The Efficacy of Soleus Push-Up in Individuals with Prediabetes: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Interventions
2.3.1. OGTT
2.3.2. SPU Education
2.3.3. OGTT with SPU Intervention
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Participants
3.2. Performing SPU Results in Improved Postprandial Glucose Tolerance
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Pilot Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OGTT | Oral Glucose Tolerance Test |
| SPU | Soleus push-up |
| EMG | Electromyograph |
| OECD | Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development |
| IFG | Impaired fasting glucose |
| IGT | Impaired glucose tolerance |
| iAUC | Incremental area under the curve |
References
- World Health Organization. Global Action Plan on Physical Activity 2018–2030: More Active People for a Healthier World; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; 101p. [Google Scholar]
- Bluher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NEAK. World Diabetes Day—November 14. [Cukorbetegség Világnapja—November 14.]. Available online: https://www.neak.gov.hu/sajtoszoba/kozlemenyek_eu_napok/egeszsegugyi_vilagnapok_cukorbetegseg (accessed on 22 March 2024). (In Hungarian)
- IDF_Atlas_10th_Edition_2021.pdf. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/idfawp/resource-files/2021/07/IDF_Atlas_10th_Edition_2021.pdf (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Hamilton, M.T.; Hamilton, D.G.; Zderic, T.W. A potent physiological method to magnify and sustain soleus oxidative metabolism improves glucose and lipid regulation. iScience 2022, 25, 104869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization; International Diabetes Federation. Definition and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus and Intermediate Hyperglycaemia: Report of a WHO/IDF Consultation. 2006. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/43588 (accessed on 23 March 2024).
- NEFMI Guideline (HÉ 2010/104.) About the Dietotherapy of Diabetes Mellitus Among Adults [Szakmai Protokoll (HÉ 2010/104.) a Diabetes Mellitus Dietoterápiájáról Felénőttkorban]. Available online: https://jogkodex.hu/doc/7756017 (accessed on 22 March 2024). (In Hungarian).
