine Vector. Bioengineered 2012, 3, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Hong, M.; Cui, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhu, R.; et al. Baculovirus Display of Varicella–Zoster Virus Glycoprotein E Induces Robust Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses in Mice. Viruses 2022, 14, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulcha, J.T.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H.; Tai, P.W.L.; Gao, G. Viral Vector Platforms within the Gene Therapy Landscape. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundstrom, K. Viral Vectors in Gene Therapy: Where Do We Stand in 2023? Viruses 2023, 15, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-X.; Cross, T.A. Influences of Membrane Mimetic Environments on Membrane Protein Structures. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2013, 42, 361–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, S.J.; Johnson, R.M.; Wootten, D.; Sexton, P.M. Membranes under the Magnetic Lens: A Dive into the Diverse World of Membrane Protein Structures Using Cryo-EM. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 13989–14017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, B.; Pražák, V.; Vasishtan, D.; Jefferys, E.E.; Hernandez-Duran, A.; Vallbracht, M.; Klupp, B.G.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Backovic, M.; Rey, F.A.; et al. The Prefusion Structure of Herpes Simplex Virus Glycoprotein B. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Zhang, W.; Krummenacher, C.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zeng, M.-S.; Xia, N.; Zeng, Y.-X.; Xu, M.; et al. Targeting Herpesvirus Entry Complex and Fusogen Glycoproteins with Prophylactic and Therapeutic Agents. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 788–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfian, P.; Levy, M.S.; Coffin, R.S.; Fearn, T.; Ayazi-Shamlou, P. Impact of Process Conditions on the Centrifugal Recovery of a Disabled Herpes Simplex Virus. Biotechnol. Prog. 2003, 19, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, J.; Schäckermann, D.; Kirmann, T.; Bertoglio, F.; Steinke, S.; Heisig, J.; Ruschig, M.; Rojas, G.; Langreder, N.; Wenzel, E.V.; et al. Baculovirus-Free Insect Cell Expression System for High Yield Antibody and Antigen Production. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blissard, G.W.; Theilmann, D.A. Baculovirus Entry and Egress from Insect Cells. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2018, 5, 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, J.; Loureiro, S.; Abrescia, N.G.A.; Stuart, D.I.; Jones, I.M. The Postfusion Structure of Baculovirus Gp64 Supports a Unified View of Viral Fusion Machines. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, S.; Bai, L.; Zhao, H.; Shang, W.; Zhong, Z.; Maimaiti, T.; Gao, X.; Ji, N.; Chao, Y.; et al. Structural Transition of GP64 Triggered by a pH-Sensitive Multi-Histidine Switch. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, G.-Y.; Hu, Y.-C. Baculovirus as a Gene Delivery Vector: Recent Understandings of Molecular Alterations in Transduced Cells and Latest Applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, M.; Berger, P. Baculovirus for Gene Delivery to Mammalian Cells: Past, Present and Future. Plasmid 2018, 98, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamura, T.; Aizaki, H.; Tani, H.; Shoji, I.; Matsuura, Y.; Ishii, K.; Chiba, T.; Saito, I. Efficient Gene Transfer into Various Mammalian Cells, Including Non-Hepatic Cells, by Baculovirus Vectors. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 2657–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kost, T. Recombinant Baculoviruses as Expression Vectors for Insect and Mammalian Cells. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1999, 10, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Lu, C.-H.; Luo, W.-Y.; Chang, Y.-H.; Sung, L.-Y.; Chiu, H.-Y.; Hu, Y.-C. Baculovirus as a Gene Delivery Vector for Cartilage and Bone Tissue Engineering. CGT 2010, 10, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasimuzzaman, M.; Van Der Loo, J.C.M.; Malik, P. Production and Purification of Baculovirus for Gene Therapy Application. JoVE 2018, 131, 57019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasimuzzaman, M.; Lynn, D.; Van Der Loo, J.C.; Malik, P. Purification of Baculovirus Vectors Using Heparin Affinity Chromatography. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2016, 3, 16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airenne, K.J.; Hiltunen, M.O.; Turunen, M.P.; Turunen, A.-M.; Laitinen, O.H.; Kulomaa, M.S.; Ylä-Herttuala, S. Baculovirus-Mediated Periadventitial Gene Transfer to Rabbit Carotid Artery. Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucoin, M.G.; Mena, J.A.; Kamen, A.A. Bioprocessing of Baculovirus Vectors: A Review. CGT 2010, 10, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwang, T.W.; Zeng, X.; Wang, S. Manufacturing of AcMNPV Baculovirus Vectors to Enable Gene Therapy Trials. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2016, 3, 15050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Heim, K.P.; Che, Y.; Chi, X.; Qiu, X.; Han, S.; Dormitzer, P.R.; Yang, X. Prefusion Structure of Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein B and Structural Basis for Membrane Fusion. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, F.; Zhen, J.; Xie, G.; Huang, H.; Silva, J.C.; Wu, T.-T.; Zhou, Z.H. Structure of the Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus gB in Post-Fusion Conformation. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e0153324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.L.; Xing, Y.; Chen, D.-H.; Roh, S.H.; Pintilie, G.D.; Bushnell, D.A.; Sommer, M.H.; Yang, E.; Carfi, A.; Chiu, W.; et al. A Glycoprotein B-Neutralizing Antibody Structure at 2.8 Å Uncovers a Critical Domain for Herpesvirus Fusion Initiation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Wang, M.; Chen, L. A Co-Expression Vector for Baculovirus-Mediated Protein Expression in Mammalian Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 594, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastronarde, D.N. Automated Electron Microscope Tomography Using Robust Prediction of Specimen Movements. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 152, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cookson, B.T.; Brennan, M.A. Pro-Inflammatory Programmed Cell Death. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 113–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punjani, A.; Rubinstein, J.L.; Fleet, D.J.; Brubaker, M.A. cryoSPARC: Algorithms for Rapid Unsupervised Cryo-EM Structure Determination. Nat. Methods. 2017, 14, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, T.; Grigorieff, N. Measuring the Optimal Exposure for Single Particle Cryo-EM Using a 2.6 Å Reconstruction of Rotavirus VP6. eLife 2015, 4, e06980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.; Mou, Z.; Liu, W.; Dubyak, G.; Dai, X. How NINJ1 Mediates Plasma Membrane Rupture and Why NINJ2 Cannot. Cell 2025, 188, 292–302.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Bosch, B.-J.; Vlak, J.M.; Van Oers, M.M.; Rottier, P.J.; Van Lent, J.W.M. Budded Baculovirus Particle Structure Revisited. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 134, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, C.R.; Caul, E.O. Potassium Tartrate-Glycerol as a Density Gradient Substrate for Separation of Small, Round Viruses from Human Feces. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1982, 16, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Steed, A.L. Advances in Understanding the Envelope Protein in Coronavirus Infection. J. Immunological. Sci. 2024, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, S. Structural and Functional Properties of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein: Potential Antivirus Drug Development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsma, S.A.; Oomens, A.G.; Blissard, G.W. The GP64 Envelope Fusion Protein Is an Essential Baculovirus Protein Required for Cell-to-Cell Transmission of Infection. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 4607–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podbilewicz, B. Virus and Cell Fusion Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 111–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Flynn, A.D. Drugging Membrane Protein Interactions. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 18, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchdoerfer, R.N.; Cottrell, C.A.; Wang, N.; Pallesen, J.; Yassine, H.M.; Turner, H.L.; Corbett, K.S.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S.; Ward, A.B. Pre-Fusion Structure of a Human Coronavirus Spike Protein. Nature 2016, 531, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Liang, Z.; Sun, J. Centrifugation-Based Purification Protocol Optimization Enhances Structural Preservation of Nucleopolyhedrovirus Budded Virion Envelopes. Insects 2025, 16, 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040424
Pan Y, Yan J, Zhang Y, Lin J, Liang Z, Sun J. Centrifugation-Based Purification Protocol Optimization Enhances Structural Preservation of Nucleopolyhedrovirus Budded Virion Envelopes. Insects. 2025; 16(4):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040424
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Yong, Jiming Yan, Yinong Zhang, Jiasheng Lin, Zhiquan Liang, and Jingchen Sun. 2025. "Centrifugation-Based Purification Protocol Optimization Enhances Structural Preservation of Nucleopolyhedrovirus Budded Virion Envelopes" Insects 16, no. 4: 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040424
APA StylePan, Y., Yan, J., Zhang, Y., Lin, J., Liang, Z., & Sun, J. (2025). Centrifugation-Based Purification Protocol Optimization Enhances Structural Preservation of Nucleopolyhedrovirus Budded Virion Envelopes. Insects, 16(4), 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040424




