Corrosion Behavior of Nickel–Titanium Continuous-Casted Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Processing of the Samples
2.2. Microstructure Observation and ASTM Analysis—Grain Size Measurements
2.3. Corrosion Testing
2.3.1. Static Immersion Test
2.3.2. Electrochemical Test
2.4. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Oxide Layers after Corrosion Testing
2.5. Indirect Cytotoxicity Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure and ASTM Analysis Results
3.2. ICP-OES Analysis of the Corrosive Medium after Static Immersion Test
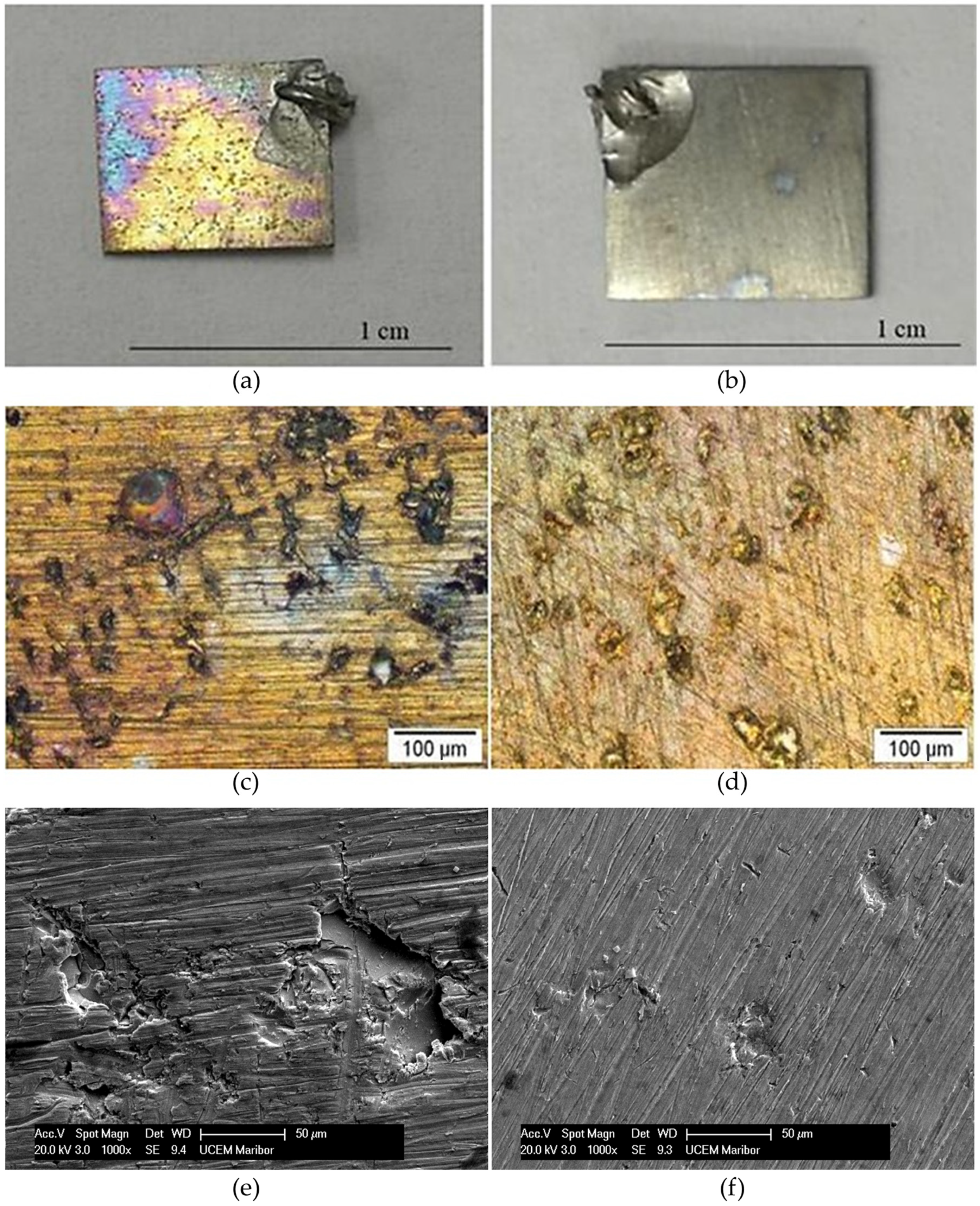
Oxide Layer Thickness after Immersion Testing
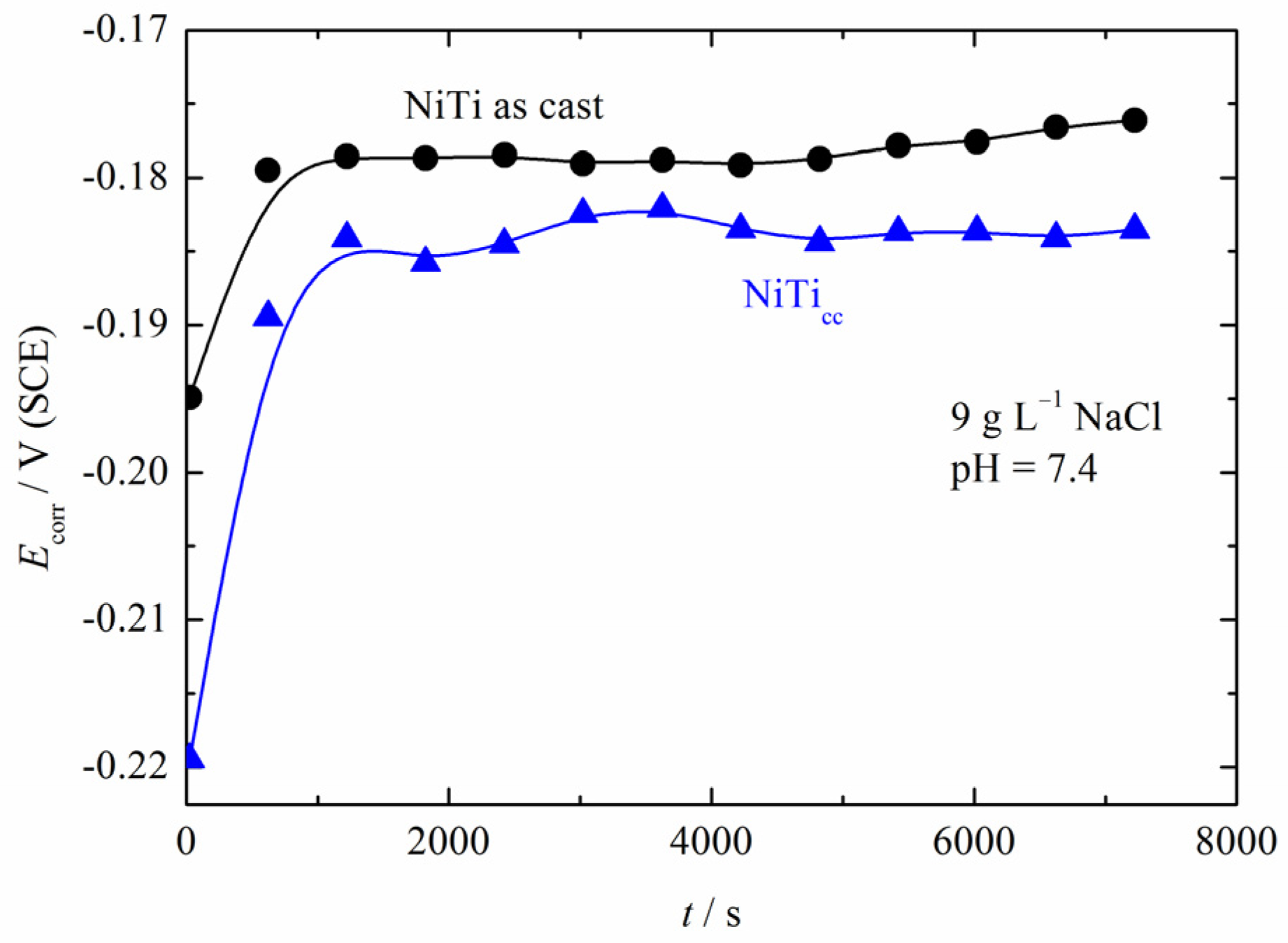
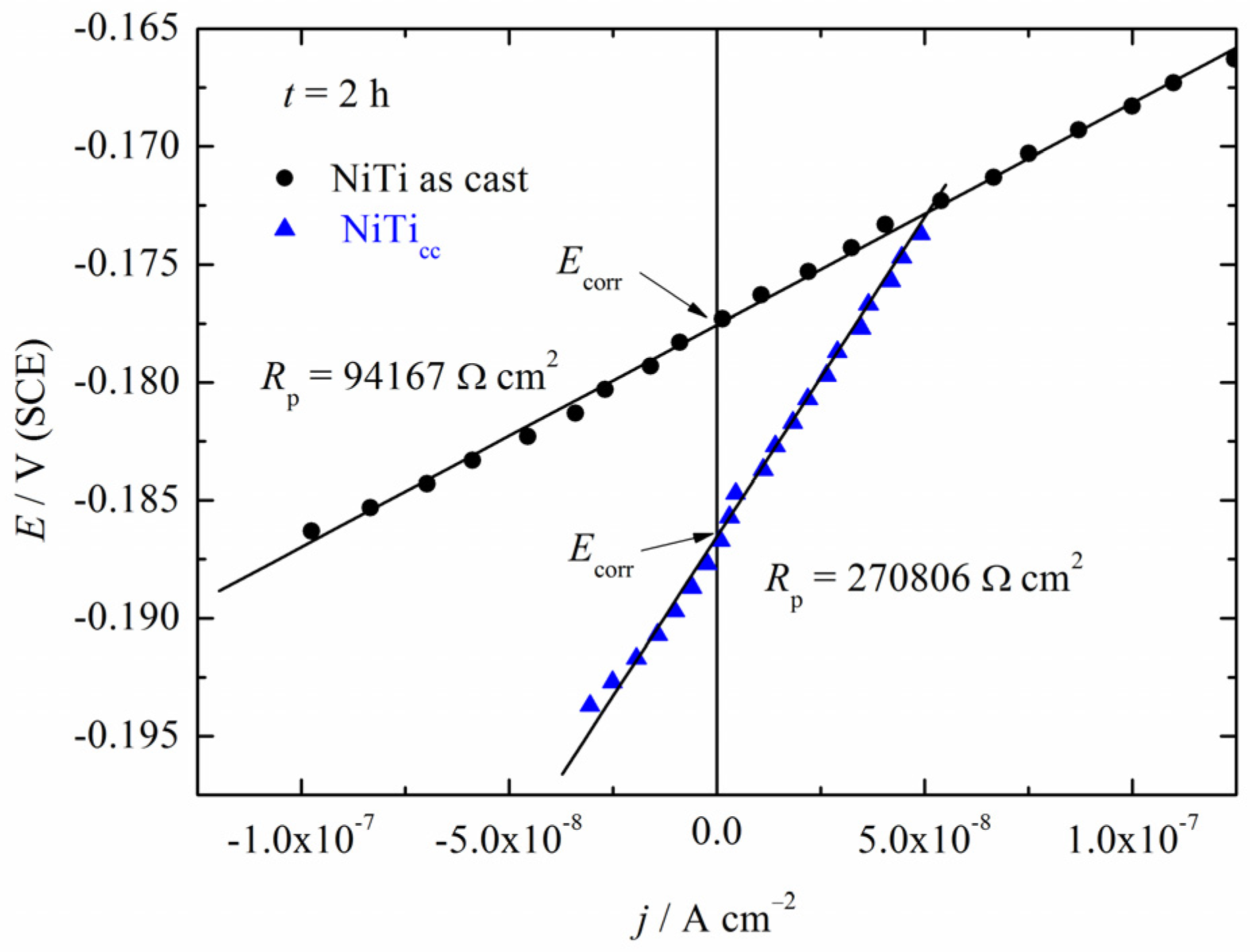
