Research on Collapse Risk Assessment of Karst Tunnels Based on BN Self-Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
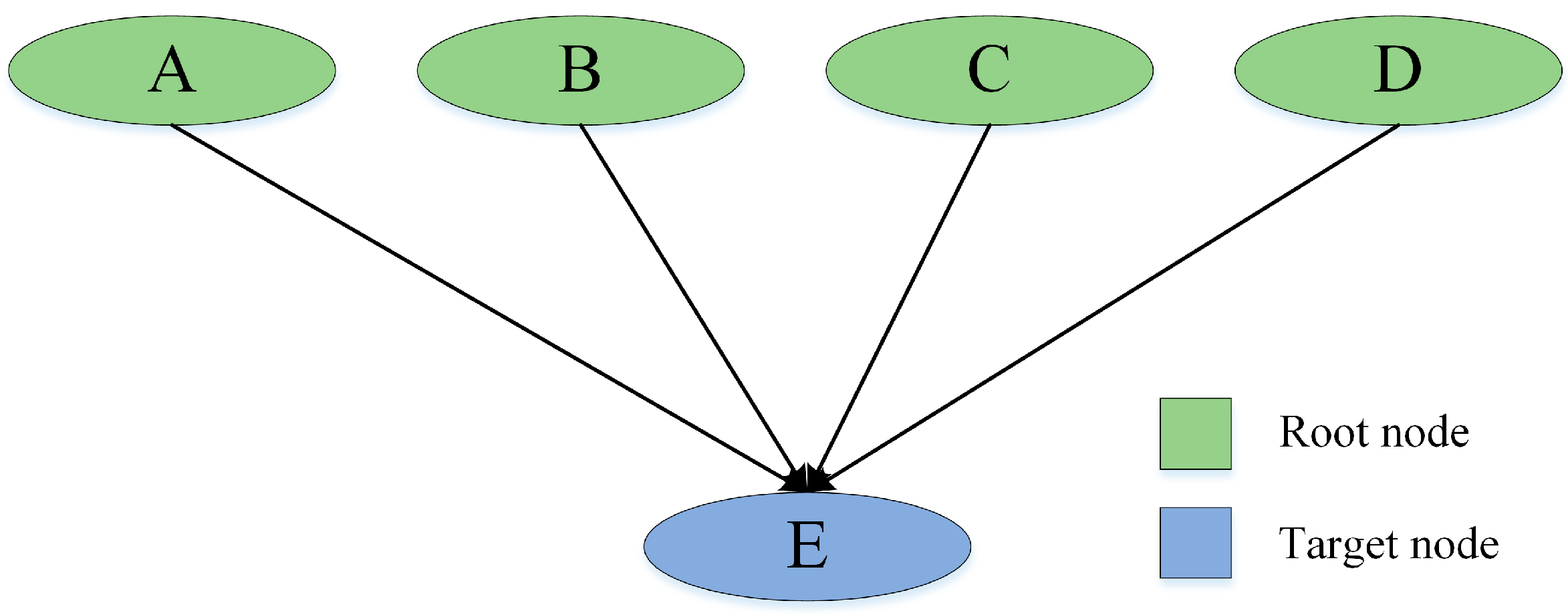
2. Bayesian Network Self-Learning Probability Prediction Method
3. Deformation Laws of Surrounding Rock during Tunnel Excavation under Different Karst Cave Parameters
3.1. Construction of the Numerical Model
3.2. Deformation Laws of Surrounding Rock
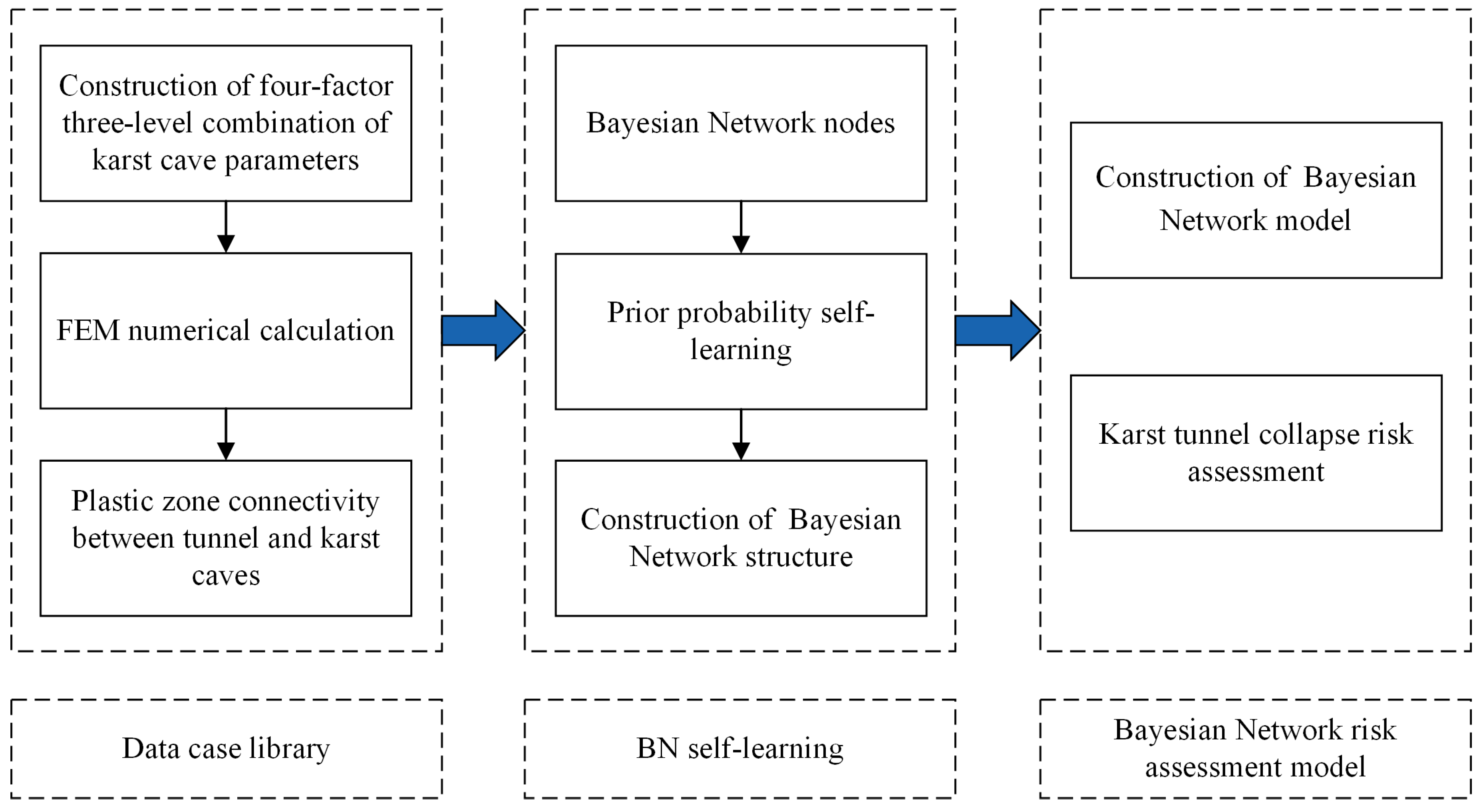
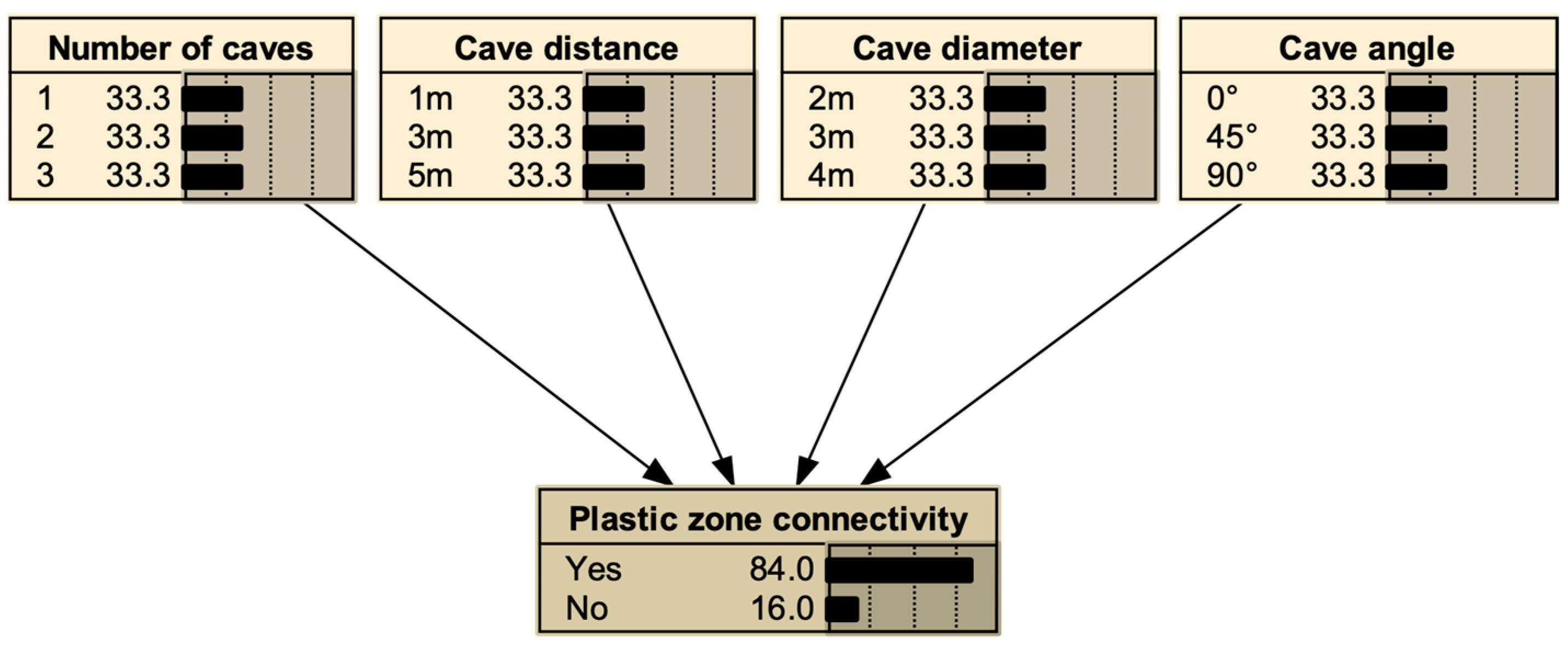
4. Construction of Bayesian Network Model
4.1. Bayesian Network Model
4.2. Network Validation and Robustness Test
5. Collapse Risk Assessment of Karst Tunnels
5.1. Posterior Probability Analysis
5.2. Comparative Analysis
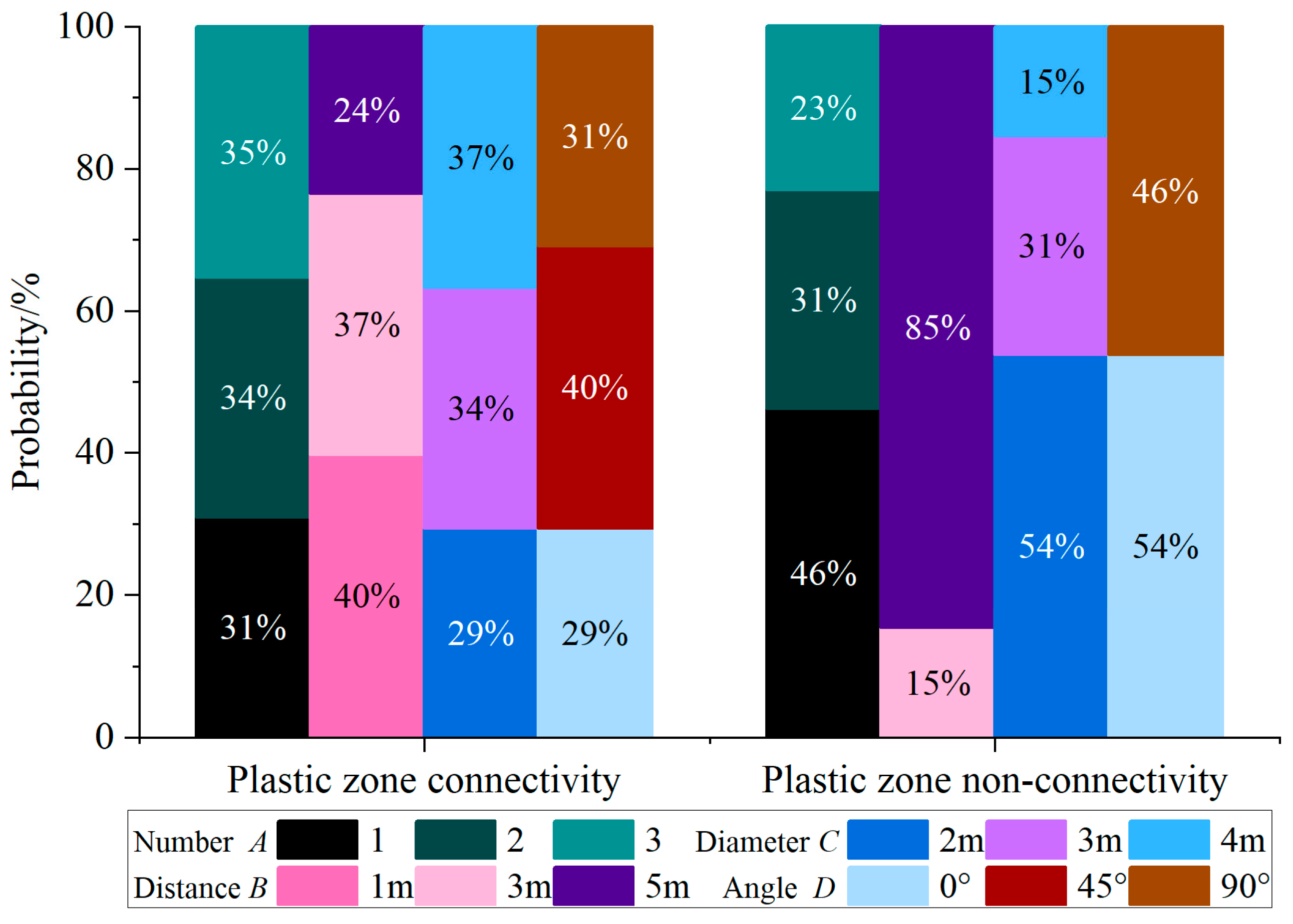
5.3. Sensitivity Analysis
6. Limitations and Prospects
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review on China’s Trafic Tunnel Enginering Research: 2022. China J. Highw. Transp. 2022, 35, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.P.; Sun, S.Q.; Wang, J.; Song, S.G.; Fang, Z.D.; Zhang, M.G. Development of compound EPB shield model test system for studying the water inrushes in karst regions. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 101, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Pei, J.H.; Cao, C.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Huang, Y.X.; Mei, G.X. Geological investigation and treatment measures against water inrush hazard in karst tunnels: A case study in Guiyang, southwest China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 124, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Lai, J.X.; Qiu, J.L.; Xu, W.; Wang, L.X.; Luo, Y.B. Geohazards, reflection and challenges in Mountain tunnel construction of China: A data collection from 2002 to 2018. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2020, 11, 766–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.B.; Zhang, Y.H.; He, S.Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, H. Hazards and treatment of karst tunneling in Qinling-Daba mountainous area: Overview and lessons learnt from Yichang-Wanzhou railway system. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Bu, L.; Shi, S.S.; Li, L.P.; Zhou, Z.Q. Prediction for Water Inrush Disaster Source and CFD-Based Design of Evacuation Routes in Karst Tunnel. Int. J. Geomech. 2022, 22, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Gao, C.L.