Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Brass-Clad Copper Stranded Wires in High-Speed Solid/Liquid Continuous Composite Casting and Drawing
Abstract
1. Introduction
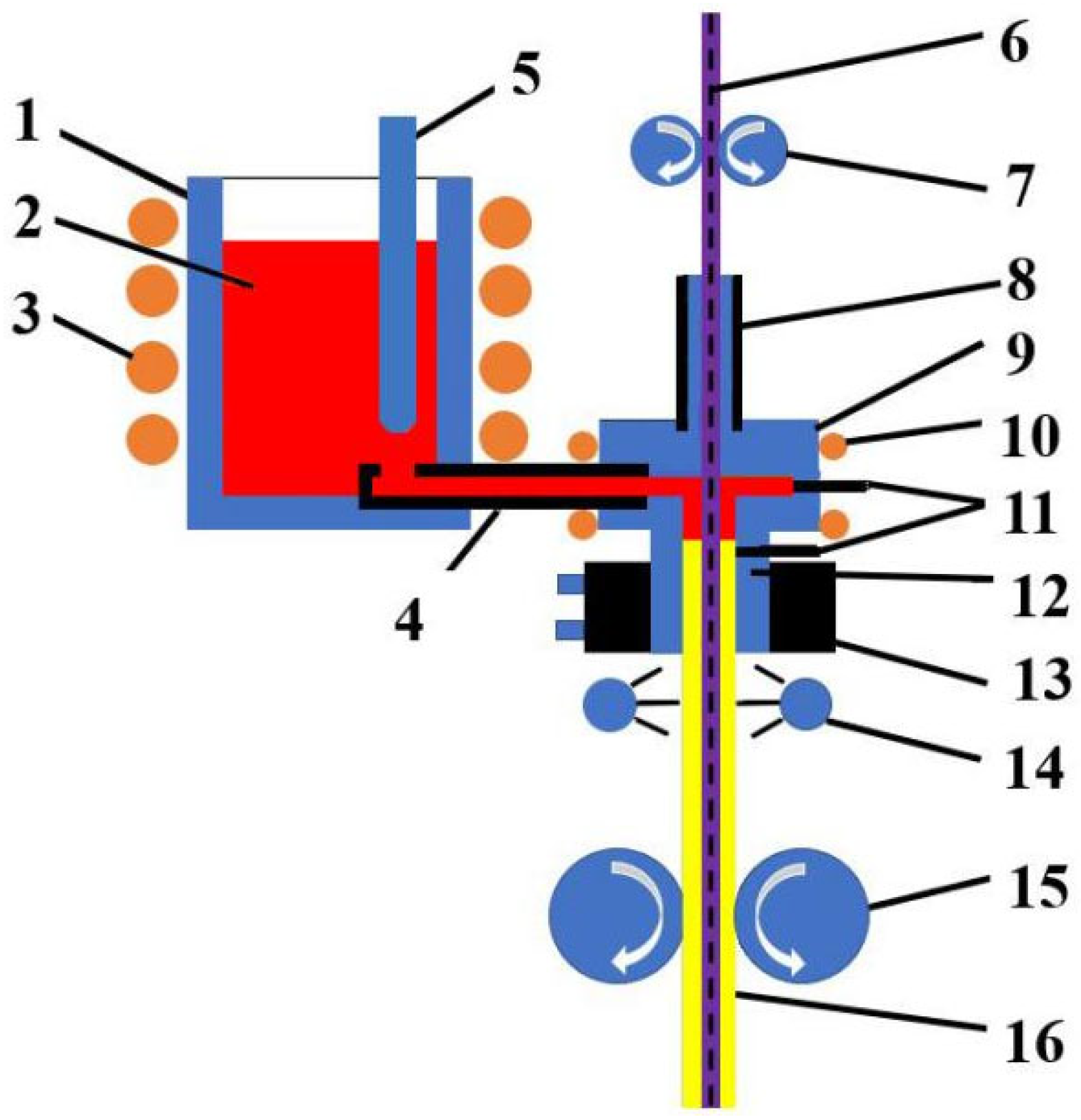
