Numerical Analysis of Steam Ejector Performance with Non-Equilibrium Condensation for Refrigeration Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The phase change condensing model is established for ejector refrigeration systems considering phase transition processes with the condensation and evaporation of massive droplets in supersonic flows.
- The optimization of pivotal ejector parameters and ejector performance is investigated considering the behavior of spontaneous condensation phenomenon.
- A novel conceptual configuration of dual-loop bi-evaporator ejector refrigeration cycles with independent temperature and humidity control strategy based on climate adaptation is proposed (see Figure 1) to deal with the varying sensible and latent loads in different climates.
- Proposing a novel dual-loop bi-evaporator ejection–compression refrigeration cycle.
- Designing the first set of ejector dimensions for a dual-loop bi-evaporator refrigeration system.
- Developing a non-equilibrium condensation model for the steam ejector.
- Validating the wet steam model by comparing it with experimental data and dry gas model.
- Studying the effect of the ejector area ratio and primary nozzle diameter ratio on the ejector performance using the wet steam model for a certain operating condition.
2. Description of Bi-Evaporator Ejection–Compression Refrigeration Cycle
3. Numerical Method
3.1. Ejector Design
3.2. CFD Modeling of Ejectors
3.2.1. Governing Equations
3.2.2. Numerical Setup
3.2.3. Grid Independence
4. Model Validation
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Dry and Wet Steam Ejector
5.2. Internal Analysis of the Ejector
5.2.1. Effect of the Primary Nozzle Outlet Diameter
5.2.2. Effect of the Mixing Chamber Throat
5.2.3. Two-Phase Flow Features
6. Conclusions and Future Works
- Neglecting the phase change process, the dry gas model results in an overestimation of steam expansion and lower temperature predictions compared to the wet steam model. The average Mach numbers are 1.97 and 1.76 for dry and wet steam models, respectively. The average static temperatures between dry and wet steam are 235.48 K and 288.88 K, respectively.
- The optimum values for the primary nozzle outlet diameter and area ratio are 2.4 and 5.0, respectively. The optimized reaches up to 0.59. In addition, the maximum deviation of for and is 16.64% and 391.95%, respectively.
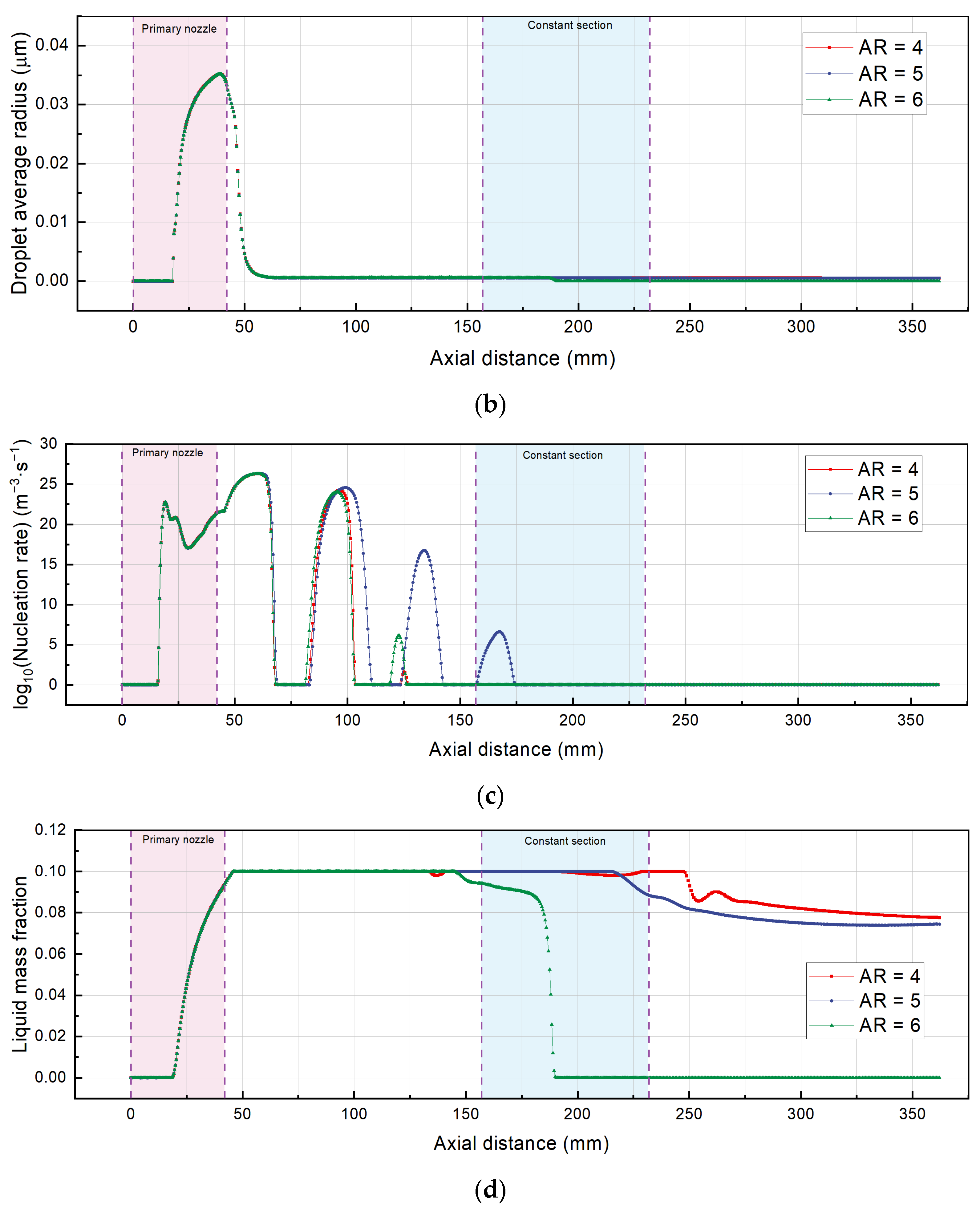
- When the increases to , the maximum Mach number decreases to about 3.39 and 3.34. The minimum liquid mass fraction is 9.14% () at the nozzle outlet, while there is an approximate growth of 9.41% when .