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Li, L.P.; Wang, M.X.; Yuan, Y.C.; Wang, J. Analysis on the Precursor Information of Water Inrush in Karst Tunnels: A True Triaxial Model Test Study. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Ma, C.Y.; Liu, R.T.; Chen, M.J.; Yan, J.; Wang, Z.J.; Duan, S.L.; Zhang, H.S. Super-absorbent swellable polymer as grouting material for treatment of karst water inrush. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2021, 31, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Qi, Y.H.; Li, Z.F.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, J. A novel treatment method and construction technology of the pipeline gushing water geohazards in karst region. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 113, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Wang, X.T.; Xu, Z.H.; Mao, D.Q.; Pan, D.D. Numerical investigation of hydraulic tomography for mapping karst conduits and its connectivity. Eng. Geol. 2021, 281, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, B. A possible prediction method to determine the top concealed karst cave based on displacement monitoring during tunnel construction. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.P.; Tu, W.F.; Shi, S.S.; Chen, J.X.; Zhang, Y.H. Mechanism of water inrush in tunnel construction in karst area. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 7, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Sun, W.T.; Cai, G.W.; Meng, G.W. Reliability analysis of shallow-buried tunnel construction adjacent to karst cave. Comput. Geotech. 2022, 145, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, S.C.; Xu, Z.H.; Guo, M.; Chen, Y.C. Assessment of a Concealed Karst Cave’s Influence on Karst Tunnel Stability: A Case Study of the Huaguoshan Tunnel, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraldi, M.; Guarracino, F. Limit analysis of collapse mechanisms in cavities and tunnels according to the Hoek-Brown failure criterion. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2009, 46, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhao, L.H.; Ling, T.H.; Yang, X.L. Rock mass collapse mechanism of concealed karst cave beneath deep tunnel. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2017, 91, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.J.; Guan, J.W.; Duan, J.F.; Huang, L.C.; Liang, Y. Stability analysis on tunnels with karst caves using the distinct lattice spring model. Undergr. Space 2021, 6, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.H.; Lin, P.; Xing, H.L.; Pan, D.D.; Huang, X. Hydro-mechanical Coupling Response Behaviors in Tunnel Subjected to a Water-Filled Karst Cave. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2021, 54, 3737–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.B.; Zhou, D.K.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.X.; Zhu, Z.G.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Gao, X.Q.; Guo, J.Q. Mechanical response characteristics of lining structure of pipeline karst tunnels in water-rich areas. Rock Soil Mech. 2022, 43, 1884–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.J.; Tang, L.; Jiang, X.Z.; Hou, W.M.; Xu, H.Y.; Ji, X.F. Model Test on Stability of Large Cross-section Highway Tunnel Adjacent to Caverns. Tunn. Constr. 2019, 39, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Xue, P.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, X.; Bian, H.B.; Wang, Y.X.; Guo, P.P. Mechanical Response Law and Parameter Influence Analysis of Karst Tunnel Dynamic Excavation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, L.F.; Zhang, C.F.; Liu, B.; Li, K.J.; Shi, H.B.; Jing, B.Y. Multi-Step Combined Control Technology for Karst and Fissure Water Inrush Disaster During Shield Tunneling in Spring Areas. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ming, W.H.; Li, J.M.; Zhou, C.Y.; Zhang, L.H. Numerical prediction of the optimal shield tunneling strategy for tunnel construction in karst regions. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.P.; Sun, S.Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.M.; Song, S.G.; Fang, Z.D. Experimental study of the precursor information of the water inrush in shield tunnels due to the proximity of a water-filled cave. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2020, 130, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.L.; Wu, H.N.; Shen, S.L.; Xu, Y.S.; Ye, G.L. Chinese karst geology and measures to prevent geohazards during shield tunnelling in karst region with caves. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.S.; Geng, Z.; Lu, L.H.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.W.; Liu, B.; Huang, X. Compound Karst Cave Treatment and Waterproofing Strategy for EPB Shield Tunnelling in Karst Areas: A Case Study. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Yu, L.; Wang, M.N.; Xia, P.X.; Sun, Y. Upper bound analysis of collapse failure of deep tunnel under karst cave considering seismic force. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 132, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Alba, V.; Neven, A.; de Rooij, R.; Filipponi, M.; Renard, P. Probabilistic estimation of tunnel inflow from a karstic conduit network. Eng. Geol. 2023, 312, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.L.; Cui, J.; Zhang, Y.L. Risk Assessment Mmodel of Karst Tunnel Flood Based on Distance Discriminant Weighting and Set Pair Cloud. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 27, 3219–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, K.; Paraskevopoulou, C.; Konstantis, S. Spatial variability of karst and effect on tunnel lining and water inflow. A probabilistic approach. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 97, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zheng, W.B.; Liao, Z.Y.; Xie, H.P.; Zhou, C.T.; Chen, S.G.; Zhu, J.B. Risk assessment of ground collapse along tunnels in karst terrain by using an improved extension evaluation method. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 129, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zheng, W.B.; Zhou, C.T.; Xie, H.P.; Long, X.T.; Tannant, D.D.; Chen, S.G.; Zhu, J.B. Evaluation of underground karst development state for tunnel construction by using the extension assessment method. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.H. Research on Intelligent Prediction Method of Hazard Risk of Water and Mud Inrush in Karst Tunnel Based on Machine Learning. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.C.; Jing, H.W.; Yu, L.Y.; Su, H.J.; Luo, N. Set pair analysis for risk assessment of water inrush in karst tunnels. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2017, 76, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Li, L.P.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Shi, S.S. Risk assessment of water inrush in karst tunnels based on attribute synthetic evaluation system. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2013, 38, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, R.-l.; Zhang, X.-n.; Lu, M. Numerical Application of Safe Thickness between a Tunnel and Surrounding Concealed Caves. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2018, 36, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.G.; Goh, A.T.C. Numerical study of pillar stresses and interaction effects for twin rock caverns. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2015, 39, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.J.; Wang, H.J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Liu, Q.; Luo, S.L. Numerical Analysis of the Mud Inflow Model of Fractured Rock Mass Based on Particle Flow. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.L.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Li, Z.H.; Li, L.P.; Cheng, S. Peridynamics simulation of surrounding rock damage characteristics during tunnel excavation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 97, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, E.; Calviño, A.; Grande, Z.; Sánchez-Cambronero, S.; Gallego, I.; Rivas, A.; Menéndez, J.M. A Markovian-Bayesian Network for Risk Analysis of High Speed and Conventional Railway Lines Integrating Human Errors. Comput.-Aided Civ. Inf. 2016, 31, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.L.; Einstein, H.H. Risk analysis during tunnel construction using Bayesian Networks: Porto Metro case study. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2012, 27, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerassis, S.; Albuquerque, M.T.D.; García, J.F.; Boente, C.; Giráldez, E.; Taboada, J.; Martín, J.E. Understanding complex blasting operations: A structural equation model combining Bayesian networks and latent class clustering. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 188, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Su, J.; Zhang, S.L.; Guo, S.Y.; Zhang, P.; Du, M.Q. A Dynamic Risk Assessment Method for Deep-Buried Tunnels Based on a Bayesian Network. Geofluids 2020, 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.W.; Guo, H.P. Introduction to Bayesian Networks; China Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Specifications for Design of Highway Tunnels; Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Mohammadfam, I.; Ghasemi, F.; Kalatpour, O.; Moghimbeigi, A. Constructing a Bayesian network model for improving safety behavior of employees at workplaces. Appl. Ergon. 2017, 58, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanpariyavatevong, K.; Wipulanusat, W.; Champahom, T.; Jomnonkwao, S.; Chonsalasin, D.; Ratanavaraha, V. Predicting Airline Customer Loyalty by Integrating Structural Equation Modeling and Bayesian Networks. Sustainability 2021, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, J. An economic basis for certain methods of evaluating probabilistic forecasts. Int. J. Man-Mach. Stud. 1978, 10, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norsys Software Corp. Scoring Rule Results & Logarithmic Loss Values. Available online: https://www.norsys.com/WebHelp/NETICA/X_Scoring_Rule_Results.htm (accessed on 8 October 2022).





