Abstract
This study presents a novel video-based risk assessment and safety management technique aimed at mitigating the risk of falling objects during tower crane lifting operations. The conventional YOLOv5 algorithm is prone to issues of missed and false detections, particularly when identifying small objects. To address these limitations, the algorithm is enhanced by incorporating an additional small object detection layer, implementing an attention mechanism, and modifying the loss function. The enhanced YOLOv5s model achieved precision and recall rates of 96.00%, with average precision (AP) values of 96.42% at an IoU of 0.5 and 62.02% across the range of IoU values from 0.5 to 0.95. These improvements significantly enhance the model’s capability to accurately detect crane hooks and personnel. Upon identifying the hook within a video frame, its actual height is calculated using an interpolation function derived from the hook’s dimensions. This calculation allows for the precise demarcation of the danger zone by determining the potential impact area of falling objects. The worker’s risk level is assessed using a refined method based on the statistical analysis of past accidents. If the risk level surpasses a predetermined safety threshold, the worker’s detection box is emphasized and flagged as a caution on the monitoring display.
1. Introduction
Tower cranes are frequently used on construction sites to transport large-scale materials and equipment. The lifting routes frequently intersect with worker operating areas. This cross-operation consequently increases risk factors, leading to safety incidents. The main types of accidents include tower overturning, falling object striking, worker falling from height, collision, tower crane component falling, electric shock, and other accidents. In recent years, digital technology has been applied to the safety management of tower cranes. For example, the feasibility of retrofitting tower cranes with smart devices for motion control was examined [1]. The information such as load bearing, vibration changes, and the condition of the steel wire rope can be obtained by the crane monitoring device. A near-field sensing system was installed on the crane to display load information on the transmitter, thus effectively preventing crane collision accidents. Ultra-wideband technology was used to precisely locate and track the operating position of the crane arm [2]. With the real-time monitoring of crane work parameters and setting the crane operating space, collisions can be prevented based on the crane’s operating area. These studies mainly focus on the prevention of crane collisions. However, the risk of falling objects striking from high altitudes is also a key point in the safety management of tower cranes, and there is an urgent need for corresponding research.
In recent years, monitoring equipment has begun to be deployed on a large scale at construction sites, and computer vision technology has been widely used to assist in construction safety management [3], providing a scientific basis for decision making for managers. The image data collected through monitoring can provide a training dataset for deep learning-based object detection algorithms, thus enabling the recognition of specific objects and scenes on the site. A Faster R-CNN model [4] was used to real-time detect whether construction workers are wearing safety hats, which helps strengthen the supervision of construction workers and prevent injuries caused by falling. By focusing on the transfer learning of the real-time detection of construction site railings, an enhanced dataset of images for the VGG-16 model training was developed, synthesizing the images of construction site backgrounds without railings and 3D railing models built in Revit, proving the possibility of using synthetic images for neural network training [5]. A robotic tower crane was developed, and LiDAR and stereo cameras with the YOLOv3 model were used to detect and track objects [6]. By combining with the inertial measurement unit (IMU)-based method, a computer vision-based approach was introduced to track load positions for load sway monitoring for blind lifts on a congested offshore platform [7]. Therefore, it is feasible to use computer vision technology to help mitigate the risk of falling objects striking during tower crane operation.
Due to the high height of the tower crane, the detection of hooks, heavy objects, and workers is a typical small target detection problem which presents the following three technical issues: (1) The heavy objects and workers on the ground are very small in the image, often only a few pixels in size; it is difficult to detect them accurately and quickly in motion. (2) In order to improve the accuracy and efficiency, the combined use of multiple cameras or other technologies is required, which would significantly increase the project cost, making it economically unfeasible. (3) The conventional computer vision-based recognition model consumes too much system resources, making them difficult to be deployed. Various attempts have been made in relevant research topics to detect small objects [8,9,10]. Recently, Pei et al. [11] proposed the SGD-YOLOv5 algorithm with a depth-to-space convolution module to enhance small target feature extraction, integrating a global attention mechanism for improved global interaction, and replacing the YOLOv5 head with a decoupled head to better balance classification and regression, thus accelerating model convergence and performance. Chen et al. [12] developed the MC-YOLOv5 algorithm for multi-class small object detection with an enhanced CB module for better edge information in small objects, a shallow network optimization to expand the receptive field and reduce missed detections, and a decoupled anchor frame-based head for training efficiency. Wu and Xu [13] developed an HSOD-Net to deal with the small object detection problem in low-resolution images. Cheng et al. [14] constructed two large-scale SODAs for driving and aerial purposes. Partial modification to the YOLO algorithm, such as BoT3 Block Optimization [15], Cross-Layer Feature Fusion, and Channel Attention [16], were also implemented. However, small object detection still encounters the following significant challenges: (1) While the incorporation of additional layers, attention mechanisms, or feature fusion strategies enhances the detection accuracy, it also substantially increases the computational load and model complexity. This can limit the suitability of these models for real-time applications in resource-constrained settings, such as on-site construction monitoring systems. (2) False positives and missed detections remain prevalent, particularly in densely populated or complex industrial scenes, which is especially critical for safety applications that rely on the accurate detection of small objects such as personnel or heavy loads.
At the same time, traditional risk assessment methods for the falling object striking from tower cranes mainly rely on parameters stipulated by regulations and standards, which are subjective and qualitative to some extent. Efforts have been made to incorporate state-of-the-art technologies to address construction accidents, including BIM-based models [17], ergonomic models [18,19], the level of preventive action methods [20], and the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process [21], for evaluating construction risk assessment. However, these methods are primarily occupationally oriented and are not well-suited for tower crane operations. Therefore, it is essential to develop risk assessment models based on the analysis of past tower crane safety accidents.
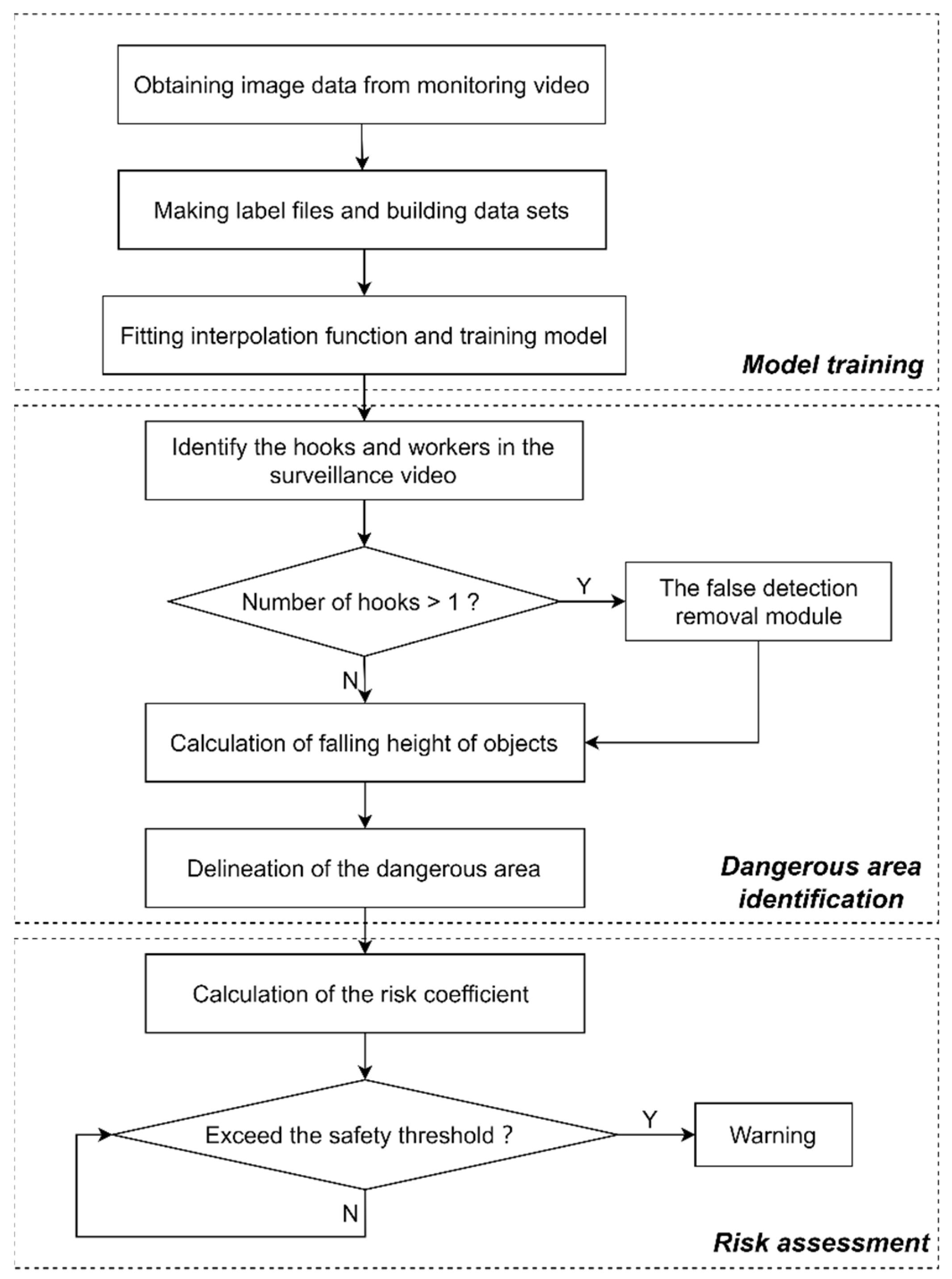
A video-based risk assessment and safety management method based on an improved small object recognition algorithm has been proposed in this paper. This method consists of the following three parts: the training part of the improved algorithm, the identification part of the object striking area, and the risk assessment part of the construction personnel, as shown in Figure 1. The specific research content is as follows:
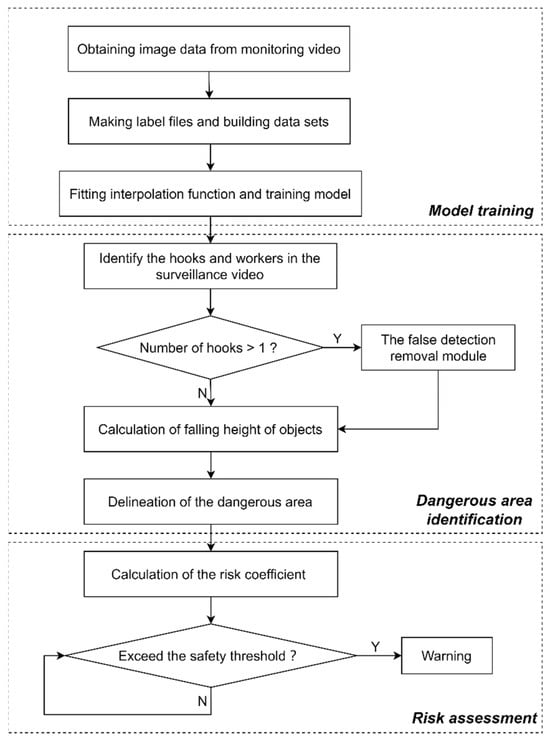
Figure 1.
Roadmap of the development of an improved small object recognition algorithm and risk assessment model.
- (1)
- The training part of the improved small object recognition algorithm. Based on the video files collected by a tower crane surveillance camera, a dataset of hooks and construction personnel is constructed, and an additional small object detection layer, an attention mechanism, and a loss function are added. Finally, the improved algorithm is trained using the dataset of hooks and construction personnel.
- (2)
- The identification part of the falling object striking area. After detecting the hook and construction personnel using the trained improved algorithm, the actual height of the hook is calculated using the interpolation function based on the hook size, and the range of the falling object striking point is determined to delineate the dangerous area.
- (3)
- The risk assessment part of construction personnel. The risk level of the worker is calculated based on the hook height, the position of the construction personnel, and the time. It is judged whether the risk level exceeds the safety threshold. When the risk level exceeds the safety threshold, the detection box of the worker is highlighted and marked as a warning.
2. Improvement of Small Object Recognition Algorithm
2.1. Selection of YOLOv5 Model
YOLOv5 [22,23] configures four different sizes of network models, namely, YOLOv5s, YOLOv5m, YOLOv5l, and YOLOv5x. Among them, YOLOv5s is the model with the smallest network depth and width but the fastest detection speed. The other three models are based on YOLOv5s, continuously deepening and widening the network to expand the network scale, enhancing the detection performance of the model while increasing the consumption of computing resources and the speed. Considering the detection accuracy, model size, and detection speed comprehensively, this paper chooses YOLOv5s as the base detection model and optimizes and improves it.
The network structure of YOLOv5s is divided into the following three parts: the backbone network, the bottleneck layer, and the prediction layer [23], as briefly described herein. The backbone network is composed of the following four modules: Focus, CONV, CSP, and SPP [24], which are used to extract the deep features of the input image; the bottleneck layer adopts the FPN [25] + PAN [26] structure. The FPN layer fuses high-level strong semantic features with the features extracted by the backbone network from top to bottom through up-sampling, and the PAN layer fuses low-level strong position features with the features extracted by the FPN layer from bottom to top through down-sampling, enhancing the expression ability of multi-scale features; the prediction layer predicts the category and bounding box position of small, medium, and large target objects through three detection scales, respectively. The bounding box loss function uses GIoU Loss [27], followed by NMS (Non-Maximum Suppression) screens, and eliminates redundant prediction boxes according to the probability value; then, it finally outputs the prediction category and bounding box position coordinates with the highest confidence.
2.2. Addition of Small Object Detection Layer
Different levels of feature encoding contain different information. Low-level feature maps have a higher resolution, extracting more position and detail information about the object, but the feature map contains more noise. High-level feature maps are rich in semantic information, but the image resolution is lower and the perception of the detail information of the object is insufficient. For small objects, the semantic information extracted from low-level feature maps is not enough, which is not conducive to the accurate classification of the target. As the network deepens, although the high-level feature map has a larger receptive field, the geometric information related to object localization is insufficient. The extracted features cannot cover all of the feature information of the object, and the effect is greatly reduced for small object detection. The transmission and fusion of multi-scale feature maps can enhance the network’s recognition ability of features and extract more comprehensive feature information from the object; at the same time, the different scale feature maps correspond to the different sizes of the anchor boxes, covering a larger range of object sizes and greatly improving the detection accuracy of the model.
