Seismic Performance Evaluation of a Chilean RC Building Damaged during the Mw8.8 Chile Earthquake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analysis of the Chilean Performance-Based Design Proposal
2.1. Earthquake Design Level
2.2. Acceptance Criteria
2.2.1. Global Acceptance Criteria
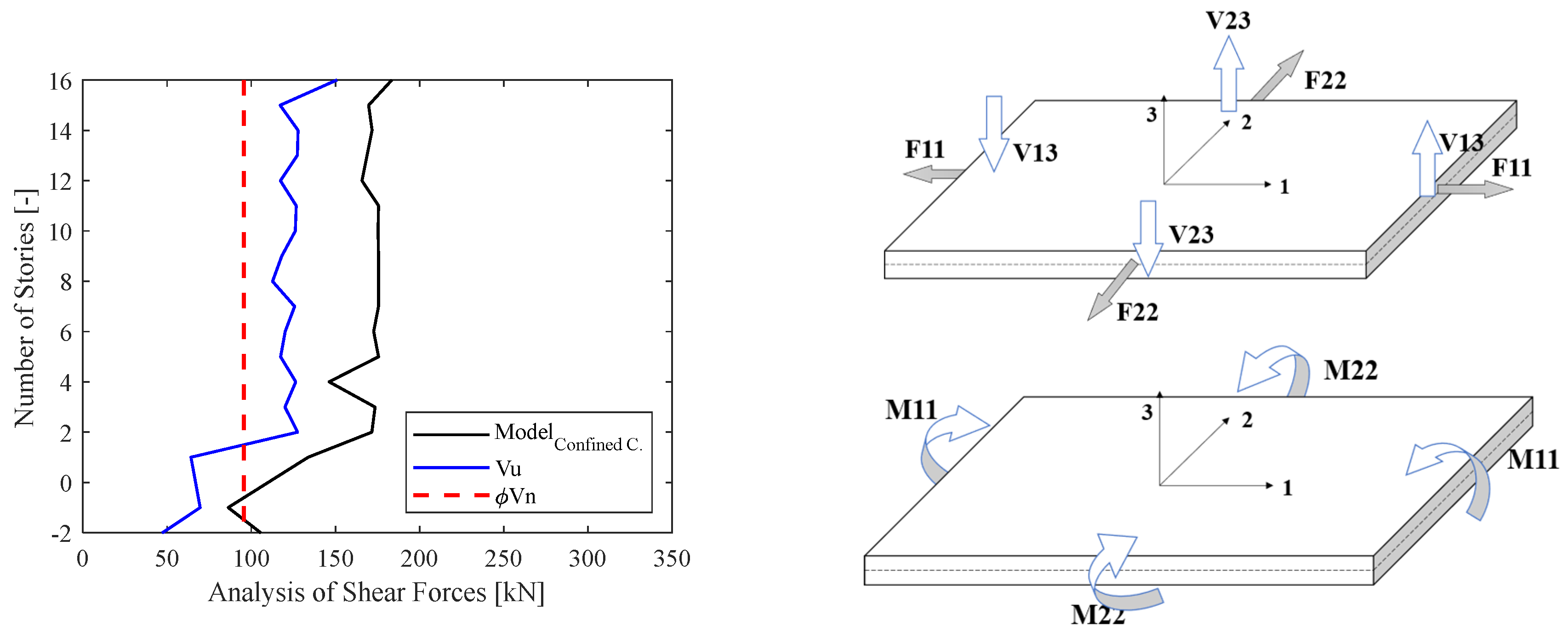
2.2.2. Local Acceptance Criteria
3. Seismic Performance of a Typical Chilean Building
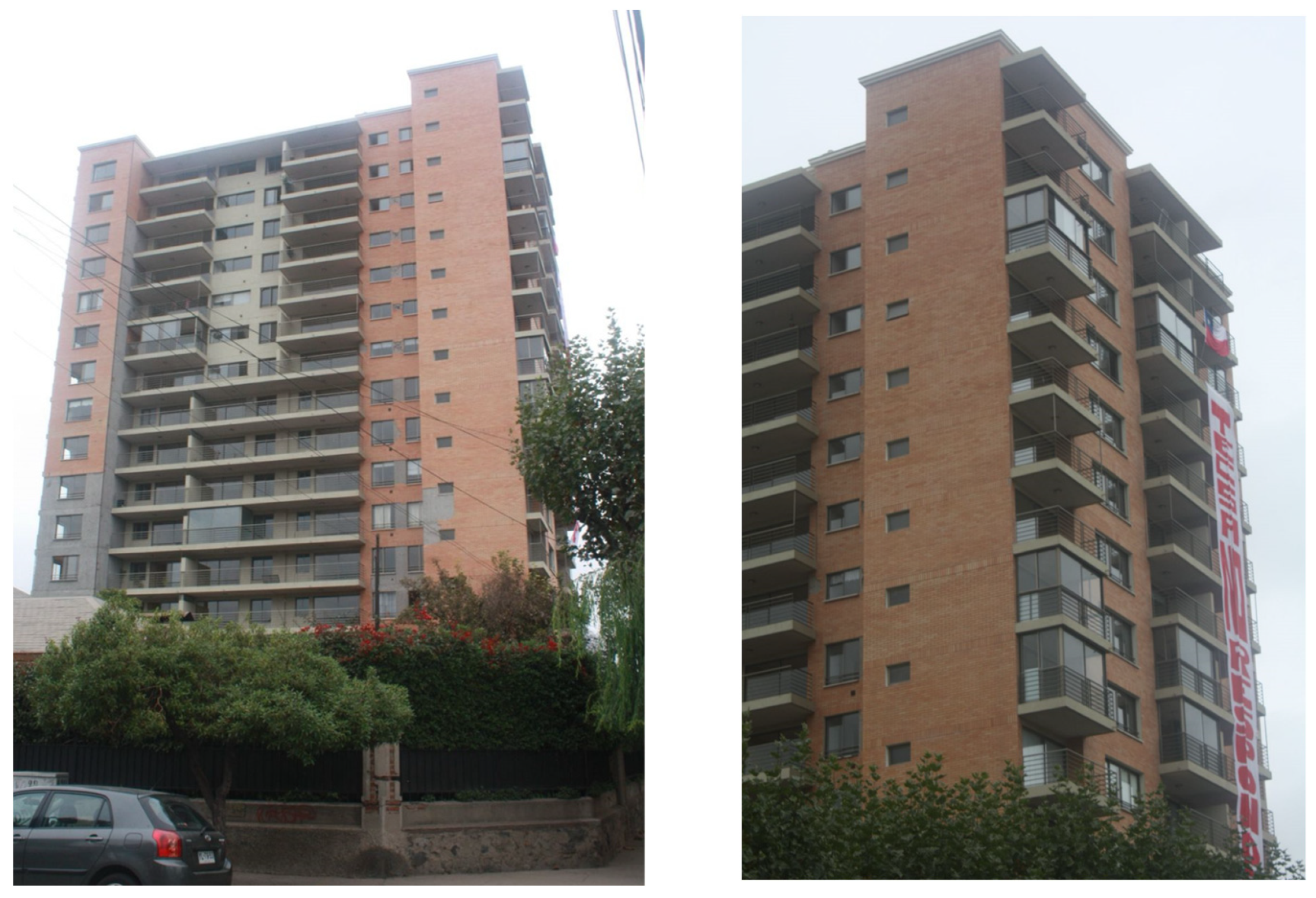
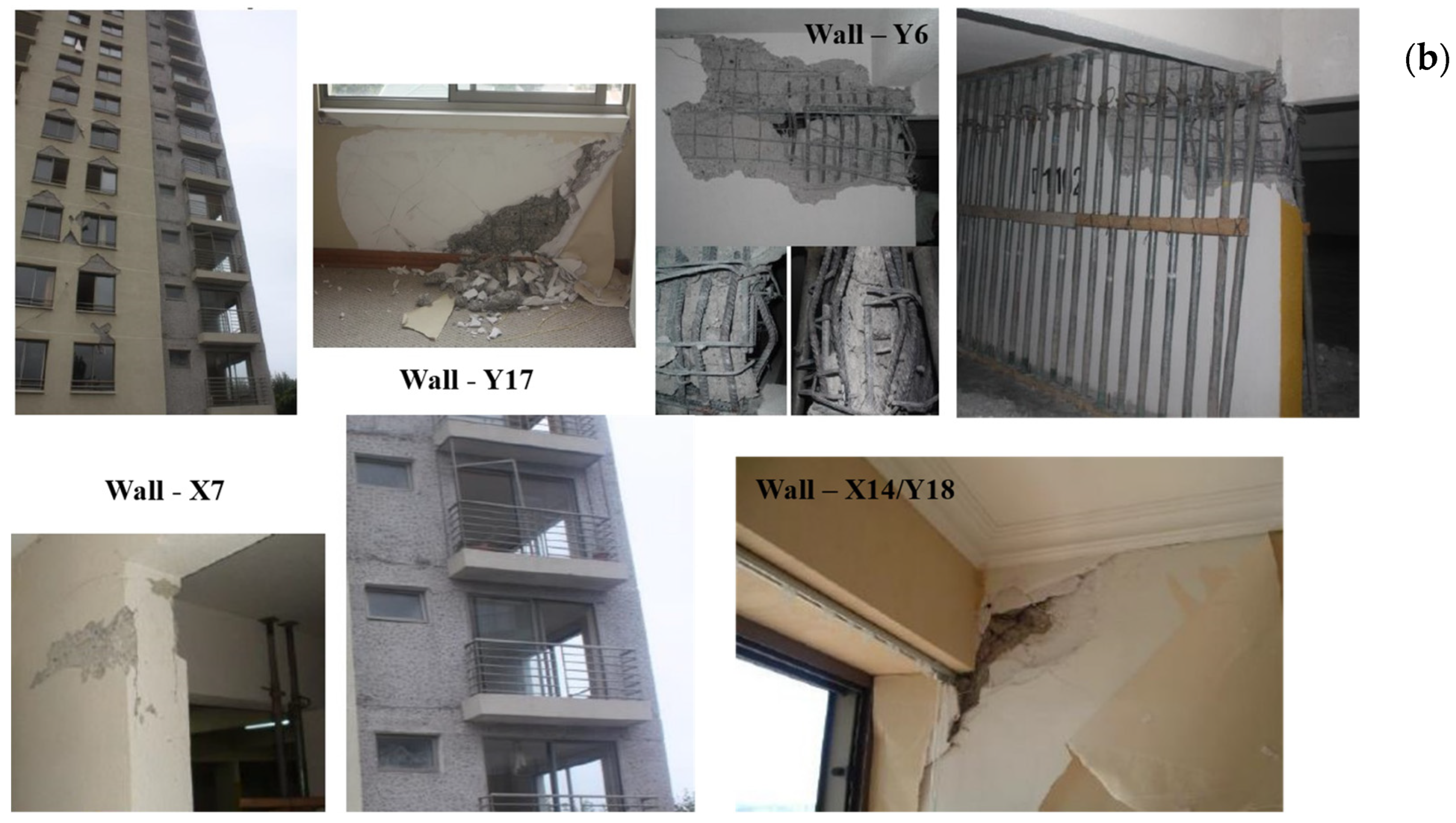
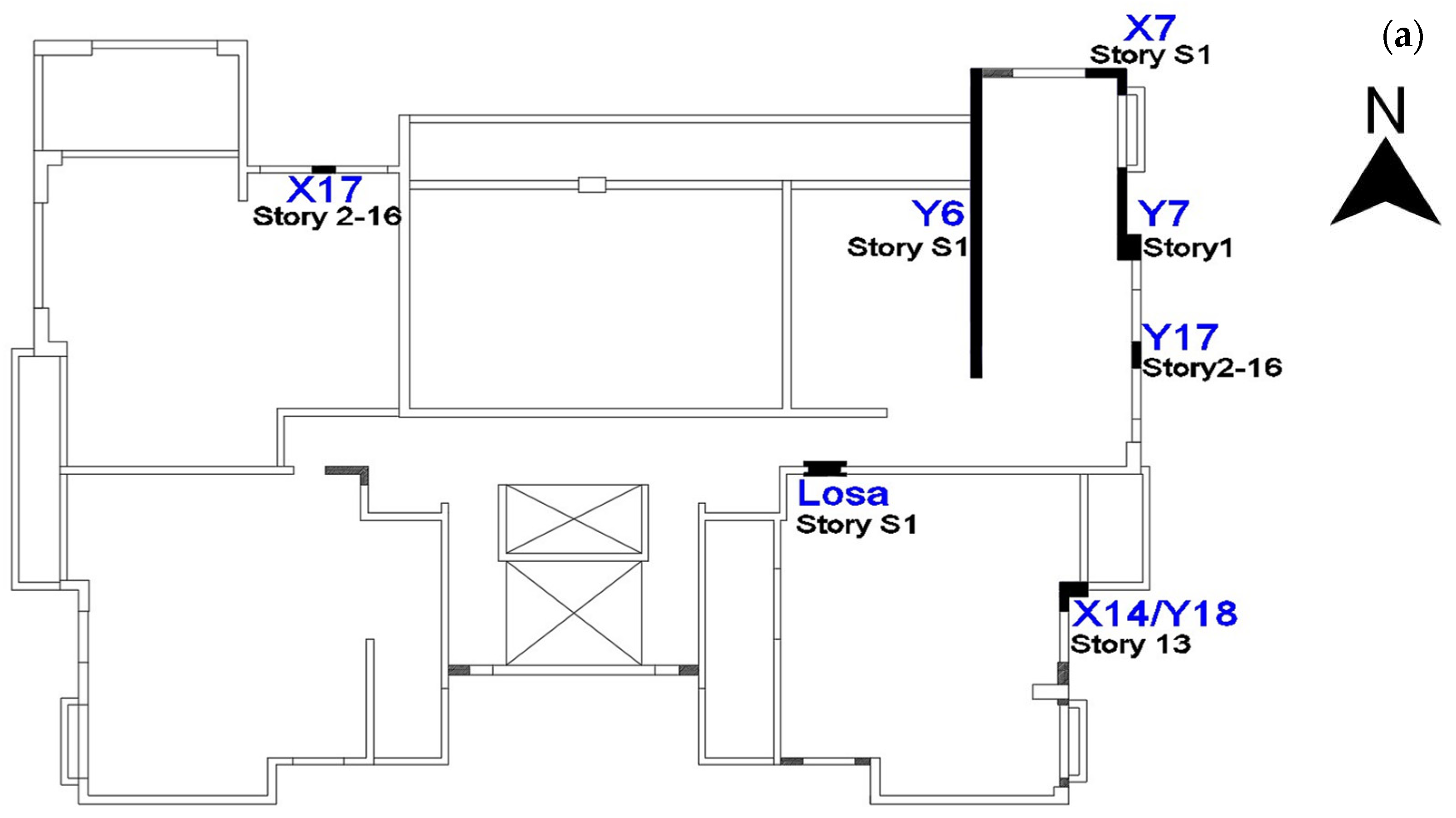
3.1. Description of Building and Observed Damages
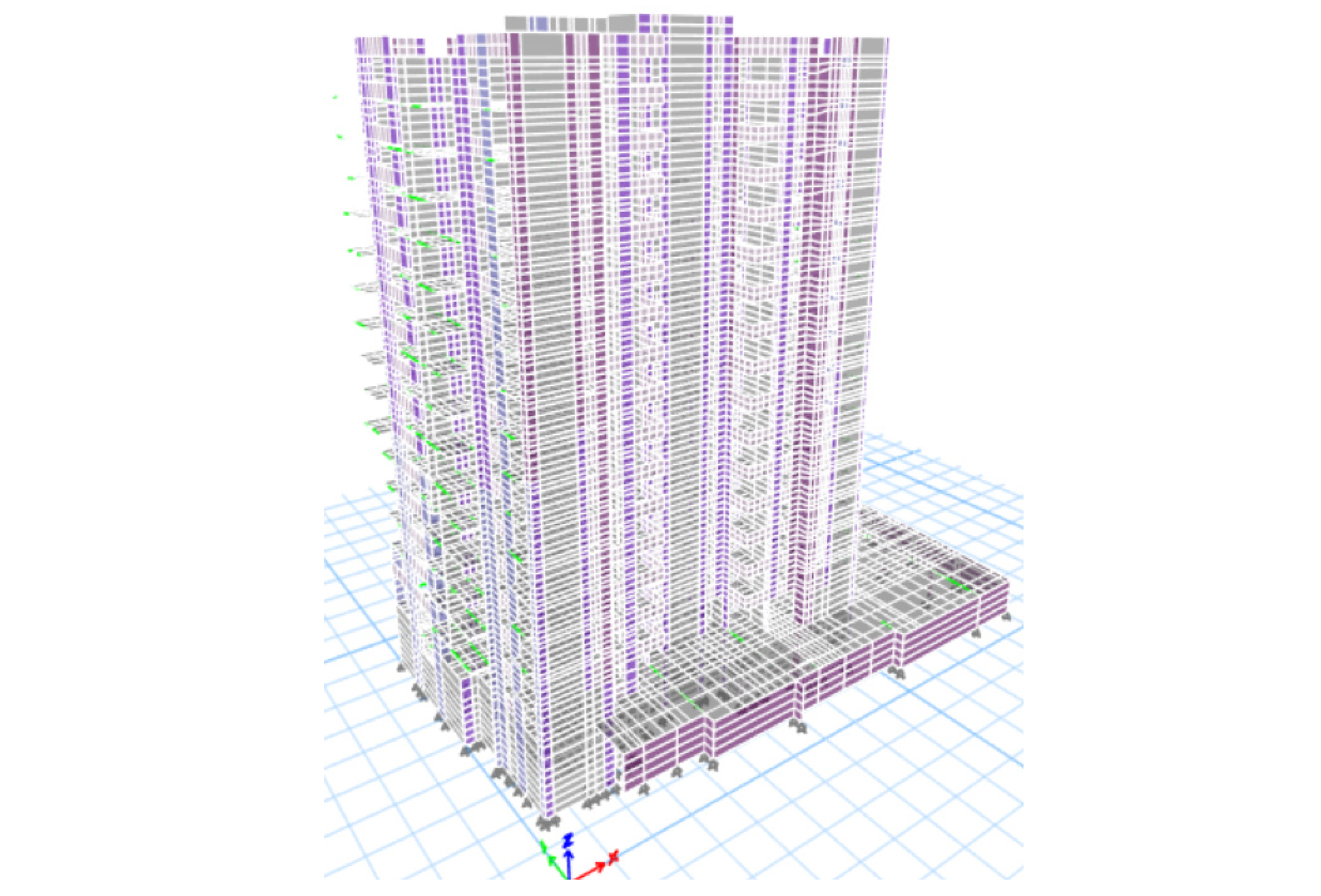
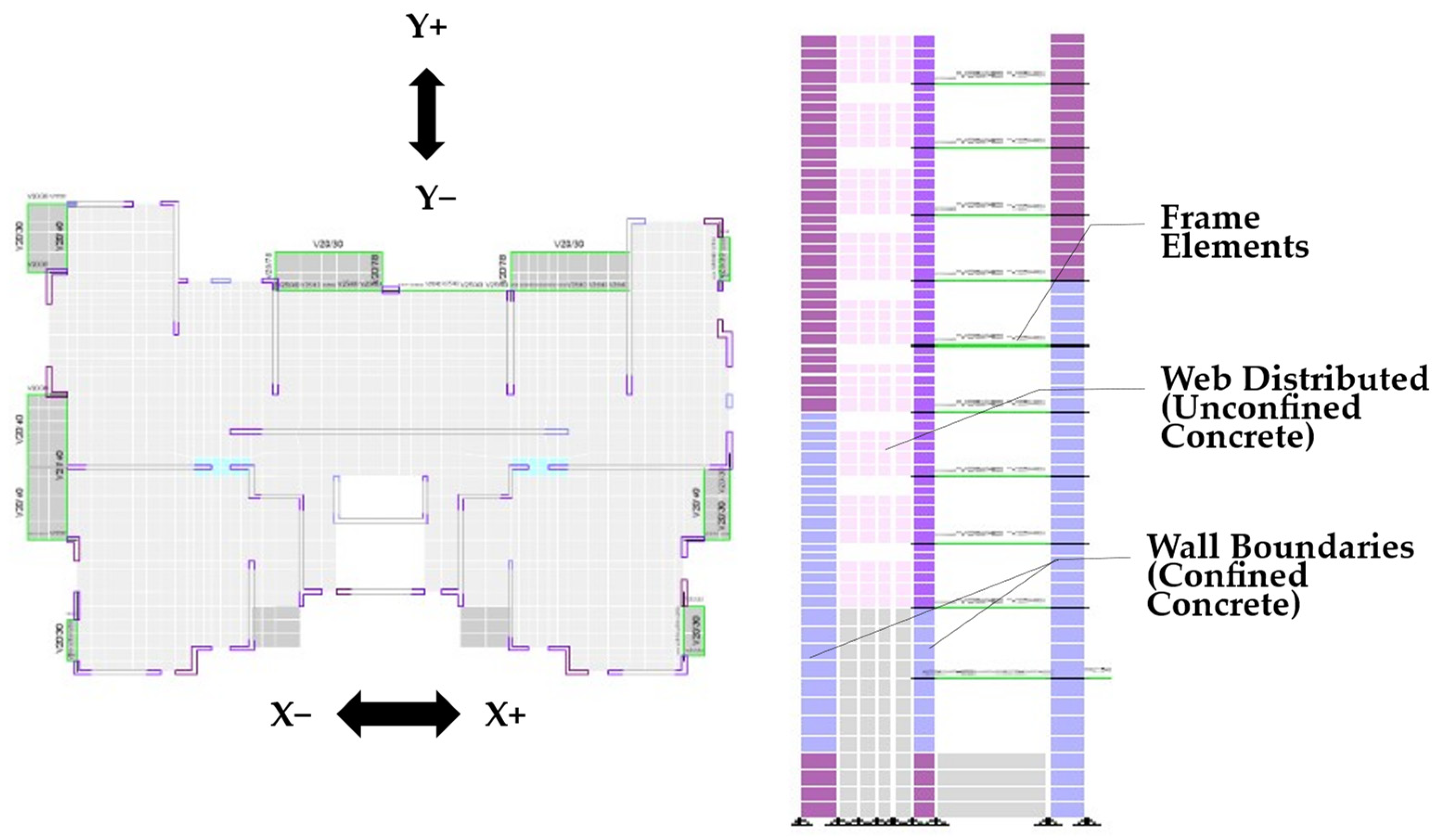
3.2. Analytical Models
3.3. Material Constitutive Models
3.4. Load Application
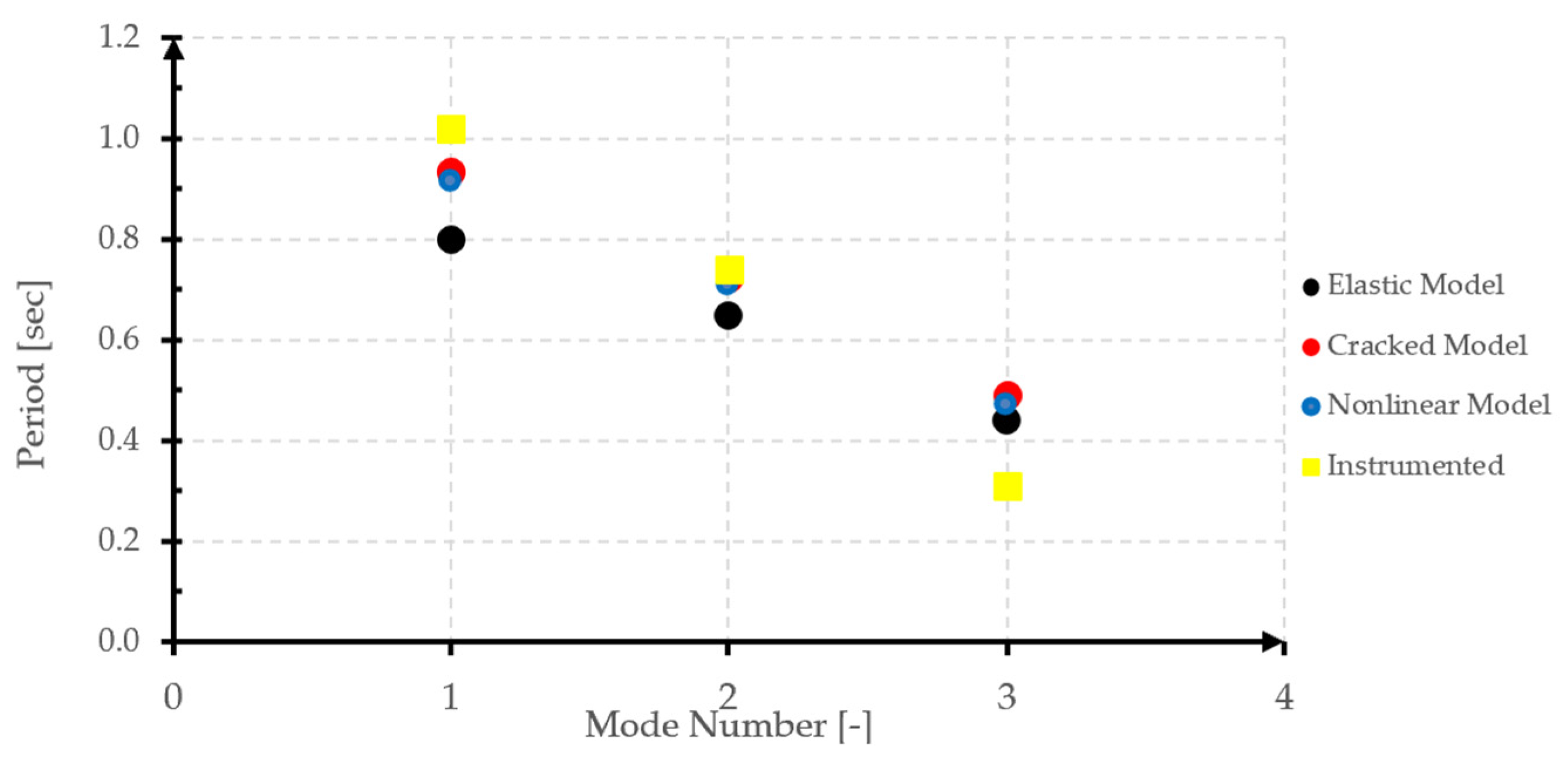
3.5. Analysis of Results
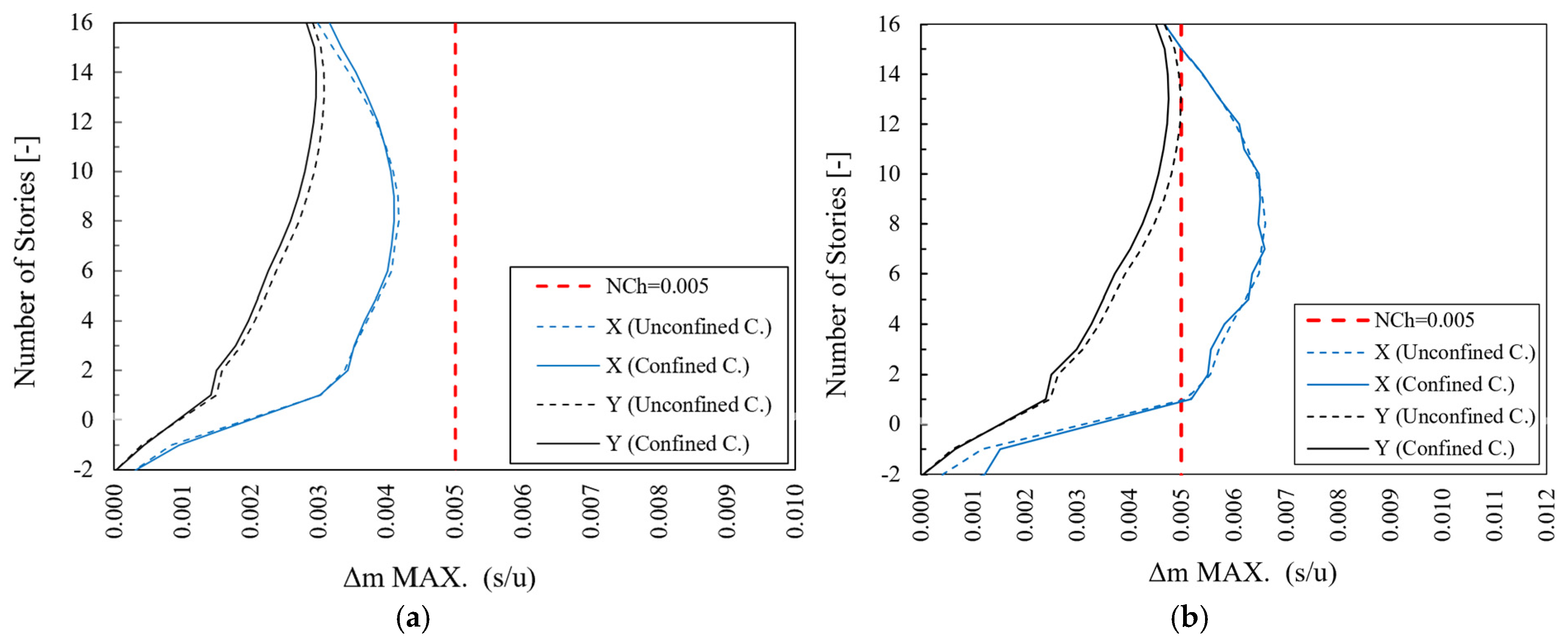
3.5.1. Global Response Analysis
3.5.2. Local Response Analysis
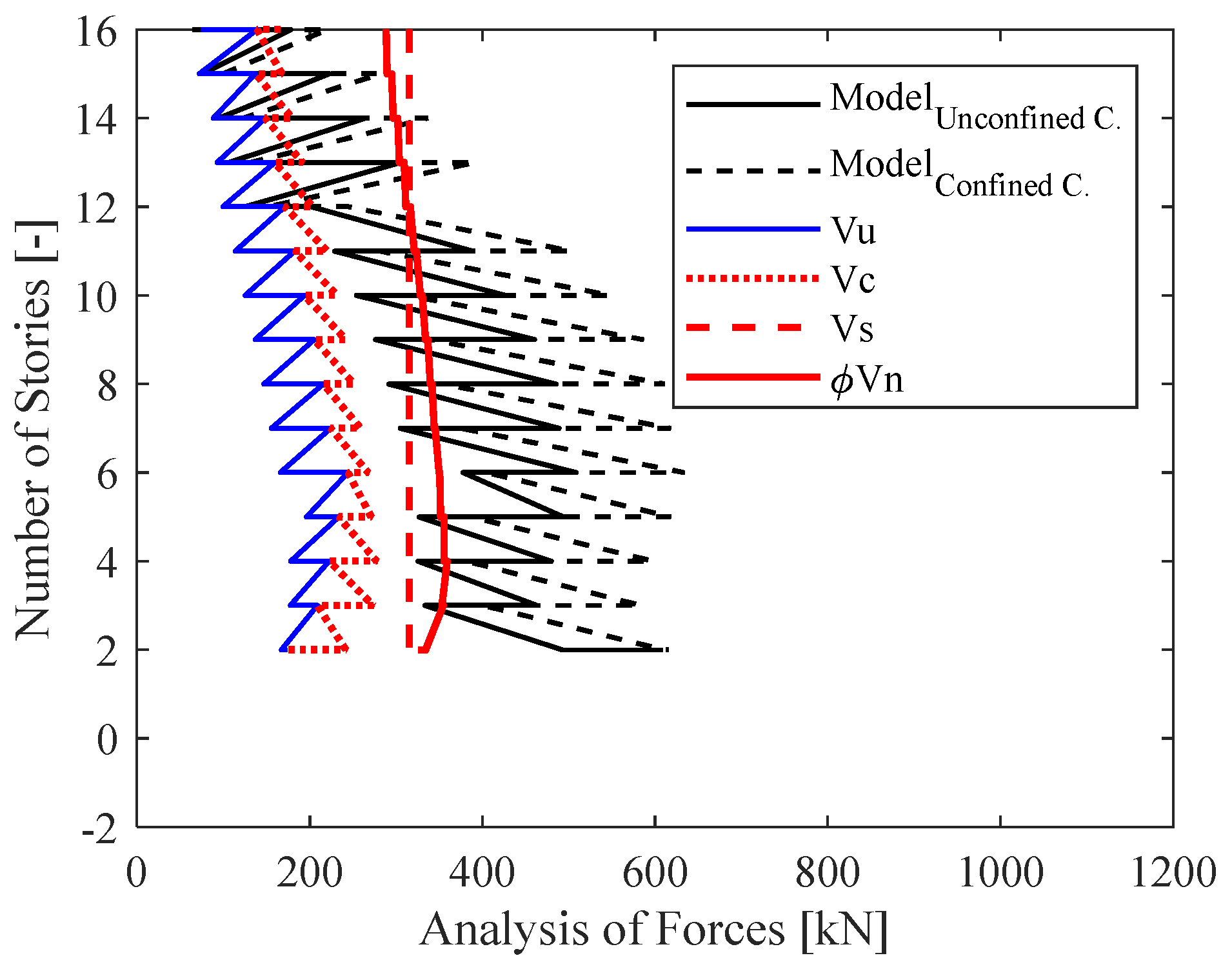