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Experimental Results
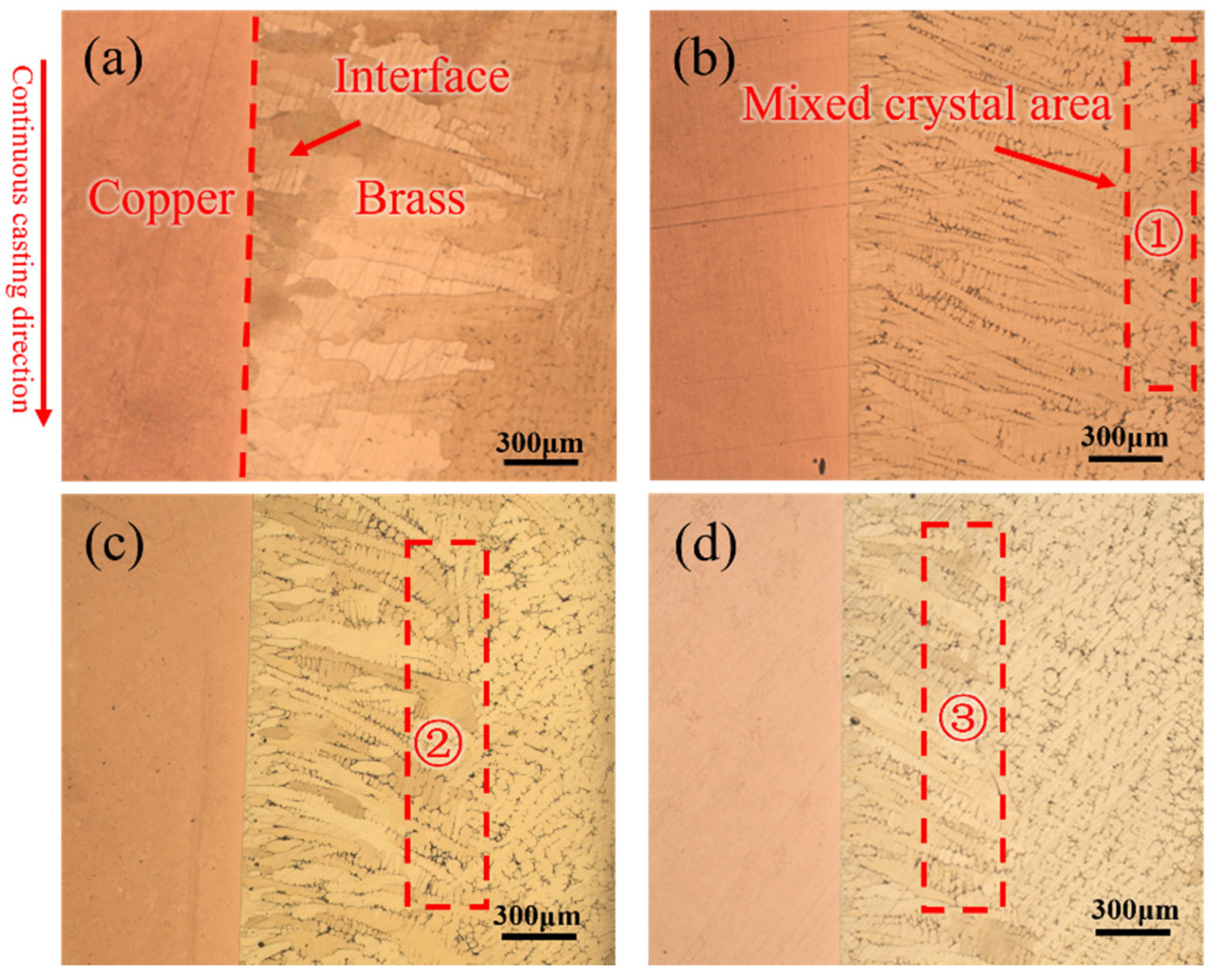
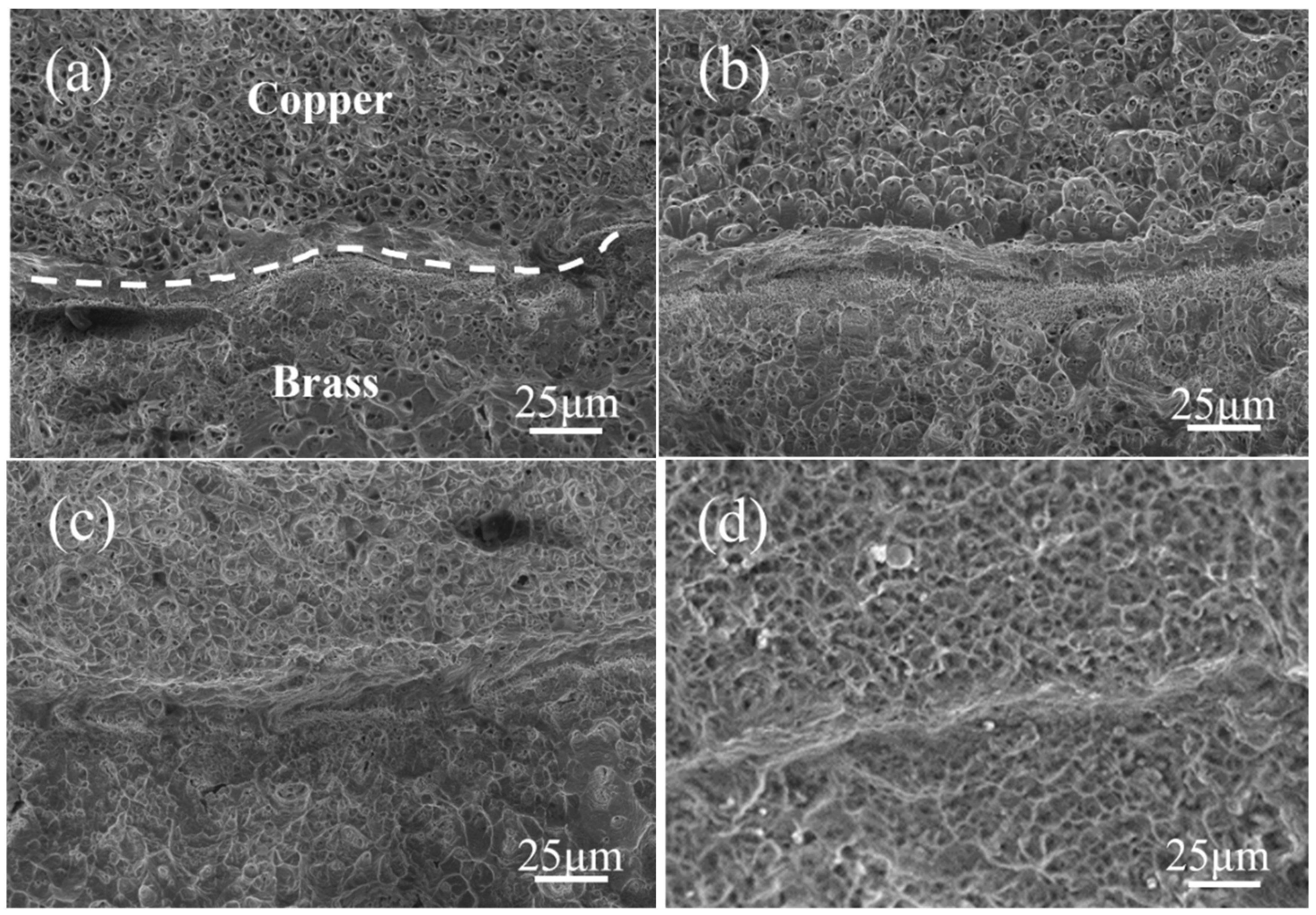
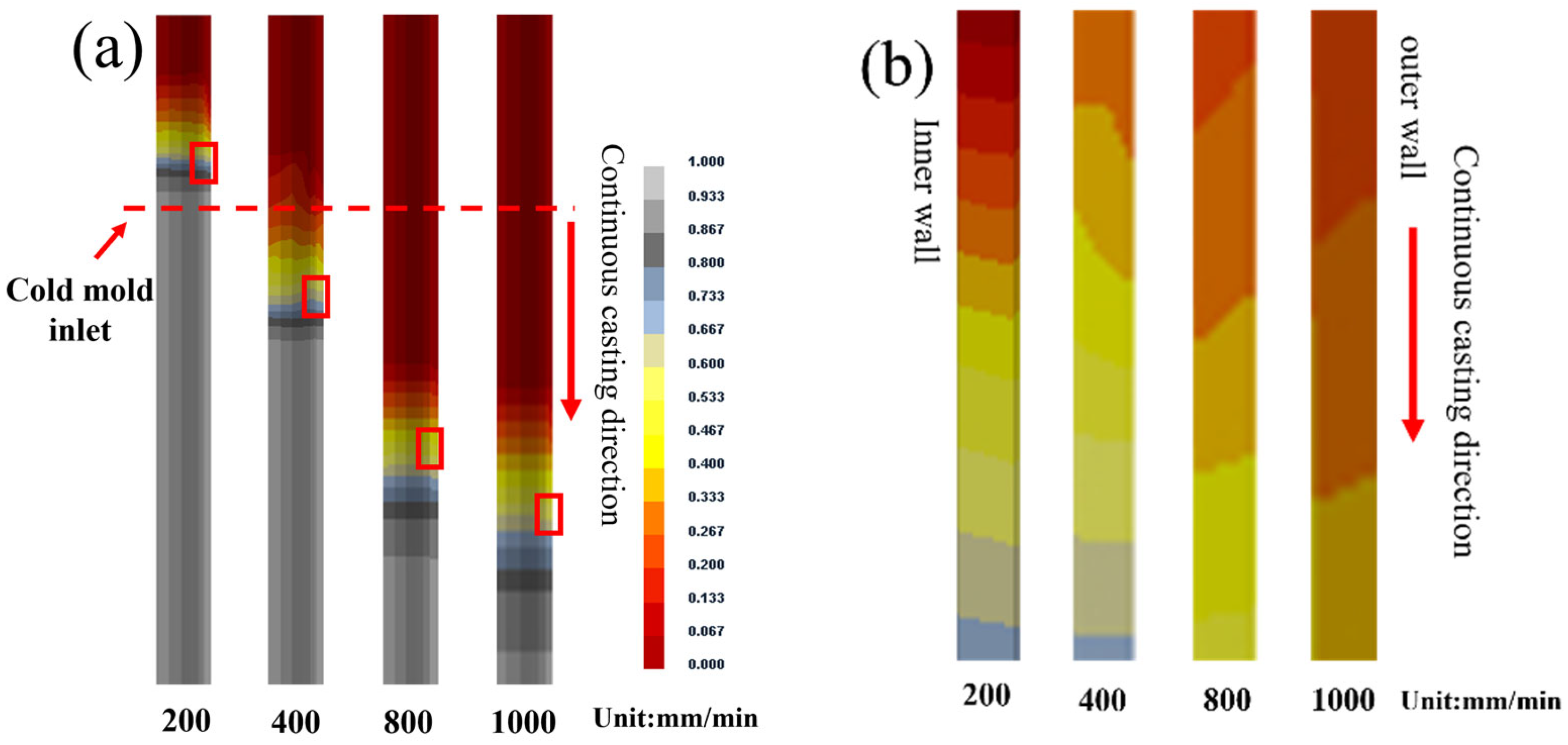
