Thermodynamic Description of the Au-Sb-Sn Ternary System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Literature Information
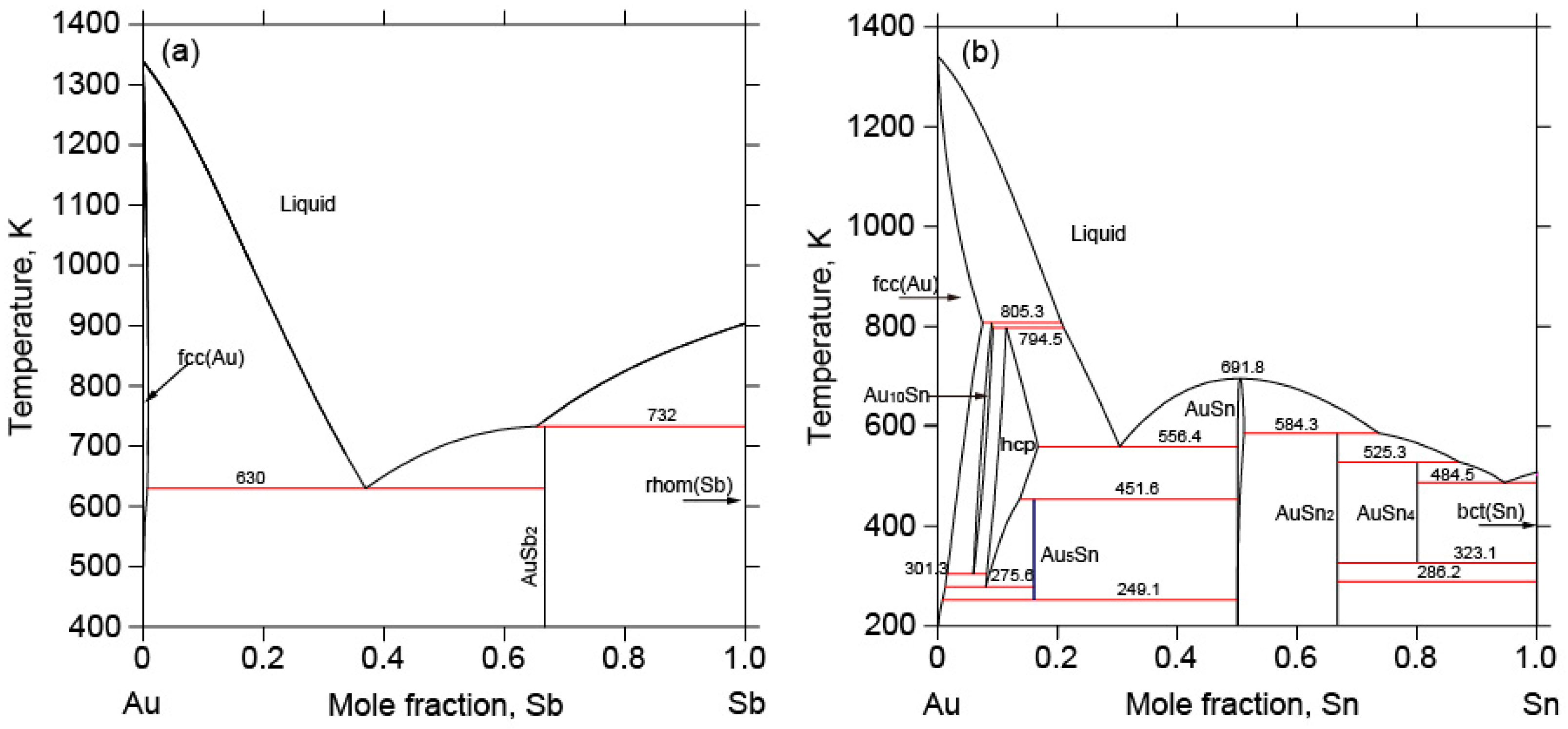
2.1. The Au-Sb Binary System
2.2. The Au-Sn Binary System
2.3. The Sb-Sn Binary System
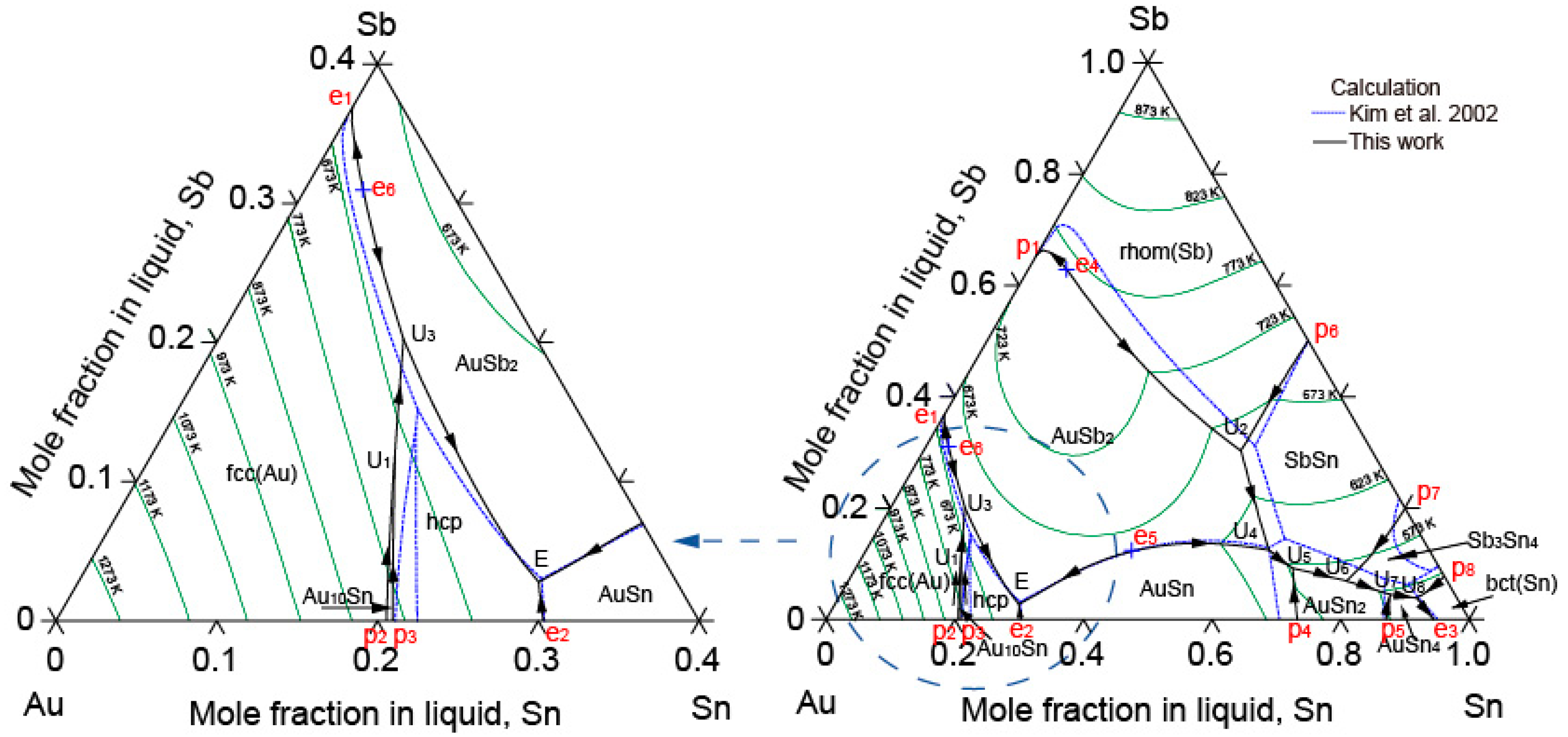
2.4. The Au-Sb-Sn Ternary System
3. Experimental Procedure
4. Thermodynamic Models
4.1. Solution Phases
4.2. Binary Compounds
5. Results and Discussion
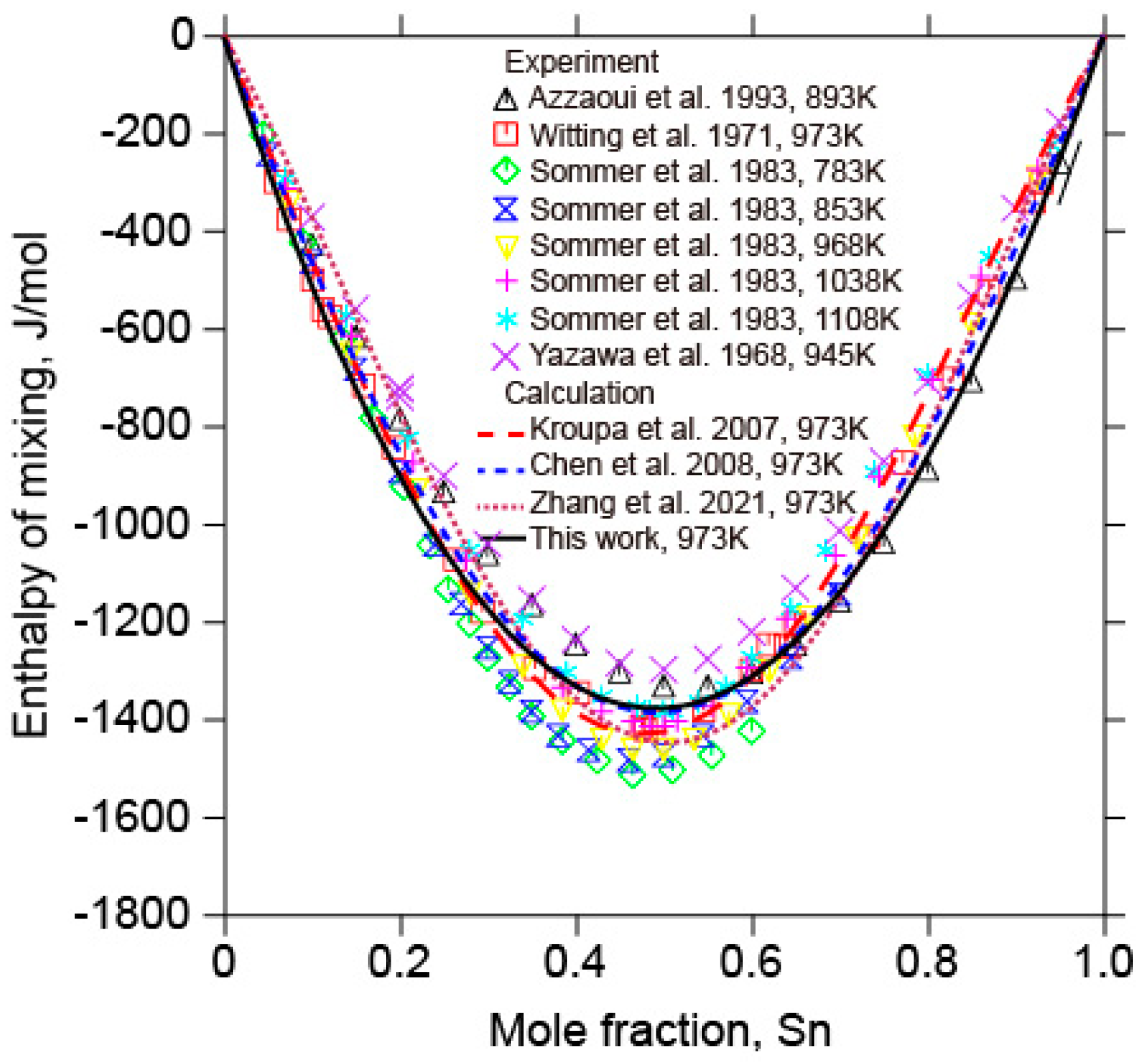
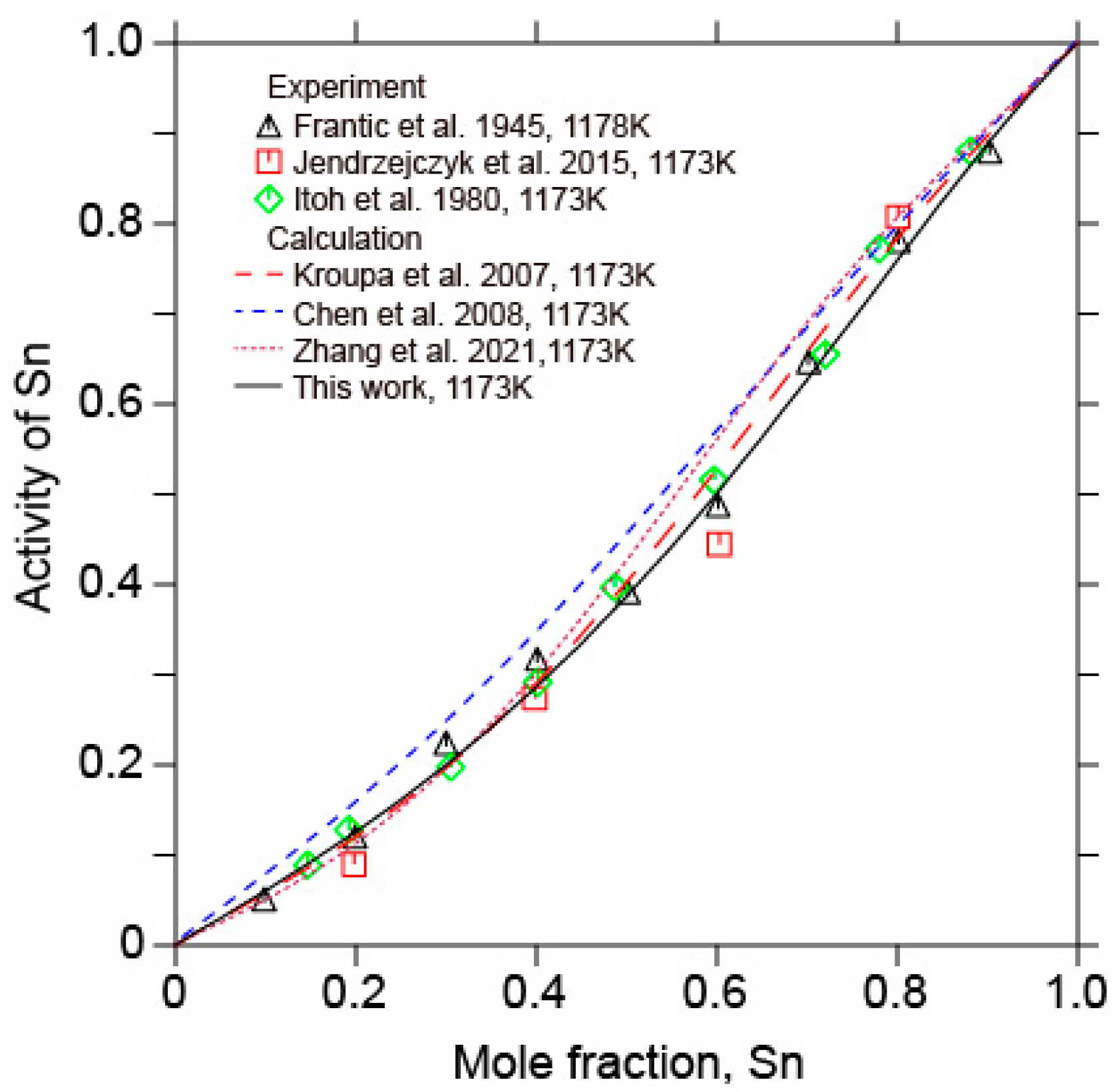
5.1. The Sb-Sn Binary System
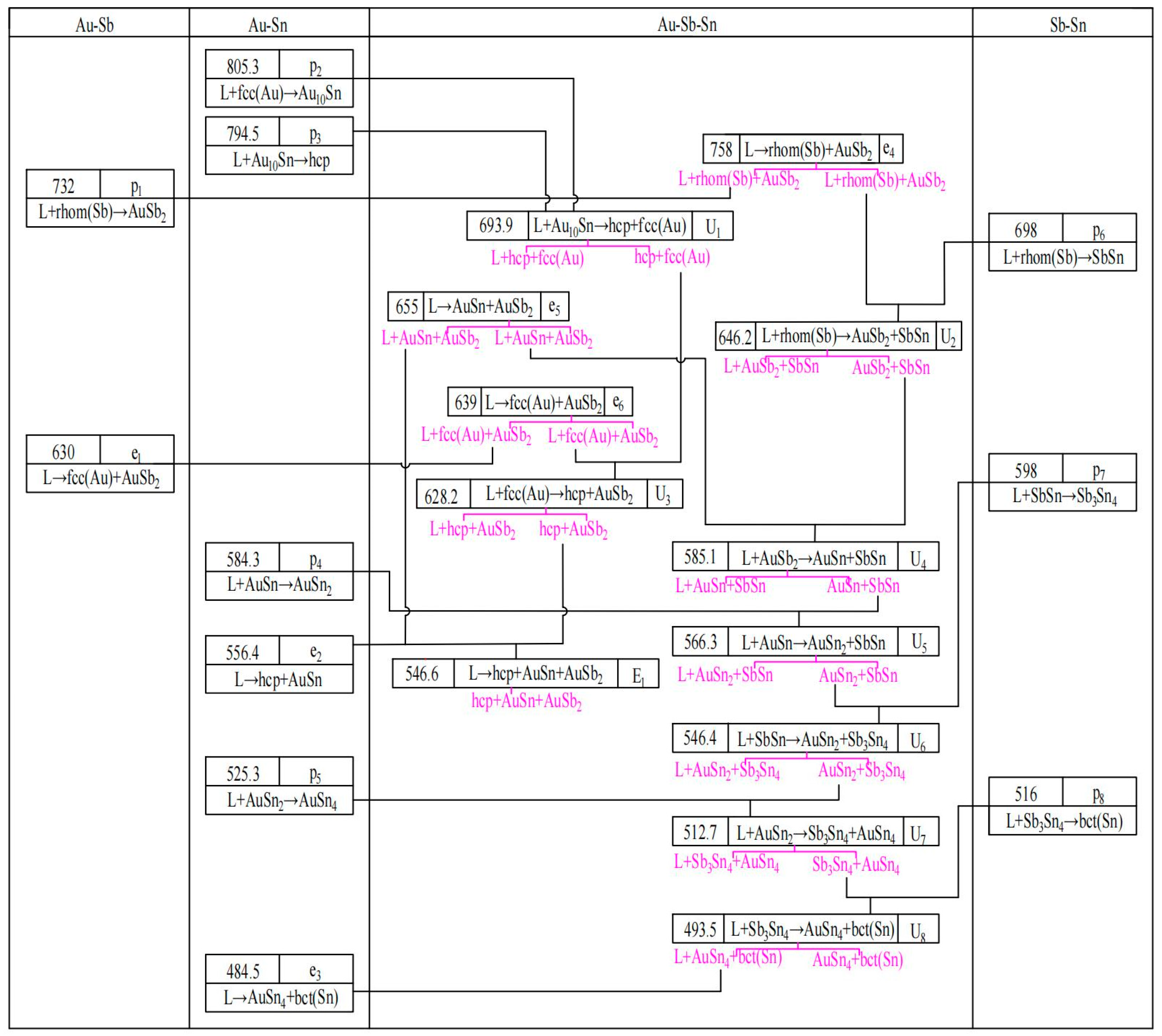
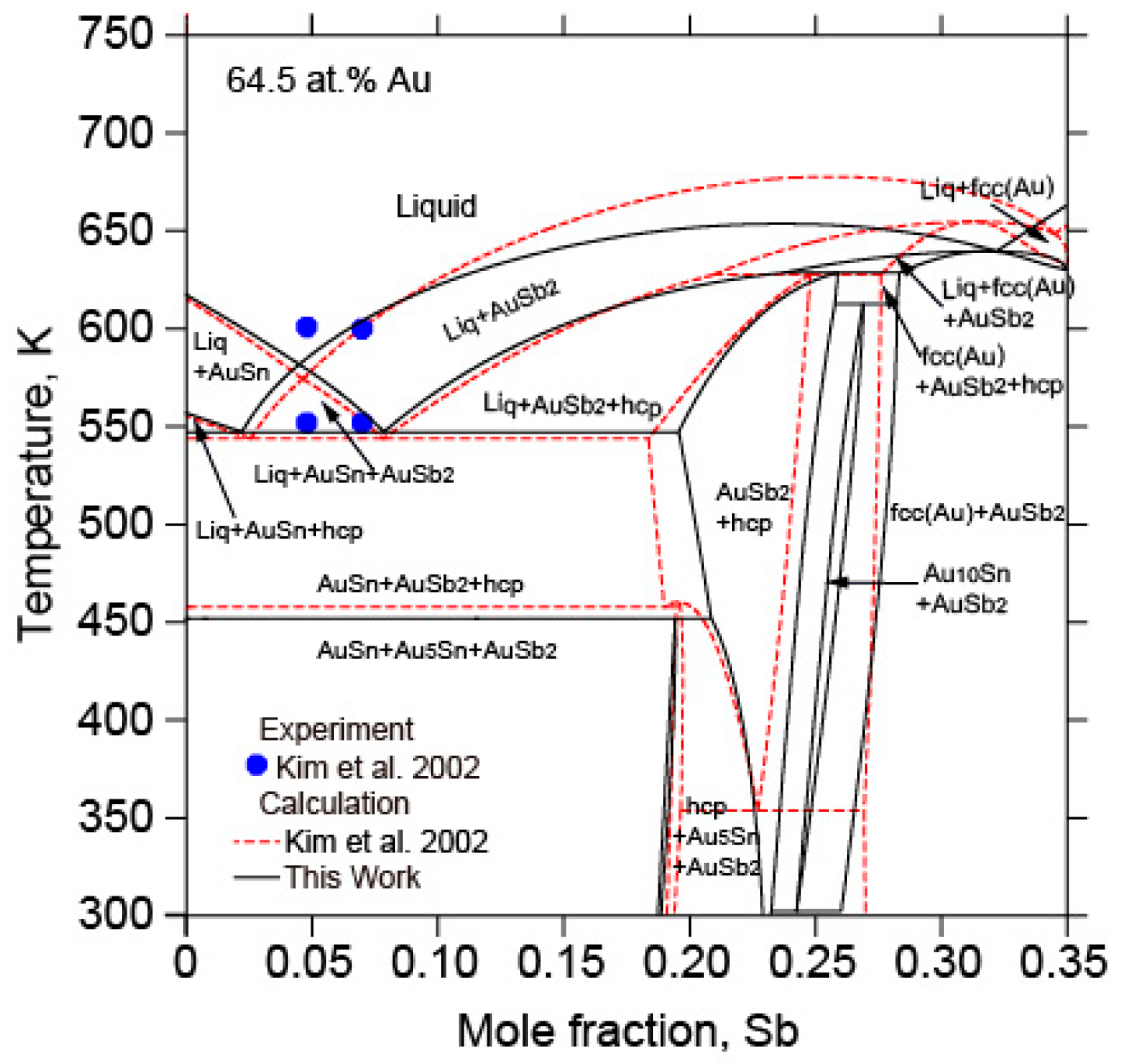
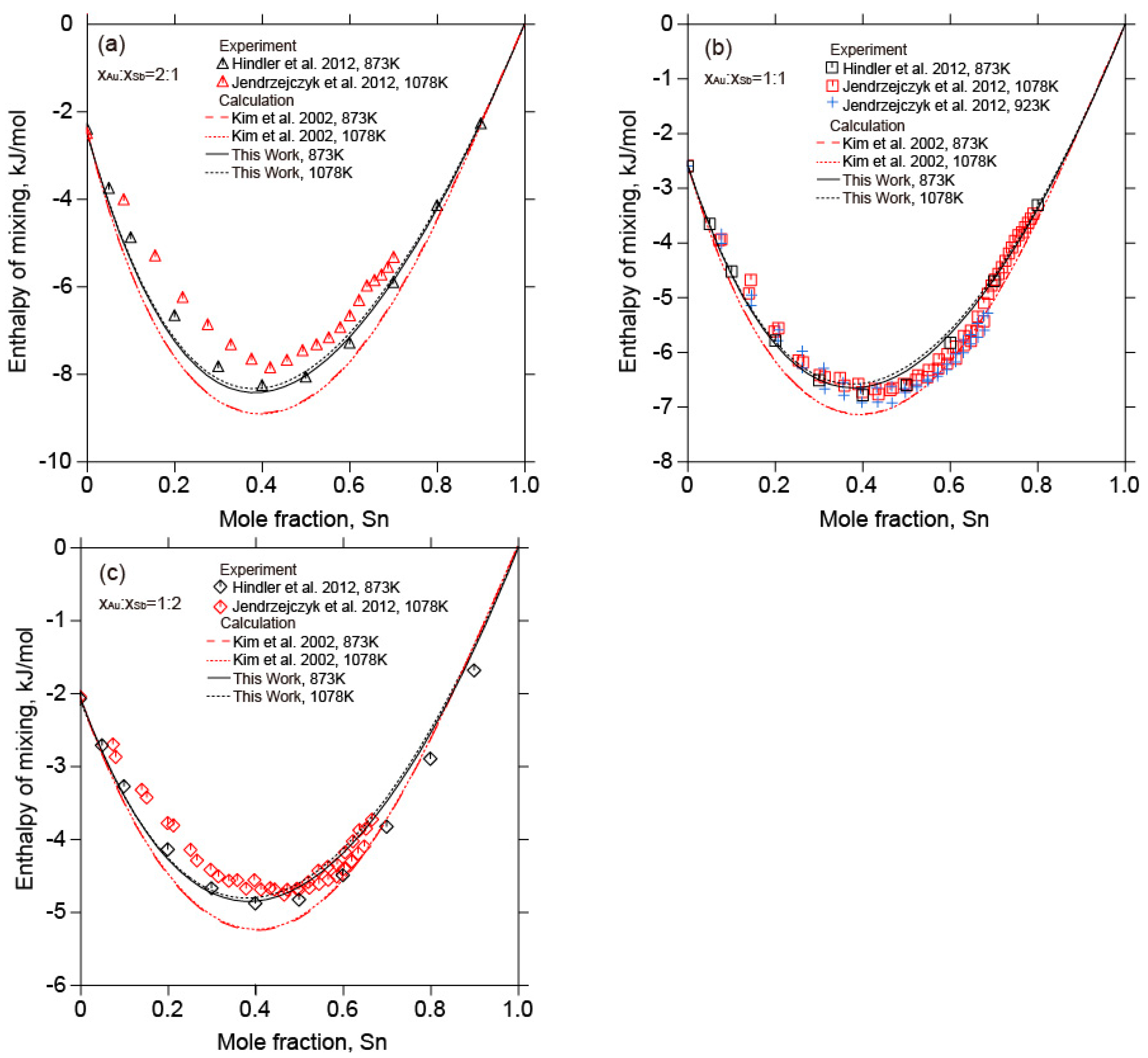
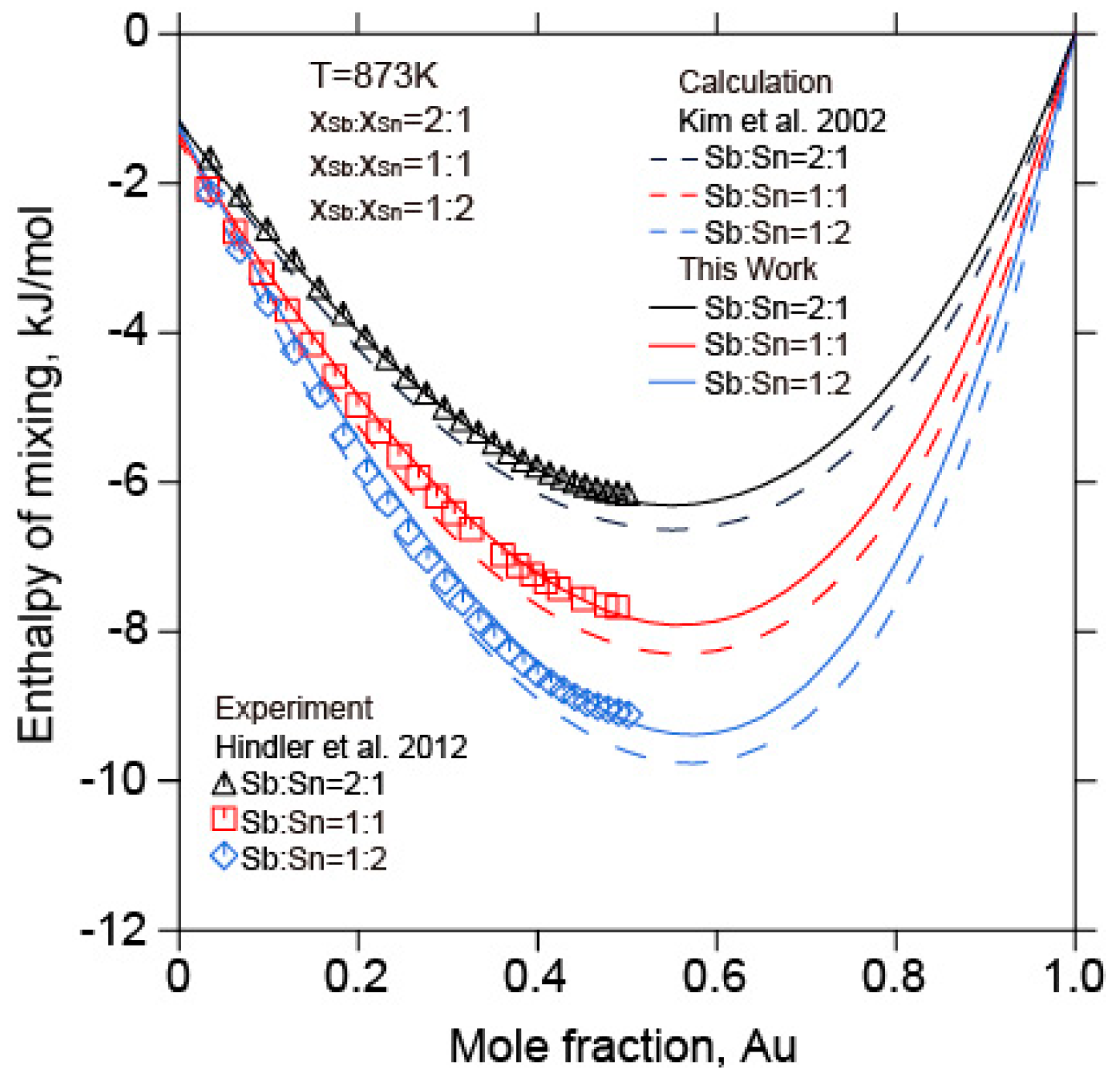
5.2. The Au-Sb-Sn Ternary System
6. Conclusions
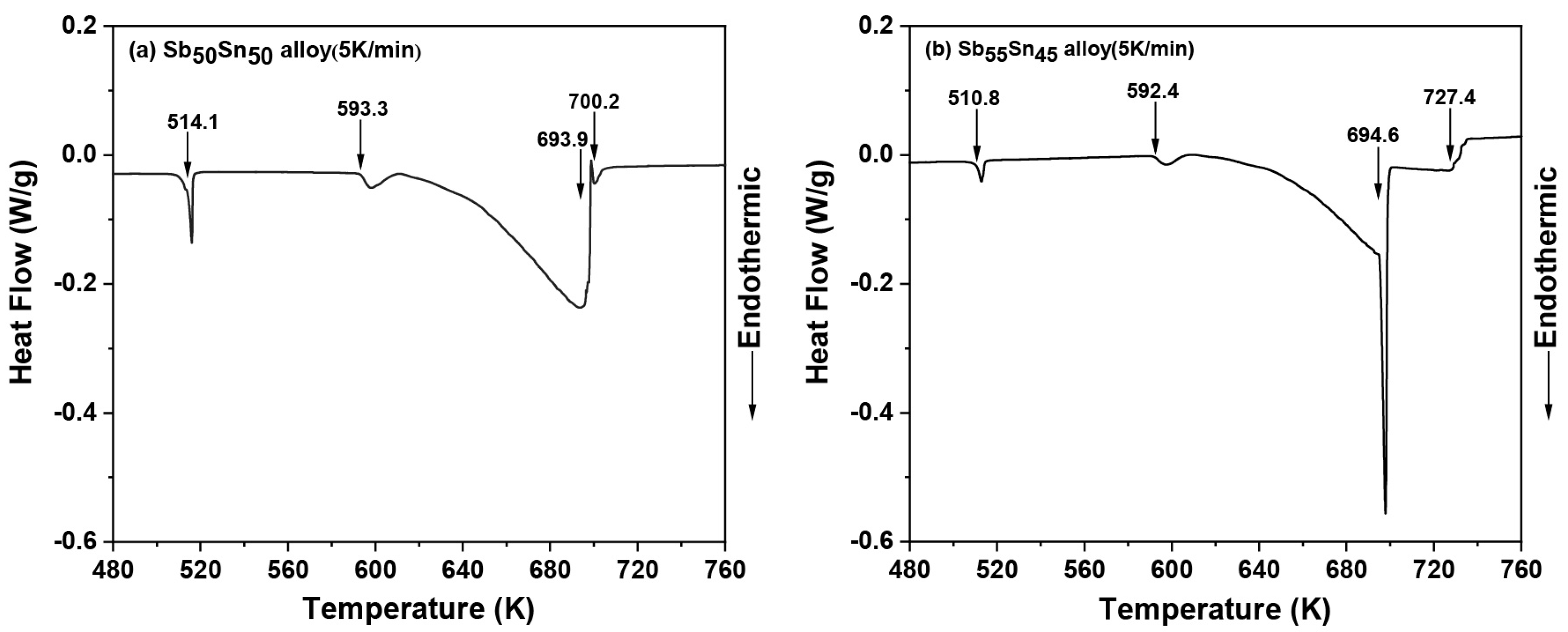
- The phase transition temperatures of five Sb-Sn alloys were measured using differential thermal analysis (DTA). The temperatures of three invariant reactions (L + Sb3Sn4 ↔ bct(Sn), L + SbSn ↔ Sb3Sn4, and L + rhom(Sb) ↔ SbSn) were determined to be 516 K, 598 K, and 695 K, respectively. Using the experimental results measured in this work and reported results, the Sb-Sn binary system was re-optimized using the CALPHAD method. The calculated results were consistent with the experimental data, including phase equilibria and thermodynamic properties.
- In combination with the previous assessments of the Au-Sn and Au-Sb binary systems and the present optimization of the Sb-Sn binary system, a thermodynamic description of the Au-Sb-Sn ternary system was performed based on the available experimental information on the Au-Sb-Sn ternary system. The calculated liquidus projection, isothermal sections, vertical sections, as well as enthalpy of mixing and activity of Sn in liquid alloys, were consistent with the reported experimental results. A self-consistent set of thermodynamic parameters were obtained to accurately describe Gibbs energies of various phases in the Au-Sb-Sn ternary system, which could serve as a sound basis for developing a thermodynamic database of multicomponent Au-Sn-based alloy systems.