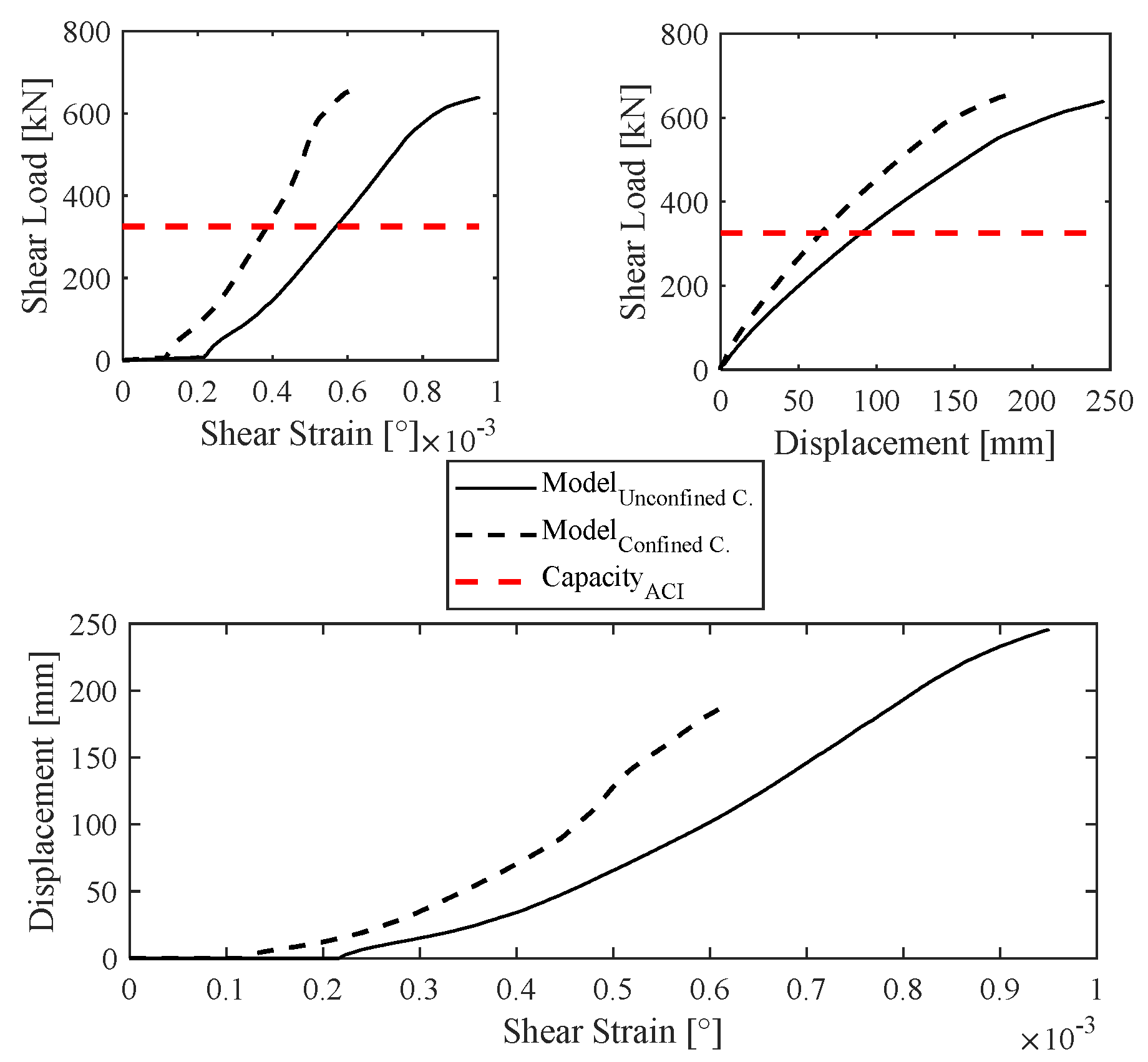
- Wall X17
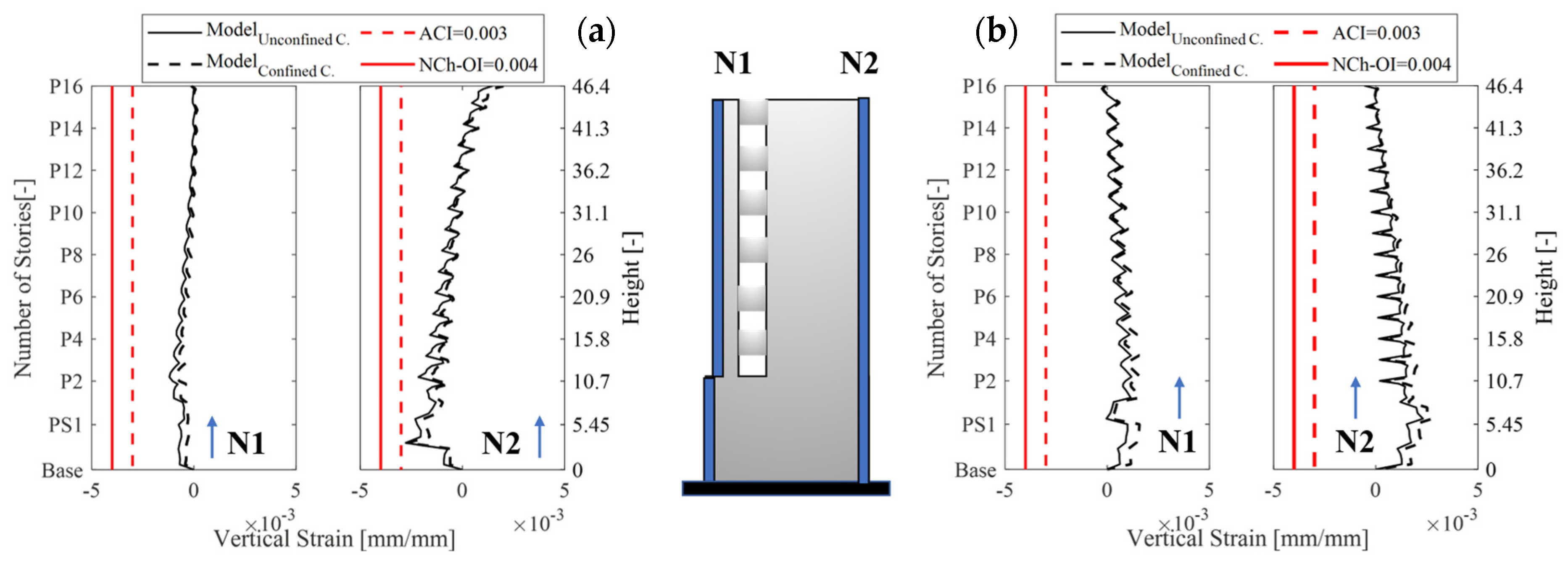
- Wall Y7
- Slabs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murota, T. Concept of the Regulation of Seismic Design of Buildings in Japan; National Disaster Prevention Center: Mexico City, Mexico, 1995; pp. 1–477. Available online: http://cidbimena.desastres.hn/pdf/spa/doc6526/doc6526.htm (accessed on 20 January 2024). (In Spanish)
- Fischinger, M.; Rejec, K.; Isaković, T. Inelastic Shear Response of RC Walls: A Challenge in Performance Based Design and Assessment. In Performance-Based Seismic Engineering: Vision for an Earthquake Resilient Society. Geotechnical, Geological and Earthquake Engineering; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Performance Based Seismic Engineering of Buildings; SEAOC-Vision 2000 Committee: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1995.
