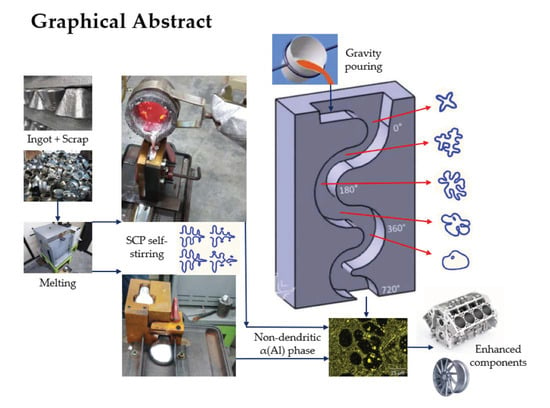
Semi-Solid Slurries for Rheocasting of Hypoeutectic Al-Si-X Alloys Produced by Self-Stirring in Serpentine Channels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Recent Developments in Slurry Forming
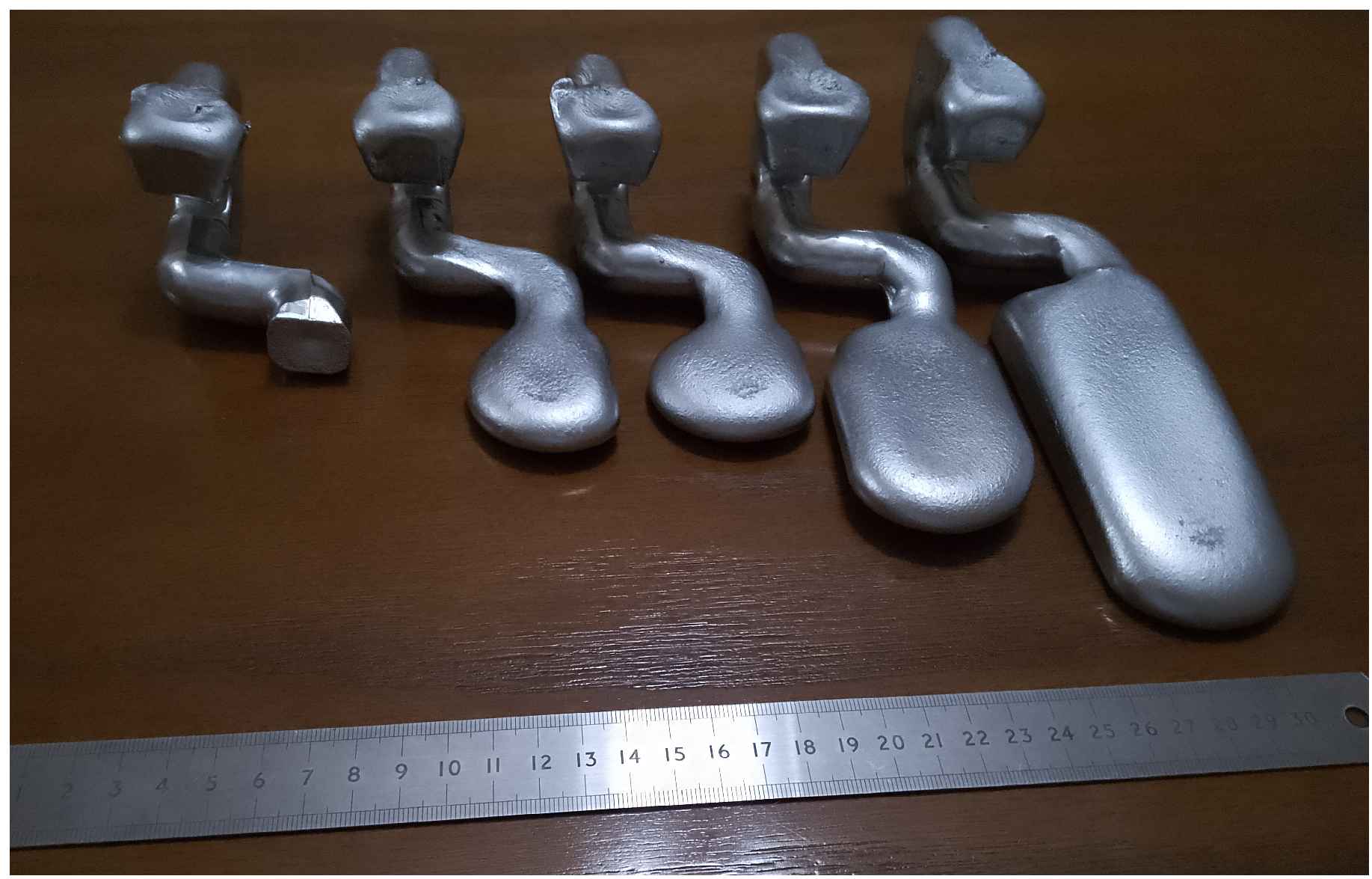
3. Experimental Procedure
4. Results and Discussion
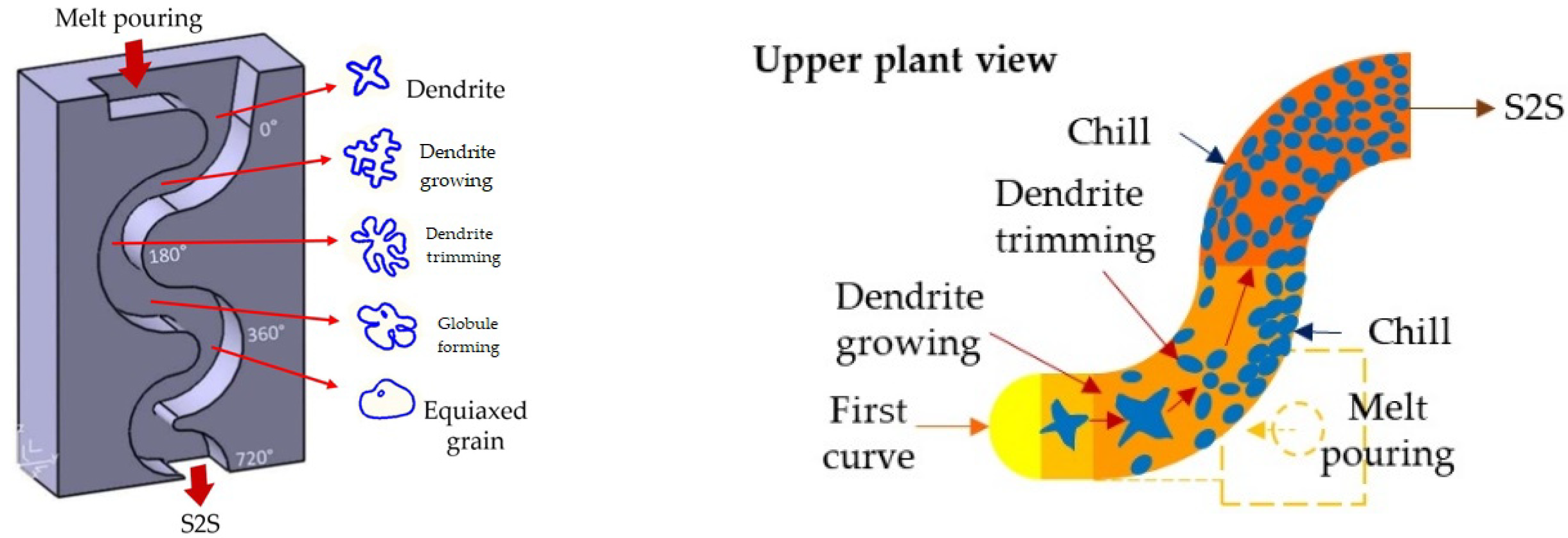
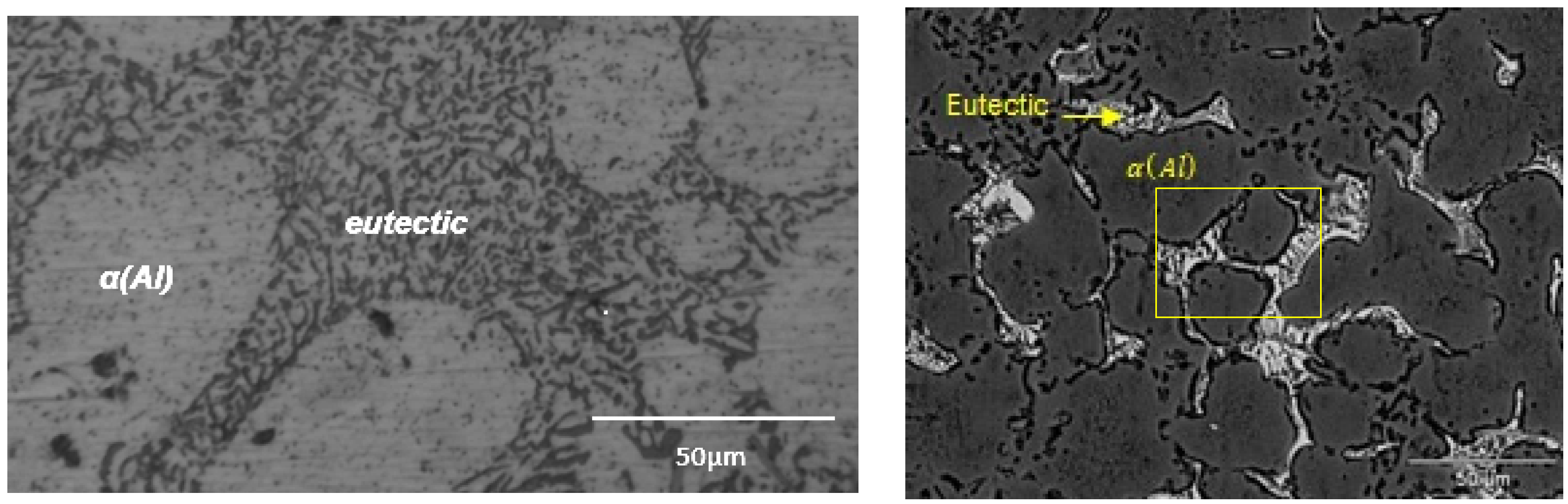
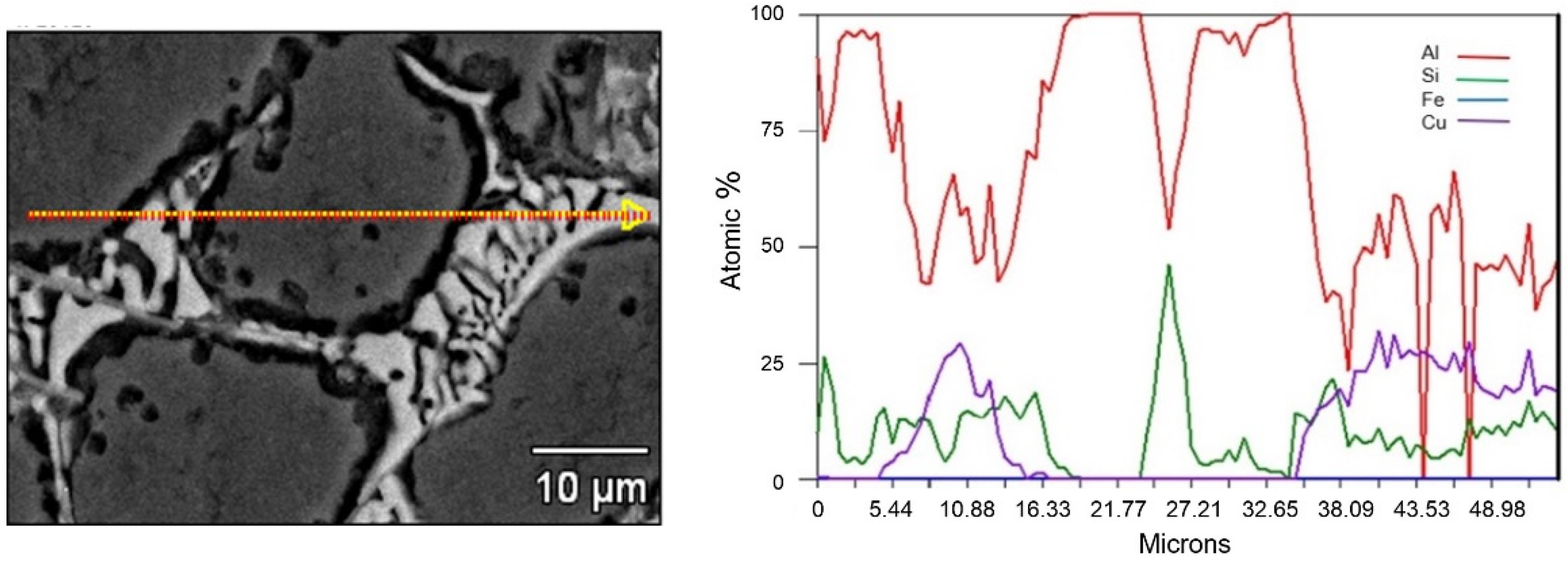
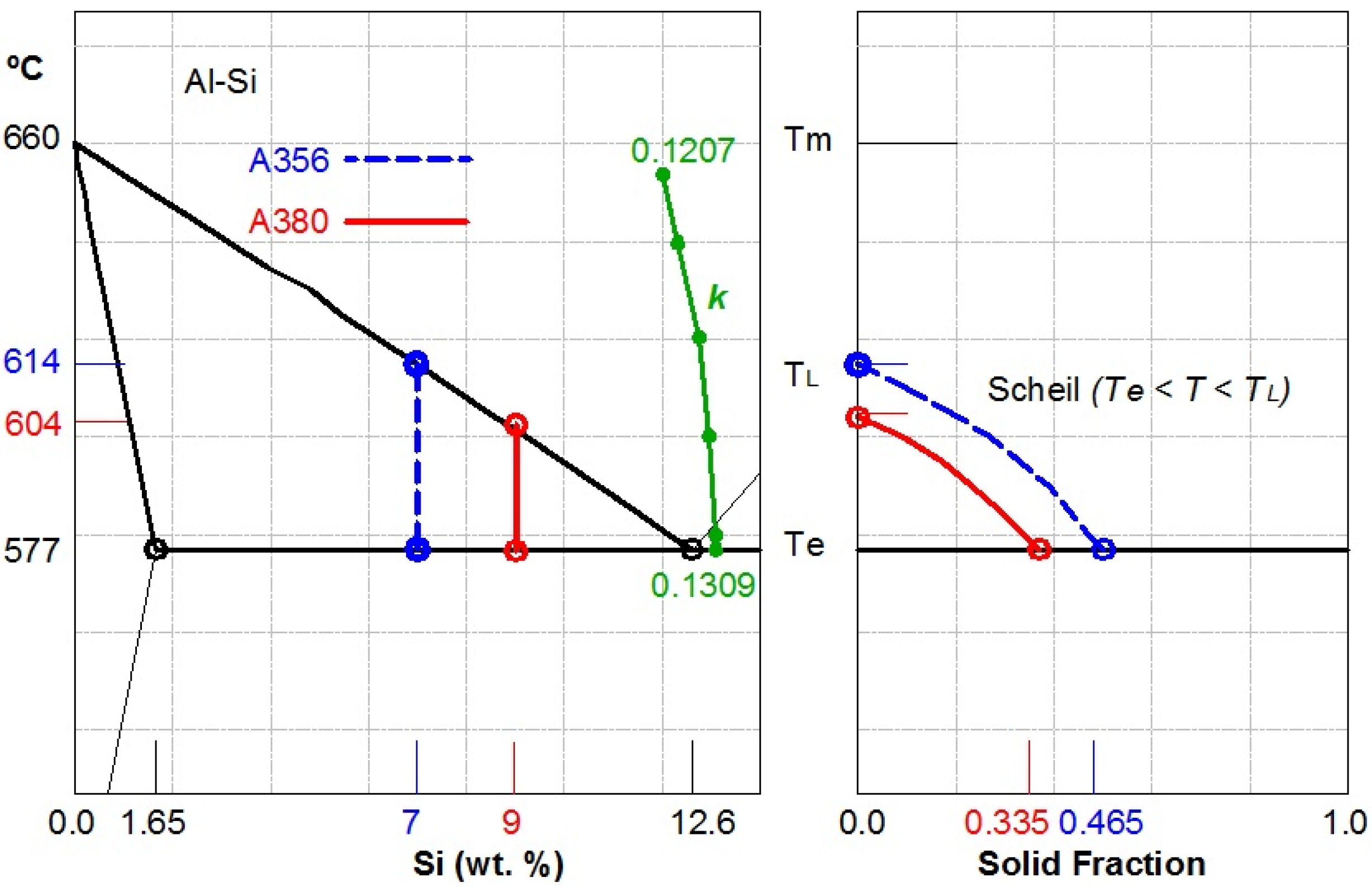
4.1. A380 Alloy Processed by Vertical SCP
4.2. A356 Alloy Processed by Horizontal SCP
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spencer, D.B.; Mehrabian, R.; Flemings, M.C. Rheological behavior of Sn-15 pct Pb in the crystallization range. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1972, 3, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannasin, J. Semi-Solid Slurry Forming of Alloys; North American Die Casting Association NADCA: Arlington Heights, IL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood, D.; Suéry, M.; Kapranos, P.; Atkinson, H.; Young, K. Semi-solid Processing of Alloys; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lu, H.; Hu, X.; Lin, F.; Li, X.; Zhu, Q. Current Progress in Rheoforming of Wrought Aluminum Alloys: A Review. Metals 2020, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modigell, M.; Pola, A.; Tocci, M. Rheological Characterization of Semi-Solid Metals: A