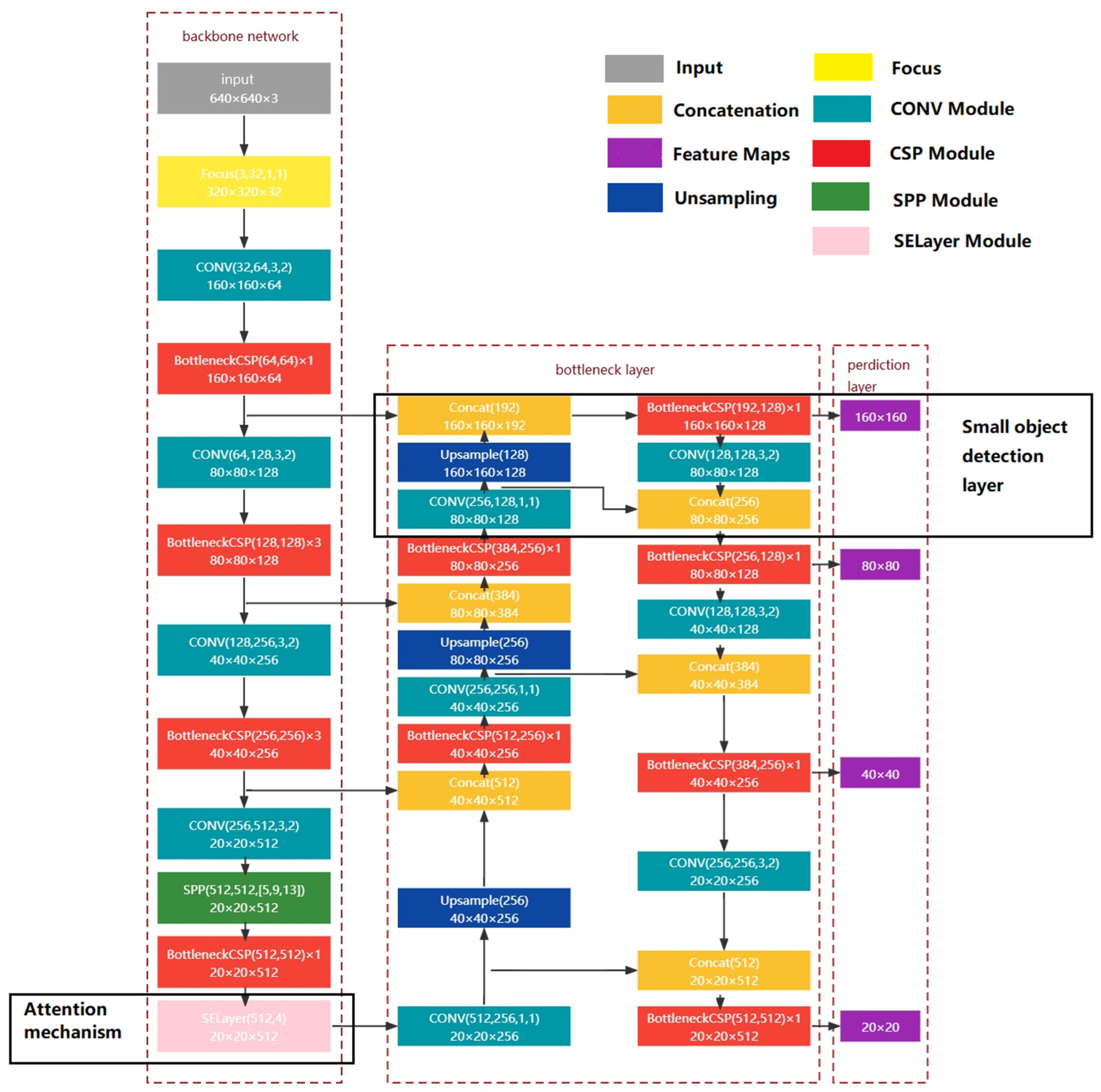
The original YOLOv5s has three detection scales. When the resolution of the input original image is 640 × 640, the 20 × 20 detection scale corresponds to a resolution area of a 32 × 32 receptive field, the 40 × 40 detection scale corresponds to a receptive field of a 16 × 16 resolution area, and the 80 × 80 detection scale corresponds to a receptive field of an 8 × 8 resolution area, which are used to detect larger, medium, and smaller objects, respectively. In this study, it is necessary to use the object detection algorithm to identify the hook of the tower crane. The hook occupies very few pixels in the tower crane safety monitoring video under normal circumstances, so one detection scale (160 × 160) is added to the original model’s three detection scales. The improved network structure is shown in Figure 2. The extracted features are passed through the FPN + PAN structure in the bottleneck layer for feature transfer and fusion operations. After two up-sampling operations in the bottleneck layer, the 80 × 80 feature map is obtained and continues to be convolved and up-sampled to obtain the 160 × 160 feature map, which is then merged with the same-resolution feature map from the main feature extraction network to obtain the 160 × 160 detection scale. At the same time, the original 80 × 80 detection scale obtained from the fusion feature map after two up-sampling operations is changed to the fusion feature map after three up-sampling operations and one down-sampling operation. The other two detection scales (40 × 40 and 20 × 20) are performed in the same way. By further deepening the network, we enhance the expression ability of small target features and output 4 scale feature maps (20 × 20, 40 × 40, 80 × 80, and 160 × 160). Extending the network to four detection scales, although the model parameters increase, enhances the network’s ability to extract low-level feature information.
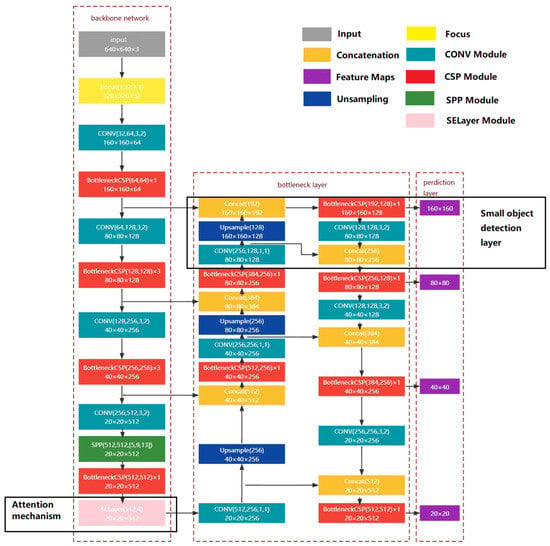
Figure 2.
Network structure of the improved YOLOv5s.
When regressing the detection box of the object, it is necessary to train and adjust the output parameters of the prediction box based on the initial anchor box, calculate the distance between the prediction box and the real box, and then update and adjust the parameters in reverse so that the model gradually converges to complete the training process [28]. After increasing the detection scale, it is necessary to add three groups of initial anchor boxes corresponding to the feature maps of the newly added detection scale. The distribution of the initial anchor boxes of the improved YOLOv5s is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Initial and improved anchor box distribution.
The 20 × 20 feature map has the lowest spatial resolution and the largest receptive field, with anchor box sizes of (116,90), (156,198), and (373,326), making it well-suited for large object detection. The 40 × 40 feature map provides an intermediate resolution and receptive field, with anchor box sizes of (30,61), (62,45), and (59,119), optimized for detecting medium-sized objects. The 80 × 80 feature map has a higher spatial resolution and a smaller receptive field, with anchor box sizes of (10,13), (16,30), and (33,23), ideal for small object detection. A new 160 × 160 feature map with the highest resolution and the smallest receptive field has been introduced, with anchor box sizes of (4,6), (7,14), and (15,10), specifically designed to improve the performance in detecting small objects. By integrating features across multiple scales, the network captures fine-grained object features more effectively, enriching the semantic and spatial information of the feature maps, which greatly enhances the model’s accuracy in detecting small-scale objects.
2.3. Addition of Attention Mechanism
The human visual processing mechanism quickly scans the overall information of the image and pays more attention to the areas that need to be focused on, thereby improving the efficiency of information screening. Based on this mechanism, the SENet channel attention module was developed [29]. The SENet channel attention module can enhance the extraction of features of interested areas. Since this module can optimize the content learned by the network and has a small computational consumption, it is considered to embed the SELayer module after the last CSP module of the YOLOv5s backbone network, as shown in Figure 2. Specifically, a channel attention SELayer module is added after the 4th BottleneckCSP structure in the backbone network, and the number of global average pooling channels is specified as 512, which is the number of channels of the output feature map of the BottleneckCSP. The SELayer module includes squeeze, excitation, and scale [29]. The squeeze operation compresses the original input features into a one-dimensional vector along the channel direction through global average pooling, that is, it compresses a 20 × 20 × 512 original input feature into a 1 × 1 × 512 feature to obtain the global information of each channel. The excitation operation uses two fully connected layers to reduce and increase the feature channels using the scaling factor r, where the scaling factor is 16. The first fully connected layer reduces the feature channel from 1 × 1 × 512 to 1 × 1 × 32 to reduce the computation, and the second fully connected layer recovers the feature channel from 1 × 1 × 32 to 1 × 1 × 512, and the scalar obtained from this is the weight of each channel. The scale operation weights and merges the weights of each channel obtained from the excitation operation (1 × 1 × 512) and the original input features (20 × 20 × 512), the outputs the weighted feature map, and uses the SELayer module to enhance the network’s learning of important channel feature information. The calculation formula of the SELayer module is as follows [29]:
where c represents the number of channels; H and W are, respectively, the height and width of the original input feature; is the original input feature; zc is the result after the squeeze operation; W1 and W2 are, respectively, the weights of the two fully connected layers used for dimension reduction and elevation; σ is the ReLU activation function; is the result after the first fully connected layer is activated by ReLU; is the Sigmoid activation function; r is the scaling factor, which is used to control the complexity of the model; nc is the weight obtained after the second fully connected layer is activated by the Sigmoid nonlinear activation; is the feature after weighted weighting; i and j are, respectively, the height and width coordinates of the feature pixel.
After this modification, the use of the channel attention mechanism enhances the network’s sensitivity to important feature channels and achieves the self-calibration of feature channels.
2.4. Improvement of Bounding Box Regression Loss Function
The loss function of YOLOv5s is composed of the following three parts: the category loss function, the confidence loss function, and the bounding box regression loss function. Among them, the bounding box regression loss function uses GIoU_Loss, which solves the problem of gradient disappearance when the IoU value is 0, when the prediction box and the real box have no intersection area. However, when the prediction box is completely wrapped by the real box, the GIoU_Loss of the prediction box at any position is the same, at which point GIoU degenerates into IoU and cannot distinguish its relative positional relationship.
In this study, the CIoU_Loss [30] loss function is used instead of the GIoU_Loss loss function, and it is trained until the loss converges. One penalty term of the CIoU_Loss loss function is the ratio of the distance between the center points of the prediction box and the real box to the diagonal distance of the minimum bounding rectangle box, which is used for distance measurement when there is a wrapping situation between the two boxes. Another penalty term is used for the measurement of the consistency of the aspect ratio of the box when the center points of the prediction box and the real box coincide. CIoU_Loss considers the overlapping area of the bounding box, the distance information of the center point of the bounding box, and the scale information of the aspect ratio, and can directly minimize the normalized distance between the prediction box and the real box, which speeds up the training convergence.
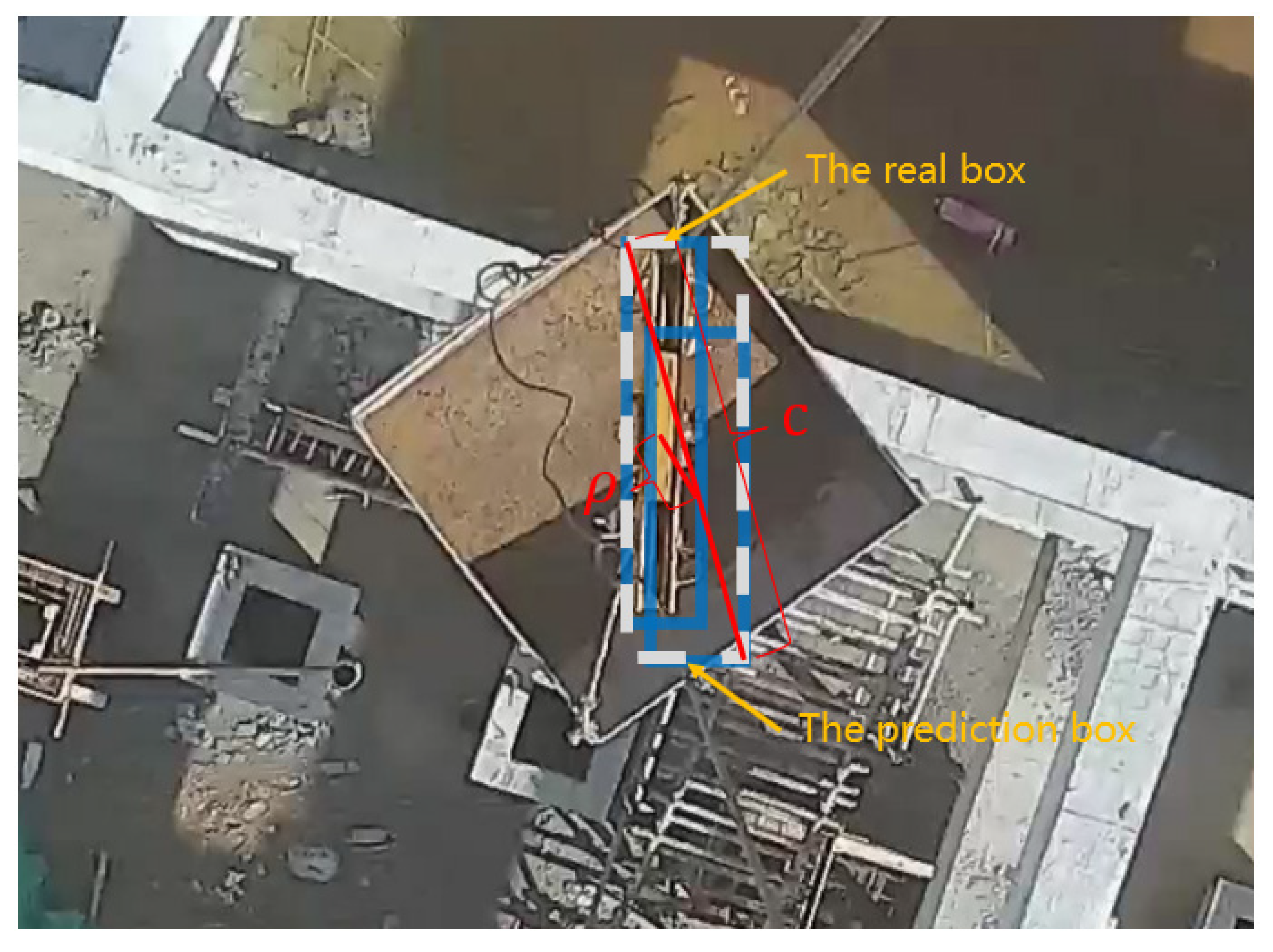
As shown in Figure 3, the upper left box is the real box, the lower right box is the prediction box, and the dashed box is the minimum bounding rectangle box of the prediction box and the real box. The calculation formula of the CIoU_Loss loss function is as follows:
where represents the prediction box; represents the real box; and are the width and height of the prediction box, respectively; and are the width and height of the real box, respectively; is the Euclidean distance between the center points of the prediction box and the real box; c is the diagonal distance of the minimum bounding rectangle box; v is a parameter to measure the consistency of the aspect ratio.
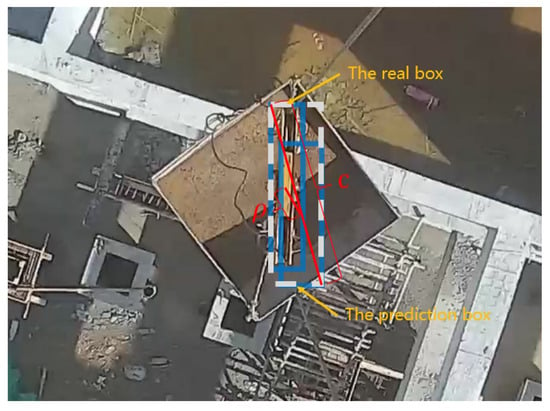
Figure 3.
Normalized distance between the prediction box and the real box.
2.5. Addition of False Detection Removal Module
Since the camera in this study is installed on the moving device above the hook, the position of the hook in the collected video is basically in the center of the image. Therefore, most of the false detections can be eliminated through the specialty of the detection box position information. The false detection removal module first uses the trained improved YOLOv5s model to identify the hook in the image to be detected, and determines whether the number of detected hooks is greater than 1. If it is not greater than 1, it outputs the detected hook result. If it is greater than 1, it retains the detection box closest to the image center point based on the position information of the hook detection box, thereby eliminating false detections to the greatest extent. The calculation formula is as follows:
where wte and hte are the width and height of the image to be detected; win and hin are the width and height of the image after input into the model; xl and yl are the coordinates of the upper left point of the i-th hook detection box in each detection image; xr and yr are the coordinates of the lower right point of the i-th hook detection box in each detection image; xi and yi are the central coordinates of the i-th hook detection box in each detection image; di is the Euclidean distance from the center of the i-th hook detection box in each detection image to the center of the detection image; p is the unique detection box finally retained.
