Abstract
Larvae of the tobacco budworm are major polyphagous pests throughout the Americas. Development of effective microbial biopesticides for this and related noctuid pests has been stymied by the natural resistance mediated innate immune response. Hemocytes play an early and central role in activating and coordinating immune responses to entomopathogens. To approach this problem we completed RNA-seq expression profiling of hemocytes collected from larvae following an in vivo challenge with bacterial and fungal cell wall components to elicit an immune response. A de novo exome assembly was constructed by combination of sequence tags from all treatments. Sequence tags from each treatment were aligned separately with the assembly to measure expression. The resulting table of differential expression had >22,000 assemblies each with a distinct combination of annotation and expression. Within these assemblies >1,400 were upregulated and >1,500 downregulated by immune activation with bacteria or fungi. Orthologs to innate immune components of other insects were identified including pattern recognition, signal transduction pathways, antimicrobial peptides and enzymes, melanization and coagulation. Additionally orthologs of components regulating hemocytic functions such as autophagy, apoptosis, phagocytosis and nodulation were identified. Associated cellular oxidative defenses and detoxification responses were identified providing a comprehensive snapshot of the early response to elicitation.
1. Introduction
Larvae of noctuid moths are major polyphagous pests of commodity crops such as maize, cotton, soybeans, alfalfa and vegetables throughout the world [1]. In North America and in Brazil larvae of the tobacco budworm, Heliothis virescens (F.) are major pests of agricultural production, feeding on cotton, maize, and soybean, as well as fruits, vegetables and ornamentals [2,3]. Control of H. virescens and other closely related heliothines would be advanced by understanding, and disrupting, the basic mechanisms underlying resistance to biological control agents such as entomopathogens and parasitoids, and identification of gene silencing targets for field applications [4,5,6]. However the molecular resources allowing fundamental laboratory and field research with the budworm to date are insufficient for this end [7,8,9].
Insects command an exquisitely evolved and powerful innate, i.e., germ-line encoded, immune response to microbial invasion which is divided between cellular and noncellular defenses [10]. Noncellular responses primarily involve the secretion of antimicrobial peptides, enzymes and other compounds into the hemocoel from immune-responsive tissues, while cellular responses are performed by several classes of hemocytes circulating within the hemocoel [11,12]. In order to effectively limit infection by microbes the innate immune system must first recognize microbial invasion, then accurately gauge the threat level presented by scattered microbial fragments, dead/nonviable, live but nonpathogenic, or live and pathogenic microbes (accurately distinguishing between invasive, commensal, mutualistic, symbiotic and pathogenic microbes); and finally, to mobilize and coordinate interacting humoral and cellular defensive components [13,14]. As classically described, an immune response is initiated against infectious non-self when Microbe-Associated Molecular Patterns (MAMPs; e.g., microbial peptidoglycans, lipopolysacharides, β–glucans, lipoproteins, CpG dinucleotides, or flagellins) bind to intracellular, transmembrane or extracellular Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs; e.g., toll receptors, C-type lectins, PGRPs, NOD-like or RIG-1-like receptors) in the presence of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (e.g., host nucleic acid, hyaluronan fragments, heat shock proteins, uric acid, ATP, or collagen fragments) [13,15]. Inducible antimicrobial peptides, inhibitors and enzymes are synthesized and released into the hemocoel [15,16]. Hemocytes become activated via PRR-linked signal transduction pathways then initiate degranulation, phagocytosis, microaggregation, nodulation, or encapsulation reactions [11,17]. Hemokine-, eicosanoid- and monoamine-mediated signaling pathways coordinate the behavioral, humoral and cellular innate responses against invading microbes [18,19,20].
Successful biological control of these pests with microbial entomopathogens requires measures that overcome or circumvent natural immunity. To better understand immune response against microbial entomopathogens we initiated a project to document the functional immunogenomics of H. virescens by identification of antimicrobial response orthologs to baculoviral, bacterial and fungal infection [8,21,22,23]. In this study we applied the technique of Illumina RNA-seq digital expression profiling to construct a hemocyte-specific de novo transcriptome, comprising >22,000 putative transcripts, against which we profiled the in vivo antimicrobial responses of hemocytes infected with bacterial or fungal elicitors within the first hours of infection.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Transcriptome Assembly
In this report we describe RNA-seq expression profiling of larval H. virescens hemocyte response to microbial elicitation in vivo. Hemocytes were collected from larvae following elicitation with bacterial or fungal cell wall components and the resulting hemocyte transcripts were sampled by collecting three technical replicate lanes of 42-base sequence tags from each treatment using the Illumina GAIIx platform yielding a total 6,239,031 kb of reads filtered of ribosomal and mitochondrial sequences. A hemocyte-specific de novo transcriptome assembly was constructed by combining these 42-base tags from all treatments and controls into a single assembly using VELVET/OASIS resulting in 22,007 contigs, each with a distinct combination of annotation and expression (mean length, 765 bp; median length, 391 bp; range, 101 to 18,452 bp). When assemblies without useful annotations were excluded 13,216 assemblies remained. The 81,872 assemblies without a significant BLAST score or annotation were excluded from the present analysis. Within this larval H. virescens hemocyte de novo transcriptome assembly we identified H. virescens orthologs of known metazoan genes by BLASTx against the NCBI NR database (cutoff e < 10−6). Of the 35,959 top BLAST hits 30,249 were arthropod species; 30,020 were insecta, 29,205 endopterygotes; 7,135 dipterans; 6,539 coleopterans; and finally 6,314 were specific to lepidopteran species [24].
The larval H. virescens de novo exome assembly contained a full complement of aminoacyl-tRNA-synthetase transcripts along with a partial complement of mitochondrial aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Within the 311 assemblies identified by genome ontology as mitochondrial were the majority of enzymes involved in oxidative phosphorylation. Additional enzymes of central metabolism were identified including those involved in amino acid, lipid and carbohydrate biosynthesis and transport, vitamin and cofactors synthesis, xenobiotic biodegradation, and purine metabolism. Transcripts annotating within the ubiquitin-proteasome cellular degradation pathway (346), mitochondrial metabolism, and protein synthesis were identified which comprised the majority of components within each category. Cytoskeletal components such as tubulins (70), actins (49), myosins, spectrins, and microtubules (38) were noted. Of particular interest for future studies, a comprehensive range of hemocytic plasma membrane proteins were identified including ion channels and transporters, G-protein coupled receptors (46), transcription factors, amino acid/carbohydrate transporters, aquaporins (6), ABC multidrug resistance transporters (26), ankyrins (27), annexins (11), cell surface receptors, 14-3-3 proteins (6), gap junctions (8) and components of the endo/exocytosis, peroxisomal and lysosomal compartments. Neuropeptides, surface and nuclear neurotransmitter and hormone receptors and enzymes involved in endocrine regulation via ecdysteroids (16) and juvenile hormones (25) were present. Retrotransposon sequences were identified within the assembly (156), as were assemblies homologous to proteins of the bracovirus and other viral families, phages, mycoplasma and other bacterial proteins. Possible low level contamination with other tissues may be indicated by the presence of transcripts for the storage proteins arylphorins, riboflavin binding hexamer, methionine rich storage protein, vitellogenin, lipophorin and putative cuticular proteins. Alternatively small amounts of these proteins may also be transcribed in H. virescens hemocytes.
Expression profiling of microbial responses was accomplished by aligning the 42-base sequence tags from each treatment to the de novo reference assembly, comparing each treatment to control levels of expression. Elicitation of the immune response of H. virescens larvae with a mixture of Gram+/Gram− bacterial cell wall components resulted in at least a 3-fold upregulation of 1,188 hemocyte assemblies and 3-fold downregulation of 968 (Figure 1). Elicitation with fungal cell wall components resulted in the upregulation of 1,424 and the downregulation of 1,504 hemocyte assemblies (Figure 1). More than 700 assemblies corresponding to known orthologs of immune system were identified and those exhibiting 3-fold alterations in expression level following microbial challenge are presented (Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4). Fungal treatment resulted in more than 3-fold upregulation of 1,191 assemblies and downregulation of 1,425 when compared to the bacterial treatment. Conversely, bacterial elicitation resulted in greater than 3-fold upregulation of 1,482 and downregulation of 1,134 assemblies when compared to the fungal elicitation. Annotated assemblies showing alteration of transcriptional expression levels following immune elicitation are discussed in separate categories below.