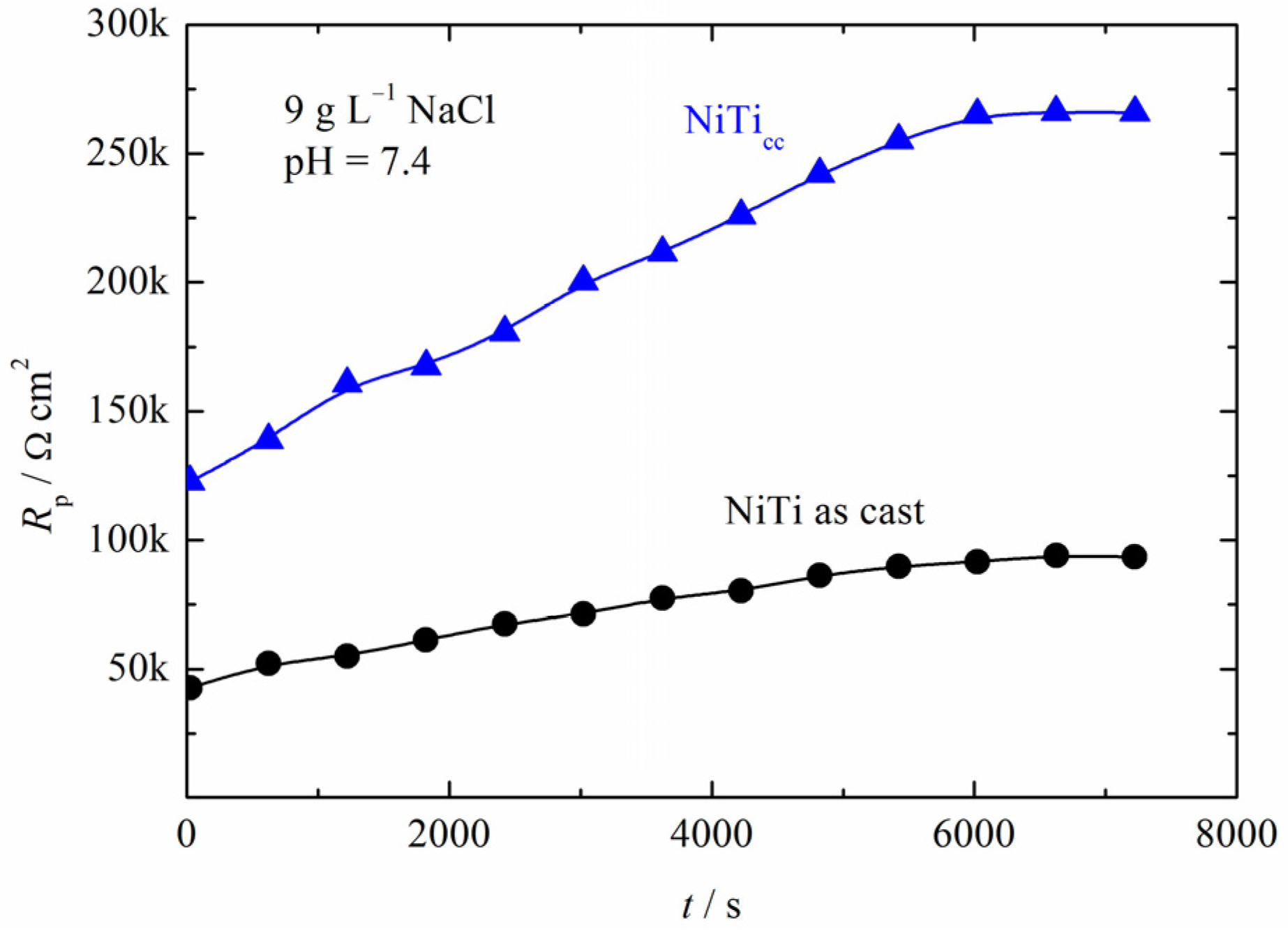
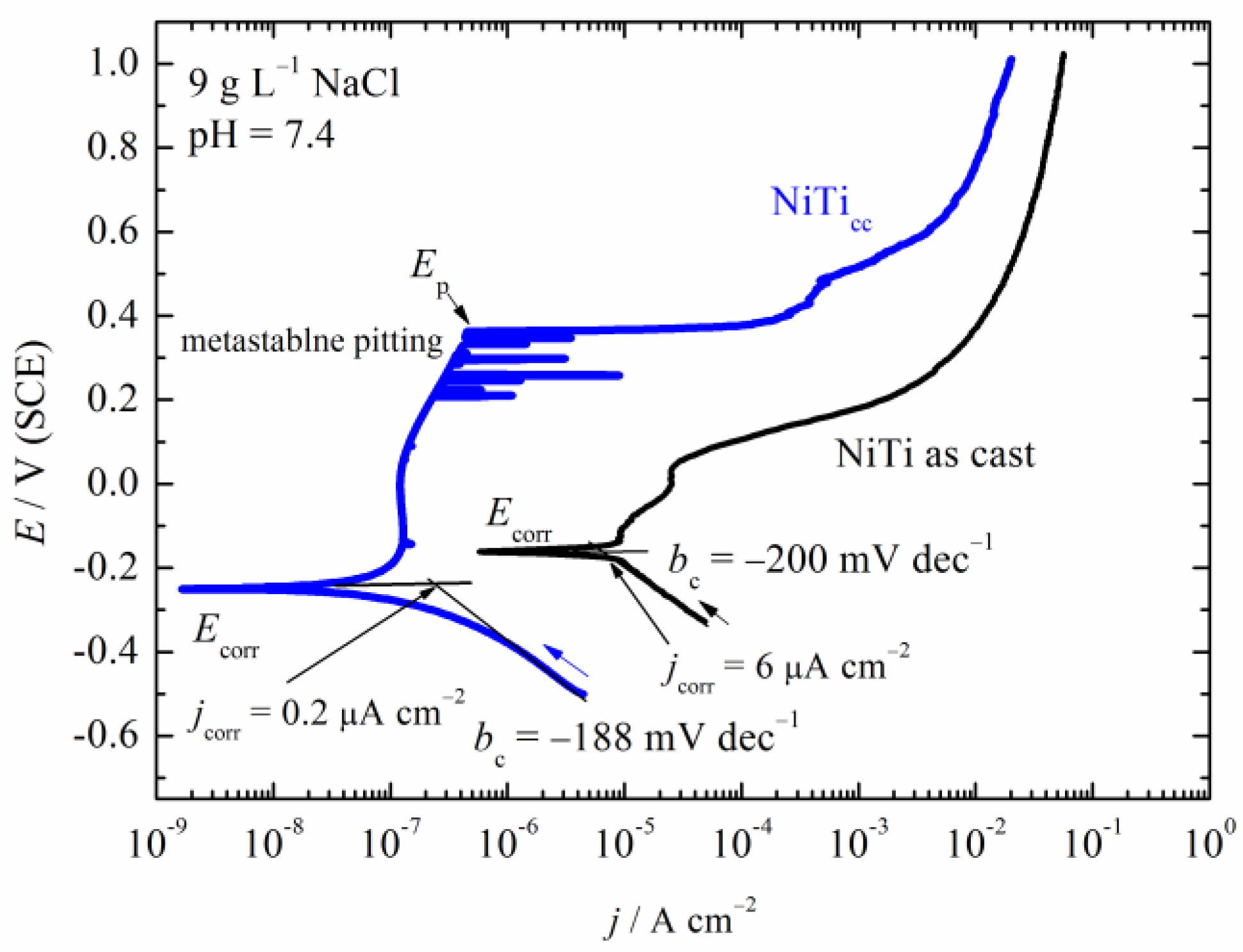
3.3. Polarization Measurements
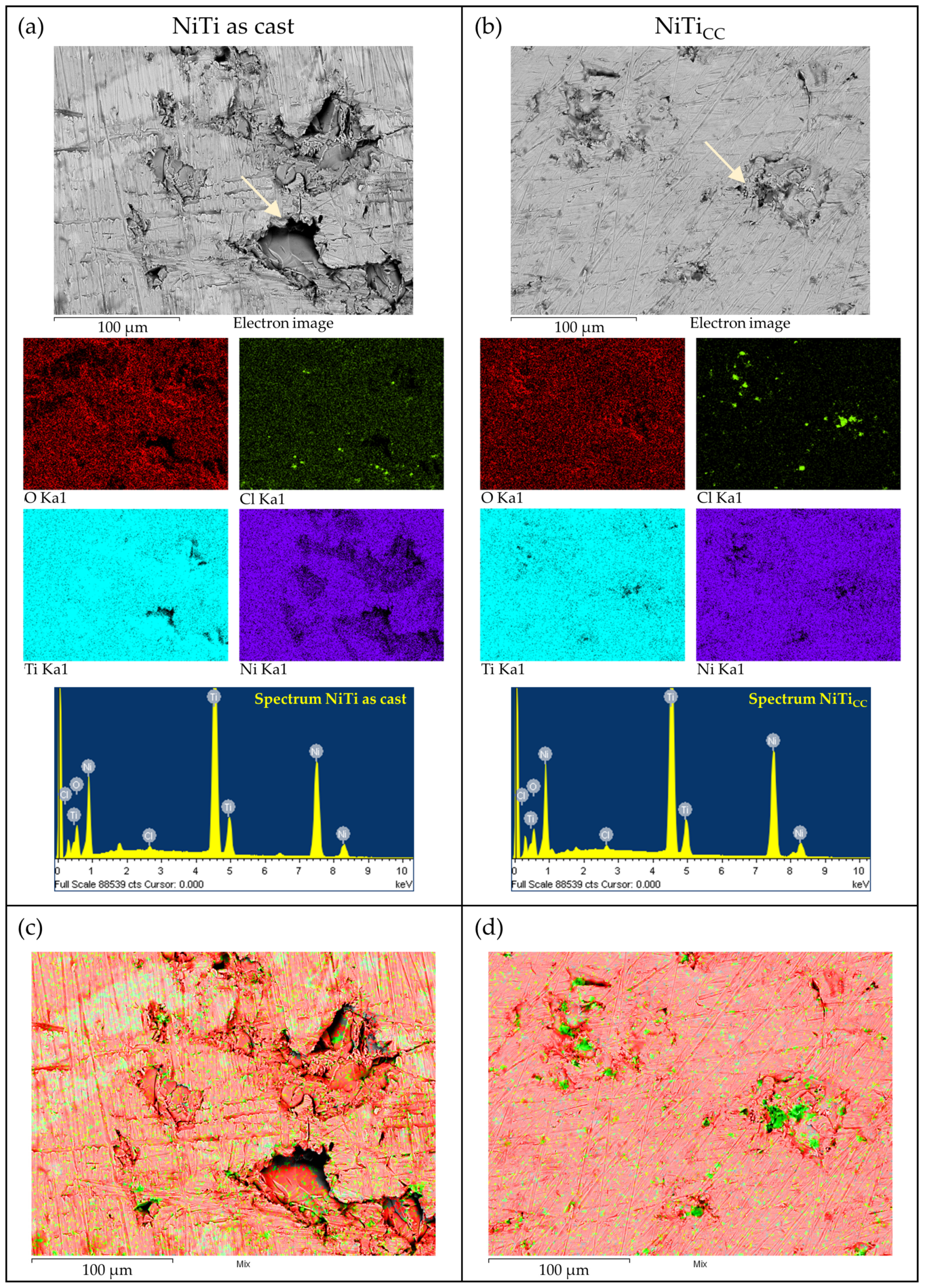
Coating Properties (Oxide Layer Thickness and Elemental Analysis) after Polarization Testing
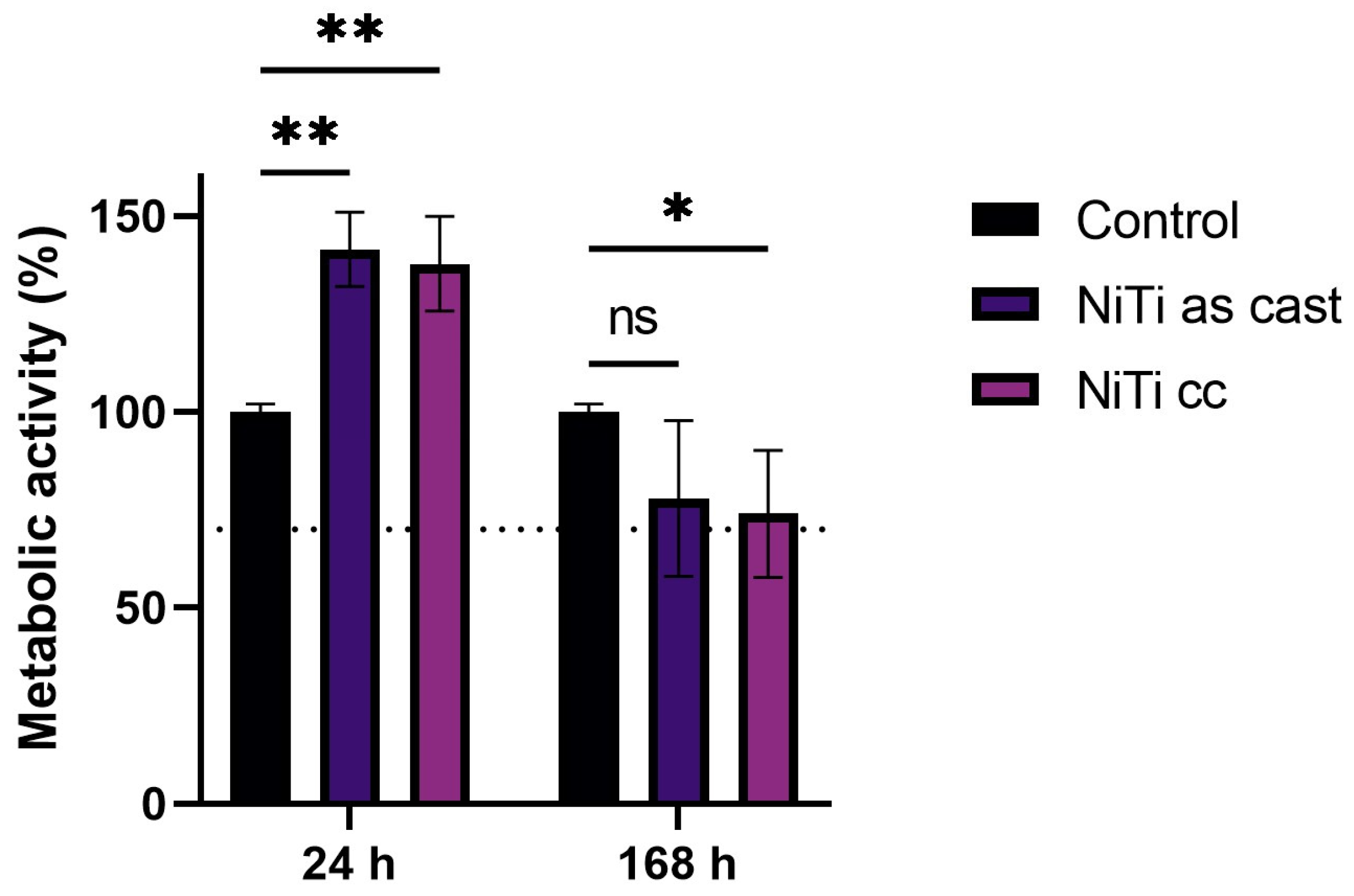
3.4. Cytotoxicity Results
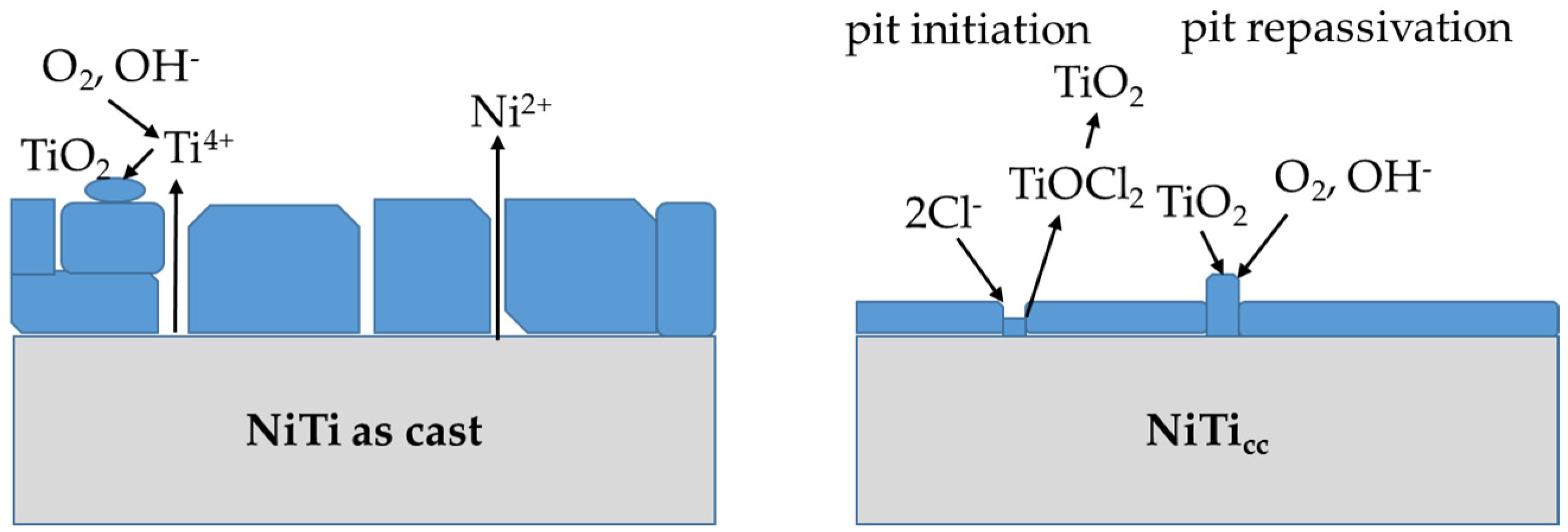
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The method of continuous casting can improve a material’s microstructure along with the corrosion resistance. Better surface stability reduces the Ni ion release.
- Continuous-cast alloys showed better protective characteristics of the surface oxide layer in comparison to commercial NiTi alloys.
- The corroded surface of the NiTi as-cast sample developed thicker oxides with uneven structures, leading to three-times-higher Ni ion release.
- High corrosion density and low corrosion potential indicated low corrosion resistance for the NiTi as-cast sample. Pitting corrosion occurred with pits in diameters up to 100 μm.
- NiTicc showed much better corrosion properties than NiTi as-cast alloys.