- Applied Technology Council. Seismic Evaluation and Retrofit of Concrete Buildings; California Seismic Safety Commission: Redwood City, CA, USA, 1996; Volume 1.
- FEMA 356 Prestandard and Commentary for the Seismic Rehabilitation of Building; No. November; Federal Emergency Management Agency: Washington DC, USA, 2000.
- PEER-TBI. Guidelines for Performance Based Seismic Design of Tall Buildings; No. May; Pacific Earthquake Engineering Center: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ASCE/SEI-41-17; Seismic Evaluation and Retrofit of Existing Buildings. American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2017. [CrossRef]
- LATBSDC. An Alternative Procedure for Seismic Analysis and Design of Tall Buildings Located in the Los Angeles Region, 2020th ed.; LATBSDC: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- ACHISINA. Performance-Based Seismic Design. An Alternative Procedure for Seismic Analysis and Design of Buildings, 1st ed.; ACHISINA: Santiago de Chile, Chile, 2017; Available online: http://www.achisina.cl/index.php/publicaciones/manuales-guias (accessed on 24 January 2024). (In Spanish)
- Regulation that Establishes the Design and Calculation Requirements for Reinforced Concrete; DS60; Ministry of Housing and Urbanism: Santiago, Chile, 2011. (In Spanish)
- Regulation That Establishes the Seismic Design of Buildings; DS61; Ministry of Housing and Urbanism: Santiago, Chile, 2011; Volume 1. Available online: https://medium.com/@arifwicaksanaa/pengertian-use-case-a7e576e1b6bf (accessed on 11 June 2011). (In Spanish)
- Ruiz, S.; Saragoni, R. Attenuation Formulas for the Chilean Subduction considering the two Mechanisms of Seismogenesis and Soil Effects (Spanish). In Congreso Chileno de Sismología e Ingeniería Antisísmica; ACHISINA: Concepción, Chile, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- NCh433; Seismic Design of Buildings. Instituto Nacional de Normalización INN: Santiago, Chile, 2012. (In Spanish)