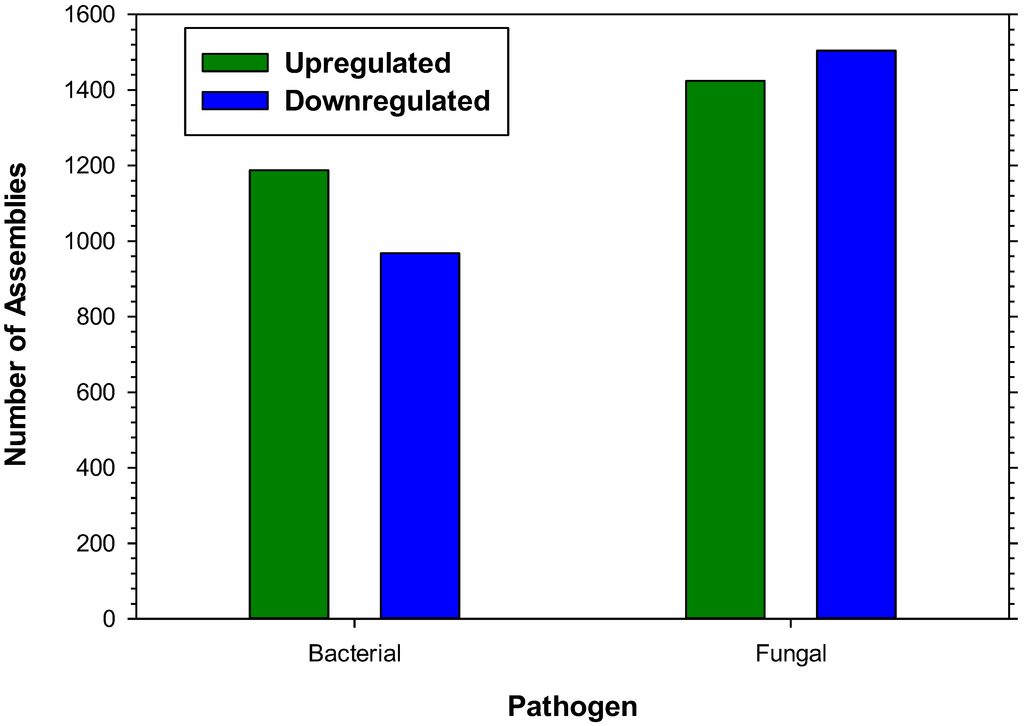
Figure 1.
Number of H. virescens larval hemocyte transcripts upregulated (green) or downregulated (blue) more than 3-fold by elicitation with either bacterial or fungal cell wall components.
Figure 1.
Number of H. virescens larval hemocyte transcripts upregulated (green) or downregulated (blue) more than 3-fold by elicitation with either bacterial or fungal cell wall components.
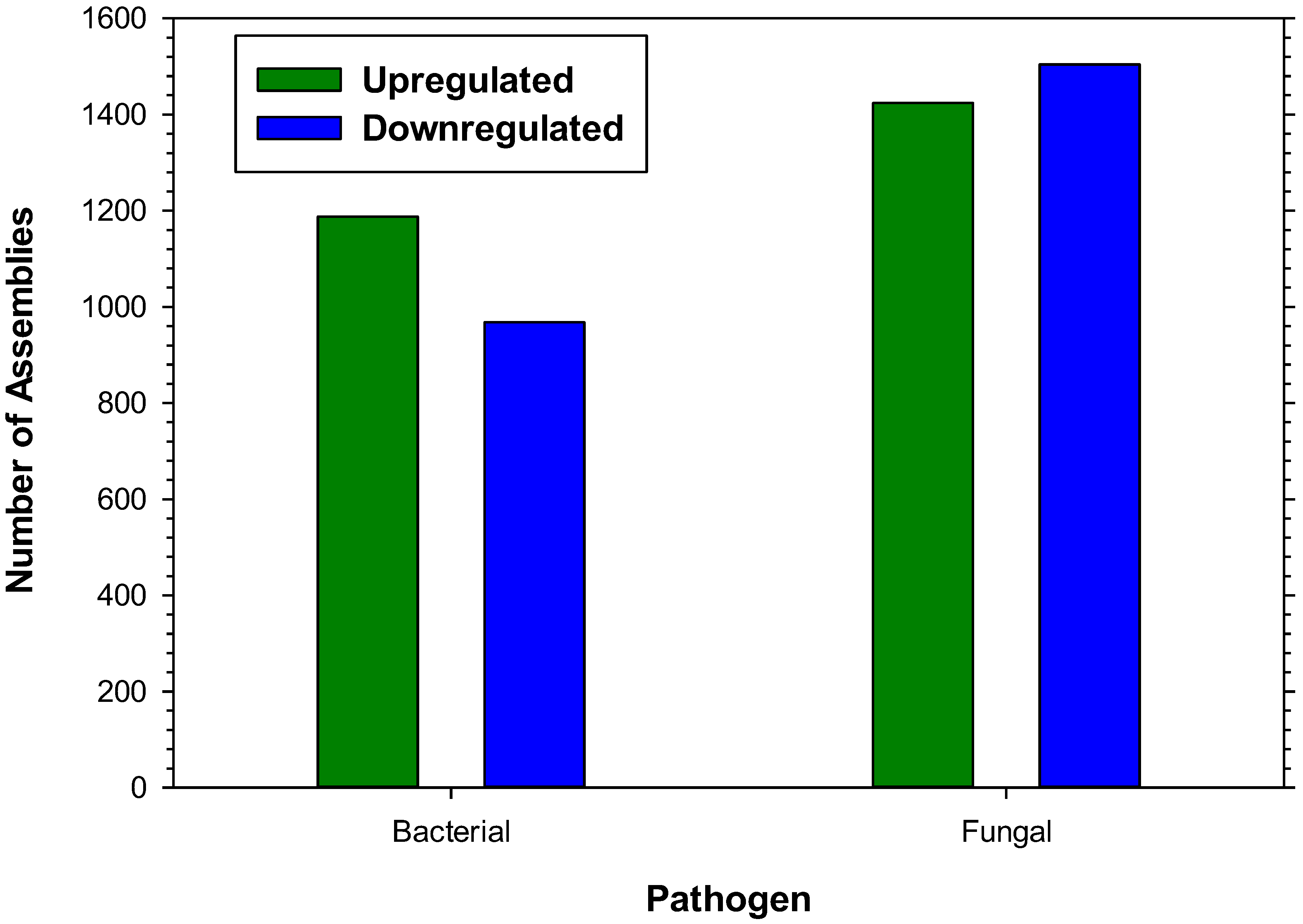

Table 1.
Pattern Recognition and Signal Transduction.
| Gene ID | Contig ID(HvUMC.) | Contr | Bac | Bac Fold Change | Fung | Fung Fold Change | Contig Length | % Cov | SpeciesTop Blast | e-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | |||||||||||
| β-1,3-Glucan Recognition Protein 2b | 2.6025.Contig1 | 47 | 138 | 2.9 | 146 | 3.1 | 239 | 77 | Helicoverpa armigera | 4E-27 | |
| C-type Lectin 10 | 2.28786.Contig1 | 32 | 112 | 3.5 | 92 | 2.9 | 487 | 52 | Bombyx mori | 2E-38 | |
| C-type Lectin | 1.single.v21-20824 | 1,723 | 4,150 | 2.4 | 7,281 | 4.2 | 3,126 | 46 | Aedes aegypti | E-122 | |
| Cyclophilin | 1.single.v31-289707 | 4 | 19 | 4.8 | 13 | 3.3 | 591 | 53 | Aedes aegypti | 1E-50 | |
| Dscam, Isoform AY | 1.single.v21-784756 | 6 | 12 | 2.0 | 18 | 3.0 | 159 | 84 | Drosophila melanogaster | 4E-17 | |
| Dscam | 1.single.v21-781454 | 6 | 14 | 2.3 | 26 | 4.3 | 192 | 92 | Pediculus h. corporus | 5E-27 | |
| F-box/LRR-repeat protein 16 | 1.single.v21-728991 | 2 | 8 | 4.0 | 12 | 6.0 | 187 | 88 | Camponotus floridanus | 4E-24 | |
| Galactose Binding Lectin, Soluble 9 | 1.single.Rem21-3740 | 142 | 508 | 3.6 | 194 | 1.4 | 696 | 51 | Mus musculus | 1E-19 | |
| Hemocytin | 1.single.Rem27-385 | 1,152 | 3,816 | 3.3 | 5,276 | 4.6 | 484 | 39 | Harpegnathos saltator | 8E-31 | |
| Immulectin-2 | 6.26705.Contig1 | 66 | 58 | 0.9 | 844 | 12.8 | 1,005 | 36 | Manduca sexta | 1E-49 | |
| Immulectin-3 | 1.single.v23-434605 | 17 | 51 | 3.0 | 44 | 2.6 | 235 | 60 | Manduca sexta | 1E-6 | |
| Integrin alpha 3 | 3.22533.Contig1 | 1,133 | 2,519 | 2.2 | 4,186 | 3.7 | 3,312 | 60 | Pseudoplusia includens | 0 | |
| Integrin Beta 1 Subunit | 1.single.Rem23-17883 | 31 | 126 | 4.1 | 66 | 2.1 | 130 | 100 | Spodoptera exigua | 3E-12 | |
| Integrin-linked Kinase | 4.1761.Contig1 | 31 | 96 | 3.1 | 102 | 3.3 | 633 | 78 | Glossina morsitans | 1E-63 | |
| Lectin 3 | 1.single.v21-686389 | 11 | 43 | 3.9 | 27 | 2.5 | 245 | 36 | Lonomia obliqua | 2E-8 | |
| Leucine Rich Protein | 1.single.v37-139619 | 8 | 15 | 1.9 | 32 | 4.0 | 227 | 36 | Aedes aegypti | 2E-8 | |
| Lipopolysaccharide Binding Protein | 3.9650.Contig1 | 2,442 | 7,490 | 3.1 | 8,921 | 3.7 | 158 | 78 | Helicoverpa armigera | 1E-11 | |
| NF-Kappa B Essential Modulator | 1.single.Rem21-38499 | 12 | 39 | 3.3 | 24 | 2.0 | 176 | 48 | Aedes aegypti | 4E-6 | |
| Paralytic Peptide Binding Protein 2 | 64.547.Contig4 | 3 | 197 | 65.7 | 1 | 0.33 | 247 | 42 | Bombyx mori | 7E-5 | |
| Peroxinectin | 2.12813.Contig1 | 6 | 25 | 4.2 | 32 | 5.3 | 190 | 45 | Ixodes scapularis | 2E-7 | |
| PGRP | 6.1191.Contig1 | 302 | 1,969 | 6.5 | 6,633 | 22.0 | 1,366 | 87 | Helicoverpa armigera | 3E-88 | |
| PGRP-SA | 1.single.v37-159335 | 71 | 171 | 2.4 | 249 | 3.5 | 232 | 78 | Tribolium castaneum | 3E-13 | |
| Scavenger Receptor | 1.single.v29-351108 | 3 | 9 | 3.0 | 14 | 4.7 | 172 | 71 | Culex quinquefasciatus | 2E-18 | |
| Toll Precursor | 15.16134.Contig1 | 178 | 550 | 3.1 | 708 | 4.0 | 2,095 | 28 | Pediculus h. corporis | 4E-58 | |
| Toll receptor 18-Wheeler | 1.single.v37-162137 | 32 | 41 | 1.3 | 98 | 3.1 | 144 | 52 | Spodoptera frugiperda | 7E-5 | |
| Down-Regulated Genes | |||||||||||
| Galectin-12 | 9.8877.v39-13988 | 139 | 358 | 2.6 | 11 | 0.08 | 218 | 48 | Harpegnathos saltator | 3E-12 | |
| Lectin 5 | 17.2309.Contig1 | 266 | 36 | 0.14 | 361 | 1.4 | 848 | 45 | Lonomia obliqua | 2E-36 | |
| NADP-Leukotriene B4 12- hydroxydehydrogenase | 1.single.v25-664428 | 12 | 5 | 0.42 | 2 | 0.17 | 424 | 63 | Culex quinquefasciatus | 2E-45 | |
Bac, Bacterial infected samples; Fung, Fungal infected samples; % Cov, percent query coverage; e-value, expect value.

