Simulation Study of Crystalline Al2O3 Thin Films Prepared at Low Temperatures: Effect of Deposition Temperature and Biasing Voltage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Simulation Method
- (1)
- The substrate (α-Al2O3) was subjected to a “thermalization campaign” of 1 ps at a given temperature of 1300 K (using Nose-Hoover temperature control) before growth was initiated.
- (2)
- Random generation of new atoms was at a rate consistent with the distribution of energy in the deposition particle generation zone, using the NVE ensemble.
- (3)
- Generation of atoms was followed by 5 ps collisional deposition for heat exchange with the substrate and energy dissipation.
- (4)
- The deposition was followed by a 1 ps thermalization run (microcanonical ensemble) to remove the remaining energy.
- (5)
- Ar particles were inserted for collision rebound during Al, O deposition.
- (6)
- There was a return to step (2) and the process was repeated. In order to show whether crystallization can occur, steps (2–6) were cycled until the number of particles deposited was not less than 2200 for Al and O, and not less than 320 for Ar particles for sputtering collisions (based on the ratio of the number of O to Ar in the mass spectrometry data).
2.2. Calculation and Analysis Methods
2.3. Sample Preparation and Characterization
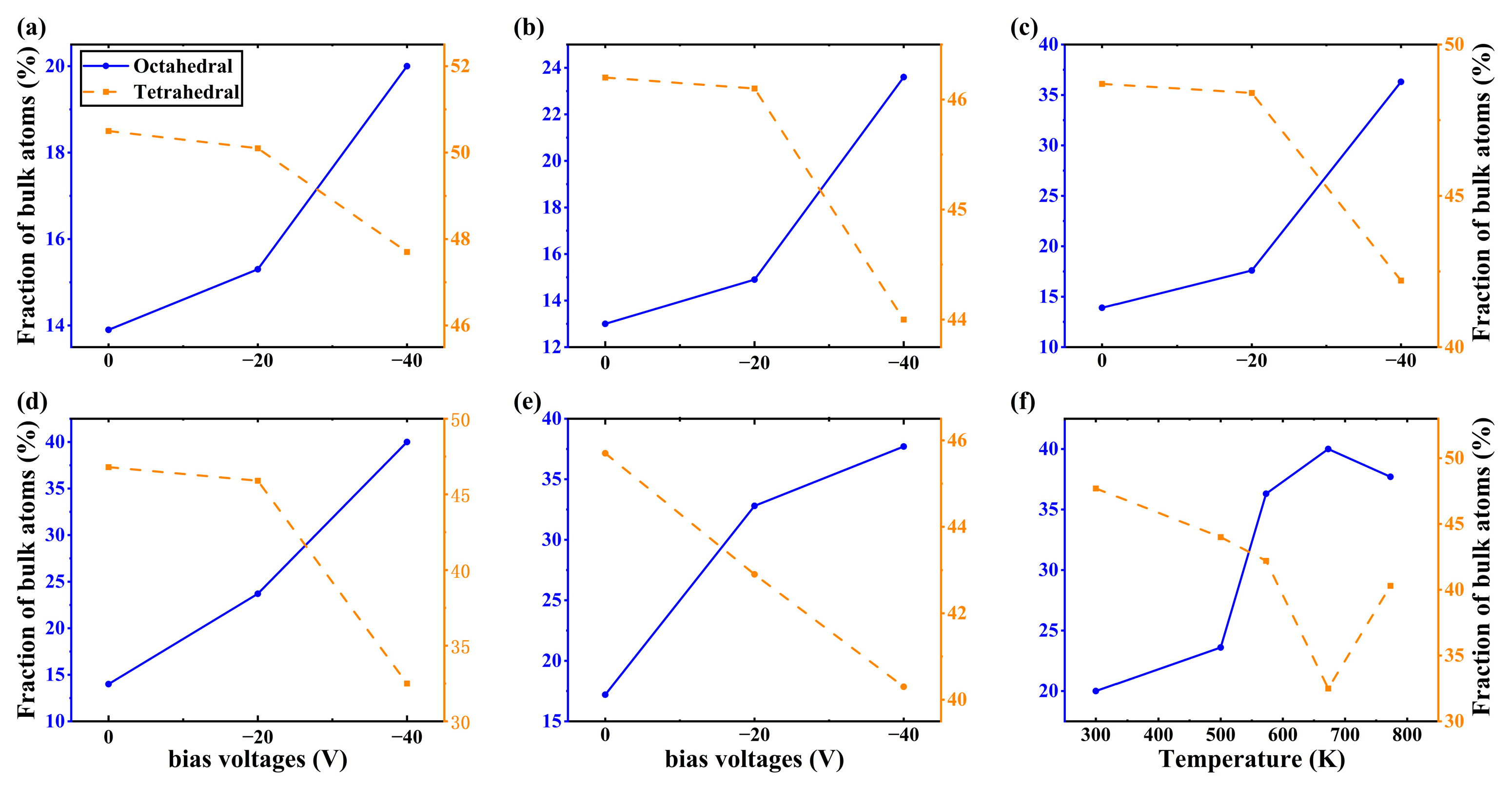
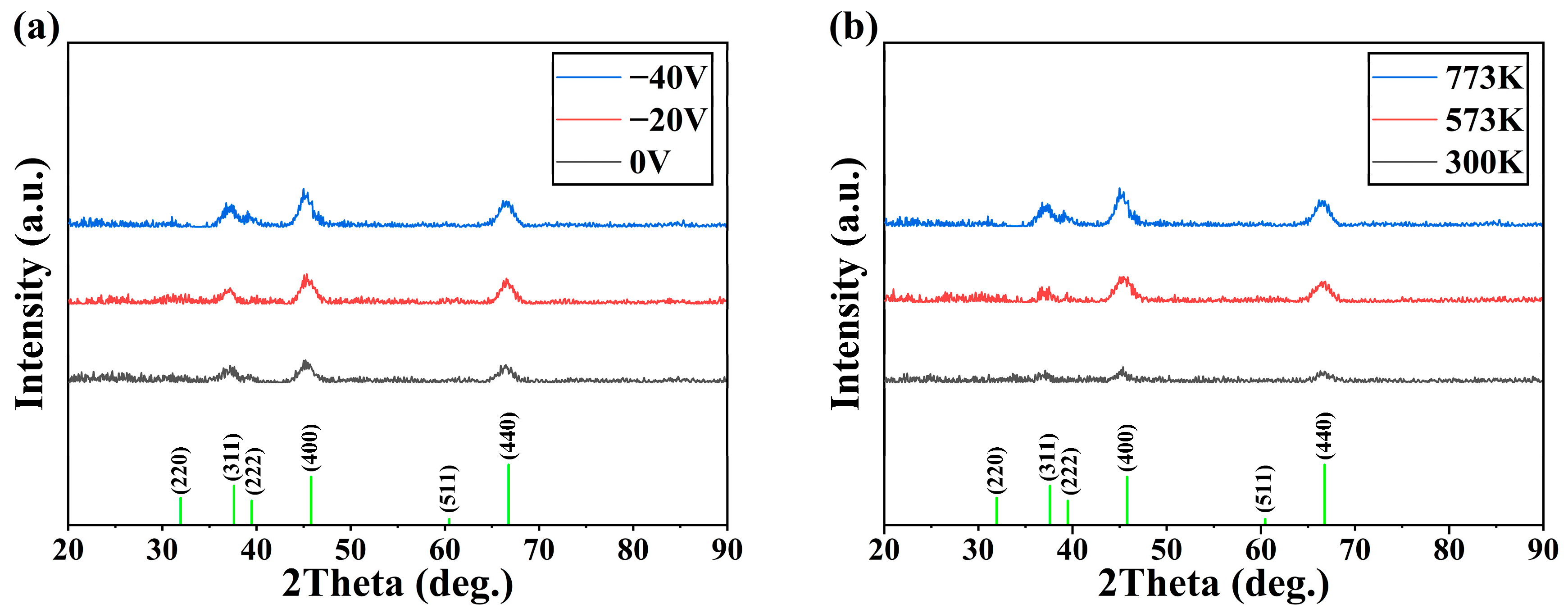
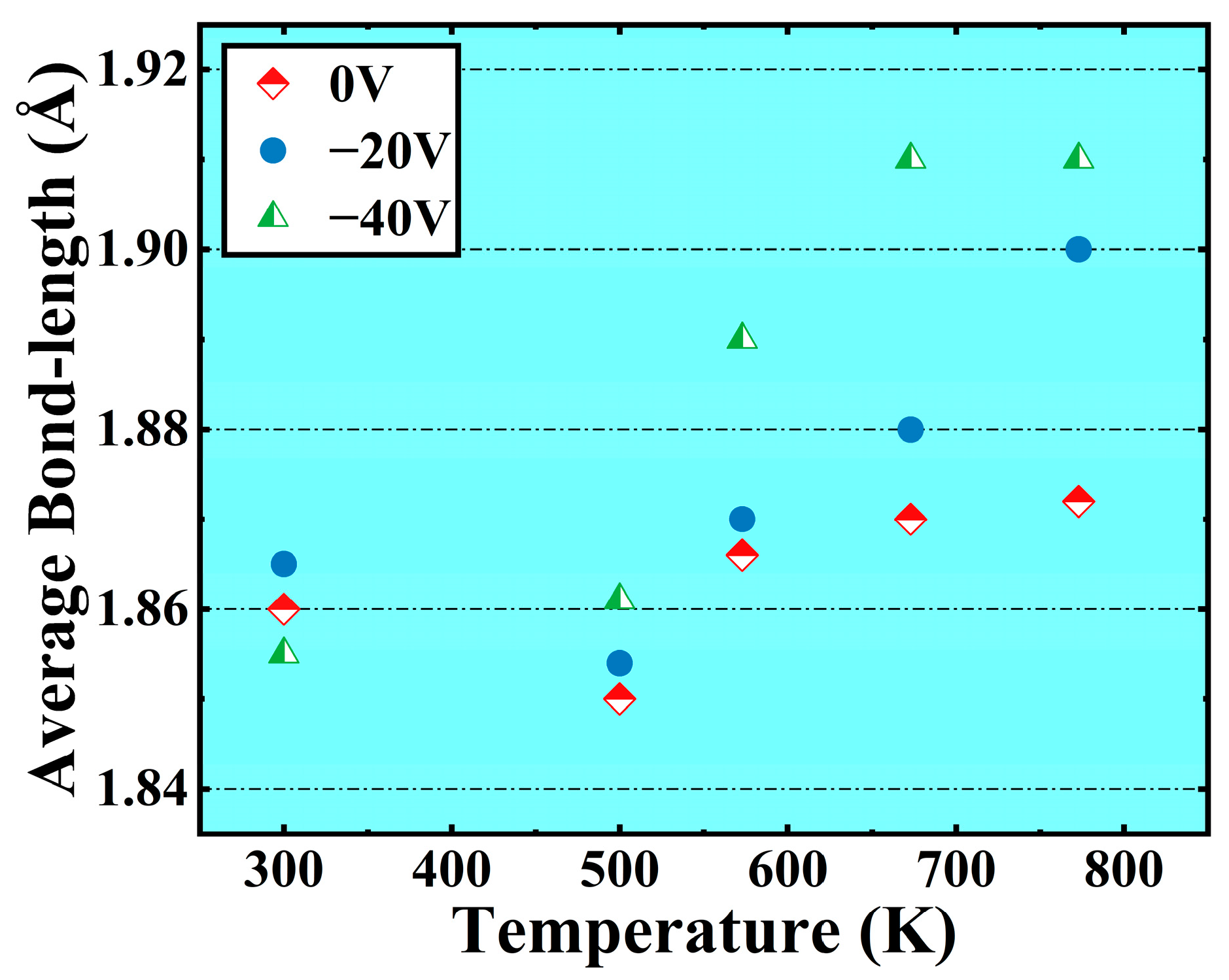
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Under low-energy particle deposition conditions, the growth of Al2O3 thin film crystals requires high deposition temperatures for optimal results. Without applying bias to the particles during the deposition process, even at 773 K, achieving a well-crystallized Al2O3 film is challenging, with only 17.2% octahedral coordination of Al content in the film.
