Scenarios of Progressive Pancake/Bending Collapse Considering Elastic/Plastic Reinforced Concrete Buildings
Abstract
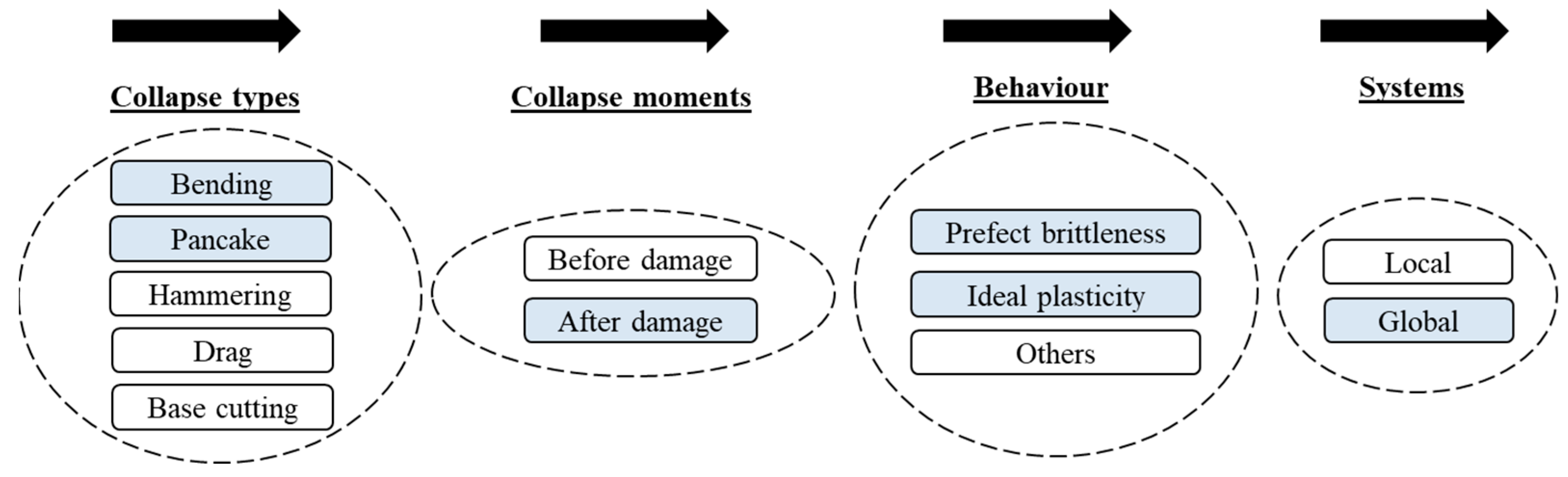
:1. Introduction