2.6. Algorithm Training and Deployment
2.6.1. Model Training Environment Setting
To ensure the reliability of the experimental data, comparative experiments were conducted under the same hardware configuration and experimental parameters. The training environment is detailed as follows: the operating system is Windows 10, with an Intel® Core™ i5-10200H CPU @ 2.40 GHz processor and an NVIDIA GeForce GTX1650 graphics card. The deep learning framework employed is Pytorch 1.5, with the programming environment being Python 3.7. The use of CUDA 10.2 and Cudnn 7.6.5 allows for GPU acceleration. Initializing the network parameters through transfer learning can enhance the model’s generalization capability to a certain extent. The experimental parameters are shown in Table 2. During the training phase, the number of iterations (epochs) is set to 100, with a batch size of 4.

Table 2.
Experimental parameters.
2.6.2. Dataset and Data Annotation
The training dataset is one of the primary factors influencing the results of model training. In this study, datasets were constructed from video footage collected at a construction site in Jiangsu Province using tower crane monitoring equipment, with frames extracted to create the dataset. Specifically, the camera mounted on the trolley of the fixed tower crane was positioned directly above the hook to capture video under varying lighting and weather conditions. Through frame extraction, a total of 1300 images were obtained to build the hook image dataset, with 800 images used for training, 200 for validation, and 300 for testing. Some examples are shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
Sample images from dataset.
The dataset also encompasses a variety of scenarios, ranging from simple scenes with large, close-range targets to complex scenes with small, distant targets. To further prevent overfitting and enhance the model adaptability, the dataset was enriched through mosaic data augmentation, random image flipping, and color space HSV enhancement during the training process. The crane hook in the original images was manually annotated using the open-source labeling tool LabelImg [31] to create the label files. The crane hook targets in the training dataset are primarily located near the center of the images and occupy very few pixels in the images, typically representing small targets.
2.6.3. Model Performance and Comparison
Initial experiments were conducted to assess the performance of baseline models under identical training conditions, comparing the following three foundational models: YOLOv5s, YOLOv5m, and YOLOv5l. Model performance was evaluated using precision (P), recall (R), and average precision (AP) as metrics, with the model size and weight serving as criteria for assessing the ease of lightweight model deployment in engineering projects. Subsequent ablation studies aimed to fulfill the requirement of ensuring model lightweighting for convenient engineering deployment while maximizing the detection effectiveness. Under the same training conditions, various modifications based on the original YOLOv5s model were tested to determine the impact of adding individual modules and combinations thereof on model performance, leading to the selection of an improved YOLOv5s model. The crane hook test set was then used to evaluate both the original YOLOv5s model and the improved YOLOv5s model, comparing and analyzing the actual detection performance of the enhanced model.
The results of the baseline model performance comparison are presented in Table 3, where AP_0.5 refers to the AP value at an Intersection Over Union (IoU) threshold of 0.5, and AP_0.5–0.95 refers to the AP value calculated over an IoU threshold range from 0.5 to 0.95 in steps of 0.05. When sufficient training data are available, a more complex neural network structure with a greater number of parameters generally performs better. As indicated by Table 3, YOLOv5m shows a certain degree of improvement in all metrics compared to YOLOv5s, with increases of 1.15% and 2.66% in AP_0.5 and AP_0.5–0.95, respectively. Although there is a performance improvement, comparing the weights reveals that the YOLOv5m model is three times the size of YOLOv5s. The training results of YOLOv5l, which is approximately six times the size of YOLOv5s, are not even as good as those of YOLOv5s, suggesting that overly large models may underfit when trained on limited datasets, resulting in less-than-ideal model effectiveness.

Table 3.
Performance of different YOLOv5 models.
The results of the ablation experiments are shown in Table 4, with model-a (M-a), model-b (M-b), and model-c (M-c) corresponding to the addition of a small object detection layer, an improved bounding box loss function, and the embedding of a channel attention mechanism, respectively. It was observed that both the incorporation of a small object detection layer and the embedding of a channel attention mechanism led to an increase in model complexity and the number of computational parameters, reflected by an increase in the weight file by 1.5 MB and 0.6 MB compared to the original YOLOv5s model. Regardless of whether a single module or a combination of modules was used for model improvement, there was generally an enhancement in all metrics, improving the model’s ability to extract the features of small objects, such as crane hooks in monitoring videos. This improvement was achieved with a minimal increase in computational overhead, effectively addressing the issue of low detection accuracy for small objects and confirming the beneficial impact of the three improvement methods on the model performance. However, the combined optimization of the model using all three modules demonstrated the best detection performance, establishing it as the improved YOLOv5s model. The precision, recall, AP_0.5, and AP_0.5–0.95 values for the improved YOLOv5s model were 96.00%, 96.00%, 96.42%, and 62.02%, respectively, showing increases of 1.1%, 3%, 3.18%, and 2.99% compared to the original model, with only a 2 MB increase in the size of the weight file. Although there was a slight increase in the model size, it had a negligible impact on the detection efficiency.

Table 4.
Performance of different YOLOv5 models.
2.6.4. Comparative Analysis of Test Set Detection Effectiveness
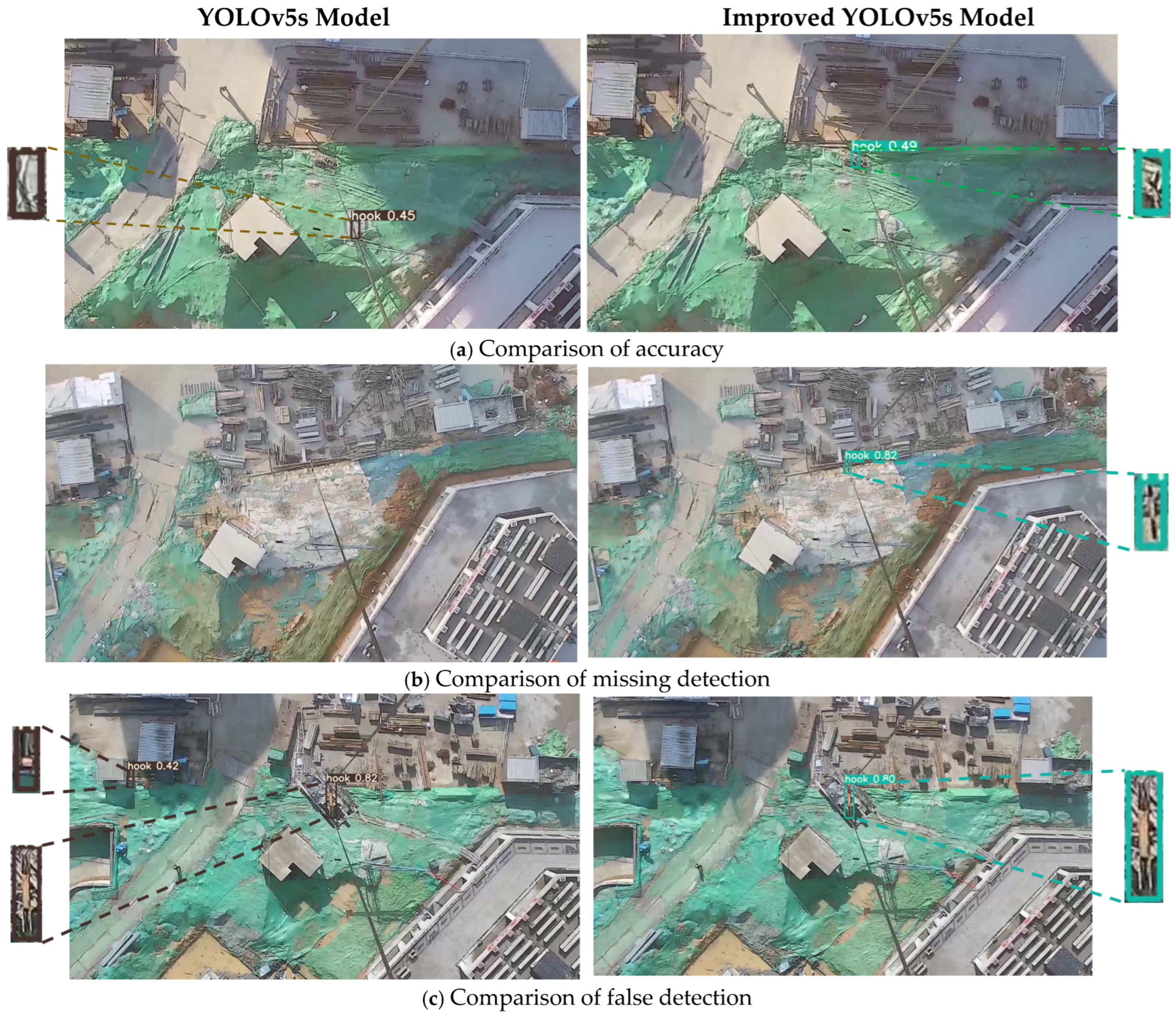
The crane hook test set was used to evaluate both the YOLOv5s model and the improved YOLOv5s model. Comparative results indicate that the YOLOv5s model, under conditions of long distances where target visibility is reduced, experiences missed and false detections of crane hooks, demonstrating an overall lower accuracy than the improved YOLOv5s model. As shown in Figure 5a, in cases where both models effectively identified the crane hook target, the improved YOLOv5s model’s prediction box more accurately encapsulates the crane hook target, indicating an enhanced localization capability of the detection network.
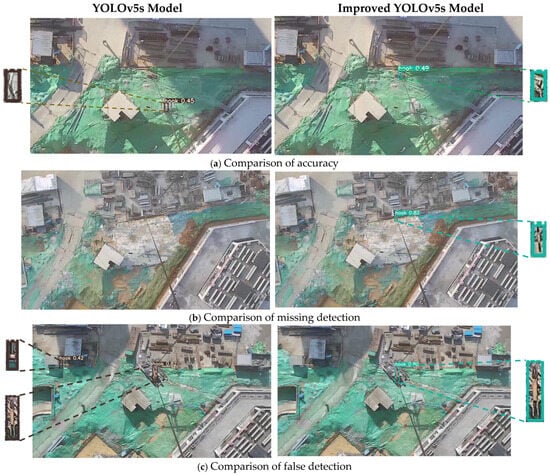

Figure 5.
Comparison of the detection effectiveness between the YOLOv5s and improved YOLOv5s models.
Figure 5b illustrates that the YOLOv5s model misses crane hook targets in scenarios with complex backgrounds and small objects, while the improved YOLOv5s model is capable of learning target features more comprehensively, reducing information loss, and effectively mitigating the issue of missed detections. In Figure 5c, due to the complexity of the construction site background, the YOLOv5s model incorrectly identifies objects with similar features to the crane hook as the crane hook itself. In contrast, the improved YOLOv5s model, by excluding the false-detection module, can effectively eliminate other interferences, maximally preserving correct detections.
Overall, in addressing the issue of the missed and false detections of small, distant targets against complex backgrounds, the improved YOLOv5s model can more accurately detect crane hooks and eliminate most false-detection frames, proving the effectiveness of the algorithm proposed in this study.
2.6.5. Comparative Analysis of Detection Effectiveness of Different Models
Comparative experiments were conducted between the improved YOLOv5s model and established object detection models (SSD, Faster RCNN, YOLOv3, and YOLOv4) under identical training conditions using the crane hook dataset. The results, as shown in Table 5, demonstrate that the improved YOLOv5s model holds a significant accuracy advantage over the other models. Even compared to YOLOv4, which had the highest accuracy among them, the improved model showed a performance increase of 6.3 percentage points in the mean AP. This clearly indicates the superior performance of the improved YOLOv5s model over other object detection models.

Table 5.
Performance of different object detection models.
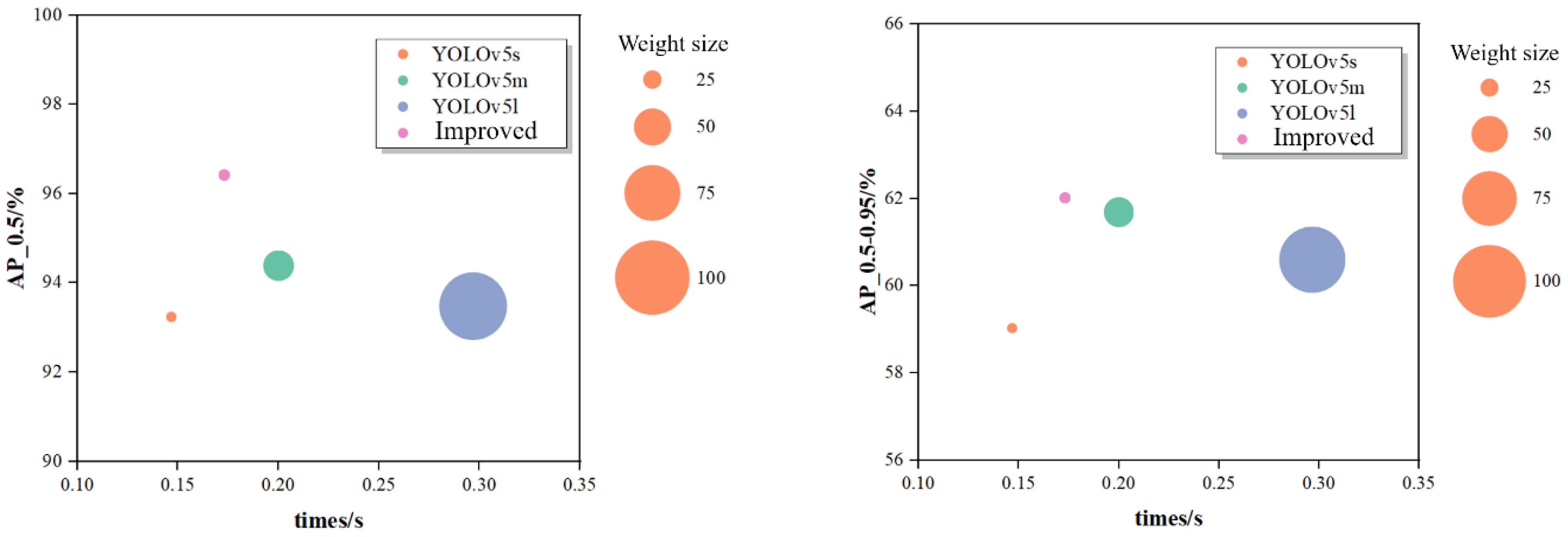
An analysis of the YOLOv5 series models in terms of average precision, detection speed, and memory usage on the crane hook dataset revealed the experimental results as depicted in Figure 6. The horizontal axis represents the average detection speed per image, while the vertical axis indicates the average precision (AP_0.5 and AP_0.5–0.95), with the size of the circles corresponding to the model’s size of the weight file.
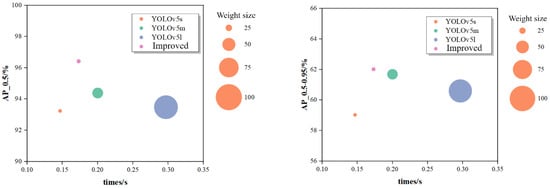
Figure 6.
Comparison of the overall performance of the YOLOv5 series model.
From the graph, it is evident that the improved YOLOv5s model scores the highest in both AP_0.5 and AP_0.5–0.95 values among the four models. The average time taken per image during the test set evaluation served as a measure of the detection speed, with the YOLOv5s, YOLOv5m, YOLOv5l, and improved YOLOv5s models recording times of 0.147 s, 0.201 s, 0.297 s, and 0.173 s, respectively. The improved YOLOv5s model, while slightly slower than the original YOLOv5s by 0.026s, was faster than both YOLOv5m and YOLOv5l by 0.027 s and 0.124 s, respectively, meeting the real-time requirements for engineering deployment. The sizes of weight files for the YOLOv5s, YOLOv5m, YOLOv5l, and improved YOLOv5s models were 14 MB, 41.2 MB, 90.7 MB, and 16 MB, respectively, indicating that, while YOLOv5m and YOLOv5l demand more memory resources and computational power, the improved YOLOv5s model is nearly as lightweight as the original YOLOv5s, with a more streamlined network suitable for practical engineering projects.
