Fabrication of a Novel Ta(Zn)O Thin Film on Titanium by Magnetron Sputtering and Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation for Cell Biocompatibilities and Antibacterial Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
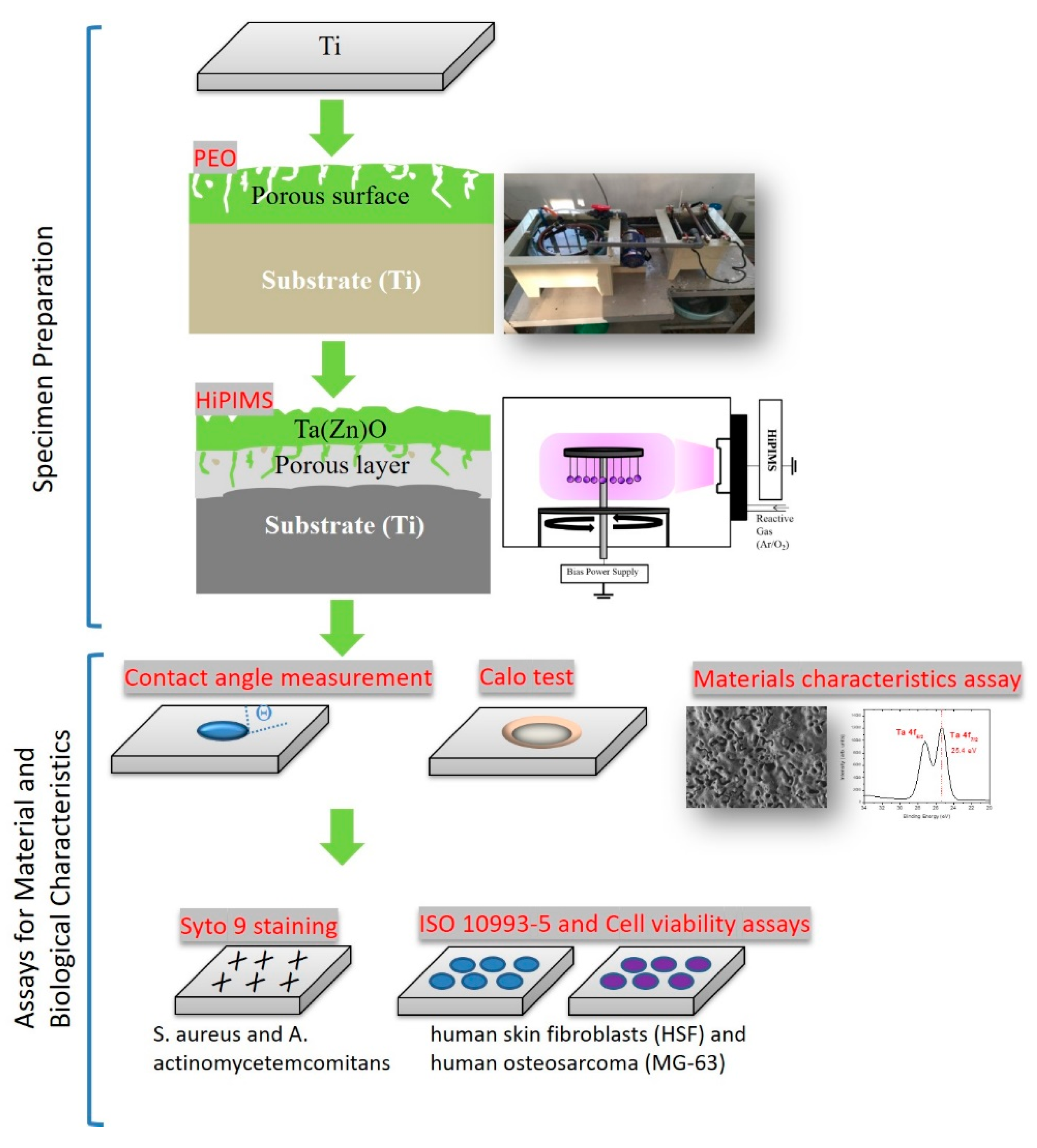
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Materials Characteristics Measurement
2.3. Contact Angle Measurement
2.4. Antibacterial Analyses
2.5. Biocompatibility Tests of Cytotoxicity and Cell Viability
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure and Surface Morphology Analyses
3.2. Antibacterial Properties
3.3. Biocompatibility Tests of Cytotoxicity and Cell Viability
4. Conclusions
- 1)
- Scanning electron microscopy and 3D laser microscopy were used to observe the morphology of the specimens. The surfaces of the Ti specimens that had been subjected to PEO were fully covered with a TiO2 layer. Through the use of HiPIMS, the deposition of the Ta2O5 and Ta(Zn)O films would not affect the porous structure on the specimen surface. The Ta2O5 and Ta(Zn)O-deposited Ti had high surface roughness and this surface roughening and porous structure may influence the biocompatibility. The results of water contact angle measurement demonstrated that the pure Ti substrate, Ta2O5, and Ta(Zn)O specimen had contact angles of 43.13 ± 10.0°, 3.3 ± 0.36°, and 16.75 ± 3.7°, respectively. The deposited Ta2O5 coating on the porous Ti was capable of enhancing surface wettability, and adding Zn to thin films increased surface hydrophobicity as compared to Ta2O5. The deposited Ta(Zn)O contained amorphous Ta2O5 and crystalline ZnO. The development of the crystalline ZnO structure during growth is controlled by the HiPIMS deposition process.