Review. Metals 2018, 8, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pola, A.; Tocci, M.; Kapranos, P. Microstructure and properties of semi-solid alloys: A literature review. Metals 2018, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menargues, S.; Baile, M.T.; Martin, E.; Raya, O.M.; Picas, J. New mechanical stirring system to study the rheological behavior of A380 second melting aluminium alloy. Res. Sq. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M. Thixocasting and rheocasting technologies, improvements going on. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2012, 54, 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, R.A.; Flemings, M.C. Evolution on particle morphology in semisolid processing. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 2205–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, K.; Gonda, V.; Réger, M.; Varga, P. Comparison of Microstructure, Density and Shrinkage Porosity for Casting and Rheocasting of AlSi7Mg Alloy. Res. Sq. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.G.; Zhu, Q.; Midson, S.P.; Atkinson, H.V.; Doug, H.B.; Zhang, F. Blistering in semi-solid die casting of aluminium alloys and its avoidance. Acta Mater. 2017, 124, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.S.; Omar, M.Z.; Syarif, J.; Mohammed, M.N. An Overview of Semisolid Processing of Aluminium Alloys. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 679820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotadia, H.R.; Hari, B.N.; Zhang, H.; Arumuganathar, S.; Fan, Z. Solidification Behavior of Intensively Sheared Hypoeutectic Al-Si Alloy Liquid. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 42, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafisi, S.; Ghomashchi, R. Semi-Solid Processing of Aluminum Alloys; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boluri Gashti, A.H.; Abedi, H.R.; Salehi, M.T. Microstructure evolution and constitutive modeling of as-cast A356 aluminum alloy in semi-solid regime. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 7720–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabazon, D.; Browne, D.J.; Carr, A.J. Experimental investigation of the transient and steady state rheological behavior of Al-Si alloys in the mushy state. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2003, A326, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarmand, M.; Salehi, M.; Shabestari, S.G.; Saghafian, H. Impact strength and structural refinement of A380 aluminum alloy produced through gas-induced semi-solid process and Sr addition. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannasin, J.; Flemings, M. Development of the Gas Induced Semi-Solid Metal Process for Aluminum Diecasting Applications. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Semi-Solid Processing of Alloys and Composites, Aachen, Germany, 16–18 September 2008; pp. 