Overall, the improved YOLOv5s model achieves the best balance between detection accuracy and speed, offering significant advantages in detecting small objects against complex backgrounds while minimizing the network size and ensuring real-time performance, demonstrating superiority over current popular object detection models.
3. Identification of Dangerous Area for Object Striking Accident
3.1. Computation of Hook Height Based on Surveillance Video
The height of the hook is conventionally monitored by an altitude sensor. To make this paper self-contained, an interpolation function was developed to calculate the height of the hook based on surveillance video. Video of the hook uniformly rising from the lowest to the highest point is collected from the surveillance camera on the tower crane’s trolley. Video images are captured at the same time interval, and discrete data points with hook height information and hook size information are recorded. The actual height of the hook can be calculated based on the rising speed of the hook and the recorded time, and the hook size information can be calculated from the label file obtained by the LabelImg annotation tool [31], as shown in Equation (14):
where w is the width of the circumscribed rectangle of the hook; h is the height of the circumscribed rectangle of the hook; size is the diagonal size of the circumscribed rectangle of the hook.
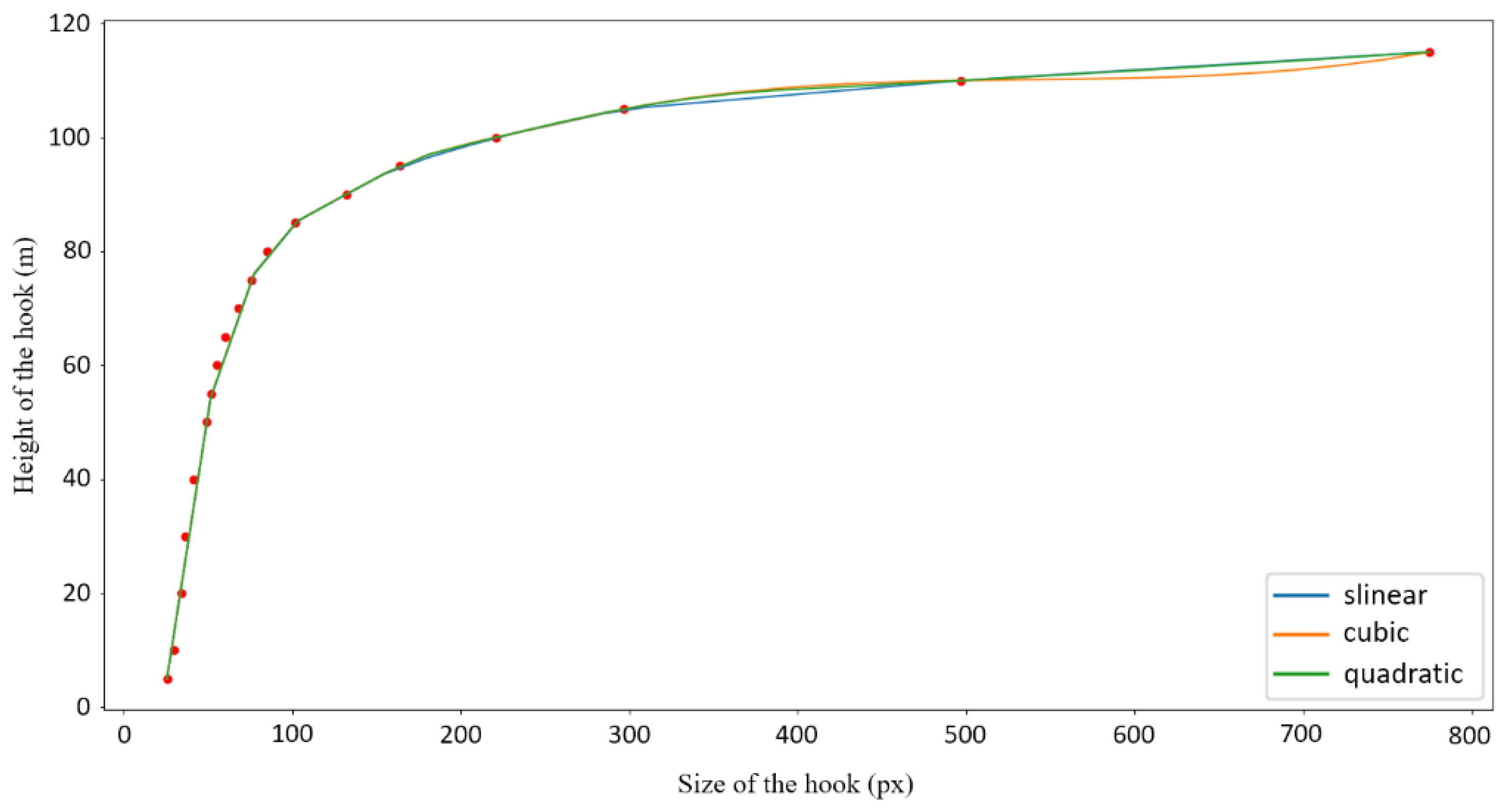
Based on discrete data points, a continuous interpolation function is constructed using the interpolation module scipy.interpolate in Python. The one-dimensional interpolation function (interp1d) is mainly used to compare the fit of the linear interpolation function (slinear), the second-order spline interpolation function (quadratic), and the third-order spline interpolation function (cubic) to the discrete data points, as shown in Figure 7. In the figure, the vertical axis is the actual height of the hook (unit: meters), and the horizontal axis is the hook size calculated from the label file. When the height of the hook is low, its size change in the surveillance image is not significant. However, when the height of the hook is high, its size change dramatically increases. The use of linear interpolation obviously cannot express the nonlinear relationship between the size of the hook and the height of the hook. From the fitting results of the second-order spline interpolation function and the third-order spline interpolation function to the data, the second-order spline interpolation function fits the discrete data points better. Therefore, the second-order spline interpolation is chosen as the interpolation function for the hook height (height) and hook size (size).
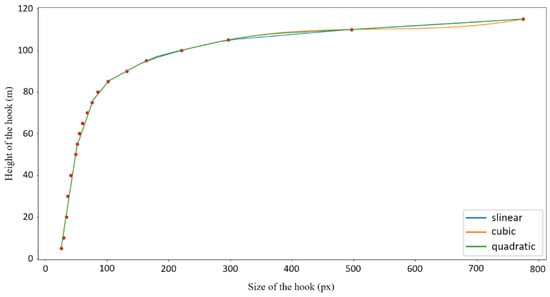
Figure 7.
Comparison of interpolation function. (red dots are measured data).
3.2. Definition of Falling Object Striking Area
There is a dynamic dangerous area moving with the hook directly below the hook. To avoid falling object striking accidents, construction personnel should be prohibited from operating in the dangerous area. Obviously, the size of the dangerous area is directly proportional to the height of the hook. When the height of the hook is high, the possible falling range of the object is larger. Therefore, the determination of the radius of the dangerous area should be appropriate. If the range of the dangerous area is defined as being too large, the risk warning will be too sensitive, affecting normal construction. If the range of the dangerous area is defined as being too small, the effect of the risk warning will be weakened, which is not conducive to the safety management of the construction site.
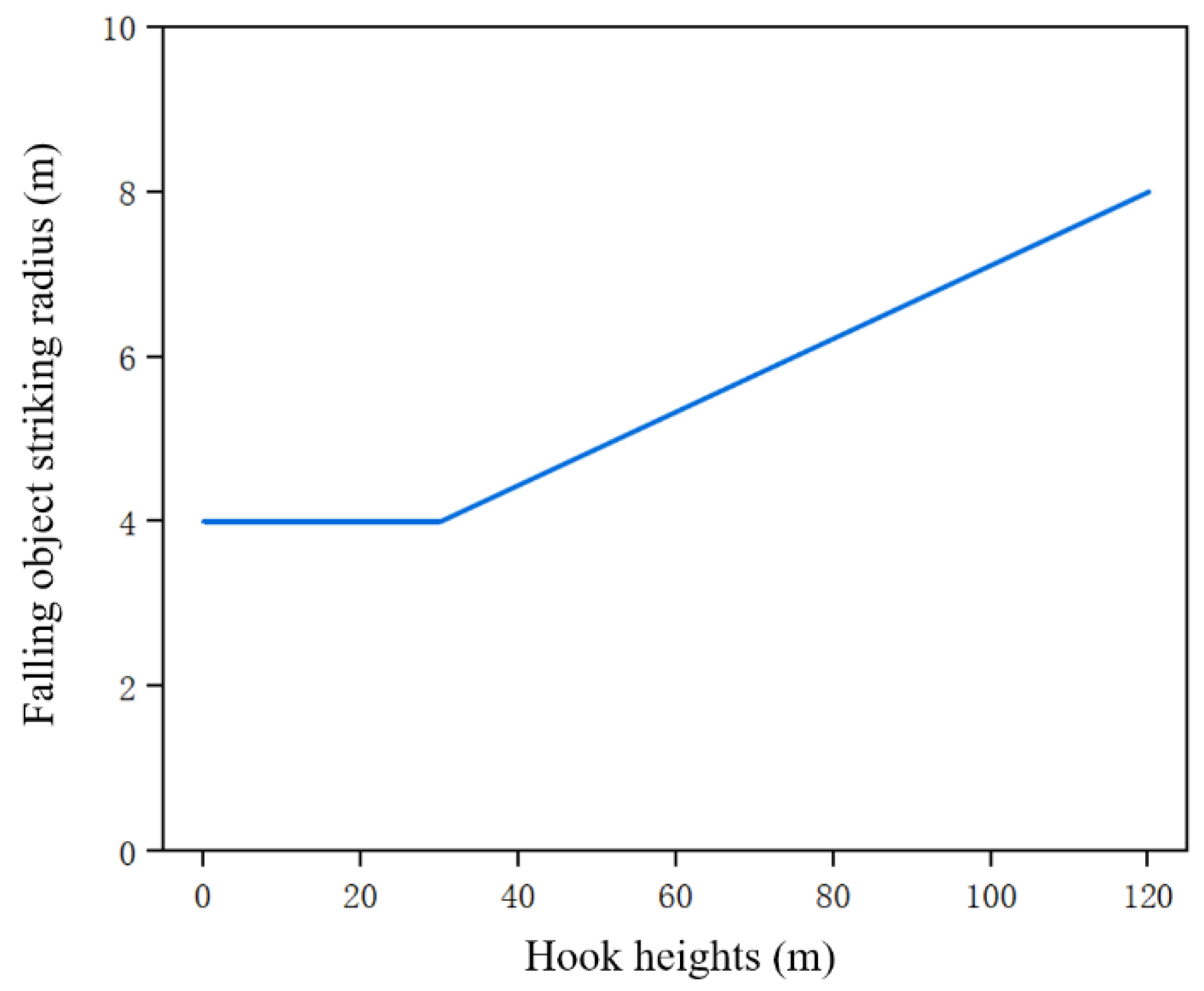
This study defined the possible falling radius according to the “Classification of Work at Heights” [32] regulation and the height of the hook. The function of the hook height and the falling object striking point range radius is shown in Figure 8. When the actual height of the hook is less than 30 m, the falling object striking radius is 4 m. When the actual height of the hook is greater than or equal to 30 m, the falling object striking radius linearly increases to 8 m with the increase in height.
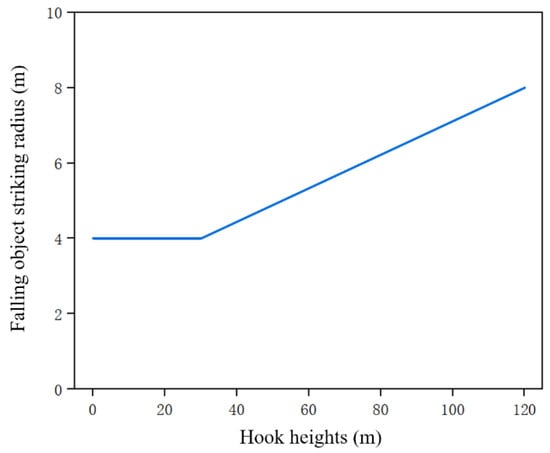
Figure 8.
Falling object striking radius based on hook heights.
The center of the falling object striking range is taken as half the distance between the center of the hook target and the center of the image, since the hook moves slightly in the center of the image due to wind disturbance. The calculation formula is as follows:
where x0 and y0 are the coordinates of the center point of the hook detection box; wte and hte are the width and height of the image to be detected, respectively; xc and yc are the coordinates of the center of the falling object striking area.
The center of the falling object striking area is obtained by the above formula, and the radius of the falling object striking area is obtained from Figure 8 based on the height of the hook. The falling object striking area is dynamically displayed in the tower crane screen to help the operator monitor the crane construction area. The detection speed of the enhanced YOLOv5s model for identifying the hook is illustrated in Figure 6, which indicates a detection time of approximately 0.173 s. Both calculations of the actual height of the hook and the impact area involve simple interpolation and require minimal time. Consequently, the total duration for the entire process is less than 0.3 s.
4. Risk Assessment of Construction Personnel
4.1. Collection and Statistical Analysis of Tower Crane Safety Accident Cases
Current risk assessment models for tower crane operation specified in regulations or standards are subjective and qualitative. Specifically, the time of the accident, frequency, severity, etc., are not taken into consideration. Therefore, to better clarify the occurrence mechanism of tower crane safety accidents, it is necessary to start with past tower crane safety accident cases, collect and collate accident investigation reports, and conduct statistical analysis on data such as the time of the accident, the frequency, and the severity. This helps explore the general characteristics and laws of tower crane safety accidents and lay a foundation for improving the tower crane risk assessment model.
4.1.1. Collection of Tower Crane Safety Accident Cases
The tower crane safety accident investigation report is compiled by the government organization in conjunction with technical experts, and provides descriptive statistics of tower crane safety accidents. It records in detail the process of the accident, the technical investigation results, the possible causes of the accident, and other specific information. From official websites of government departments at all levels, emergency management departments, safety production supervision and administration bureaus, and safety management networks, a total of 117 tower crane safety accident cases with detailed accident investigation reports from 2017 to 2022 were collected in China (with only 1 case in 2022), forming a tower crane safety accident database. Due to the timeliness of information released by the government and related media, the collected case database is not complete, but it has certain typicality and representativeness. By combing through each accident case in the tower crane safety accident database, identifying and extracting the attribute information of tower crane safety accidents [33], the general characteristics of the accident and the cost of the accident can be determined. The details of the accident attribute information are shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
Attribute information of tower crane safety accidents.
After analyzing the contents of the tower crane safety accident investigation report and extracting the attribute information of 117 tower crane safety accidents, according to the accident classification regulations of the “Regulations on Reporting and Investigation and Handling of Production Safety Accidents” [34], 102 cases are general accidents and 15 cases are major accidents. According to statistics, these 117 tower crane safety accidents resulted in a total of 170 deaths and 52 injuries, with an average of 1.45 deaths and 0.44 injuries per accident. The number of deaths is 3.2 times the number of injuries. There are 106 accidents with records of direct economic loss, and the total direct economic loss is about RMB 152.8 million (around USD 21.8 million), with an average direct economic loss of RMB 1.3 million RMB (about USD 0.19 million) per accident. Thus, once a tower crane safety accident occurs, it causes significant personal injury and death and huge economic losses to the personnel involved. Therefore, tower cranes have become one of the major hazards at construction sites.
Through the statistics of the information of 117 tower crane safety accidents that occurred in China in the past five years, according to the geographical division of China, the number of tower crane safety accidents in the northeast, northwest, north, central, south, east, and southwest are 2, 5, 6, 12, 38, 44, and 10, respectively. Among them, the eastern and southern regions belong to the areas where accidents frequently occur, while other areas are areas where accidents occur less frequently, because these two regions have faster economic development and active construction activities, and they are in the coastal areas, which are easily affected by adverse weather such as typhoons. The number of tower crane safety accidents in the first, second, third, and fourth quarters of the year are 11, 39, 35, and 32, respectively, indicating that the collected tower crane safety accident data cover all areas and all time periods, and the analysis of accident characteristics is universal. The following selects the accident type, accident stage, and accident time to statistically analyze the accident cases.