3.1. As-Cast Brass-Clad Copper Stranded Wire Composite Billet
3.2. Evolution of Microstructure and Properties in Drawing Process
3.2.1. Mechanical Properties Evolution
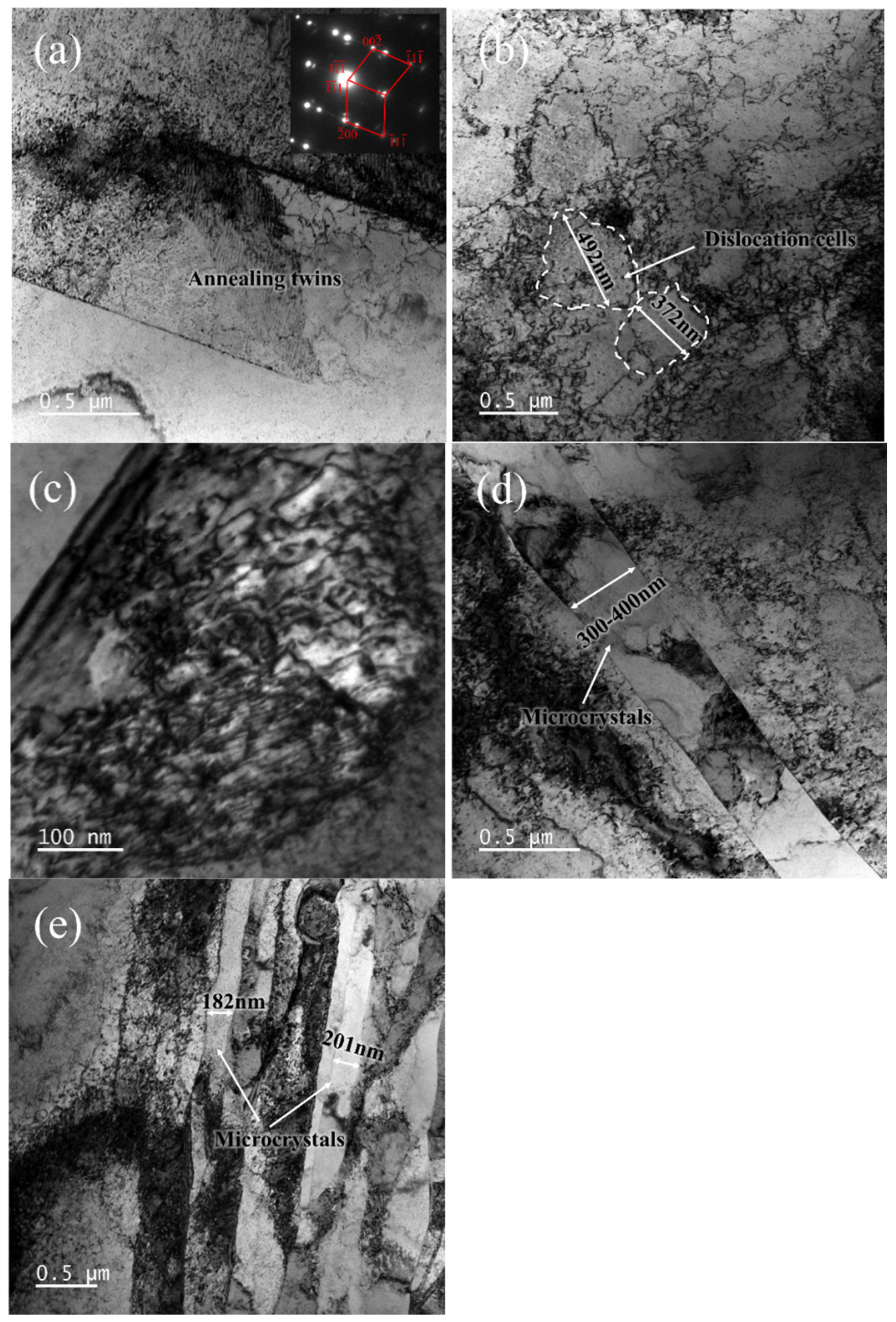
