Production of Refined and Modified Closed-Cell Aluminum Foams by Melt-Foaming Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Tooling
2.2. Fabrication of A356 Aluminum Alloy Foams
2.3. Foam Characterization
3. Results
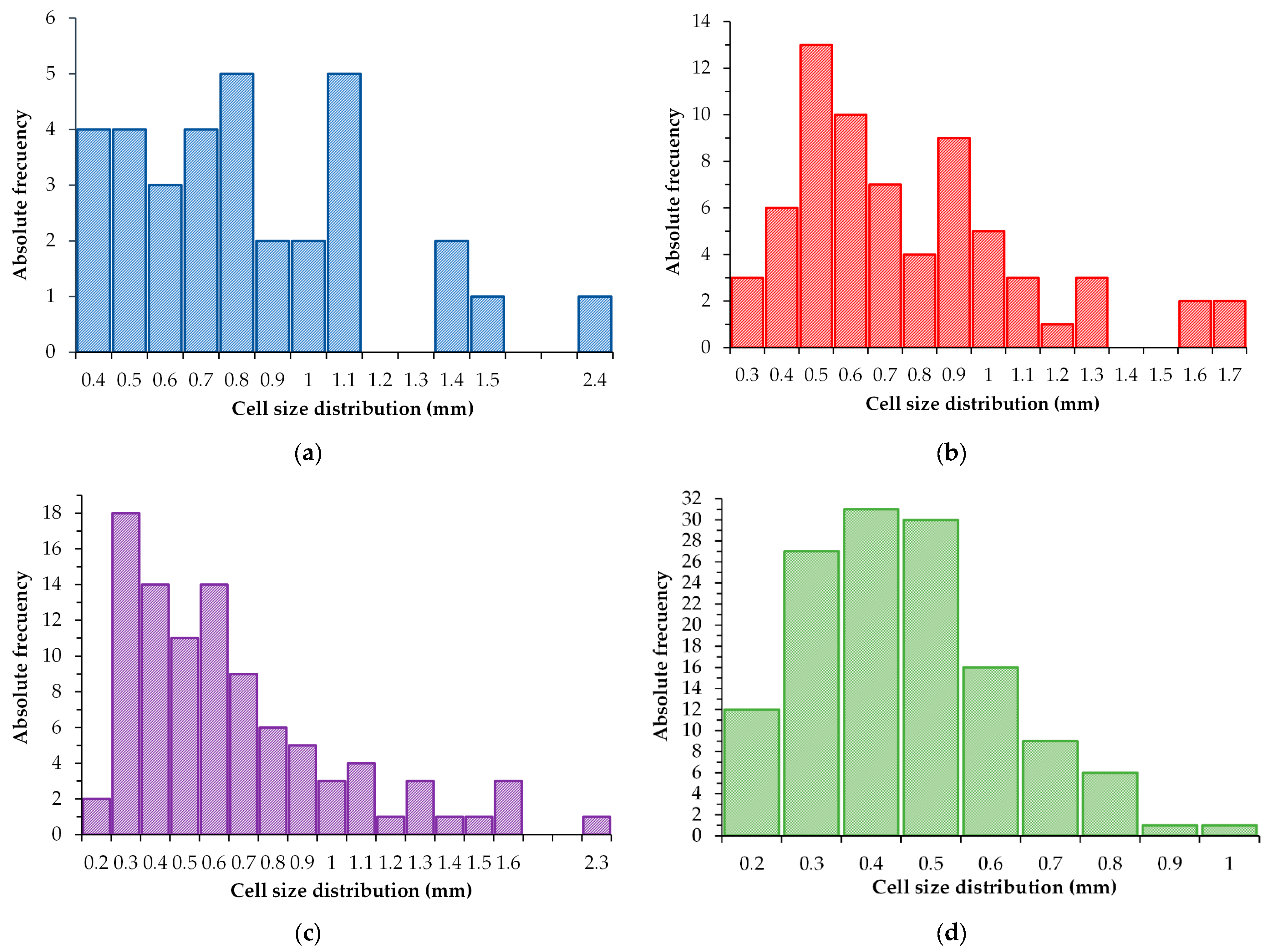
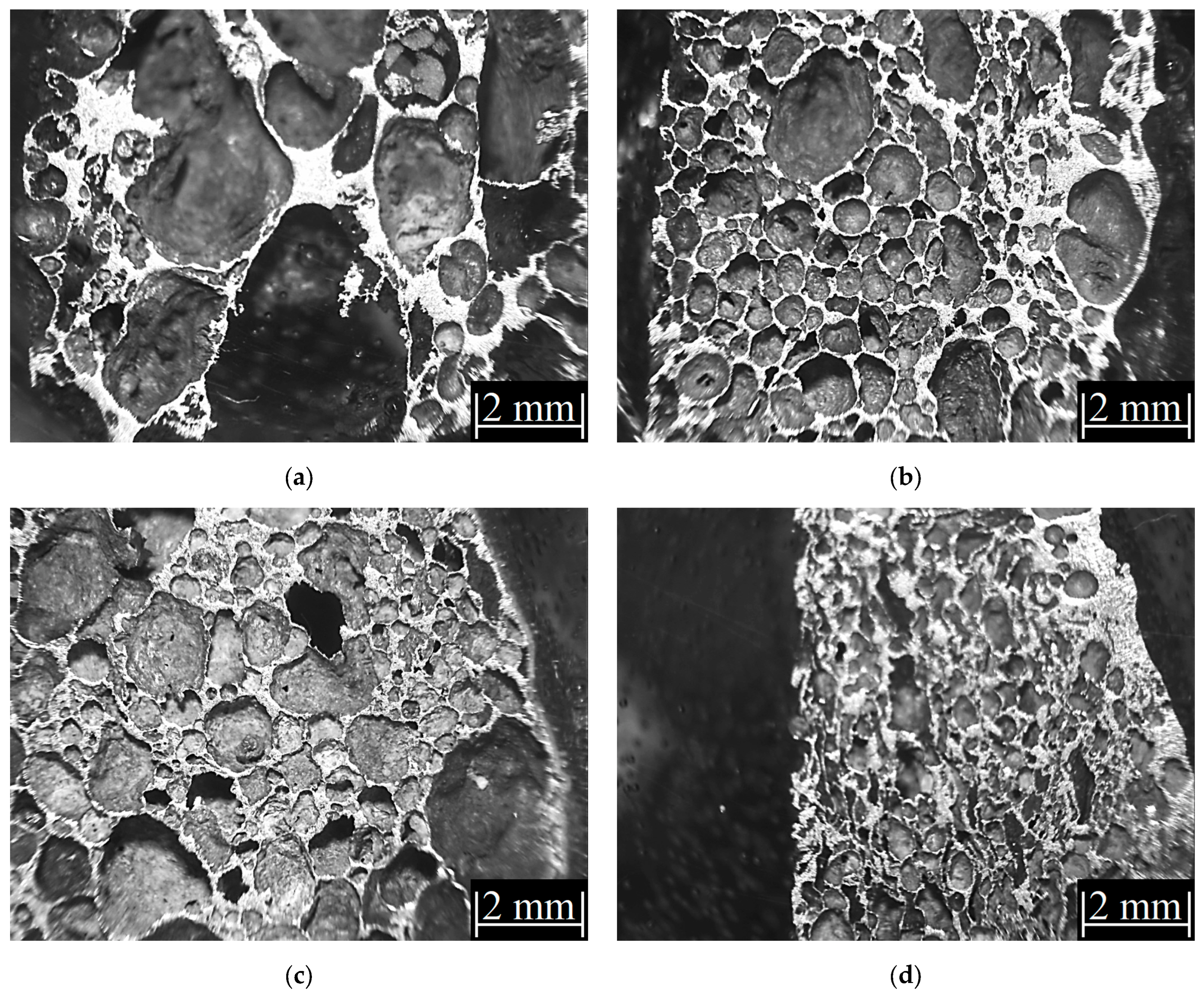
3.1. Structure Properties of the A356 Aluminum Alloys Foams
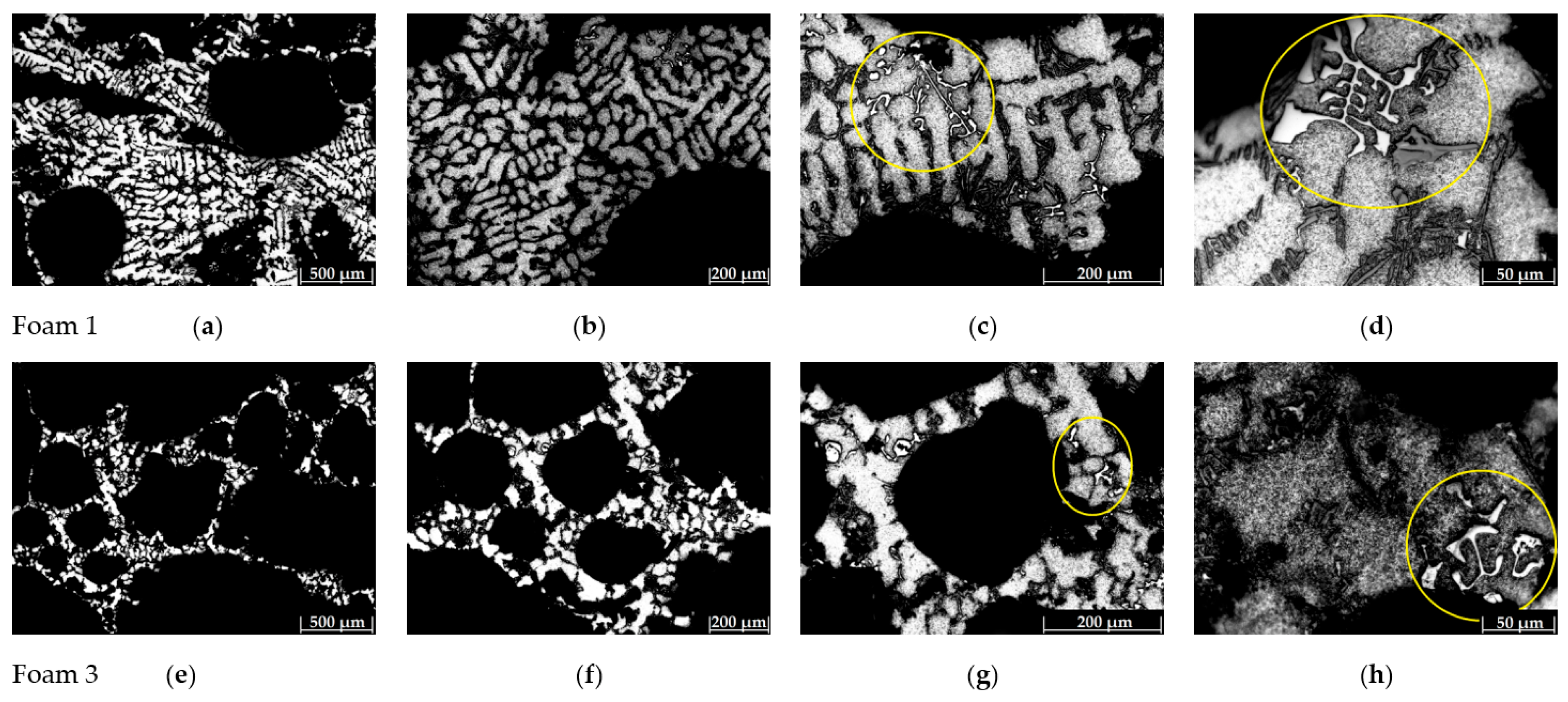
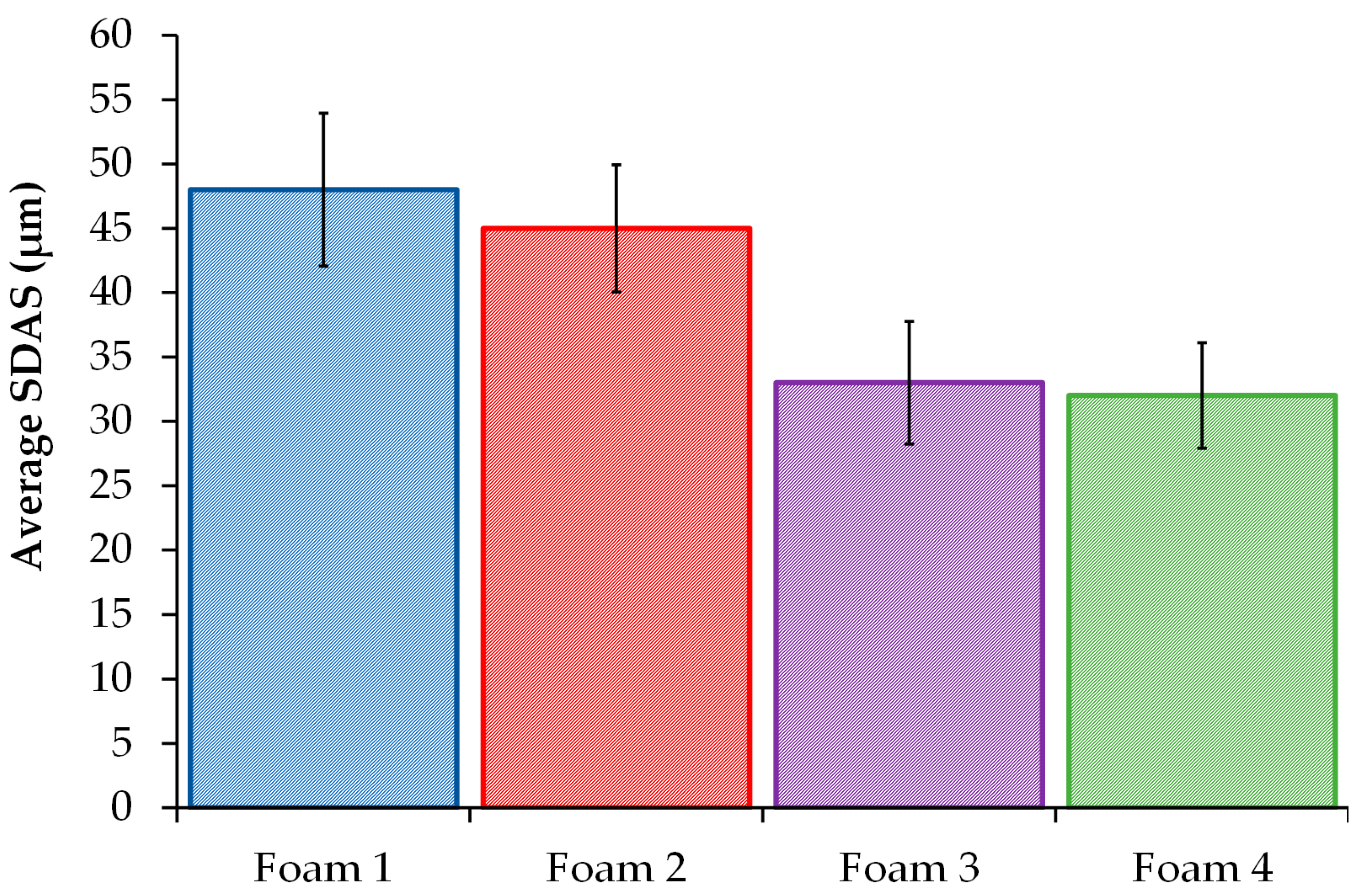
3.2. SDAS Determination
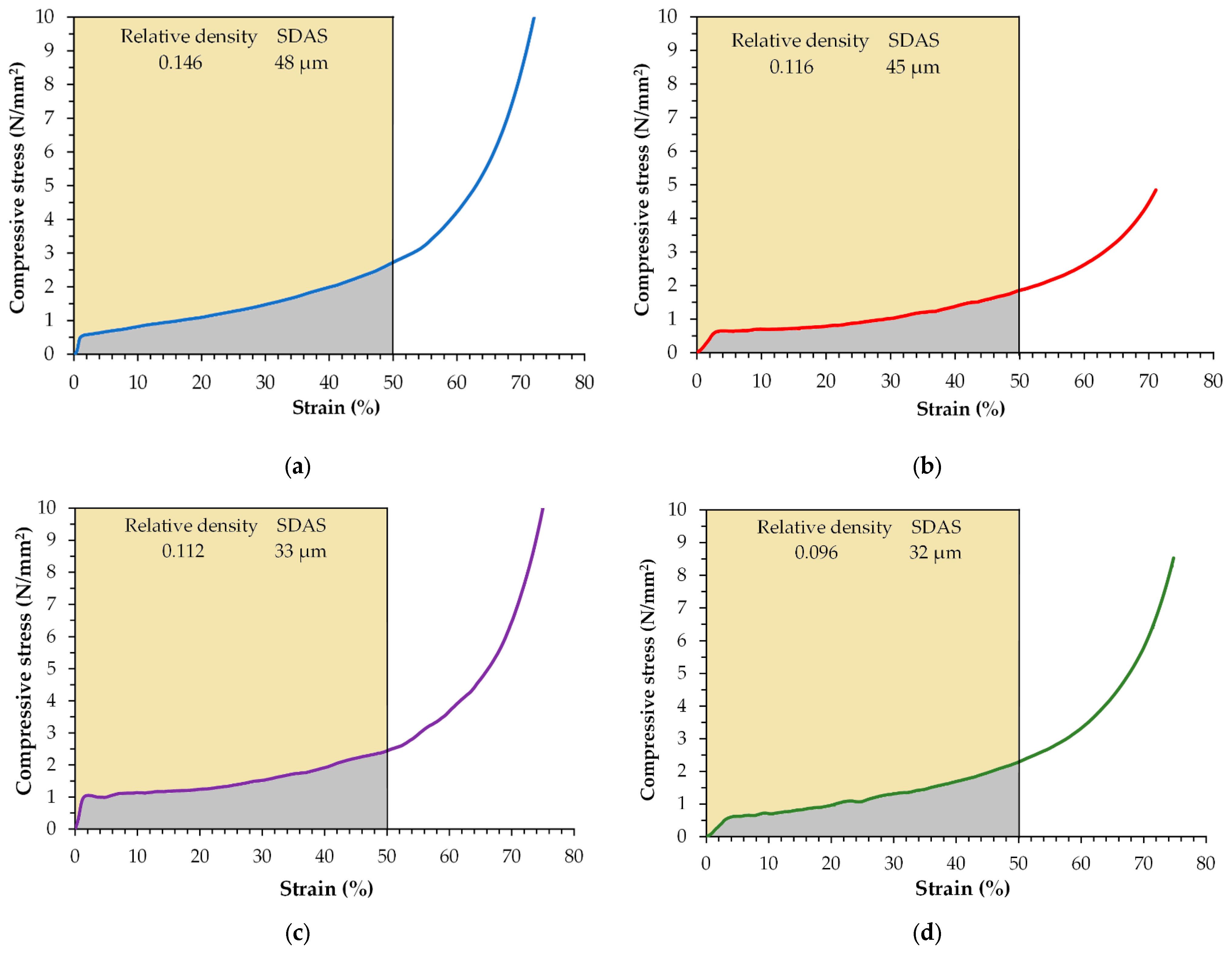
3.3. Compressive Behavior
4. Conclusions
- 1.
- A melt route process was established to obtain closed-cell A356 aluminum alloy foams refined and modified using 0.05% of Al-5Ti-1B and Al-10Sr of the mass charge, respectively, to 700 °C.
- 2.
- A uniform-size cell distribution with the lowest relative density and the highest porosity was obtained for the refined and modified A356 aluminum alloy foams.
- 3.
- The high solidification rate imposed during the cooling step allows obtaining lower SDAS values in foam regions closer to the mold walls; furthermore, the lowest SDAS values were obtained in the refined foams where the Al-5Ti-1B master alloy effectively refined the grain size of the A356 aluminum alloy foam while the addition of the Al-10Sr master alloy caused the formation of solid solution dendrites and a fine irregular fibrous form of silicon rather than the usual acicular structure.
- 4.
- The modification and refinement of the cell wall is a feasible way to improve foam performance, as was pointed out by the compression tests where the highest energy-absorption capacity was obtained for the foams with the lowest SDAS.