Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Machining Particle-Reinforced Al-Based Metal Matrix Composites—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction

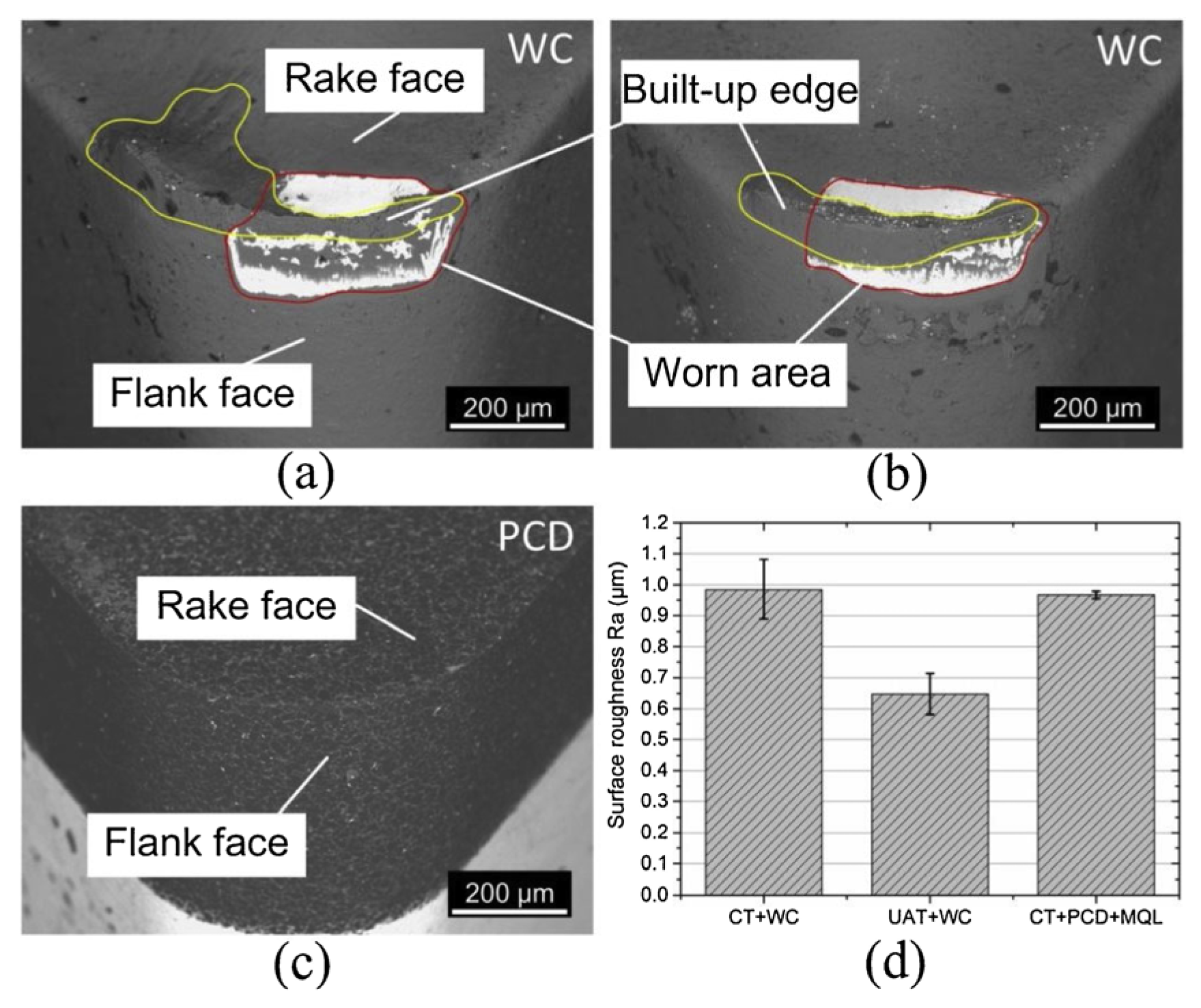
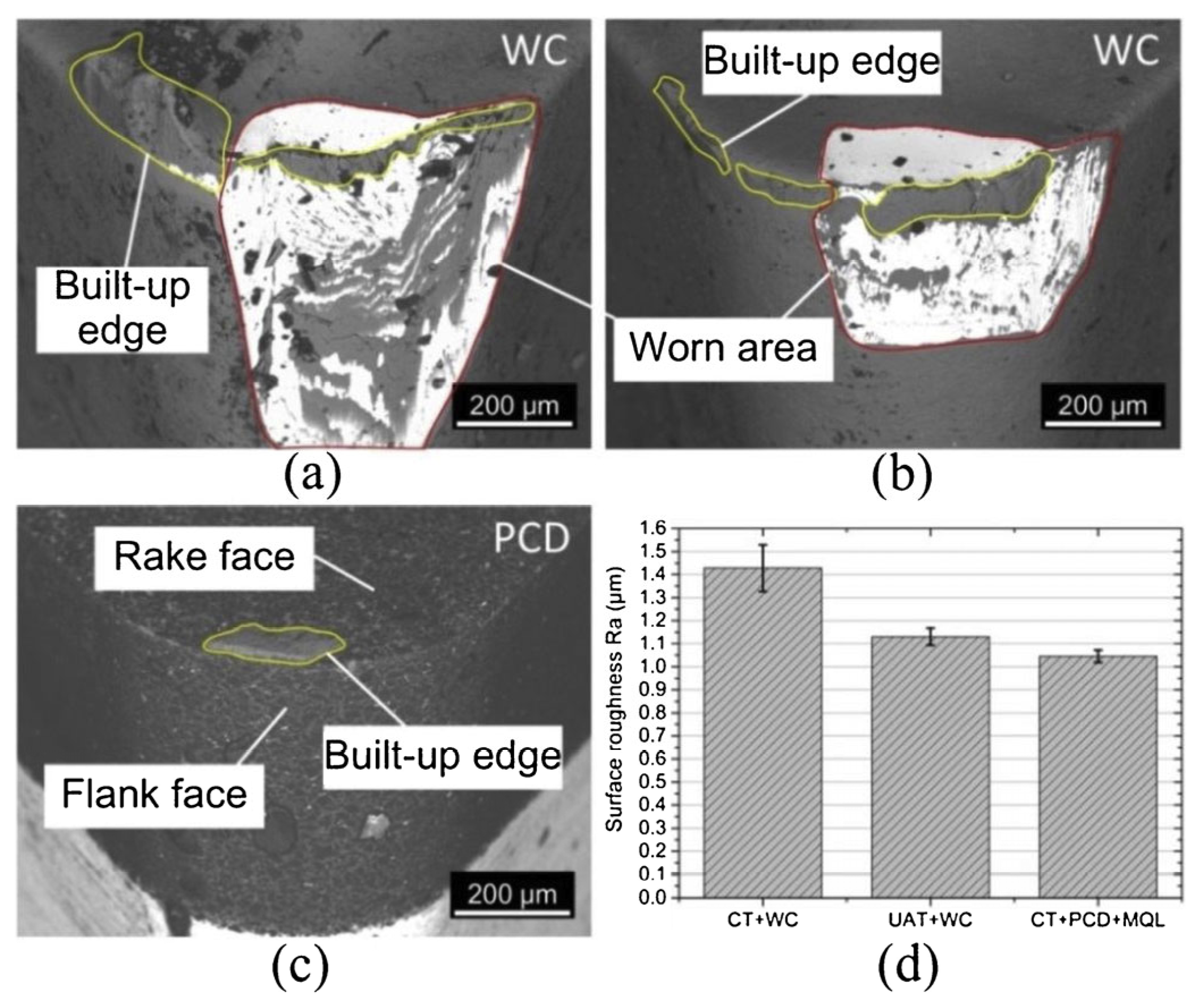
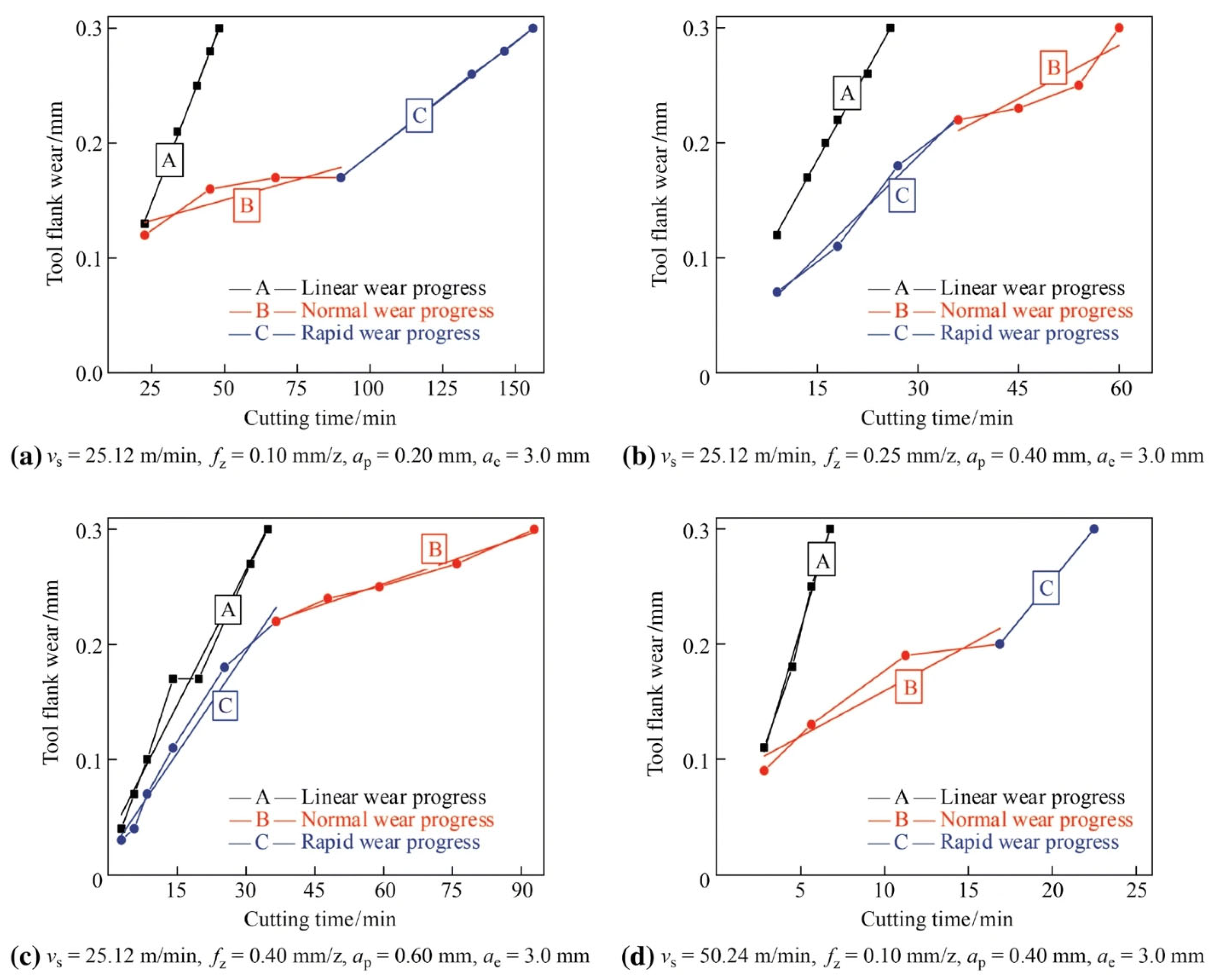
2. Tool Wear and Tool Life
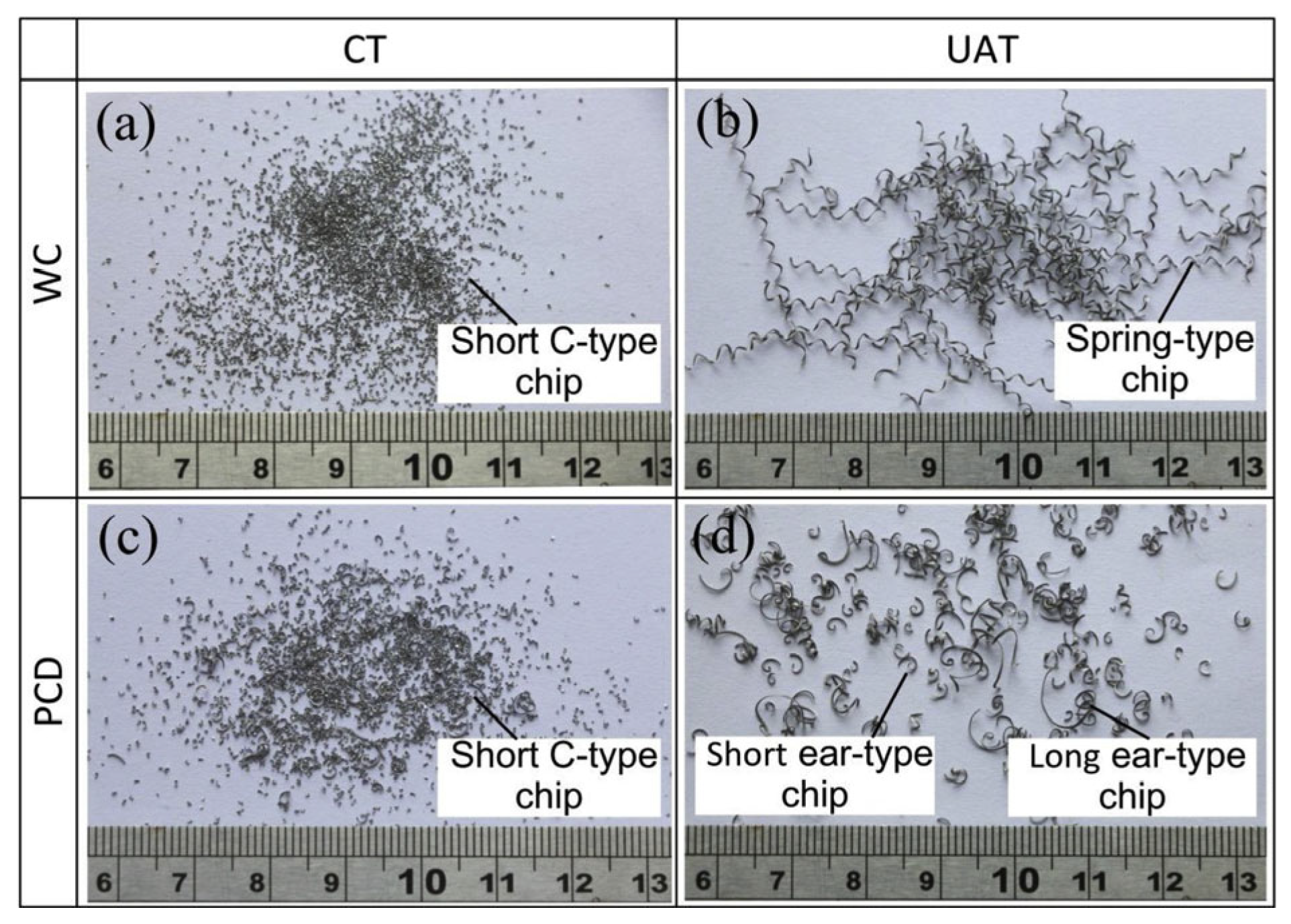