- Ni ions released in the conditioning cell mediums of both samples led to a statistically significant decrease in cell viability over seven days.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eliaz, N. Corrosion of Metallic Biomaterials: A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeraya-Calderón, F.; Jáquez-Muñoz, J.M.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Olgui-Coca, J.; Lopez-Leon, L.D.; Estupiñán-López, F.; Lira-Martínez, A.; Gaona Tiburcio, C. Corrosion Resistance of Titanium Alloys Anodized in Alkaline Solutions. Metals 2023, 13, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.; Jahadakbar, A.; Dehghan, A.; Moghaddam, N.S.; Amerinatanzi, A.; Elahinia, M. In Vitro Corrosion Assessment of Additively Manufactured Porous NiTi Structures for Bone Fixation Applications. Metals 2018, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryhänen, J.; Niemi, E.; Serlo, W.; Niemelä, E.; Sandvik, P.; Pernu, H.; Salo, T. Biocompatibility of nickel-titanium shape memory metal and its corrosion behavior in human cell cultures. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 35, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, M.; Gilliland, D.; Ceccone, G.; Chiesa, R.; Cigada, A. Electrochemical release testing of nickel-titanium orthodontic wires in artificial saliva using thin layer activation. Acta Biomater. 2005, 1, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taqa, A.; Fathi, W.; Mohammed, R. Evaluation of Nickel Ion Release from Orthodontic Wires in Different Types of Artificial Saliva. Al-Rafidain Dent. J. 2014, 14, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-H.; Huang, T.-K.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chen, L.-K.; Chou, M.-Y.; Huang, H.-H. Corrosion Resistance of Different Nickel-Titanium Archwires in Acidic Fluoride-containing Artificial Saliva. Angle Orthod. 2010, 80, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pound, B. Susceptibility of nitinol to localized corrosion. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 77, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, G.S.; Li, T.; Scully, J.R. Perspective—Localized corrosion: Passive film breakdown vs pit growth stability. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, C180–C181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Hashmi, M.F. Partial Pressure of Oxygen. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Beetham, R. Scientific Committee of the Association of Clinical Biochemists A Review of Blood pH and Blood-Gas Analysis. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1982, 19, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, E.; Orlov, A.; Borisov, E.; Repnin, A.; Kuzin, S.; Golubkov, N.; Popovich, A. TiNi Alloy Lattice Structures with Negative Poisson’s Ratio: Computer Simulation and Experimental Results. Metals 2022, 12, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Zhao, J.; Misra, R.D.K.; Guo, F.; Xie, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Shang, C. Deep Learning-Based Understanding of Defects in Continuous Casting Product. Metals 2023, 13, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Z.; Soltani, M.K.; Shalavi, S.; Asgary, S. A Review of the Various Surface Treatments of NiTi Instruments. Iran. Endod. J. 2014, 9, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, S.J.L.; Dreher, M.L.; Zheng, J.; Chen, L.; Madamba, D.; Miyashiro, K.; Trépanier, C.; Nagaraja, S. Effects of Oxide Layer Composition and Radial Compression on Nickel Release in Nitinol Stents. Shap. Mem. Superelast. 2015, 1, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabalovskaya, S.A.; Anderegg, J.; Laab, F.; Thiel, P.A.; Rondelli, G. Surface conditions of Nitinol wires, tubing, and as-cast alloys. The effect of chemical etching, aging in boiling water, and heat treatment. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2003, 65, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, B.; Carroll, W.; Rochev, Y.; Hynes, M.; Bradley, D.; Plumley, D. Influence of Nitinol wire surface treatment on oxide thickness and composition and its subsequent effect on corrosion resistance and nickel ion release. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2006, 79A, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trepanier, C.; Venugopalan, R.; Pelton, A.R. Corrosion Resistance and Biocompatibility of Passivated NiTi. In Shape Memory Implants; Yahia, L., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 35–45. ISBN 978-3-642-64118-3. [Google Scholar]