4.1.2. Statistical Analysis by Accident Type
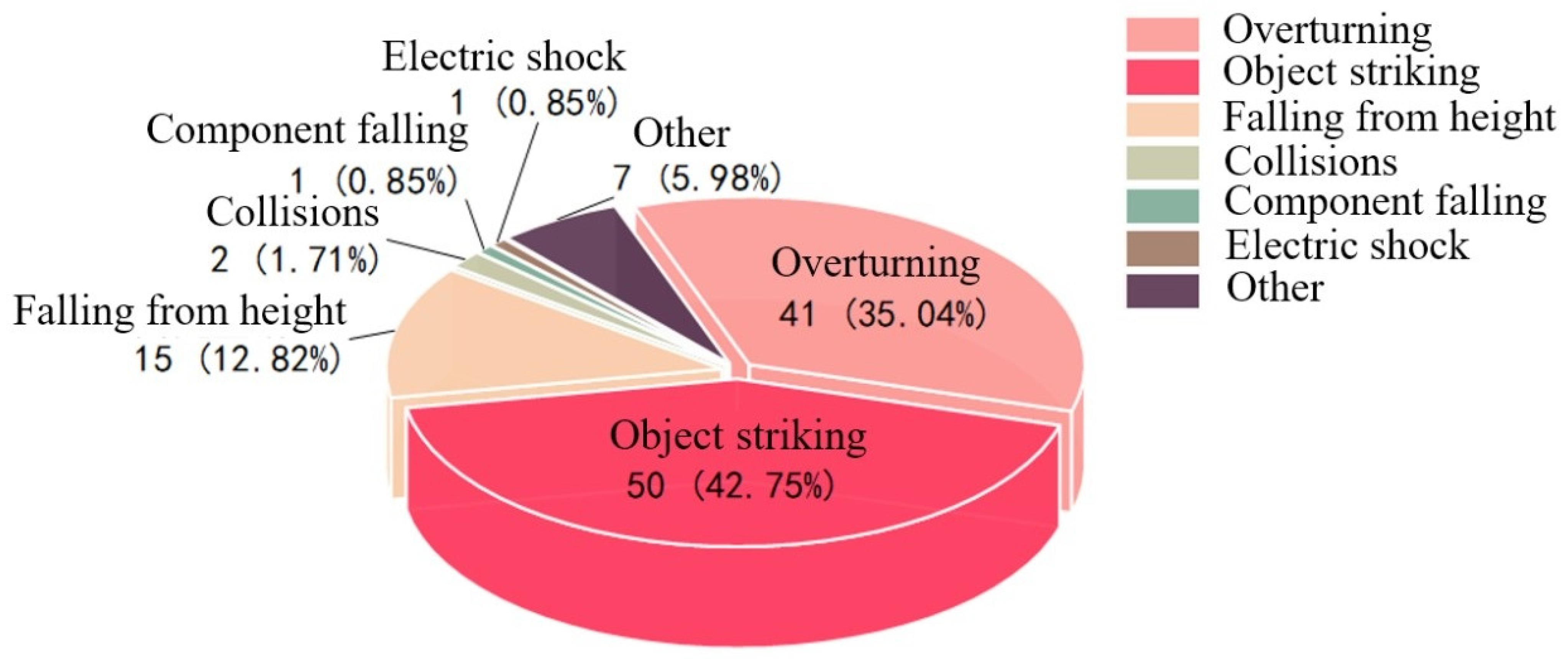
The 117 tower crane safety accidents are divided into the following seven types: tower overturning, falling object striking, falling from height, collisions, component falling, electric shock, and others (each type of accident is relatively independent). The statistical distribution of the tower crane safety accident case database in this study by type of accident is shown in Figure 9. The results show that the most frequent occurrence is falling object striking accidents, with a total of 50 cases, accounting for 42.74% of the total number of tower crane safety accidents, which is comparable to tower overturning accidents, with a total of 41 cases, accounting for 35.04% of the total number of tower crane safety accidents. The sum of the two accounts for as high as 77.78% of cases, which are the main types of accidents affecting tower crane safety. Therefore, this article focuses on the prevention of falling object striking accidents. There were 15 cases of workers falling from high places and 7 cases of other accidents, ranking third and fourth, respectively. There was a total of four cases of collision accidents, tower crane component falling accidents, and electric shock accidents, and the frequency of occurrence was relatively low, accounting for less than 5%.
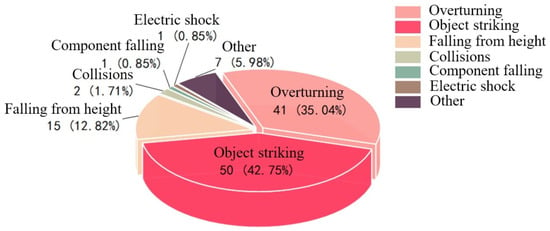
Figure 9.
Percentage of tower crane safety accident types (data are listed in the Supplementary Material).
4.1.3. Statistical Analysis by Accident Stage
Among the 117 tower crane safety accidents, referring to the “Technical specification for safety installation operation and dismantlement of tower crane in construction” (JGJ196-2010) [35], tower crane safety accidents are divided into the installation stage (including top-lifting and adding-sections operation), the operation stage (including daily maintenance), and the dismantling stage (including the lowering sections operation).
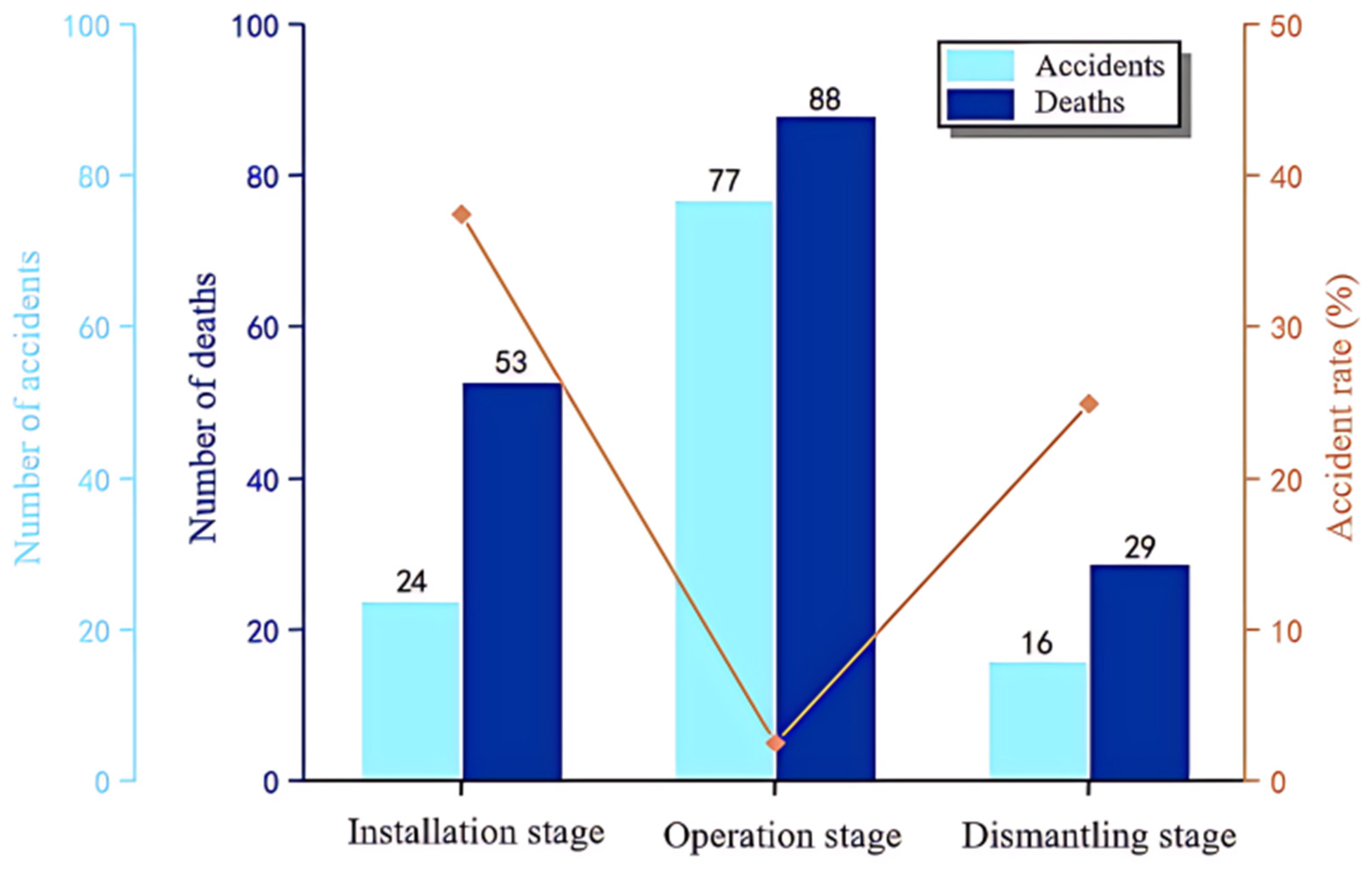
According to the data, the number of accidents, the number of deaths, and the rate of major accidents in each stage are shown in Figure 10. The results show that the number of accidents (77 cases) and the number of deaths (88 people) during the use phase are the highest, accounting for 65.8% and 51.8% of the total, respectively, which is significantly higher than the installation phase and the dismantling phase. This indicates that most tower crane safety accidents occur during the daily operations of the tower crane. The accident occurrence rates in the installation phase and the dismantling phase are 20.5% and 13.7%, respectively, which are obviously lower than the use phase, but the rates of major accidents are 37.5% and 25%, respectively, which are much higher than the 2.6% major accident rate in the operation phase. This indicates that each accident in the installation and dismantling phase causes more serious casualties, because the installation and dismantling phases mainly involve high-altitude and high-difficulty operations. The connection of the tower body is weak, and the safety risk is high, which can easily cause tower crane overturning accidents and cause large-scale casualties.
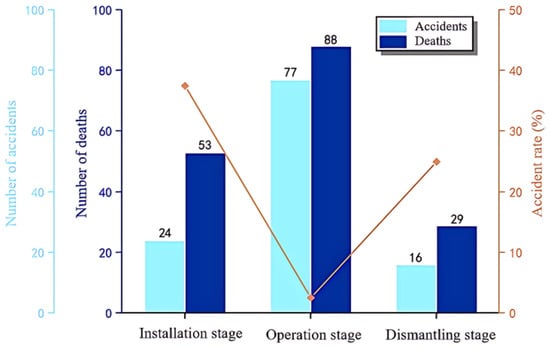
Figure 10.
Number of accidents, number of deaths, and major accident rate at each stage (data are listed in the Supplementary Material).
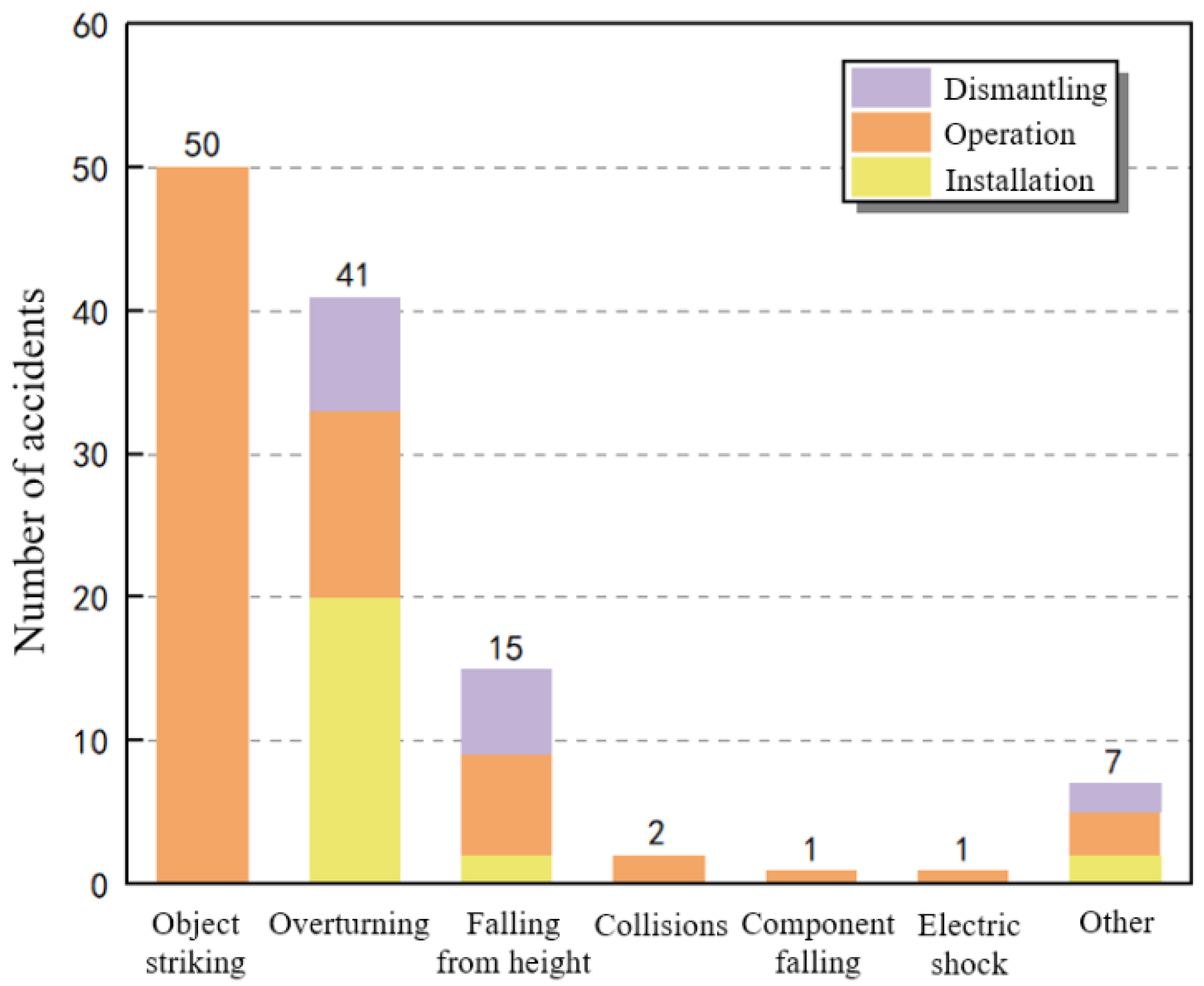
The different types of accidents that happened in each stage are shown in Figure 11. The results show that there were 50 cases of falling object striking accidents, all of which occurred during the operation stage. This is because, when the tower crane is carrying out horizontal and vertical transportation operations daily, improper operation by construction personnel or the presence of a force majeure may cause the connection between the tower crane and the hoisted object to be unreliable, ultimately leading to the occurrence of falling object striking accidents. During the installation and dismantling stages, transportation operations are suspended, and the possibility of falling object striking accidents is extremely small. There were 41 cases of tower overturning accidents, of which 20 occurred during the installation stage, 13 during the operation stage, and 8 during the dismantling stage. Most overturning accidents occur during the installation and dismantling phases, when the tower structure is the weakest and the possibility of overturning accidents is greater. There were 15 cases of worker falling from high places accidents, of which 2 occurred during the installation stage, 7 during the operation stage, and 6 during the dismantling stage. During the installation and dismantling phases, construction workers work at high altitudes for a long time. Accidental falls may occur when safety protection devices are not in place. Accidental falls may occur when tower crane operators climb up and down the tower body during the operation stage. The probabilities of collision, component falling, electric shock, and other accidents are relatively low, most of which occur during the operation stage, which is related to the longer time span of the operation stage.