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, C.D. Variability in the tensile properties of squeeze-cast Al-Si-Cu-Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 488, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejiofor, J.U.; Reddy, R.G. Developments in the processing and properties of particulate Al-Si composites. JOM 1997, 49, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.X.; Li, R.D.; Zhao, Y.H.; He, L.Z.; Li, C.X.; Guan, H.R.; Hu, Z.Q. Age-hardening behavior of cast Al–Si base alloy. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 2096–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeenager, V.K.; Pancholi, V.; Daniel, B.S.S. The effect of aging on energy absorption capability of closed cell aluminum foam. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 585, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozan, S.; Taskin, M.; Kolukisa, S.; Ozerdem, M.S. Application of ANN in the prediction of the pore concentration of aluminum metal foams manufactured by powder metallurgy methods. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2008, 39, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Kader, M.A.; Hazell, P.J.; Brown, A.D.; Saadaftar, M.; Quadir, M.Z.; Escobedo, J.P. Investigation of microstructural and mechanical properties of cell walls of closed-cell aluminium alloy foams. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 666, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G.J.; Zhen, S. Review metallic foams: Their production, properties and applications. J. Mater. Sci. 1983, 18, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukhan, N. Metal Foams, Fundamentals and Applications, 1st ed.; Destech Publications Inc.: Lancaster, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.W.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.X. Research on Key Technologies for Batch Preparation of Aluminum Foam Slabs by Melt Foaming Process. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2009, 38, 306–310. [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi, T.; Itoh, M.; Akiyama, S.; Kitahara, A. ALPORAS Aluminum Foam: Production Process, Properties, and Applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2000, 2, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, I.; Kenny, L.D.; Sang, H. Stabilized Metal Foam Body. US Patent No. 5,112,697, 15 August 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, S.; Ueno, H.; Imagawa, K.; Kitahara, A.; Nagata, S.; Morimoto, K.; Nishikawa, T.; Itoh, M. Foamed metal and method of producing same. US Patent No. 4,713,227, 15 December 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, D.; Omar, H.; Stergioudi, F.; Tsipas, S.; Michailidis, N. A novel method for producing Al-foams and evaluation on their compression behavior. J. Porous Mater. 2010, 17, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banhart, J. Metal foams: Production and stability. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2006, 8, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Nava, M.; Cruz-Ramírez, A.; Suárez Rosales, M.A.; Gutiérrez-Pérez, V.H.; Sánchez-Martinez, A. Fabrication of aluminum alloy foams by using alternative thickening agents via melt route. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 698, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, S.W.; Wang, Y.; Toguri, J.M. Aluminum foam stabilization by solid particles. Can. Metall. Q. 1999, 38, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byakova, A.; Kartuzov, I.; Nakamura, T.; Gnyloskurenko, S. The role of foaming agent and processing route in mechanical performance of fabricated aluminum foams. