Study on the Air Inlet Velocity and Temperature Distribution in an Inclined Tunnel with Single Shaft under Natural Ventilation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis
2.1. Dimensionless Longitudinal Inlet Air Velocity
2.2. Distribution of the Maximum Smoke Temperature under the Ceiling
3. Model Setup
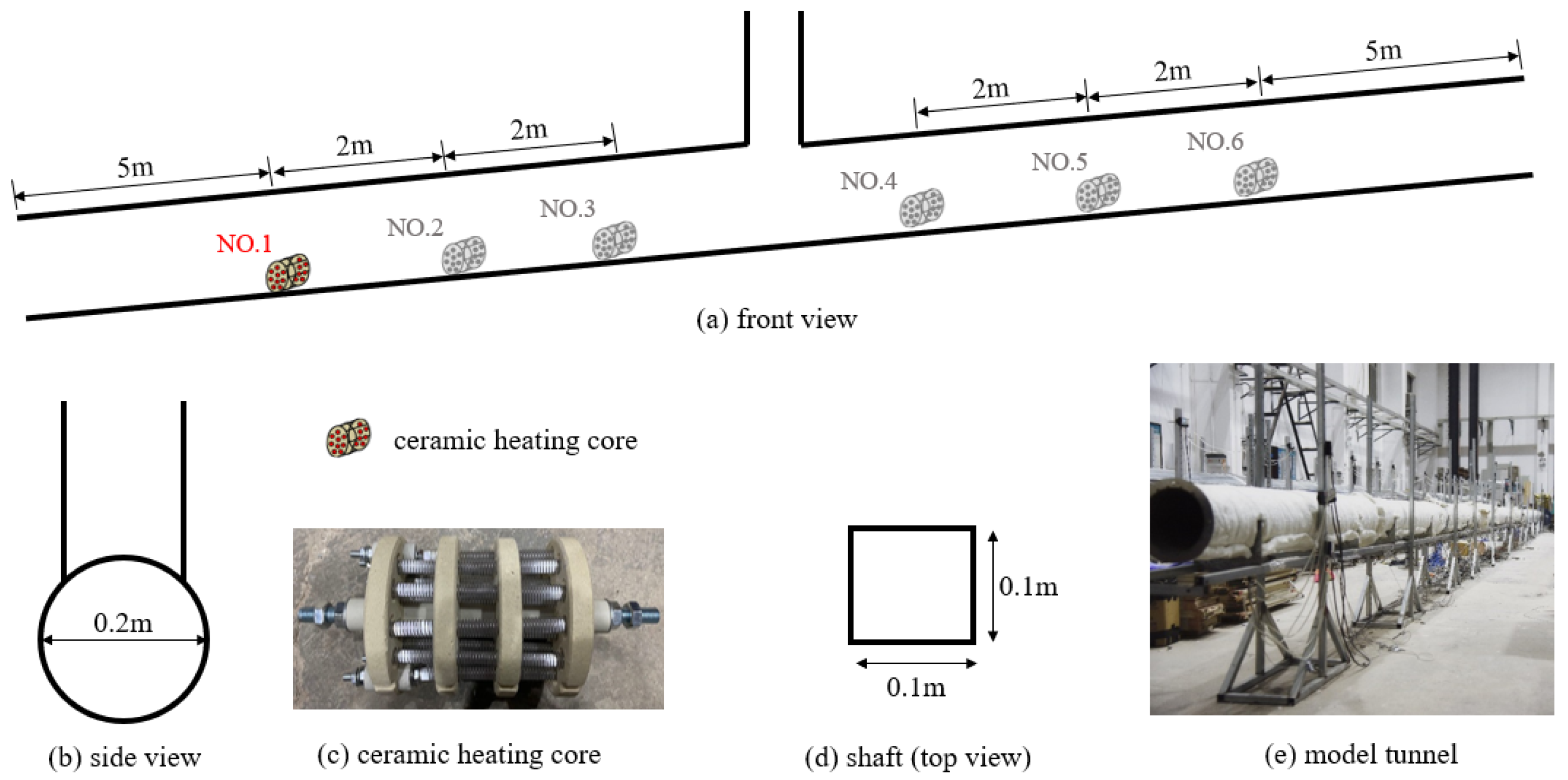
3.1. Experimental Model
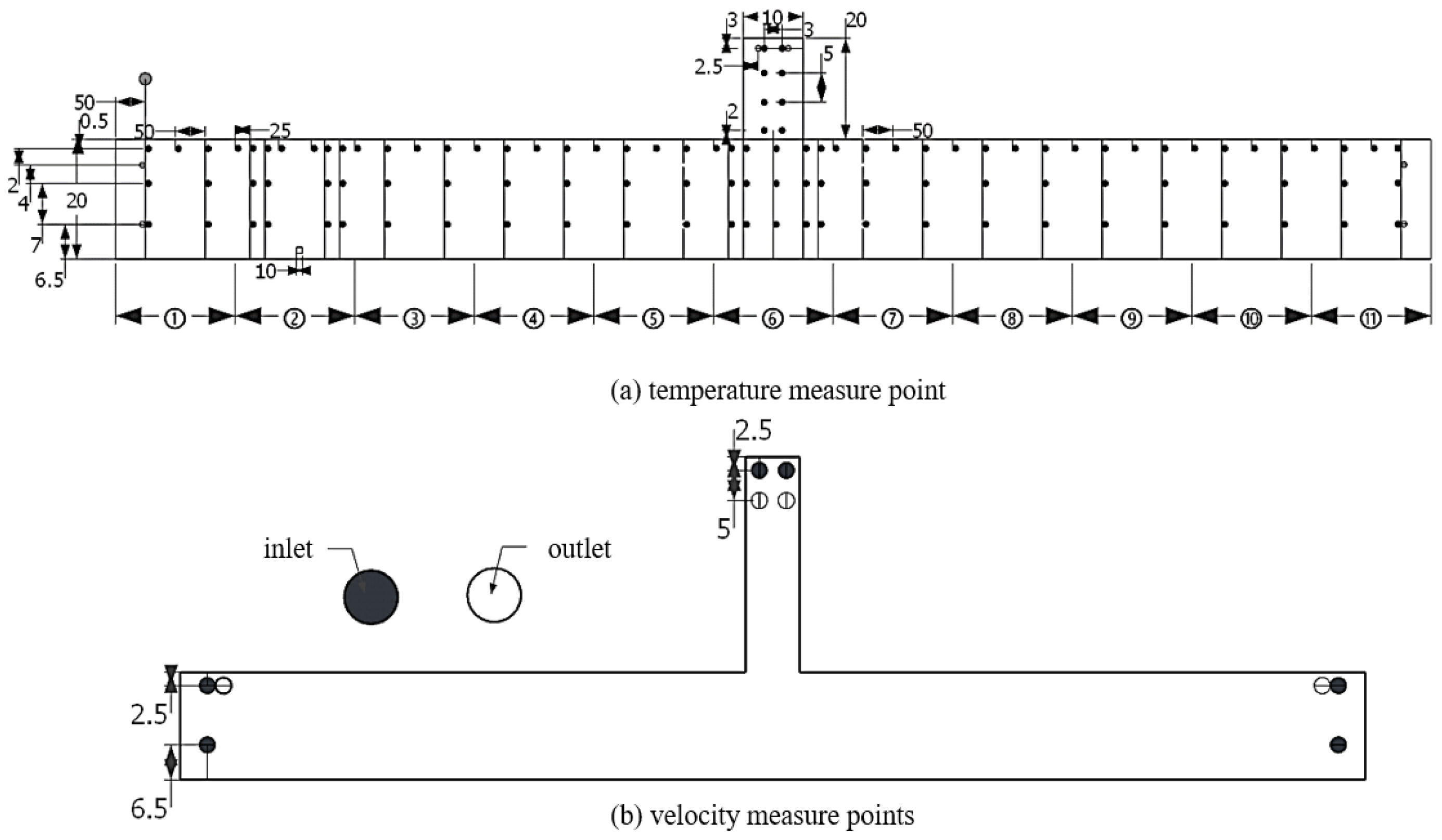
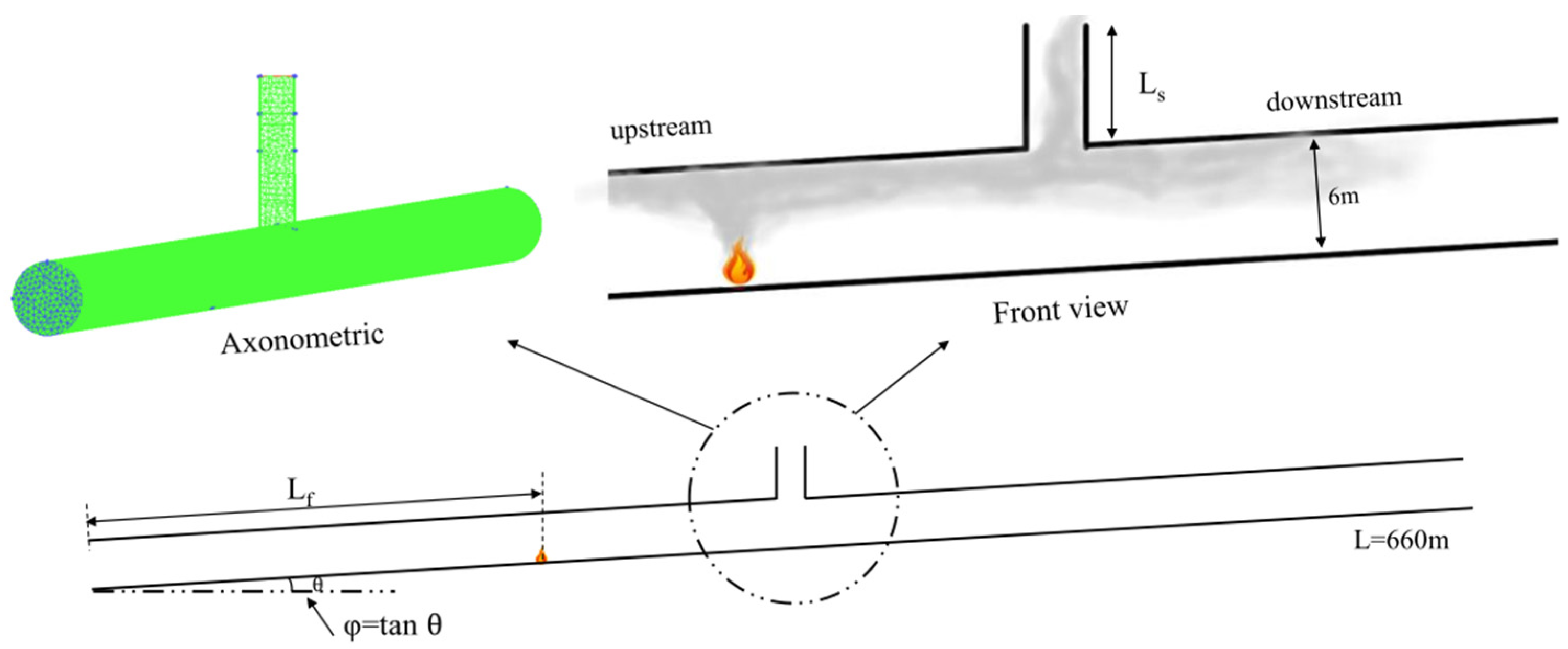