| Parameter Number | Number of Karst Caves A | Distance to Karst Caves B | Diameter of Karst Caves C | Angle of Karst Caves D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 m | 2 m | 0° |
| 2 | 2 | 3 m | 3 m | 45° |
| 3 | 3 | 5 m | 4 m | 90° |
| Stratum | Volumetric Weight γ/(kN/m3) | Elastic Modulus E/GPa | Poisson’s Ratio υ | Cohesion c/MPa | Internal Friction Angle φ/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limestone | 25.1 | 24 | 0.25 | 1 | 40 |
| No. | Number of Karst Caves A | Distance to Karst Caves B | Diameter of Karst Caves C | Angle of Karst Caves D | Plastic Zone Connectivity E | No. | Number of Karst Caves A | Distance to Karst Caves B | Diameter of Karst Caves C | Angle of Karst Caves D | Plastic Zone Connectivity E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 m | 2 m | 0° | ● | 42 | 2 | 3 m | 3 m | 90° | ● |
| 2 | 1 | 1 m | 2 m | 45° | ● | 43 | 2 | 3 m | 4 m | 0° | ● |
| 3 | 1 | 1 m | 2 m | 90° | ● | 44 | 2 | 3 m | 4 m | 45° | ● |
| 4 | 1 | 1 m | 3 m | 0° | ● | 45 | 2 | 3 m | 4 m | 90° | ● |
| 5 | 1 | 1 m | 3 m | 45° | ● | 46 | 2 | 5 m | 2 m | 0° | ○ |
| 6 | 1 | 1 m | 3 m | 90° | ● | 47 | 2 | 5 m | 2 m | 45° | ● |
| 7 | 1 | 1 m | 4 m | 0° | ● | 48 | 2 | 5 m | 2 m | 90° | ○ |
| 8 | 1 | 1 m | 4 m | 45° | ● | 49 | 2 | 5 m | 3 m | 0° | ● |
| 9 | 1 | 1 m | 4 m | 90° | ● | 50 | 2 | 5 m | 3 m | 45° | ● |
| 10 | 1 | 3 m | 2 m | 0° | ○ | 51 | 2 | 5 m | 3 m | 90° | ○ |
| 11 | 1 | 3 m | 2 m | 45° | ● | 52 | 2 | 5 m | 4 m | 0° | ● |
| 12 | 1 | 3 m | 2 m | 90° | ● | 53 | 2 | 5 m | 4 m | 45° | ● |
| 13 | 1 | 3 m | 3 m | 0° | ○ | 54 | 2 | 5 m | 4 m | 90° | ○ |
| 14 | 1 | 3 m | 3 m | 45° | ● | 55 | 3 | 1 m | 2 m | 0° | ● |
| 15 | 1 | 3 m | 3 m | 90° | ● | 56 | 3 | 1 m | 2 m | 45° | ● |
| 16 | 1 | 3 m | 4 m | 0° | ● | 57 | 3 | 1 m | 2 m | 90° | ● |
| 17 | 1 | 3 m | 4 m | 45° | ● | 58 | 3 | 1 m | 3 m | 0° | ● |
| 18 | 1 | 3 m | 4 m | 90° | ● | 59 | 3 | 1 m | 3 m | 45° | ● |
| 19 | 1 | 5 m | 2 m | 0° | ○ | 60 | 3 | 1 m | 3 m | 90° | ● |
| 20 | 1 | 5 m | 2 m | 45° | ● | 61 | 3 | 1 m | 4 m | 0° | ● |
| 21 | 1 | 5 m | 2 m | 90° | ○ | 62 | 3 | 1 m | 4 m | 45° | ● |
| 22 | 1 | 5 m | 3 m | 0° | ○ | 63 | 3 | 1 m | 4 m | 90° | ● |
| 23 | 1 | 5 m | 3 m | 45° | ● | 64 | 3 | 3 m | 2 m | 0° | ● |
| 24 | 1 | 5 m | 3 m | 90° | ● | 65 | 3 | 3 m | 2 m | 45° | ● |