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 4, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Nava, M.; Cruz-Ramírez, A.; Suárez-Rosales, M.A.; Hernández-Pérez, M.A. Thermodynamic analysis of the aluminum alloy foaming process by melt route. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 32, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, R.F. Metallurgical aspects of Al-Si eutectic piston alloys. Br. Foundrym. 1971, 64, 430–438. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Grain refinement of A356 alloy by Al-Ti-B-C master alloy and its effect on mechanical properties. Mater. Des. 2013, 47, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, D. Aluminum Casting Technology, 2nd ed.; AFS: Des Plaines, IL, USA, 2001; pp. 28–323. [Google Scholar]
- Shabani, M.O.; Mazahery, A.; Bahmani, A.; Davami, P.; Varahram, N. Solidification of A356 Al alloy: Experimental study and modeling. Kov. Mater. 2011, 49, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Sreekumar, K. Effect of pores and acicular eutectic silicon particles on the performance of Al–Si–Mg (AS7G03) casting. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2009, 16, 2433–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemings, M.; Kattamis, T.Z.; Bardes, B.P. Dendrite arm spacing in aluminium alloys. AFS Trans. 1991, 99, 501–506. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, B.; Garro, M.; Tagliano, C. Dendrite arm spacing in aluminium alloy cylinder heads produced by gravity semi-permanent mold. Metall. Sci. Technol. 2003, 21, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ananthanarayanan, L.; Gruzleski, J.E. Thermal Analysis Studies on the Effect of Cooling Rate on the Microstructure of the 319 Aluminium Alloy. AFS Trans. 