3.2. Numerical Simulation Model
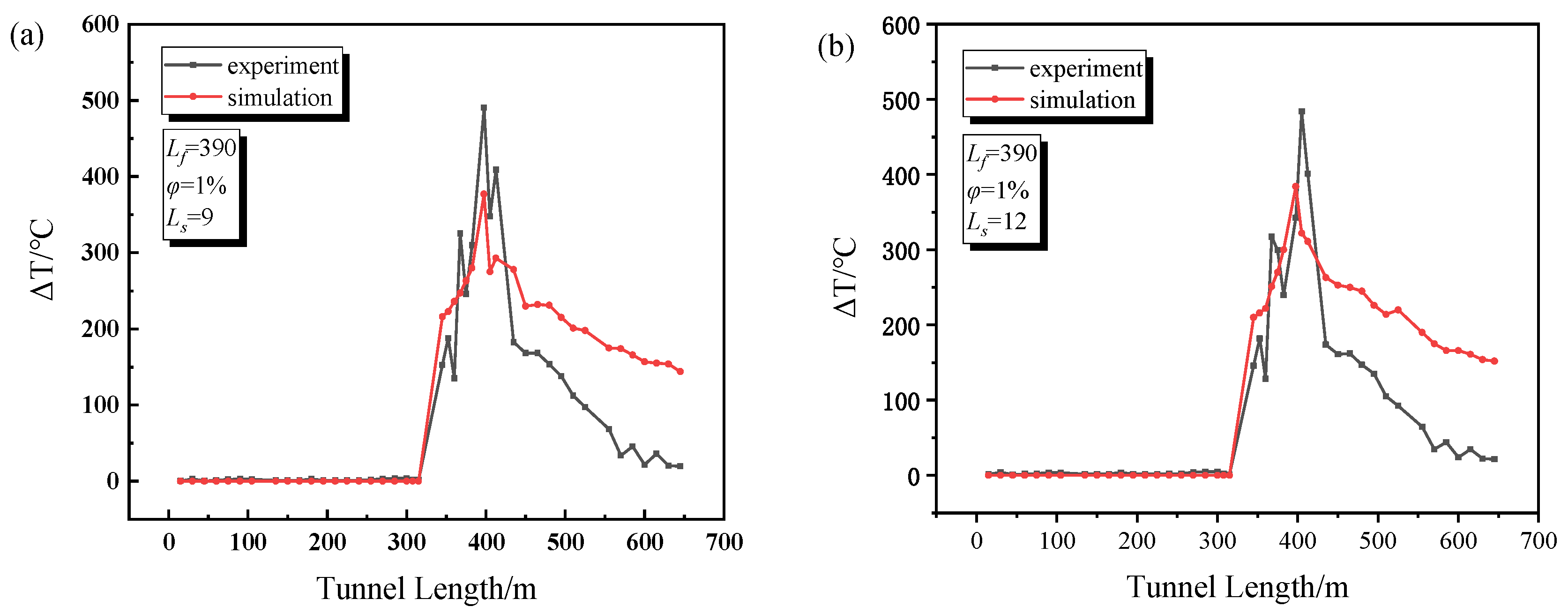
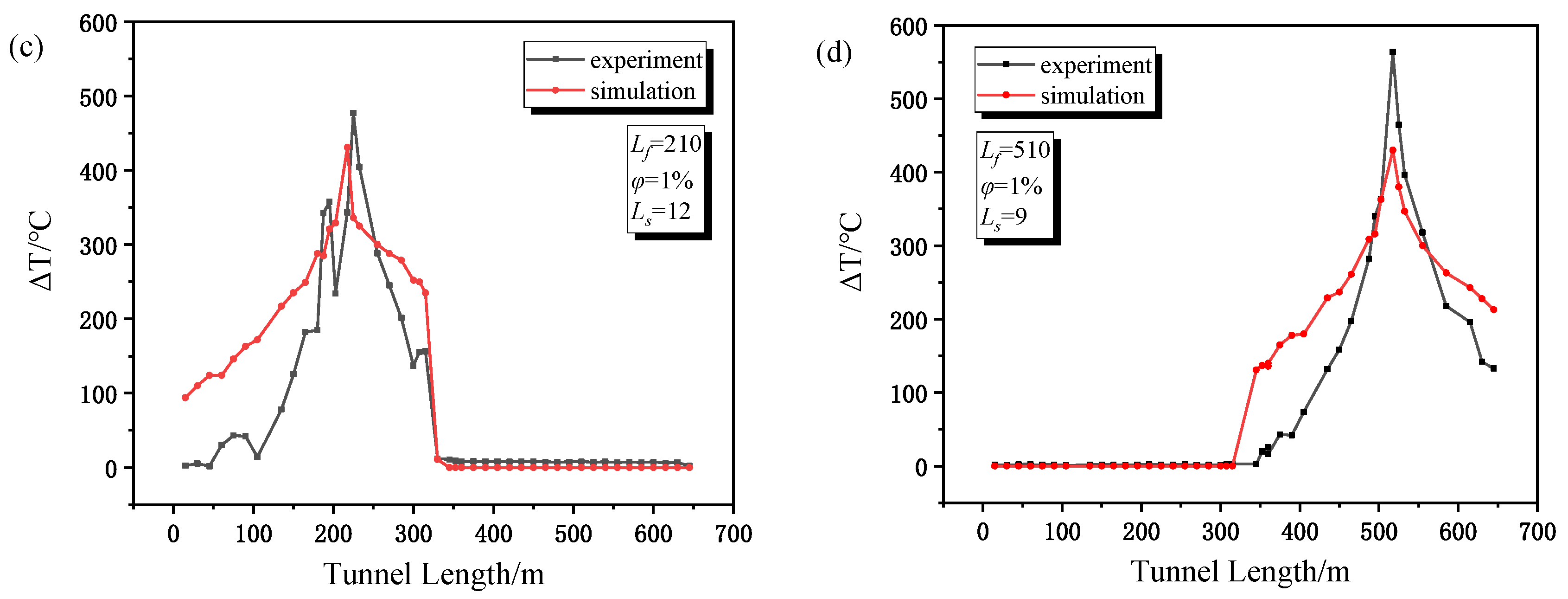
3.3. Experimental Verification
4. Results and Discussion
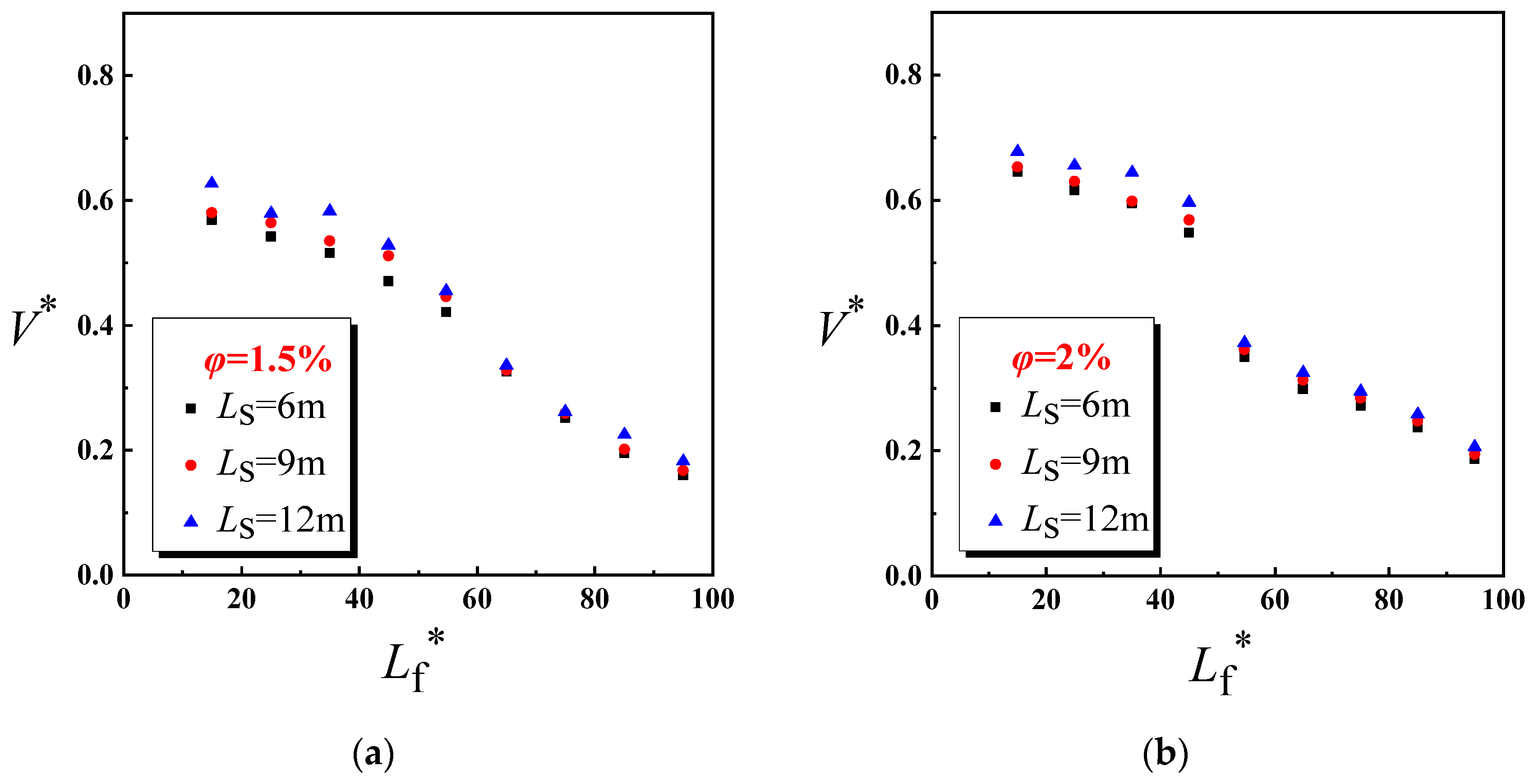
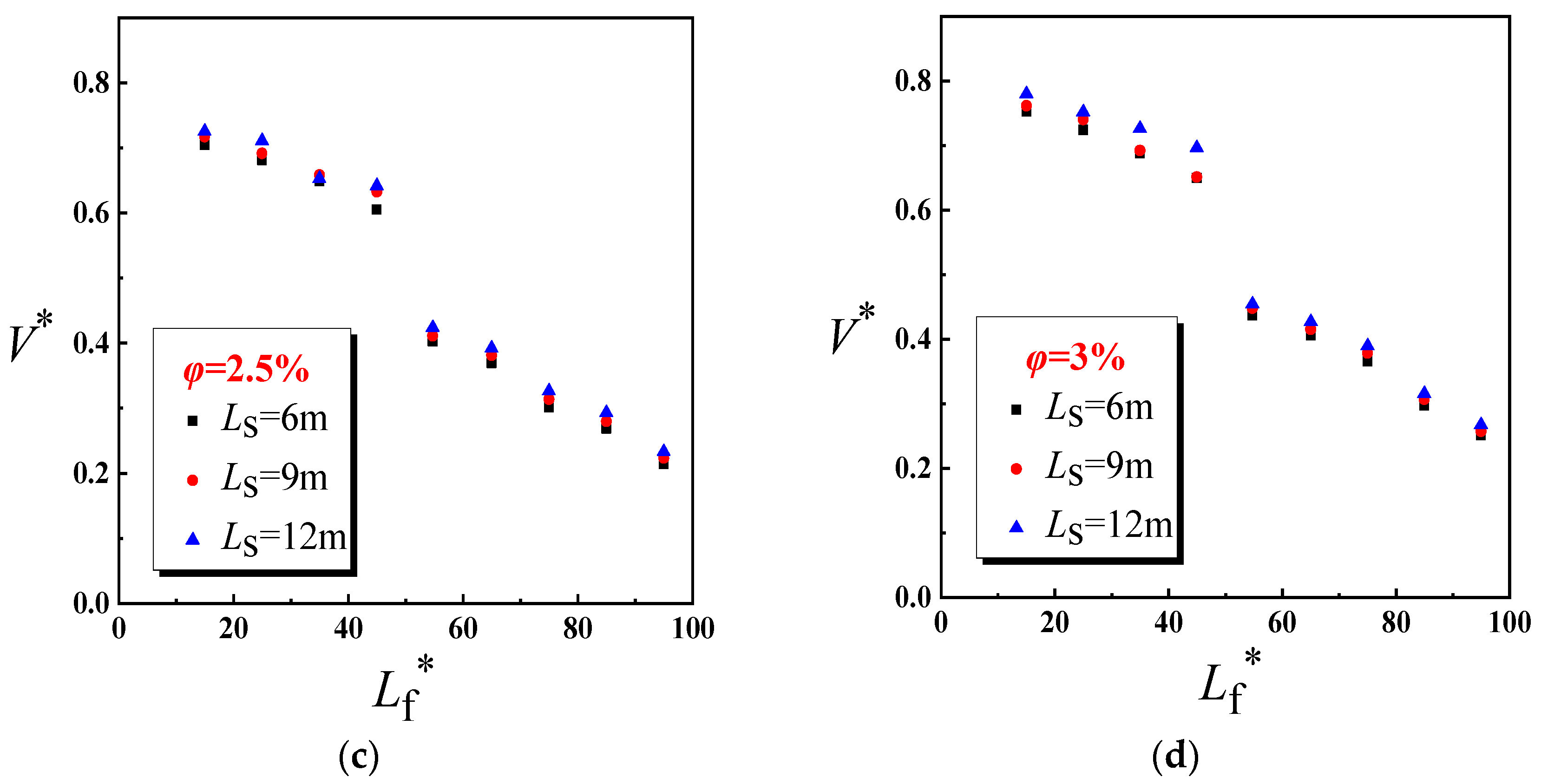
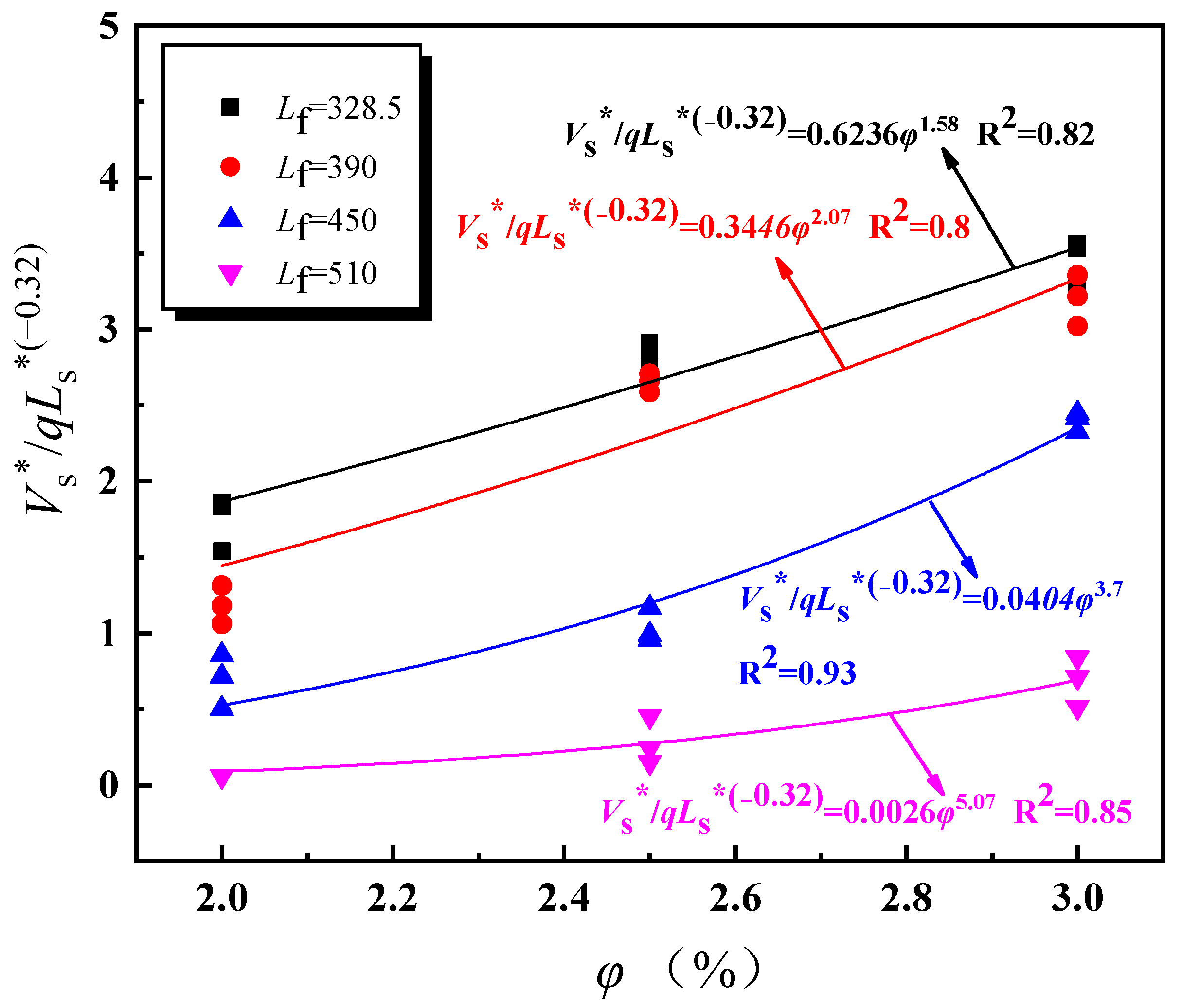
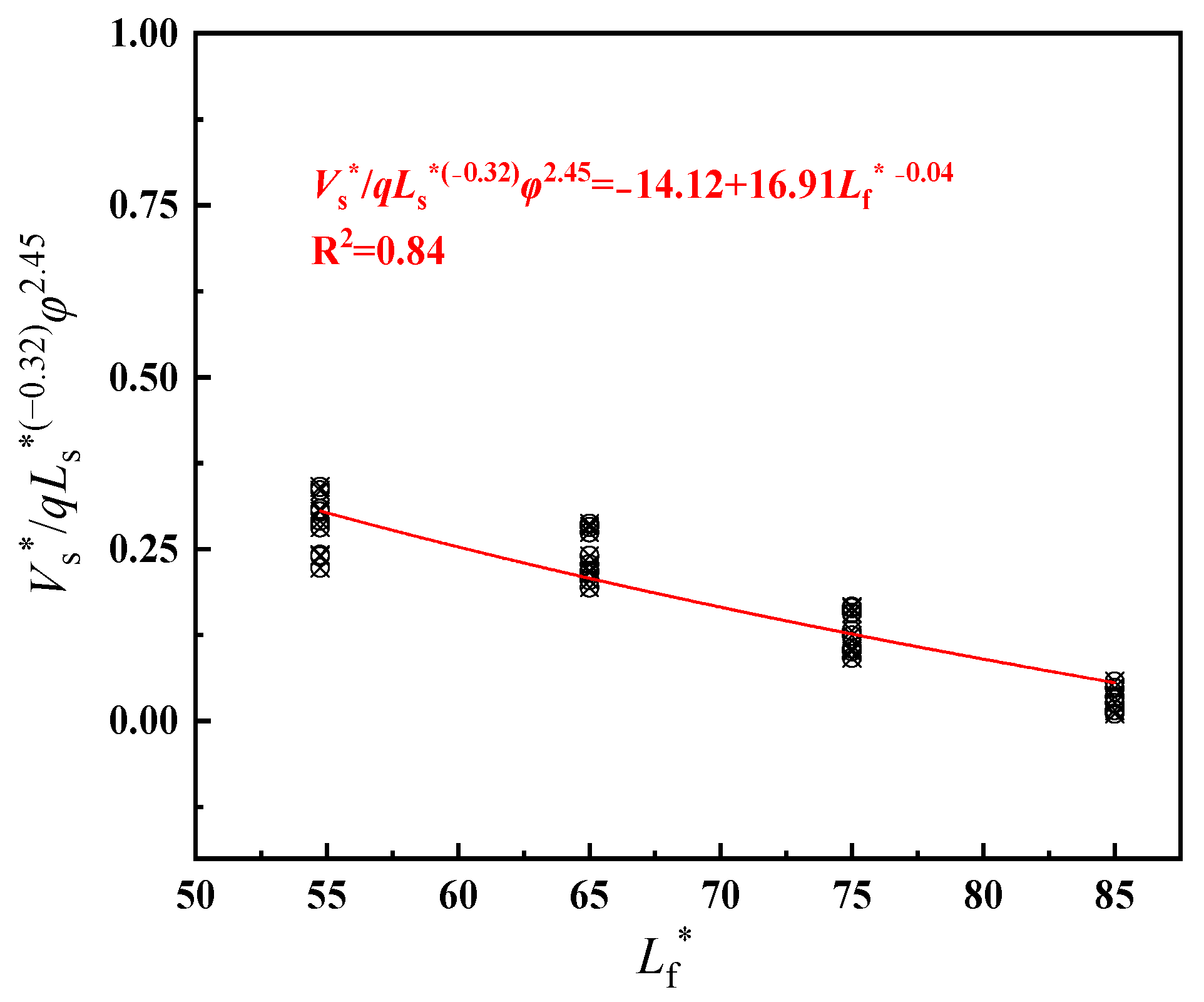
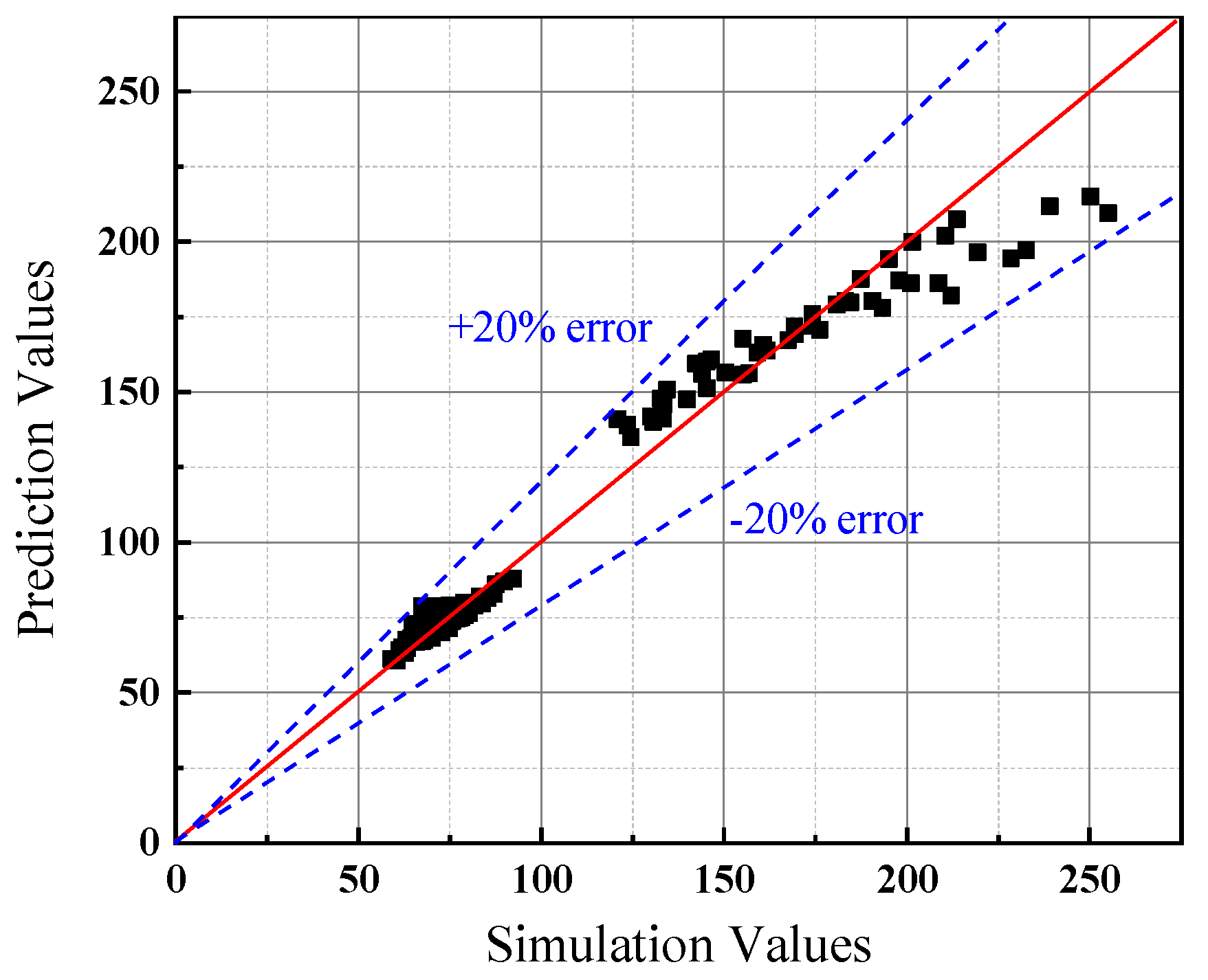
4.1. Dimensionless Longitudinal Inlet Air Velocity
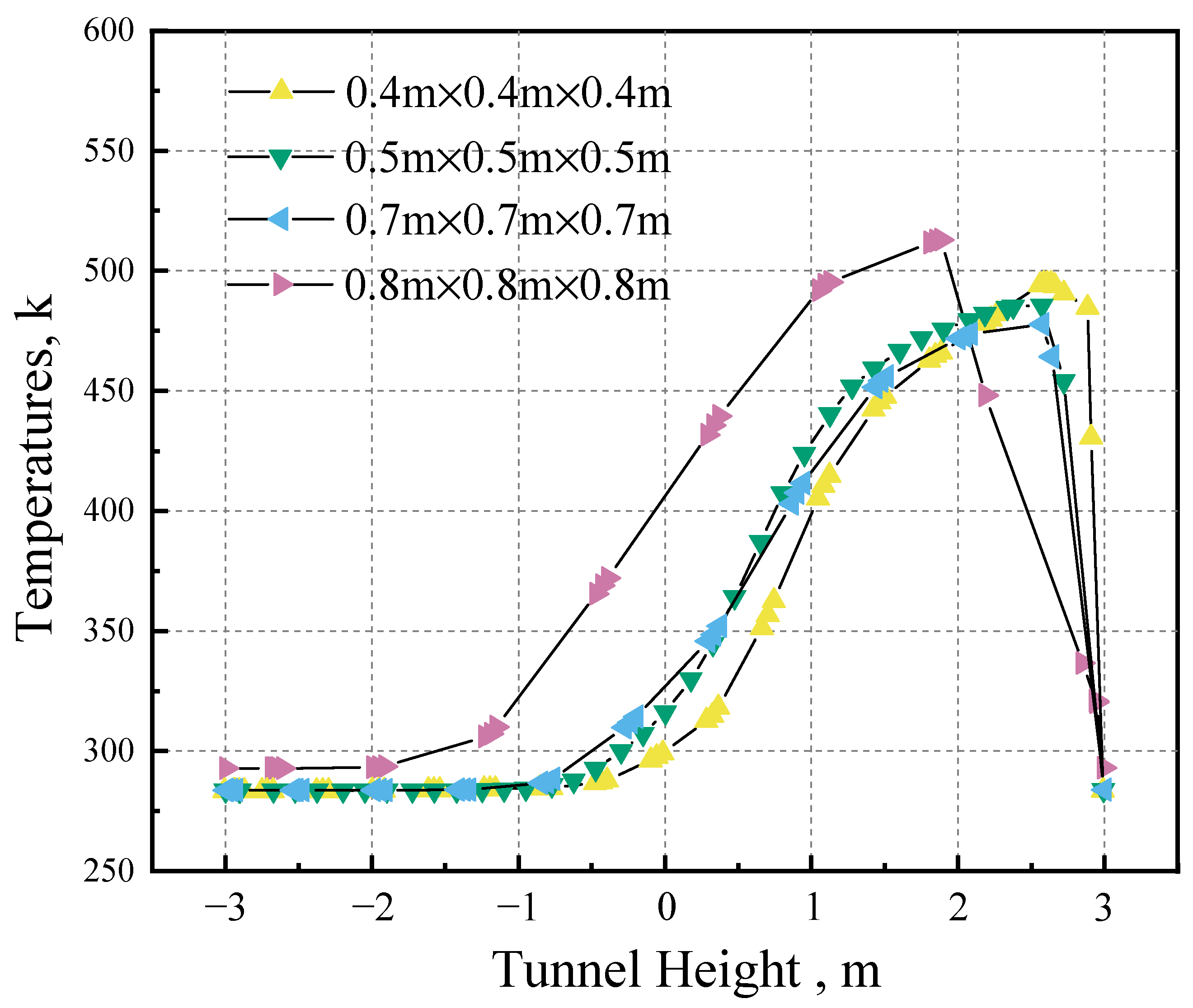