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wannasin, J.; Janudom, S.; Rattanochaikul, T.; Canyook, R.; Burapa, R.; Chucheep, T.; Thanabumrungkul, S. Research and development on the gas induced semi solid process for industrial applications. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Semi-Solid Processing of Alloys and Composites, Busan, Republic of Korea, 11–13 September 2010; pp. 544–548. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, M.; Meng, S.; Fu, Y.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Guan, R. Solidification behavior and enhanced properties of semi-solid Al-8.5Si-0.5Fe alloys fabricated by rheo-diecasting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 3160–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.-Y.; Mao, W.-M.; Geng, X.-X. Preparation of semi-solid 6061 aluminum alloy slurry by serpentine channel pouring. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-Y.; Mao, W.-M.; Wang, W.-P.; Zheng, Z.-K. Preparation of semi-solid A380 aluminum alloy slurry by serpentine channel. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-Y.; Mao, W.-M.; Wang, W.-P.; Zheng, Z.-K.; Yue, R. Investigation of rheo-diecasting mold filling of semi-solid A380 aluminum alloy slurry. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2017, 24, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Kumar, M.; Samanta, S.; Dutta, P.; Ghosh, D. Semisolid Processing of A380 Al Alloy Using Cooling Slope. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2014, 29, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Samanta, S.K.; Das, R.; Dutta, P. Optimization of degree of sphericity of primary phase during cooling slope casting of A356 Al alloy: Taguchi method and regression análisis. Measurement 2014, 55, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Samanta, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Dutta, P. Phase Field Simulation of Equiaxed Microstructure Formation during Semi-solid Processing of A380 Alloy. ISIJ Int. 2014, 54, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hirt, G.; Kopp, R. (Eds.) Thixoforming, Semi-Solid Metal Processing; Wiley-VCH: Weihnheim, Germany, 2009; pp. 344–345. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, W.; El-Hadad, S. Ultrasonication effects on the microstructure characteristics of the A380 die cast alloy. Int. J. Met. 2019, 13, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, A.W.; Fisher, D.J. Fundamentals of Solidification; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Wollerau, Switzerland, 1992; ISBN 0-87849-804-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bonatti, R.S.; Bortolozo, A.D.; Baldo, R.F.G.; Poloni, E.; Osório, W.R. Anisotropic Tensile and Compressive Strengths of Al–4 wt.