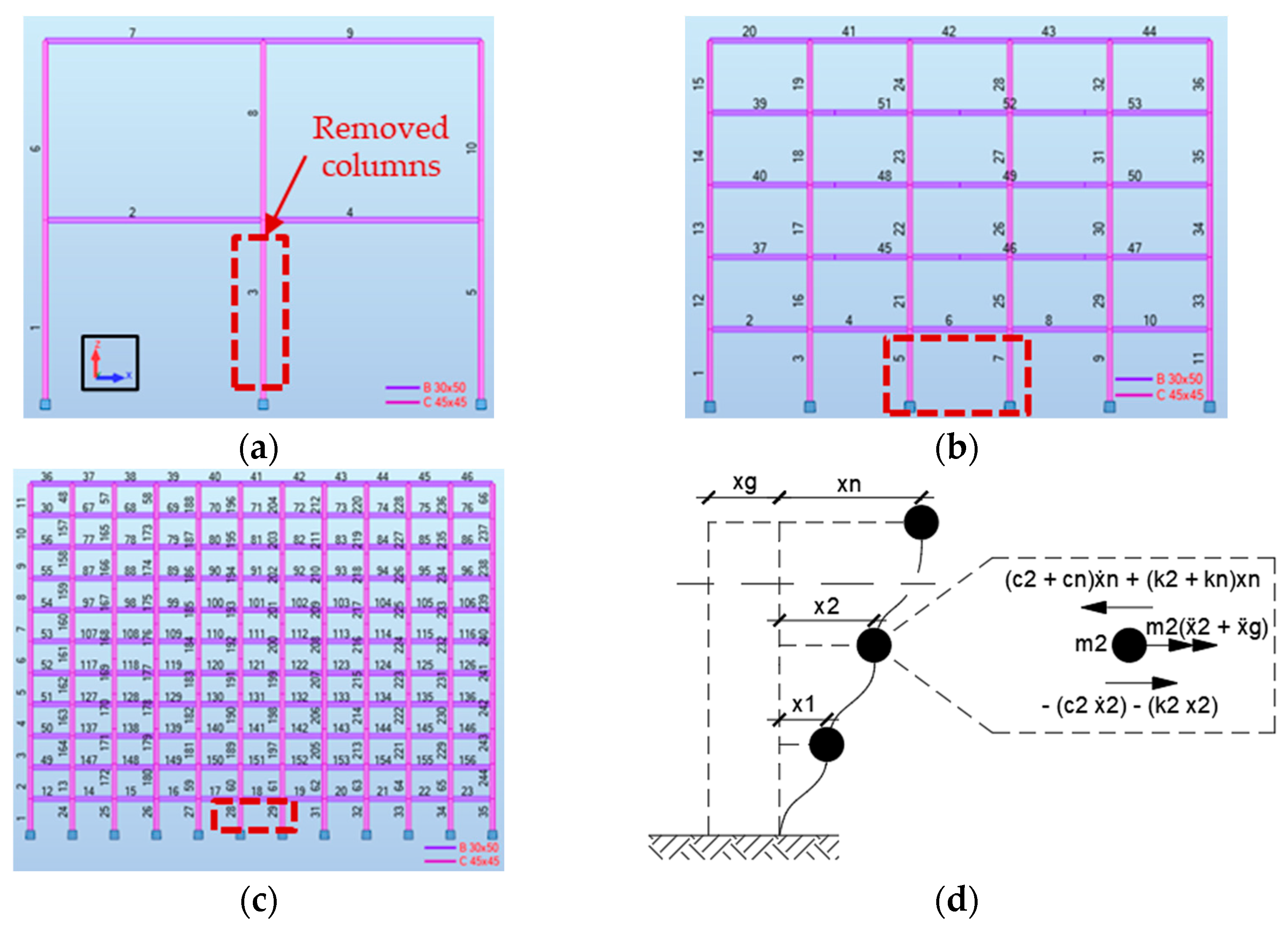
2. Structural Scheme
2.1. Dynamic Equilibrium
2.2. Collapse Loadings
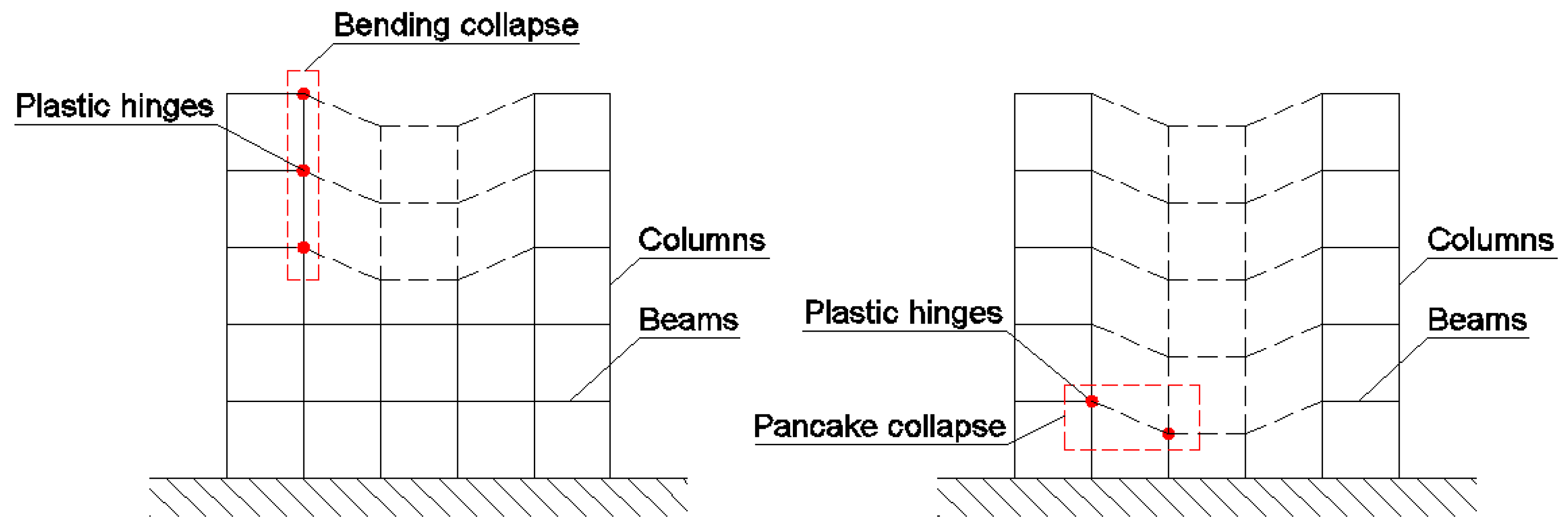
2.2.1. Bending Mechanisms