Table 2.
Melanization and Coagulation.
| Gene ID | Contig ID(HvUMC.) | Contr | Bac | Bac Fold Change | Fung | Fung Fold Change | Contig Length | % Cov | SpeciesTop BLAST | e-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | |||||||||||
| Brasiliensin Thrombin Inhibitor | 1.single.v23-492316 | 114 | 195 | 1.7 | 453 | 4.0 | 792 | 41 | Triatoma basiliensis | 6E-32 | |
| DOPA Decarboxylase | 1.single.v21-586620 | 76 | 120 | 1.6 | 621 | 8.2 | 1,394 | 94 | Mamestra brassicae | 0 | |
| Hemocyte Protein-Glutamine Gamma- Glutamyltransferase | 1.single.v23-275987 | 232 | 374 | 1.6 | 1,449 | 6.2 | 2,292 | 34 | Camponotus floridanus | 0 | |
| Hemolymph Proteinase 18 | 3.3815.Contig1 | 490 | 710 | 1.4 | 4,941 | 10.1 | 1,350 | 41 | Manduca sexta | 8E-74 | |
| Hemolymph Proteinase 19 | 1.single.v21-731703 | 14 | 54 | 3.9 | 22 | 1.6 | 369 | 69 | Manduca sexta | 2E-49 | |
| Immulectin-2 | 6.26705.Contig1 | 66 | 58 | 0.9 | 844 | 12.8 | 1,005 | 36 | Manduca sexta | 1E-49 | |
| Immulectin-3 | 1.single.v23-434605 | 17 | 51 | 3.0 | 44 | 2.6 | 235 | 60 | Manduca sexta | 1E-6 | |
| Laccase-4-like | 1.single.Rem21-26133 | 6 | 31 | 5.2 | 13 | 2.2 | 292 | 56 | Bombus terrestris | 1E-22 | |
| Laccase-7-like | 2.7276.Contig1 | 9 | 33 | 3.7 | 14 | 1.6 | 269 | 55 | Acyrthosiphon pisum | 8E-23 | |
| Prophenoloxidase Activating Enzyme | 3.18472.Contig1 | 40 | 166 | 4.2 | 168 | 4.2 | 135 | 95 | Helicoverpa armigera | 4E-16 | |
| Reeler | 1.single.v21-527354 | 7 | 189 | 27.0 | 549 | 78.4 | 502 | 77 | Bombyx mori | 1E-61 | |
| Serpin-like Protein | 1.single.v21-800532 | 2 | 4 | 2.0 | 20 | 10.0 | 167 | 83 | Antheraea mylitta | 7E-19 | |
| Transglutaminase | 1.single.Rem21-50794 | 2 | 6 | 3.0 | 13 | 6.5 | 185 | 76 | Apis mellifera | 2E-18 | |
| Yellow 2 | 1.single.Rem21-90085 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 11 | 5.5 | 124 | 57 | Bombyx mori | 6E-6 | |
| Yellow-b | 1.single.v23-9110 | 832 | 2,954 | 3.6 | 2,802 | 3.4 | 1,833 | 78 | Heliconius melpomene | 0 | |
| Yellow-f | 1.single.v39-31578 | 49 | 147 | 3.0 | 154 | 3.1 | 559 | 85 | Bombyx mori | 6E-92 | |
| Down-Regulated Genes | |||||||||||
| Hemolymph Proteinase 17 | 1.single.v21-676209 | 395 | 19 | 0.05 | 72 | 0.18 | 1,979 | 51 | Manduca sexta | 1E-168 | |
| Hemolymph Proteinase 20 | 2.20519.Contig1 | 15 | 3 | 0.20 | 4 | 0.27 | 253 | 51 | Manduca sexta | 3E-17 | |
| Phenylalanine Hydroxylase | 1.single.v25-669762 | 14 | 3 | 0.21 | 2 | 0.14 | 250 | 95 | Papilio xuthus | 3E-41 | |
Bac, Bacterial infected samples; Fung, Fungal infected samples; % Cov, percent query coverage; e-value, expect value.

Table 3.
Antimicrobials And Effectors.
