The Influence of Cr Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-25Mn-10Al-1.2C Lightweight Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure Evolution
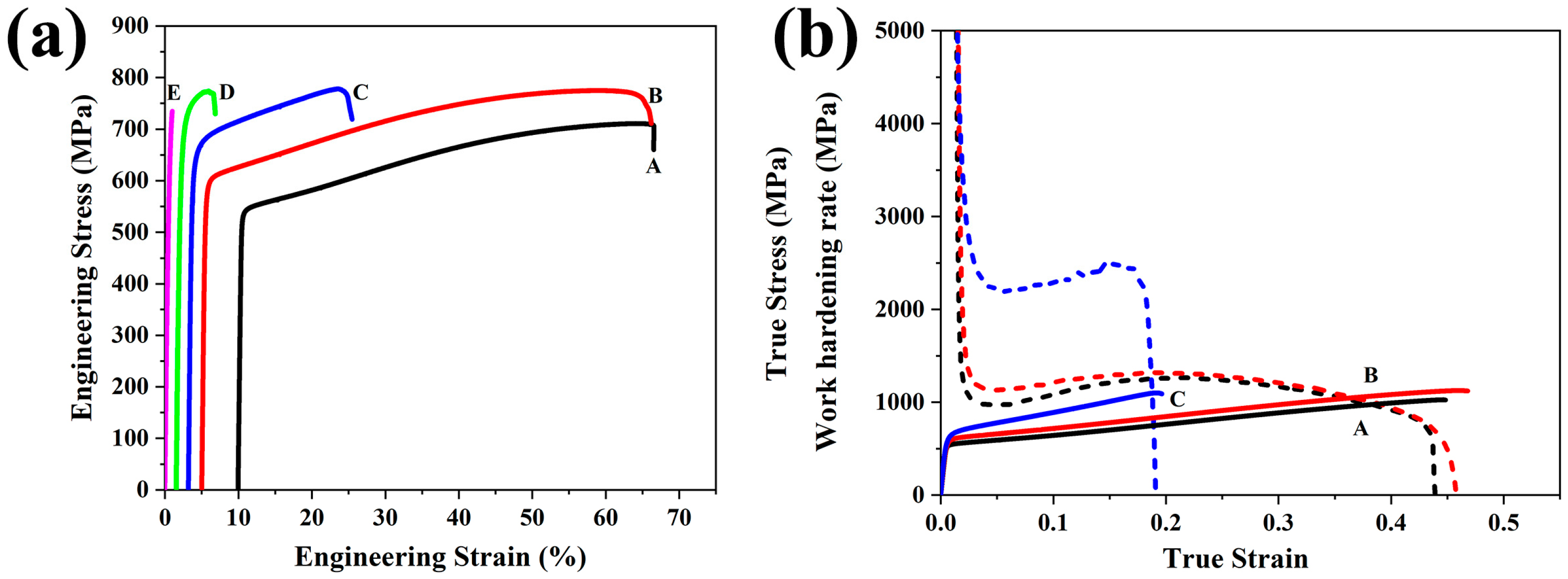
3.2. Mechanical Properties and Deformation Behavior
3.3. Precipitation of Intragranular κ-Carbides
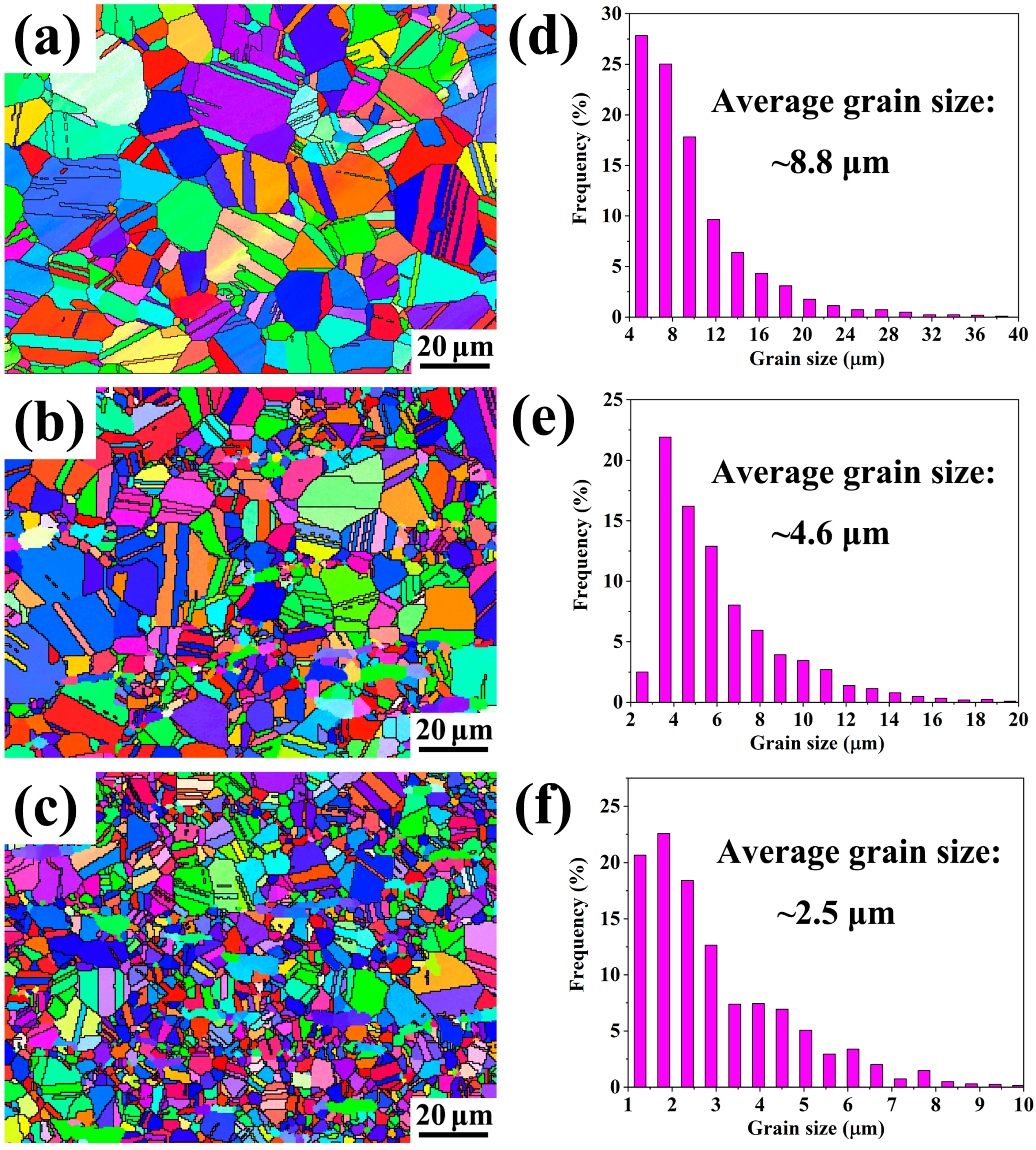
3.4. Refinement of Austenite Grain
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The Fe-25Mn-10Al-1.2C steel without Cr contains a fully austenitic single phase. With the addition of Cr content, the volume fraction of ferrite continuously increased. After the Cr content exceeds 5 wt%, the distinct peaks of various ordered structure phases appeared. The Cr–rich phase was confirmed as a Cr7C3 carbide through XRD structure combined with EDS composition. Significant precipitation of Cr7C3 carbides was observed when the Cr content exceeded 5 wt%.