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.; Wu, M.; Pu, J.; Xue, S. Novel Au-Based Solder Alloys: A Potential Answer for Electrical Packaging Problem. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xue, S.; Liu, H.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H. Research Progress of Au-20Sn Solder for Electronic Packaging. Cailiao Daobao 2019, 33, 2483–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Minter, J.; Lee, N. A brief review on high-temperature, Pb-free die-attach materials. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rerek, T.; Skowronski, L.; Kobierski, M.; Naparty, M.K.; Derkowska-Zielinska, B. Microstructure and opto-electronic properties of Sn-rich Au-Sn diffusive solders. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 451, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, M.; Sadeghi, B.; Wang, R.; Liu, H.; Cavaliere, P. Increasing shear strength of Au-Sn bonded joint through nano-grained interfacial reaction products. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 7050–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, D.; Xiong, J.; Chen, C.; Song, T.; Li, L.; Huang, S. Microstructure evolution and properties of rapidly solidified Au-20Sn eutectic solder prepared by single-roll technology. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 781, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, M. Structure and Properties of Au–Sn Lead-Free Solders in Electronic Packaging. Mater. Trans. 2022, 63, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Tang, C.Y.; Liu, L.B.; Zhou, H.Y.; Jin, Z.P. Thermodynamic description of the Au-Ag-Ge ternary system. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 512, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, H.M. A thermodynamic study of phase equilibria in the Au-Sb-Sn solder system. J. Electron. Mater. 2002, 31, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, K.; Breimer, H.; Gohle, R. The structure of the gold-indium, gold-tin, gold-indium-tin, and gold-tin-antimony systems. Z. Fur Met. 1959, 50, 146–153. [Google Scholar]