| Gene ID | Contig ID (HvUMC.) | Contr | Bac | Bac Fold Change | Fung | Fung Fold Change | Contig Length | % Cov | Species Top BLAST | e-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | |||||||||||
| Antibacterial Protein 3Tox | 35.7580.Contig4 | 63 | 1,115 | 17.7 | 2,810 | 44.6 | 270 | 77 | Heliothis virescens | 1E-24 | |
| Antimicrobial Protein 5Tox | 24.13350.Contig4 | 16 | 451 | 28.2 | 538 | 33.6 | 314 | 64 | Bombyx mori | 2E-27 | |
| Antimicrobial Protein 6Tox | 24.13350.Contig5 | 16 | 273 | 17.1 | 766 | 47.9 | 267 | 55 | Bombyx mori | 2E-19 | |
| Attacin A Precursor | 3.25069.Contig1 | 4 | 156 | 39.0 | 587 | 146.8 | 735 | 100 | Heliothis virescens | E-68 | |
| Carboxylesterase | 3.2554.Contig1 | 9 | 49 | 5.4 | 92 | 10.2 | 445 | 87 | Helicoverpa armigera | 3E-70 | |
| Cecropin 3 | 34.474.Contig1 | 123 | 1,336 | 10.9 | 1,333 | 10.8 | 366 | 86 | Helicoverpa armigera | 3E-31 | |
| Cecropin A2 | 34.474.Contig3 | 275 | 917 | 3.3 | 598 | 2.2 | 301 | 66 | Helicoverpa armigera | 3E-14 | |
| Cecropin D | 11.9800.Contig1 | 25 | 246 | 9.8 | 411 | 16.4 | 345 | 74 | Helicoverpa armigera | 2E-17 | |
| Chymotrypsin Inhibitor CI-8A | 1.single.v37-179791 | 285 | 450 | 1.6 | 1,453 | 5.1 | 493 | 71 | Bombyx mori | 3E-65 | |
| Cobatoxin B Long Form | 1.single.v29-23061 | 2,365 | 25,592 | 10.8 | 21,264 | 9 | 555 | 51 | Spodoptera frugiperda | 9E-16 | |
| Gallerimycin | 6.18346.Contig1 | 21 | 372 | 17.7 | 846 | 40.3 | 362 | 78 | Helicoverpa armigera | 9E-27 | |
| Gloverin-like Antibacterial Protein | 5.6087.Contig1 | 13 | 420 | 32.3 | 645 | 49.6 | 426 | 82 | Heliothis virescens | 5E-68 | |
| Hemolin | 3.4762.Contig1 | 313 | 3,201 | 10.2 | 6,907 | 22.1 | 1,239 | 96 | Heliothis virescens | 0 | |
| Immune Inducible Protein | 3.5943.Contig1 | 38 | 759 | 20.0 | 1,773 | 46.7 | 294 | 79 | Helicoverpa armigera | 2E-22 | |
| Inducible Metalloproteinase Inhibitor | 1.single.v21-505063 | 133 | 518 | 3.9 | 178 | 1.3 | 693 | 53 | Galleria mellonela | 1E-17 | |
| I-type Lysozyme | 3.8206.Contig1 | 290 | 509 | 1.8 | 1,038 | 3.6 | 795 | 57 | Sitophilus zeamais | 6E-42 | |
| Heliocin Precursor | 12.13910.Contig1 | 26 | 361 | 13.9 | 813 | 31.3 | 583 | 86 | Heliothis virescens | 3E-49 | |
| Kazal-type Inhibitor | 2.5500.Contig1 | 4 | 21 | 5.3 | 5 | 1.3 | 351 | 48 | Panstrongylus megistus | 6E-20 | |
| Lysozyme | 3.27236.Contig1 | 6,536 | 16,912 | 2.6 | 23,565 | 3.6 | 355 | 99 | Heliothis virescens | 3E-67 | |
| Metalloproteinase Inhibitor 3 | 1.single.v21-774328 | 56 | 102 | 1.8 | 211 | 3.8 | 1,054 | 42 | Tribolium castaneum | 2E-39 | |
| Nimrod-like Protein | 4.7692.Contig1 | 315 | 1,043 | 3.3 | 2,122 | 6.7 | 843 | 47 | Tribolium castaneum | 2E-47 | |
| Viresin | 2.22031.Contig1 | 28 | 35 | 1.2 | 194 | 6.9 | 448 | 90 | Heliothis virescens | 9E-61 | |
| Virescein Precursor | 2.19097.Contig1 | 0 | 19 | 19.0 | 65 | 65.0 | 193 | 100 | Heliothis virescens | 3E-6 | |
| Down-Regulated Genes | |||||||||||
| Adamts-7 Metallopeptidase | 1.single.v37-182137 | 33 | 6 | 0.18 | 3 | 0.09 | 167 | 69 | Aedes aegypti | 7E-16 | |
| Chemosensory Protein | 1.single.Rem23-43567 | 22 | 3 | 0.14 | 19 | 0.87 | 304 | 100 | Heliothis virescens | 4E-33 | |
| Immune-related Hdd13 | 3.8673.Contig1 | 106 | 28 | 0.26 | 18 | 0.17 | 340 | 56 | Hyphantria cunea | 1E-31 | |
| Odorant Binding Protein | 1.single.v29-513279 | 26 | 2 | 0.08 | 30 | 1.15 | 179 | 98 | Heliothis virescens | 3E-27 | |
Bac, Bacterial infected samples; Fung, Fungal infected samples; % Cov, percent query coverage; e-value, expect value.

Table 4.
Cellular Stress Response.
| Gene ID | Contig ID(HvUMC.) | Contr | Bac | Bac Fold Change | Fung | Fung Fold Change | Contig Length | % Cov | SpeciesTop BLAST | e-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | |||||||||||
| Antennal Cytochrome P450 CYP4 | 1.single.v37-177294 | 5 | 49 | 9.8 | 1 | 0.20 | 271 | 78 | Mamestra brassicae | 2E-28 | |
| Antennal Cytochrome P450 CYP9 | 1.single.v27-352481 | 27 | 32 | 1.2 | 280 | 10.4 | 701 | 78 | Mamestra brassicae | 1E-103 | |
| Autophagy-like Protein Atg12 | 2.26567.Contig1 | 4 | 9 | 2.3 | 17 | 4.3 | 265 | 69 | Biston betularia | 1E-10 | |
| Autophagy-related Protein B2-like | 1.single.v29-386662 | 2 | 6 | 3.0 | 8 | 4.0 | 714 | 50 | Acromyrmex echinatior | 6E-51 | |
| Autophagy-related Protein 9A | 2.9906.Contig1 | 3 | 8 | 2.7 | 15 | 5.0 | 170 | 60 | Danio rerio | 3E-13 | |
| Calcium & Integrin-binding Protein 1 | 1.single.v35-260454 | 11 | 33 | 3.0 | 19 | 1.7 | 231 | 61 | Harpegnathos saltator | 1E-13 | |
| Calnexin 99A, Isoform C | 1.single.v39-34103 | 29 | 96 | 3.3 | 81 | 2.8 | 241 | 73 | Drosophila melanogaster | 1E-30 | |
| Calpain Protein | 6.18445.Rem27-3414 | 42 | 126 | 3.0 | 90 | 2.1 | 205 | 85 | Bombyx mori | 1E-5 | |
| Calponin/Transgelin | 3.3375.Contig1 | 121 | 134 | 1.1 | 466 | 3.9 | 854 | 91 | Aedes aegypti | 9E-84 | |
| CarE | 1.single.v21-683558 | 167 | 271 | 1.6 | 536 | 3.2 | 152 | 80 | Spodoptera exigua | 0 | |
| Carboxyl/choline Esterase | 1.single.v25-663787 | 11 | 48 | 4.4 | 58 | 5.3 | 242 | 75 | Helicoverpa armigera | 6E-30 | |
| Catalase | 1.single.Rem23-39568 | 39 | 58 | 1.5 | 384 | 9.8 | 152 | 92 | Spodoptera litura | 3E-15 | |
| Fasciclin-1 | 1.single.v29-874 | 3489 | 29527 | 8.5 | 15189 | 4.4 | 1459 | 56 | Danaus plexippus | 5E-94 | |
| Ferritin Heavy Chain | 1.single.v23-133164 | 10 | 60 | 6.0 | 0 | 0 | 159 | 92 | Trichoplusia ni | 8E-20 | |
| Glutathione Synthetase | 3.11637.Contig1 | 5 | 36 | 7.2 | 16 | 3.2 | 275 | 60 | Harpegnathos saltator | 1E-6 | |
| Glutathione S-transferase | 1.single.v21-548409 | 16 | 72 | 4.5 | 238 | 14.9 | 639 | 73 | Amyelois transitella | 2E-86 | |
| Gossypol-induced Cytochrome P450 | 1.single.v35-24142 | 3111 | 13869 | 4.5 | 5967 | 1.9 | 1908 | 79 | Helicoverpa armigera | 0 | |
| Hemicentin-like Protein 2 | 1.single.v33-251 | 235 | 1084 | 4.6 | 651 | 2.8 | 363 | 50 | Spodoptera frugiperda | 2E-20 | |
| Innexin 1 | 1.single.Rem21-52588 | 76 | 243 | 3.2 | 359 | 4.7 | 200 | 82 | Pediculus h. corporis | 1E-25 | |
| Innexin 3 | 3.4996.Rem23-8776 | 35 | 168 | 4.8 | 245 | 7.0 | 263 | 68 | Harpegnathos saltator | 5E-25 | |
| Laminin A Chain | 2.31786.Contig1 | 100 | 317 | 3.2 | 142 | 1.4 | 844 | 69 | Aedes aegypti | 2E-64 | |
| Laminin-like Protein Epi-1 | 1.single.v25-592818 | 11 | 34 | 3.1 | 40 | 3.6 | 236 | 58 | Camponotus floridanus | 2E-16 | |
| NADPH Oxidase 5-like | 1.single.v21-32103 | 31 | 143 | 4.6 | 187 | 6.0 | 382 | 77 | Acyrthosiphon pisum | 2E-49 | |
| Papilin | 3.16799.Contig1 | 120 | 742 | 6.2 | 556 | 4.6 | 1366 | 40 | Harpegnathos saltator | 5E-63 | |
| Peroxidasin | 1.single.v21-283343 | 806 | 1896 | 2.4 | 2986 | 3.7 | 4327 | 50 | Tribolium castaneum | 0 | |
| Selenium-binding protein | 2.31409.Contig1 | 154 | 388 | 2.5 | 785 | 5.1 | 355 | 59 | Pediculus h. corporus | 8E-30 | |
| Talin-2-like | 2.27492.Contig1 | 26 | 63 | 2.4 | 89 | 3.4 | 1280 | 75 | Bombus terrestris | 1E-178 | |
| Teneurin-3 Isoform 1 | 1.single.v21-374519 | 217 | 652 | 3.0 | 703 | 3.2 | 597 | 88 | Apis mellifera | 4E-98 | |
| Transferrin | 4.13853.Contig1 | 28 | 101 | 3.6 | 187 | 6.7 | 1071 | 33 | Aedes aegypti | 2E-44 | |
| Down-Regulated Genes | |||||||||||
| Apoptosis Inducing Factor, Putative | 1.single.v21-402220 | 272 | 286 | 1.1 | 54 | 0.20 | 391 | 62 | Ixodes scapularis | 7E-16 | |
| Calnexin, Putative | 1.single.Rem21-38232 | 26 | 18 | 0.69 | 5 | 0.19 | 159 | 68 | Ixodes scapularis | 1E-14 | |
| Ferrochelatase precursor | 1705.v27-585704 | 16 | 3 | 0.188 | 3 | 0.188 | 149 | 66 | Chironomus sp. | 7E-11 | |
| Flavin-dependent Monooxygenase | 1.single.v21-786790 | 79 | 24 | 0.30 | 36 | 0.46 | 501 | 97 | Helicoverpa armigera | 2E-87 | |
Bac, Bacterial infected samples; Fung, Fungal infected samples; % Cov, percent query coverage; e-value, expect value.