- (2)
- The bias is conducive to the deposition of crystalline Al2O3 films at low temperatures. When the bias of −40 V is applied, the content of octahedral coordination of Al in the Al2O3 film is 36.3% and that of ternary 421 increases by 6% at T = 573 K, the crystallinity in the film rises, and the Al2O3 crystal is dominated by γ phases. However, the average coordination number in the film remains mostly below 5, indicating a significant presence of defects. This observation may be attributed to the fast deposition of Al+ ions and slow deposition of O- ions.
- (3)
- The low-temperature preparation of crystalline Al2O3 films is attributed to the energy of the particles, and the application of a bias enables the diffusion of the thin particles to be enhanced, compensating for the crystallization energy supplied by the substrate temperature and allowing the films to be prepared at low temperatures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Xiong, J.; Guo, Z.; Liu, J.; You, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; et al. Effects of Nano-Al2O3 Addition on Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Wear Resistance of Ti(C, N)-Based Cermets. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mat. 2023, 115, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarraga-Medina, E.G.; Caballero-Espitia, D.L.; Jurado-Gonzalez, J.; Lopez, J.; Marquez, H.; Contreras-Lopez, O.E.; Tiznado, H. Al2O3-Y2O3 Nanolaminated Slab Optical Waveguides by Atomic Layer Deposition. Opt. Mater. 2020, 103, 109822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Hou, X. Improving the Heat Transfer Capability and Thermal Stability of Vehicle Engine Oils Using Al2O3/TiO2 Nanomaterials. Powder Technol. 