- Humpston, G. The Constitution of Some Ternary Au-Based Solder Alloys; University of Brunel: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hindler, M.; Guo, Z.; Mikula, A. Lead-free solder alloys: Thermodynamic properties of the (Au+Sb+Sn) and the (Au+Sb) system. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2012, 55, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jendrzejczyk-Handzlik, D.; Fitzner, K. Mixing enthalpies of liquid Au-Sb-Sn alloys. Mon. Für Chem. Chem. Mon. 2012, 143, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendrzejczyk-Handzlik, D.; Fitzner, K. Thermodynamic properties of liquid (antimony+tin) and (gold+antimony+tin) alloys determined from e.m.f. measurements. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2015, 85, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ågren, J. The materials genome and CALPHAD. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 1635–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, P.Y. A thermodynamic evaluation of the Au-Sb and Au-Ti systems. Thermochim. Acta 1989, 155, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.S.; Liu, C.L.; Wang, C.; Jin, Z.P.; Ishida, K. Thermodynamic modeling of the Au-ln-Sb system. J. Electron. Mater. 2003, 32, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Liu, L.B.; Zhou, H.Y.; Jin, Z.P. Thermodynamic modeling of the Au-Sb-Si ternary system. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierlotka, W. Thermodynamic description of the binary Au-Sb and ternary Au-In-Sb systems. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 579, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.Q.; Tao, X.M.; Laurila, T.; Vuorinen, V.; Paulasto-Kröckel, M. Thermodynamic modeling of Au-Ce-Sn ternary system. Calphad 2013, 42, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, P.Y. A thermodynamic evaluation of the Au-Sn system. Thermochim. Acta 1988, 130, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.S.; Liu, C.L.; Ishida, K.; Jin, Z.P. Thermodynamic Modeling of the Au-In-Sn System. J. Electron. Mater. 2003, 32, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.Q.; Jin, S.; Zhang, L.G.; Wang, J.S.; Tao, X.M.; Liu, H.S.; Jin, Z.P. Thermodynamic Assessment of the Au-Co-Sn Ternary System. J. Electron. Mater. 