2.2. Pattern Recognition Receptors
PRRs act as sentinels to microbial incursion by first binding to MAMPs, then activating specific signal transduction pathways. A number of H. virescens orthologs of different PRR classes were identified among the hemocyte transcripts. Hemocyte assemblies orthologous to the β-1,3-glucan recognition protein family which includes Gram− bacteria-binding protein were identified (Table 1). Peptidoglycan binding recognition protein (PGRP) transcript levels were upregulated by microbial elicitation (Table 1). Small secreted PGRP-Small secreted A (PGRP-SA) forms bind Gram+ bacteria, activating the toll pathway via cleavage of Spätzle; and Gram- recognizing PGRP-long transmembrane F form activating the imd pathway were elevated following bacterial or fungal elicitation of larvae (Table 1). Representatives of the Ca+2-dependent C-type lectins were identified including lipopolysaccharide binding protein and orthologous assemblies of immulectins-2, and -3. In these expression profiling experiments C-type lectins were also induced by bacterial elicitation, as was previously observed using quantitative RT-PCR of H. virescens hemocytes [8]. The class of galactose binding lectins and galectins, was also represented among the annotated assemblies, as were hemocytin and additional lectins of various classes (Table 1).
Additional PRRs involved in recognition of microbial infection and upregulated by elicitation were attacin, hemolin, scolexin, and scavenger receptors (Table 1). Transcripts of the lipopolysaccharide-binding leucine rich repeat protein leureptin were identified. Leureptin associates with M. sexta hemocytes and interacts with MD-2-related lipid recognition protein to effect lipopolysaccharide activation of the toll signaling pathway [25]. Leucine rich repeat proteins were upregulated by either fungal or bacterial elicitation, or both (Table 1). Integrin is a cell surface pattern recognition receptor which can for example recognize collagen IV fragments associated with tissue damage [15]. Per os gene silencing of a Plutella xylostella β-integrin inhibited E. coli stimulated hemocyte nodulation and also caused excess larval mortality [26]. H. virescens hemocytic integrin transcription was upregulated by bacterial and fungal elicitation (Table 1). Expression of H. virescens hemocytic neuroglian and tetraspanin orthologs was not altered by microbial infection.
Several assemblies orthologous to the Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule (Dscam) [27] PRR were identified among the H. virescens hemocyte transcripts (Table 1). Dscam are expressed from a single gene with multiple exons and are processed into thousands of variants via differential splicing and participate in phagocytosis and nervous system development. Surprisingly few Dscam orthologous transcripts were identified in H. virescens hemocytes when compared to Drosophila melanogaster which is known to generate more than 38,000 splice variants [27]. More detailed studies using this same dataset will become possible when a tiling array of the H. virescens Dscam gene is constructed.
One final class of putative insect PRRs, the circulating plasma lipoprotein particle lipophorin and its associated protein apolipophorin-III, were identified within our larval hemocyte transcriptome but exhibited no alteration in expression levels. In Bombyx mori and other insects lipophorin and apolipophorin-III serve as PRRs for β–1,3-glucans, lipopolysaccharide, and lipoteichoic acid [28]. Additionally, lipophorin may be directly microbicidal [29] and apolipophorin-III exhibits antiplasmodial activity [30].
PRR activation at remote locations can be signaled to immune responsive tissues such as hemocytes via peptide chemokines [11]. Orthologs of proteins involved in this activation process were identified within the H. virescens transcripts including hemocyte aggregation inhibitor, macrophage migration inhibitory factor, imaginal disc growth factor, and paralytic peptide binding proteins-1 and -2. Growth blocking peptide circulating in the hemolymph is proteolytically processed to the active peptide following stressors such as heat, injury and bacteria in Drosophila, activating antimicrobial peptide synthesis via the Gram- sensitive imd pathways [31]. Expression of the identified H. virescens hemocytic assemblies orthologous to growth-blocking peptide and growth blocking peptide binding protein were unaffected by microbial elicitation, in agreement with our previous work [8]. Octopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine have also been implicated as modulators of hemocyte activation [18], and we identified assemblies of H. virescens hemocyte neurotransmitter receptors orthologous to both which were not upregulated by immune elicitation. Larval Chilo suppressalis hemocyte octopamine transporters were also not upregulated by fungal or bacterial injections [18].
2.3. Signal Transduction
Insect immune-responsive tissues respond to microbial activation of PRRs via several signal transduction pathways, the most well studied of which are the Gram+ and fungal responsive toll pathway, the Gram- responsive imd-JNK pathway, and the JAK/STAT pathway [16]. In this study of immune-stimulated H. virescens hemocytes over 1200 assemblies annotating as signal transduction pathway components were present (e.g., apoptosis, toll, imd, JAK/STAT, prostaglandin, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, insulin/IGF/mTOR, G-protein coupled receptors, adenylate/guanylate cyclases, calreticulin, Rac, ras, protein kinases/phosphatases, phospholipases, etc.) however only a very few of these assemblies exhibited alterations in their expression levels as a result of the treatments employed. Therefore, only those whose transcription was upregulated more than 3-fold by the treatments are shown in Table 1.
Immune activation of lepidopteran hemocytes via eicosanoid intermediates has been well documented [20,32]. MAMP binding by PRRs in hemocytes or fat bodies may cause the release of plasmatocyte spreading peptide which in turn activates a hemocytic signal transduction pathway whereby the C20 fatty acid arachidonic acid is cleaved from the inner leaflet of cells by an activated phospholipase A2 (PLA2), and is subsequently oxidized to bioactive eicosanoids such as prostaglandins by cytosolic cyclooxygenase or lipoxygenase. Hemocyte actions mediated by the PLA2 signaling pathway include phagocytosis, cellular spreading, microaggregation and nodulation as well as prophenoloxidase activation [32]. Inhibition of lepidopteran PLA2 either by chemical means, gene silencing, or by entomopathogenic bacteria leads to profound immunosuppression [32]. Several H. virescens orthologs of enzymes within this transduction pathway were identified, among them a PLA2, a secretory PLA2, PLA2-activating protein, prostaglandin E synthase 2, prostaglandin reductase 1, prostamide/prostaglandin F synthase, NADP-dependent leukotriene B4 12-hydroxydehydrogenase, leukotriene A4 hydrolase, and peroxinectin. Of these orthologs only two, peroxinectin (upregulated 5×) and NADP-dependent leukotriene B4 12-hydroxydehydrogenase (downregulated 6×) exhibited differential regulation in hemocytes following bacterial or fungal elicitation (Table 1). Interruption of hemocytic signal transduction pathways mediated via eicosanoids using RNAi [32] may now be a feasible approach in H. virescens using the sequences discussed above. These newly identified orthologs may prove useful in teasing out the multiple interacting regulatory pathways coordinating the innate cellular immune responses of H. virescens hemocytes against entomopathogens.
2.4. Melanization, Nodulation and Encapsulation
The enzyme prophenoloxidase (PPO) is proteolytically activated by a cascade of serine protease initiated by PRR activation [12]. Expression of the H. virescens PPO-1, and PPO-2 assemblies were not altered by microbial elicitation. This confirms our earlier report [22] in which the expression of these key plasma multicopper oxidases was not affected by bacterial or baculoviral infection. The majority of components of the PPO activation pathway isolated from Manduca sexta were identified in this survey, including PPO activating enzymes, immunolectins-2 and -3, and hemolymph proteinases-6, and -21, Spätzle cleaving proteinase-8 (Table 2) [12]. Assemblies orthologous to M. sexta pattern recognition serine proteinase precursor (proHP14) were identified, however in our experiments no upregulation was observed upon bacterial or fungal elicitation. Serpins involved in throttling the above serine protease PPO activating cascade were also identified which were upregulated following fungal elicitation (Table 2), while pacifastin-related serine protease inhibitor precursor was not. Enzymes preceding PPO in the melanization pathway, phenylalanine hydroxylase, and following PPO in the pathway, DOPA decarboxylase, arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase and laccases were present (Table 2). Hemolymph clotting cascade orthologs were present (Table 2). Upon bacterial elicitation H. virescens hemocytes release a β-amyloid-like protein (p102) which participates in melanization and encapsulation reactions [33]. Assemblies matching p102 were identified within the hemocyte transcriptome, along with amyloid binding proteins; however no change in their transcript levels was detected upon microbial elicitation. A reelin-domain assembly orthologous to the B. mori Reeler involved in nodulation reactions was highly upregulated by both bacterial and fungal elicitation [34] (Table 2). Orthologs to the EGF repeat containing phagocytosis regulating peptides draper and eater were identified within this assembly but expression levels were unaffected by the treatments. Formation of the invertebrate form of gap junctions between cells is accomplished by adjoining hexamers of innexins (invertebrate connexins) during nodulation and encapsulation reactions of H. virescens hemocytes [35]. Within our de novo transcriptome we identified H. virescens orthologs of innexins-1 and -3 both of which were upregulated by bacterial (4.8-fold) and fungal (7-fold) elicitation (Table 4).