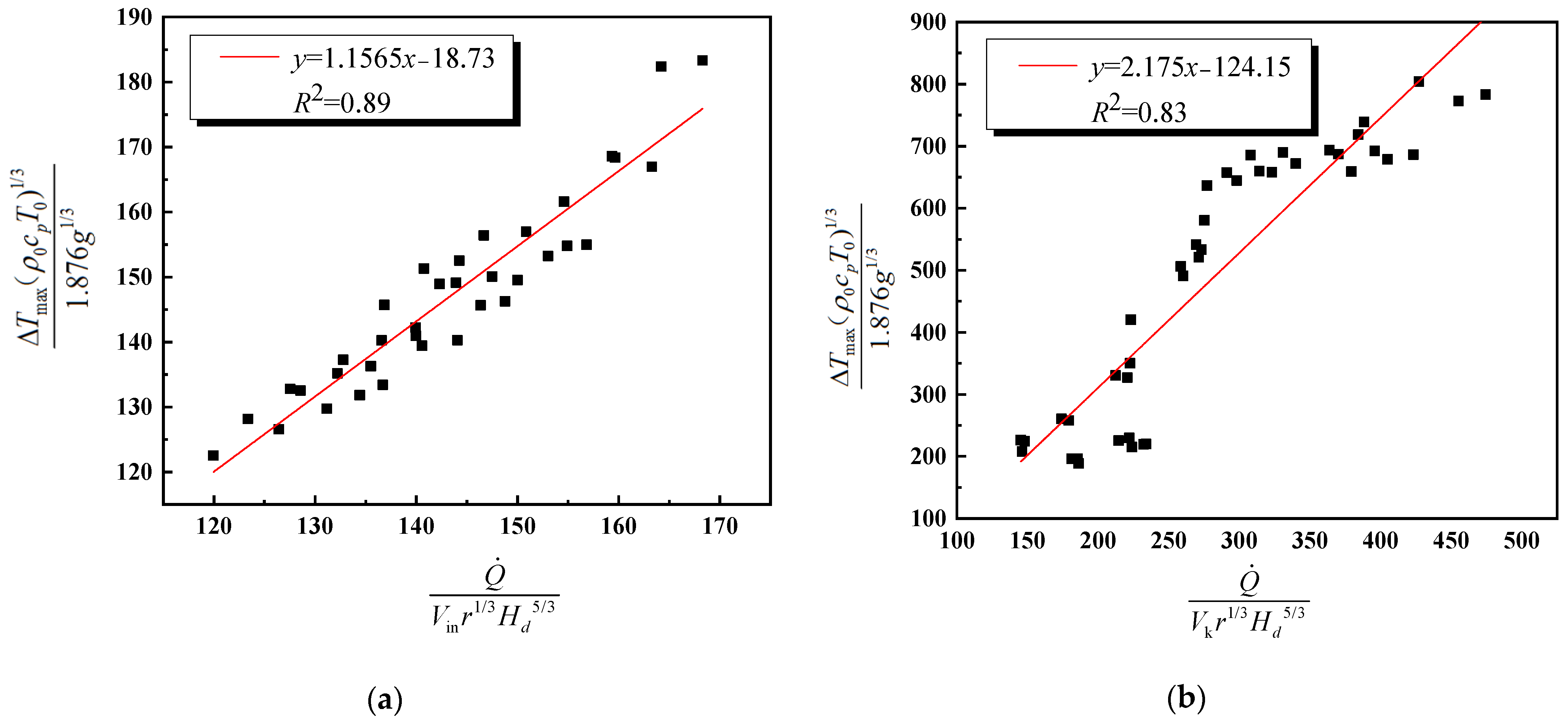
4.2. Distribution of the Maximum Smoke Temperature under the Ceiling
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The longitudinal air inlet velocity under nature ventilation is used to replace the longitudinal ventilation velocity under mechanical ventilation. When Lf ≤ 330 m, the air inlet velocity at tunnel entrance equals to the longitudinal air inlet velocity. When Lf > 330 m, the tunnel shaft also acts as air supplement