2020, 363, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, I.; Bendersky, L.A.; Brandon, D.G.; Rühle, M. Cubic to Monoclinic Phase Transformations in Alumina. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 3659–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Elleuch, O.; Wan, Z.; Zuo, P.; Janicki, T.D.; Alfieri, A.D.; Babcock, S.E.; Savage, D.E.; Schmidt, J.R.; Evans, P.G.; et al. Phase Selection and Structure of Low-Defect-Density γ-Al2O3 Created by Epitaxial Crystallization of Amorphous Al2O3. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 57598–57608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Minorello, S.; Zhou, Z.; Urakawa, A. Integrated CO2 Capture and Reduction Catalysis: Role of γ-Al2O3 Support, Unique State of Potassium and Synergy with Copper. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 140, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, C. Selective Stereoretention of Carbohydrates upon C-C Cleavage Enabling D-Glyceric Acid Production with High Optical Purity over a Ag/γ-Al2O3 Catalyst. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2024, 136, e202403547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirtas, H.; Cug, H.; Elkilani, R. Properties of Al2O3 Particle Reinforced Composites Coating on IF Steel. Surf. Eng. 2022, 38, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gecu, R.; Birol, B.; Ozcan, M. Improving Wear and Corrosion Protection of AISI 304 Stainless Steel by Al2O3-TiO2 Hybrid Coating via Sol-Gel Process. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 2022, 100, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kateb, M.; Gudmundsson, J.T.; Ingvarsson, S. Effect of Substrate Bias on Microstructure of Epitaxial Film Grown by HiPIMS: An Atomistic Simulation. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2020, 38, 043006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsov, V.; Macák, K.; Schneider, J.M.; Helmersson, U.; Petrov, I. A Novel Pulsed Magnetron Sputter Technique Utilizing Very High Target Power Densities. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 122, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Martinez-Martinez, D.; Chemin, J.-B.; Choquet, P. Tuning the Characteristics of Al2O3 Thin Films Using Different Pulse Configurations: Mid-Frequency, High-Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering, and Their Combination. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 466, 129648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianu, E. The Influence of Deposition Parameters on Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of AZO Thin Film. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2021, 23, 270–274. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Ye, R.; Bakhit, B.; Petrov, I.; Hultman, L.; Greczynski, G. Improving Oxidation and Wear Resistance of TiB2 Films by Nano-Multilayering with Cr. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 436, 128337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houska, J.; Zeman, P. Role of Al in Cu-Zr-Al Thin Film Metallic Glasses: Molecular Dynamics and Experimental Study. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2023, 222, 112104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houska, J.; Rezek, J.; Cerstvy, R. Dependence of the ZrO2 Growth on the Crystal Orientation: Growth Simulations and Magnetron Sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 572, 151422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, M.; Lopez-Cazalilla, A.; Sarakinos, K.; Rosaz, G.J.; Carlos, C.P.A.; Leith, S.; Calatroni, S.; Himmerlich, M.; Djurabekova, F. Growth of Nb Films on Cu for Superconducting Radio Frequency Cavities by Direct Current and High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering: A Molecular Dynamics and Experimental Study. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 476, 130199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.C.; Zhang, T.F.; Mane, R.S.; Kim, K.-H.; Kang, M.C.; Zou, C.W.; Wang, Q.M. Low-Temperature Deposition of Nanocrystalline Al2O3 Films by Ion Source-Assisted Magnetron Sputtering. Vacuum 2018, 149, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houska, J. Pathway for a Low-Temperature Deposition of α-Al2O3: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 235, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, A.-V.; Fang, T.-H.; Nguyen, V.-T.; Chen, T.-H. Investigating the Structures and Residual Stress of Cux(FeAlCr)100−x Film on Ni Substrate Using Molecular Dynamics. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.P.; Aktulga, H.M.; Berger, R.; Bolintineanu, D.S.; Brown, W.M.; Crozier, P.S.; in ’t Veld, P.J.; Kohlmeyer, A.; Moore, S.G.; Nguyen, T.D.; et al. LAMMPS—A Flexible Simulation Tool for Particle-Based Materials Modeling at the Atomic, Meso, and Continuum Scales. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2022, 271, 108171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigumonrong, D.P.; Music, D.; Schneider, J.M. Efficient Supercell Design for Surface and Interface Calculations of Hexagonal Phases: α-Al2O3 Case Study. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2011, 50, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houska, J. Quantitative Investigation of the Role of High-Energy Particles in Al2O3 Thin Film Growth: A Molecular-Dynamics Study. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 254, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M. Molecular Dynamics Study of the Structures and Bulk Moduli of Crystals in the System CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1996, 23, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sun, L.; Deng, W.-Q. Combination Rules for Morse-Based van Der Waals Force Fields. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 1672–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourits, F.M.; Rummens, F.H.A. A Critical Evaluation of Lennard–Jones and Stockmayer Potential Parameters and of Some Correlation Methods. Can. J. Chem. 1977, 55, 3007–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubenzer, A.; Dischler, B.; Brandt, G.; Koidl, P. Rf-plasma Deposited Amorphous Hydrogenated Hard Carbon Thin Films: Preparation, Properties, and Applications. J. Appl. Phys. 1983, 54, 4590–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houska, J.; Machanova, P.; Zitek, M.; Zeman, P. Molecular Dynamics and Experimental Study of the Growth, Structure and Properties of Zr–Cu Films. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 828, 154433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breilmann, W.; Maszl, C.; Hecimovic, A.; Keudell, A. von Influence of Nitrogen Admixture to Argon on the Ion Energy Distribution in Reactive High Power Pulsed Magnetron Sputtering of Chromium. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 135203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, K.; Luan, B.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.-Q. First-Principles Lattice Dynamics and Thermodynamic Properties of α-, θ-, κ- and γ-Al2O3 and Solid State Temperature-Pressure Phase Diagram. Acta Mater. 