| 25 | 1 | 5 m | 4 m | 0° | ○ | 66 | 3 | 3 m | 2 m | 90° | ● |
| 26 | 1 | 5 m | 4 m | 45° | ● | 67 | 3 | 3 m | 3 m | 0° | ● |
| 27 | 1 | 5 m | 4 m | 90° | ● | 68 | 3 | 3 m | 3 m | 45° | ● |
| 28 | 2 | 1 m | 2 m | 0° | ● | 69 | 3 | 3 m | 3 m | 90° | ● |
| 29 | 2 | 1 m | 2 m | 45° | ● | 70 | 3 | 3 m | 4 m | 0° | ● |
| 30 | 2 | 1 m | 2 m | 90° | ● | 71 | 3 | 3 m | 4 m | 45° | ● |
| 31 | 2 | 1 m | 3 m | 0° | ● | 72 | 3 | 3 m | 4 m | 90° | ● |
| 32 | 2 | 1 m | 3 m | 45° | ● | 73 | 3 | 5 m | 2 m | 0° | ○ |
| 33 | 2 | 1 m | 3 m | 90° | ● | 74 | 3 | 5 m | 2 m | 45° | ● |
| 34 | 2 | 1 m | 4 m | 0° | ● | 75 | 3 | 5 m | 2 m | 90° | ○ |
| 35 | 2 | 1 m | 4 m | 45° | ● | 76 | 3 | 5 m | 3 m | 0° | ● |
| 36 | 2 | 1 m | 4 m | 90° | ● | 77 | 3 | 5 m | 3 m | 45° | ● |
| 37 | 2 | 3 m | 2 m | 0° | ● | 78 | 3 | 5 m | 3 m | 90° | ○ |
| 38 | 2 | 3 m | 2 m | 45° | ● | 79 | 3 | 5 m | 4 m | 0° | ● |
| 39 | 2 | 3 m | 2 m | 90° | ● | 80 | 3 | 5 m | 4 m | 45° | ● |
| 40 | 2 | 3 m | 3 m | 0° | ● | 81 | 3 | 5 m | 4 m | 90° | ● |
| 41 | 2 | 3 m | 3 m | 45° | ● |
| Nodes | Node Range | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of karst caves | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Distance to karst caves | 1 m | 3 m | 5 m |
| Diameter of karst caves | 2 m | 3 m | 4 m |
| Angle of karst caves | 0° | 45° | 90° |
| Predicted Value | Actual Value | Error Rate | Total Error Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |||
| 731 | 9 | Yes | 1.22% | 4.43% |
| 31 | 132 | No | 19.02% | |
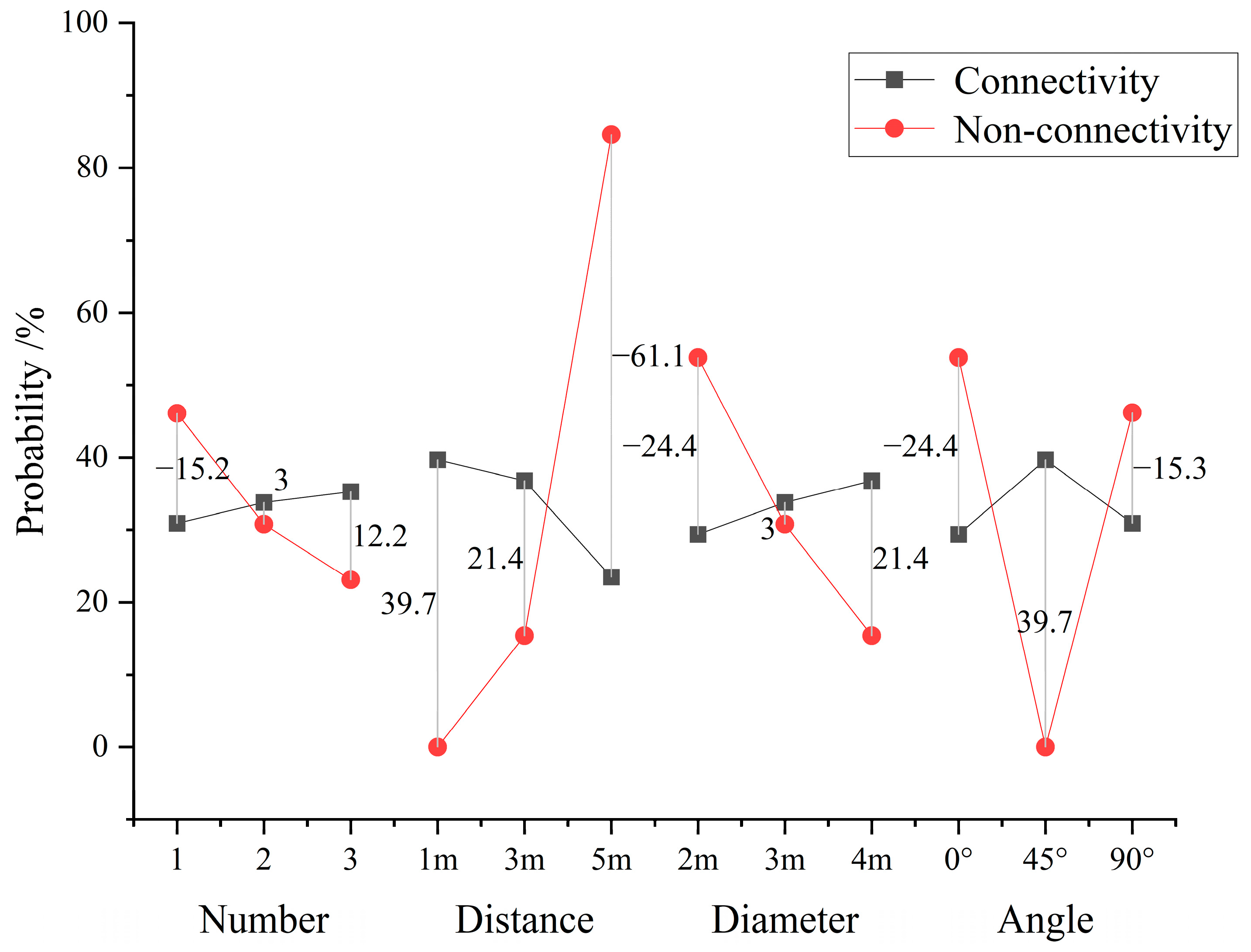
| Plastic Zone Connectivity | Plastic Zone Connectivity | Total Change | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |||||||
| Probability | Change | Change Rate | Probability | Change | Change Rate | |||
| 1 | 30.9 | −2.1 | 6.36% | 46.1 | 13.1 | 39.70% | −15.2 | |
| Number of karst caves | 2 | 33.8 | 0.8 | 2.42% | 30.8 | −2.2 | 6.67% | 3 |
| 3 | 35.3 | 2.3 | 6.97% | 23.1 | −9.9 | 30.00% | 12.2 | |
| 1 m | 39.7 | 6.7 | 20.30% | 0 | −33 | 100.00% | 39.7 | |
| Distance of karst caves | 3 m | 36.8 | 3.8 | 11.52% | 15.4 | −17.6 | 53.33% | 21.4 |
| 5 m | 23.5 | −9.5 | 28.79% | 84.6 | 51.6 | 156.36% | −61.1 | |
| 2 m | 29.4 | −3.6 | 10.91% | 53.8 | 20.8 | 63.03% | −24.4 | |
| Diameter of karst caves | 3 m | 33.8 | 0.8 | 2.42% | 30.8 | −2.2 | 6.67% | 3 |
| 4 m | 36.8 | 3.8 | 11.52% | 15.4 | −17.6 | 53.33% | 21.4 | |