- 2)
- Antibacterial properties against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria were performed. Compared to the untreated Ti, both specimens with Ta2O5 and Ta(Zn)O thin films showed lower intensity of the relative fluorescence with Syto 9 stain in both these two bacterial colonies, and they had improved antibacterial abilities against S. aureus and A. actinomycetemcomitans. The Ta(Zn)O deposited by HiPIMS exhibited the lowest intensity in both of the S. aureus and A. actinomycetemcomitans bacterial colonies, and it showed the best antibacterial performance.
- 3)
- The results of the ISO-10993-5 cell cytotoxicity and cell viability MTT assay tests revealed that the Ta2O5 or Ta(Zn)O coated Ti had better cell viability and lower cytotoxicity in HSF cells, and both coatings possessed high biocompatibilities in this study. The cell activity of Ta(Zn)O coated Ti decreased slightly when reacting to the MG63 cells. The result showed that the Ta2O5 coating on Ti surface with porous structure improved adhesion, migration, and proliferation for the osteoblastic cell. Due to the different properties of cells, HSF and MG-63 cells represented different behaviors of cell cytoxicity and cell viability in each kind of coating specimens on Ti.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, M.; Chen, Y.; Biao, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B. Bio-functionalization of biomedical metals. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Thouas, G.A. Metallic implant biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2015, 87, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devgan, S.; Sidhu, S.S. Evolution of surface modification trends in bone related biomaterials: A review. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 233, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouirfa, H.; Bouloussa, H.; Migonney, V.; Falentin-Daudré, C. Review of titanium surface modification techniques and coatings for antibacterial applications. Acta Biomater. 2019, 83, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafuerte, K.R.V.; Martinez, C.D.J.H.; Dantas, F.T.; Carrara, H.H.A.; dos Reis, F.J.C.; Palioto, D.B. The impact of chemotherapeutic treatment on the oral microbiota of patients with cancer: A systematic review. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2018, 125, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortazavi, G.; Jiang, J.; Meletis, E.I. Investigation of the plasma electrolytic oxidation mechanism of titanium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 488, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, C.E.; Golozar, M.; Best, S.M.; Brooks, R.A. Cell response to plasma electrolytic oxidation surface-modified low-modulus β-type titanium alloys. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 176, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, O.; Gururaj, S.; Pujari-Palmer, S.; Karlsson Ott, M.; Strømme, M.; Engqvist, H.; Welch, K. Titanium surface modification to enhance antibacterial and bioactive properties while retaining biocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-T.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Huang, H.-L.; Hsu, J.-T.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wu, A.Y.-J. Characterization and antibacterial performance of bioactive Ti–Zn–O coatings deposited on titanium implants. Thin Solid Films 2013, 528, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Cheng, M.; Jiang, G.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Tantalum implanted entangled porous titanium promotes surface osseointegration and bone ingrowth. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wei, S.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, H. Effect of Ta2O5/TiO2 thin film on mechanical properties, corrosion and cell behavior of the NiTi alloy implanted with tantalum. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, B.R.; Sporer, S.; Poggie, R.A.; Della Valle, C.J.; Jacobs, J.J. Experimental and clinical performance of porous tantalum in orthopedic surgery. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4671–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanzlik, J.A.; Day, J.S.; Contributors, A.; Group, I.R.S. Bone ingrowth in well-fixed retrieved porous tantalum implants. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Issack, P.S. Use of porous tantalum for acetabular reconstruction in revision hip arthroplasty. JBJS 2013, 95, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencharit, S.; Byrd, W.C.; Altarawneh, S.; Hosseini, B.; Leong, A.; Reside, G.; Morelli, T.; Offenbacher, S. Development and applications of porous tantalum trabecular metal-enhanced titanium dental implants. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.-Y.; Huang, H.-L.; Chen, H.-J.; Lai, C.-H.; Wen, C.-Y. Antibacterial properties and cytocompatibility of tantalum oxide coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 259, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareci, D.; Chelariu, R.; Gordin, D.-M.; Ungureanu, G.; Gloriant, T. Comparative corrosion study of Ti–Ta alloys for dental applications. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 3625–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nayak, T.R.; Hong, H.; Cai, W. Biomedical applications of zinc oxide nanomaterials. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, H.-J.; Cho, Y.-E.; Kim, T.; Shin, H.-I.; Kwun, I.-S. Zinc may increase bone formation through stimulating cell proliferation, alkaline phosphatase activity and collagen synthesis in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2010, 4, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Yamaguchi, R. Action of zinc on bone metabolism in rats: Increases in alkaline phosphatase activity and DNA content. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1986, 35, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Cao, H.; Qiao, Y.; Meng, F.; Zhu, H.; Liu, X. Osteogenic activity and antibacterial effect of zinc ion implanted titanium. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 117, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghupathi, K.R.; Koodali, R.T.; Manna, A.C. Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, K.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J.; Ho, W. Review on the improvement of the photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of ZnO. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 727, 792–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banoee, M.; Seif, S.; Nazari, Z.E.; Jafari-Fesharaki, P.; Shahverdi, H.R.; Moballegh, A.; Moghaddam, K.M.; Shahverdi, A.R. ZnO nanoparticles enhanced antibacterial activity of ciprofloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2010, 93, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, H.; Geng, Z.; Huang, X.; Hang, R.; Ma, Y.; Yao, X.; Tang, B. Microstructure and cytotoxicity evaluation of duplex-treated silver-containing antibacterial TiO2 coatings. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 45, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-L.; Tsai, M.-T.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chang, Y.-Y. Antibacterial and biological characteristics of tantalum oxide coated titanium pretreated by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Thin Solid Films 2019, 688, 137268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greczynski, G.; Zhirkov, I.; Petrov, I.; Greene, J.E.; Rosen, J. Control of the metal/gas ion ratio incident at the substrate plane during high-power impulse magnetron sputtering of transition metals in Ar. Thin Solid Films 2017, 642, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alias, R.; Mahmoodian, R.; Genasan, K.; Vellasamy, K.M.; Hamdi Abd Shukor, M.; Kamarul, T. Mechanical, antibacterial, and biocompatibility mechanism of PVD grown silver–tantalum-oxide-based nanostructured thin film on stainless steel 316L for surgical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 107, 110304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rack, P.D.; Potter, M.D.; Woodard, A.; Kurinec, S. Negative ion resputtering in Ta2Zn3O8 thin films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1999, 17, 2805–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Hong, L.Y.; Jung, J.; Kim, D.-P.; Kim, H.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, J.R.; Ree, M. The biocompatability of mesoporous inorganic–organic hybrid resin films with ionic and hydrophilic characteristics. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, I.; Barna, P.B.; Hultman, L.; Greene, J.E. Microstructural evolution during film growth. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2003, 21, S117–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirica, E.; Kowach, G.; Du, H. Modified Structure Zone Model to Describe the Morphological Evolution of ZnO Thin Films Deposited by Reactive Sputtering. Cryst. Growth Des. 2004, 4, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozetic, M.; Vesel, A.; Primc, G.; Eisenmenger-Sittner, C.; Bauer, J.; Eder, A.; Schmid, G.H.S.; Ruzic, D.N.; Ahmed, Z.; Barker, D.; et al. Recent developments in surface science and engineering, thin films, nanoscience, biomaterials, plasma science, and vacuum technology. Thin Solid Films 2018, 660, 120–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sul, Y.-T. The significance of the surface properties of oxidized titanium to the bone response: Special emphasis on potential biochemical bonding of oxidized titanium implant. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3893–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennakesavulu, K.; Reddy, M.M.; Reddy, G.R.; Rabel, A.M.; Brijitta, J.; Vinita, V.; Sasipraba, T.; Sreeramulu, J. Synthesis, characterization and photo catalytic studies of the composites by tantalum oxide and zinc oxide nanorods. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1091, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dai, W.; Wu, G.; Guan, N.; Li, L. Fabrication of Ta2O5 films on tantalum substrate for efficient photocatalysis. Catal. Commun. 2015, 65, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NuLi, Y.-N.; Fu, Z.-W.; Chu, Y.-Q.; Qin, Q.