- (2)
- The steel without Cr in the as-cast state contained fine κ-carbides, with sizes ranging from approximately 100 to 500 nm. After solution treatment at 1050 °C, the precipitated phase became finer, with sizes around 2 to 20 nm. In the steel with a 5 wt% Cr content, there were few κ-carbides, and the size mostly was smaller than 5 nm. This indicates that the addition of 5% Cr significantly inhibited the nucleation of κ-carbides and promoted the formation of Cr–rich Cr7C3 carbides. After cold rolling, followed by recrystallization annealing at 950 °C, the austenite grain sizes were 8.8 μm, 4.6 μm, and 2.5 μm for Cr contents of 0 wt%, 2.5 wt%, and 5 wt%, respectively. The results indicate that the addition of Cr can play a significant role in refining grain size.
- (3)
- The tensile strength of the steel without Cr is 708 MPa, with an elongation of 56.5% and a strength–ductility product of 40 GPa%. The addition of 2.5 wt% Cr enhanced both strength and ductility synergistically. When the Cr content exceeds 5 wt%, the strength increased while the elongation decreased due to the precipitation of Cr7C3 carbides. The steel with 5 wt% Cr exhibited excellent high-strain hardening ability. As the Cr content increases to 10 wt%, the steel becomes completely brittle.
- (4)
- The addition of an appropriate Cr content synergistically enhances both strength and ductility, suggesting that this steel could be a promising candidate for applications requiring high strength and good formability. However, the precipitation of Cr7C3 carbides at higher Cr contents, which leads to a decrease in ductility, indicates that careful consideration of alloy composition is necessary to avoid brittleness. The findings of this study could also be extended to other alloy systems, contributing to the broader understanding of alloy design and property optimization in lightweight steels.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, D.G.; Ding, H.; Han, D.; Cai, M.H. Improvement of the yield strength of Fe-11Mn-xAl-yC medium-Mn lightweight steels by tuning partial recrystallization and intra-granular κ-carbide strengthening. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 833, 142553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ge, Y.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Feng, Y.L.; Chen, C.; Zhang, F.C. Tensile Properties and Microstructure Evolutions of Low-Density Duplex Fe-12Mn-7Al-0.2C-0.6Si Steel. Materials 2022, 15, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Kang, T.; Li, F.; Gao, P.F.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.Z. Dynamic recrystallization behavior and microstructure evolution of low-density high-strength Fe-Mn-Al-C steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piston, M.; Bartlett, L.; Limmer, K.R.; Field, D.M. Microstructural Influence on Mechanical Properties of a Lightweight Ultrahigh Strength Fe-18Mn-10Al-0.9C-5Ni (wt%) Steel. Metals 2020, 10, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaško, T.; Šetina, B.B.; Medved, J.; Burja, J. High-Temperature Oxidation Behaviour of Duplex Fe-Mn-Al-Ni-C Lightweight Steel. Crystals 2022, 12, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Lee, G.; Koo, M.; Song, H.; Ko, W.S.; Sohn, S.S. Effects of Mn Segregations on Intergranular Fracture in a Medium-Mn Low-Density Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2022, 94, 2200240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Rana, R.; Haldar, A.; Ray, R.K. Current state of Fe-Mn-Al-C low density steels. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 89, 345–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Li, X.; Yi, H. The κ-Carbides in Low-Density Fe-Mn-Al-C Steels: A Review on Their Structure, Precipitation and Deformation Mechanism. Metals 2020, 10, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Jo, M.; Kim, D.W. Vanadium or copper alloyed duplex lightweight steel with enhanced hydrogen embrittlement resistance at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 817, 141347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.T.; He, Y.L.; Zhu, N.Q.; Ding, M.L.; Liu, R.D.; Zhang, Y. Deformation Mechanism