%Cu Alloy Powder: Part 1—Effects of Compaction Loads and Heat Treatments. Metals 2023, 13, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzig, J.A.; Rappaz, M. Solidification; CRC Press: Cham, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, A.; Chávez, F.; Hernández, R. Simplified rheocasting of Al-Si alloys sheared by mechanical stirring. Key Eng. Mater. 2015, 651–653, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, A.; Chávez, J.F. Stir Casting and Atmospheric Pouring of A380 Alloy with Sr Addition. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2113, 140003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.-L.; Guo, H.-M.; Ma, T.-F.; Jin, H.-L. Microstructure evolution in semi-solid A356 aluminium alloy treated by ICTE process. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 39, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, A.V.R.; Brollo, G.L.; Tamayo, D.V.; Zoqui, E.J. Thixoforming of an Al-Si-Zn-Mg Alloy–Thermodynamic Characterization, Microstructural Evolution and Rheological Behavior. Mater. Res. 2021, 24, e20200313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




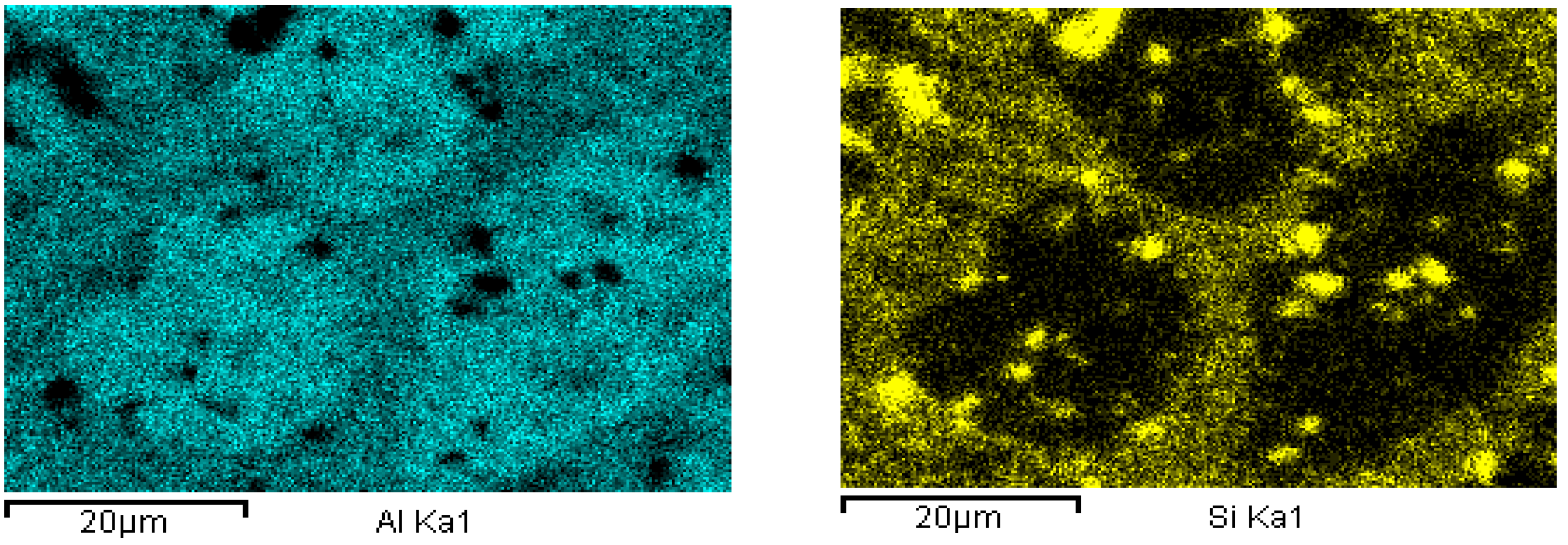


| Alloy | Casting Process | Tensile Strength, (MPa) | Strain, (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A356 | HPDC + T6 | 227 | 3 |
| A356 | RHDC | 243 | 4 |
| A356 | RHDC + T6 | 277 | 14 |
| A380 | HPDC + T6 | 317 | 3 |
| Si | Mg | Cu | Fe | Mn | Zn | Ni | Ti | Sr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A380 | 9.00 | 0.012 | 4.050 | 0.361 | 0.012 | 0.051 | 0.015 | 0.014 | 0.0001 |