2.5. Antimicrobials and Other Effectors
Activation of the toll, imd signal transduction pathways upregulates transcription of a suite of typically cationic antibacterial and antifungal antimicrobial peptides by hemocytes, fat bodies, Malpighian tubules, midgut, reproductive, cuticular and other tissues [16,36]. Antimicrobial peptides previously isolated from tissues of immune-stimulated H. virescens larvae include cecropins, heliocin [37], attacin, virescein, and heliomicin [38]. Cecropins are a class of amphipathic antibacterial peptides widespread in nature [16]. Three cecropins have been chromatographically purified from H. virescens plasma, and transcript assemblies corresponding to each were identified among the upregulated elements in this study (Table 3). Transcription of the peptide virescin, first isolated from immune-stimulated larval H. virescens plasma [39], matches an assembly which was upregulated 7-fold in hemocytes by fungal elicitation (Table 3). Transcription of the moricin-like antibacterial peptide virescein was highly upregulated in hemocytes by both bacterial (19-fold) and fungal (65-fold) treatments (Table 3). An assembly corresponding to heliocin, a proline-rich lebocin-like glycosylated H. virescens antibacterial peptide [38], was upregulated by both classes of microbial elicitations. Substantial upregulation of the glycine-rich antibacterial peptides gloverin and attacin occurred following microbial elicitation (Table 3).
The defensin related peptide heliomicin exhibited only antifungal activity even though its synthesis was induced by septic injury with a suspension of gram positive and gram negative bacteria [38]. However the assembly corresponding to heliomicin precursor exhibited no upregulation by either bacterial or fungal treatment in our experiments. Instead a related defensin annotating as gallerimicin-like was highly upregulated by microbial elicitation (Table 3). Additional defensin-related antimicrobial peptides were identified within our assembly, including x-Tox peptides found only in Lepidoptera. These peptides encode variable repeats of a cysteine stabilized alpha-beta sheet (CS- αβ) scorpion toxin related motif [40]. An earlier EST effort identified Hv-3-Tox in transcripts from immune-stimulated larval H. virescens hemocytes which encoded three of these motifs [8]. The S.frugiperda ortholog of this protein, encoding 11 CS-αβ-motifs was expressed solely in the granulocytes and plasmatocytes [40,41]. In agreement with these authors we observed significant upregulation of these H. virescens X-tox assemblies in our hemocyte transcript survey (Table 3). The H. virescens hemocytic orthologs of the Drosophila 14-3-3ε necessary for the secretion of antimicrobial peptides from hemocytes [42] were identified, but did not exhibit differential regulation by either fungal or bacterial elicitation.
Infection induces the synthesis of host antimicrobial proteases and protease inhibitors targeted against microbial virulence factors [43]. In these experiments inducible metalloproteinase inhibitor proteins were upregulated in hemocytes by bacterial but not by fungal elicitation (Table 3). Orthologs of a pacifastin-like serine protease inhibitor along with several other uncharacterized serine and cysteine protease inhibitors were identified in this study. Two metalloprotease inhibitors were significantly upregulated by either bacterial or fungal elicitation (Table 3). The effectors attacin and hemolin were also significantly upregulated by microbial infection. Attacin transcription was elevated 39-fold by bacterial elicitation and 146.8-fold by fungal elicitation (Table 3). In this report hemolin upregulation observed 10.2-fold in bacterially elicited hemocytes and 22.1-fold in fungally elicited larval hemocytes. These values are somewhat greater than the range previously demonstrated using quantitative RT-PCR in bacterially elicited H. virescens larval hemocytes and fat bodies [21].
2.7. Cellular Response Factors
Activation of the immune system by microbial incursion can alter expression of several additional classes of cellular metabolic pathways exemplars of which are presented in Table 4. Glutathione S-transferase, glutathione synthetase, and catalase were upregulated by fungal elicitation; but superoxide dismutase, thioredoxin, thioredoxin peroxidase, and thioredoxin reductase were not significantly upregulated. Cellular oxidative defenses utilized against microbes such as the respiratory burst superoxide generating NADPH-oxidase complex [48] were elevated 4.6-fold by bacterial and 6-fold by fungal elicitation (Table 4). Nitric oxide synthase also was identified, but no significant difference in expression was observed in hemocytes removed from immune elicited larvae. A large number of assemblies orthologous to insect carboxylesterases were identified, some of which are induced by both fungal and bacterial elicitation (Table 4).
Utilization of the micronutrient iron may shift during infection of H. virescens larvae [49,50]. In agreement with this previous work we found that transcript levels for both ferritin and transferrin were elevated by bacterial and fungal elicitation (Table 4). Larval Bombyx mori midgut expression of arginine kinase was elevated following BmNPV infection within resistant strains [51], however in this study of H. virescens hemocytes expression of arginine kinase was not altered by microbial infection (Table 4). An ortholog of Bombyx mori ganglioside-induced differentiation-associated protein was identified [52] but exibited no significant change in transcript level. Three H. virescens orthologs of the Bt-induced Spodoptera littoralis REPAT (Response to Pathogens) were identified [53]. Expression of these orthologs was not altered in hemocytes by bacterial or fungal elicitation of H. virescens larvae, though this may have been due to the strains of bacteria used in the present experiments. Enzymes of several classes involved in xenobiotic metabolism were upregulated in hemocytes following infection (Table 4). Of the carboxyl/choline esterase gene family 18 orthologous assemblies were identified along with three acetylcholinesterases. One of the carboxyl/choline esterases identified was upregulated 4.4-fold by bacterial and 5.3-fold by fungal infection (Table 4). Of the 13 UDP-glycosyltransferases detoxification enzyme assemblies none were significantly up- or down-regulated by the treatments used in this study. Over 78 assemblies orthologous to the multidrug resistance proteins of the ATP-binding cassette class were present. Greater than 80 cytochrome P450s were identified, several of which were upregulated either by bacterial or fungal elicitation, or both (Table 4). H. virescens larvae defoliate cotton throughout the Americas; thus it was expected that detoxification enzymes which allow feeding on this crop would be identified, though not necessarily in hemocytes. An H. virescens ortholog of the H. armigera gossypol-induced cytochrome P450 was upregulated 4.5-fold by bacterial elicitation (Table 4).
H. armigera larval development was stunted by feeding on transgenic cotton plants expressing double stranded RNAi against this enzyme [54]. H. virescens also feeds widely on host plants which deploy glucosinolates as inactive precursors to highly toxic isothiocyanate feeding deterrents. Inactivation of isothiocyanates in insect tissues is achieved by desulphation [55], nitrilases coupled to amidases, or by conjugation to glutathione [56]. Interestingly our hemocyte assembly encoded the detoxification enzyme glucosinolate sulphatase, and the activating enzyme myrosinase, the former of which was upregulated 28-fold by bacterial and 6.8-fold by fungal elicitation of larvae. Nitrilases and amidases also were present though expression was not affected by the treatments employed. Among the other xenobiotic detoxification pathway enzymes were 42 assemblies orthologous to glutathione S-transferases of other Lepidoptera. In other noctuid moths glutathione S-transferases have been demonstrated to detoxify glucosinolates. Two of these GSTs exhibited upregulation following microbial elicitation (Table 4).
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Insects, Infection, and RNA Isolation
Heliothis virescens eggs were received from the North Carolina State University Dept. of Entomology Insectary (Raleigh, NC, USA). Larvae were reared individually on an artificial wheat germ based diet (BioServ, Frenchtown, NJ, USA) under standard conditions of 14 h:10 h (L:D) photoperiod, 55% RH, 28 °C [23]. To eliminate the possibility of contaminating nucleic acid sequences from injection of live/dead pathogens into experimental insects only purified cell wall components were used to activate the antimicrobial immune response. Early 5th instar larvae were punctured with a tungsten needle dipped into a suspension of 1 µg/mL lipopolysaccharide and 1 µg/mL peptidoglycan (Sigma Chem. Co., St. Louis, MO, USA) in phosphate buffered saline to mimic infection with Gram− and Gram+ bacteria [21]. The antifungal response was activated by puncture of early 5th instar larvae with a tungsten needle dipped into a suspension of 1 µg/mL β-glucan, 1 µg/mL curdlan and 1 µg/mL laminarin (Sigma Chem. Co., St. Louis, MO, USA) in PBS. Control larvae were subjected to sterile puncture with a tungsten needle dipped into PBS. At 12 hrs post puncture hemocytes were collected from 30 insects from each treatment according to previously published methods [23]. Larvae were bled through a punctured anterior proleg into ice cold PBS containing a crystal of PTU to prevent melanization. Hemocytes were pelleted by centrifugation at 5000 × g for 4 min. and stored at −85 °C. Total RNA was extracted from hemocytes using RNeasy™ kits (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) [23].