2009, 38, 2158–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grolier, V.; Schmid-Fetzer, R. Thermodynamic evaluation of the Au-Sn system. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2007, 98, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Takaku, Y.; Ohnuma, I.; Ishida, K. Thermodynamic assessment of phase equilibria in the Sn-Au-Bi system with key experimental verification. J. Mater. Res. 2010, 25, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmetterer, C.; Polt, J.; Flandorfer, H. The phase equilibria in the Sb-Sn system-Part I: Literature review. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 728, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. Sb-Sn (Antimony-Tin). J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2012, 33, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, C.; Gierlotka, W.; Zi, A.; Chen, P.; Wu, H. Phase equilibria of the Sn-Sb binary system. J. Electron. Mater. 2008, 37, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmetterer, C.; Polt, J.; Flandorfer, H. The phase equilibria in the Sb-Sn system-Part II: Experimental results. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 743, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierlotka, W. On the binary Sb-Sn system: Ab initio calculation and thermodynamic remodeling. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 55, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Y. A thermodynamic assessment of the Mg-Sn-Sb ternary system. Calphad 2021, 75, 102361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, H.; Okuda, K.; Ishida, K. Thermodynamic study of phase equilibria in the Pb-Sn-Sb system. J. Phase Equilib. 1995, 16, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. Sb-Sn (Antimony-Tin). J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 1998, 19, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predel, B.; Schwermann, W. Constitution and thermodynamics of antimony-tin system. J. Inst. Met. 1971, 99, 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- Jönsson, B.; Ågren, J. Thermodynamic assessment of Sb-Sn system. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1986, 2, 913–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroupa, A.; Vízdal, J. The Thermodynamic Database for the Development of Modern Lead-Free Solders. Defect Diffus. Forum 2007, 263, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzone, G.; Delsante, S.; Li, D.; Novakovic, R. New Insights into Phase Equilibria of the Sb-Sn System. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2021, 42, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysenko, V.A. Thermodynamic reassessment of the Sb-Sn and In-Sb-Sn systems. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 776, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittig, F.E.; Gehring, E. Die Mischungswärmen des Antimons mit B-Metallen: III. Die Systeme mit Zinn und Blei. Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 1967, 71, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.; Lück, R.; Rupf-Bolz, N.; Predel, B. Chemical short range order in liquid Sb-Sn alloys proved with the aid of the dependence of the mixing enthalpies on temperature. Mater. Res. Bull. 1983, 18, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzaoui, M.; Notin, M.; Hertz, J. Ternary experimental excess functions by means of high-order polynomials: Enthalpy of mixing of liquid Pb-Sn-Sb alloys. Int. J. Mater. Res. 1993, 84, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantik, R.O.; Mcdonald, H.J. A Thermodynamic study of the tin-antimony system. Trans. Electrochem. Soc. 1945, 88, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Koiko, K.; Narita, Y. Activity measurement of Pb-Sn and Sn-Sb based molten alloys. Nippon Kogo Kaishi 1980, 96, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Prince, A.; Raynor, G.V.; Evans, D.S. Phase Diagrams of Ternary Gold Alloys; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; pp. 411–413. [Google Scholar]
- Version 5.0 of Unary Database. Available online: https://www.sgte.net/en/free-pure-substance-database (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Redlich, O.; Kister, A.T. Thermodynamics of Nonelectrolyte Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1948, 40, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggianu, Y.M.; Gambino, M.; Bros, J.P. Enthalpies of formation of liquid alloys bismuth-gallium-tin at 723k-choice of an analytical representation of integral and partial thermodynamic functions of mixing for this ternary-system. J. Chim. Phys. Phys.