- The ejector reduces 60.46% of outlet Mach number () as compared to the ejector (). Droplet growth only takes place within the primary nozzle and no longer continues as the flow enters the mixing section. The nucleation occurs in two regions for the ejector, and the nucleation occurs in three regions for the ejector.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbols | Unit | |
| Diameter | ||
| Total energy | ||
| Specific enthalpy | ||
| Nucleation rate | ||
| Knudsen number | ||
| Turbulent kinetic energy | ||
| Boltzmann’s constant | ||
| and | Length | mm |
| Mach number | ||
| Number of liquid droplets | ||
| Pressure | ||
| Heat transfer rate | ||
| Condensation coefficient | ||
| Droplet radius | ||
| Gas constant | ||
| Saturation ratio | ||
| Time | ||
| Temperature | or °C | |
| Velocity components | ||
| V | Average droplet volume | |
| Greeks | ||
| and | Tuning parameter | |
| Liquid mass fraction | ||
| Specific heat ratio | ||
| Mixing layer growth rate | ||
| Turbulent dissipation rate | ||
| Efficiency | ||
| Non-isothermal correction coefficient | ||
| Thermal conductivity | ||
| Dynamic viscosity | ||
| Density | ||
| Liquid surface tension | ||
| τ | Stress tensor | Pa |
| Mass generation rate | ||
| Abbreviations | ||
| AR | Area ratio | |
| BECRC | Bi-evaporator ejection–compression refrigeration cycle | |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics | |
| COP | Coefficient of performance | |
| ER | Entrainment ratio | |
| ERC | Ejector refrigeration cycle | |
| GCI | Grid convergence index | |
| NEC | Non-equilibrium condensation | |
| NXP | Nozzle exit position | |
| SERC | Solar ejector refrigeration cycle | |
| VCC | Vapor compression cycle | |
| VGE | Variable geometry ejector | |
| Subscripts | ||
| 1, 2, 3... | State point | |
| b | Boiling | |
| Critical | ||
| Droplet | ||
| Liquid | ||
| Liquid-vapor | ||
| p | Primary flow | |
| s | Secondary flow | |
| Saturation | ||
| Vapor | ||
Appendix A
References
- Hamzaoui, M.; Nesreddine, H.; Aidoun, Z.; Balistrou, M. Experimental study of a low grade heat driven ejector cooling system using the working fluid R245fa. Int. J. Refrig. 2018, 86, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, J. Theoretical analysis on a new direct expansion solar assisted ejector-compression heat pump cycle for water heater. Sol. Energy 2017, 142, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, L.; Xue, H. Performance analysis and optimization of a steam ejector through streamlining of the primary nozzle. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 27, 101356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaebi, H.; Rostamzadeh, H. Design and optimization of a novel dual-loop bi-evaporator ejection/compression refrigeration cycle. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 151, 240–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwesigye, A.; Dworkin, S.B. Performance analysis and optimization of an ejector refrigeration system using alternative working fluids under critical and subcritical operation modes. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 176, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.; Kaushik, S.; Tyagi, S. Current status and technological advancements in adsorption refrigeration systems: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 154, 111808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, N.; Pandya, B. Integration of evacuated solar collectors with an adsorptive ice maker for hot climate region. Energy Built Environ. 2022, 3, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Cai, J.; Ji, J.; Han, K.; Ke, W. Experimental investigation on the heating and cooling performance of a solar air composite heat source heat pump. Renew. Energy 2020, 161, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazzini, G.; Milazzo, A.; Mazzelli, F. Ejectors for Efficient Refrigeration: Design, Applications and Computational Fluid Dynamics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Braimakis, K. Solar ejector cooling systems: A review. Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 566–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashtoush, B.M.; Al-Nimr, M.A.; Khasawneh, M.A. A comprehensive review of ejector design, performance, and applications. Appl. Energy 2019, 240, 138–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besagni, G.; Mereu, R.; Inzoli, F. Ejector refrigeration: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 373–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ierin, V.; Volovyk, O.; Shestopalov, K. An improved cascade mechanical compression–ejector cooling cycle. Energy 2019, 170, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, H.D. Enhanced ejector refrigeration cycles powered by low grade heat. Part 1. Systems characterization. Int. J. Refrig. 1990, 13, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.-W. Solar powered combined ejector-vapour compression cycle for air conditioning and refrigeration. Energy Convers. Manag. 1997, 38, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wang, Q.; Mao, N.; Chen, G.; Gao, Z. Refrigerant evaluation and performance comparison for a novel hybrid solar-assisted ejection-compression refrigeration cycle. Sol. Energy 2018, 160, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, M.; Yu, J. An improved 1-D thermodynamic modeling of small two-phase ejector for performance prediction and design. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 204, 118006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.J.; Chang, J.M.; Wang, C.P.; Petrenko, V.A. A 1-D analysis of ejector performance. Int. J. Refrig. 1999, 22, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, M.; Chong, D.; Yan, J.; Little, A.B.; Bartosiewicz, Y. A 1D model to predict ejector performance at critical and sub-critical operational regimes. Int. J. Refrig. 2013, 36, 1750–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besagni, G.; Cristiani, N.; Croci, L.; Guédon, G.R.; Inzoli, F. Computational fluid-dynamics modelling of supersonic ejectors: Screening of modelling approaches, comprehensive validation and assessment of ejector component efficiencies. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 186, 116431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besagni, G.; Inzoli, F. Computational fluid-dynamics modeling of supersonic ejectors: Screening of turbulence modeling approaches. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 117, 122–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chong, D.; Yan, J.; Liu, J. The numerical analysis of the effect of geometrical factors on natural gas ejector performance. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 59, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Chung, H.J.; Kim, Y. Performance characteristics of an R600a household refrigeration cycle with a modified two-phase ejector for various ejector geometries and operating conditions. Appl. Energy 2017, 205, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.; Ren, P.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, D.; Huang, S.; Jia, X. Numerical studies on wide-operating-range ejector based on anodic pressure drop characteristics in proton exchange membrane fuel cell system. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Xie, H.; Liu, S.; Yan, G.; Yu, J. Experimental investigation on the influence of ejector geometry on the pull-down performance of an ejector-enhanced auto-cascade low-temperature freezer. Int. J. Refrig. 2021, 131, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolka, J.; Palacz, M.; Bodys, J.; Banasiak, K.; Fic, A.; Bulinski, Z.; Nowak, A.J.; Hafner, A. Performance comparison of fixed- and controllable-geometry ejectors in a CO2 refrigeration system. Int. J. Refrig. 