3.2. Sequence Generation
Hemocyte RNA pools were submitted to University of Missouri Bond Life Sciences Center DNA Core for Illumina GAIIx sequencing (http://www.biotech.rnet.missouri.edu/dnacore/). Libraries were constructed according to the standard Illumina RNA-seq protocol (Part# 1004898 Rev. A, rev Sept 08; http://www.illumina.com) from the pooled PCR products except for the fragmentation step as detailed [23].
3.3. De Novo Exome Assembly
Illumina reads were first cleaned of low quality bases at the 3’ end, and limited to only those reads longer than 31 bases. The de novo assembly was performed using VELVET (v1.0; http://www.ebi.ac.uk/~zerbino/velvet/; 8/29/2011) and OASES (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/~zerbino/oases/; 8/29/2011) with kmers ranging from 21 to 41 in increments of 2. Clusters of contigs with no mismatches were reduced to the longest member using VMATCH (v2.1.4; http://www.vmatch.de/; 8/29/2011). To further reduce redundancy contigs were assembled using TGICL (http://www.compbio.dfci.harvard.edu/tgi/software/; 8/29/2011) to a final count of 103,879. The sequences were annotated by sequence similarity to NR proteins.
The reads from each sample were aligned to the final set of contigs using SOAP v2 (http://soap.genomics.org.cn/soapaligner.html; 8/29/2011). Contigs were grouped by the NR accession id annotation, and only those Illumina reads were retained that aligned within one and only one such group. Within each group, the expression profile of the sequences was compared one to another and a correlation coefficient generated for each comparison. When two sequences in a group had an r value of 0.8 or more the one with the greater number of hits was retained. The process of measuring the correlation coefficient and winnowing contigs from within a group was continued recursively until left with those sequences whose expression patterns and NR accessions made them unique [57]. In this way all sequences were compared within a group and different expression profiles within each group were retained. The resulting table of differential expression had 22,007 assemblies each with a distinct combination of annotation and expression. Functional categories of contig and singleton sequences resulting from this assembly were annotated using a local installation of BLAST2GO (http://www.blast2go.org; 8/29/2011). All sequences have been deposited (http://www. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomeprj/49697).
3.4. Identification of Differentially Regulated Genes
Larval gene expression was analyzed in a semi-quantitative fashion by normalizing the number of times sequence tags aligning with an mRNA assembly were detected in the hemocytes of infected larvae compared to those of controls. We analyzed genes that were shown to be upregulated or down regulated by a factor of three and that had an e-value < 10−5 [23].
4. Conclusions
The objective of this effort was to conduct a deep sequence sampling survey utilizing RNA-seq in order to identify as many immune effectors as possible for future studies of immunity with this larval lepidopteran model of entomopathogen infection. Hemocytes are the primary immune responders to microbial infection and this easily collected tissue was expected to express most of the animal’s immune repertoire. Similar deep sampling surveys of other immune responsive tissues with RNA-seq will be needed to round out these initial efforts; however substantial genomic resources have been generated which include the transcripts of major cell surface receptors and signal transduction pathway components. Hemocytes are easily targeted within the hemocoel by injection of gene silencing double stranded RNAi. Sequence resources generated by this study will enable specific, targeted disruption of hemocyte immune system regulatory pathways or other signal transduction pathways in vivo [26,32,46,58,59,60,61,62,63]. Importantly, in this study a significant number of differentially regulated transcripts were found which had no identifiable function. These numerous, but unknown transcripts indicate that many aspects of hemocyte function during infection have yet to be discovered. Although restricted to a single tissue, hemocytes, many of these newly identified signal transduction and receptor transcripts, or closely related ones, will also be present in other tissues of H. virescens, opening up rich new grounds for studies using this insect model.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Bill Spollen, Sean Blake, and Nathan Bivens of the University of Missouri Bond Life Sciences Center DNA Core for assistance with sequence generation and analysis. We thank Jonathan Breitenbach for analytical help, and Larry Brown for technical assistance. This work was supported by the USDA Agricultural Research Service. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this article is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the U.S. Department of Agriculture. All programs and services of the U.S. Department of Agriculture are offered on a nondiscriminatory basis without regard to race, color, national origin, religion, sex, age, marital status, or handicap.
References
- Cho, S.; Mitchell, A.; Mitter, C.; Regier, J.; Matthews, M.; Robertson, R. Molecular phylogenetics of heliothine moths (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae: Heliothinae), with comments on the evolution of host range and pest status. Syst. Entomol. 2008, 33, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albernaz, K.C.; Silva-Brandao, K.L.; Fresia, P.; Consoli, F.L.; Omoto, C. Genetic variability and demographic history of Heliothis virescens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) populations from Brazil inferred by mtDNA sequences. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2012, 103, 333–343. [Google Scholar]
- Fitt, G.P. The ecology of Heliothis species in relation to agroecosystems. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1989, 34, 17–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, J.A.; Bogaert, T.; Clinton, W.; Heck, G.R.; Feldmann, P.; Ilagan, O.; Johnson, S.; Plaetinck, G.; Munyikwa, T.; Pleau, M.; et al. Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.B.; Cai, W.J.; Wang, J.W.; Hong, G.J.; Tao, X.Y.; Wang, L.J.; Huang, Y.P.; Chen, X.Y. Silencing a cotton bollworm P450 monooxygenase gene by plant-mediated RNAi impairs larval tolerance of gossypol. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, W.B.; VanEngelsdorp, D.; Hayes, J.; Westervelt, D.; Glick, E.; Williams, M.; Sela, I.; Maori, E.; Pettis, J.; Cox-Foster, D.; et al. Large-Scale field application of RNAi technology reducing Israeli acute paralysis virus disease in honey bees (Apis mellifera, Hymenoptera: Apidae). PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govind, G.; Mittapalli, O.; Griebel, T.; Allmann, S.; Bocker, S.; Baldwin, I.T. Unbiased transcriptional comparisons of generalist and specialist herbivores feeding on progressively defenseless Nicotiana attenuata plants. PLoS One 2010, 5, e8735. [Google Scholar]
- Shelby, K.S.; Popham, H.J.R. Analysis of ESTs generated from immune-stimulated hemocytes of larval Heliothis virescens. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 101, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.; Heidel, A.; Heckel, D.G.H; Groot, A.T. Transcriptome analysis of the sex pheromone gland of the noctuid moth Heliothis virescens. BMC Genomics 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafatos, F.; Waterhouse, R.; Zdobnov, E.; Christophides, G. Comparative Genomics of Insect Immunity. In Insect Infection and Immunity: Evolution, Ecology, and Mechanisms; Rolff, J., Reynolds, S.E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 86–105. [Google Scholar]
- Strand, M.R. Insect Hemocytes and Their Role in Immunity. In Insect Immunology; Beckage, N.E., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 49–68. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Vilcinskas, A.; Kanost, M.R. Immunity in Lepidopteran Insects. In Invertebrate Immunity; Soderhall, K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 708, pp. 163–180, Advances in Experimental Biology and Medicine. [Google Scholar]
- Blander, J.M.; Sander, L.E. Beyond pattern recognition: Five immune checkpoints for scaling the microbial threat. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, J.; Oldenvi, S.; Fahlander, C.; Daenthanasanmak, A.; Steiner, H. Growing bacteria shed elicitors of Drosophila humoral immunity. J. Innate Immun. 2012, 4, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altincicek, B.; Berisha, A.; Mukherjee, K.; Spengler, B.; Rommp, A.; Vilcinskas, A. Identification of collagen IV derived danger/alarm signals in insect immunity by nanoLC-FTICR MS. Biol. Chem. 2009, 390, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, N.A.; Welchman, D.P.; Lemaitre, B. Recognition and Response to Microbial Infection in Drosophila. In Insect Infection and Immunity: Evolution, Ecology, and Mechanisms; Rolff, J., Reynolds, S.E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 13–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kanost, M.R.; Nardi, J.B. Innate Immune Responses of Manduca Sexta. In Molecular Biology and Genetics of the Lepidoptera; Goldsmith, M.R., Marec, F., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 271–292. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Wu, S.-F.; Li, X.-H.; Adamo, S.A.; Ye, G.-Y. The characterization of a concentration-sensitive–adrenergic-like octopamine receptor found on insect immune cells and its possible role in mediating stress hormone effects on immune function. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.S.; Castro, D.P.; Figueiredo, M.B.; Genta, F.A.; Azambuja, P. Trypanosoma rangeli: A new perspective for styding the modulation of immune reactions of Rhodnius prolixus. Parasit. Vectors 2009, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrsyl, P.; Dobes, P.; Wang, Z.; Hauling, T.; Wilhelmsson, C.; Theopold, U. Clotting factors and eicosanoids protect against nematode infections. J. Innate Immunol. 2011, 3, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenius, O.; Popham, H.J.R.; Shelby, K.S. Bacterial, but not baculoviral infections stimulate hemolin expression in noctuid moths. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, K.S.; Popham, H.J.R. Cloning and characterization of the secreted hemocytic prophenoloxidases of Heliothis virescens. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2008, 69, 127–142. [Google Scholar]