in some conditions, the longitudinal air inlet is the confluence of two streams. Through the dimensional analysis, the expression of dimensionless longitudinal inlet air velocity in an inclined tunnel with single shaft under natural ventilation is obtained. The air inlet velocity at tunnel entrance decreases exponentially as Lf increases, and increases exponentially with the increase in φ and Ls. The shaft air inlet velocity decreases exponentially as Lf and Ls increase, and increases exponentially with the increase in φ.
- (2)
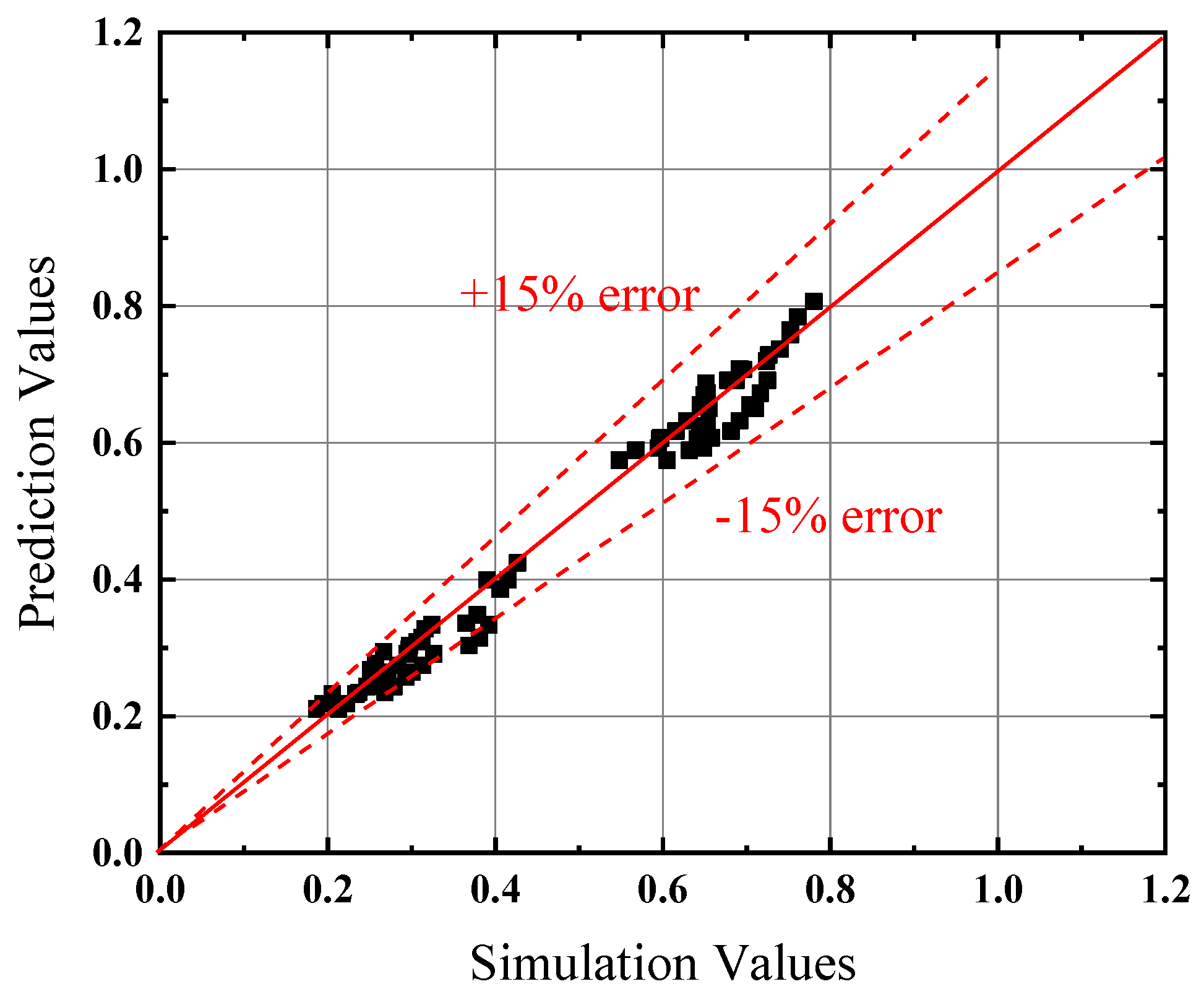
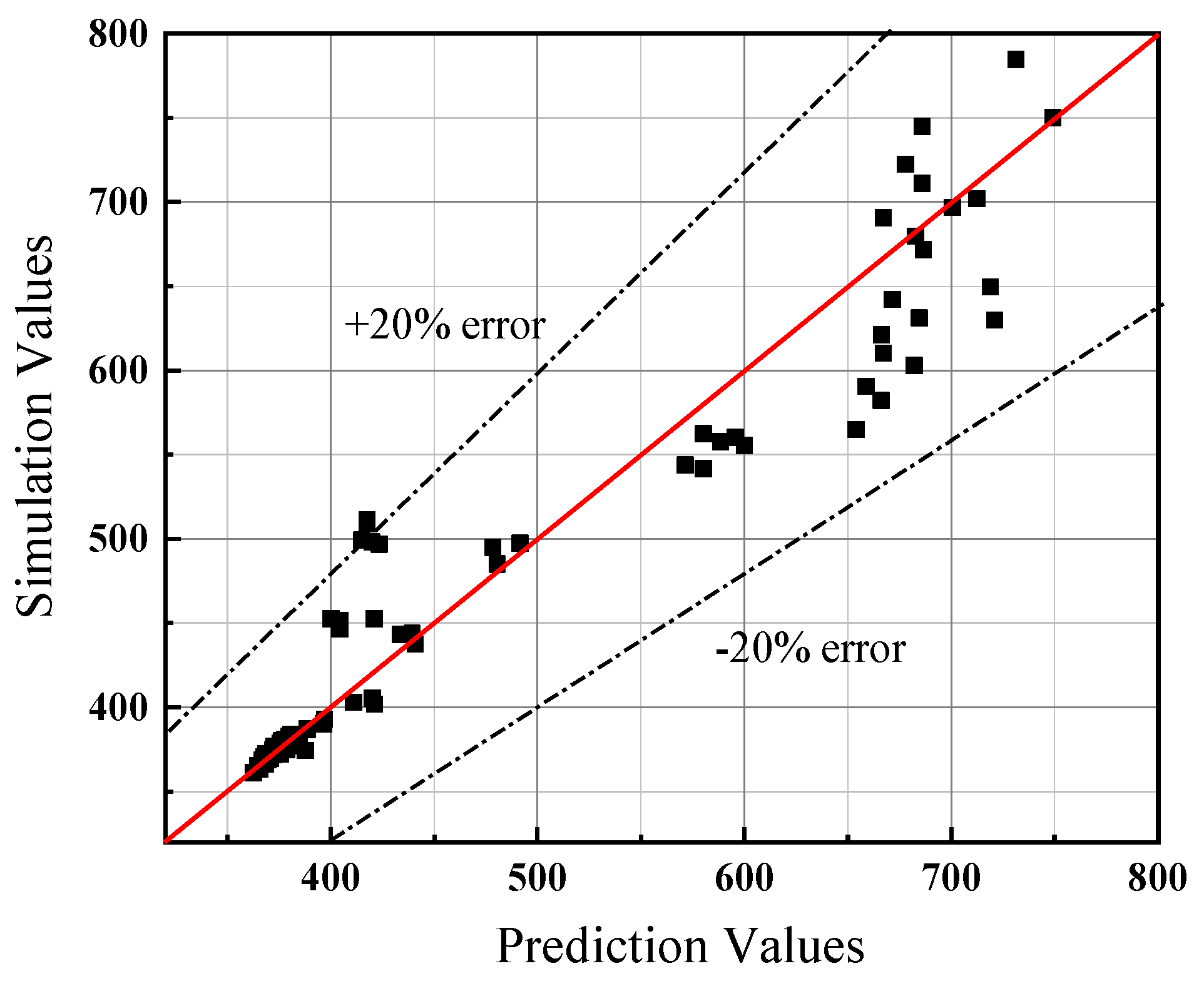
- Based on the analysis of non-dimension longitudinal inlet air velocity, an empirical prediction formula of the maximum smoke temperature under the tunnel ceiling in inclined tunnel with single shaft under natural ventilation is obtained. The error range between the simulation and prediction results is within 20%.