- Shabalovskaya, S.; Anderegg, J.; Van Humbeeck, J. Critical overview of Nitinol surfaces and their modifications for medical applications. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 447–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshaer, R.N.; Ibrahim, K.M. Study of Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Corrosion Behavior of As-Cast Ni-Ti and Ti-6Al-4V Alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 32, 7831–7845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lojen, G.; Stambolić, A.; Šetina Batič, B.; Rudolf, R. Experimental Continuous Casting of Nitinol. Metals 2020, 10, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stambolić, A.; Jenko, M.; Kocijan, A.; Žužek, B.; Drobne, D.; Rudolf, R. Determination of mechanical and functional properties by continuous vertical cast NiTi rod. Mater. Tehnol. 2018, 52, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miličić Lazić, M.; Majerič, P.; Lazić, V.; Milašin, J.; Jakšić, M.; Trišić, D.; Radović, K. Experimental Investigation of the Biofunctional Properties of Nickel–Titanium Alloys Depending on the Type of Production. Molecules 2022, 27, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacoban, S.; Mareci, D.; Bolat, G.; Munteanu, C.; Souto, R.M. Multiscale Electrochemical Investigation of the Corrosion Resistance of Various Alloys Used in Dental Prostheses. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannella, V.; Altomare, R.; Chiaramonte, G.; Di Bella, S.; Mira, F.; Russotto, L.; Pisano, P.; Guercio, A. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Endodontic Pins on L929 Cell Line. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 3469525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, H.; Mayer, S.; Scheu, C. Microstructure and Properties of Engineering Materials. In Neutrons and Synchrotron Radiation in Engineering Materials Science; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–20. ISBN 978-3-527-68448-9. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Du, Z.; Hu, Z. Study on the Effect of Ni Addition on the Microstructure and Properties of NiTi Alloy Coating on AISI 316 L Prepared by Laser Cladding. Materials 2021, 14, 4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashreghi, A.; Zare, H. Investigation of nucleation and growth mechanism during electrochemical deposition of nickel on fluorine doped tin oxide substrate. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2016, 16, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahinia, M.; Shayesteh Moghaddam, N.; Taheri Andani, M.; Amerinatanzi, A.; Bimber, B.A.; Hamilton, R.F. Fabrication of NiTi through additive manufacturing: A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 83, 630–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Directive 2004/96/EC of 27 September 2004 Amending Council Directive 76/769/EEC as Regards Restrictions on the Marketing and Use of Nickel for Piercing Post Assemblies for the Purpose of Adapting Its Annex I to Technical Progress (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/eudr/2004/96/contents (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Baričević, M.; Mravak-Stipetić, M.; Stanimirović, A.; Blanuša, M.; Kern, J.; Lončar, B.; Andabak, A.; Baričević, D. Salivary concentrations of nickel and chromium in patients with burning mouth syndrome. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2011, 19, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lethabane, M.L.; Olubambi, P.A.; Chikwanda, H.K. Corrosion behaviour of sintered Ti–Ni–Cu–Nb in 0.9% NaCl environment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Chu, C.; Xin, Y.; Wu, S.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Chu, P.K. Corrosion products and mechanism on NiTi shape memory alloy in physiological environment. J. Mater. Res. 2010, 25, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parangusan, H.; Bhadra, J.; Al-Thani, N. A review of passivity breakdown on metal surfaces: Influence of chloride- and sulfide-ion concentrations, temperature, and pH. Emergent Mater. 2021, 4, 1187–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, P.; Maurice, V.; Strehblow, H.