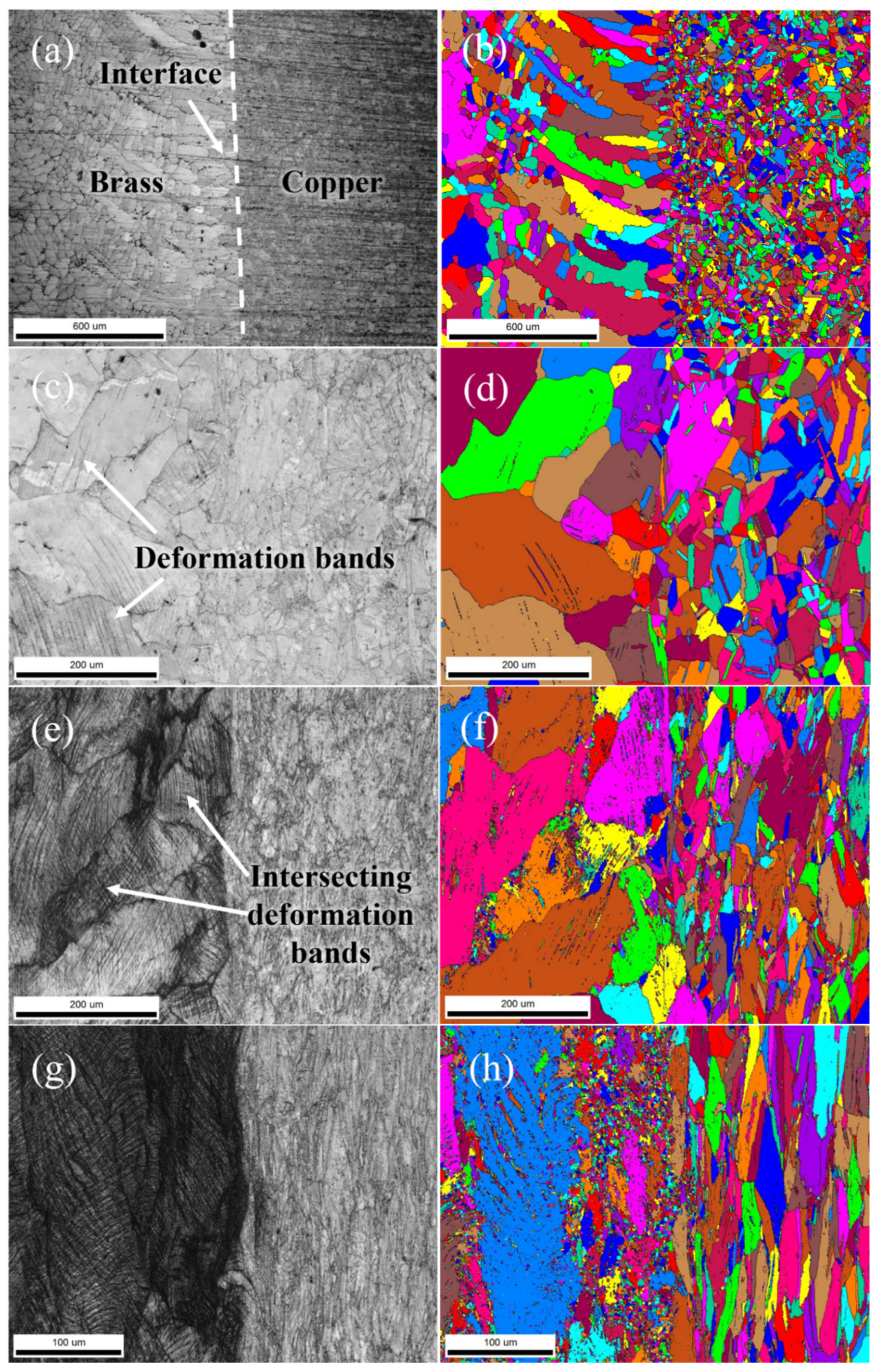
3.2.2. Microstructure Evolution
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Continuous Casting Speeds on As-Cast Microstructure of Brass Cladding Layers and Kness of Interface Diffusion Layers
4.2. Relationship Between Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Drawing Process
4.3. Technology Application
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- When the casting speed increased from 200 mm/min to 1000 mm/min, the microstructure of the brass cladding transformed from radial columnar grains to columnar grains angled relative to the radial direction.