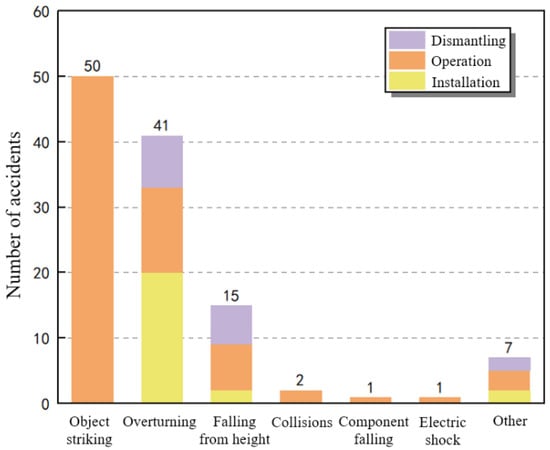
Figure 11.
Different accident types that happened in each stage (data are listed in the Supplementary Material).
In summary, falling object striking accidents are the main type of tower crane safety accidents, and the number of accidents and casualties during the operation stage are far higher than during the installation and dismantling stages. Falling object striking accidents basically occur during the operation stage, so research on the prevention of falling object striking accidents during the operation stage is particularly important.
4.1.4. Statistical Analysis by Accident Time
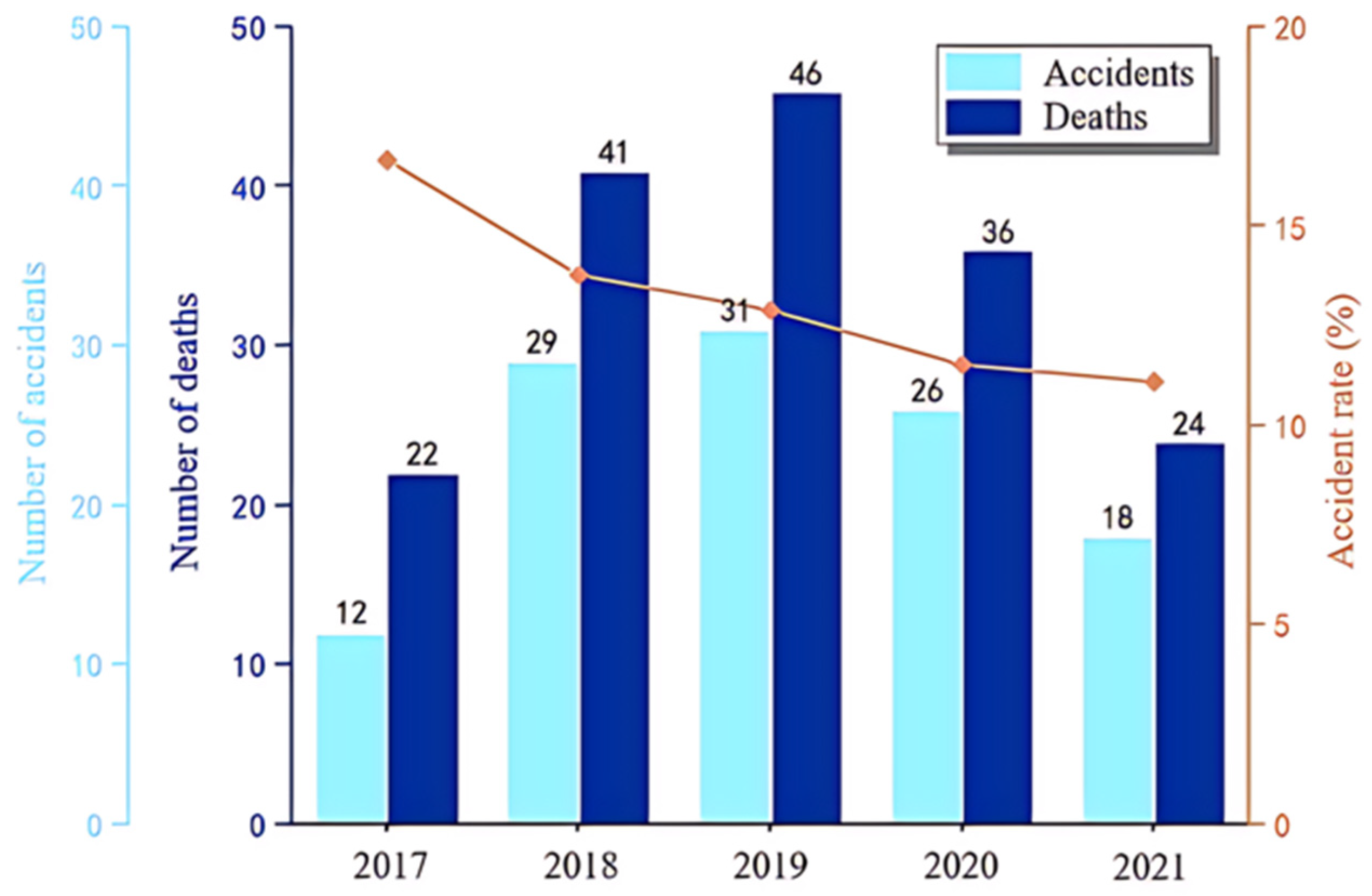
The number of tower crane safety accidents, the number of deaths, and the rate of major accidents in China from 2017 to 2021 are summarized and statistically analyzed, as shown in Figure 12. The number of tower crane safety accidents were 12, 29, 31, 26, and 18, in succession, and the number of deaths were 22, 41, 46, 36, and 24, respectively. The number of tower crane safety accidents and the number of deaths in China in the past five years have shown a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. After 2019, the safety production management work on the construction site has been effective, and the accident rate in 2020 and 2021 has significantly decreased. Of course, it does not rule out the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, the rates of major tower crane safety accidents from 2017 to 2021 were 16.67%, 13.79%, 12.9%, 11.54%, and 11.11%, respectively. The decreasing rate of major accidents since 2017 means that the safety management level of construction sites has been steadily improved.
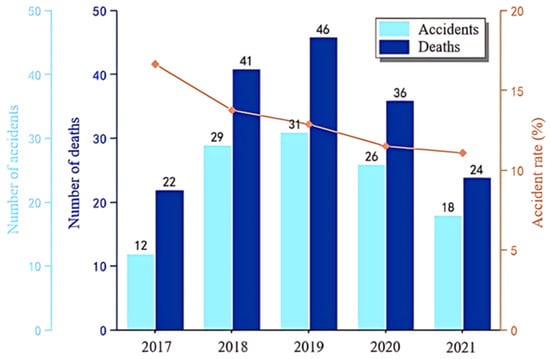
Figure 12.
The number of tower crane safety accidents, the number of deaths, and the rate of major accidents in China from 2017 to 2021 (data are listed in the Supplementary Material).
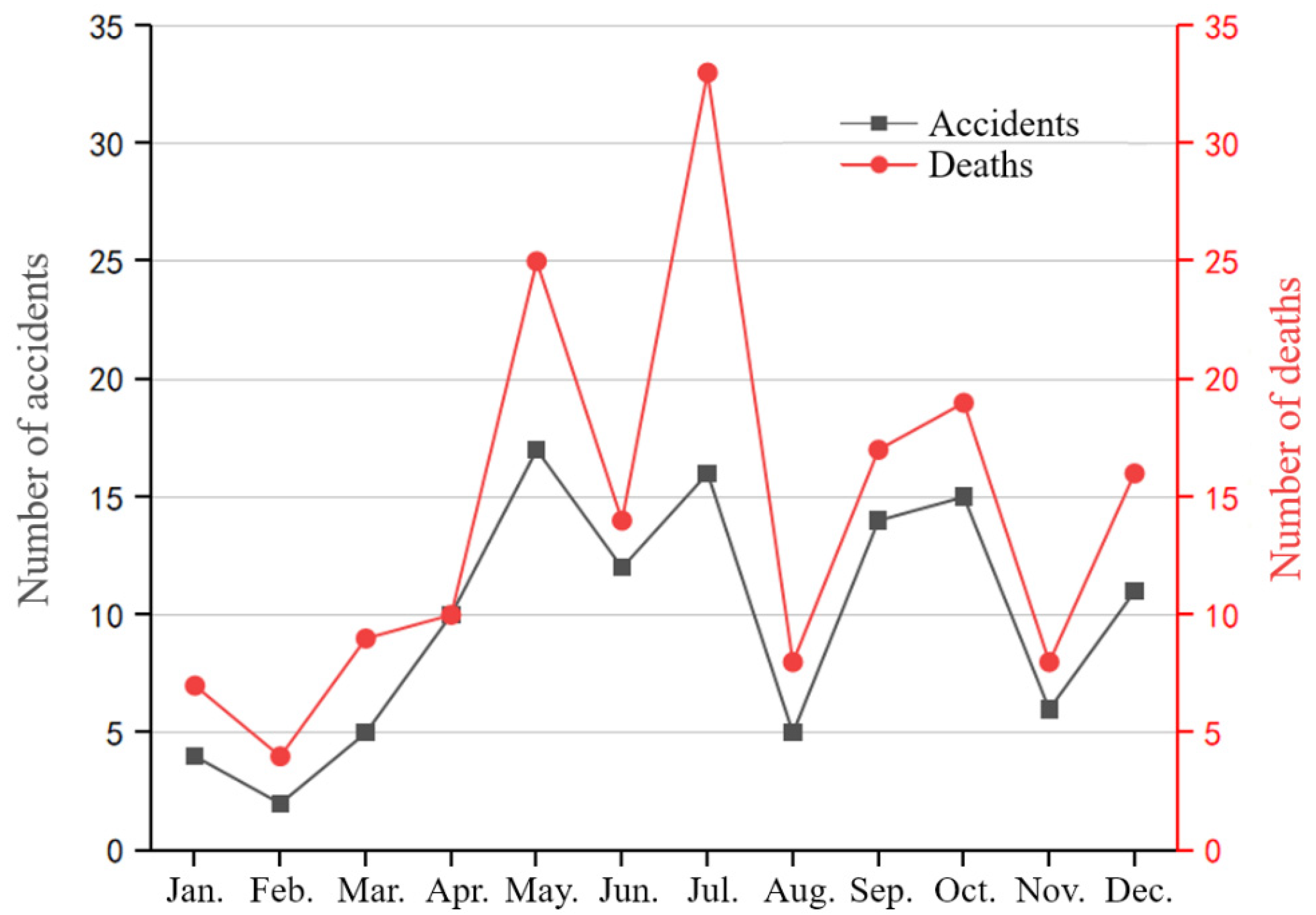
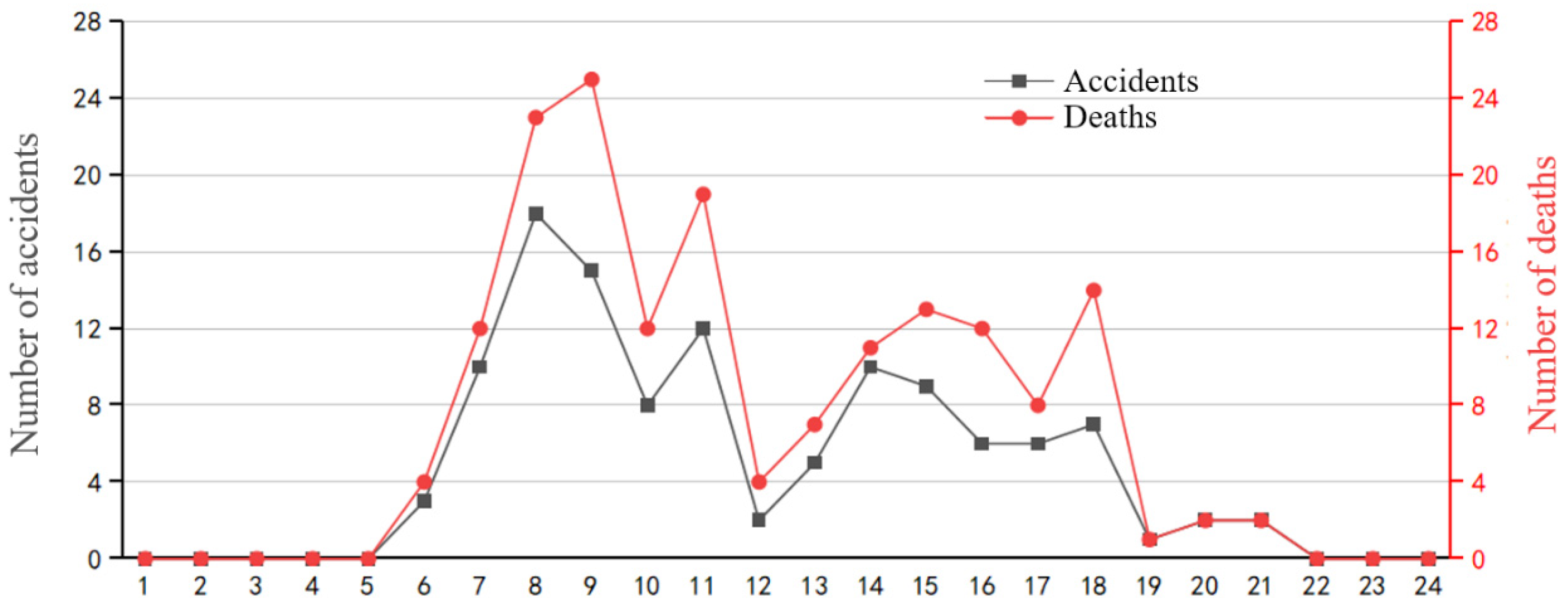
The number of tower crane safety accidents and the number of deaths in China from 2017 to 2021 are summarized and statistically analyzed by the month, as shown in Figure 13. The number of tower crane safety accidents and the number of deaths each month fluctuate to a certain extent, which is related to the season and climate. Less than five tower crane safety accidents occurred in January and February. This is because the weather is cold in most areas in winter and it is close to Chinese New Year. Most construction activities are suspended, and the rate of tower crane safety accidents is significantly reduced. From March to May, as the weather gradually warms up and construction projects resume work and production, the number of tower crane safety accidents and the number of casualties show an upward trend. Among them, May is the month with the most accidents, with a total of 17 tower crane safety accidents. There was a slight improvement in June, and the number of accidents relatively decreased. This might be because June is “Safety Production Month” every year. The promotion of safety production knowledge has further enhanced the safety awareness of each participant, effectively reducing production accidents. In July, the continuous high-temperature and heavy outdoor work, plus the hot environmental conditions, put related workers under unfavorable conditions for high-risk operations. It is a high-accident month, causing the most deaths, up to 33 people. The highest temperature is in August. The government issued a “High Temperature Time-Limited Stop Work Order” that effectively avoids the high-temperature period, which, to a certain extent, guarantees the safety of workers, and the number of safety accidents has decreased. In September and October, the temperature is suitable, the tower crane operation activities on the construction site increase, and the risk of accidents increases accordingly. In November, it is close to winter, construction activities decrease, and the rate of tower crane safety accidents is relatively reduced. In summary, May and July are the months with frequent tower crane safety accidents in China, and June, September, October, and December are the months with high tower crane safety accidents. The tower crane safety management work on the construction site should be strengthened during these periods.
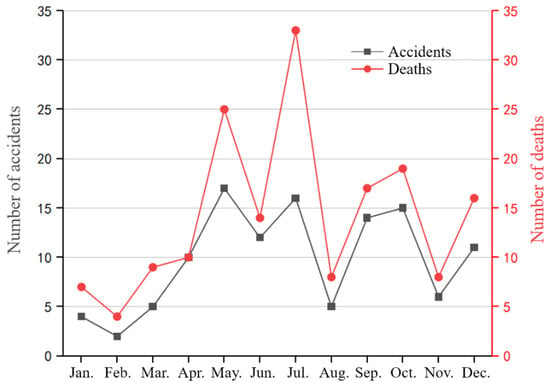
Figure 13.
The number of tower crane safety accidents and the number of deaths in China from 2017 to 2021 (analyzed by the month; data are listed in the Supplementary Material).