| A356 | 7.12 | 0.338 | 0.003 | 0.369 | 0.011 | 0.032 | 0.015 | 0.011 | 0.0001 |
| Pouring Temperature, (°C) | Globule Size GLS, (µm) | Shape Factor, C |
|---|---|---|
| 690 | 48 ± 4 | 0.41 ± 0.03 |
| 660 | 51 ± 2 | 0.52 ± 0.03 |
| 630 | 43 ± 2 | 0.59 ± 0.03 |
| 615 | 39 ± 2 | 0.68 ± 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfredo, H.; José Federico, C.; Aldo, H.; Miguel Ángel, S. Semi-Solid Slurries for Rheocasting of Hypoeutectic Al-Si-X Alloys Produced by Self-Stirring in Serpentine Channels. Metals 2024, 14, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14040413
Alfredo H, José Federico C, Aldo H, Miguel Ángel S. Semi-Solid Slurries for Rheocasting of Hypoeutectic Al-Si-X Alloys Produced by Self-Stirring in Serpentine Channels. Metals. 2024; 14(4):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14040413
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfredo, Hernández, Chávez José Federico, Hernández Aldo, and Suárez Miguel Ángel. 2024. "Semi-Solid Slurries for Rheocasting of Hypoeutectic Al-Si-X Alloys Produced by Self-Stirring in Serpentine Channels" Metals 14, no. 4: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14040413
APA StyleAlfredo, H., José Federico, C., Aldo, H., & Miguel Ángel, S. (2024). Semi-Solid Slurries for Rheocasting of Hypoeutectic Al-Si-X Alloys Produced by Self-Stirring in Serpentine Channels. Metals, 14(4), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14040413