- Forster, H.; Haslbeck, M.; Mehnert, H. Metabolic studies following the oral ingestion of different doses of glucose. Diabetes 1972, 21, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouns, F.; Bjorck, I.; Frayn, K.N.; Gibbs, A.L.; Lang, V.; Slama, G.; Wolever, T.M. Glycaemic index methodology. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2005, 18, 145–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO Standard No. 15197:2013; In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems—Requirements for Blood-Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Testing in Managing Diabetes Mellitus. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/54976.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Welcome to SENIAM. Available online: http://www.seniam.org/ (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Cresswell, A.G.; Loscher, W.N.; Thorstensson, A. Influence of gastrocnemius muscle length on triceps surae torque development and electromyographic activity in man. Exp. Brain Res. 1995, 105, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, R.A.; Hermanson, J.W. Horse soleus muscle: Postural sensor or vestigial structure? Anat. Rec. A Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 2006, 288, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkodi, B. Psoriasis, is it a microdamage of our “sixth sense”? A neurocentric view. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.H.; Lukacs, V.; de Nooij, J.C.; Zaytseva, D.; Criddle, C.R.; Francisco, A.; Jessell, T.M.; Wilkinson, K.A.; Patapoutian, A. Piezo2 is the principal mechanotransduction channel for proprioception. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolignier, S.; Eijkelkamp, N.; Wood, J.N. Mechanical allodynia. Pflug. Arch. 2015, 467, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.J.; Son, J.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Ju, J.S.; Park, M.K.; Lee, M.K.; Ahn, D.K. Blockade of piezo2 pathway attenuates inflammatory and neuropathic pain in the orofacial area. Pain Res. Manag. 2024, 2024, 9179928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Tian, H.; Tian, Y.; Fu, X. A hierarchical mechanotransduction system: From macro to micro. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2302327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchyna, T.M. Piezo channels and gsmtx4: Two milestones in our understanding of excitatory mechanosensitive channels and their role in pathology. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2017, 130, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.M.; Moehring, F.; Itson-Zoske, B.; Fan, F.; Stucky, C.L.; Hogan, Q.H.; Yu, H. Piezo2 mechanosensitive ion channel is located to sensory neurons and nonneuronal cells in rat peripheral sensory pathway: Implications in pain. Pain 2021, 162, 