- (3)
- A new correlation for the calculation of the distribution of maximum smoke temperature under the tunnel ceiling in inclined tunnel with single shaft under natural ventilation is obtained. And the error range between the simulation and prediction results is within 20%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takeuchi, S.; Tanaka, F.; Yoshida, K.; Moinuddin, K.A.M. Effects of Scale Ratio and Aspect Ratio in Predicting the Longitudinal Smoke-Temperature Distribution during a Fire in a Road Tunnel with Vertical Shafts. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. 2018, 80, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Mao, Y.; Park, H. A Numerical Study on the Effect of the Shaft Group Arrangement on the Natural Ventilation Performance in Tunnel Fires. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. 2020, 103, 103464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, A.N. Fire Safety in Tunnels. Fire Saf. J. 2009, 44, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, N. Fire Incident Data for Australian Road Tunnels. Fire Saf. J. 2020, 111, 102909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvel, R.O.; Beard, A.N.; Jowitt, P.W. The Influence of Longitudinal Ventilation Systems on Fires in Tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. 2001, 16, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Yang, R.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, L. Decentralized Inverse Model for Estimating Building Fire Source Location and Intensity. J. Thermophys. Heat. Transf. 2013, 27, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabat, F.; Salizzoni, P.; Creyssels, M.; Mos, A.; Wingrave, J.; Correia, H.; Marro, M. Smoke Control in Tunnel with a Transverse Ventilation System: An Experimental Study. Build. Environ. 2020, 167, 106480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.; Wang, X.; Kong, X.; Xu, H. Effects of Fire Source Position on Smoke Extraction Efficiency by Natural Ventilation through a Board-Coupled Shaft during Tunnel Fires. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 3975–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Xu, Z.; Markert, F.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Q.; Tao, H.; Wang, Z.; Fan, C. Experimental Study of Heat Exhaust Efficiency with Natural Ventilation in Tunnel Fire: Impact of Shaft Height and Heat Release Rate. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2020, 201, 104173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Han, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, C.; Liu, X. Numerical Study of Natural Ventilation in Urban Shallow Tunnels: Impact of Shaft Cross Section. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 42, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; He, K.; Yao, Y.; Peng, M.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Cheng, X. Investigation on the Critical Shaft Height of Plug-Holing in the Natural Ventilated Tunnel Fire. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 132, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Gao, Z.H.; Fan, C.G.; Zhong, W.; Sun, J.H. A Study of the Effect of Plug-Holing and Boundary Layer Separation on Natural Ventilation with Vertical Shaft in Urban Road Tunnel Fires. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf. 2012, 55, 6032–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Chen, T.; Yuan, Z.; Xie, Y.; Yu, N. Critical Shaft Height for Complete Smoke Exhaustion during Fire at the Worst Longitudinal Fire Location in Tunnels with Natural Ventilation. Fire Saf. J. 2020, 116, 103207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhong, W. Experimental Study of the Influence of Natural Ventilation by Shaft on the Maximum Ceiling Temperature of Buoyancy Plume in Tunnel Fires. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. 2021, 108, 103715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klote, J.H. Smoke Control. In SFPE Handbook of Fire Protection Engineering, 1st ed.; 3–143 to 3–157; Society of Fire Protection Engineers and National Fire Protection Association: Quincy, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Wan, H.; Li, K.; Han, J.; Sun, J. A Numerical Study on Upstream Maximum Temperature in Inclined Urban Road Tunnel Fires. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf. 2015, 88, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.K.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, J.H.; Dang, J.F.; Chow, N.C.L. A Study on Tilted Tunnel Fire under Natural Ventilation. Fire Saf. J. 2016, 81, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ding, L.; Wan, H.; Ji, J.; Gao, Z.; Yu, L. Numerical Investigation on the Effect of Tunnel Width and Slope on Ceiling Gas Temperature in Inclined Tunnels. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2020, 152, 106272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Gao, Z.; Han, J.; Ji, J.; Ye, M.; Zhang, Y. A Numerical Study on Smoke Back-Layering Length and Inlet Air Velocity of Fires in an Inclined Tunnel under Natural Ventilation with a Vertical Shaft. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 138, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merci, B. One-Dimensional Analysis of the Global Chimney Effect in the Case of Fire in an Inclined Tunnel. Fire Saf. J. 2008, 43, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Wang, Z.; Ding, L.; Yu, L.; Gao, Z.; Wan, H. Effects of Ambient Pressure on Smoke Movement and Temperature Distribution in Inclined Tunnel Fires. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 145, 106006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurioka, H.; Oka, Y.; Satoh, H.; Sugawa, O. Fire Properties in near Field of Square Fire Source with Longitudinal Ventilation in Tunnels. Fire Saf. J. 2003, 38, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.H.; Huo, R.; Peng, W.; Chow, W.K.; Yang, R.X. On the Maximum Smoke Temperature under the Ceiling in Tunnel Fires. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. 2006, 21, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Ingason, H. The Maximum Ceiling Gas Temperature in a Large Tunnel Fire. Fire Saf. J. 2012, 48, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.H.; Huo, R.; Li, Y.Z.; Wang, H.B.; Chow, W.K. Full-Scale Burning Tests on Studying Smoke Temperature and Velocity along a Corridor. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. 2005, 20, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delichatsios, M.A. The Flow of Fire Gases under a Beamed Ceiling. Combust. Flame 1981, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.; Oka, H.; Imazeki, O. Ceiling-Jet Thickness and Vertical Distribution along Flat-Ceilinged Horizontal Tunnel with Natural Ventilation. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. 2016, 53, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.Z. Study on the Effect of Slope on the Fire Spreading Characteristics in Extra-Long Road Tunnels; Central South University: Changsha, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Du, T.; Yang, D.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Z. Experimental Study on Mixing and Stratification of Buoyancy-Driven Flows Produced by Continuous Buoyant Source in Narrow Inclined Tank. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf. 2018, 121, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Lei, B.; Ingason, H. The Maximum Temperature of Buoyancy-Driven Smoke Flow beneath the Ceiling in Tunnel Fires. Fire Saf. J. 2011, 46, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yang, X. Fire temperature distribution of sloping tunnels. Fire Sci. Technol. 2016, 35, 1677–1679. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Kang, J. Dynamic Numerical Simulation of Coal Mine Fire for Escape Capsule Installation. Saf. Sci. 2012, 50, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gong, X.; Peng, Y.; Lin, X.; Kim, C.-N. Effects of the Ventilation Duct Arrangement and Duct Geometry on Ventilation Performance in a Subway Tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. 2011, 26, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Lan, S.; Wang, X.; Bu, R.; Zhou, Y. Study on the Smoke Back-Layering Length in a Tilted Tunnel with Vertical Shaft under Natural Ventilation. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 39, 102412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