- LATBSDC. An Alternative Procedure for Seismic Analysis and Design of Tall Buildings located in the Los Angeles Region, 2014th ed.; LATBSDC: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Petrone, F.; McCallen, D.; Buckle, I.; Wu, S. Direct measurement of building transient and residual drift using an optical sensor system. Eng. Struct. 2018, 176, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, R.; Lafontaine, M.; Bonelli, P.; Boroschek, R.; Guendelman, T.; Massone, L.M.; Saragoni, R.; Rojas, F.; Yañez, F. The quest for resilience: The Chilean practice of seismic design for reinforced concrete buildings. Earthq. Spectra 2021, 37, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahumada, M. Finite Element Modeling of HA Slender Walls with Discontinuities at the Base. Design Recommendations. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad de Chile, Santiago de Chile, Chile, 2014. (In Spanish). [Google Scholar]
- Massone, L.M.; Polanco, P.; Herrera, P. Experimental and analytical response of RC wall boundary elements. In Proceedings of the NCEE 2014—10th U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering: Frontiers of Earthquake Engineering, Anchorage, Alaska, 21–25 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cáceres, I. Compilation of Information on Flexural Compression Damage in Reinforced Concrete Walls for the Earthquake of February 27, 2010 and Study of Deformation Demands; Universidad de Chile: Santiago de Chile, Chile, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- FEMA 306, Evaluation of Earthquake-Damaged Concrete and Masonry Wall Buildings, 1st ed.; Applied Technology Council: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; Available online: https://www.atcouncil.org/files/FEMA306.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Anas, S.M.; Alam, M.; Umair, M. Experimental and numerical investigations on performance of reinforced concrete slabs under explosive-induced air-blast loading: A state-of-the-art review. Struct. J. 2021, 31, 428–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Dong, Z.Q.; Li, H.N. Simplified Collapse-Prevention Evaluation for the Reserve System of Low-Ductility Steel Concentrically Braced Frames. J. Struct. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Dong, Z.Q.; Yu, D.H. Seismic damage characteristics and evaluation of aboveground-underground coupled structures. Eng. Struct. 2023, 283, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.; Priestley, M.; Gill, W.D. Ductility of Square Confined Concrete Columns. J. Struct. Div. 1982, 108, 929–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCh430; Norma Chilena Oficial NCh430.Of2008 Hormigón Armado—Requisitos de Diseño y Cálculo. Instituto Nacional de Normalización INN: Santiago, Chile, 2008.