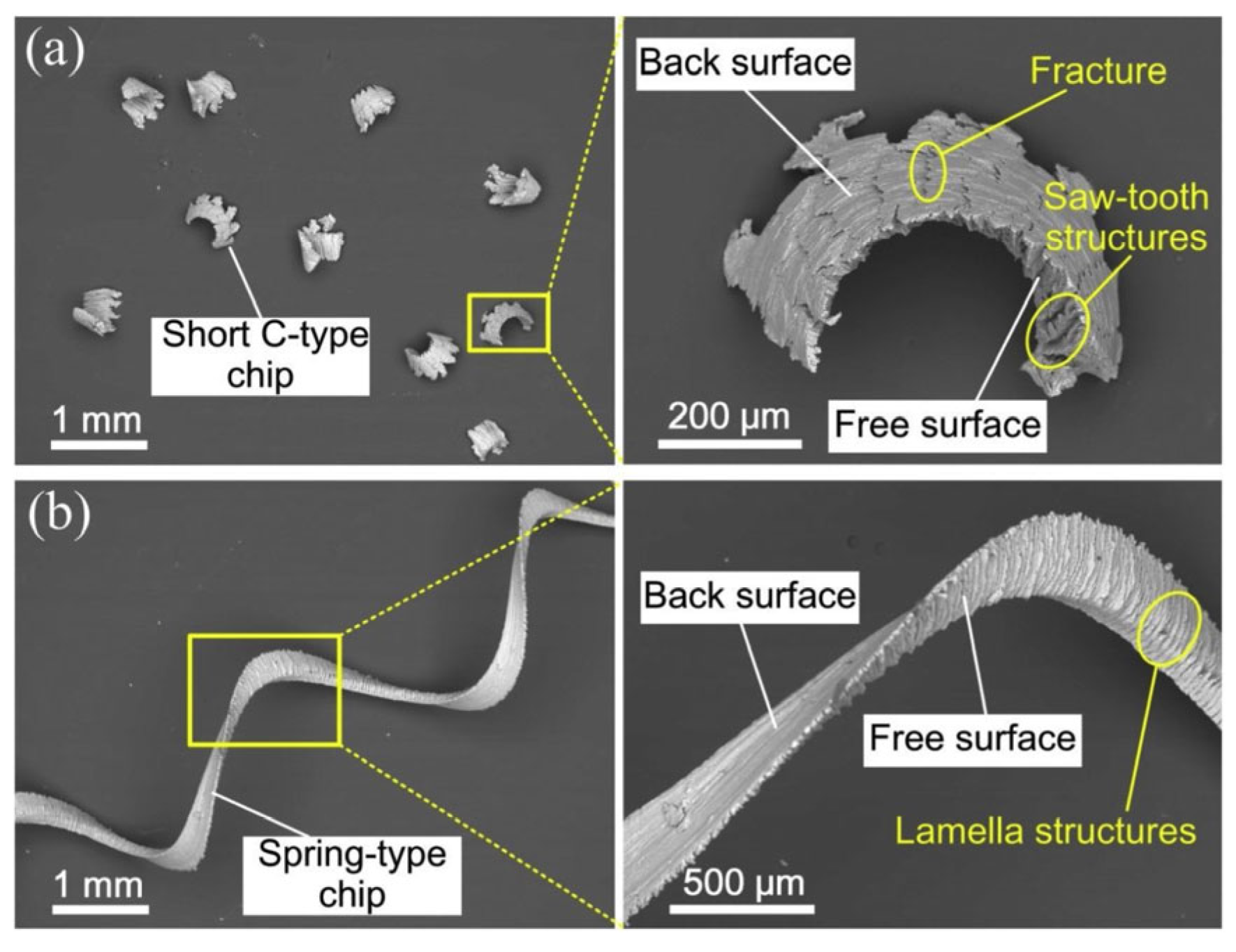
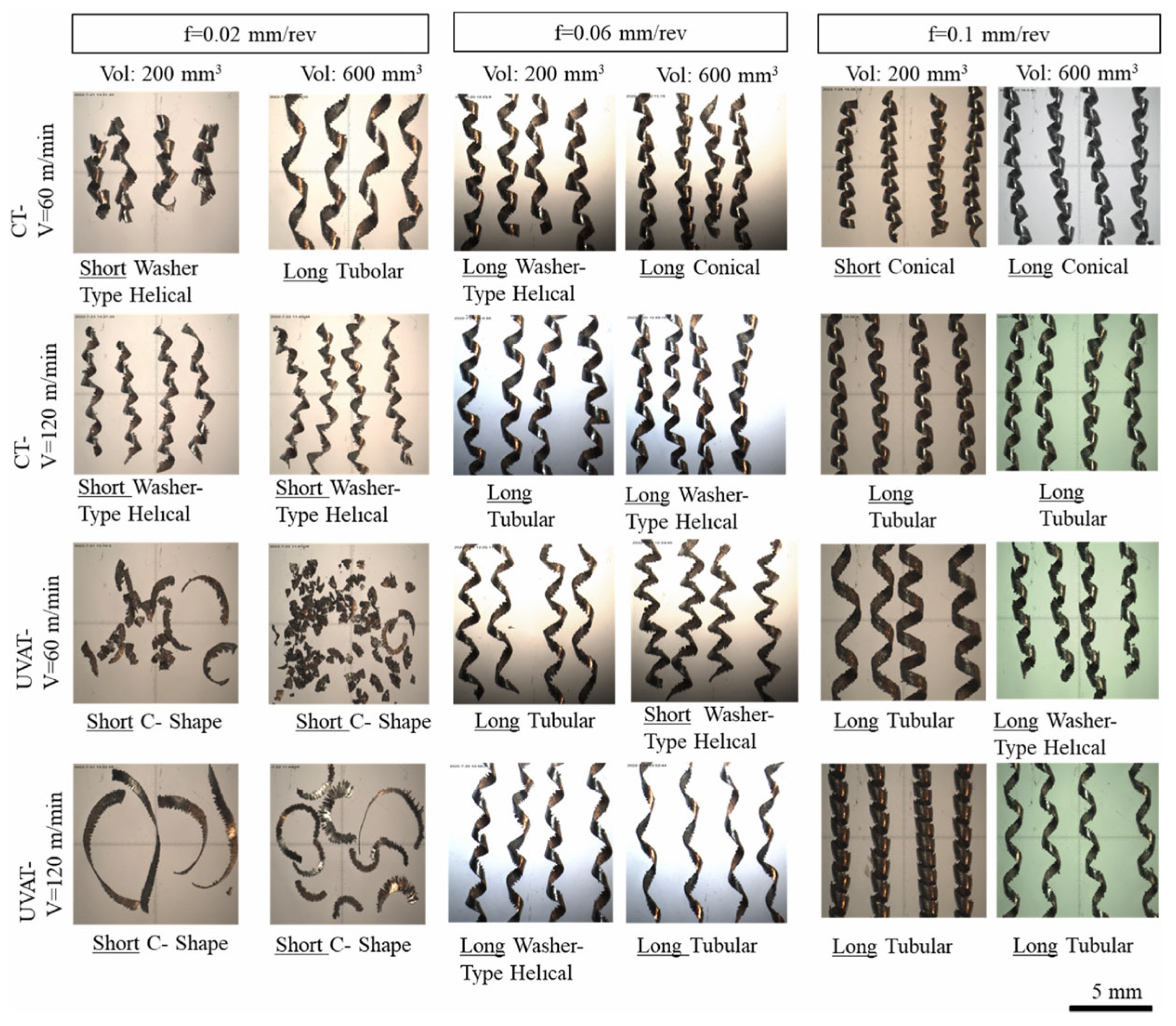
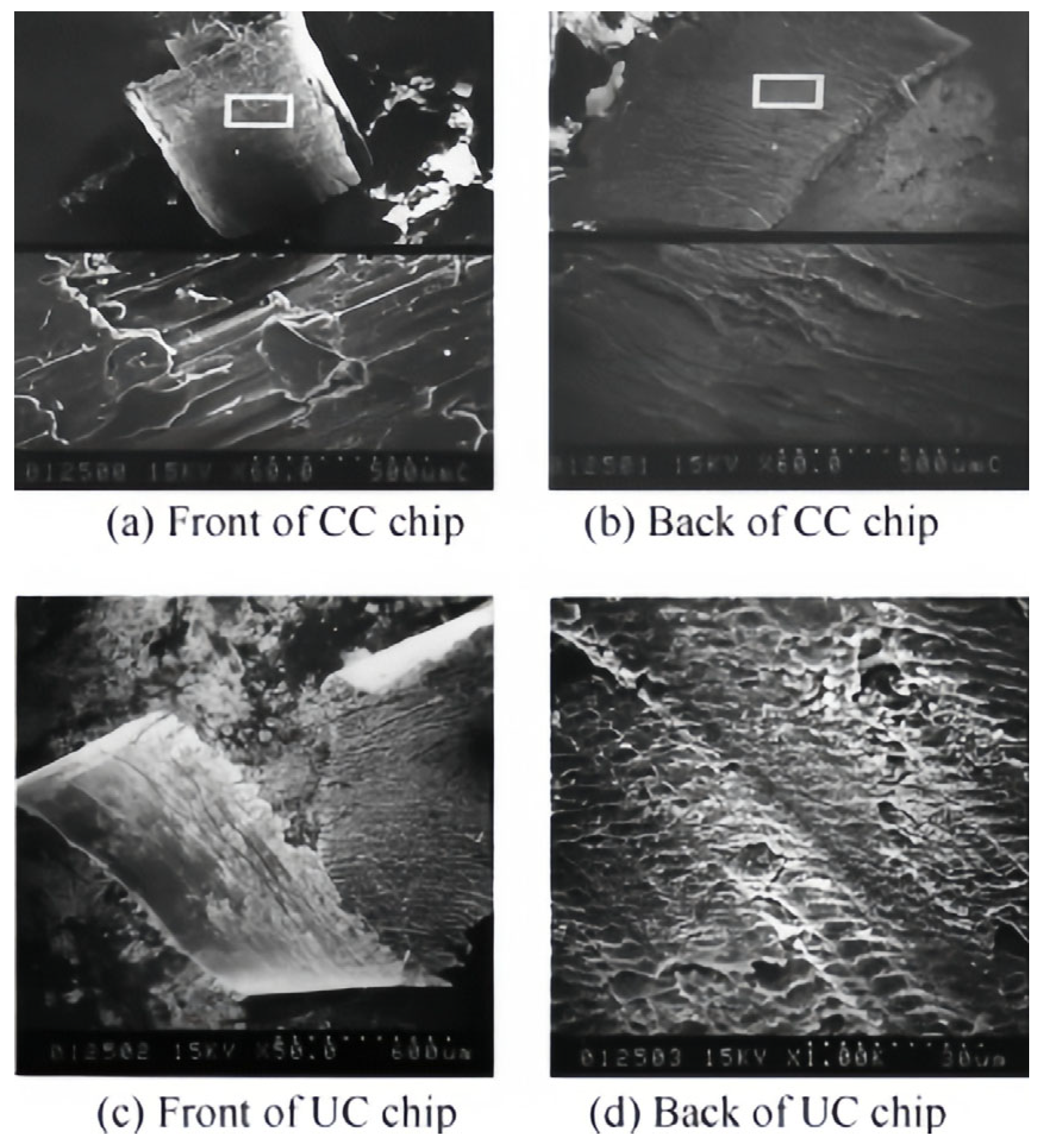
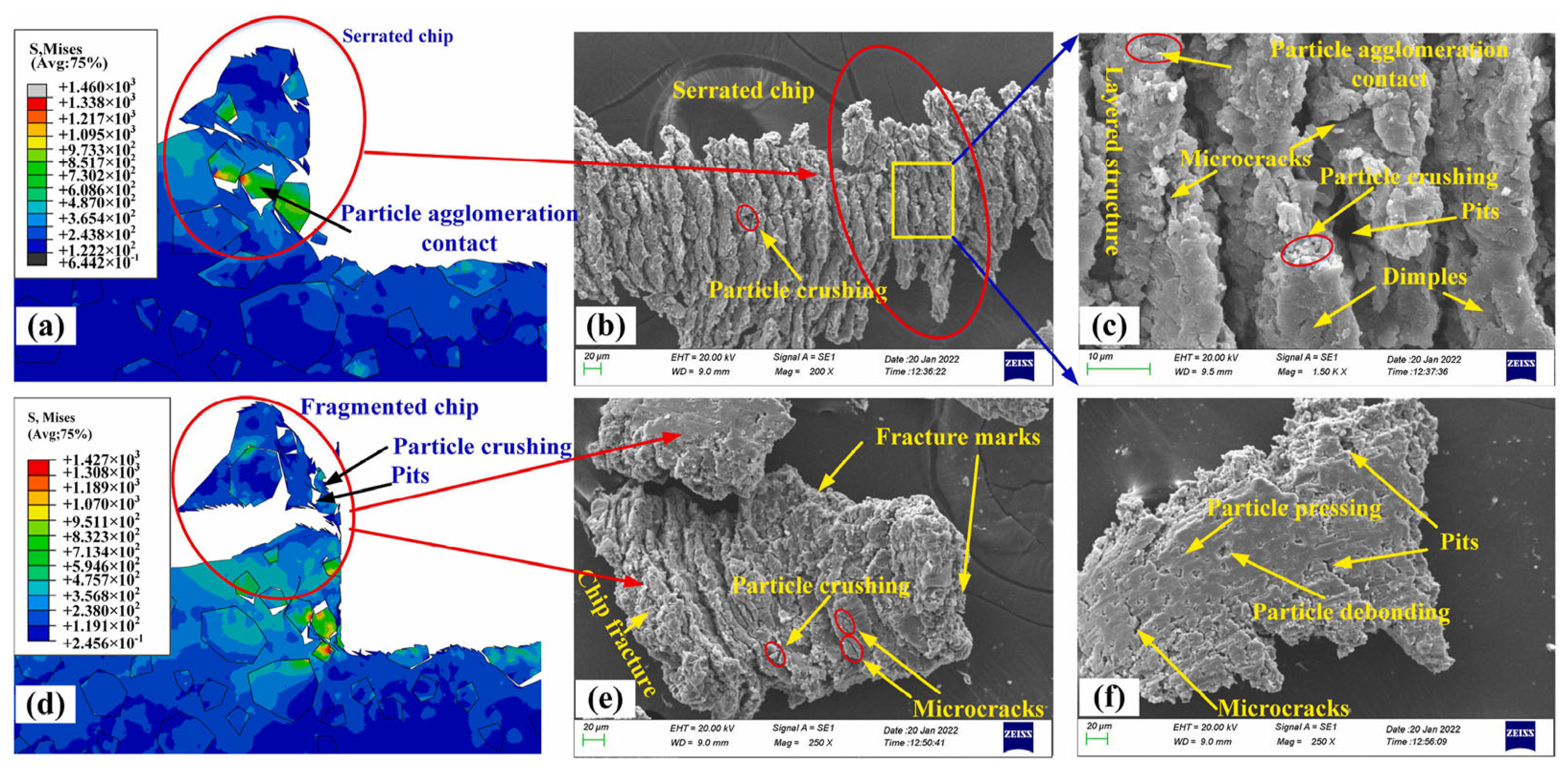
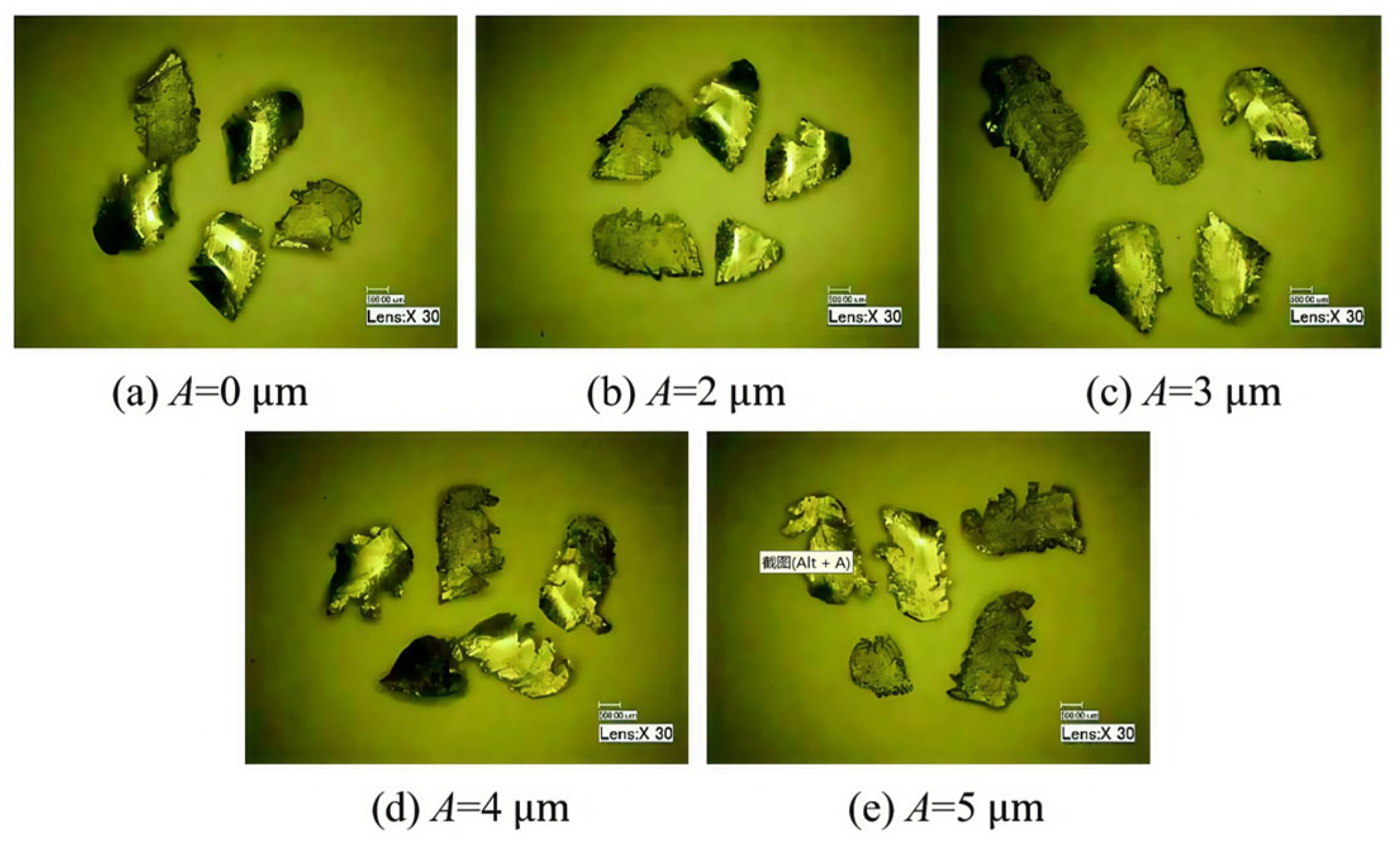
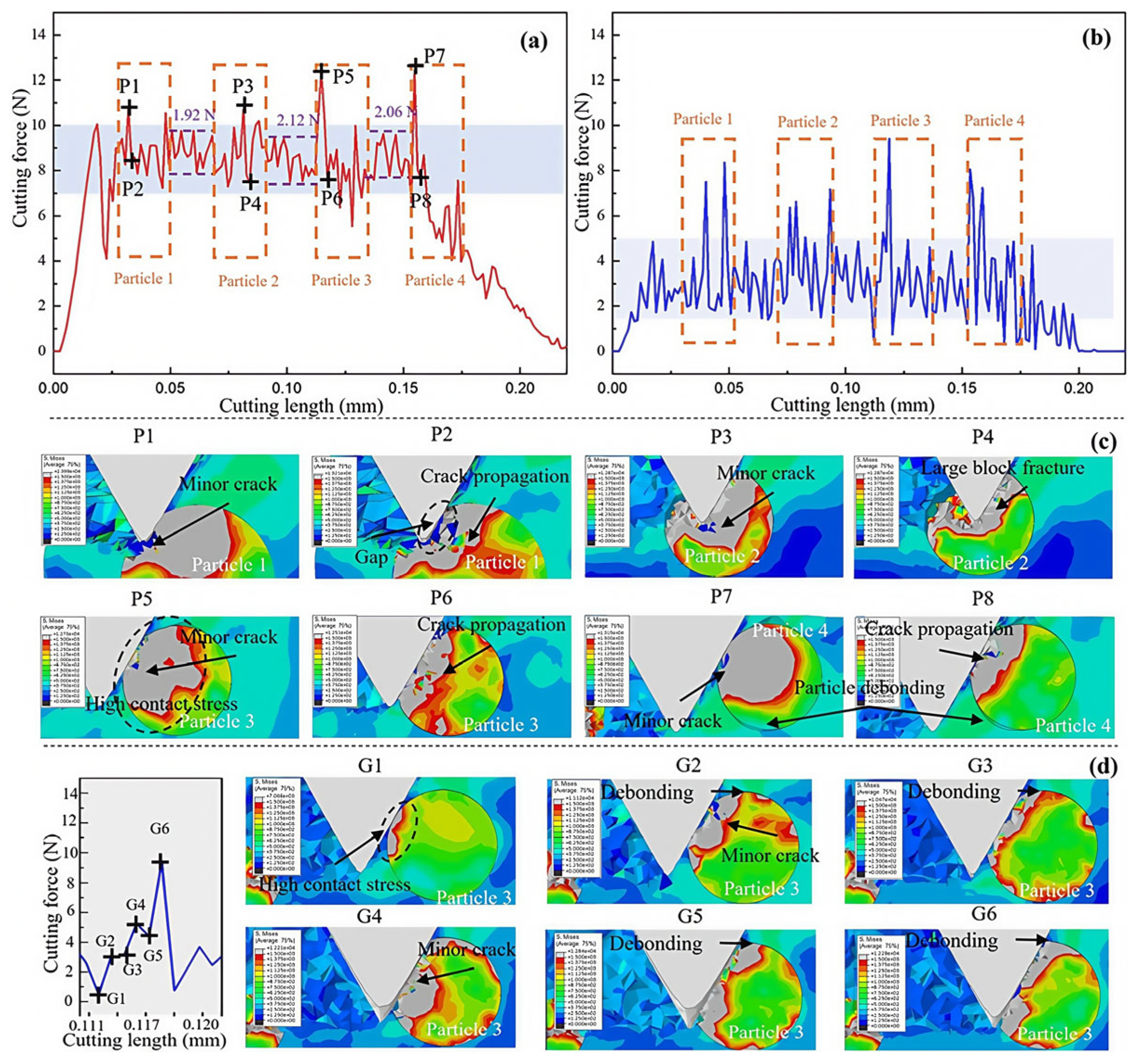
3. Chip Formation
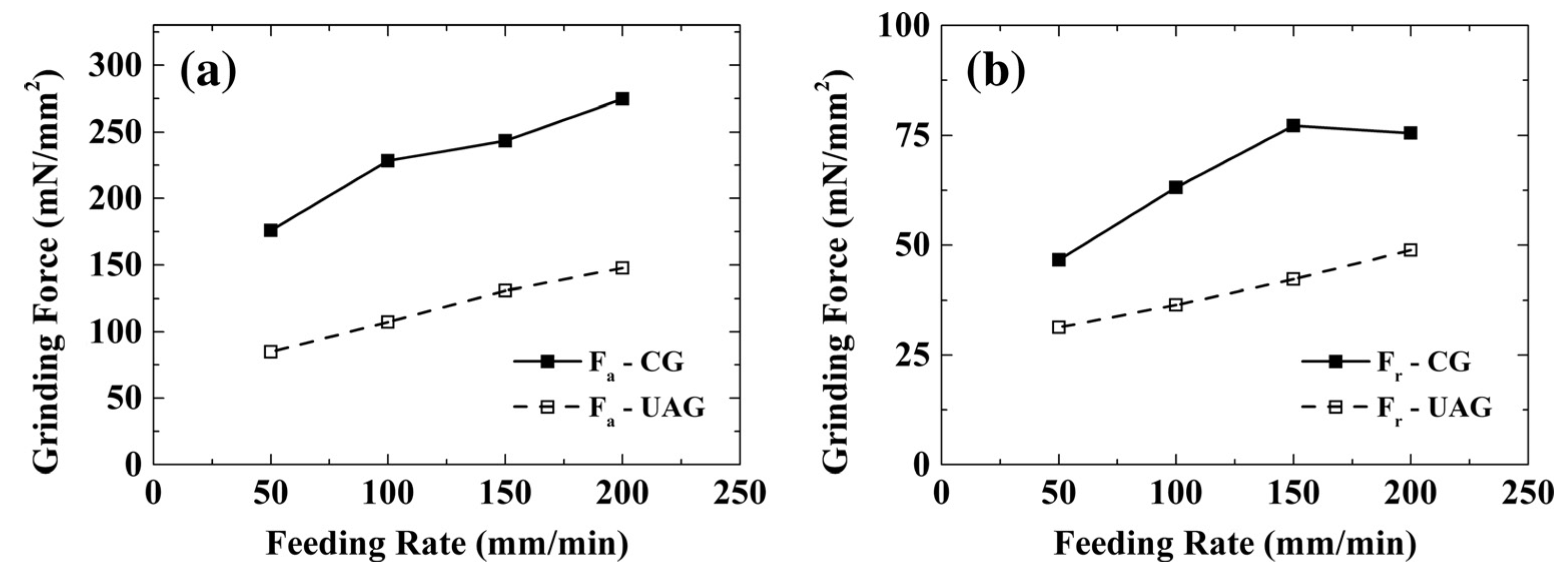
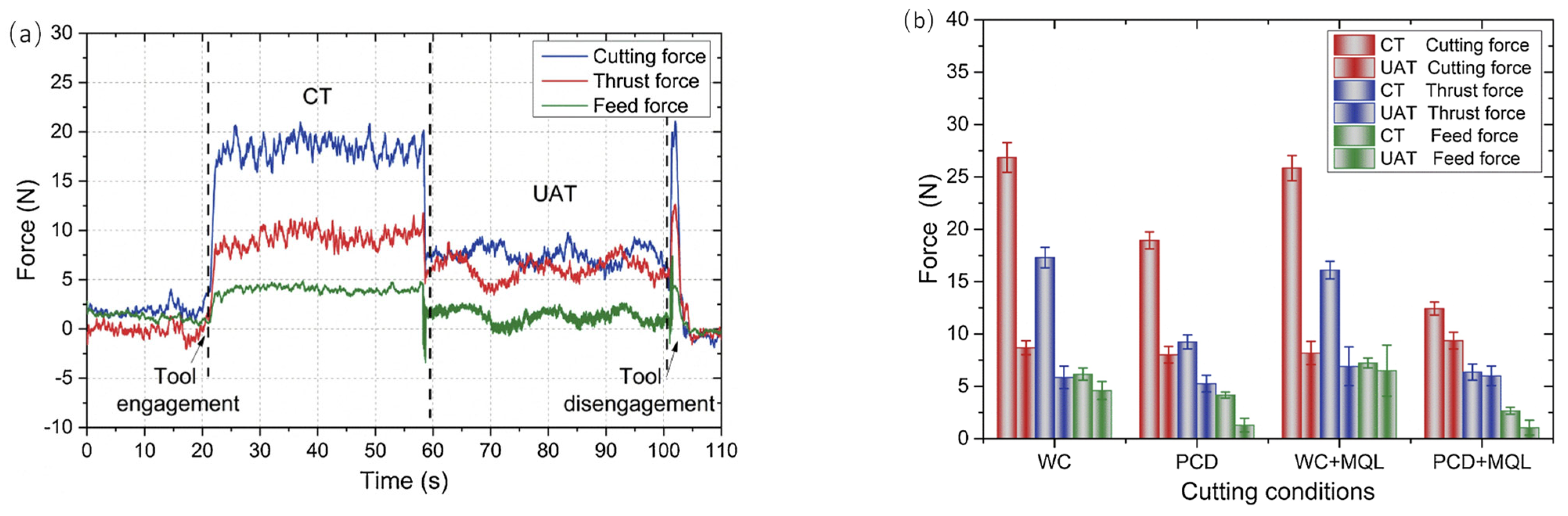