1992, 141, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Vandersluis, E.; Ravindran, C. Comparison measurement methods for secondary dendrite arm spacing. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2017, 6, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanumantha, R.D.; Tagore, G.R.N.; Ranga, J.G. Evolution of artificial neural network (ANN) model for predicting secondary dendritic arm spacing in aluminum alloy casting. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2010, 32, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zeng, J. Effect of SDAS on homogenization of Al–Si–Mg casting alloys. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 97, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, M.; Davidson, C.; StJohn, D. Grain morphology of as-cast wrought aluminium alloys. Mater. Trans. 2011, 52, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Su, G.C.; Ju, C.W.; Wang, W.C.; Yan, W.L. Effect of modification treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-0.35%Mg-7.0%Si cast alloy. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4408–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askeland, D.; Pradeep, F.; Wendelin, W. The Science and Engineering of Materials, 6th ed.; Cengage Learning, Inc.: Stamford, CT, USA, 2011; pp. 337–341. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Xiao, W.; Hanada, S.; Yamagata, H.; Ma, C. The effect of scandium addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Si-Mg alloy: A multi-refinement modifier. Mater. Charact. 2018, 110, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Miao, S.; Li, X.; Xia, X.; Ding, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W. Synergistic effect of Sr and La on the microstructure and mechanical properties of A356.2 alloy. Mater. Des. 2017, 114, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmhus, D.; Banhart, J. Properties of heat-treated aluminum foams. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 349, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro, J.; Solórzano, E.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.A.; Kennedy, A.R. Effect of solidification rate on pore connectivity of aluminum foams and its consequences on mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 672, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iasiello, M.; Bianco, N.; Chiu, W.K.S.; Naso, V. Thermal conduction in open-cell metal foams: Anisotropy and Representative Volume Element. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 137, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Topin, F. Impact of anisotropy on geometrical and thermal conductivity of metallic foam structures. J. Porous Media 2015, 18, 949–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zou, H.; Tang, D.; Wen, D.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X. Inhomogeneity in pore size appreciably lowering thermal conductivity for porous thermal insulators. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 130, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Fang, Q.Z.; Yu, H.; Hu, Q. Numerical simulation on thermal properties of closed-cell metal foams with different cell size distributions and cell shapes. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 100968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birol, Y. Impact of grain size on mechanical properties of AlSi7Mg0.3 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 559, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y. Foaming process and properties of 6063 aluminum foams by melt foaming method. Mater. Trans. 2017, 58, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacsán, N.; Murty, M.; Vinod, G.; García, F.; Banhart, J. New Foam Stabilizing Additive for Aluminium. In Proceedings of the Metfoam 2007, Montreal, QC, Canada, 5–7 September 2007; DES Tech. Publications: Lancaster, PA, USA; pp. 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kori, S.; Murty, B.; Chakraborty, M. Development of an efficient grain refiner for Al-7Si alloy and its modification with strontium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 283, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavakumar, K.; Mukunda, P.; Chakraborty, M. Influence of grain refinement and modification on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-7Si and Al-7Si-2.5Cu cast alloys. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, E.; Golbahar, B.; Samuel, A.; Doty, H.; Valtierra, S.; Samuel, F. Effect of grain refiner on the tensile and impact properties of Al-Si-Mg cast alloys. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
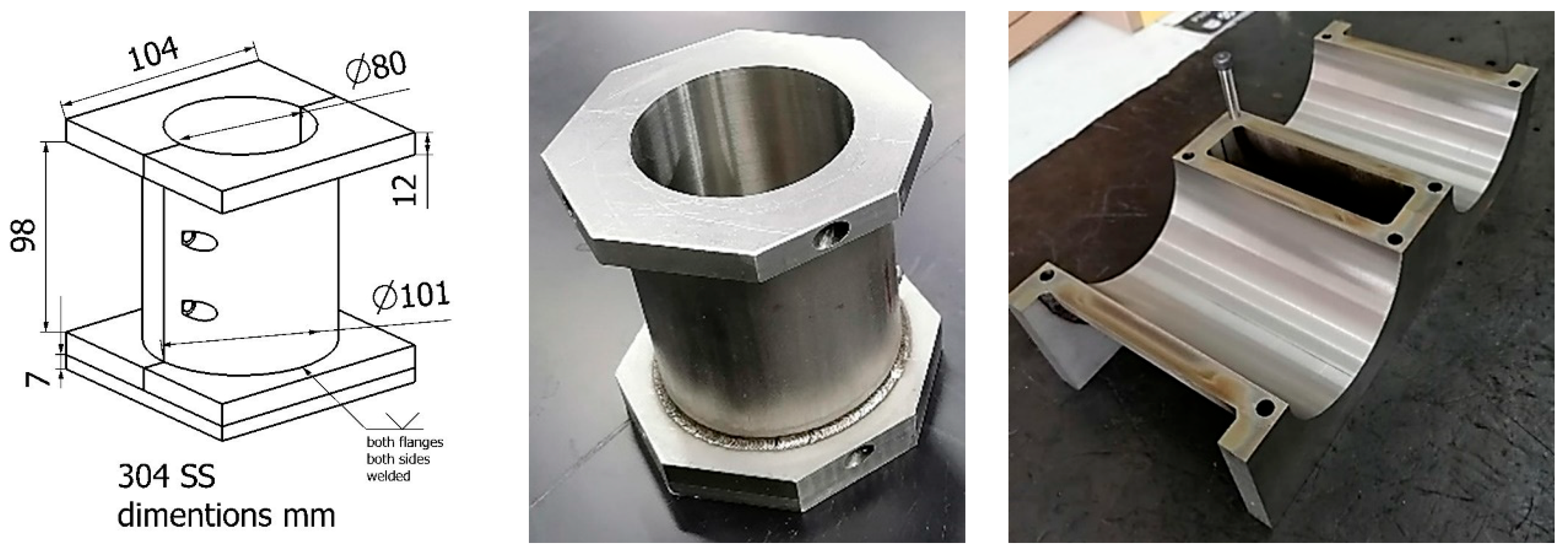
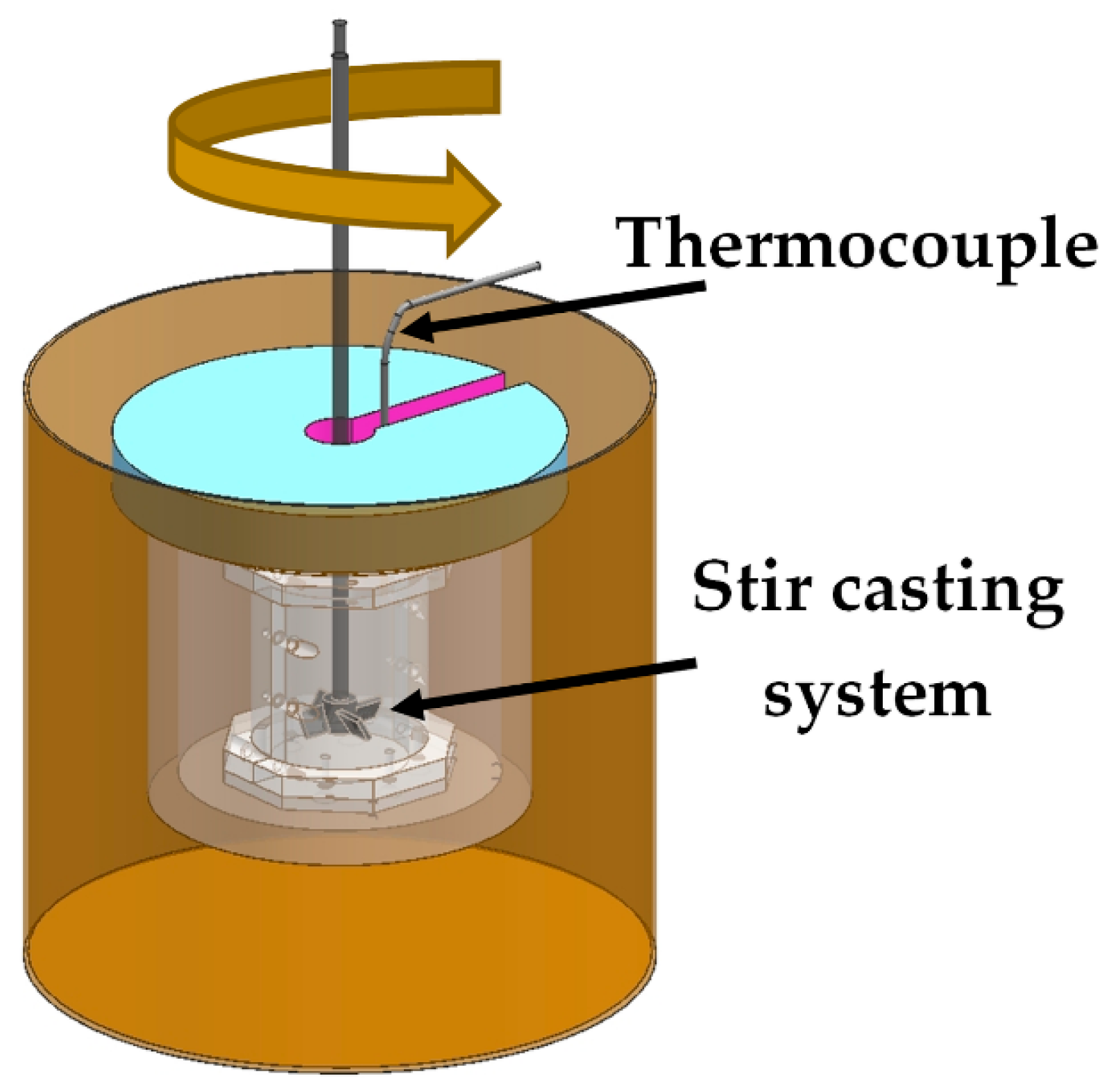
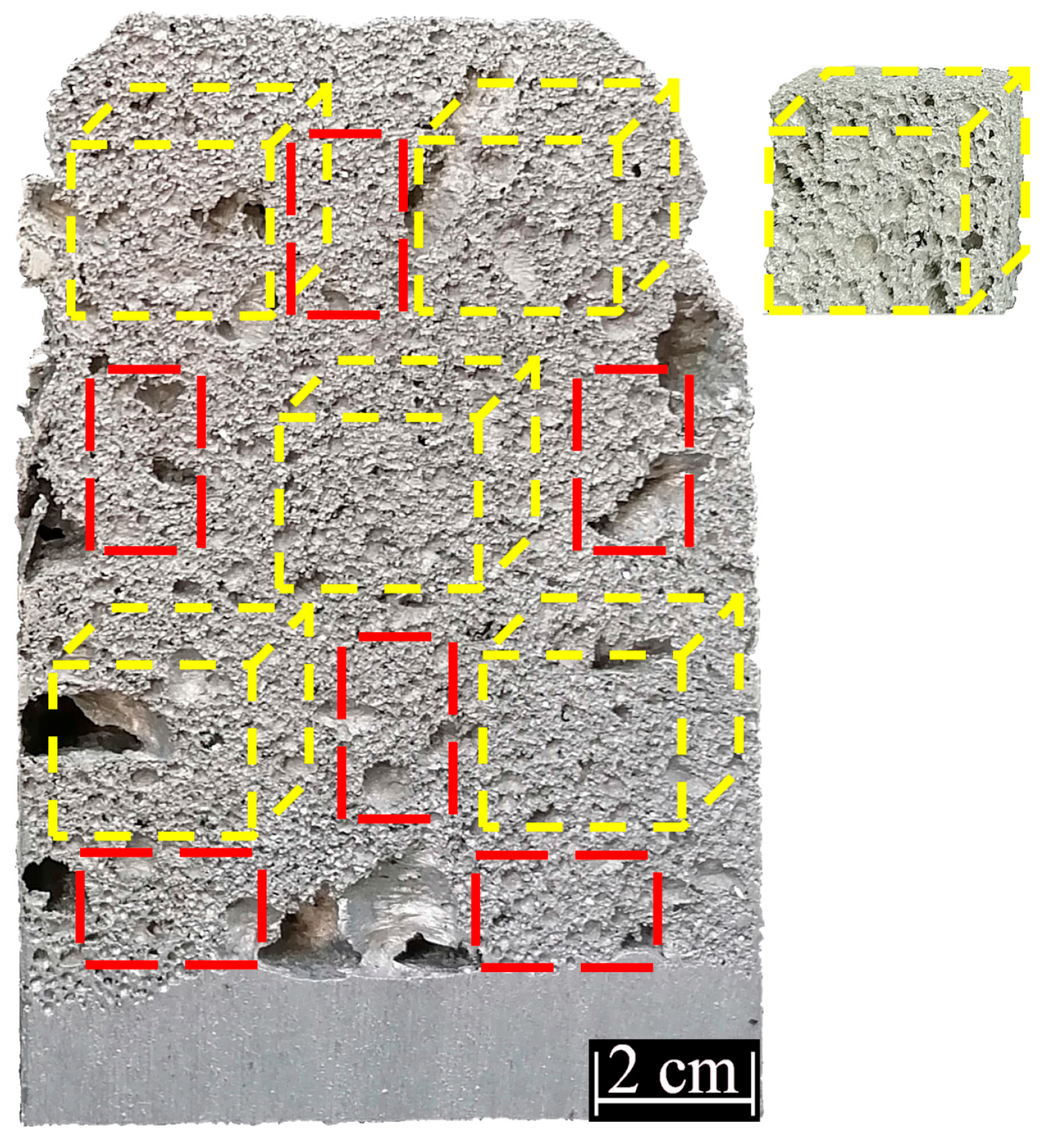
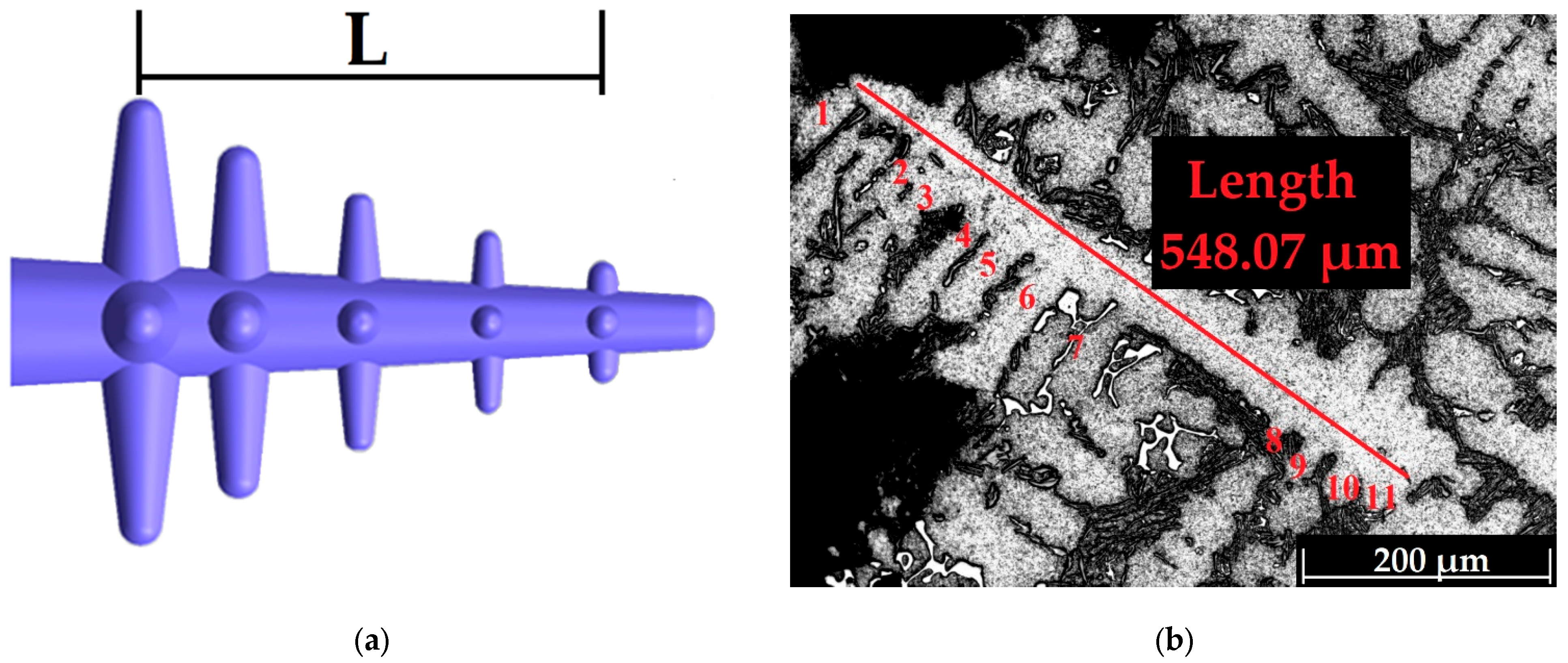



| Agents | Purity (%) | Particle Size (µm) |
|---|---|---|
| Barite (BaSO4) | 96 | 45 |
| Calcite (CaCO3) | 98.5 | 14 |
| Al-5Ti-1B | 5Ti, 1B | 400 |
| Al-10Sr | 10 Sr | 400 |
| Alloy | wt % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A356 | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Al |
| 7.32 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.38 | 91.69 | |
| Experimental Condition | Foam Sample | Density * (g cm−3) | Relative Density */A356 alloy | Pr (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without melt treatment | 1 | 0.389 | 0.146 | 85.4 |