- (2)
- The shear strength of the brass-clad copper stranded wire composites under different casting speeds ranged from 130 to 170 MPa, demonstrating excellent metallurgical bonding quality at the interface between the brass cladding and the pure copper strand wires.
- (3)
- As the total deformation increased from 11.9 to 81.5%, the tensile strength increased from 334 to 534 MPa. The primary deformation mechanism of the copper stranded wires was dislocation slip, while that of the brass cladding progressed from dislocation planar slip to deformation twinning and finally to shear deformation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sang, T.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xia, W. The application research of the railway through-line groundwire. Electr. Wire Cable 2019, 5, 14–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Hei, G.; Li, J. The structure improvement for railway composite through-line ground wire. Electr. Wire Cable 2016, 5, 8–11, 44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X. The application of the continuous aluminium extruding cosnform to produce Al alloy-sheathed through-railway ground wire. Electr. Wire Cable 2007, 4, 19–20, 23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhang, T.A.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Effect of process parameters on surface quality and bonding quality of brass cladding copper stranded wire prepared by continuous pouring process for clad. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 8025–8035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ling, L.; Xie, J. Influences of preparing parameters on surface quality and interface bonding state of brass cladding copper stranded wire by inversion solidification. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2018, 28, 693–704. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, R.; Liu, X. Preparation and properties of copper-aluminum composite strips and foils by horizontal continuous composite casting and rolling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 322, 118168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav; Chakraborty, P.; Vejendla, S.B.P. Deformation and annealing of brass. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 64, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Zhou, T.; Jiang, X. Deformation mechanism and properties evolution of a copper alloy with ultra-high strength after cold drawing and subsequent aging treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 912, 146952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Gan, X. Deformation mechanisms of the Cu-15Ni-8Sn-0.18Nb alloy in as-quenched and aged conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 919, 147477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.C.; Tao, N.R. Effect of deformation mechanisms on the strength-ductility trade-off of Cu and CuAl alloy. Scr. Mater. 2022, 212, 114559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Lv, W.; Li, P.; Gong, Y.; Tao, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhu, X. Mechanical properties and deformation kinetics of bulk Cu–Al–Zn alloy subjected to rolling and annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 609, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kog, N.; Watanabe, C.; Miura, H. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Cu 38 mass%Zn alloy fabricated by different rolling pass schedules. Mater. Trans. 2022, 63, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Sun, J.; Fu, Y.; Xu, B.; Han, Y.; Chen, J.; Han, J.; Wu, H.; Wu, G. Preparing thick gradient surface layer in Cu-Zn alloy via ultrasonic severe surface rolling for strengthductility balance. Materials 2022, 15, 7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.; Son, K.; Cho, H. Experimental analysis of deformation texture evolutions in pure Cu, Cu-37Zn, Al-6Mg, and −8Mg alloys at cold-rolling processes. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 934, 167879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, G.; Zhou, M.; Jing, K.; Hu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, C.; Sun, Y.; Tian, B.; Li, X.; et al. Hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of the Cu-1.5Ti-(0.5Fe) alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 4961–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huang, T.; Song, K.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Effect of large deformation on microstructure and properties of copper alloy wire. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 5136–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadong, R.; Zhongyuan, Z.; Zhaoshun, G.; Ling, Z.; Tingting, Z.; Jiangli, X.; Zhixiang, T.; Bo, D.; Yongsheng, L.; Liye, X. Effect of plastic deformation on microstructure and properties of Cu-(1 wt%–6 wt%) Ag alloy. J. Wuhan. Univ. Technol. Mater. 