-Chim. Biol. 1975, 72, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundman, B.; Jansson, B.; Andersson, J. The thermo-calc databank system. Calphad 1985, 9, 153–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliev, V.; Feutelais, Y.; Sghaier, M.; Legendre, B. Thermodynamic investigation in In-Sb, Sb-Sn and In-Sb-Sn liquid systems. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 314, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwase, K.; Aoki, N.; Osawa, A. DTA measurements in Sb-Sn alloys. Sci. Rep. Tohoku Imp. Univ. 1931, 20, 353. [Google Scholar]
- Loebe, R. Uber die Konstitution der ternaren Lagierungen von Blei, Zinn und Antimon. Metallurgie 1911, 8, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Witting, F.E.; Gehring, E. The activity of mixing antimony with tin metals. Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 1971, 372–376. [Google Scholar]
- Yazawa, A.; Kawashima, T.; Itagaki, K. Measurements of Heats of Mixing in Liquid Alloys with the Adiabatic Calorimeter. J. Jap. I. Met. 1968, 32, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Phases/Models | Thermodynamic Parameters | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| liquid:(Au,Sb,Sn) | [18] | |
| [18] | ||
| [20] | ||
| [20] | ||
| [20] | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| bct:(Sb,Sn) | This work | |
| This work | ||
| fcc:(Au,Sb,Sn) | [18] | |
| [20] | ||
| [20] | ||
| hcp:(Au,Sb,Sn) | [20] | |
| [20] | ||
| rhom:(Sb,Sn) | This work | |
| Au10Sn:(Au,Sn) | [20] | |
| [20] | ||
| [20] | ||
| [20] | ||
| AuSb2:(Au)0.333333:(Sb,Sn)0.666667 | [18] | |
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| Au5Sn:(Au)0.84:(Sn)0.16 | [20] | |
| AuSn:(Sn)0.333:(Sn,Va)0.333:(Au)0.334 | [20] | |
| [20] | ||
| [20] | ||
| AuSn2:(Au)0.3333:(Sn)0.6667 | [20] | |
| AuSn4:(Au)0.2:(Sn)0.8 | [20] | |
| SbSn:(Sb,Sn)0.5:(Sb,Sn)0.5 | This work | |
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| This work | ||
| Sb3Sn4:(Sb)0.43:(Sn)0.57 | This work |