The number of tower crane safety accidents and the number of deaths in China from 2017 to 2021 are summarized and statistically analyzed within 24 h of a day, as shown in Figure 14. The most tower crane safety accidents occur during the day time. The period from 7:00 to 11:00 in the morning is the time when the most accidents occur in a day. Because it is the peak period of tower crane operations, the range of operations for each process overlaps, and the intensity of lifting operations is relatively high, which directly leads to a higher number of tower crane safety accidents. From 12:00 to 13:00, during the lunch break, most construction workers stop work and rest, tower crane operations are significantly reduced, and the accident rate decreases accordingly. The period from 14:00 to 18:00 in the afternoon is also a high-accident period. Continuous operations consume the energy of construction workers, which can easily make them feel tired, and the awareness of safety risk prevention is reduced, adversely affecting the safety of tower crane operations. In addition, there are fewer tower crane safety accidents during the night periods from 1:00 to 6:00 and 19:00 to 24:00, when tower crane operations are not scheduled. From the figure, 8:00, 9:00, and 11:00 are the peak times for tower crane safety accidents. The tower crane safety management work on the construction site should be strengthened during these periods.
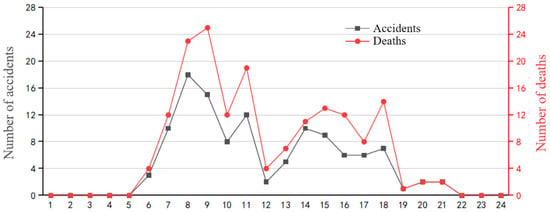
Figure 14.
The number of tower crane safety accidents and the number of deaths in China from 2017 to 2021 (analyzed within 24 h of a day; data are listed in the Supplementary Material).
4.2. Improved LEC Method for Risk Assessment
4.2.1. Traditional LEC Method
The LEC method [36] is a semi-quantitative risk assessment method for operators in potentially dangerous environments, and it is often used in hazard source evaluations at construction sites. The traditional LEC method quantitatively evaluates the danger level of operators by multiplying the values of three factors, and the calculation formula is as follows:
where D is the danger level of operating conditions; L (likelihood) is the possibility of an accident occurring; E (exposure) is the frequency of exposure to a dangerous environment; C (consequence) is the possible outcome of an accident or dangerous event. Typically, the values of factors related to system risk are determined based on empirical grading. The grading values of the three factors are shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Grading values of the LEC.
The values of the three factors are determined by referring to Table 7 according to the actual situation, and the danger level D value of the operators can be obtained through Equation (17). The risk level based on the operation danger level D is shown in Table 8. The traditional LEC method is easily affected by individual subjective factors in practical application, and the evaluation result has certain limitations. In this paper, it is corrected according to the statistical analysis of past accidents.

Table 8.
Grading values of the LEC.
4.2.2. Improvement Based on Statistical Analysis of Past Accident Cases
Considering the risk assessment of falling object striking accidents during the tower crane operation stage, improvements are made to the LEC method according to the statistical analysis in Section 4.1. The number of tower crane accidents is related to time, and the occurrence rate is slightly different at different months and times. Thus, the risk of tower crane accidents varies with time. Therefore, when evaluating the risk of workers, a time correction factor is added. According to the frequent-accident months, high-accident months, frequent-accident times, and high-accident times obtained from the statistical results in Section 4.1.4, the correction factor values at different months and times are determined. The calculation formula of the revised risk assessment method is shown as follows:
where the definition of D, L, E, and C are the same as in Equation (17), R1 is the correction factor for the month, and R2 is the correction factor for the time.
In Equation (18), L is the possibility of an accident occurring. Since it is applied in the risk assessment of a specific tower crane falling object striking accident scene, the value is taken as one according to the original definition of the formula (Table 7), indicating that the possibility is very small and unexpected. As discussed in Section 4.1.1 and Section 4.1.2, only 117 accidents occurred over a five-year period (2017–2022), with 42.74% of them involving falling objects.
E is the frequency of exposure to a dangerous environment. Being exposed in a dangerous environment, the closer to the center of the falling object striking area, the greater the probability of workers being injured, and the corresponding E value is higher. When the position of the worker in the circular falling striking area moves from the center to the edge, the E value correspondingly decreases from 10 to 0. Consider introducing the probability density function of the standard normal distribution for quantifying the E value. Specifically, establishing a corresponding function between the distance of the worker from the center of the danger area and the probability density function of the standard normal distribution.
The probability density function of the standard normal distribution is given in Equation (19). Based on established principles, the domain interval [0, 3] corresponds to a range in the codomain that decreases from to , as follows:
where x is a random variable and represents the probability density.
By linearly correlating the value of x with the distance between the worker and the center of the danger area, and by aligning the codomain range with the defined range of E ([0, 10]), the calculation formulae are as follows:
where d denotes the distance of the worker from the center of the danger area, R is the radius of the danger area, E represents the frequency of exposure to the dangerous environment, and Emax is the maximum value of E, set at 10.
After recognizing the falling object striking area and the position of the worker using the improved YOLOv5s model, the distance of the worker from the center of the danger area is calculated, and the E value is determined according to Equation (19) to Equation (21).
C is the possible consequence of an accident, and its value is approximately determined by the calculated hook height. The C value is 5 when the hook height is below 20 m, the C value is 15 when the hook height is between 20 and 50 m, and the C value is 40 when the hook height is above 50 m.
R1 is the month correction factor. By analyzing falling object strike accidents, it was found that there are frequent-accident months in May and July. Therefore, the R1 value is 1.2 for the frequent-accident month, the R1 value is 1.1 for the high-accident months of June, September, October, and December, and the R1 value is 1.0 for the other months. Similarly, R2 is the time correction factor. The R2 value is 1.2 for the frequent-accident times at 8 o’clock, 9 o’clock, and 11 o’clock. The R2 value is 1.1 for the high-accident times at 7 o’clock, 10 o’clock, 13 o’clock, 14 o’clock, 15 o’clock, 16 o’clock, 17 o’clock, and 18 o’clock. The R2 value is 1.0 for the other times during a day.
Finally, according to the project’s ability to withstand the risk of falling object strikes, the highest level of danger that is willing to be tolerated is determined (Dmax = 50). When the real-time calculated risk level D value of the worker exceeds the safety alarm threshold Dmax, the worker in the detection frame is highlighted in real-time in the tower crane monitoring screen to give a warning, thereby reminding the tower crane operator and the safety management personnel of the construction site to respond in time and require them to exit the danger area.
5. Model Deployment and Application
5.1. Hardware Platform Setup
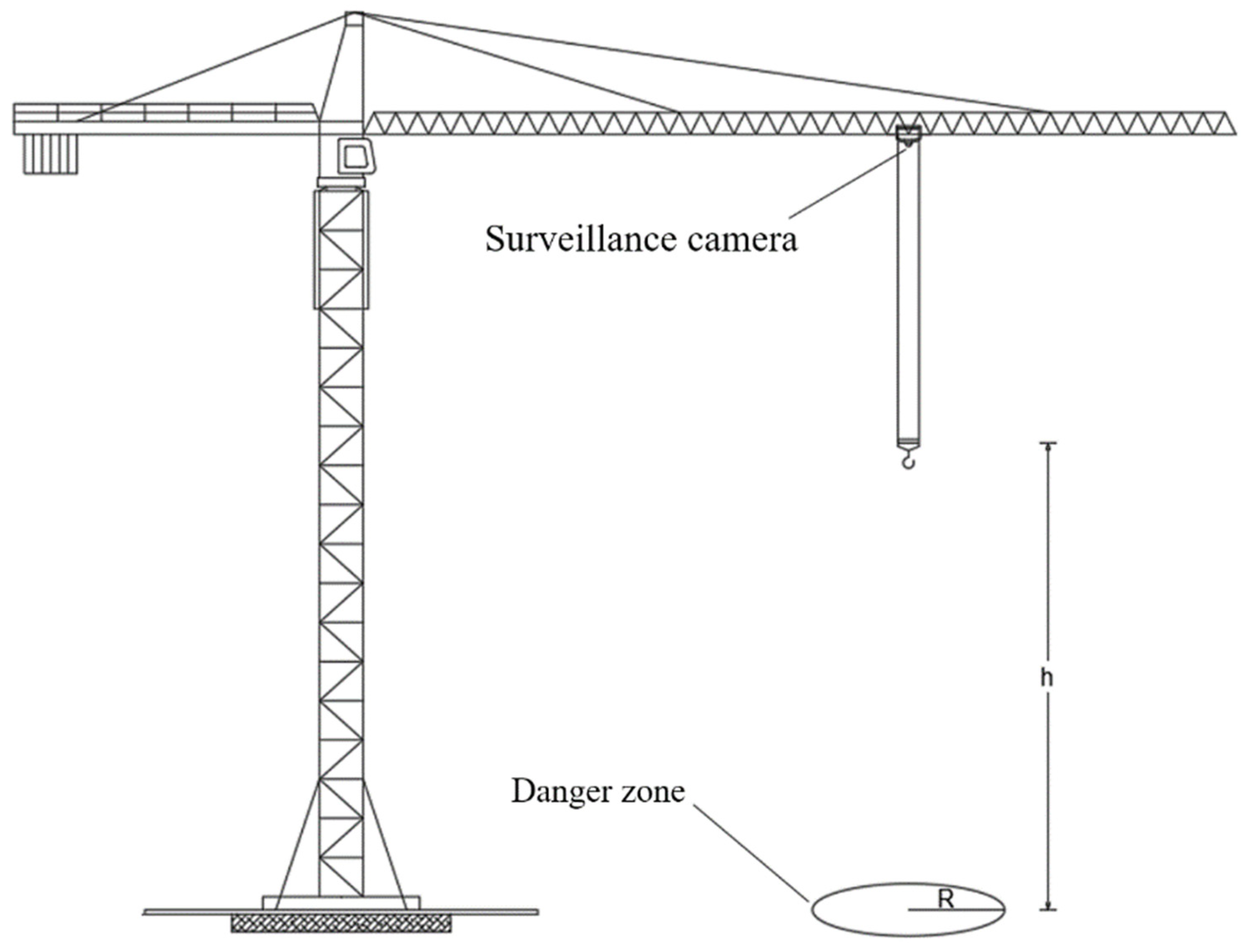
In order to collect and transmit video data from the construction site, a surveillance camera is mounted beneath the trolley of the tower crane, ensuring that the camera moves in sync with the trolley’s movements. The installation location is depicted in Figure 15. The camera is set to continuously capture the operations of the crane hook, with a fixed shooting angle that keeps the crane hook target at the center of the image frame. The resolution of the captured images is not less than 1920 × 1080 pixels.
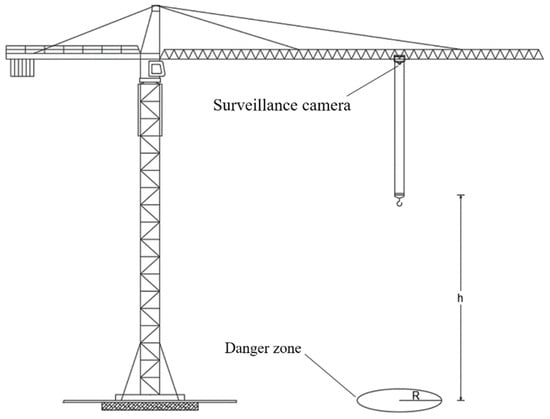
Figure 15.
Schematic of the hardware setup.
A charging device is securely attached to the main arm of the tower crane. When the trolley is retracted, the camera docks with the charging device to ensure it is adequately powered. A wireless bridge is installed at an appropriate location to facilitate the wireless transmission of video data to computer systems, enabling remote access to the monitoring platform. This completes the setup of the hardware platform. This setup is designed to ensure the continuous, high-quality monitoring of crane operations, enabling precise and real-time data collection for analysis or remote observation.
5.2. System Workflow
The workflow for the data analysis and processing based on the improved YOLOv5s for visual recognition algorithm assisted safety management of tower crane is as follows:
- (1)
- Training dataset construction: Utilize surveillance cameras to collect video data under various natural environmental conditions. By extracting frames from these videos, images of crane hooks and construction personnel are obtained to form an image dataset. These images are then annotated using the LabelImg tool.
- (2)
- Interpolation function determination: Capture a segment of video data of the crane hook moving uniformly from the lowest to the highest point. Extract images at equal time intervals and use the time information to determine the crane hook’s height. Record discrete data points containing the crane hook’s height and size, and apply a second-order spline curve interpolation method to generate continuous functions, obtaining interpolation functions for both the crane hook’s height and size.
- (3)
- Target detection training phase: Train the improved YOLOv5s model using the constructed dataset of crane hooks and construction personnel images. The training process generates a weight file that records the model parameters, with Section 2.6.1 providing a reference for the training environment and parameters.
- (4)
- Elimination of false detections: Specify the video path for target detection and use the trained weight file for the real-time detection of crane hooks and construction personnel in the surveillance video. Employ the false detection elimination module within the detection model to remove any falsely detected crane hooks, retaining only the actual crane hook target.
- (5)
- Crane hook height calculation: Utilize the crane hook height calculation module within the detection model. This module uses the crane hook target size information and the interpolation function to calculate the actual height of the crane hook.
- (6)
- Dangerous area demarcation: Employ the dangerous area identification module within the detection model. This module defines the dangerous area directly beneath the crane hook in the surveillance video, which is based on the method for determining the range of falling object striking points. The dangerous area is marked with a red circle and is displayed in real-time in the surveillance video.
- (7)
- Danger warning display: Use the construction personnel risk assessment module within the detection model to calculate the risk level of construction personnel in the surveillance video in real-time. This calculation is based on the crane hook height, personnel location, and monitoring time, according to the modified LEC method. Determine the alarm threshold on the basis of balancing the operational efficiency and safety. When the threshold is exceeded, the model highlights the detected frame of the construction personnel in the tower crane monitoring screen with a red marker as a warning. Also, an alarm is sent to the worker via wearable devices.
5.3. Case Study
The system was deployed at a construction site in Jiangsu Province for practical testing. The buildings at this site are approximately 150 m tall, and the primary construction phase spans one and a half years, covering seasons from spring to winter. This timeframe provides suitable conditions for testing the tower crane lifting equipment and safety control system.