- Darwin, D.; Pecknold, D.A.W. Inelastic Model for Cyclic Biaxial Loading of Reinforced Concrete; University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, United States: Urbana-Champaign, IL, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Darwin, D.; Pecknold, D.A. Analysis of cyclic loading of plane RC structures. Comput. Struct. 1977, 7, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mander, J.B.; Priestley, M.J.N.; Park, R. Theoretical Stress-Strain Model for Confined Concrete. Struct. Eng. J. 1988, 114, 1804–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatcioglu, M.; Razvi, S. Strength and Ductility of Confined Concrete. J. Struct. Eng. 1992, 118, 1590–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belarbi, A.; Hsu, T.T.C. Constitutive Laws of Concrete in Tension and Reinforcing Bars Stiffened By Concrete. Struct. J. 1994, 91, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massone, L.M.; Orakcal, K.; Wallace, J. Shear-flexure interaction for structural walls. ACI Simp. Pap. 2006, SP-236, 127–150. [Google Scholar]
- Forcellini, D. Seismic fragility of tall buildings considering soil structure interaction (SSI) effects. Struct. J. 2022, 45, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACI 318R-19; Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary. American Concrete Institute: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Paulay, T.; Priestley, M.N. Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete and Masonry Buildings; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Forcellini, D. An expeditious framework for assessing the seismic resilience (SR) of structural configurations. Struct. J. 2023, 56, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneau, M.; Reinhorn, A. Exploring the concept of seismic resilience for acute care facilities. Earthq. Spectra 2007, 23, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarfone, R.; Morigi, M.; Conti, R. Assessment of dynamic soil-structure interaction effects for tall buildings: A 3D numerical approach. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. J. 2020, 128, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ETABS. CSI: Analysis Reference Manual, 2016th ed.; 2016; Volume 1, Available online: www.csiamerica.com (accessed on 16 March 2024).










| Performance Level | Vision 2000 | FEMA 356 | TBI/LATBSDC | ASCE 41 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drift Transient | Drift Permanent | Drift Transient | Drift Permanent | Drift Transient | Drift Permanent | Loss of Resistance | Drift Transient | Drift Permanent | |
| Operational | <±0.2% | ||||||||
| Immediate Occupancy | <±0.5% | 1% | Negligible | 0.50% | Negligible | Minor or non-structural damage | Negligible | ||
| Life Safety | <±1.5% | <±0.5% | 2% | 1% | Enough to cause non-structural damage | Notable | |||
| Collapse Prevention | <±2.5% | <±2.5% | 4% | 4% | 0.03 Қi */0.045 Қi ** | 0.01 Қi */0.015 Қi ** | 20% | Extensive | |
| Earthquake Design Level | Vision 2000 | FEMA 356 | TBI/LATBSDC | ASCE 41 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequent | 50%/30 years | 50%/30 years | ||
| Occasional | 50%/50 years | |||
| Rare | 10%/50 years | 10%/50 years | 10%/50 years | |
| Very Rare | 10%/100 years | 2%/50 years | 10%/100 years | 2%/50 years |
| Global Acceptability Criteria | LATBSDC | Chilean Code |
|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2017 | |
| Performance Level→ | Serviceability Evaluation | Immediate Occupancy |
| Inter-Story Drift | 0.5% | 0.5–0.7% |
| Performance Level→ | Collapse Prevention Evaluation | Additional Deformation Capacity |
| Peak Transient Drift | 0.03 Қi */0.045 Қi ** | Not Applicable |
| Peak Permanent Drift | 0.01 Қi */0.015 Қi ** | |
| Loss of Resistance | 20% |
| Earthquake Design Level | Performance Level | |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate Occupancy | Additional Deformation Capacity | |
| Design Earthquake | ⃝ | |
| Maximum Earthquake Considered | ⃝ | |
| Performance Levels | Inter-Story Drift | |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate Occupancy | Fragile non-structural elements | 0.005 |
| Ductile non-structural elements | 0.007 | |
| Additional Deformation Capacity | Not applicable | |
| Deformation-Controlled Elements | Description | Performance Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immediate Occupancy | Additional Deformation Capacity | ||||
| Unconfined Boundary Element | Confined Boundary Element | Unconfined Boundary Element | Confined Boundary Element | ||
| Concrete structural walls | Concrete’s strain | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.003 | 0.015 |
| Steel’s strain | 0.03 | 0.05 | |||
| Structural columns in concrete frames | Plastic rotation | 0.005 | 0.025 | ||
| Structural beams in concrete frames | Plastic rotation | 0.01 | 0.02 | ||
| Concrete coupling beams | Plastic rotation | 0.01 | - | ||
| Model Types | Description | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Lineal | 100% Inertia Model | X/Y |
| Cracked Model Reducing the out-of-plane bending slabs’ inertia by 25%. | X/Y | |
| Nonlinear | Unconfined C. Model Representative of buildings designed with NCh433 (2009). | X/Y |
| Confined C. Model Representative of buildings designed with NCh433 (2012) | X/Y | |
| Confined C. Model Reducing the inertia of the elastic slabs by 40% in membrane and a 10% in bending. | X/Y |
| Material | Quality | f’c/Fy [MPa] |
|---|---|---|
| Concrete | H30 | 25 |
| Steel | A630-420H | 420 |
| Load Type | Description | Load | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Live Load | Parking lots | 50 | [MPa] |
| Departments and halls | 20 | [MPa] | |
| Terraces | 25 | [MPa] | |
| Dead Load | Partition walls | 10 | [MPa] |
| Over slab | 10 | [MPa] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suquillo, B.; Rojas, F.; Massone, L.M. Seismic Performance Evaluation of a Chilean RC Building Damaged during the Mw8.8 Chile Earthquake. Buildings 2024, 14, 1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14041028
Suquillo B, Rojas F, Massone LM. Seismic Performance Evaluation of a Chilean RC Building Damaged during the Mw8.8 Chile Earthquake. Buildings. 2024; 14(4):1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14041028
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuquillo, Betzabeth, Fabián Rojas, and Leonardo M. Massone. 2024. "Seismic Performance Evaluation of a Chilean RC Building Damaged during the Mw8.8 Chile Earthquake" Buildings 14, no. 4: 1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14041028
APA StyleSuquillo, B., Rojas, F., & Massone, L. M. (2024). Seismic Performance Evaluation of a Chilean RC Building Damaged during the Mw8.8 Chile Earthquake. Buildings, 14(4), 1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14041028