Investigation on Low Density 18Mn Steels under Different Solid Solution Treatments. Metals 2021, 11, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Tan, Y.; Malik, A.; Wang, Y.W.; Naqvi, S.Z.H.; Cheng, H.W.; Tian, J.B.; Meng, X.M. Dynamic Compressive Mechanical Behavior and Microstructure Evolution of Rolled Fe-28Mn-10Al-1.2C Low-Density Steel. Material 2022, 15, 3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Liu, D.; Cai, M.; Zhang, Y. Austenite-Based Fe-Mn-Al-C Lightweight Steels: Research and Prospective. Metals 2022, 12, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, K.; Singh, A. Microstructural evolution after heat treatment of high specific strength steel: Fe-13Al-16Mn-5Ni-0.8C and correlation with tensile properties. Materialia 2022, 22, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Chen, X.P.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.X.; Cao, W.Q.; Liu, Q. Evolution of microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of Fe-30Mn-11Al-1.2C low-density steel during cold rolling. Mater. Charact. 2021, 174, 111013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Lu, W.J.; Zhao, H.; He, J.Y.; Wang, K.; Zhou, B.C.; Ponge, D.; Raabe, D.; Li, Z.M. Formation mechanism of κ-carbides and deformation behavior in Si-alloyed FeMnAlC lightweight steels. Acta Mater. 2020, 198, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.Y.; Zhou, Z.M.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Tang, D.; Liang, J.H.; He, Q. Tensile Behavior and Deformation Mechanism of Fe-Mn-Al-C Low Density Steel with High Strength and High Plasticity. Metals 2019, 9, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Tang, Z.Y.; You, Z.Y.; Guan, G.F.; Ding, H.; Misra, D. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Deformation Behavior of Fe-28.7Mn-10.2Al-1.06C High Specific Strength Steel. Metals 2022, 12, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Duh, J.G.; Tsai, S.Y. Corrosion resistance and microstructural evaluation of the chromized coating process in a dual phase Fe-Mn-Al-Cr alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 153, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Wu, C.C.; Liu, T.F. The influence of Cr alloying on microstructures of Fe-Al-Mn-Cr alloys. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Tsai, C.Y.; Chao, C.G.; Liu, T.F. Effect of chromium content on corrosion Behaviors of Fe-9Al-30Mn-(3,5,6.5,8)Cr-1C alloys. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 2973–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, Y.H.; Wang, C.S.; Tsai, C.Y.; Chao, C.G.; Liu, T.F. Corrosion behaviors of austenitic Fe-30Mn-7Al-xCr-1C alloys in 3.5% NaCl solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, G.D.; Lin, C.L.; Chao, C.G.; Liu, T.F. A New Austenitic FeMnAlCrC Alloy with High-Strength, High-Ductility, and Moderate Corrosion Resistance. Mater. Trans. 2010, 51, 2318–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wang, C. Effect of Micro-Alloyed/Alloyed Elements on Microstructure and Properties of Fe-Mn-Al-C Lightweight Steel. Metals 2022, 12, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F.; Ou, K.L.; Chen, C.S.; Wang, C.H. Research of phase transformation on Fe-8.7Al-28.3Mn-1C-5.5Cr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 488, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.S.; Cheng, H.C.; Huang, C.F.; Chao, C.Y.; Qu, K.L.; Yu, C.H. Effects of C and Cr content on high-temperature microstructures of Fe-9Al-30Mn-xC-yCr alloys. Mater. Charact. 2010, 61, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Park, S.J.; Moon, J.; Jang, J.H.; Ha, H.Y.; Lee, T.H.; Hong, H.U.; Lee, B.H.; Han, H.N.; Lee, Y.J.; et al. Characterization of microstructural evolution in austenitic Fe-Mn-Al-C lightweight steels with Cr content. Mater. Charact. 2020, 170, 110717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Hu, C.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, J.H.; Song, C.J.; Zhai, Q.J. Microstructures, mechanical properties and deformation of near-rapidly solidified low-density Fe-20Mn-9Al-1.2C-xCr steels. Mater. Des. 2020, 186, 108307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Hu, C.H.; Jiang, Y.S.; Addad, A.; Ji, G.; Song, C.J.; Zhai, Q.J. The effect of Cr content on intragranular κ-carbide precipitation in Fe-Mn-Al-(Cr)-C low-density steels: A multiscale investigation. Mater. Charact. 