| Alloys (at.%) | Heating Rate K/min | Phase Transformation Temperature (K) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L + Sb3Sn4 ↔ bct(Sn) | L + SbSn ↔ Sb3Sn4 | — | L + rhom(Sb) ↔ SbSn | Liquidus | ||
| Sb28Sn72 | 5 | 516.5 | 597.9 | — | — | 625.2 |
| 10 | 516.8 | 598.2 | — | — | 622.9 | |
| Sb32Sn68 | 5 | 516.6 | 598.0 | 612.9 | — | 640.1 |
| 10 | 516.6 | 600.6 | 618.9 | — | 642.2 | |
| Sb38Sn62 | 5 | 516.0 | 597.8 | 615.5 | — | 660.5 |
| 10 | 516.4 | 598.4 | 619.2 | — | 660.8 | |
| Sb50Sn50 | 5 | 514.1 | 593.3 | — | 693.9 | 700.2 |
| 10 | 513.7 | 591.9 | — | 693.7 | 700.6 | |
| Sb55Sn45 | 5 | 510.8 | 592.4 | — | 694.6 | 727.4 |
| 10 | 510.6 | 593.5 | — | 692.9 | 728.6 | |
| Reactions | Type | T (K) | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L + rhom(Sb) ↔ SbSn | Peritectic | 695 | — | — | — | [51] (exp.) |
| 698 | — | — | — | [50] (exp.) | ||
| 698 | 0.504 | — | 0.652 | [34] (exp.) | ||
| 703 | — | — | — | [49] (exp.) | ||
| 698.2 | 0.502 | 0.841 | 0.625 | [36] (cal.) | ||
| 697.2 | 0.493 | 0.881 | 0.627 | [28] (cal.) | ||
| 698 | — | — | — | [29] (exp.) | ||
| 697.5 | 0.489 | 0.869 | 0.674 | [30] (cal.) | ||
| 693 | — | — | — | [37] (exp.) | ||
| 698.0 | 0.527 | 0.860 | 0.629 | [31] (cal.) | ||
| 694.6 | — | — | — | This work (exp.) | ||
| 698.3 | 0.500 | 0.869 | 0.633 | This work (cal.) | ||
| L + SbSn ↔ Sb3Sn4 | Peritectic | 598 | — | — | — | [50] (exp.) |
| 597 | 0.210 | — | 0.430 | [34] (exp.) | ||
| 598 | — | — | — | [49] (exp.) | ||
| 598.2 | 0.215 | 0.492 | 0.400 | [36] (cal.) | ||
| 595.7 | 0.184 | 0.470 | 0.430 | [28] (cal.) | ||
| 599 | — | — | 0.428 | [29] (exp.) | ||
| 595.6 | 0.194 | 0.462 | 0.428 | [30] (cal.) | ||
| 594 | — | 0.490 | 0.430 | [37] (exp.) | ||
| 594.4 | 0.199 | 0.496 | 0.428 | [31] (cal.) | ||
| 598 | — | — | — | This work (exp.) | ||
| 598.1 | 0.199 | 0.492 | 0.428 | This work (cal.) | ||
| L + Sb3Sn4 ↔ bct(Sn) | Peritectic | 517 | — | — | — | [51] (exp.) |
| 519 | — | — | — | [50] (exp.) | ||
| 523 | 0.060 | — | 0.100 | [34] (exp.) | ||
| 518 | — | — | — | [49] (exp.) | ||
| 518.9 | 0.090 | 0.400 | 0.108 | [36] (cal.) | ||
| 516.7 | 0.062 | 0.430 | 0.105 | [28] (cal.) | ||
| 517 | — | 0.428 | — | [29] (exp.) | ||