| 2 | 0.309 | 0.116 | 88.1 | |
| With melt treatment | 3 | 0.315 | 0.112 | 88.4 |
| 4 | 0.254 | 0.096 | 90.4 |
| Experimental Condition | Foam Sample | σ0 (N/mm2) | Plateau Stress σpl (N/mm2) | Energy Absorption W (MJ m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without melt treatment | 1 | 0.58 | 1.49 | 0.69 |
| 2 | 0.63 | 1.04 | 0.49 | |
| With melt treatment | 3 | 1.04 | 1.53 | 0.74 |
| 4 | 0.62 | 1.30 | 0.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poot Manzanilla, A.J.; Cruz Ramírez, A.; Colin García, E.; Romero Serrano, J.A.; Sánchez Alvarado, R.G.; Suárez Rosales, M.Á. Production of Refined and Modified Closed-Cell Aluminum Foams by Melt-Foaming Method. Metals 2023, 13, 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13030622
Poot Manzanilla AJ, Cruz Ramírez A, Colin García E, Romero Serrano JA, Sánchez Alvarado RG, Suárez Rosales MÁ. Production of Refined and Modified Closed-Cell Aluminum Foams by Melt-Foaming Method. Metals. 2023; 13(3):622. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13030622
Chicago/Turabian StylePoot Manzanilla, Alberto Jesús, Alejandro Cruz Ramírez, Eduardo Colin García, José Antonio Romero Serrano, Ricardo Gerardo Sánchez Alvarado, and Miguel Ángel Suárez Rosales. 2023. "Production of Refined and Modified Closed-Cell Aluminum Foams by Melt-Foaming Method" Metals 13, no. 3: 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13030622
APA StylePoot Manzanilla, A. J., Cruz Ramírez, A., Colin García, E., Romero Serrano, J. A., Sánchez Alvarado, R. G., & Suárez Rosales, M. Á. (2023). Production of Refined and Modified Closed-Cell Aluminum Foams by Melt-Foaming Method. Metals, 13(3), 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13030622