2022, 186, 111801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, W.P.; Jiang, Z.F.; Liu, L.S.; Fu, Z.Q. Microstructure and mechanical properties of an Fe-20Mn-11Al-1.8C-5Cr alloy prepared by powder metallurgy. Vacuum 2017, 137, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Song, C.; Zhai, Q. Ultra-high strength medium-Mn lightweight steel by dislocation slip band refinement and suppressed intergranular κ-carbide with Cr addition. Mater. Charact. 2022, 190, 112042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, K.; Kimura, Y.; Mishima, Y. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of the γ/κ Two Phase Fe-Mn-Al-C (-Cr) Alloys. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2000, 646, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.D.; Park, K.-T. Microband-induced plasticity in a high Mn-Al-C light steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2008, 496, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Hwang, S.; Park, K.-T. Origin of extended tensile ductility of a Fe-28Mn-10Al-1C steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2009, 40, 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Song, R.; Li, Y.; Sun, T.; Wang, K. Tensile deformation of low density duplex Fe-Mn-Al-C steel. Mater. Des. 2015, 76, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Liu, Y.; Addad, A.; Ji, G.; Song, C.; Zhai, Q. Revisiting the formation mechanism of intragranular κ-carbide in austenite of a Fe-Mn-Al-Cr-C low-density steel. Scr. Mater. 2021, 199, 113836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Liang, J.; Godfrey, A.; Wang, Y.; Weng, Y.; Cao, W. Effect of alloying content on microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe-Mn-Al-C low-density steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 886, 145675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Park, S.-J.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, T.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Hong, H.-U.; Han, H.N.; Lee, J.; Lee, B.H.; Lee, C. Investigations of the microstructure evolution and tensile deformation behavior of austenitic Fe-Mn-Al-C lightweight steels and the effect of Mo addition. Acta Mater. 2018, 147, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Steels | Fe | Mn | Al | C | Cr | Density/g∙cm−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A(0Cr) | Bal. | 24.6 | 10.4 | 1.22 | 0 | 6.63 |
| B(2.5Cr) | Bal. | 25.2 | 10.2 | 1.24 | 2.47 | 6.64 |
| C(5Cr) | Bal. | 24.8 | 9.8 | 1.19 | 5.15 | 6.66 |
| D(7.5Cr) | Bal. | 25.4 | 10.3 | 1.17 | 7.53 | 6.59 |
| E(10Cr) | Bal. | 24.9 | 9.7 | 1.23 | 10.12 | 6.65 |
| Steels | YS/MPa | UTS/MPa | TE/% | UTS∗TE/GPa∙% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A(0Cr) | 527 | 708 | 56.5 | 40.0 |
| B(2.5Cr) | 559 | 773 | 61.5 | 47.5 |
| C(5Cr) | 585 | 775 | 21.2 | 16.4 |
| D(7.5Cr) | 597 | 771 | 5.1 | 3.9 |
| E(10Cr) | - | 732 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, R.; Du, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, Y. The Influence of Cr Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-25Mn-10Al-1.2C Lightweight Steel. Metals 2024, 14, 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14060687
Bai R, Du Y, He X, Zhang Y. The Influence of Cr Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-25Mn-10Al-1.2C Lightweight Steel. Metals. 2024; 14(6):687. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14060687
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Rui, Yunfei Du, Xiuli He, and Yaqin Zhang. 2024. "The Influence of Cr Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-25Mn-10Al-1.2C Lightweight Steel" Metals 14, no. 6: 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14060687
APA StyleBai, R., Du, Y., He, X., & Zhang, Y. (2024). The Influence of Cr Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-25Mn-10Al-1.2C Lightweight Steel. Metals, 14(6), 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14060687