2024, 263, 119513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tane, M.; Kimizuka, H.; Ichitsubo, T. Two Distinct Crystallization Processes in Supercooled Liquid. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 194505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, P.; Sridharan, M.; Sillassen, M.; Bøttiger, J. α-Cr2O3 Template-Texture Effect on α-Al2O3 Thin-Film Growth. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 7447–7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohara, T.; Tamagaki, H.; Ikari, Y.; Fujii, H. Deposition of α-Al2O3 Hard Coatings by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 185, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.N.; Anaraky, M.; Shafeizadeh, Z.; Parbrook, P.J. Optimization of Nanocrystalline γ-Alumina Coating for Direct Spray Water-Cooling of Optical Devices. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2014, 37, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y. Deposition of Nanostructured Crystalline Alumina Thin Film by Twin Targets Reactive High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
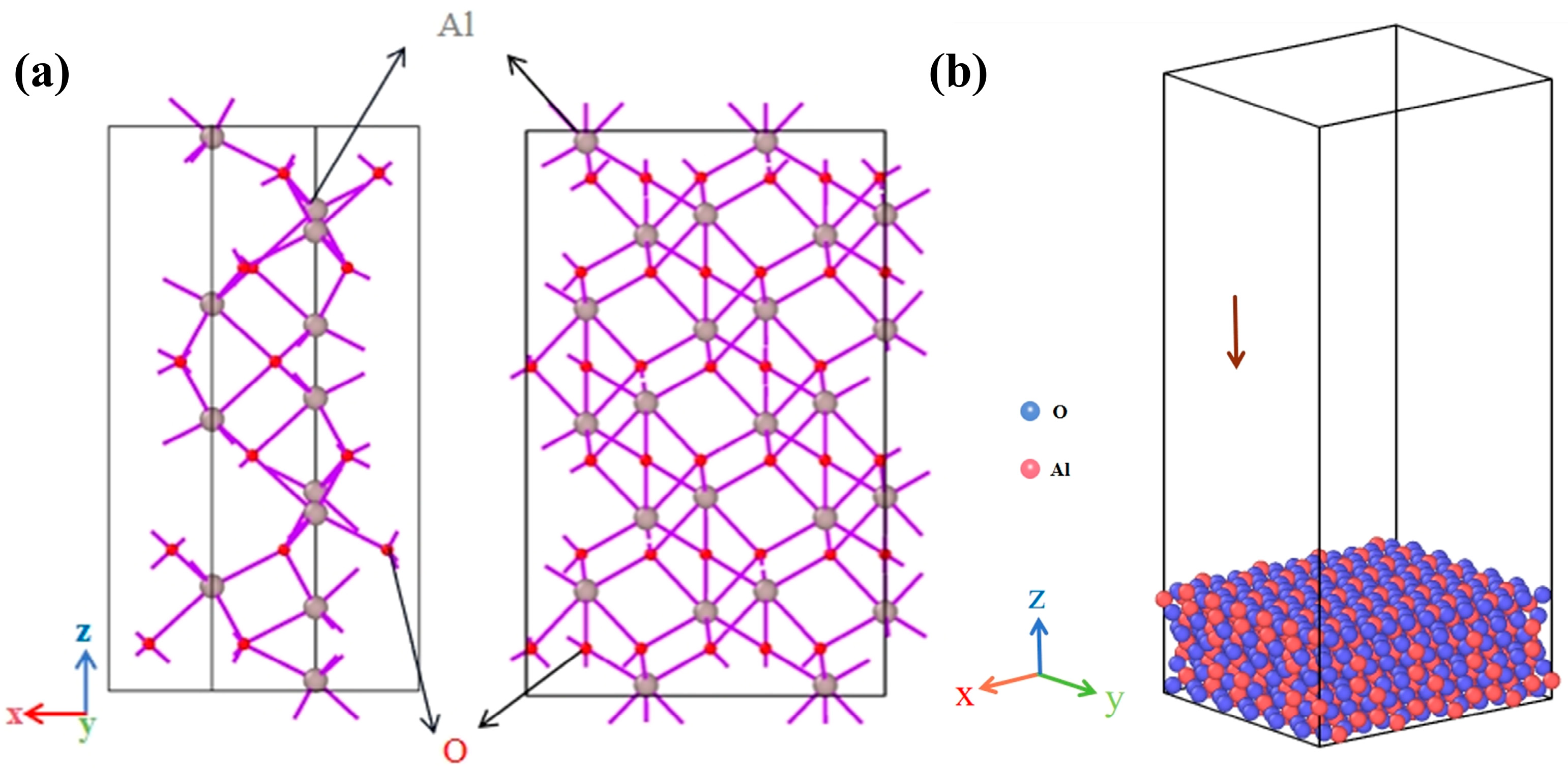
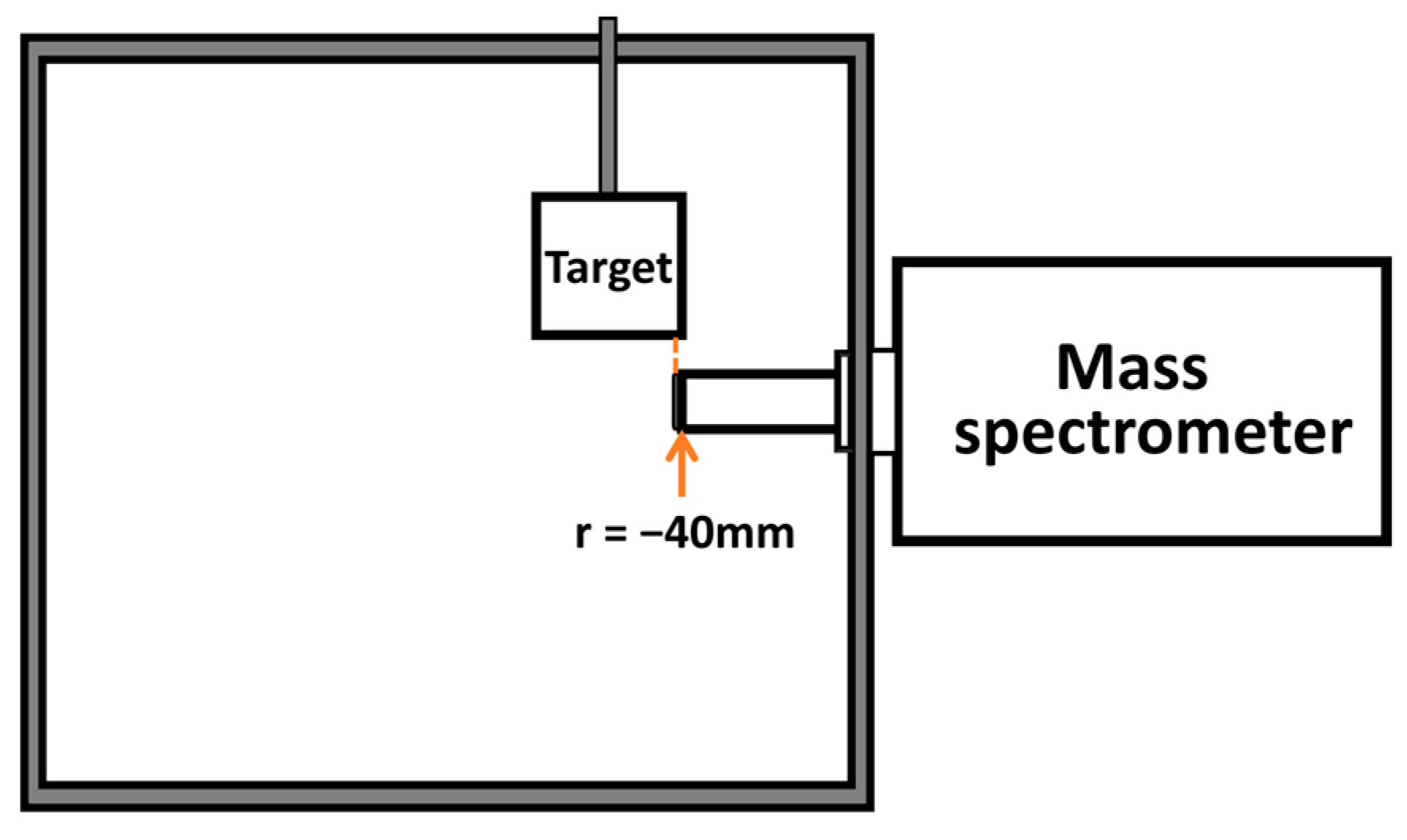

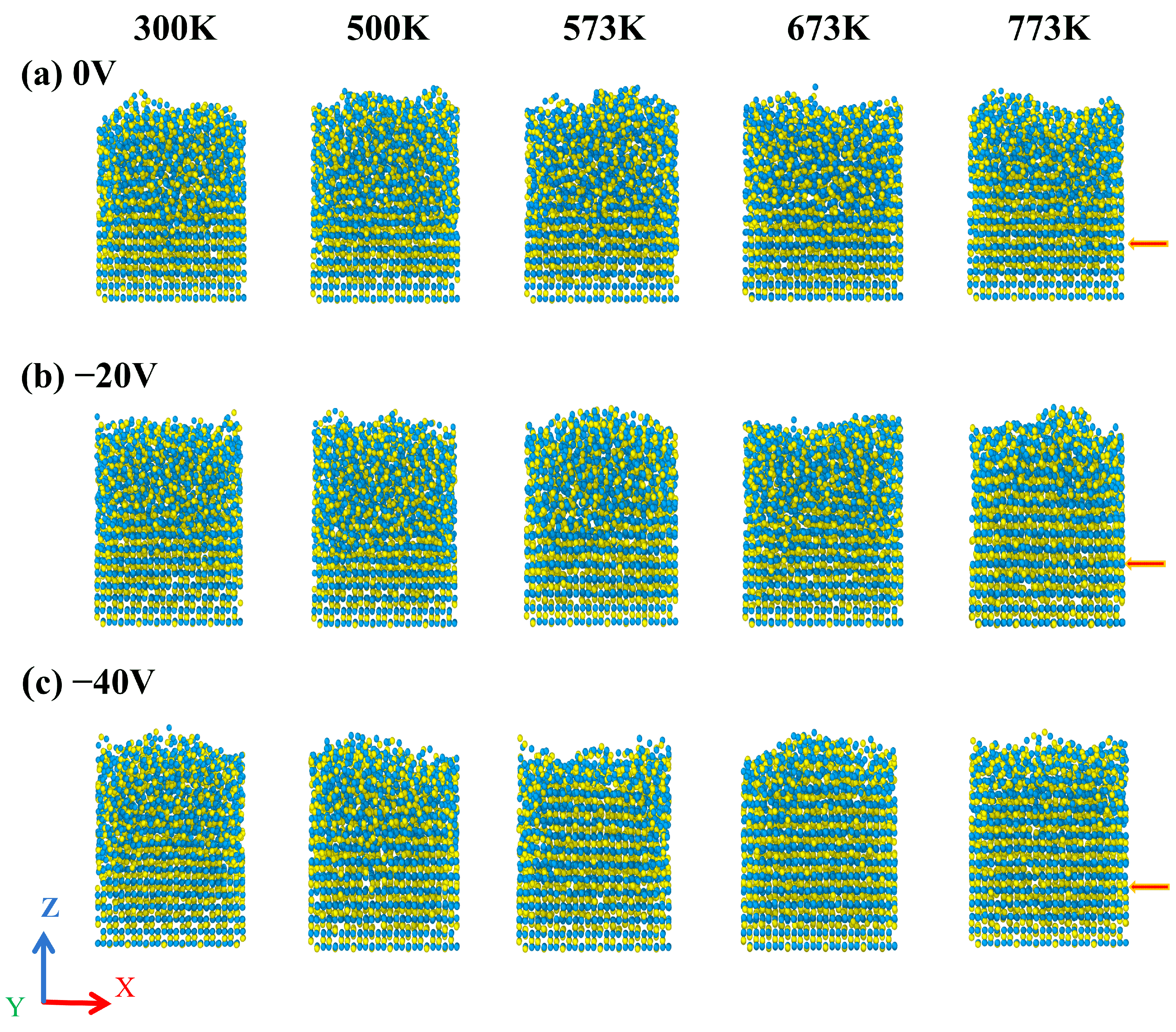
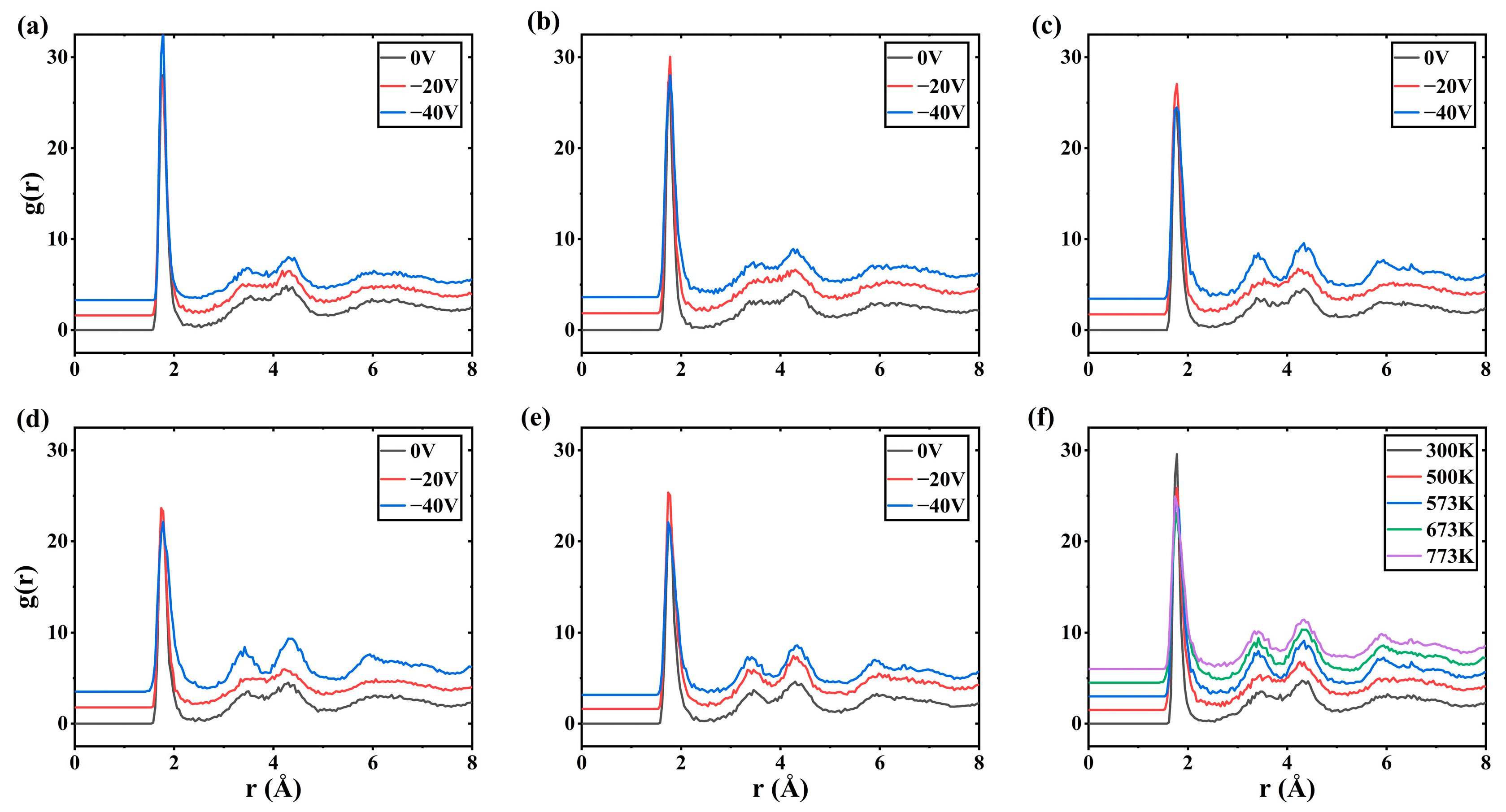



| Interacting Particles | A (eV) | ρ (Å) | C (eV·A6) |
|---|---|---|---|
| O-O | 6463.4 | 0.276 | 85.22 |
| Al-O | 28,480 | 0.172 | 34.63 |
| Al-Al | 31,574,470 | 0.068 | 14.07 |
| Potential Function Coefficients | Ar | Al | O |
|---|---|---|---|
| ε | 0.00978 eV | 0.39217 eV | 0.00844 eV |
| σ | 3.465 Å | 2.62 Å | 3.541 Å |
| Samples | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate temperature (K) | 300 | 573 | 773 | 773 | 773 |
| Substrate bias (V) | −40 | −40 | −40 | −20 | 0 |
| Energy Division | 27Al+ | 16O− | 36Ar+ |
|---|---|---|---|