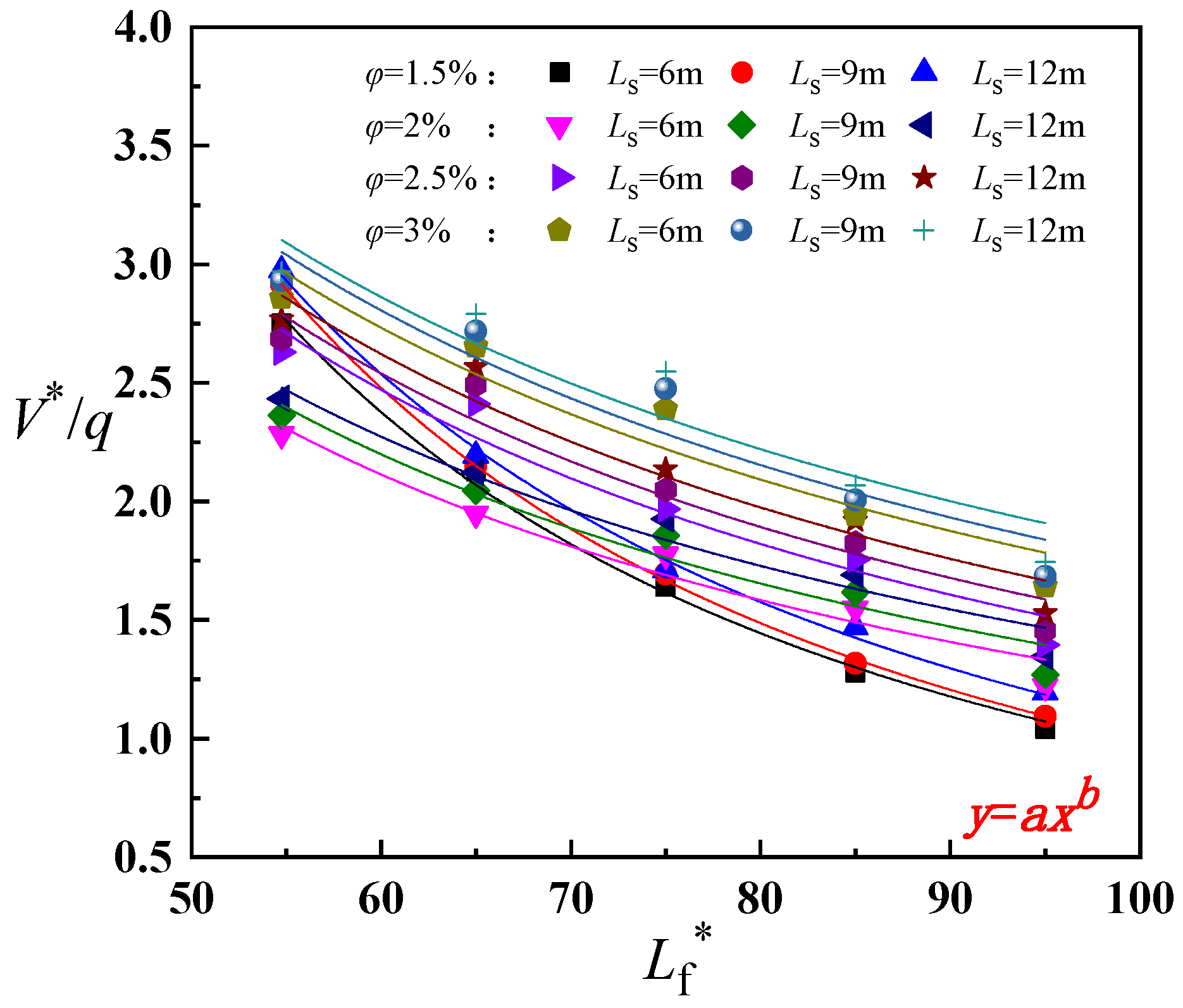
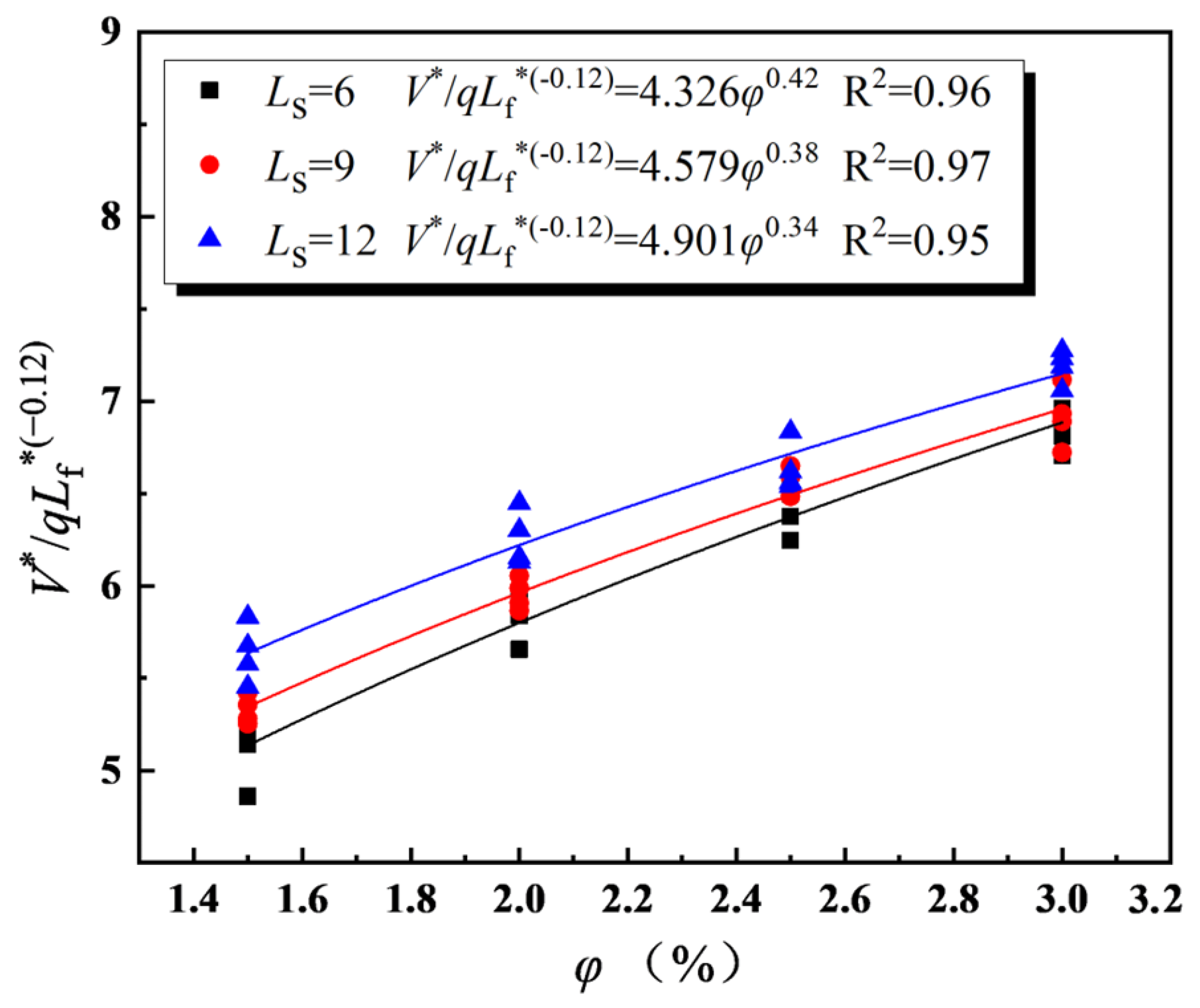
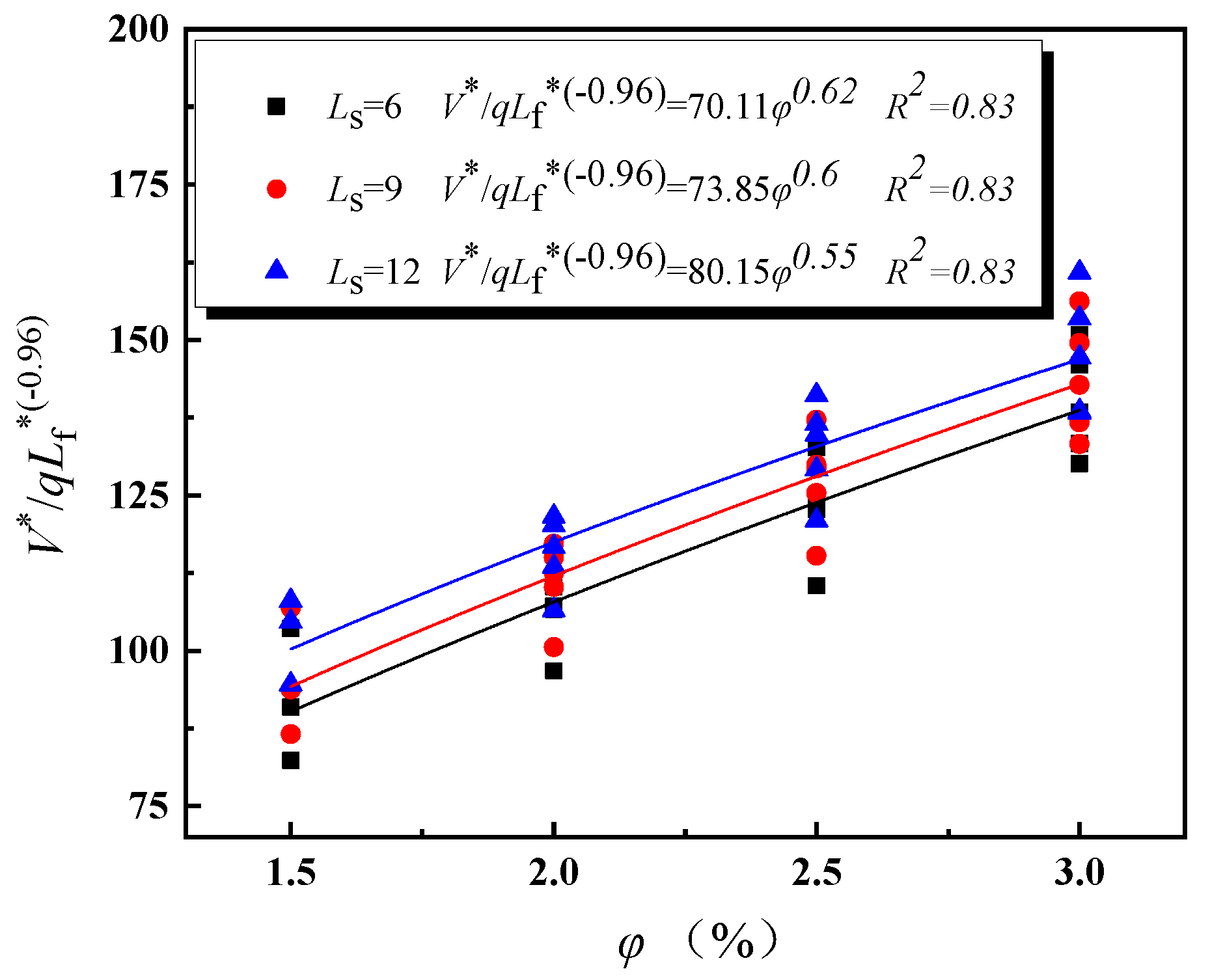
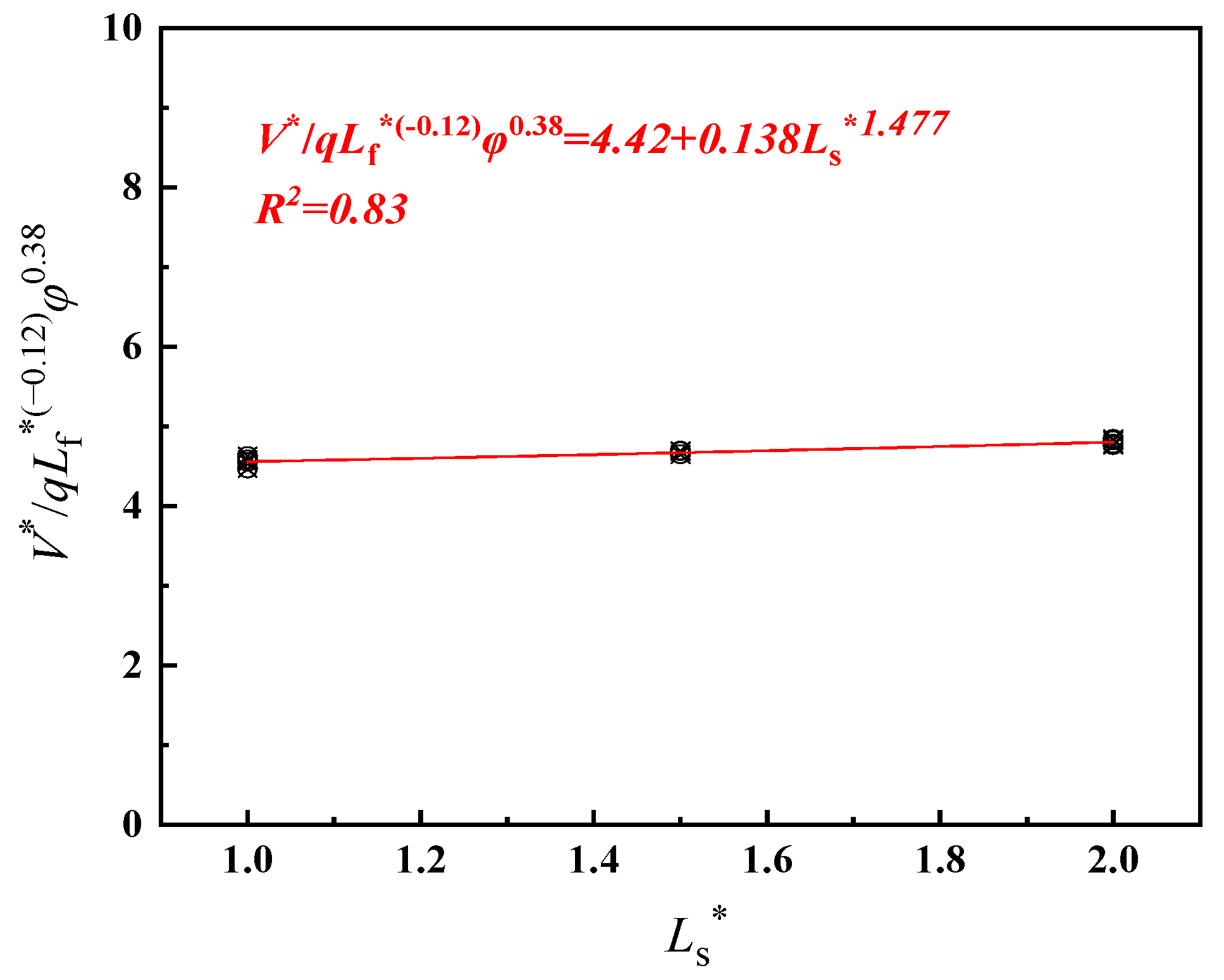
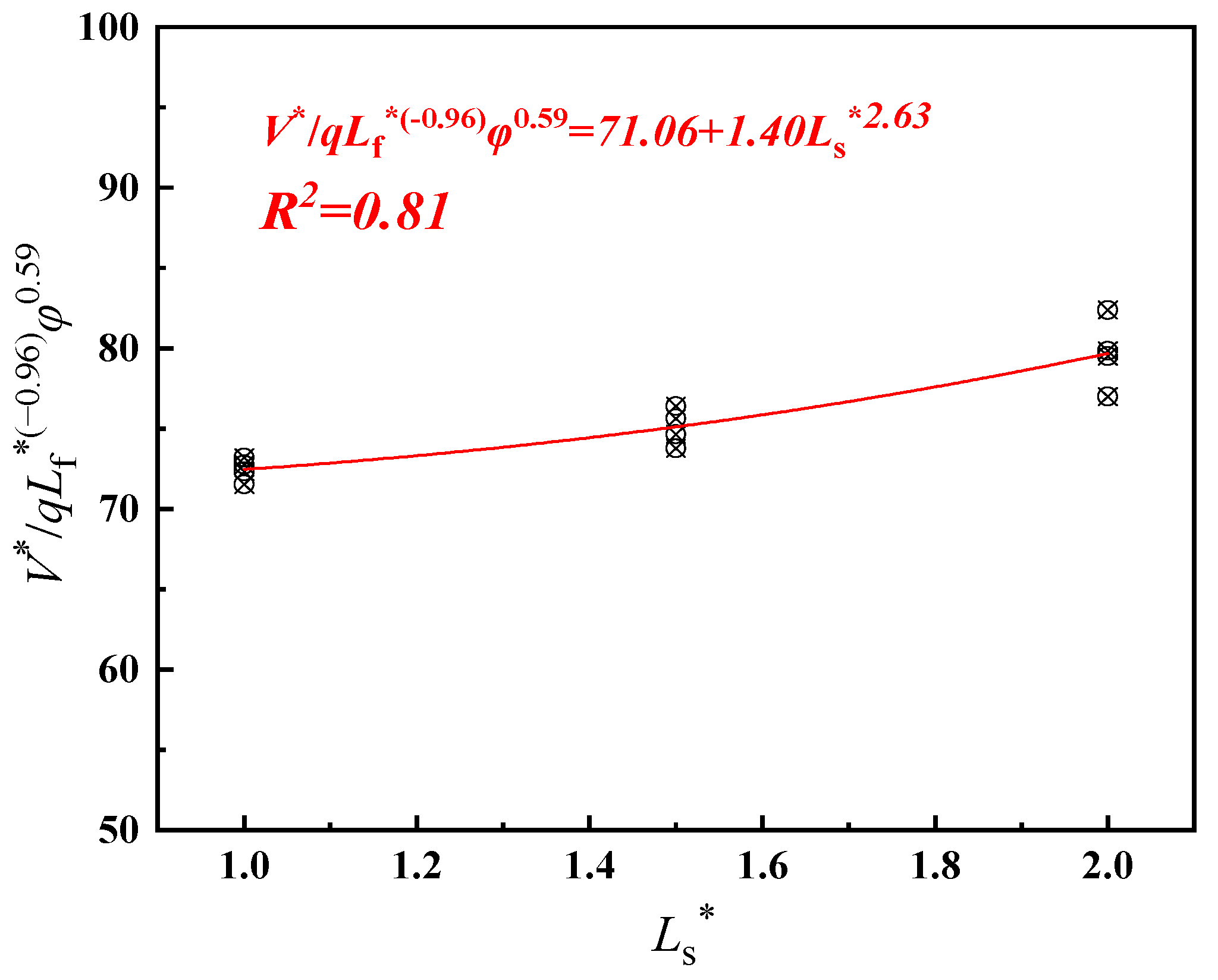

| Simulation No. | Slope Gradient | Shaft Height (m) | Fire Source Location (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1–9 | 0.5% | 6 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 |
| 10–18 | 9 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 | |
| 19–27 | 12 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 | |
| 28–36 | 1% | 6 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 |
| 37–45 | 9 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 | |
| 46–54 | 12 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 | |
| 55–63 | 1.5% | 6 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 |
| 64–72 | 9 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 | |
| 73–81 | 12 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 | |
| 82–90 | 2% | 6 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 |
| 91–99 | 9 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 | |
| 100–108 | 12 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 | |
| 109–117 | 2.5% | 6 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 |
| 118–126 | 9 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 | |
| 127–135 | 12 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 | |
| 136–144 | 3% | 6 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 |
| 145–153 | 9 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 | |
| 154–162 | 12 | 90/150/210/270/328.5/390/450/510/570 |
| Slope | 1.5% | 2% | 2.5% | 3% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaft Height | 6 | 9 | 12 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 6 | 9 | 12 |
| b | −0.16 | −0.11 | −0.13 | −0.13 | −0.12 | −0.1 | −0.12 | −0.11 | −0.11 | −0.12 | −0.13 | −0.09 |
| R2 | 0.86 | 0.9 | 0.78 | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.75 | 0.86 | 0.94 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 0.85 | 0.95 |
| Slope | 2% | 2.5% | 3% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaft Height | 6 | 9 | 12 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 6 | 9 | 12 |
| b | −1 | −0.99 | −0.95 | −1 | −1 | −0.99 | −0.93 | −0.92 | −0.88 |
| R2 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.9 | 0.89 | 0.87 |
| Fire Source Location | 328.5 | 390 | 450 | 510 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope(%) | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 2.5 | 3 |
| b | −0.55 | −0.24 | −0.21 | −0.62 | −0.26 | −0.17 | −0.99 | −0.63 | −0.25 | −1.9 | −0.94 |
| R2 | 0.87 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, L.; Lan, S.; Wang, X.; Bu, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y. Study on the Air Inlet Velocity and Temperature Distribution in an Inclined Tunnel with Single Shaft under Natural Ventilation. Buildings 2023, 13, 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13040842
Yi L, Lan S, Wang X, Bu R, Zhao J, Zhou Y. Study on the Air Inlet Velocity and Temperature Distribution in an Inclined Tunnel with Single Shaft under Natural Ventilation. Buildings. 2023; 13(4):842. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13040842
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Liang, Shihan Lan, Xiaofei Wang, Rongwei Bu, Jiaming Zhao, and Yang Zhou. 2023. "Study on the Air Inlet Velocity and Temperature Distribution in an Inclined Tunnel with Single Shaft under Natural Ventilation" Buildings 13, no. 4: 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13040842
APA StyleYi, L., Lan, S., Wang, X., Bu, R., Zhao, J., & Zhou, Y. (2023). Study on the Air Inlet Velocity and Temperature Distribution in an Inclined Tunnel with Single Shaft under Natural Ventilation. Buildings, 13(4), 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13040842