2016, 65, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besagni, G.; Cristiani, N. Multi-scale evaluation of an R290 variable geometry ejector. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 188, 116612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, S.; Lebre, P.M.; Oliveira, A.C. CFD study of a variable area ratio ejector using R600a and R152a refrigerants. Int. J. Refrig. 2013, 36, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.R.; Varga, S.; Soares, J.; Oliveira, A.C.; Lopes, A.M.; de Almeida, F.G.; Carneiro, J.F. Experimental results with a variable geometry ejector using R600a as working fluid. Int. J. Refrig. 2014, 46, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, J.; Dolz, V.; García-Cuevas, L.M.; Ponce-Mora, A. Numerical evaluation of a solar-assisted jet-ejector refrigeration system: Screening of environmentally friendly refrigerants. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 210, 112681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nguyen, V.; Varga, S.; Soares, J.; Dvorak, V.; Oliveira, A.C. Applying a variable geometry ejector in a solar ejector refrigeration system. Int. J. Refrig. 2020, 113, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Liu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Gong, X.; Lu, L.; Chua, K.J. Study on evolution laws of two-phase choking flow and entrainment performance of steam ejector oriented towards MED-TVC desalination system. Energy 2022, 242, 122967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Tang, Y. Numerical study for the influences of primary steam nozzle distance and mixing chamber throat diameter on steam ejector performance. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 132, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Hu, Q.; Yu, M.; Han, Z.; Cui, W.; Liang, D.; Ma, H.; Pan, X. Numerical investigation on the influence of mixing chamber length on steam ejector performance. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 174, 115204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Chen, W.; Zheng, J.; Chong, D.; Yan, J. Numerical simulation study on the influence of primary nozzle deviation on the steam ejector performance. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 179, 107633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Li, S.; Li, R. Numerical study on the auxiliary entrainment performance of an ejector with different area ratio. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 185, 116369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariafar, K.; Buttsworth, D.; Al-Doori, G.; Malpress, R. Effect of mixing on the performance of wet steam ejectors. Energy 2015, 93, 2030–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Gong, L.; Ding, H.; Yang, Y. Steam ejector performance considering phase transition for multi-effect distillation with thermal vapour compression (MED-TVC) desalination system. Appl. Energy 2020, 279, 115831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, C.; Wang, C.; Sun, C. Energy efficiency and exergy destruction of supersonic steam ejector based on nonequilibrium condensation model. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 189, 116704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Dykas, S.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Optimization of the primary nozzle based on a modified condensation model in a steam ejector. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 171, 115090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Z. Numerical study on carbon dioxide capture in flue gas by converging-diverging nozzle. Fuel 2022, 320, 123889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Karvounis, N.; Walther, J.H.; Ding, H.; Wen, C. Effect of area ratio of the primary nozzle on steam ejector performance considering nonequilibrium condensations. Energy 2022, 237, 121483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabir, E.; Dmitrii, B.; Konstantin, A.; Kim, H.D. Numerical estimation of non-equilibrium condensation of steam in supersonic nozzles. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 4649–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Niu, C.; Shen, S.; Mu, X.; Zhang, L. Double choking characteristics of three-dimensional steam ejector with non-equilibrium condensing. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 211, 118446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Feng, J.; Peng, X. Phase change characteristics and their effect on the performance of hydrogen recirculation ejectors for PEMFC systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 47, 1144–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadpour, D.; Lakzian, E.; Gholizadeh, M.; Ding, H.; Han, X. Numerical modeling of droplets injection in the secondary flow of the wet steam ejector in the refrigeration cycle. Int. J. Refrig. 2022, 136, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, S.; Niu, C.; Mu, X.; Zhang, L. The effect of variable motive pressures on the performance and shock waves in a supersonic steam ejector with non-equilibrium condensing. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 185, 108034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, X.; Lu, J. Analysis and Selection of Working Fluid for Marine Ejection-Compression Air-Conditioning System. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Power and Renewable Energy (ICPRE), Shanghai, China, 23–26 September 2022; pp. 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chang, Z.; Tian, Q.; Wu, C.; Wang, X. Performance Predictions of Dry and Wet Vapors Ejectors Over Entire Operational Range. Energies 2017, 10, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecker, W. Steam-jet refrigeration. In Refrigeration and Air Conditioning; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1958; pp. 194–205. [Google Scholar]
- Cardemil, J.M.; Colle, S. A general model for evaluation of vapor ejectors performance for application in refrigeration. Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 64, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Cai, W.; Wen, C.; Li, Y. Fuel ejector design and simulation model for anodic recirculation SOFC system. J. Power Sources 2007, 173, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, A.; Elahi, S.; Pahangeh, H. Design and analysis of a novel solar compression-ejector cooling system with eco-friendly refrigerants using hybrid photovoltaic thermal (PVT) collector. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2022, 32, 101311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, P.G. Condensation of water vapour during supersonic expansion in nozzles. J. Fluid Mech. 1966, 25, 593–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.B. Two-Dimensional, Nonequilibrium, Wet-Steam Calculations for Nozzles and Turbine Cascades. J. Turbomach. 1992, 114, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, J.; Mo, Y.; Chen, W.; Xiao, Q.; Li, Y.; Yan, J. Numerical simulation on the direct contact condensation in a steam-water two-phase ejector with non-condensable gas. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 185, 108030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, N.; Boroomand, M.; Sharifi, M. Numerical assessment of steam nucleation on thermodynamic performance of steam ejectors. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 52, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Walther, J.H.; Yan, Y.; Wen, C. CFD modeling of condensation process of water vapor in supersonic flows. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 115, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Li, B.; Ding, H.; Akrami, M.