2750–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Leddy, H.A.; Chen, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Zelenski, N.A.; McNulty, A.L.; Wu, J.; Beicker, K.N.; Coles, J.; Zauscher, S.; et al. Synergy between piezo1 and piezo2 channels confers high-strain mechanosensitivity to articular cartilage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5114–E5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harraz, O.F.; Klug, N.R.; Senatore, A.J.; Hill-Eubanks, D.C.; Nelson, M.T. Piezo1 is a mechanosensor channel in central nervous system capillaries. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.Z.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Heo, J.; Sachs, F. A mechanosensitive ion channel regulating cell volume. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2010, 298, C1424–C1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rode, B.; Shi, J.; Endesh, N.; Drinkhill, M.J.; Webster, P.J.; Lotteau, S.J.; Bailey, M.A.; Yuldasheva, N.Y.; Ludlow, M.J.; Cubbon, R.M.; et al. Piezo1 channels sense whole body physical activity to reset cardiovascular homeostasis and enhance performance. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonkodi, B. Delayed onset muscle soreness and critical neural microdamage-derived neuroinflammation. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jammal Salameh, L.; Bitzenhofer, S.H.; Hanganu-Opatz, I.L.; Dutschmann, M.; Egger, V. Blood pressure pulsations modulate central neuronal activity via mechanosensitive ion channels. Science 2024, 383, eadk8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hamill, O.P. Piezo2-peripheral baroreceptor channel expressed in select neurons of the mouse brain: A putative mechanism for synchronizing neural networks by transducing intracranial pressure pulses. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2021, 20, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkodi, B. Progressive irreversible proprioceptive piezo2 channelopathy-induced lost forced peripheral oscillatory synchronization to the hippocampal oscillator may explain the onset of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathomechanism. Cells 2024, 13, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daulhac, L.; Mallet, C.; Courteix, C.; Etienne, M.; Duroux, E.; Privat, A.M.; Eschalier, A.; Fialip, J. Diabetes-induced mechanical hyperalgesia involves spinal mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in neurons and microglia via n-methyl-d-aspartate-dependent mechanisms. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Ohki, I.; Murakami, K.; Ozawa, S.; Wang, Y.; Murakami, M. The gateway reflex regulates tissue-specific autoimmune diseases. Inflamm. Regen. 