| 517.2 | 0.071 | 0.428 | 0.098 | [30] (cal.) | ||
| 516 | — | — | — | [37] (exp.) | ||
| 516.8 | 0.052 | 0.428 | 0.088 | [31] (cal.) | ||
| 516 | — | — | — | This work (exp.) | ||
| 516.6 | 0.078 | 0.428 | 0.101 | This work (cal.) | ||
| Reactions | Type | T(K) | Composition (at.%) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L → hcp + AuSn + AuSb2 | E | 553.2 | — | — | [44] |
| 543.4 | 68.3 | 3.1 | [9] (cal.) | ||
| 546.7 | 68.6 | 2.8 | This work | ||
| L + Au10Sn → fcc(Au) + hcp | U1 | 638.6 | 70.7 | 13.9 | [9] (cal.) |
| 693.9 | 72.8 | 12.2 | This work | ||
| L + rhom(Sb) → AuSb2 + SbSn | U2 | ~697 | — | — | [44] |
| 626.1 | 17.8 | 31.0 | [9] (cal.) | ||
| 646.2 | 20.2 | 30.4 | This work | ||
| L + fcc(Au) → hcp + AuSb2 | U3 | 627.1 | 70.0 | 15.2 | [9] (cal.) |
| 628.2 | 68.3 | 20.2 | This work | ||
| L + AuSb2 → AuSn + SbSn | U4 | 585.1 | 24.7 | 12.7 | This work |
| L + AuSn → AuSn2 + SbSn | U5 | 566.3 | 22.5 | 9.1 | This work |
| L + SbSn → AuSn2 + Sb3Sn4 | U6 | 546.4 | 15.6 | 7.0 | This work |
| L + AuSn2 → Sb3Sn4 + AuSn4 | U7 | 503.7 | 9.5 | 7.4 | [9] (cal.) |
| 512.7 | 10.0 | 4.5 | This work | ||
| L + Sb3Sn4 → AuSn4 + bct(Sn) | U8 | 493.2 | — | — | [44] |
| 491.3 | 6.4 | 6.2 | [9] (cal.) | ||
| 493.5 | 6.2 | 3.9 | This work | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, J.; Tong, Q.; Rong, M.; Ye, H.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J. Thermodynamic Description of the Au-Sb-Sn Ternary System. Metals 2023, 13, 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13061082
Ge J, Tong Q, Rong M, Ye H, Bai Y, Wang J. Thermodynamic Description of the Au-Sb-Sn Ternary System. Metals. 2023; 13(6):1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13061082
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Jing, Qingsong Tong, Maohua Rong, Hongjian Ye, Yuchen Bai, and Jiang Wang. 2023. "Thermodynamic Description of the Au-Sb-Sn Ternary System" Metals 13, no. 6: 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13061082
APA StyleGe, J., Tong, Q., Rong, M., Ye, H., Bai, Y., & Wang, J. (2023). Thermodynamic Description of the Au-Sb-Sn Ternary System. Metals, 13(6), 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13061082