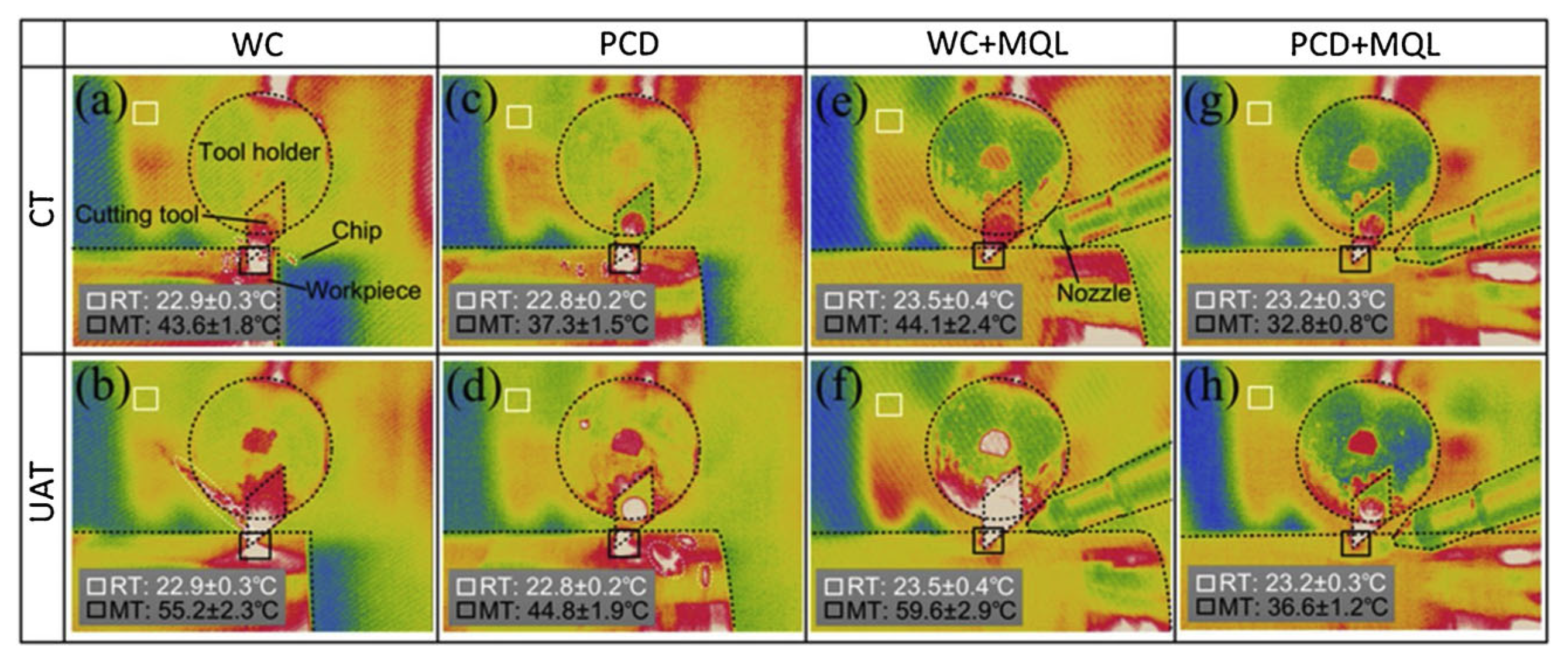
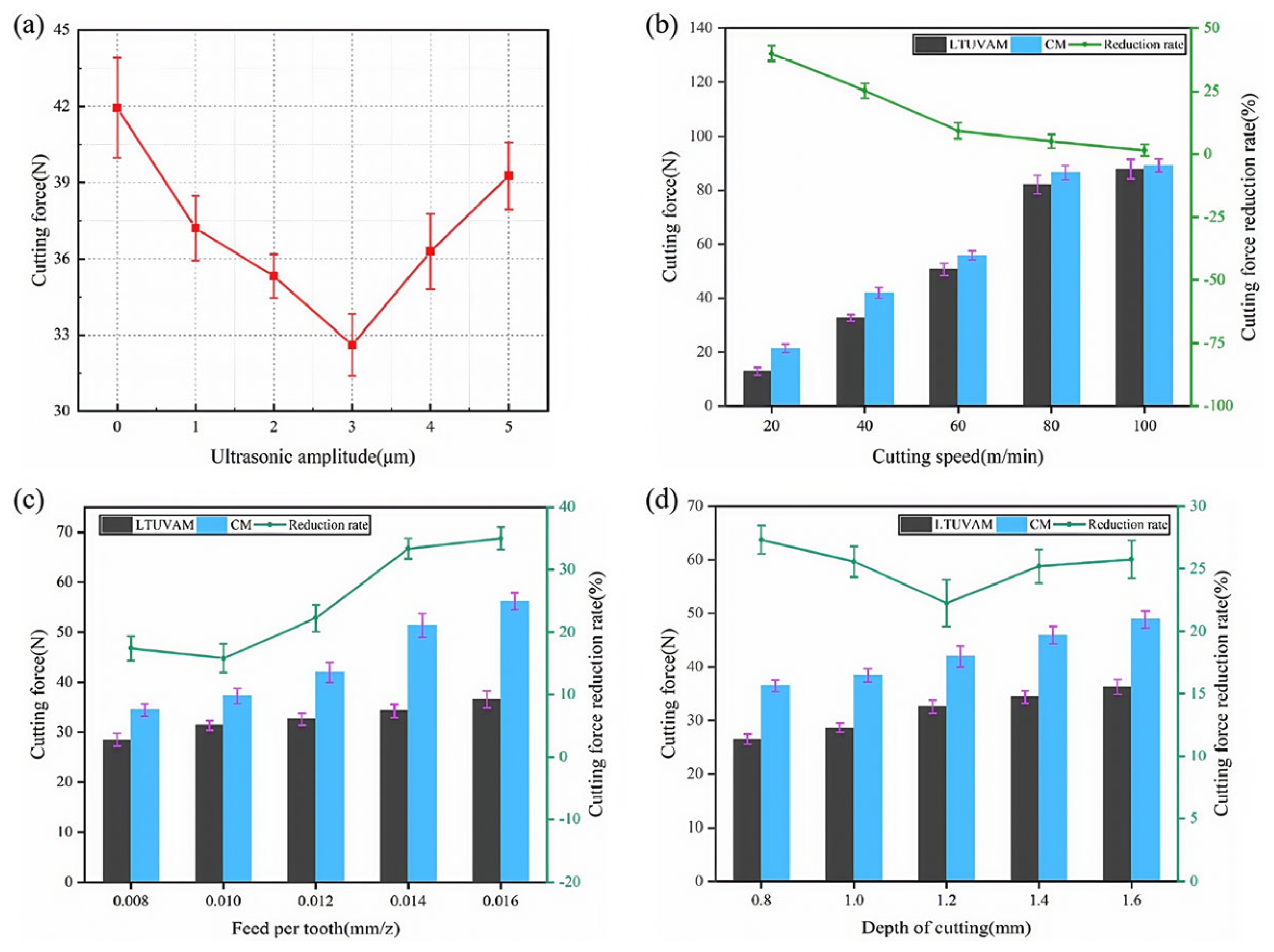
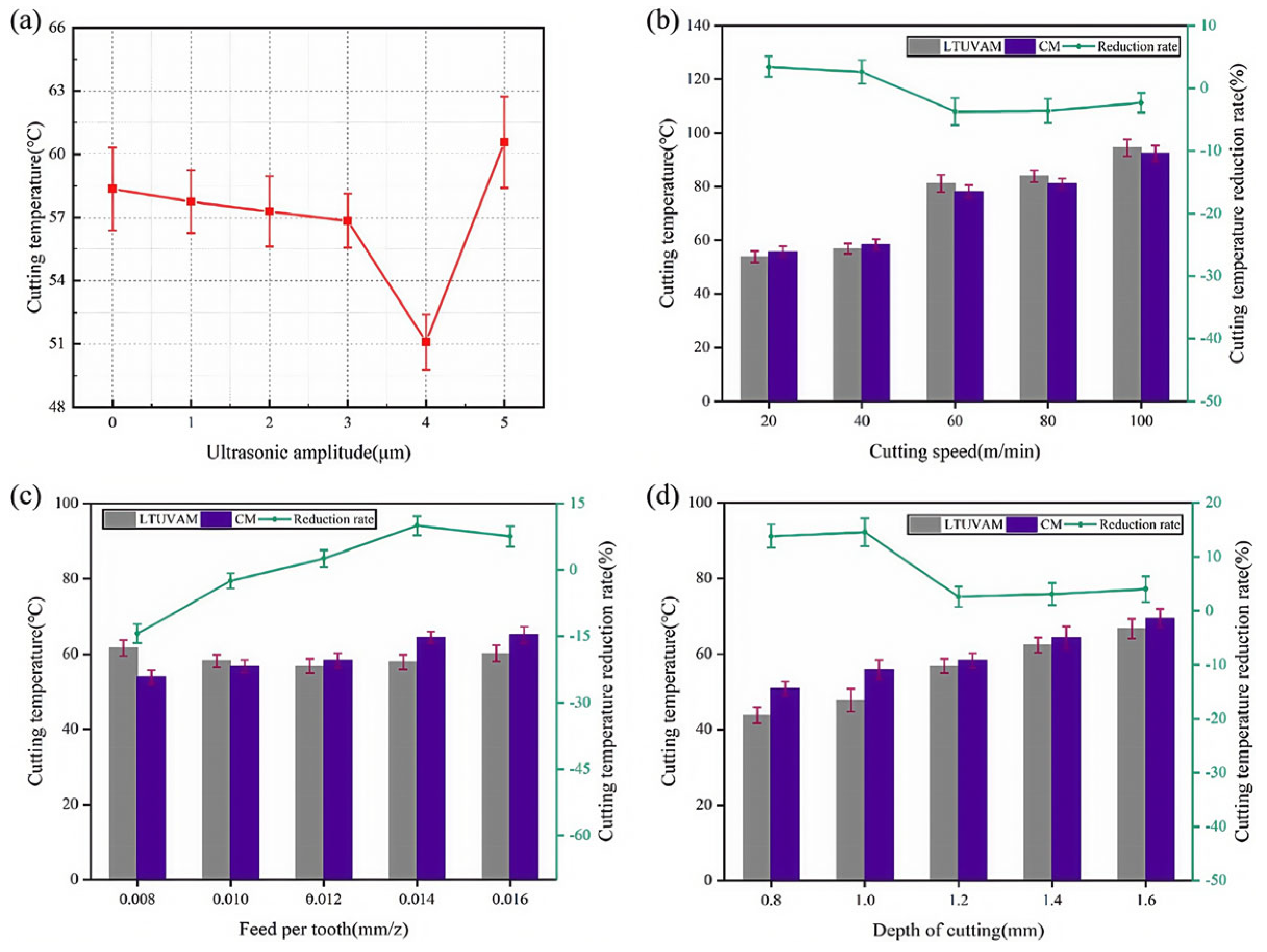
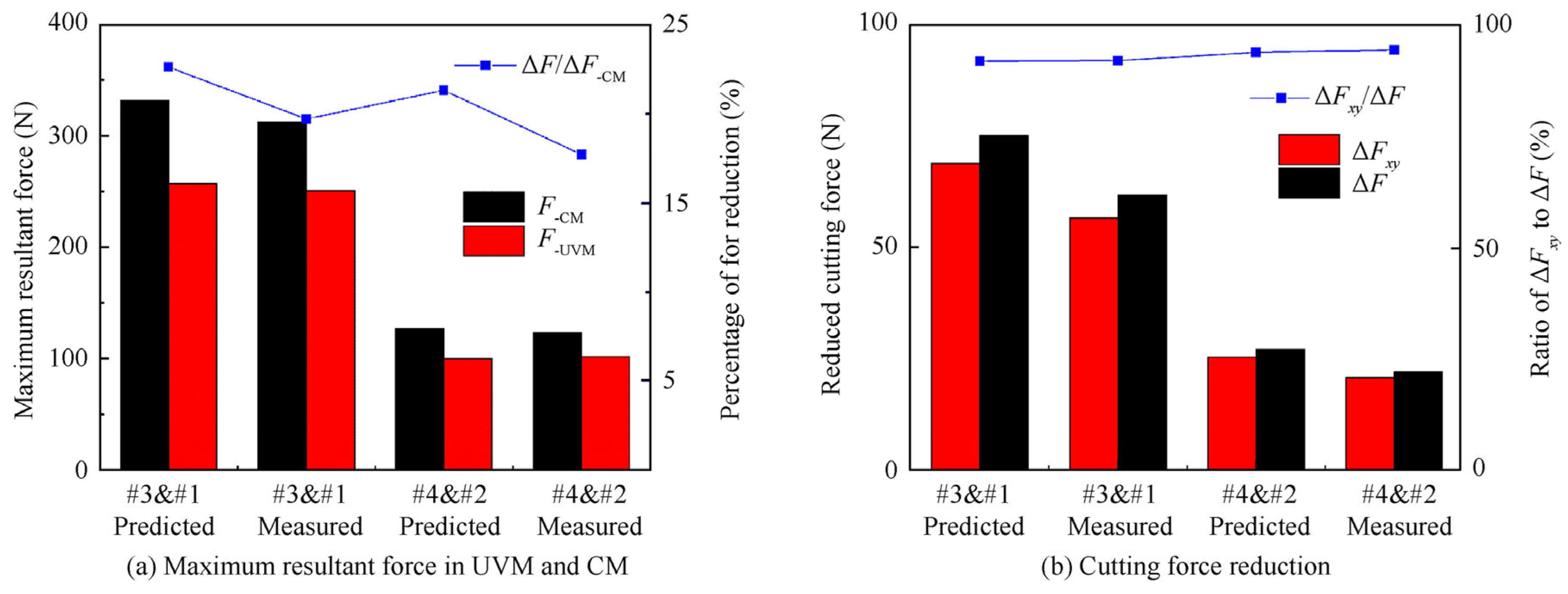
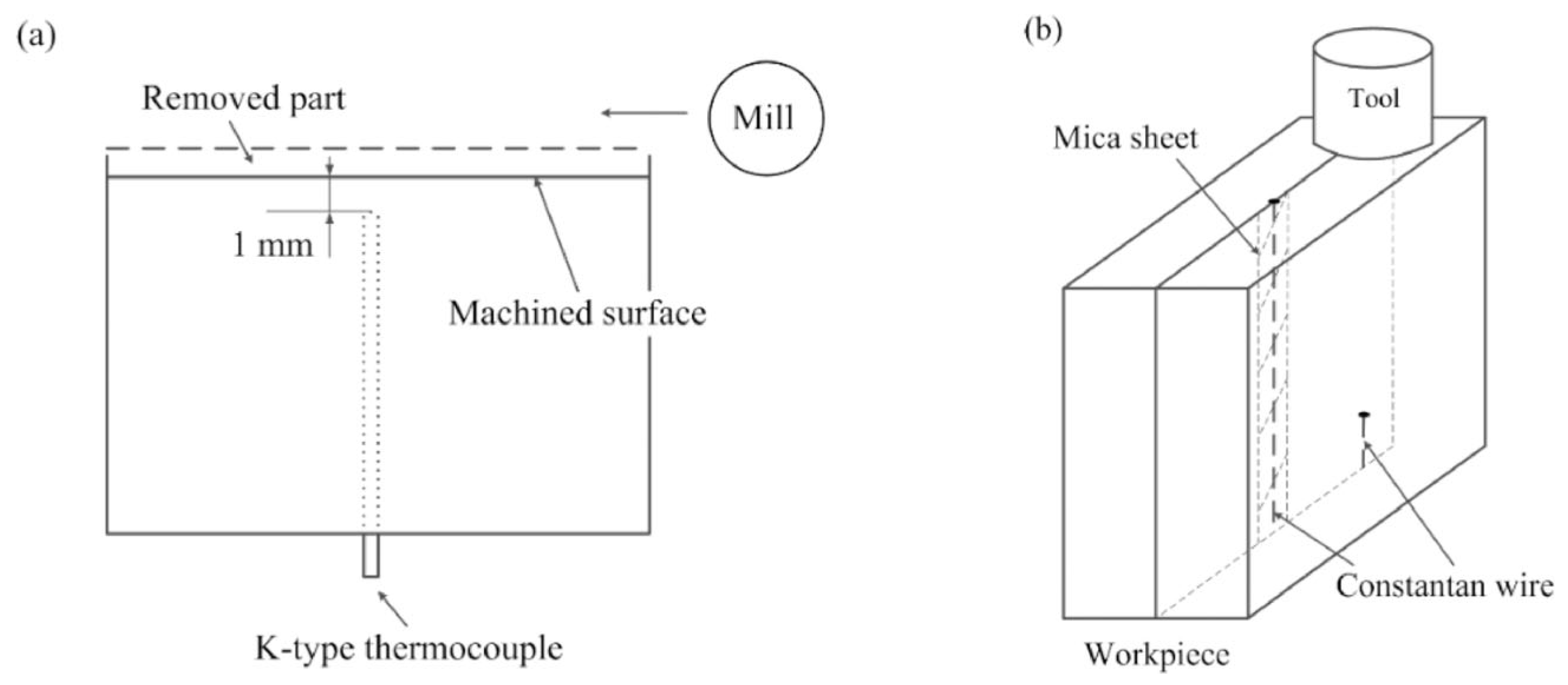
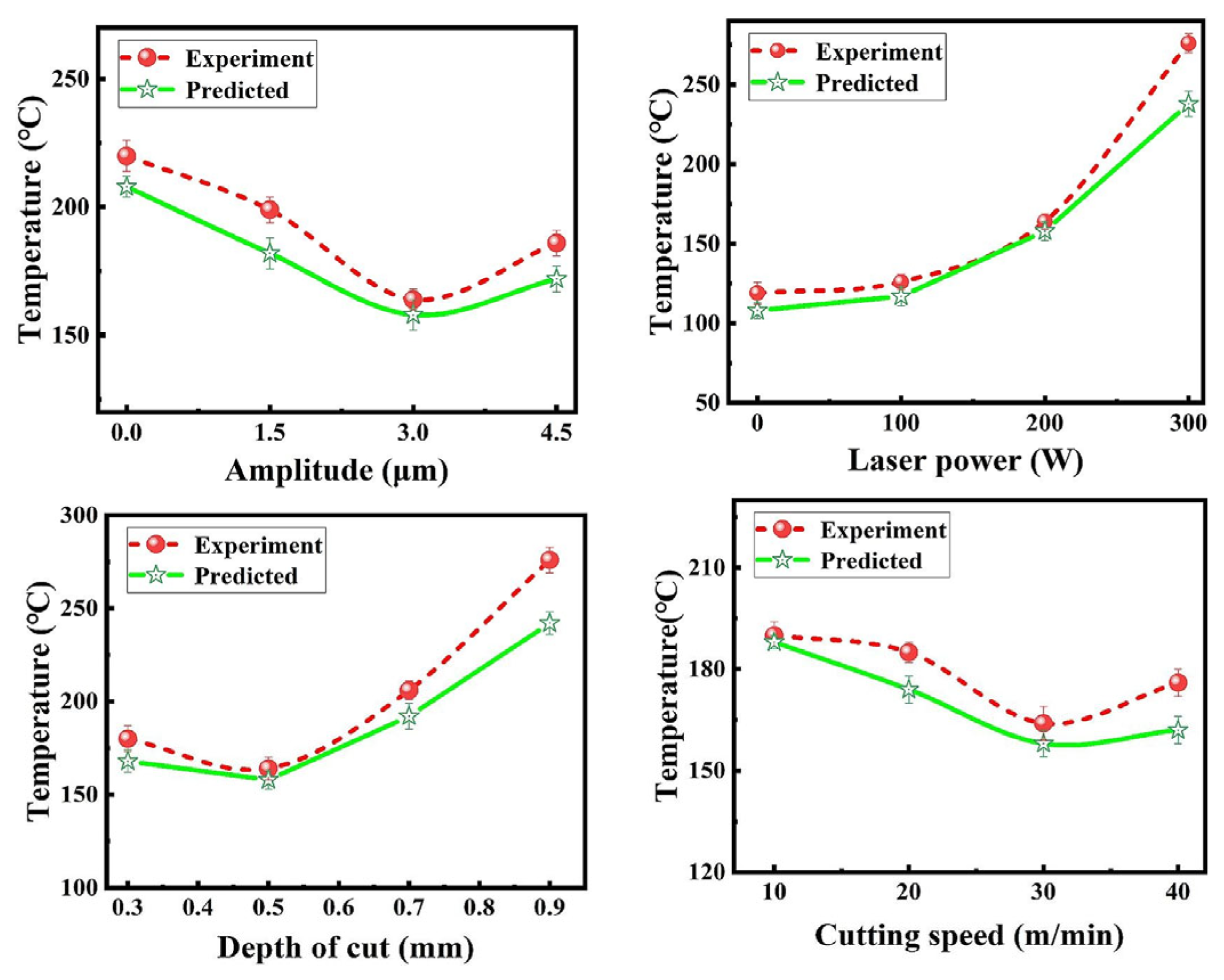
4. Cutting Force and Temperature
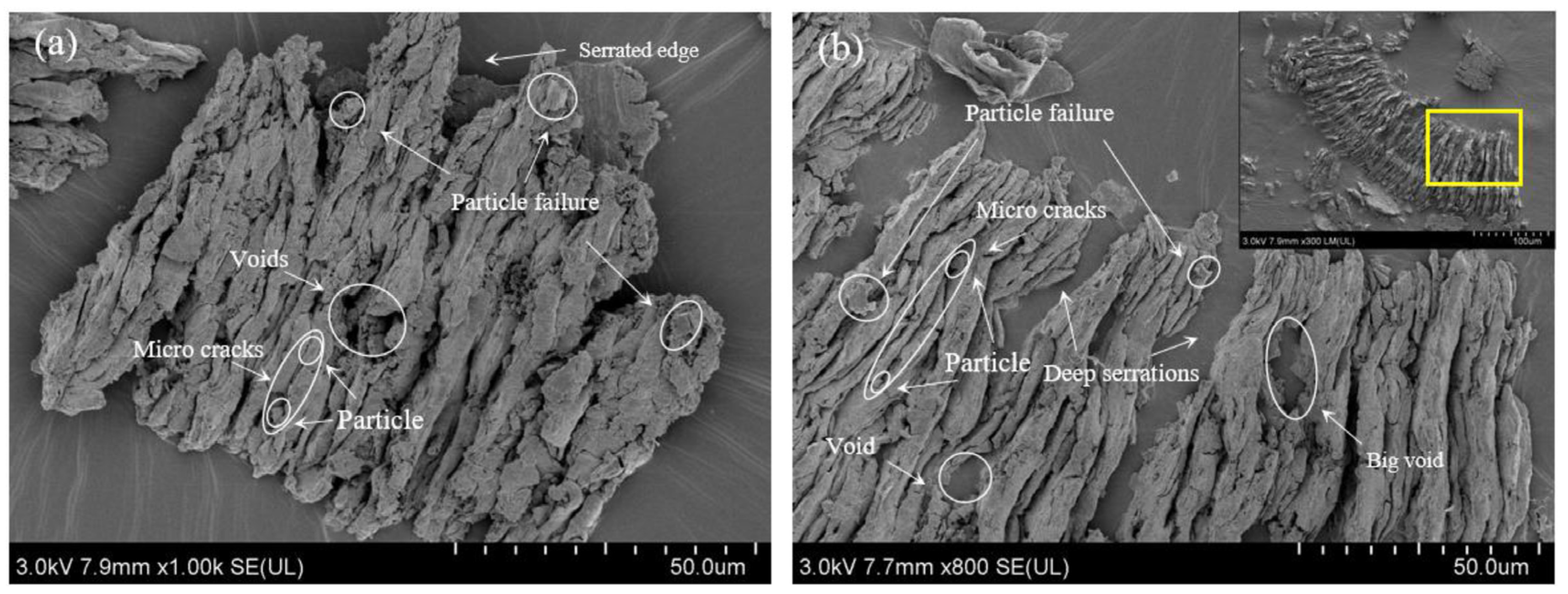
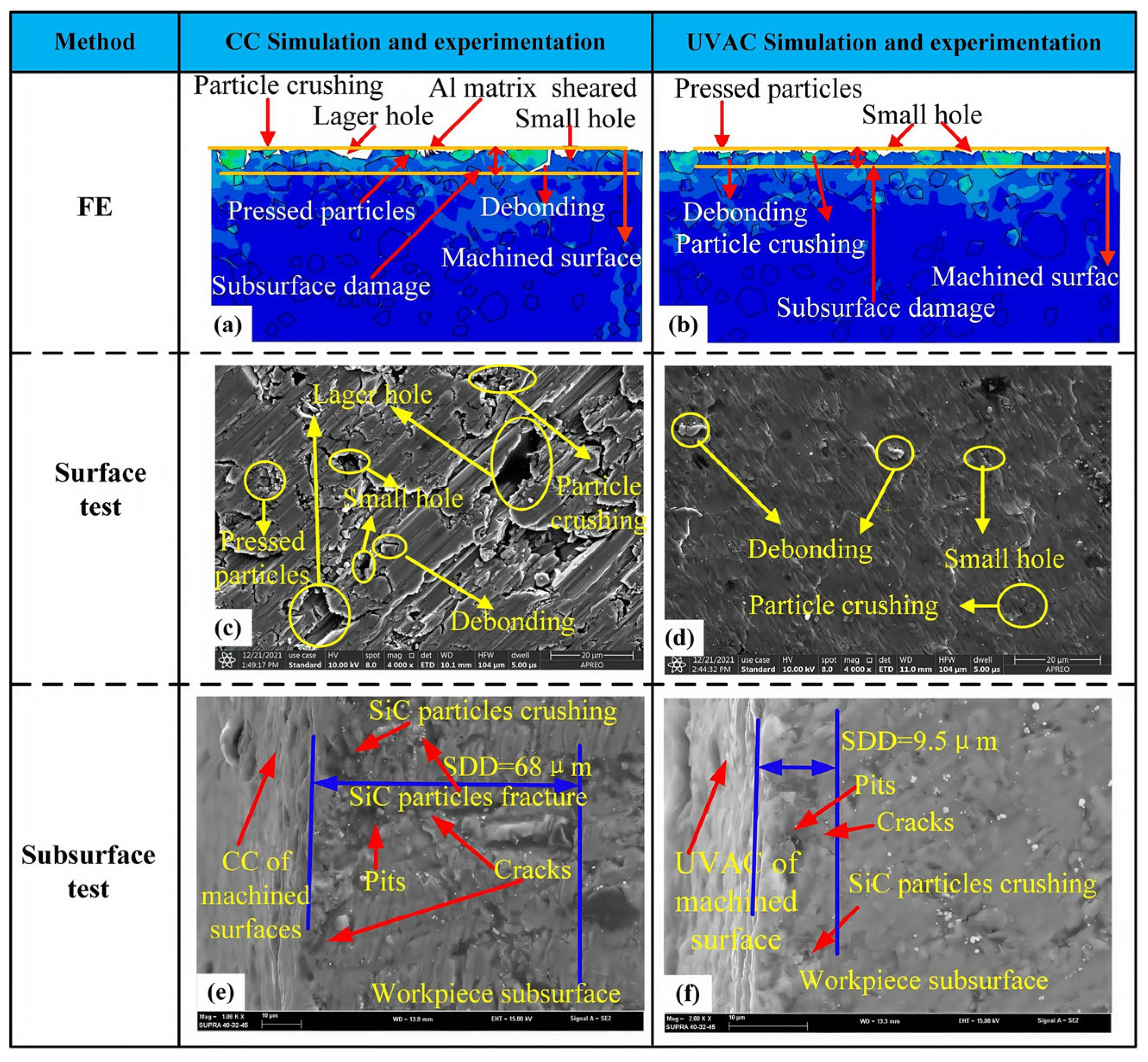