2024, 44, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkodi, B.; Marsovszky, L.; Csorba, A.; Balog, A.; Kopper, B.; Keller-Pinter, A.; Nagy, Z.Z.; Resch, M.D. Disrupted neural regeneration in dry eye secondary to ankylosing spondylitis-with a theoretical link between piezo2 channelopathy and gateway reflex, wdr neurons, and flare-ups. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.A.; Ellis, S.; Bain, J. Carbonic anhydrase activity in skeletal muscle fiber types, axons, spindles, and capillaries of rat soleus and extensor digitorum longus muscles. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1982, 30, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, R.; Vasques, J.; Duarte, J.A.; Cabri, J.M. Knee proprioception after exercise-induced muscle damage. Int. J. Sports Med. 2010, 31, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschenes, M.R.; Brewer, R.E.; Bush, J.A.; McCoy, R.W.; Volek, J.S.; Kraemer, W.J. Neuromuscular disturbance outlasts other symptoms of exercise-induced muscle damage. J. Neurol. Sci. 2000, 174, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, M.; Blannin, A.K.; Walsh, N.P.; Field, C.N.; Pritchard, J.C. Effect of exercise-induced muscle damage on the blood lactate response to incremental exercise in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1998, 77, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.C.; Huang, M.J.; Lima, L.C.R.; Chou, T.Y.; Wang, H.H.; Tu, J.H.; Lin, S.C.; Nosaka, K. Changes in insulin sensitivity and lipid profile markers following initial and secondary bouts of multiple eccentric exercises. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 917317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.J.; Watson, S.; Zanato, C.; Dall, S.; De Nooij, J.C.; Pace-Bonello, B.; Shenton, F.C.; Sanger, H.E.; Heinz, B.A.; Broad, L.M.; et al. The atypical ‘hippocampal’ glutamate receptor coupled to phospholipase d that controls stretch-sensitivity in primary mechanosensory nerve endings is homomeric purely metabotropic gluk2. Exp. Physiol. 2024, 109, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkodi, B.; Radovits, T.; Csulak, E.; Kopper, B.; Sydó, N.; Merkely, B. Orthostasis is impaired due to fatiguing intensive acute concentric exercise succeeded by isometric weight-loaded wall-sit in delayed-onset muscle soreness: A pilot study. Sports 2023, 11, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abarkan, M.; Gaitan, J.; Lebreton, F.; Perrier, R.; Jaffredo, M.; Mulle, C.; Magnan, C.; Raoux, M.; Lang, J. The glutamate receptor gluk2 contributes to the regulation of glucose homeostasis and its deterioration during aging. Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Barghouth, M.; Dou, H.; Luan, C.; Wang, Y.; Karagiannopoulos, A.; Jiang, X.; Krus, U.; Fex, M.; Zhang, Q.; et al. A critical role of the mechanosensor piezo1 in glucose-induced insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



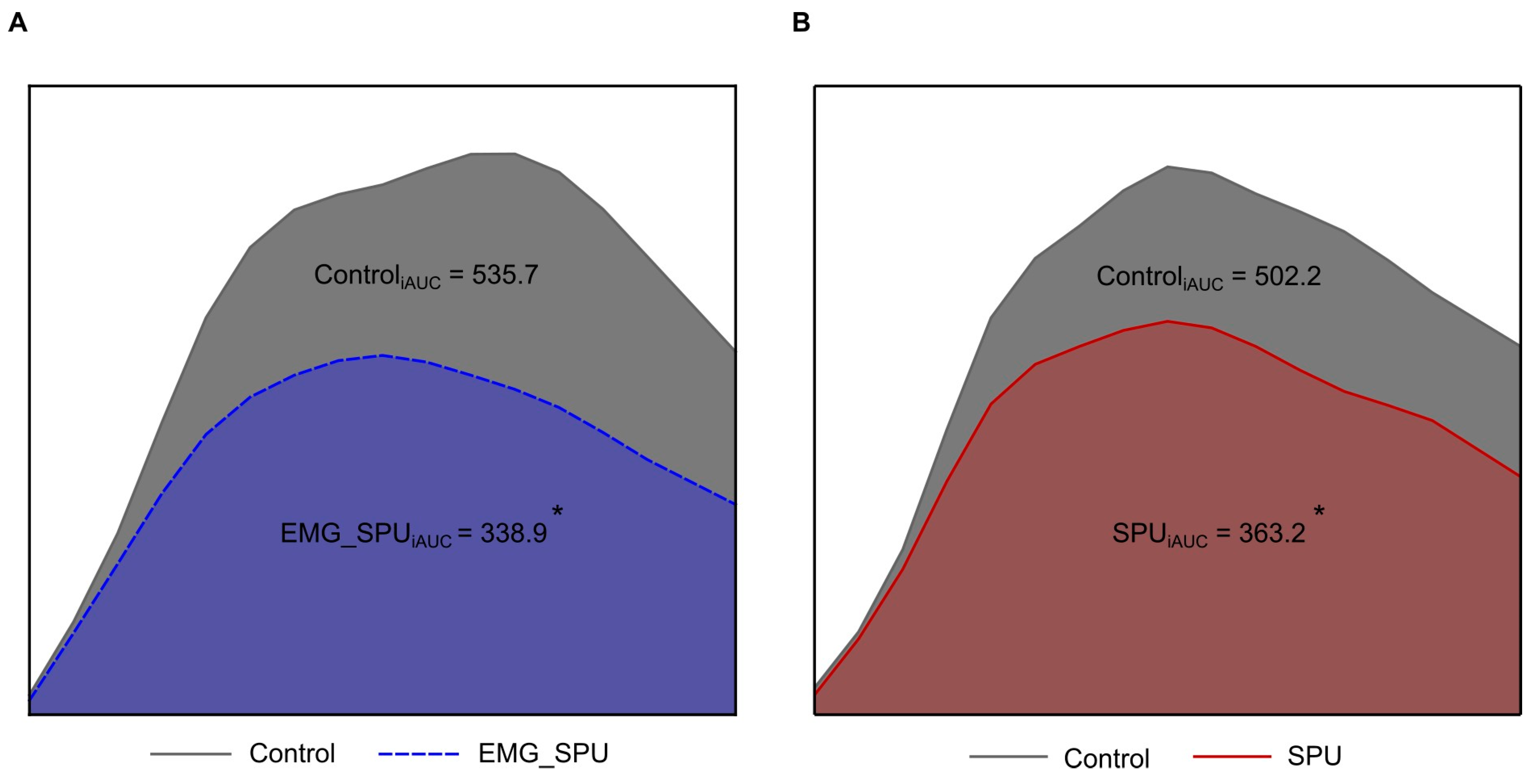
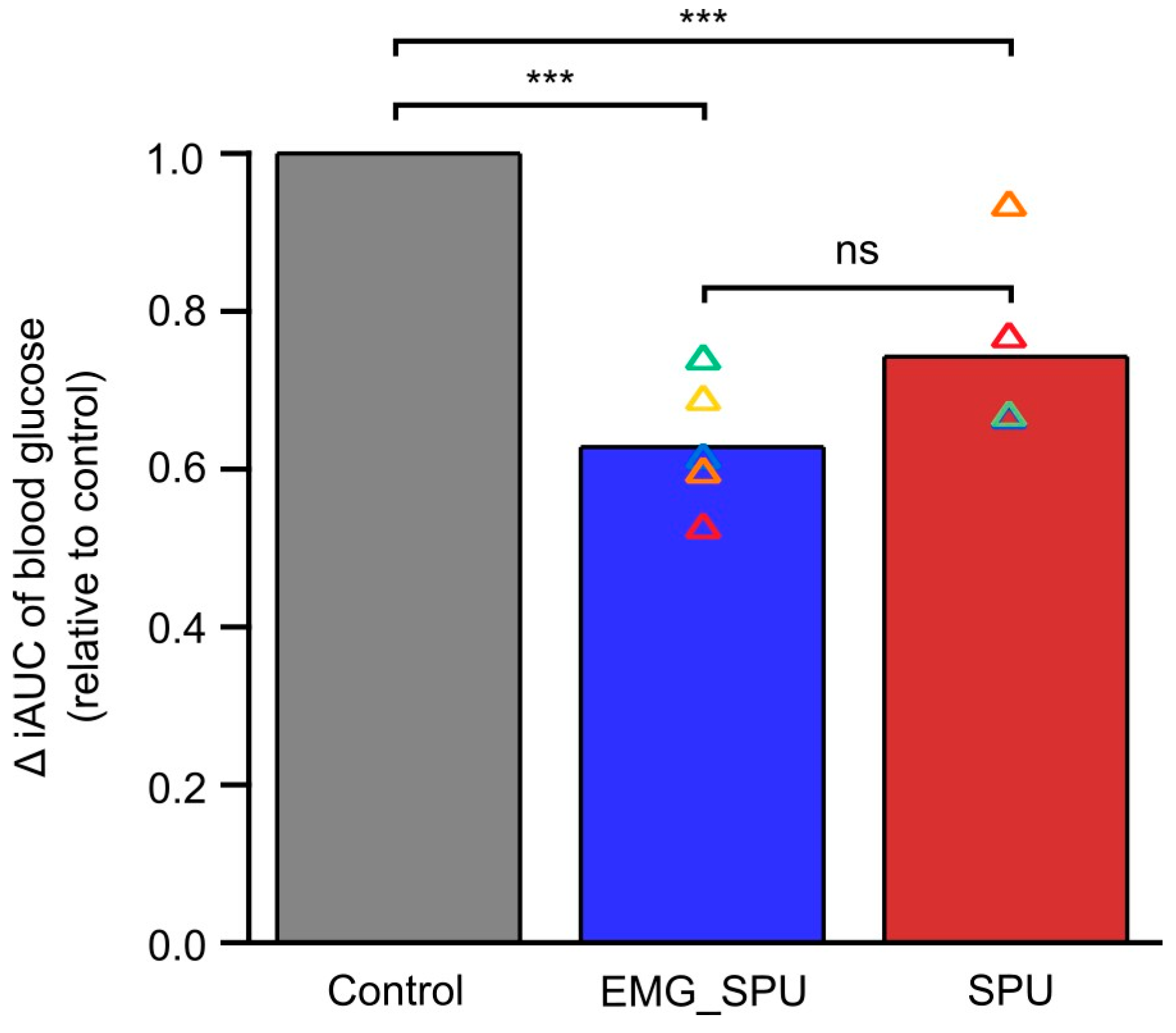
| OGTT | With EMG Feedback | Without EMG Feedback | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (Minutes) | Control (n = 5) | SPU (n = 5) | Δmmol/L | Control (n = 5) | SPU (n = 5) | Δmmol/L |
| 0 | 6.2 ± 0.1 | 6.2 ± 0.1 | −0.1 ± 0.1 | 6.3 ± 0.1 | 6.2 ± 0.1 | −0.1 ± 0.1 |
| 15 | 8 ± 0.2 | 7.7 ± 0.2 | −0.3 ± 0.2 | 7.8 ± 0.1 | 7.6 ± 0.1 | −0.2 ± 0.1 |
| 30 | 10.4 ± 0.5 | 9.1 ± 0.3 | −1.3 ± 0.3 * | 10.4 ± 0.3 | 9.5 ± 0.3 | −1 ± 0.2 * |
| 45 | 11.6 ± 0.4 | 9.8 ± 0.4 | −1.8 ± 0.2 *** | 11.4 ± 0.4 | 10.1 ± 0.3 | −1.3 ± 0.3 * |
| 60 | 11.9 ± 0.4 | 10 ± 0.5 | −1.8 ± 0.1 ** | 12.1 ± 0.3 | 10.4 ± 0.3 | −1.7 ± 0.3 * |
| 75 | 12.2 ± 0.4 | 9.8 ± 0.4 | −2.5 ± 0.2 *** | 11.8 ± 0.3 | 10.1 ± 0.4 | −1.7 ± 0.4 * |
| 90 | 12 ± 0.4 | 9.4 ± 0.5 | −2.6 ± 0.3 ** | 11.4 ± 0.3 | 9.6 ± 0.5 | −1.8 ± 0.3 * |
| 105 | 11.1 ± 0.5 | 8.8 ± 0.4 | −2.3 ± 0.4 * | 10.7 ± 0.4 | 9.3 ± 0.4 | −1.4 ± 0.4 * |
| 120 | 10 ± 0.5 | 8.3 ± 0.4 | −1.7 ± 0.4 * | 10.1 ± 0.3 | 8.7 ± 0.4 | −1.5 ± 0.3 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elek, D.; Tóth, M.; Sonkodi, B.; Ács, P.; Kovács, G.L.; Tardi, P.; Melczer, C. The Efficacy of Soleus Push-Up in Individuals with Prediabetes: A Pilot Study. Sports 2025, 13, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13030081
Elek D, Tóth M, Sonkodi B, Ács P, Kovács GL, Tardi P, Melczer C. The Efficacy of Soleus Push-Up in Individuals with Prediabetes: A Pilot Study. Sports. 2025; 13(3):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13030081
Chicago/Turabian StyleElek, Dávid, Miklós Tóth, Balázs Sonkodi, Pongrác Ács, Gábor L. Kovács, Péter Tardi, and Csaba Melczer. 2025. "The Efficacy of Soleus Push-Up in Individuals with Prediabetes: A Pilot Study" Sports 13, no. 3: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13030081
APA StyleElek, D., Tóth, M., Sonkodi, B., Ács, P., Kovács, G. L., Tardi, P., & Melczer, C. (2025). The Efficacy of Soleus Push-Up in Individuals with Prediabetes: A Pilot Study. Sports, 13(3), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13030081