- Breitenbach, J.E.; Shelby, K.S.; Popham, H.J.R. Baculovirus induced transcripts in hemocytes from the noctuid moth, Heliothis virescens. Viruses 2011, 3, 2047–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beldade, P.; McMillan, W.O.; Papanicolaou, A. Butterfly genomics eclosing. Heredity 2008, 100, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ragan, E.J.; Kanost, M.R. Leureptin: A soluble, extracellular leucine-rich repeat protein from Manduca sexta that binds lipopolysaccharide. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.M.; Kim, Y. Target-Specific feeding toxicity of β1 integrin dsRNA against diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 78, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, J.; Lun, C.M.; Majeske, A.J.; Sacchi, S.; Schrankel, C.S.; Smith, L.C. Invertebrate immune diversity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 959–9774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdybicka-Barabas, A.; Staczek, S.; Mak, P.; Piersiak, T.; Skrzyrpiek, T.; Cytrynska, M. The effect of Galleria mellonella apolipophorin III on yeasts and filamentous fungi. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, Y.; Sekimizu, K.; Kaito, C. Silkworm apolipophorin protein inhibits Staphylococcus aureus virulence. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 39360–39369. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, L.; Noh, J.Y.; Jo, Y.H.; Oh, S.H.; Kumar, S.; Noh, M.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Cha, S.J.; Seo, S.J.; Kim, I.; et al. Apolipophorin-III mediates antiplasmodial epithelial responses in Anopheles gambiae (G3) mosquitoes. PLoS One 2010, 5, e15410. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuzuki, S.; Ochiai, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Kurata, S.; Ohnishi, A.; Hayakawa, Y. Drosophila growth-blocking peptide-like factor mediates acute immune reactions during infections and non-infectious stress. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-A.; Kim, Y. Eicosanoid biosynthesis is activated via Toll, but not Imd signal pathway in response to fungal infection. J. Invertbr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falabella, P.; Riviello, L.; Pascale, M.; Di Lelio, I.; Tettamanti, G.; Grimaldi, A.; Iannone, C.; Monti, M.; Pucci, P.; Tamburro, A.M.; et al. Functional amyloids in insect immune response. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.-Y.; Xue, J.; Wu, W.-J.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Z.-Y.; Zhang, C.-X. An immune-induced Reeler protein is involved in the Bombyx mori melanization cascade. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 441, 696–706. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, K.; Turnbull, M.W. Characterization of nonjunctional hemichannels in caterpillar cells. J. Insect Sci. 2011, 11, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.B.N.A.; Dong, Y.; Garver, L.; Dimoupoulos, G. Specificity of the Innate Immune System: A Closer look at the Mosquito Pattern-Recognition Receptor Repertoire. In Insect Infection and Immunity: Evolution, Ecology, and Mechanisms; Rolff, J., Reynolds, S.E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 69–85. [Google Scholar]
- Gennaro, R.; Zanetti, M.; Benincasa, M.; Podda, E.; Miani, M. Pro-Rich antimicrobial peptides from animals: Structure, biological functions and mechanism of action. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2002, 8, 763–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberty, M.; Ades, S.; Uttenweiler-Joseph, S.; Brookhart, G.; Bushey, D.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Bulet, P. Insect immunity. Isolation from the lepidopteran Heliothis virescens of a novel insect defensin with potent antifungal activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 9320–9326. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, K.T.; Ourth, D.D. Viresin: A novel antibacterial protein from immune hemolymph of Heliothis virescens pupae. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destoumieux-Garzon, D.; Brehelin, M.; Bulet, P.; Boublik, Y.; Girad, P.-A.; Baghdiguian, S.; Zumbihl, R.; Escoubas, J.-M. Spodoptera frugiperda X-tox protein, an immune related defensin rosary, has lost the function of ancestral defensins. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6795. [Google Scholar]
- Girard, P.-A.; Boublik, Y.; Wheat, C.W.; Volkoff, A.-N.; Cousserans, F.; Brehelin, M.; Escoubas, J.-M. X-Tox: An atypical defensin derived family of immune-related proteins specific to Lepidoptera. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shandala, T.; Woodcock, J.M.P.Y.; Biggs, L.; Skoulakis, E.M.C.; Brooks, D.A.; Lopez, A.F. Drosophila 14-3-3ε has a crucial role in anti-microbial peptide secretion and innate immunity. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 123, 2165–2174. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, H.; Altincicek, B.; Glockner, G.; Vilcinskas, A. A comprehensive transcriptome and immune-gene repertoire of the lepidopteran model host Galleria mellonella. BMC Genomics 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabin, L.R.; Hanna, S.L.; Cherry, S. Innate antiviral immunity in Drosophila. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Flenniken, M.L.; Kunitomi, M.; Tassetto, M.; Andino, R. The Antiviral Role of RNA Interference. In Insect Viruses; Asgari, S., Johnson, K.N., Eds.; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2010; pp. 367–388. [Google Scholar]
- Aronstein, K.; Oppert, B.; Lorenzen, M.D. RNAi in Agriculturaly-Important Arthropods. In RNA Processing; Grabowski, P., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 157–180. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, W.; Peng, X.; Chen, R.; Du, B.; Zhu, L.; He, G. Knockdown of midgut genes by dsRNA-transgenic plant-mediated RNA interference in the hemipteran insect Nilaparvata lugens. PLoS One 2011, 6, e20504. [Google Scholar]
- Renwick, J.; Reeves, E.P.; Wientjes, F.B.; Kavanagh, K. Translocation of proteins homologous to human neutrophil p47phox and p67phox to the cell membrane in activated hemocytes of Galleria mellonella. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2007, 31, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popham, H.J.R.; Sun, R.; Shelby, K.S.; Robertson, J.D. Changes in trace metals in hemolymph of baculovirus-infected noctuid larvae. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 146, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popham, H.J.R.; Sun, R.; Shelby, K.S.; Robertson, J.D. Iron levels change in larval Heliothis virescens Tissues following baculovirus infection. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 148, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Deng, X.; Qian, H.; Wu, P.; Qin, G.; Guo, X. Cloning, characterization, and expression analysis of a novel BmGDAP1 gene from silkworm, Bombyx mori, involved in cytoplastic polyhedrosis virus infect. Gene 2012, 497, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Shi, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Yao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chang, C.; Shi, J.; Cao, J.; Kong, J.; et al. Arginine kinase is highly expressed in a resistant strain of silkworm (Bombyx mori, Lepidoptera): Implication of its role in resistance to Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 158B, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-Cerrillo, G.; Ferré, J.; de Maagd, R.A.; Herrero, S. Functional interactions between members of the REPAT family of insect pathogen-induced proteins. Insect Mol. Biol. 2012, 21, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.-B.; Tao, X.-Y.; Xue, X.-Y.; Wang, L.-J.; Chen, X.-Y. Cotton plants expressing CYP6AE14 dsRNAi show enhanced resistance to bollworms. Transgenic Res. 2011, 20, 655–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratzka, A.; Vogel, H.; Kliebenstein, D.J.; Mitchell-Olds, T.; Kroymann, J. Disarming the mustard oil bomb. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11223–11228. [Google Scholar]
- Schramm, K.; Vassao, D.G.; Reichelt, M.; Gershenzon, J.; Wittstock, U. Metabolism of glucosinolate-derived isothiocyanates to glutathione conjugates in generalist lepidopteran herbivores. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isom, S.C.; Spollen, W.G.; Blake, S.M.; Bauer, B.K.; Springer, G.K.; Prather, R.S. Transcriptional profiling of day 12 porcine embryonic disc and trophectoderm samples using ultra-deep sequencing technologies. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2010, 77, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popham, H.J.R.; Shelby, K.S.; Popham, T.W. Effect of dietary Se supplementation on resistance to baculovirus infection. Biol. Control 2005, 32, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, K.S.; Popham, H.J.R. Plasma phenoloxidase of larval Heliothis virescens is virucidal. J. Insect Sci. 2006, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, W.B.; Allen, M.L. RNAi-Mediated knockdown of IAP in Lygus lineolaris induces mortality in adult and pre-adult life stages. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2011, 138, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, C.; Bulmer, M.S. Molecular antifungal defenses in subterranean termites: RNAi reveals in vivo roles of termicins and GNBPs against a naturally encountered pathogen. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 36, 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Dong, Z.; Duan, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Xia, Q. Genome-Wide identification and immune response analysis of serine protease inhibitor genes in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. PLoS One 2012, 7, e31168. [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer, M.S.; Bachelet, I.; Raman, R.; Rosengaus, R.B.; Sasisekharan, R. Targeting an antimicrobial effector function in insect immunity as a pest control strategy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2009, 106, 12652–12657. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