| 0° | 29.4 | −3.6 | 10.91% | 53.8 | 20.8 | 63.03% | −24.4 | |
| Angle of karst caves | 45° | 39.7 | 6.7 | 20.30% | 0 | −33 | 100.00% | 39.7 |
| 90° | 30.9 | −2.1 | 6.36% | 46.2 | 13.2 | 40.00% | −15.3 | |
| Total Change (Absolute Value) | Rank | |
|---|---|---|
| Distance of karst caves 5 m | 61.1 | 1 |
| Distance of karst caves 1 m | 39.7 | 2 |
| Angle of karst caves 45° | 39.7 | 3 |
| Diameter of karst caves 2 m | 24.4 | 4 |
| Angle of karst caves 0° | 24.4 | 5 |
| Distance of karst caves 3 m | 21.4 | 6 |
| Diameter of karst caves 4 m | 21.4 | 7 |
| Angle of karst caves 90° | 15.3 | 8 |
| Number of karst caves 1 | 15.2 | 9 |
| Number of karst caves 3 | 12.2 | 10 |
| Number of karst caves 2 | 3 | 11 |
| Diameter of karst caves 3 m | 3 | 12 |
| Number of Karst Caves | Distance of Karst Caves | Diameter of Karst Caves | Angle of Karst Caves | Probability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 77.8 | |||
| 2 | 85.2 | |||
| 3 | 88.9 | |||
| 1 m | 100 | |||
| 3 m | 92.6 | |||
| 5 m | 59.3 | |||
| 2 m | 74.1 | |||
| 3 m | 85.2 | |||
| 4 m | 92.6 | |||
| 0° | 74.1 | |||
| 45° | 100 | |||
| 90° | 77.8 |
| Karst Cave Parameters | Distance to Karst Caves | Angle of Karst Caves | Diameter of Karst Caves | Number of Karst Caves |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity coefficient | 0.18347 | 0.10555 | 0.03157 | 0.01127 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, H.; Su, Y. Research on Collapse Risk Assessment of Karst Tunnels Based on BN Self-Learning. Buildings 2024, 14, 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14030685
Sun J, Wang Y, Wu X, Wang X, Fang H, Su Y. Research on Collapse Risk Assessment of Karst Tunnels Based on BN Self-Learning. Buildings. 2024; 14(3):685. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14030685
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jinglai, Yan Wang, Xu Wu, Xinling Wang, Hui Fang, and Yue Su. 2024. "Research on Collapse Risk Assessment of Karst Tunnels Based on BN Self-Learning" Buildings 14, no. 3: 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14030685
APA StyleSun, J., Wang, Y., Wu, X., Wang, X., Fang, H., & Su, Y. (2024). Research on Collapse Risk Assessment of Karst Tunnels Based on BN Self-Learning. Buildings, 14(3), 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14030685