-H. Localized corrosion (pitting): A model of passivity breakdown including the role of the oxide layer nanostructure. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 2698–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asserghine, A.; Filotás, D.; Nagy, L.; Souto, R.M.; Nagy, G. Do titanium biomaterials get immediately and entirely repassivated? A perspective. Npj Mater. Degrad. 2022, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincic Mlinaric, M.; Durgo, K.; Katic, V.; Spalj, S. Cytotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by nickel and titanium ions from dental alloys on cells of gastrointestinal tract. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 383, 114784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchenko, E.; Baigonakova, G.; Dubovikov, K.; Kokorev, O.; Yasenchuk, Y.; Vorozhtsov, A. In Vitro Bio-Testing Comparative Analysis of NiTi Porous Alloys Modified by Heat Treatment. Metals 2022, 12, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouwels, S.D.; Sigaeva, A.; de Boer, S.; Eichhorn, I.A.; Koll, L.; Kuipers, J.; Schirhagl, R.; Heijink, I.H.; Burgess, J.K.; Slebos, D.-J. Host–device interactions: Exposure of lung epithelial cells and fibroblasts to nickel, titanium, or nitinol affect proliferation, reactive oxygen species production, and cellular signaling. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2023, 34, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrzanowski, W.; Neel, E.A.A.; Armitage, D.A.; Zhao, X.; Knowles, J.C.; Salih, V. In vitro studies on the influence of surface modification of Ni-Ti alloy on human bone cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 93, 1596–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, P. Wound healing and the role of fibroblasts. J. Wound Care 2013, 22, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balać, I.; Bugarski, B.; Ćosić, I.; Dramićanin, M.; Đorđević, D.; Filipović, N.D.; Ignjatović, N.L.; Janaćković, Đ.T.; Kojić, M.; Manojlović, V.; et al. Biomaterijali; Materials Research Society, Institute of Technical Sciences of the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Art: Belgrade, Serbia, 2010; ISBN 978-86-80321-23-3. [Google Scholar]
- Mani, G.; Porter, D.; Grove, K.; Collins, S.; Ornberg, A.; Shulfer, R. Surface finishing of Nitinol for implantable medical devices: A review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 2763–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
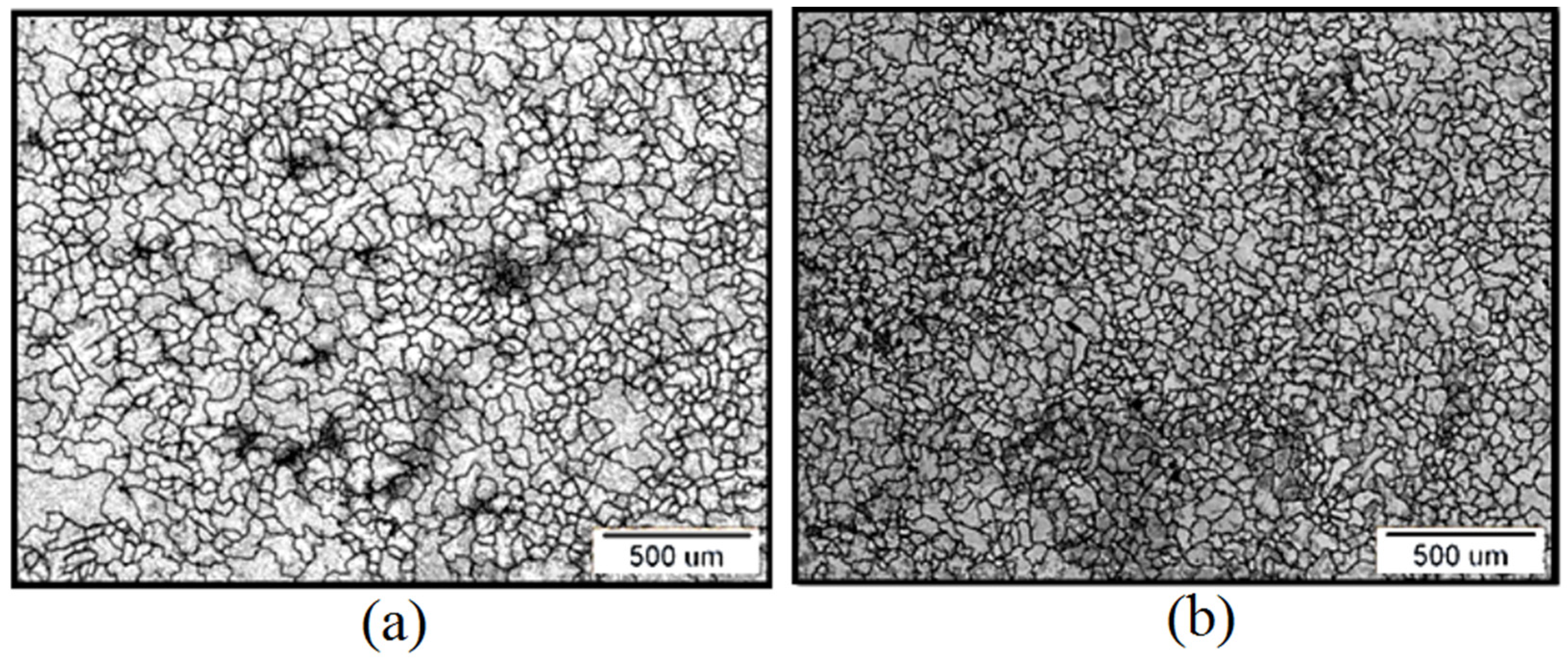
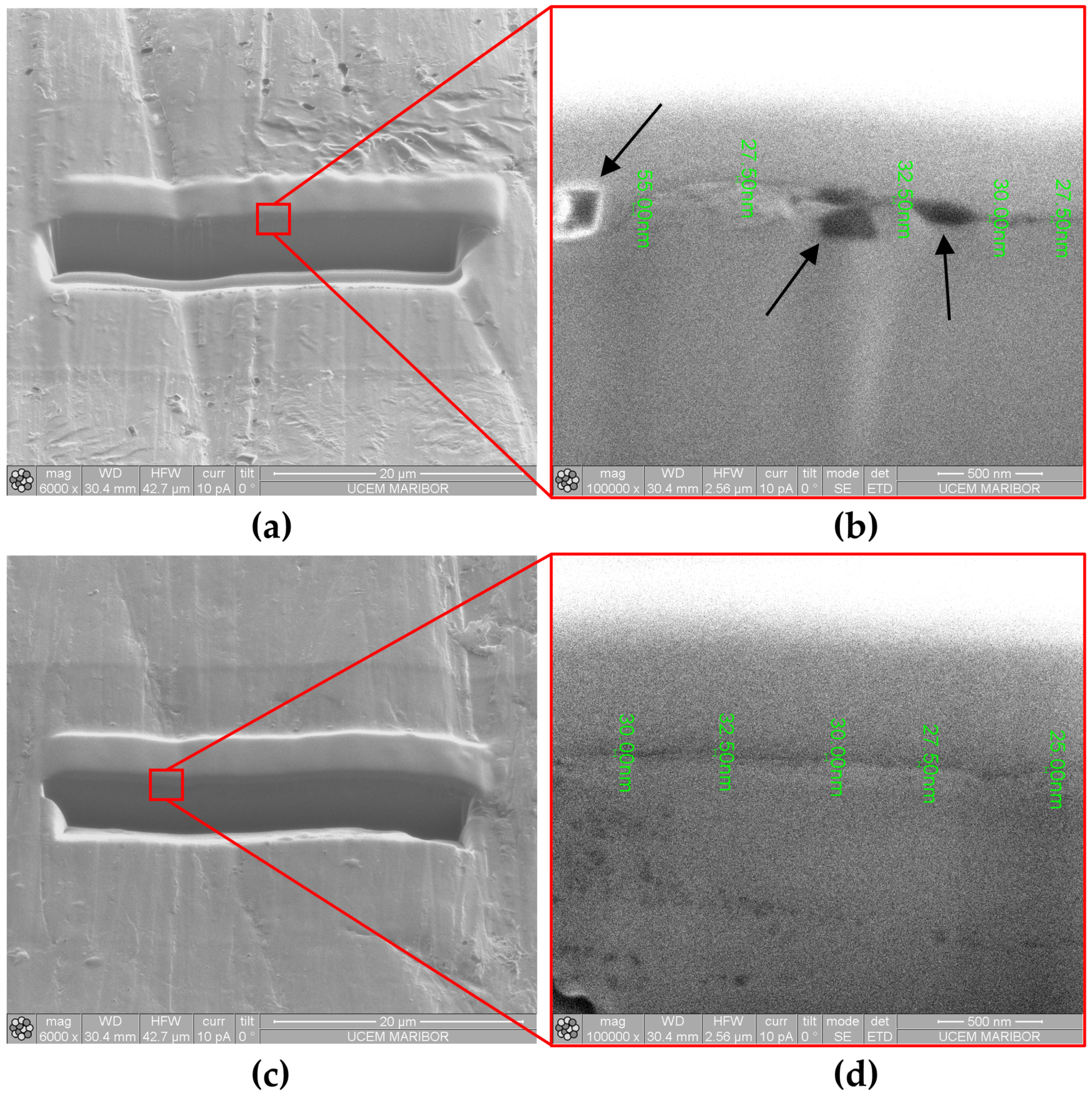
| Sample | Grain Number (G) | Number of Grains (per mm2) | Average Grain Size (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiTi as cast | 5 | 256 | 0.0527 |
| NiTicc | 7 | 1024 | 0.0234 |
| Sample | Nickel | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| NiTi as cast | 2.33 | 2.17 |
| NiTicc | 1.22 | 0.631 |
| Reference solution | >0.02 | >0.01 |
| NiTi as Cast | NiTicc | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | 161.25 | 44.83 |
| St. Dev. | 30 | 6.74 |
| Min | 133.33 | 33.33 |
| Max | 254.17 | 60 |
| N | 20 | 25 |
| Element | Weight% | Atomic% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiTi as Cast | NiTicc | NiTi as Cast | NiTicc | |
| O | 16.59 | 14.16 | 39.46 | 35.28 |
| Cl | 0.34 | 0.40 | 0.37 | 0.45 |
| Ti | 43.22 | 41.06 | 34.34 | 34.16 |
| Ni | 39.85 | 44.37 | 25.83 | 30.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lazić, M.M.; Mitić, D.; Radović, K.; Đorđević, I.; Majerič, P.; Rudolf, R.; Grgur, B.N. Corrosion Behavior of Nickel–Titanium Continuous-Casted Alloys. Metals 2024, 14, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14010088
Lazić MM, Mitić D, Radović K, Đorđević I, Majerič P, Rudolf R, Grgur BN. Corrosion Behavior of Nickel–Titanium Continuous-Casted Alloys. Metals. 2024; 14(1):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14010088
Chicago/Turabian StyleLazić, Minja Miličić, Dijana Mitić, Katarina Radović, Igor Đorđević, Peter Majerič, Rebeka Rudolf, and Branimir N. Grgur. 2024. "Corrosion Behavior of Nickel–Titanium Continuous-Casted Alloys" Metals 14, no. 1: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14010088
APA StyleLazić, M. M., Mitić, D., Radović, K., Đorđević, I., Majerič, P., Rudolf, R., & Grgur, B. N. (2024). Corrosion Behavior of Nickel–Titanium Continuous-Casted Alloys. Metals, 14(1), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14010088