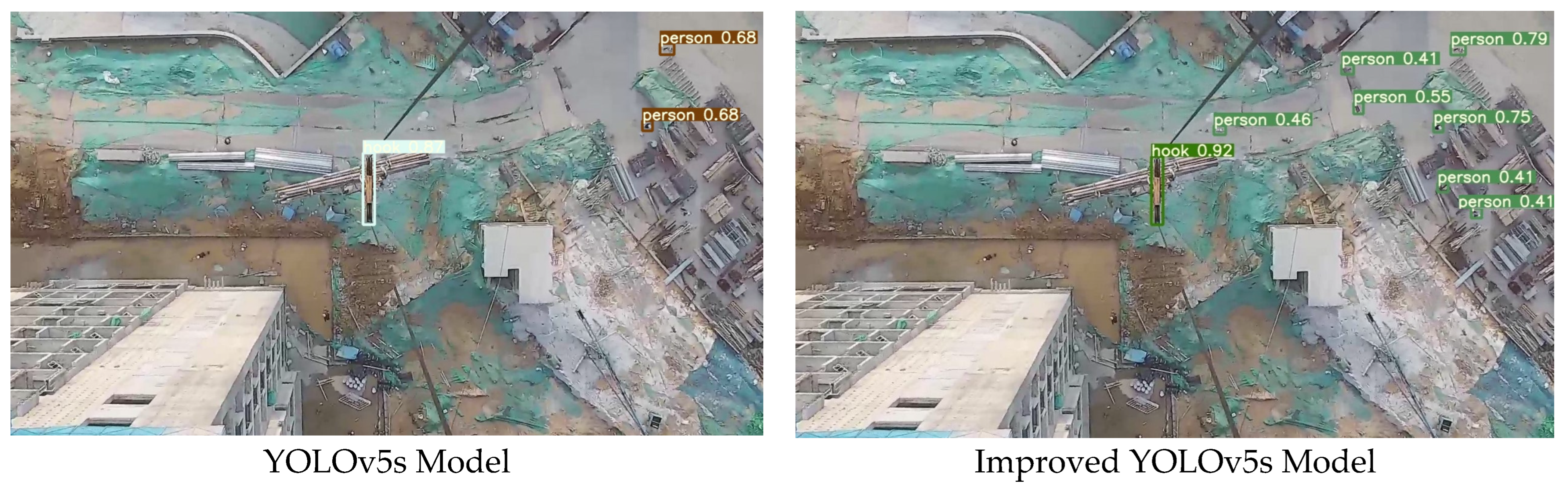
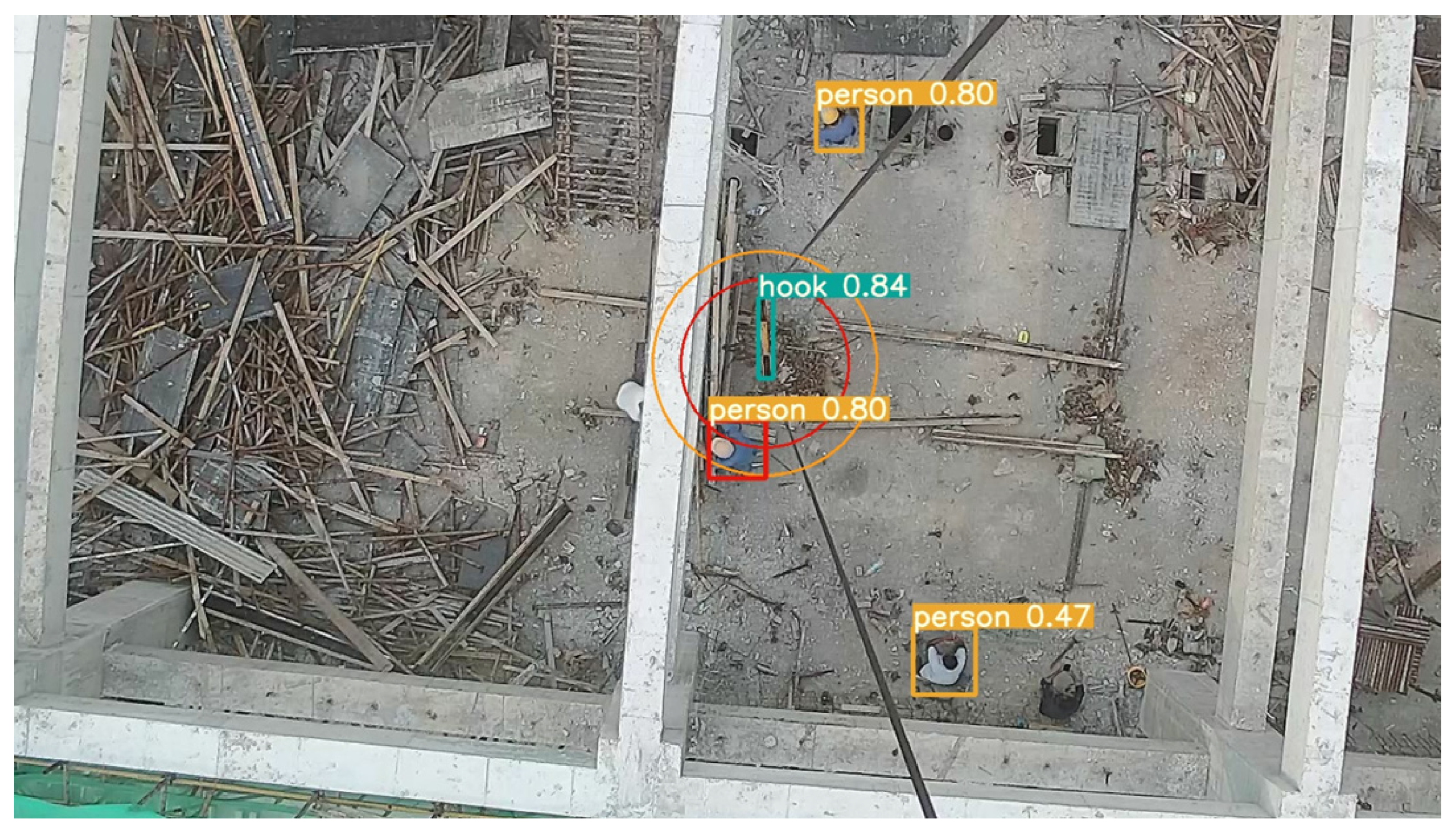
This comparison highlights the significant improvements in the detection accuracy achieved by the improved model over the original YOLOv5s, as shown in Figure 16. The original model’s limitations are evident in its inability to correctly identify and locate many construction personnel, compromising its effectiveness in evaluating the danger posed to workers and preventing subsequent accidents caused by falling objects. Conversely, the improved YOLOv5s model demonstrates a marked improvement in the detection performance, accurately identifying most targets.

Figure 16.
Comparison of hook and personnel detection.
The danger area around a tower crane is calculated by the method stated in Section 3.2. The danger area is marked with a red circle, and a caution area, extending 2 m beyond the danger zone radius, is marked with an orange circle. These areas are displayed in real-time on the monitoring video to complete the delineation of the danger zone, as shown in Figure 17.

Figure 17.
Real-time risk assessment shown in the monitoring screen.
The risk level, which includes the frequency of the exposure to danger, is calculated according to the method described in Section 4.2.2. Once the level of danger to personnel is calculated, a safety alarm threshold within the danger zone is established based on balancing the operational efficiency and safety, . If the LEC value exceeds this threshold, the system highlights the frame of the affected construction worker in the tower crane monitoring video in red, as shown Figure 17. This alert mechanism serves as a warning to crane operators and site safety managers, urging them to take immediate action to mitigate risks, thereby facilitating the dynamic monitoring and objective quantification of safety risks associated with tower crane lifting and transport activities.
6. Discussion and Constraints
This study theoretically develops a tower crane small object detection algorithm that relies solely on visual recognition. By addressing issues such as false positives and missed detections, the algorithm ensures high accuracy and speed of detection while maintaining relatively low storage and computational resource usage. Through the analysis of past accident characteristics, the distribution patterns of tower crane falling object striking accidents were determined for both annual and daily occurrences. This analysis led to the improvement of the traditional LEC model, resulting in the development of a semi-quantitative risk assessment method. In practical applications, the small object detection algorithm and risk assessment method developed in this study can effectively assist in the safety protection and coordination between tower crane operators and ground construction personnel during most daylight hours in clear weather throughout the year.
However, the improved YOLOv5s model faces two main challenges. Firstly, the accuracy of visual recognition models is highly dependent on the quality and diversity of the training data. Although the training data include year-round video recordings, covering conditions such as post-rain and post-snow construction sites, severe weather events like heavy rain, snow, and fog are limited due to safety regulations [35] that halt tower crane operations under such conditions. Consequently, the model’s visual recognition system exhibits reduced adaptability to environmental changes, with the recognition accuracy dropping in ongoing snow, rain, or foggy conditions.
Secondly, visual recognition technology is sensitive to lighting conditions. Under low light, excessive brightness, or reflective surfaces, the recognition accuracy can significantly decline, especially in outdoor environments, presenting a challenge to model stability. This study’s training dataset includes images captured under various daylight conditions, ensuring reliable recognition accuracy during daytime. However, at night, construction lights are typically positioned to illuminate the rooftop work area, with limited ground lighting. Thus, the model can only recognize workers and hooks in areas illuminated by work lights, failing to detect hooks and workers in unlit ground areas. Additionally, due to lighting reflections, the recognition performance may degrade. However, this limitation does not fundamentally undermine the importance and effectiveness of this study. Statistical data in Figure 14 indicate that high-intensity construction periods and high-risk times primarily occur between 7:00 and 18:00. Under these lighting and weather conditions, the model can accurately and quickly identify workers and hooks.
The setting of the alarm threshold is crucial to the system implementation. If the threshold is set too low, the system will remain in a constant alert state, leading to interruptions in construction and project delays. Conversely, if set too high, the system remains dormant and fails to provide effective warnings. In this study, a threshold of 50 was subjectively defined to balance efficiency and safety. In the future, a more scientific approach, such as big data analysis, will be employed to establish a reasonable threshold.
7. Conclusions
This paper proposes a small object recognition model based on deep learning and computer vision, and applies it to the demarcation of the dangerous areas of tower cranes.
Based on the YOLOv5s model, three improvements, namely, a small object detection layer, a channel attention module, and a modified bounding box loss function, were added to the object detection network to enhance its feature extraction capability. Subsequently, a dataset was constructed using tower crane monitoring equipment, and experiments on the basic model’s performance were conducted. The results verify that the improved YOLOv5s model can balance the detection speed with accuracy compared to the conventional YOLOv5 models. Ablation experiments show that the model incorporating all three improvements performs the best, establishing it as the improved YOLOv5s model. Its precision, recall, mAP_0.5, and mAP_0.5–0.95 values are 96.00%, 96.00%, 96.42%, and 62.02%, respectively, representing increases of 1.1%, 3%, 3.18%, and 2.99% compared to the original model, with only a 2 MB increase in the weight file, achieving a significant performance improvement. Comparative analysis of the detection effects before and after the model improvement using the test dataset shows that the improved YOLOv5s model significantly mitigates the issues of missed and false detections of crane hook targets. Comparative experiments with other object detection models demonstrate the advanced performance of the improved YOLOv5s model.
Based on the enhanced capabilities of the improved YOLOv5s model, a visual recognition algorithm-assisted safety management approach for tower cranes was introduced. This approach integrates a crane hook height calculation module and a falling object striking area identification module directly into the detection phase of the model. Moreover, a risk assessment module, informed by the LEC method and the statistical analysis of historical accidents, was developed. The practical application of this algorithm and method has demonstrably enabled the dynamic surveillance of dangerous zones beneath crane hooks, the real-time assessment of worker risk, and the proactive display of danger warnings.
In essence, this method not only addresses the critical issue of visual blind spots for tower crane operators but also empowers both the operators and construction safety managers. It sharpens their focus on the critical overlap between falling object striking zones and construction worker activity areas, encouraging the adoption of pre-emptive safety measures. Consequently, this enhances both the operational safety and the level of safety oversight on construction sites.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/buildings14123728/s1, Table S1: Case information.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.S. and Z.T.; Methodology, X.S.; Software, X.L. and T.H.; Validation, T.H. and Z.T.; Formal analysis, X.L.; Investigation, Y.W.; Writing—original draft, X.L.; Writing—review & editing, X.S.; Supervision, Z.T.; Funding acquisition, X.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 52279131 and 51909072].
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this work, the authors used ChatGPT in order to review grammar and polish the text. After using this tool/service, the authors reviewed and edited the content as needed and take full responsibility for the content of the publication.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Yao Wang was employed by the company China Railway First Survey and Design Institute Group Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Rosenfeld, Y.; Shapira, A. Automation of existing tower cranes: Economic and technological feasibility. Autom. Constr. 1998, 7, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Cho, J.; Ham, S.; Lee, T.; Lee, G.; Yun, S.-H.; Yang, H.-J. A BIM-and sensor-based tower crane navigation system for blind lifts. Autom. Constr. 2012, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinosho, T.D.; Oyedele, L.O.; Bilal, M.; Ajayi, A.O.; Delgado, M.D.; Akinade, O.O.; Ahmed, A.A. Deep learning in the construction industry: A review of present status and future innovations. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Ding, L.; Luo, H.; Rose, T.M.; An, W. Detecting non-hardhat-use by a deep learning method from far-field surveillance videos. Autom. Constr. 2018, 85, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, Z.; Chen, H.; Luo, X. Transfer learning and deep convolutional neural networks for safety guardrail detection in 2D images. Autom. Constr. 2018, 89, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andonovski, B.; Jianqiang, L.; Jeyaraj, S.; Quan, A.Z.; Yonggao, X.; Tech, A.W. Towards a Development of Robotics Tower Crane System. In Proceedings of the 2020 16th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV), Shenzhen, China, 13–15 December 2020; pp. 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Chen, J.; Cho, Y.K.; Kim, K.; Zhang, S.; Perez, E. Vision-based load sway monitoring to improve crane safety in blind lifts. J. Struct. Integr. Maint. 2018, 3, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K.; Sun, M. MSFYOLO: Feature fusion-based detection for small objects. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2022, 20, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Wushouer, M.; Tuerhong, G. Small Object Detection Method based on Improved YOLOv5. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Virtual Reality, Human-Computer Interaction and Artificial Intelligence (VRHCIAI), Changsha, China, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 144–149. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, X.; Wan, Y.; Wang, J.; Lyu, H. An Improved YOLOv5 Method for Small Object Detection in UAV Capture Scenes. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 14365–14374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, X.; Gao, L.; Yu, S.; Zheng, X. SGD-YOLOv5: A Small Object Detection Model for Complex Industrial Environments. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Yokohama, Japan, 30 June–5 July 2024; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Sun, T.; Lou, H.; Duan, X.; Bi, L.; Liu, L. MC-YOLOv5: A Multi-Class Small Object Detection Algorithm. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xu, S. From Point to Region: Accurate and Efficient Hierarchical Small Object Detection in Low-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Yuan, X.; Yao, X.; Yan, K.; Zeng, Q.; Xie, X.; Han, J. Towards Large-Scale Small Object Detection: Survey and Benchmarks. IEEE Trans. Pattern. Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 13467–13488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, L.; Bi, L.; Liu, H. Small object detection algorithm based on improved yolov5. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Control, Electronics and Computer Technology (ICCECT), Jilin, China, 28–30 April 2023; pp. 280–283. [Google Scholar]
- Chuai, Q.; He, X.; Li, Y. Improved Traffic Small Object Detection via Cross-Layer Feature Fusion and Channel Attention. Electronics 2023, 12, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Lee, Y.; Choi, J. BIM-based Hazard Recognition and Evaluation Methodology for Automating Construction Site Risk Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, R.; Choi, J.H. Emerging Trends of Ergonomic Risk Assessment in Construction Safety Management: A Scientometric Visualization Analysis. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Obonyo, E. Applying incremental Deep Neural Networks-based posture recognition model for ergonomics risk assessment in construction. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 50, 101374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpio-de Los Pinos, A.J.; González-García, M.L.N. Development of the Protocol of the Occupational Risk Assessment Method for Construction Works: Level of Preventive Action. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdinia, M.; Yarandi Mohsen, S.; Jafarinia, E.; Soltanzadeh, A. Development of a New Technique for Safety Risk Assessment in Construction Projects Based on Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process. ASCE-ASME J. Risk Uncertain. Eng. Syst. Part A Civ. Eng. 2021, 7, 04021037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Stoken, A.; Borovec, J.; Changyu, L.; Hogan, A.; Diaconu, L.; Poznanski, J.; Yu, L.; Rai, P.; Ferriday, R. Ultralytics/yolov5: v3.0. Zenodo 2020. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2020zndo...4154370J/abstract (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rezatofighi, H.; Tsoi, N.; Gwak, J.; Sadeghian, A.; Reid, I.; Savarese, S. Generalized intersection over union: A metric and a loss for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, W.; Ziyun, S.; Ping, G.; Longmei, Z. Improved Leukocyte Detection Algorithm of YOLOv5. J. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2022, 58, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tzutalin LabelImg. 2015. Available online: https://github.com/tzutalin/labelImg (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- State Administration of Work Safety. Classification of Work at Heights; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yuqi, K.; Tingsheng, Z.; Ling, J.; Wei, Z. Mining and analysis of association rules in tower crane accident cases. China Saf. Sci. J. 2021, 31, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Council of the People’s Republic of China. Regulations on Reporting and Investigation and Handling of Production Safety Accidents; The Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical Specification for Safety Installation Operation and Dismantlement of Tower Crane in Construction; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, K.J.; Kinney, G.F. A practical safety analysis system for hazards control. J. Saf. Res. 1980, 12, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).