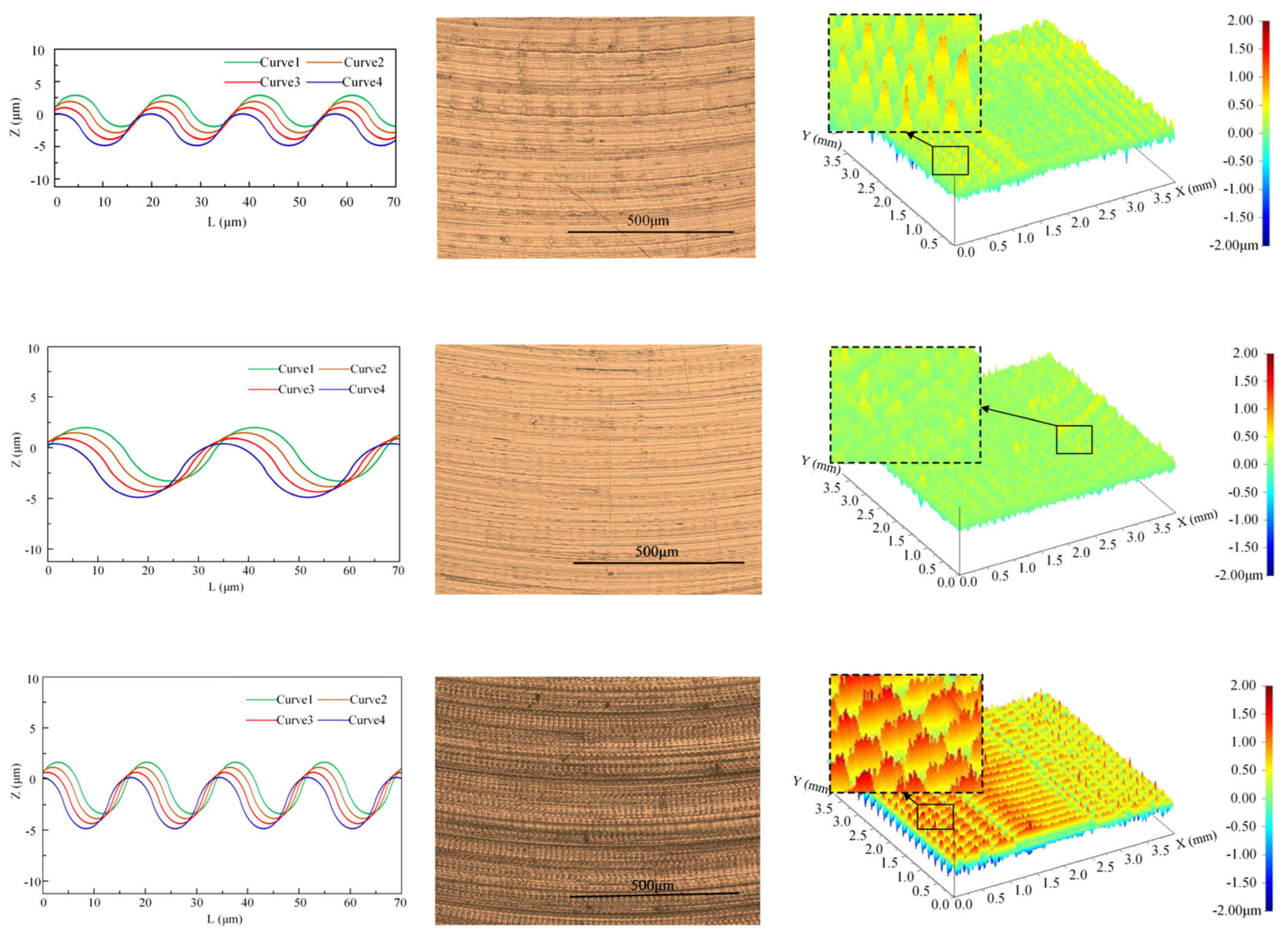
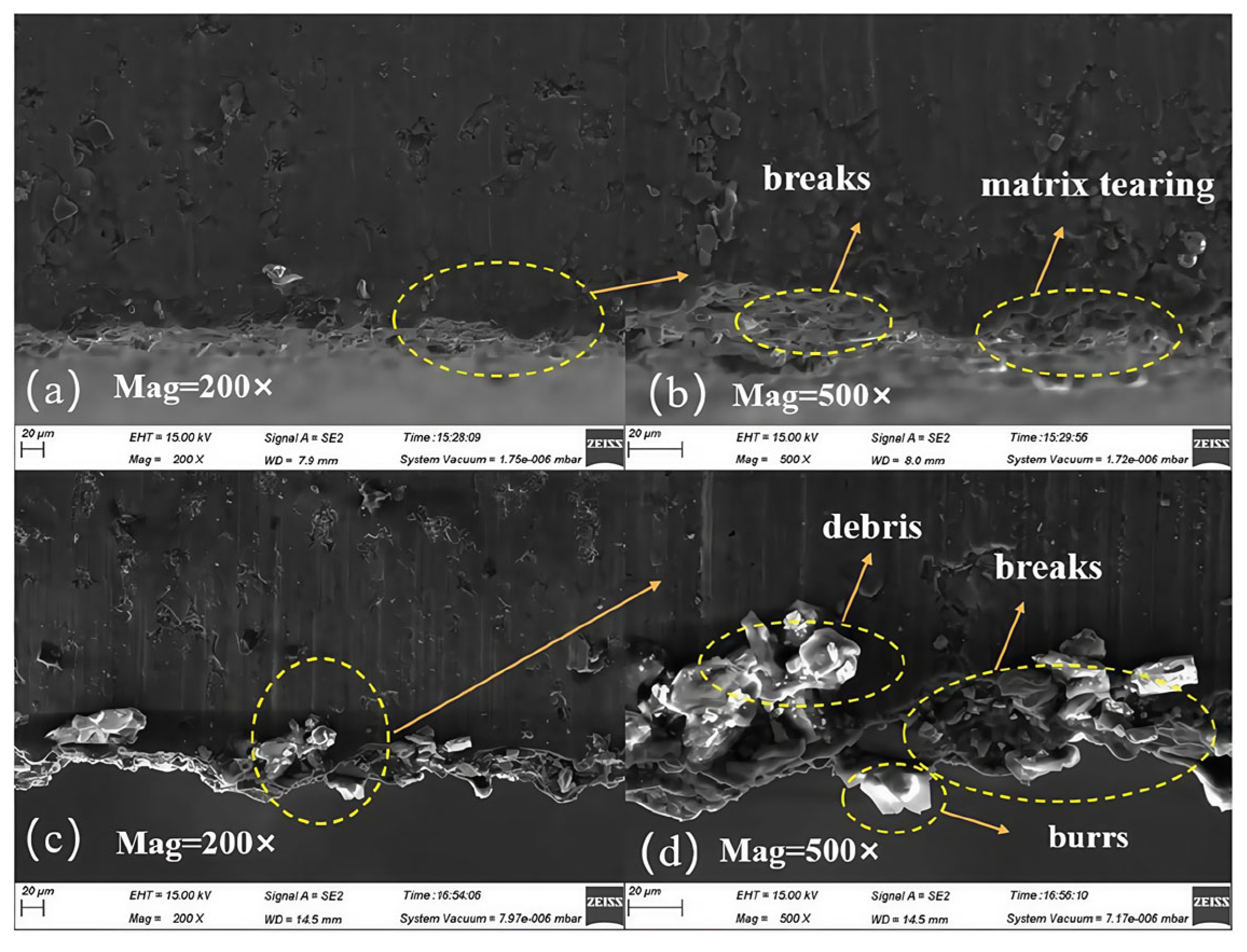
5. Surface Integrity
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Ultrasonic vibration-assisted machining effectively mitigates frictional forces and contact stresses during the cutting process by periodically altering the contact state between the tool and the workpiece, thereby significantly reducing tool wear rates and extending tool life. Additionally, ultrasonic vibrations facilitate chip fracture and ejection, resulting in finer and more uniform chip morphology, which reduces the formation of long or spiral chips and minimizes the risk of chip entanglement and blockage, thus enhancing the continuity and stability of the machining process.