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y. Thermodynamics analysis of CO2 condensation in supersonic flows for the potential of clean offshore natural gas processing. Appl. Energy 2022, 310, 118523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Niu, C.; Shen, S.; Mu, X.; Zhang, L. Turbulence Model Comparative Study for Complex Phenomena in Supersonic Steam Ejectors with Double Choking Mode. Entropy 2022, 24, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianthong, K.; Seehanam, W.; Behnia, M.; Sriveerakul, T.; Aphornratana, S. Investigation and improvement of ejector refrigeration system using computational fluid dynamics technique. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, H.A.; Abdullah, H.M.; Rehman, Z.; Lee, B.; Baik, Y.-J.; Cho, J.; Imran, M.; Masud, M.; Saleem, M.; Butt, M.S. Numerical Modeling of Ejector and Development of Improved Methods for the Design of Ejector-Assisted Refrigeration System. Energies 2020, 13, 5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Pourranjbar, D.; Dykas, S.; Li, H.; Chen, J. The comprehensive analysis of the relationship between the latent heat, entrainment ratio, and ejector performance under different superheating degree conditions considering the non-equilibrium condensation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 200, 117701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jiang, P. Experimental and numerical investigation of the effect of shock wave characteristics on the ejector performance. Int. J. Refrig. 2014, 40, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbarghthi, A.F.; Mohamed, S.; Nguyen, V.V.; Dvorak, V. CFD Based Design for Ejector Cooling System Using HFOS (1234ze(E) and 1234yf). Energies 2020, 13, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besagni, G.; Mereu, R.; Chiesa, P.; Inzoli, F. An Integrated Lumped Parameter-CFD approach for off-design ejector performance evaluation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 697–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, X. A visual mass transfer study in the ejector considering phase change for multi-effect distillation with thermal vapour compression (MED-TVC) desalination system. Desalination 2022, 532, 115722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Performance comparison of ejectors in ejector-based refrigeration cycles with R1234yf, R1234ze(E) and R134a. Environ Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 57166–57182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Shi, C.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Chong, D.; Yan, J. Theoretical analysis of ejector refrigeration system performance under overall modes. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriveerakul, T.; Aphornratana, S.; Chunnanond, K. Performance prediction of steam ejector using computational fluid dynamics: Part 2. Flow structure of a steam ejector influenced by operating pressures and geometries. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2007, 46, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriveerakul, T.; Aphornratana, S.; Chunnanond, K. Performance prediction of steam ejector using computational fluid dynamics: Part 1. Validation of the CFD results. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2007, 46, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Dykas, S.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Accurate condensing steam flow modeling in the ejector of the solar-driven refrigeration system. Energy 2020, 212, 118690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yan, Y.; Ding, H.; Wen, C. Performance of supersonic steam ejectors considering the nonequilibrium condensation phenomenon for efficient energy utilisation. Appl. Energy 2019, 242, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruangtrakoon, N.; Thongtip, T.; Aphornratana, S.; Sriveerakul, T. CFD simulation on the effect of primary nozzle geometries for a steam ejector in refrigeration cycle. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2013, 63, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wen, C.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Han, Y.; Cheung, S.C.-P.; Kook, S.; Yeoh, G.H. A novel thermal management system for battery packs in hybrid electrical vehicles utilising waste heat recovery. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 195, 123199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Jin, Z.; Qin, X. Performance evaluation and operation optimization of the steam ejector based on modified model. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 163, 114388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, N. Numerical study of non-equilibrium condensing supersonic steam flow in a jet-pump based on supersaturation theory. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 165, 105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyarmathy, G. Grundlagen Einer Theorie der Nassdampfturbine. Ph.D. Thesis, Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule Zürich, Zurich, Switzerland, 1962. [Google Scholar]

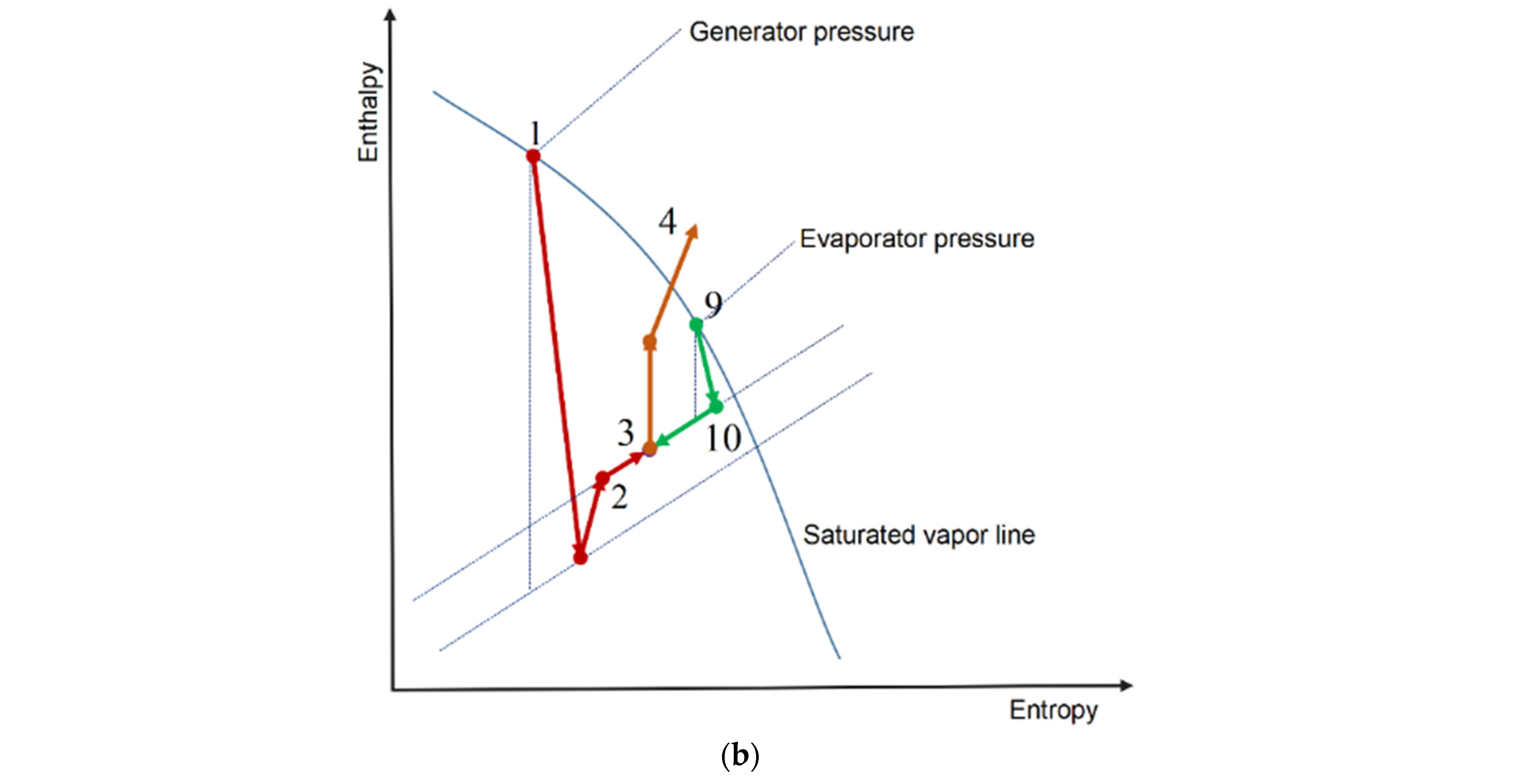
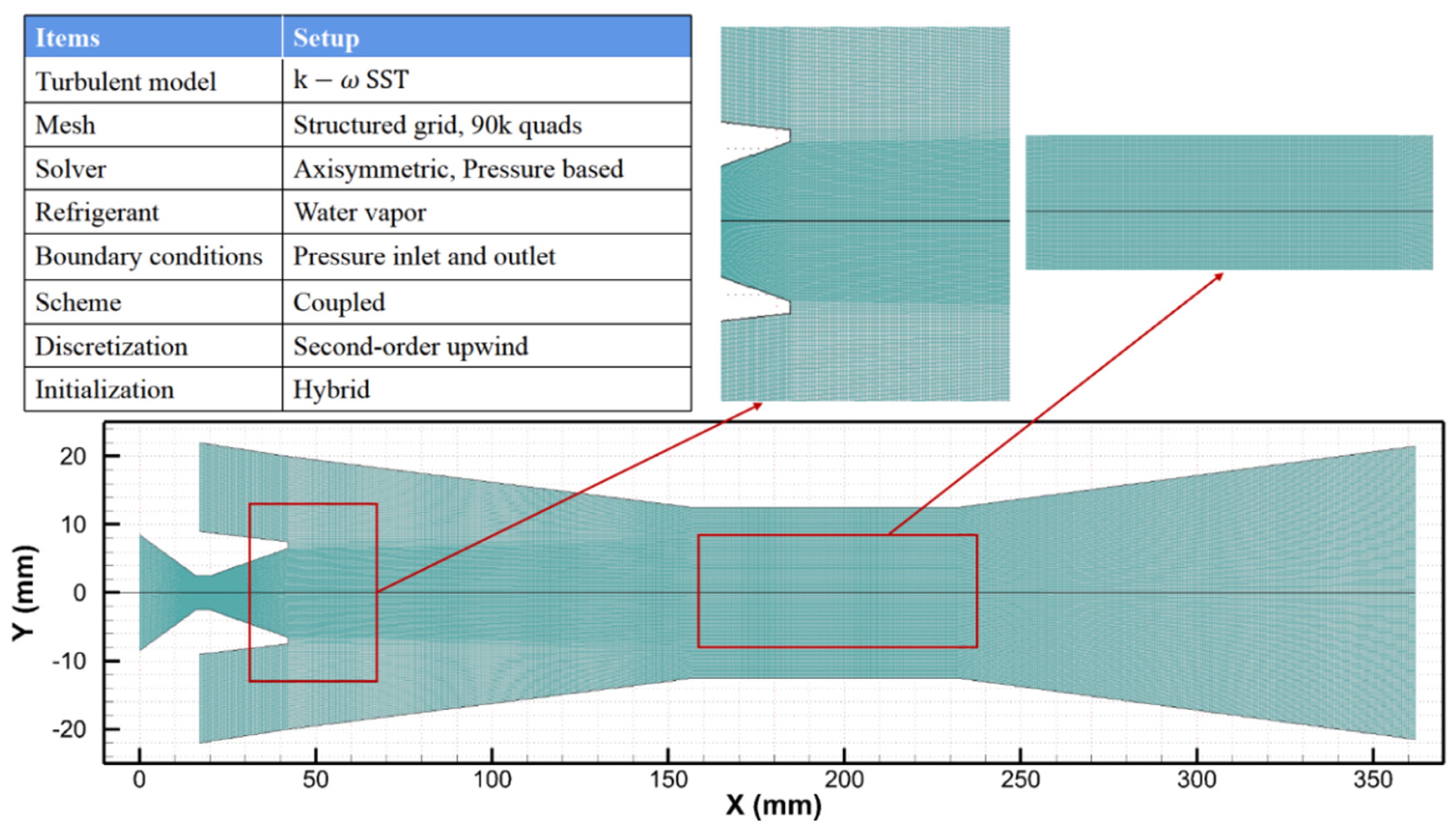




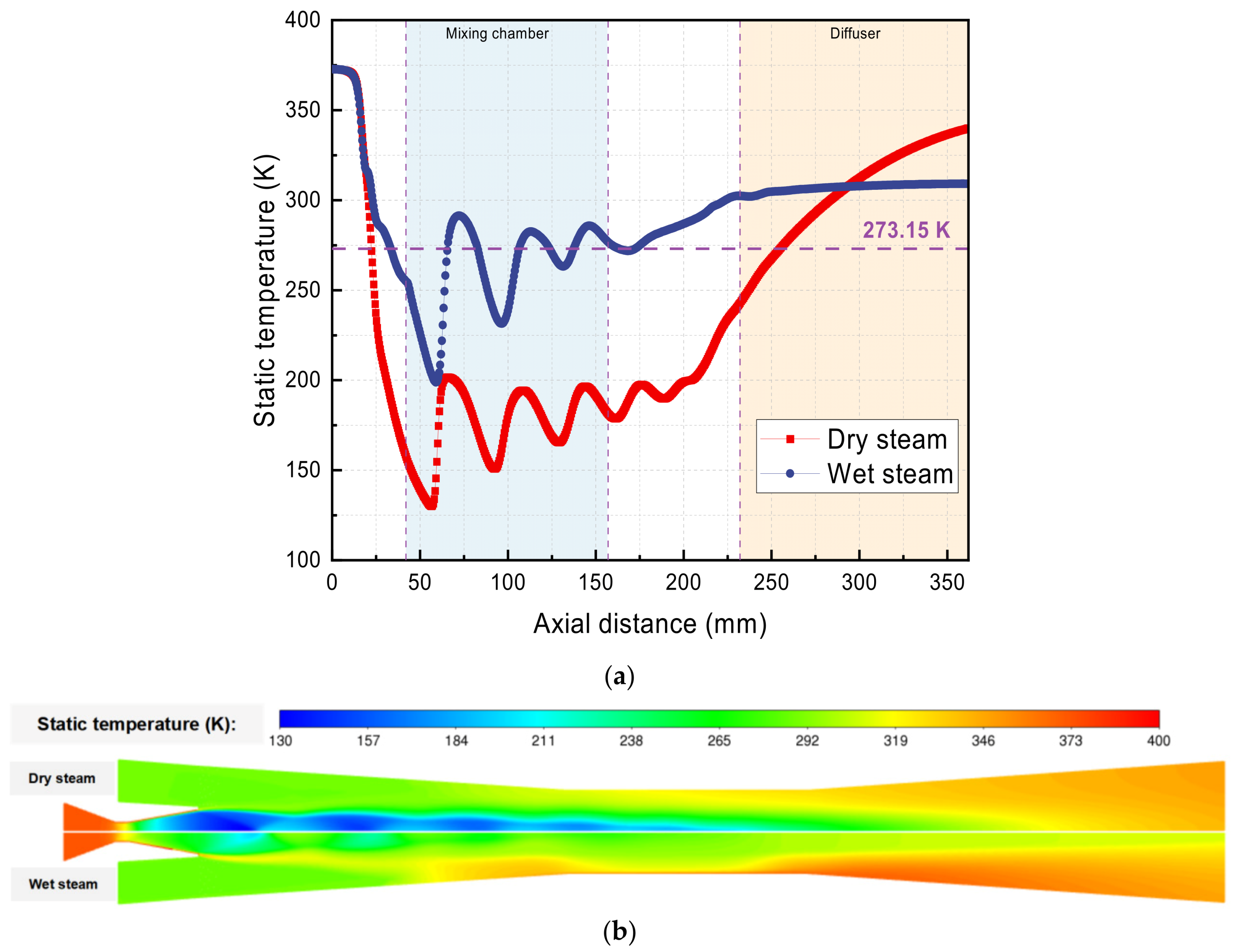


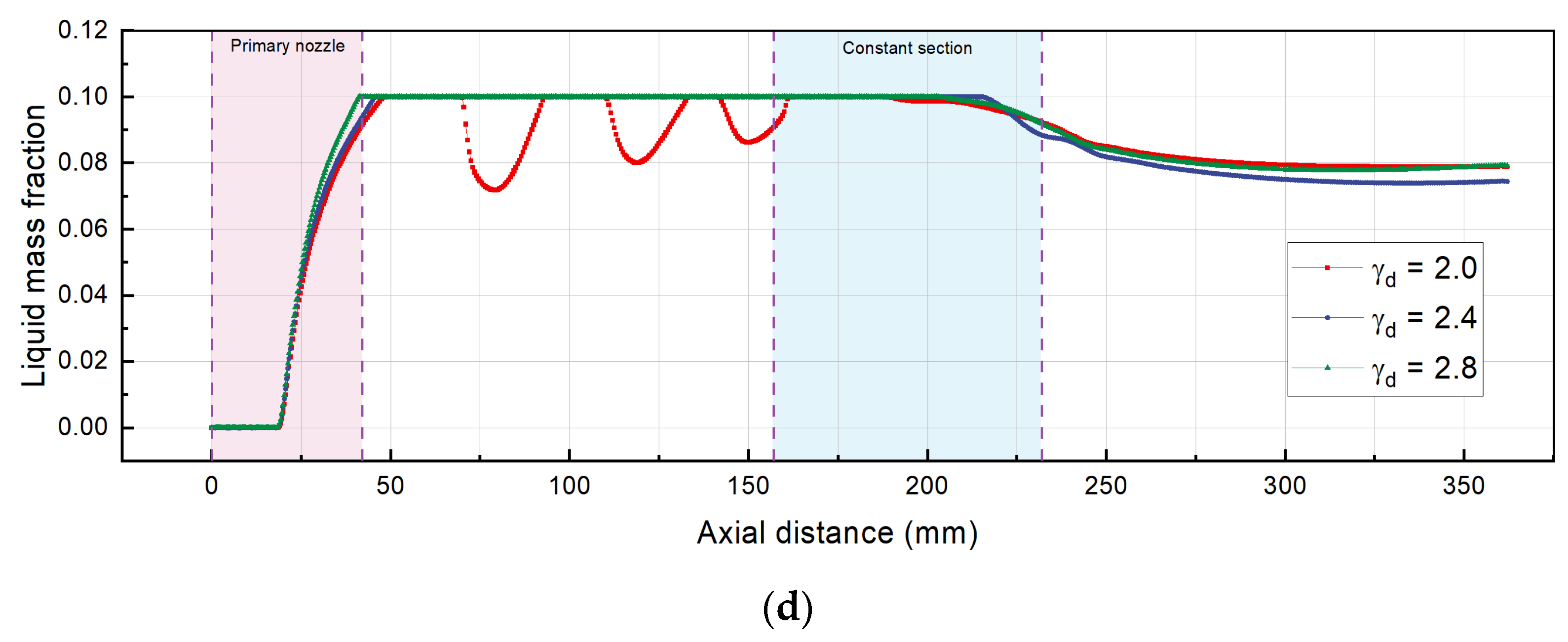



| Reference | Model | Area Ratio and Nozzle Exit Position |
|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. [22] | CFD, natural gas | The varies between 3.6 and 7.2 mm to obtain the maximum entrainment ratio. In addition, it is displayed between for the optimal pressure ratio. |
| Jeon et al. [23] | Experiment, R600a | The maximum pressure ratio was attained at NXP = 3 mm. |
| Pei et al. [24] | CFD, Hydrogen gas | When the NXP exceeds the optimal range, the hydrogen entrainment ratio drops sharply in the entire operating range. The optimum ranges from . |
| Bai et al. [25] | Experiment, R23/R600a | The main factors affecting the available freezing temperature and the cooling rate are the mixing chamber length and the nozzle throat, rather than the mixing chamber diameter and the position of the nozzle outlet. |
| Reference | Study | Fluid | Operating Conditions | Key Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Varga et al. [28] | CFD Spindle | R152a R600a | By adjusting the position of the spindle, an improvement in the entrainment ratio of up to 177% is achieved. | |
| Pereira et al. [29] | Experimental Spindle | R600a | The COP is increased up to 85% with the variable geometry ejector. | |
| Galindo et al. [30] | Theoretical Spindle | R1234yf | There was an improvement in COP from 0.34 and 0.31 (in July and May, respectively) to 0.42 and 0.48. | |
| Van Nguyen et al. [31] | Experimental Spindle, NXP | R600a | The COP is increased by 24% compared to the fixed geometry ejector. | |
| Besagni and Cristiani [27] | Theoretical Spindle | R290 | Increasing the area ratio by 33% resulted in an average COP enhancement of 57.1%. |
| Reference | Remarks |
|---|---|
| Zhang et al. [40] | This study presented a modified condensation model to optimize steam ejector performance. The primary nozzle is optimized using the Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm method, resulting in a 27.5% increase in entrainment ratio. |
| Li et al. [44] | This study investigated the relationship between double choking characteristics and ejector performance. Results showed that the double choking mode occurs when the minimum distance between the sonic velocity line and the wall is 0.21 mm, and the second choking position is 4 mm downstream of the diffuser entrance. |