2024, 39, 747–753. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, F. Principal shear bands in metal plastic deformation. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 1998, 41, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanchuan, T.; Juwen, X.; Zeyun, C.; Wenhui, W.; Xinlei, Z.; Xingchang, T.; Longzhi, Z. Cold rolling deformation behavior and interface transition layer evolution of Cu-Be/Cu-Zn laminated composite. Mater. Rep. 2021, 35, 1177–1182. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Basor, I.; Gadhu, R.; Sofyan, B.T. Effects of deformation and annealing temperature on the Microstructures and Hardness of Cu-29Zn-0.6Bi Brass. Key Eng. Mater. 2017, 748, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Tarasov, S.Y.; Filippov, A.V.; Fortuna, S.V.; Vorontsov, A.V. Microstructure and tensile properties of Cu–Zn brass after severe plastic deformation. In Proceedings of the Advanced Materials with Hierarchical Structure for New Technologies and Reliable Structures, Tomsk, Russia, 1–5 October 2018; Volume 2051, p. 20301. [Google Scholar]
- Pokharel, R.; Niu, T.; Ricci, S.; Clausen, B.; Balogh, L.; Ravkov, L.; Martinez, R.; Lee, C.; Vogel, S.; Cady, C.M.; et al. Alloying effects on deformation induced microstructure evolution in copper. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodyakova, A.; Tkachev, M.; Pilipenko, A.; Belyakov, A.; Kaibyshev, R. Effect of deformation methods on microstructure, texture, and properties of a Cu–Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 876, 145126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, R.; Song, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhou, F.; Huang, K.; Liu, D.; et al. Effects of cold deformation and aging on the phase transformation and mechanical properties of a Cu-15Ni-8Sn alloy. Mater. Charact. 2024, 210, 113796. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Jing, K.; Zhou, M.; Chu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, W.; Ma, S. Microstructure and hot deformation behavior of the Cu-0.3Zr(−0.2Mg) alloys. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 42, 111539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, A.; Tkachev, M.; Pilipenko, A.; Lugovskaya, A.; Belyakov, A.; Kaibyshev, R. Effect of the deformation temperature on the deformation behavior of a Cu-Cr-Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1014, 12033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.F.; Toth, L.S.; Zhang, Y.D.; Hoffman, M. Unexpected brass-type texture in rolling of ultrafine-grained copper. Scr. Mater. 2014, 92, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Drawing Pass | Outer Diameter/mm | Percentage Reduction in Area of this Pass/% | Total Percentage Reduction in Area Reduction/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 16.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 15.3 | 11.9 | 11.9 |
| 2 | 13.8 | 18.6 | 28.3 |
| 3 | 12.6 | 16.6 | 40.2 |
| 4 | 11.5 | 16.7 | 50.2 |
| 5 | 10.6 | 15.0 | 57.7 |
| 6 | 9.2 | 24.7 | 68.1 |
| 7 | 8.4 | 16.6 | 73.4 |
| 8 | 8.0 | 9.3 | 75.9 |
| 9 | 7.5 | 12.1 | 78.8 |
| 10 | 7.0 | 12.9 | 81.5 |
| Casting Speed/mm/min | 200 | 400 | 800 | 1000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Gradient (TG)/°C/mm | 2.86 | 2.72 | 2.02 | 1.91 |
| Solidification Rate (SR)/°C/s | 9.50 | 18.30 | 23.53 | 31.80 |
| TG × SR | 27.14 | 49.75 | 47.51 | 60.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Liu, X.; Xie, J. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Brass-Clad Copper Stranded Wires in High-Speed Solid/Liquid Continuous Composite Casting and Drawing. Metals 2025, 15, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050482
Lei Y, Liu X, Jiang Y, Zhao F, Liu X, Xie J. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Brass-Clad Copper Stranded Wires in High-Speed Solid/Liquid Continuous Composite Casting and Drawing. Metals. 2025; 15(5):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050482
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Yu, Xiao Liu, Yanbin Jiang, Fan Zhao, Xinhua Liu, and Jianxin Xie. 2025. "Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Brass-Clad Copper Stranded Wires in High-Speed Solid/Liquid Continuous Composite Casting and Drawing" Metals 15, no. 5: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050482
APA StyleLei, Y., Liu, X., Jiang, Y., Zhao, F., Liu, X., & Xie, J. (2025). Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Brass-Clad Copper Stranded Wires in High-Speed Solid/Liquid Continuous Composite Casting and Drawing. Metals, 15(5), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050482