- (2)
- The periodic separation and elastic recovery of the material induced by ultrasonic vibrations lead to a reduction in both the average and peak cutting forces, decreasing the load on the machine tool and improving machining precision and efficiency. The reduction in cutting forces, coupled with efficient chip removal, facilitates faster heat dissipation, preventing localized overheating in the cutting zone and maintaining the quality of the machined workpiece.
- (3)
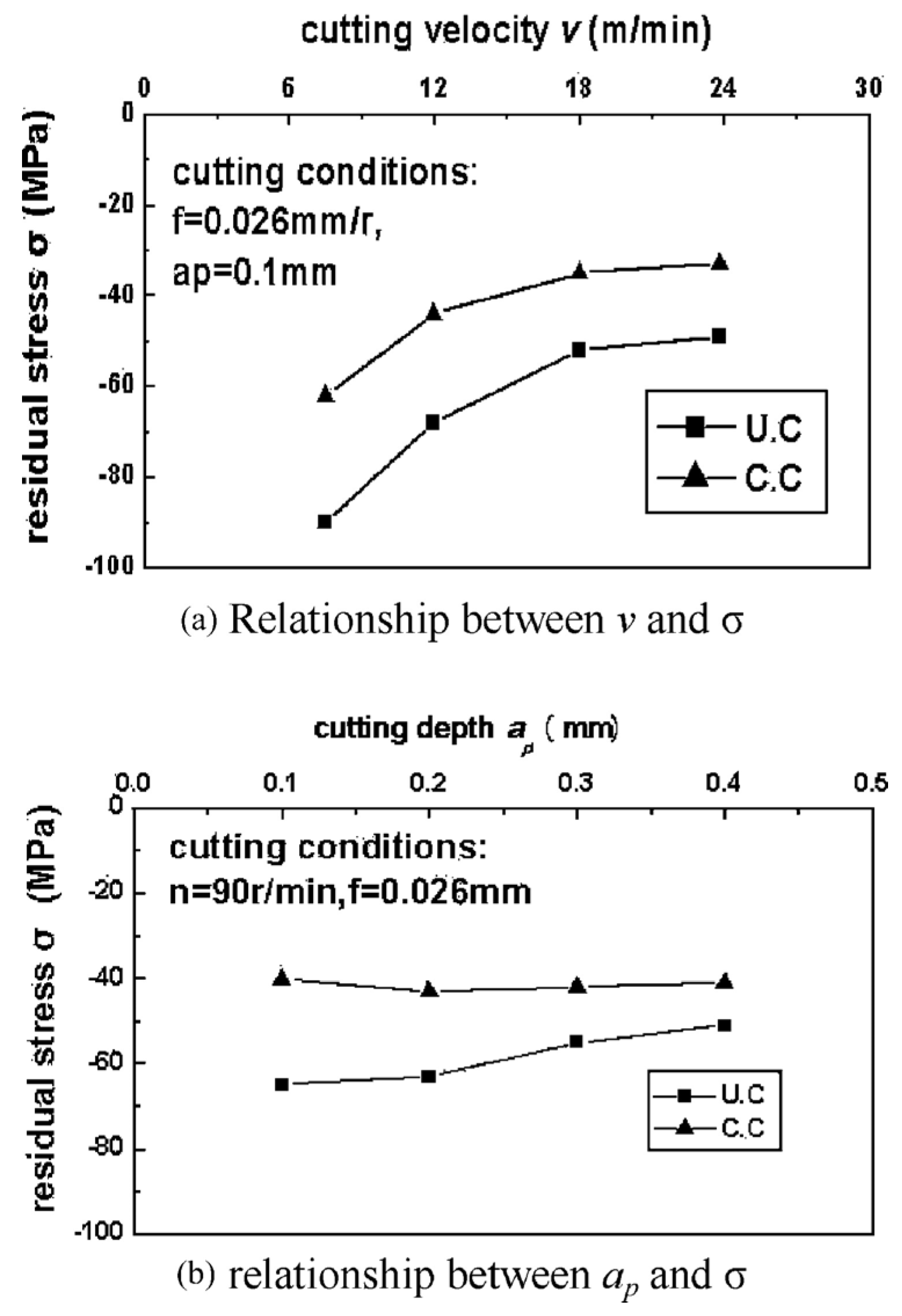
- Ultrasonic vibration-assisted machining significantly diminishes residual stresses, microcracks, and surface roughness on the machined surface, thereby enhancing surface quality. This is particularly important for particle-reinforced Al-based matrix composites, which are highly sensitive to surface defects, as ultrasonic vibration technology represents a critical approach for achieving high-quality machining.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, L.; Zhou, C.Z.; Wen, Q.; Li, M.S.; Zhong, H.; Ji, S.D. Ultrasonic-promoted rapid transient liquid phase bonding of high volume fraction SiC particle reinforced aluminum-based metal matrix composite in low temperature. Ultrasonics 2020, 106, 106159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beffort, O.; Long, S.Y.; Cayron, C.; Kuebler, J.; Buffat, P.A. Alloying effects on microstructure and mechanical properties of high volume fraction SiC-particle reinforced Al-MMCs made by squeeze casting infiltration. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.N.; Ma, Z.Y.; Li, S.Z.; Li, S.; Bi, J. Effect of particle-size on wear behavior of SiC particulate-reinforced aluminum-alloy composites. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1995, 14, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.Y.; Ren, S.; He, X.B.; Qin, M.L.; Qu, X.H. Study on methods to strengthen SiC performs for SiCp/Al composites by pressureless infiltration. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 468, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, Q.Z.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y.; Liu, Y. Experimental and modeling investigation on SiCp distribution in powder metallurgy processed SiCp/2024 Al composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 5582–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z. Mechanical behavior and fabrication characteristics of aluminum metal matrix composite alloys. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2001, 20, 921–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasali, E.; Pakseresht, A.H.; Alizadeh, M.; Shirvanimoghaddam, K.; Ebadzadeh, T. Vanadium carbide reinforced aluminum matrix composite prepared by conventional, microwave and spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Wang, W.H.; Shi, Y.Y.; Jiang, R.S.; Lin, K.Y.; Song, G.D.; Shao, M.; Liu, X.F.; Li, J.C.; Shan, C.W. Machining performance of in-situ TiB2 particle reinforced Al-based metal matrix composites: A literature review. J. Adv. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 2021003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, F.; Qiu, X.; An, D.; He, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Xie, Z.P. Effects of La and Ce on microstructure and properties of SiC/Al composites. Ceram. Int. 2019, 46, 1232–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Wang, F.; Shen, W.; Qiu, X.P.; He, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Xie, Z.P. Influence of interface thermal resistance on thermal conductivity of SiC/Al composites. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 23815–23819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.F.; Wang, W.H.; Jiang, R.S.; Lin, K.Y.; Song, G.D. Tool wear mechanisms for milling in situ TiB2 particle-reinforced Al matrix composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 86, 3517–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.Y.; Wang, W.H.; Jiang, R.S.; Xiong, Y.F. Effect of tool nose radius and tool wear on residual stresses distribution while turning in situ TiB2/7050 Al metal matrix composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 100, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Cho, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, S.K.; Jo, I. Microstructural Evolution and Strengthening Mechanism of SiC/Al Composites Fabricated by a Liquid-Pressing Process and Heat Treatment. Materials 2019, 12, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.P.; Seah, W.K.H. Tool wear acceleration in relation to workpiece reinforcement percentage in cutting of metal matrix composites. Wear 2001, 247, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozben, T.; Kilickap, E.; Cakir, O. Investigation of mechanical and machinability properties of SiC particle reinforced Al-MMC. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 198, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftci, I.; Turker, M.; Seker, U. Evaluation of tool wear when machining SiCp-reinforced Al-2014 alloy matrix composites. Mater. Des. 2004, 25, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugazhenthi, A.; Kanagaraj, G.; Dinaharan, I.; Selvam, J.D.R. Turning characteristics of in situ formed TiB2 ceramic particulate reinforced AA7075 aluminum matrix composites using polycrystalline diamond cutting tool. Measurement 2018, 121, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.S.; Wang, W.H.; Song, G.D.; Wang, Z.Q. Experimental investigation on machinability of in situ formed TiB2 particles reinforced Al MMCs. J. Manuf. Process. 2016, 23, 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Manna, A.; Bhattacharayya, B. Influence of machining parameters on the machinability of particulate reinforced Al/SiC-MMC. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2005, 25, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikouei, S.M.; Kouchakzadeh, M.A.; Yousefi, R.; Kadivar, M.A. Investigation of cutting model in machining of Al/SiCp metal matrix composite. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 117, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar]
- Pramanik, A.; Zhang, L.C.; Arsecularatne, J.A. Prediction of cutting forces in machining of metal matrix composites. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.F.; Wang, W.H.; Jiang, R.S.; Lin, K.Y. A study on cutting force of machining in situ TiB2 particle-reinforced 7050Al alloy matrix composites. Metals 2017, 7, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Gu, L.; He, G.J. A review on conventional and nonconventional machining of SiC particle-reinforced aluminium matrix composites. Adv. Manuf. 2020, 8, 279–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugazhenthi, A.; Dinaharan, I.; Kanagaraj, G.; Selvam, J.D.R. Predicting the effect of machining parameters on turning characteristics of AA7075/TiB2 in situ aluminum matrix composites using empirical relationships. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandakrishnan, V.; Mahamani, A. Investigations of flank wear, cutting force, and surface roughness in the machining of Al-6061-TiB2 in situ metal matrix composites produced by flux-assisted synthesis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 55, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamani, A. Influence of process parameters on cutting force and surface roughness during turning of AA2219-TiB2/ZrB2 in-situ metal matrix composites. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghinattia, E.; Bertolini, R.; Sorgato, M.; Ghiotti, A.; Bruschi, S. Tool wear and surface finish analysis after drilling Al-SiC metal matrix composite with DLC-coated tools at varying feed. In Proceedings of the 7th CIRP Conference on Surface Integrity, Procedia CIRP, Bremen, Germany, 15–17 May 2024; Volume 123, pp. 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, P.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.Z.; Guo, G.Y. Study on the surface quality of 60vol% SiCp/Al2024 composites with large-grained. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C-J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2022, 236, 5391–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallab, M.E.; Sklad, M. Machining of Al/SiC particulate metal matrix composites part II Workpiece surface integrity. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1998, 83, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gong, Y.D.; Liang, G.Q.; Cai, M.; Han, B. Face Grinding Surface Quality of High Volume Fraction SiCp/Al Composite Materials. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 34, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.F.; Wang, W.H.; Jiang, R.S.; Lin, K.Y.; Song, G.D. Surface integrity of milling in-situ TiB2 particle reinforced Al matrix composites. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2016, 54, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.J.; Zhu, X.C.; Lu, S.X.; Zhang, H.Z. Research Progress of Low Damage Machining Technology for SiCp/Al Composites. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2021, 50, 1084–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Azarhoushang, B.; Tawakoli, T. Development of a novel ultrasonic unit for grinding of ceramic matrix composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 57, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehl, D.E.; Dow, T.A. Review of vibration-assisted machining. Precis. Eng. 2008, 32, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.C.; Zhu, L.D.; Zhang, G.X.; Zhang, G.X.; Ni, C.B.; Lin, B. Review of ultrasonic vibration-assisted machining in advanced materials. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2020, 156, 103594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.M. Study on the cutting force in elliptical ultrasonic vibration cutting. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2019, 885, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Ramón, J.