| low energy | 0~3.15 eV | 0~8 eV | |
| percentage | 35% | 80% | |
| average | 1.2 eV | 2.45 eV | |
| moderate energy | 3.15~13.2 eV | 8~34 eV | |
| percentage | 55% | 17% | 3.5 eV |
| average | 7.5 eV | 18.6 eV | |
| high energy | 13.2~25.5 eV | 34~60 eV | |
| percentage | 10% | 3% | |
| average | 16.9 eV | 48 eV |
| Temperature | 300 K | 500 K | 573 K | 673 K | 773 K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rq (Å) | 1.39 ± 0.05 | 1.37 ± 0.02 | 1.42 ± 0.03 | 1.36 ± 0.03 | 0.92 ± 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, W.; Ju, J.; Sun, Y.; Weng, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, E. Simulation Study of Crystalline Al2O3 Thin Films Prepared at Low Temperatures: Effect of Deposition Temperature and Biasing Voltage. Metals 2024, 14, 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14080875
Jiang W, Ju J, Sun Y, Weng L, Wang Z, Wang X, Liu J, Wang E. Simulation Study of Crystalline Al2O3 Thin Films Prepared at Low Temperatures: Effect of Deposition Temperature and Biasing Voltage. Metals. 2024; 14(8):875. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14080875
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Wei, Jianhang Ju, Yuanliang Sun, Ling Weng, Zhiyuan Wang, Xiaofeng Wang, Jinna Liu, and Enhao Wang. 2024. "Simulation Study of Crystalline Al2O3 Thin Films Prepared at Low Temperatures: Effect of Deposition Temperature and Biasing Voltage" Metals 14, no. 8: 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14080875
APA StyleJiang, W., Ju, J., Sun, Y., Weng, L., Wang, Z., Wang, X., Liu, J., & Wang, E. (2024). Simulation Study of Crystalline Al2O3 Thin Films Prepared at Low Temperatures: Effect of Deposition Temperature and Biasing Voltage. Metals, 14(8), 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14080875