-Z. Electrochemical and electrochromic characteristics of Ta2O5–ZnO composite films. Solid State Ionics 2003, 160, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezek, J.; Novák, P.; Houška, J.; Pajdarová, A.D.; Kozák, T. High-rate reactive high-power impulse magnetron sputtering of transparent conductive Al-doped ZnO thin films prepared at ambient temperature. Thin Solid Films 2019, 679, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A.N.; Shamberger, P.J.; Hu, J.J.; Muratore, C.; Bultman, J.E.; Voevodin, A.A. Microstructure of ZnO thin films deposited by high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2015, 579, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-Y.; Lai, C.-H.; Hsu, J.-T.; Tang, C.-H.; Liao, W.-C.; Huang, H.-L. Antibacterial properties and human gingival fibroblast cell compatibility of TiO 2/Ag compound coatings and ZnO films on titanium-based material. Clin. Oral Investig. 2012, 16, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidambe, A. Biocompatibility of advanced manufactured titanium implants—A review. Materials 2014, 7, 8168–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, F.; Li, Z.; Liu, X. Synthesis of tantalum thin films on titanium by plasma immersion ion implantation and deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 229, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Yang, L.; Pan, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Tang, T.; Wei, J. Influences of tantalum pentoxide and surface coarsening on surface roughness, hydrophilicity, surface energy, protein adsorption and cell responses to PEEK based biocomposite. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 174, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagherian, B.H.; Claridge, R.J. The Use of Tantalum Metal in Foot and Ankle Surgery. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 50, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paolis, M.; Zucchini, R.; Romagnoli, C.; Romantini, M.; Mariotti, F.; Donati, D.M. Middle term results of tantalum acetabular cups in total hip arthroplasty following pelvic irradiation. Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 2019, 53, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidulych, M.; Pleskunov, P.; Kratochvíl, J.; Mašková, H.; Kočová, P.; Nikitin, D.; Hanuša, J.; Kyliána, K.; Štěrbabc, J.; Biederman, H.; et al. Convex vs concave surface nano-curvature of Ta2O5 thin films for tailoring the osteoblast adhesion. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 393, 125805–125812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannozzi, L.; Gouveia, P.J.; Pingue, P.; Canale, C.; Ricotti, L. Novel ultra-thin films based on a blend of PEG-b-PCL and PLLA and doped with ZnO nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 21398–21410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.; Schwartz, Z.; Hummert, T.; Schraub, D.; Simpson, J.; Lankford, J., Jr.; Dean, D.D.; Cochran, D.L.; Boyan, B. Effect of titanium surface roughness on proliferation, differentiation, and protein synthesis of human osteoblast-like cells (MG63). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1995, 29, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, R. The effect of surface roughness on fibroblast adhesion in vitro. Injury 1996, 27, S/C38–S/C43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Van Der Mei, H.C.; Subbiahdoss, G.; de Vries, J.; Rustema-Abbing, M.; Kuijer, R.; Busscher, H.J.; Ren, Y. Soft tissue integration versus early biofilm formation on different dental implant materials. Dent. Mater. 2014, 30, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wytrwal, M.; Koczurkiewicz, P.; Zrubek, K.; Niemiec, W.; Michalik, M.; Kozik, B.; Szneler, E.; Bernasik, A.; Madeja, Z.; Nowakowska, M.; et al. Growth and motility of human skin fibroblasts on multilayer strong polyelectrolyte films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 461, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.-L.; Tsai, M.-T.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Lin, Y.-J.; Hsu, J.-T. Fabrication of a Novel Ta(Zn)O Thin Film on Titanium by Magnetron Sputtering and Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation for Cell Biocompatibilities and Antibacterial Applications. Metals 2020, 10, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050649
Huang H-L, Tsai M-T, Chang Y-Y, Lin Y-J, Hsu J-T. Fabrication of a Novel Ta(Zn)O Thin Film on Titanium by Magnetron Sputtering and Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation for Cell Biocompatibilities and Antibacterial Applications. Metals. 2020; 10(5):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050649
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Heng-Li, Ming-Tzu Tsai, Yin-Yu Chang, Yi-Jyun Lin, and Jui-Ting Hsu. 2020. "Fabrication of a Novel Ta(Zn)O Thin Film on Titanium by Magnetron Sputtering and Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation for Cell Biocompatibilities and Antibacterial Applications" Metals 10, no. 5: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050649
APA StyleHuang, H.-L., Tsai, M.-T., Chang, Y.-Y., Lin, Y.-J., & Hsu, J.-T. (2020). Fabrication of a Novel Ta(Zn)O Thin Film on Titanium by Magnetron Sputtering and Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation for Cell Biocompatibilities and Antibacterial Applications. Metals, 10(5), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050649