-M. Microtexturing of industrial surfaces via radial ultrasonic vibration-assisted machining: An analytical model and experimental validation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 482, 130718. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.D.; Xiao, D.H.; Teng, X.Y. Influence of vibration parameters on ultrasonic vibration cutting micro-particles reinforced SiC/Al metal matrix composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 6057–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, M.; Dong, G.J. Experimental investigation on rotary ultrasonic face grinding of SiC/Al composites. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.W.; Zou, P.; Wang, A.Q.; Wei, S.Y.; Fang, R. Research on three-dimensional ultrasonic vibration-assisted turning cutting force. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 91, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Eow, Y.T.; Ngoi, B.K.A.; Lim, E.N. Vibration assisted precision machining of steel with PCD tools. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2003, 18, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, C.; Rahman, M. Effect of machining parameters in ultrasonic vibration cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2008, 48, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, C.; Rahman, M.; Neo, K.S. Machinability study of tungsten carbide using PCD tools under ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2009, 49, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.W.; Lin, G. Ultrasonic vibration turning of an aluminium-based metal matrix composite reinforced with SiC particles. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 27, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Lin, G. Diamond turning of a metal matrix composite with ultrasonic vibrations. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2005, 20, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.P.; Fan, H.J.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Y.L. Research on Grinding Force of Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Grinding of C/SiC Composite Materials. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Hu, Z.W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.Q.; Jin, J.F.; Peng, Q.; Xu, X.P. Insights into scratching force in axial ultrasonic vibration-assisted single grain scratching. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 112, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.H.; Tang, J.Y.; Chen, H.F.; Shao, W. A comprehensive investigation of surface generation and material removal characteristics in ultrasonic vibration assisted grinding. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 156, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guangheng, D.Y.; Zhao, J.N.; Dong, Y.H.; Zhang, X.F.; Jiang, X.M.; Lin, B. Study on key factors influencing the surface generation in rotary ultrasonic grinding for hard and brittle materials. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 38, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Jiang, B.; Xu, X.P. Study on wear of diamond wheel in ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding ceramic. Wear 2015, 332, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, B.S.; Pandey, B. Effect of turning parameters on aluminium metal matrix composites-a review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 225, 012276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muguthu, J.N.; Dong, G.; Ikua, B.W. Optimization of machining parameters influencing machinability of Al2124SiCp (45%wt) metal matrix composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 49, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njuguna, M.J.; Gao, D.; Hao, Z. Tool wear, surface integrity and dimensional accuracy in turning Al2124SiCp (45%wt) metal matrix composite using CBN and PCD tools. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2013, 6, 4138–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, R.A.; Jamil, M.; Laghari, A.A.; Khan, A.M.; Akhtar, S.S.; Mekid, S. A critical review on tool wear mechanism and surface integrity aspects of SiCp/Al MMCs during turning Prospects and challenges. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 2825–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, R.A.; Li, J.; Xie, Z.; Wang, S.Q. Modeling and optimization of tool wear and surface roughness in turning of Al/SiCp using response surface methodology. 3D Res. 2018, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, R.A.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Study of machining process of SiCp/Al particle reinforced metal matrix composite using finite element analysis and experimental verification. Materials 2020, 13, 5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, R.A.; Li, J.G.; Mia, M. Effects of turning parameters and parametric optimization of the cutting forces in machining SiCp/Al 45 wt% composite. Metals 2020, 10, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, R.A.; Gupta, M.K.; Li, J.G. Evolutionary algorithm for the prediction and optimization of SiCp/Al metal matrix composite machining. J. Prod. Syst. Manuf. Sci. 2020, 2, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Laghari, R.A.; Li, J. Modeling and optimization of cutting forces and effect of turning parameters on SiCp/Al 45% vs SiCp/ Al 50% metal matrix composites A comparative study. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, R.; Andrea, G.; Alagan, N.T.; Bruschi, S. Tool wear reduction in ultrasonic vibration-assisted turning of SiC-reinforced metal-matrix composite. Wear 2023, 523, 204785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.J.; Zhang, H.J.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.J. Experimental investigation on ultrasonic vibration-assisted turning of SiCp/Al composites. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2013, 28, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gu, Y.; Lin, J.Q.; Zhao, H.B.; Liu, S.Y.; Xu, Z.S.; Yu, H.; Fu, X.B. Finite element analysis and experimental study on the cutting mechanism of SiCp/Al composites by ultrasonic vibration-assisted cutting. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 35406–35421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Roy, A.; Sun, R.L.; Silberschmidt, V.V. Enhanced machinability of SiC-reinforced metal-matrix composite with hybrid turning. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 268, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Chen, T.; Liu, F.; Zhang, C. Investigation of ultrasonic-assisted drilling temperature of SiCp/Al composites. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2024, 39, 1910–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.P.; Zhang, H.H.; Fan, Y.H. Tool wear mathematical model of PCD during ultrasonic elliptic vibration cutting SiCp/Al composite. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2025, 126, 106967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.F.; Wang, W.H.; Jiang, R.S.; Lin, K.Y. Machinability of in situ TiB2 particle reinforced 7050Al matrix composites with TiAlN coating tool. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 3813–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.F.; Wang, W.H.; Jiang, R.S.; Lin, K.Y. Analytical model of workpiece temperature in end milling in-situ TiB2/7050Al metal matrix composites. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 149, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.S.; Chen, X.F.; GE, R.; Wang, W.H.; Song, G.D. Influence of TiB2 particles on machinability and machining parameter optimization of TiB2/Al MMCs. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2018, 31, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.F.; Wang, W.H.; Shi, Y.Y.; Jiang, R.S.; Shan, C.W.; Liu, X.F.; Lin, K.Y. Investigation on surface roughness, residual stress and fatigue property of milling in-situ TiB2/7050Al metal matrix composites. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Wang, W.H.; Jiang, R.S.; Xiong, Y.F.; Lin, K.Y. Tool wear mechanisms in axial ultrasonic vibration assisted milling in-situ TiB2/7050Al metal matrix composites. Adv. Manuf. 2020, 8, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.S.; Lu, M.M.; Lin, J.Q.; Yang, Y.K. Experimental and simulation study of ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting SiCp/Al composites Chip formation and surface integrity study. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 1595–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Liu, C.S.; Zhu, X.S.; Xu, K.W. Research on the vibration cutting performance of particle reinforced metallic matrix composites SiCp/Al. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 129, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.L.; Jing, L.; Wang, C.H.; Li, S.J.; Qiu, X.Y.; Li, C.P.; Xiang, D.H. Study on effect of vibration amplitude on cutting performance of SiCp/Al composites during ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 2219–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Zani, L.; Abdul-Kadir, A.; Roy, A.; Baxevanakis, K.P.; Jones, L.C.R.; Silberschmidt, V.V. Hybrid-hybrid turning of micro-SiCp/AA2124 composites: A comparative study of laser-and-ultrasonic vibration-assisted machining. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 86, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.S.; Zhao, B.; Gao, G.F.; Jiao, F. Research on the characteristics of the cutting force in the vibration cutting of a particle-reinforced metal matrix composites SiCp/Al. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 129, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.G.; Zheng, F.F.; Zhu, X.L.; Kang, R.K.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.Q. Characterization of material removal in ultrasonically assisted grinding of SiCp/Al with high volume fraction. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 2827–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, W.B.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.B.; Chen, S.P.; Fu, Z.X.; Zhao, B. Longitudinal-torsional coupled rotary ultrasonic machining end surface grinding of SiCf/SiC composites A mechanical model of cutting force. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 129, 1227–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.H.; Shi, Z.L.; Feng, H.R.; Wu, B.F.; Zhang, Z.M.; Chen, Y.B.; Niu, X.X.; Zhao, B. Finite element analysis of ultrasonic assisted milling of SiCp/Al composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 3477–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.L.; Dai, F.P.; Jing, L.; Wang, X.H.; Liu, L.P. Study on the processing performance of 60% SiCp/Al composite materials assisted by longitudinal and torsional ultrasonic vibration milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 135, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.L.; Xiang, D.H.; Feng, H.R.; Wu, B.F.; Zhang, Z.M.; Gao, G.F.; Zhao, B. Finite Element and Experimental Analysis of Ultrasonic Vibration Milling of High-Volume Fraction SiCp/Al Composites. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2021, 22, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.H.; Yao, Y.; Xu, Z.P.; Yao, X.B.; Zhao, B.; Ding, W.F. Material removal characterization during axial ultrasonic vibration grinding SiCp/Al composites with a single diamond grain. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 134, 5267–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.F.; Xiang, D.H.; Peng, P.C.; Li, Y.Q.; Yuan, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.M.; Gao, G.F.; Zhao, B. Establishment of scratching force model for micro-removal of SiCp/Al composites by ultrasonic vibration. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 307, 117677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Q.; Wang, C.; Lu, M.M.; Zhou, J.K.; Zhao, S.X.; Liu, Y.Y. Modeling and investigation of cutting force for SiCp/Al composites during ultrasonic vibration-assisted turning. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process. Mech. Eng. 2022, 236, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.K.; Tong, J.L.; Zhang, Z.P.; Ye, Y.Q.; Zhai, H.J.; Tao, H.Q. Modeling and experimental analysis of ultrasonic vibration drilling force prediction model for tiny small holes in high body fraction aluminum-based silicon carbide composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 131, 3885–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Yuan, S.M.; Batako, A.; Chen, B.C.; Gao, X.X.; Li, Z.; Amin, M. Modeling for ultrasonic vibration-assisted helical grinding of SiC particle-reinforced Al-MMCs. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 131, 5223–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Wang, W.H.; Jiang, R.S.; Xiong, Y.F.; Lin, K.Y.; Li, J.C.; Shan, C.W. Analytical model of cutting force in axial ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling in-situ TiB2/7050Al PRMMCs. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Guimarães, B.M.; da Silva Fernandes, C.M.; Amaral de Figueiredo, D.; Correia Pereira da Silva, F.S.; Macedo Miranda, M.G. Cutting temperature measurement and prediction in machining processes: Comprehensive review and future perspectives. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 2849–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, K.; Mathew, J.; Joseph, M.A. An investigation of cutting force and tool–work interface temperature in milling of Al-SiCp metal matrix composite. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 227, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chou, Y.K. Cutting tool temperature analysis in heat-pipe assisted composite machining. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2007, 129, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.K.; Liu, J. CVD diamond tool performance in metal matrix composite machining. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1872–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Kishawy, H.A. Influence of alumina particles on the mechanics of machining metal matrix composites. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Wang, W.H.; Jiang, R.S.; Xiong, Y.F.; Lin, K.Y.; Li, J.C.; Shan, C.W. Analytical model of workpiece temperature in axial ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling in situ TiB2/7050Al MMCs. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 1659–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.C.; Tian, T.; Xiang, D.H.; Yu, H.H.; Niu, K.; Gao, W.; Yuan, Z.J.; Gao, G.F. Research on cutting temperature of laser-ultrasonic composite turning of high volume fraction SiCp/Al composite materials. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2025, 57, 103100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.X.; Zhang, X. Investigation on the cutting mechanism of SiCp/Al composites in ultrasonic elliptical vibration machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 4707–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Wang, W.H.; Jiang, R.S.; Xiong, Y.F.; Lin, K.Y.; Li, J.C. Investigation on surface roughness in axial ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling of in situ TiB2/7050Al MMCs. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 111, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Wang, W.H.; Jiang, R.S.; Xiong, Y.F.; Shan, C.W. Comparative investigation on surface integrity for conventional and ultrasonic vibration-assisted cutting of in situ TiB2/7050Al MMCs. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 1949–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Wang, W.H.; Jiang, R.S.; Xiong, Y.F.; Shan, C.W. Residual stress prediction in axial ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling in situ TiB2/7050Al MMCs. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 7591–7606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.H.; Li, B.; Peng, P.C.; Shi, Z.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Gao, G.F.; Zhao, B. Study on formation mechanism of edge defects of high-volume fraction SiCp/Al composites by longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J Mech. Eng. Sci. 2022, 236, 6219–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, H.T.; Feng, P.F.; Zhang, J.F.; Yu, D.W.; Wu, Z.J. Material removal mechanism in rotary ultrasonic machining of high-volume fraction SiCp/Al composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 2099–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.C.; Xiang, D.H.; Lei, X.F.; Shi, Z.L.; Li, B.; Liu, G.F.; Zhao, B.; Gao, G.F. Study on the edge defects of high volume fraction 70% SiCp/Al composites in ultrasonic-assisted milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 122, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.F.; Liang, G.Q.; Zhang, J.F. Ultrasonic vibration-assisted scratch characteristics of silicon carbide-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 10817–10823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Q.; Ling, L. Material deformation and removal mechanism of SiCp/Al composites in ultrasonic vibration assisted scratch test. Ceram. Int. 2018, 15133–15144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Yuan, S.M.; Gao, X.X.; Zhang, Z.K.; Chen, B.C.; Li, Z.; Batako, A.D.L. Surface and subsurface formation mechanism of SiCp/Al composites under ultrasonic scratching. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Qu, D.; Qiao, G.C. Multi-phase modeling of SiC particle removal mechanism in ultrasonic vibration–assisted scratching of SiCp/Al composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 113, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Zhang, H.J.; Zhou, M. Study on surface defect formation mechanism in ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding of SiCp/Al composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 129, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.J.; Xiang, D.H.; Peng, P.C.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Li, B.H.; Su, B.; Gao, G.F.; Zhao, B. Analysis of microscopic deformation mechanism of SiCp/Al composites induced by ultrasonic vibration nanoindentation. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.X.; Yuan, S.M.; Li, Q.L.; Chen, B.C.; An, W.Z.; Wang, L.Y. Ductile-brittle transition mechanism of SiC particle-reinforced Al-MMCs under ultrasonic assisted grinding with single grain. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 3655–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






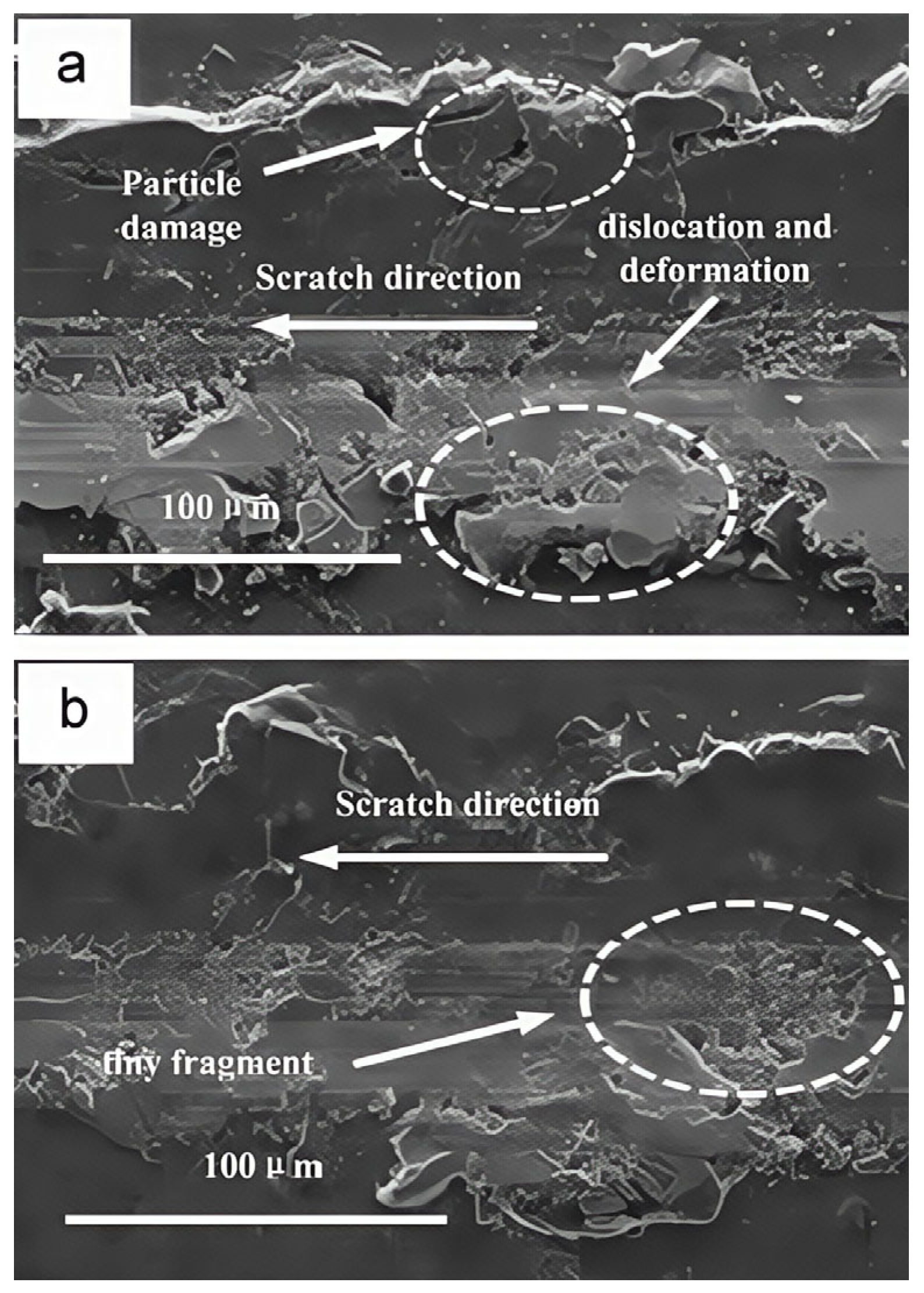

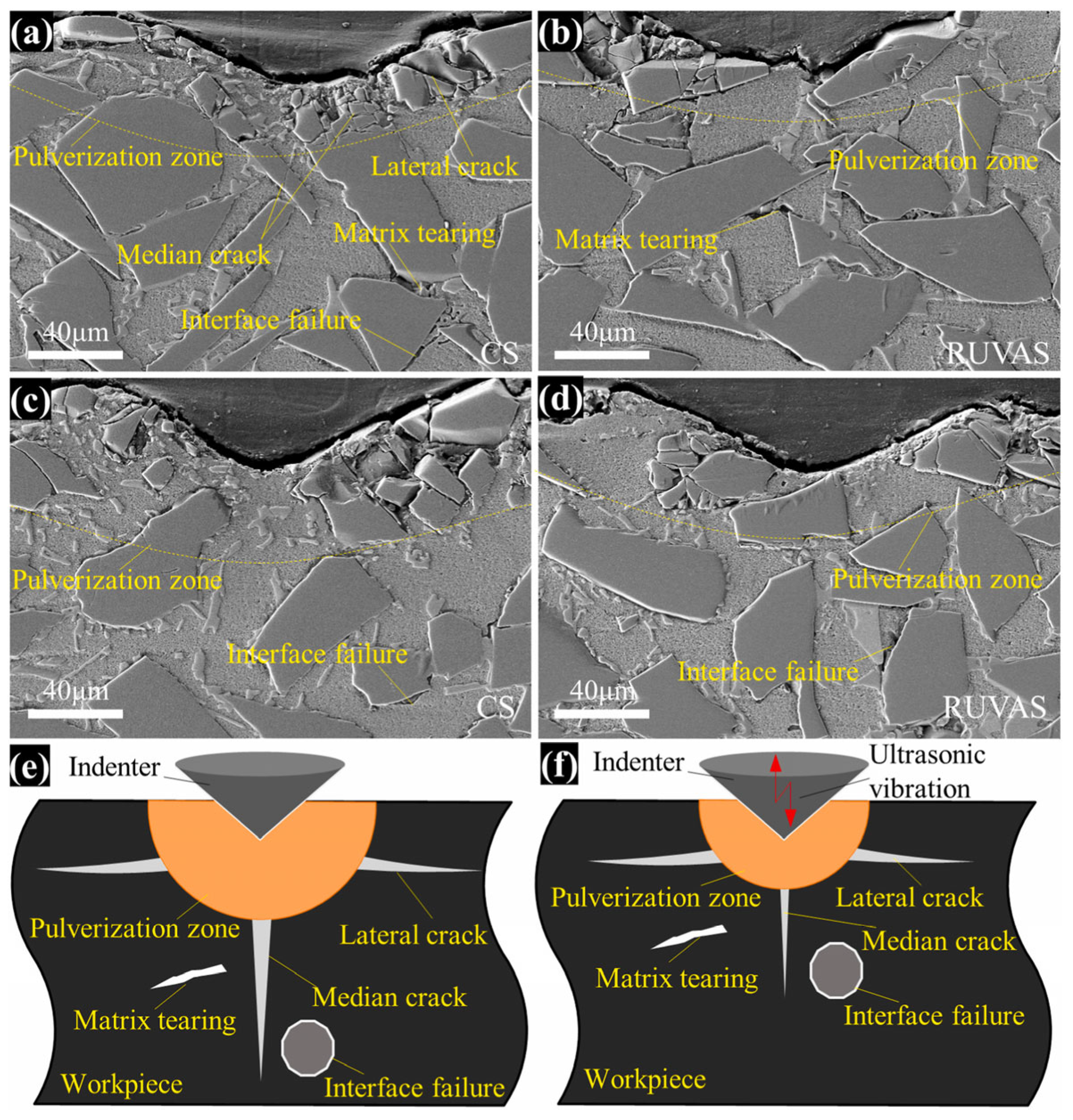
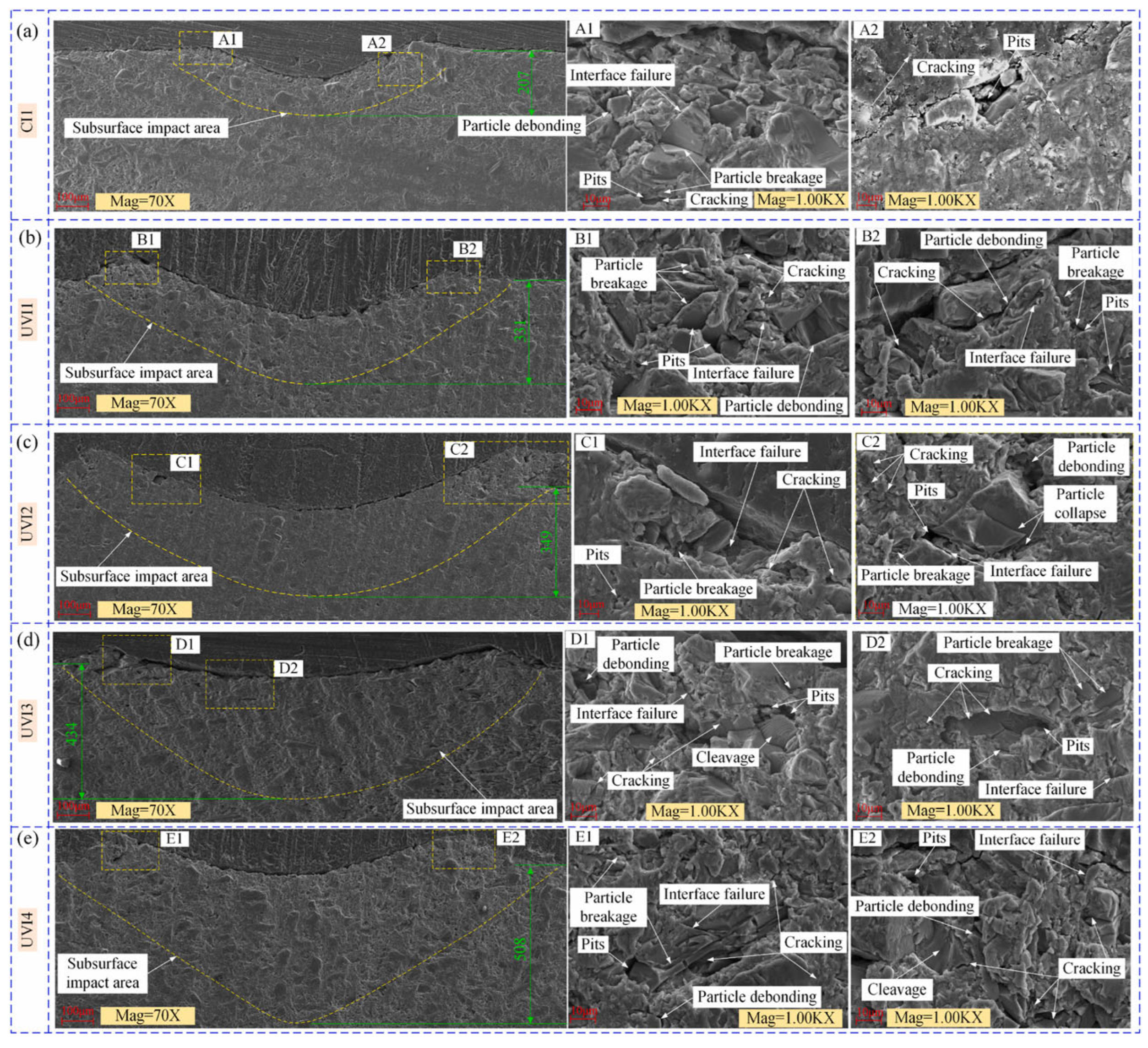
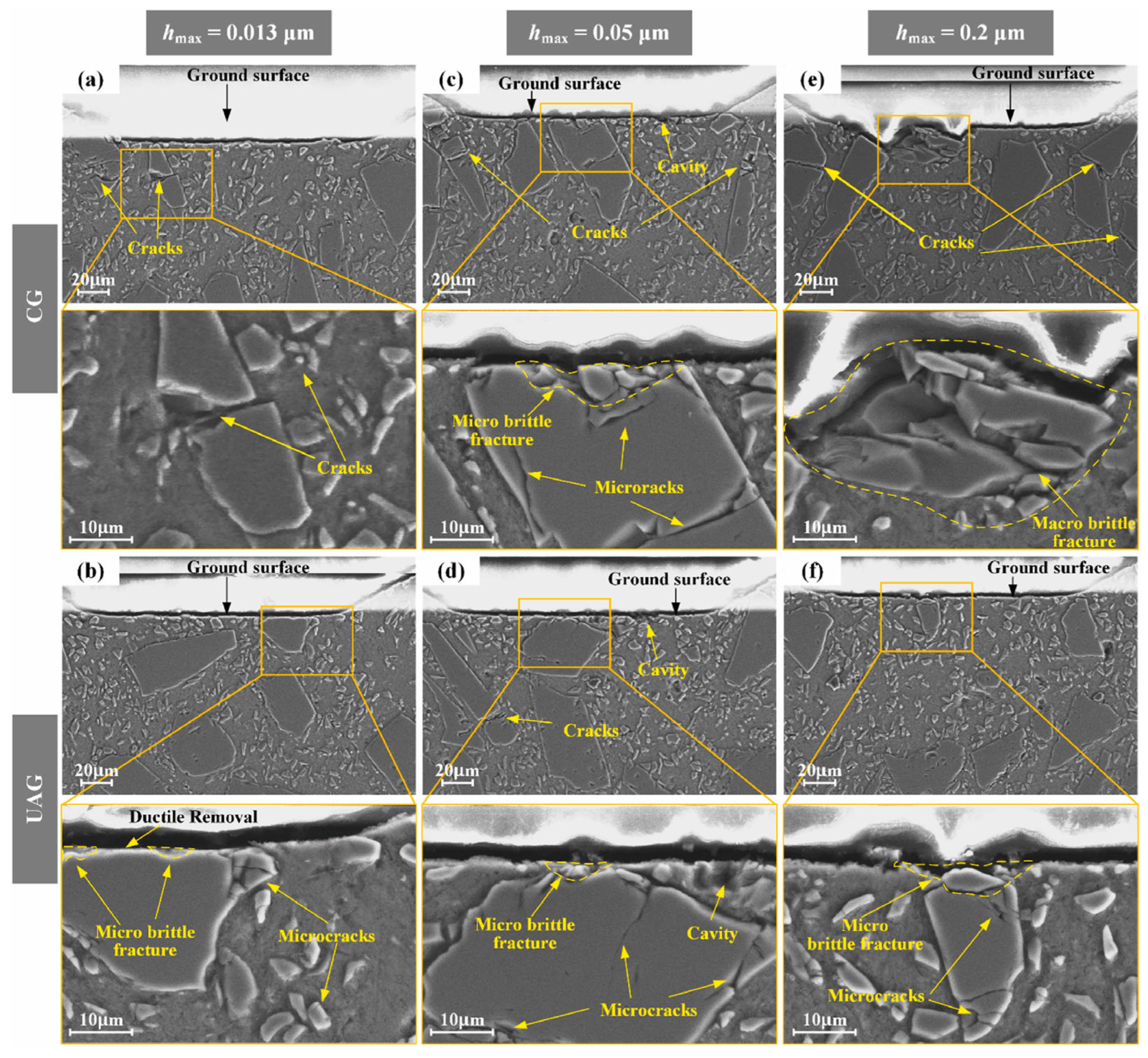
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Xiong, Y.; Yang, Q. Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Machining Particle-Reinforced Al-Based Metal Matrix Composites—A Review. Metals 2025, 15, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050470
Liu X, Xiong Y, Yang Q. Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Machining Particle-Reinforced Al-Based Metal Matrix Composites—A Review. Metals. 2025; 15(5):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050470
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaofen, Yifeng Xiong, and Qingwei Yang. 2025. "Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Machining Particle-Reinforced Al-Based Metal Matrix Composites—A Review" Metals 15, no. 5: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050470
APA StyleLiu, X., Xiong, Y., & Yang, Q. (2025). Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Machining Particle-Reinforced Al-Based Metal Matrix Composites—A Review. Metals, 15(5), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050470