| Han et al. [45] | This study analyzed the effect of phase change on the performance of a hydrogen recirculation ejector in proton exchange membrane fuel cell systems. The results showed that a higher entrainment ratio predicted by the two-phase flow model compared to the single-phase flow model. Droplet nucleation occurs at the junction of primary and secondary flow, with the nucleation rate increasing with primary flow pressure. |
| Dadpour et al. [46] | This study investigated the effect of droplets injection at secondary flow on the performance of ejector refrigeration cycle. Results showed that a decrease in COP, and entrainment ratio with increasing wetness and number of droplets in the secondary flow. |
| Li et al. [47] | The study examined how variable motive pressures affect the performance and shock waves in the system. Results indicated that increasing the motive pressure led to an improvement in the entrainment ratio and a reduction in the strength of the condensation shock wave, but it also resulted in an increase in the total pressure loss coefficient. |
| Refrigerant | (°C) | (MPa) | (°C) | Weight | ODP | GWP | Safety Group | Fluid Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R141b | 204.4 | 4.21 | 32.1 | 116.95 | 0.11 | 725 | A2 | dry |
| R245fa | 153.9 | 3.65 | 15.1 | 134.05 | 0 | 1050 | B1 | |
| R1336mzz(Z) | 171.3 | 2.90 | 33.4 | 164.10 | 0 | 2 | A1 | |
| R1233zd(E) | 166.0 | 3.60 | 19.0 | 131.0 | 0 | 4.5 | A1 | |
| R245fa2 | 171.7 | 3.43 | 29.24 | 150.0 | 0 | 286 | ||
| R365mfc | 186.9 | 3.27 | 40.18 | 148.1 | 0 | 1110 | ||
| R134a | 101.0 | 4.10 | −26.0 | 102.03 | 0 | 1430 | A1 | Wet |
| R290 | 96.68 | 4.25 | −42.1 | 44.1 | 0 | 3 | A3 | |
| R1234ze(Z) | 150.1 | 3.53 | 9.28 | 114 | 0 | 6 | A2L | |
| R1234yf | 94.7 | 3.38 | −29.49 | 114 | 0 | 4 | A2L | Isentropic |
| R1234ze(E) | 109.4 | 3.63 | −19.28 | 114 | 0 | 6 | A2L | |
| R600a | 134.7 | 3.64 | −11.68 | 58.12 | 0 | 4 | A3 |
| Temperature (°C) | Pressure (kPa) | |
|---|---|---|
| Primary flow | 100 | 101.42 |
| Secondary flow | 18 | 2.53 |
| Mixed flow | / | 5.95 |
| Diameter | Value (mm) | Length | Value (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nozzle entrance | 17 | Nozzle convergent section length | 16 |
| Nozzle throat | 5 | Nozzle throat length | 4 |
| Nozzle exit | 13 | Nozzle divergent section length | 22 |
| Mixing throat | 25 | Mixing chamber length | 190 |
| Suction chamber inlet | 40 | Constant-area Mixing chamber length | 75 |
| Diffuser outlet | 43 | Diffuser length | 130 |
| Grid Number | Secondary Mass Flow Rate | Error | Entrainment Ratio | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 k | 1.487 | / | 0.572 | / |
| 60 k | 1.462 | 1.68% | 0.583 | 1.92% |
| 90 k | 1.454 | 0.55% | 0.577 | 1.03% |
| 110 k | 1.443 | 0.48% | 0.575 | 0.35% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, Y.; Li, S.; Lu, J.; Xu, Y.; Yong, Y.; Xing, D. Numerical Analysis of Steam Ejector Performance with Non-Equilibrium Condensation for Refrigeration Applications. Buildings 2023, 13, 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13071672
Lei Y, Li S, Lu J, Xu Y, Yong Y, Xing D. Numerical Analysis of Steam Ejector Performance with Non-Equilibrium Condensation for Refrigeration Applications. Buildings. 2023; 13(7):1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13071672
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Yu, Shengyu Li, Jun Lu, Ye Xu, Yong Yong, and Dingding Xing. 2023. "Numerical Analysis of Steam Ejector Performance with Non-Equilibrium Condensation for Refrigeration Applications" Buildings 13, no. 7: 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13071672
APA StyleLei, Y., Li, S., Lu, J., Xu, Y., Yong, Y., & Xing, D. (2023). Numerical Analysis of Steam Ejector Performance with Non-Equilibrium Condensation for Refrigeration Applications. Buildings, 13(7), 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13071672