2.2.2. Pancake Mechanisms
2.2.3. Activation of Collapse Mechanisms
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Materials
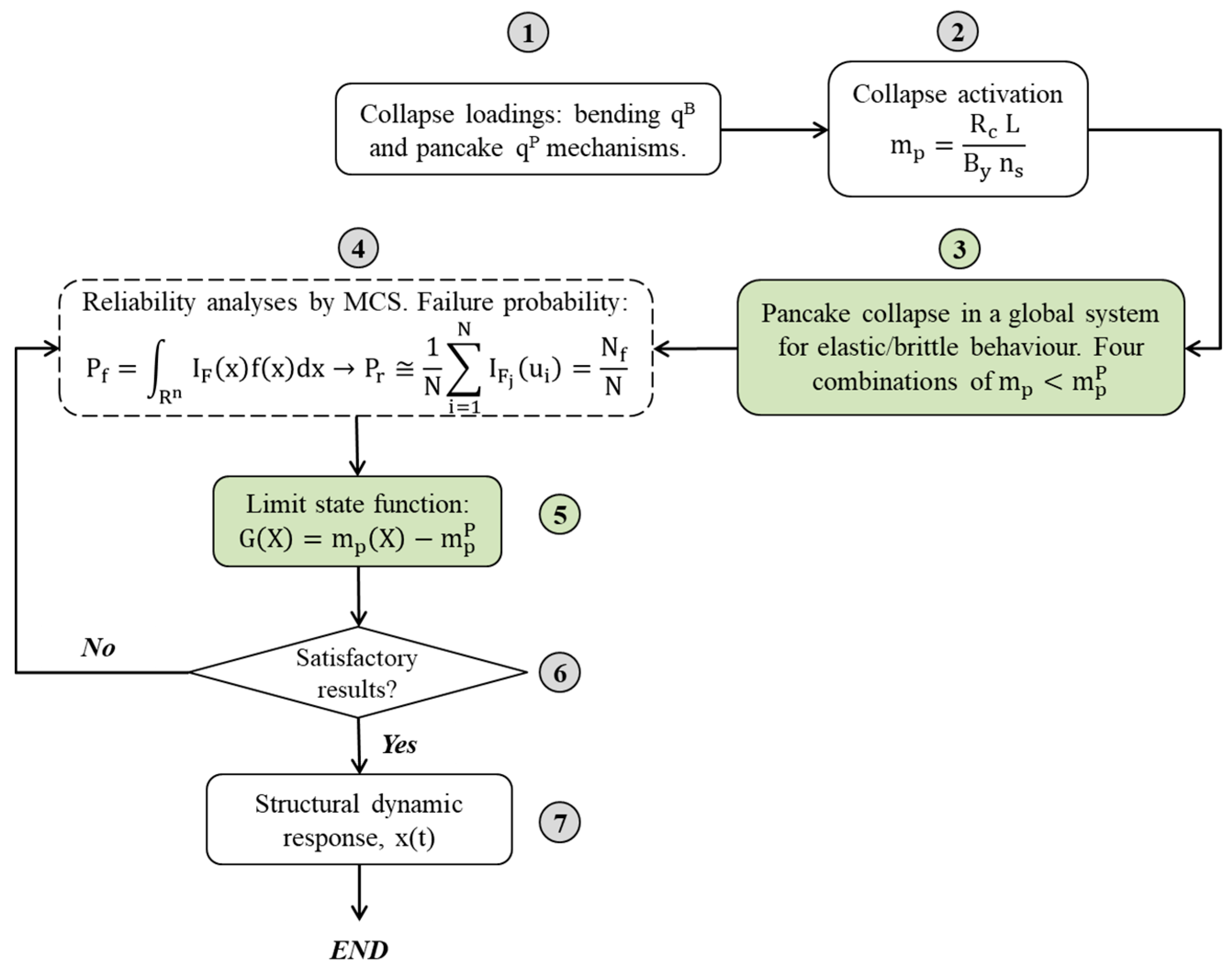
3.2. Methodology
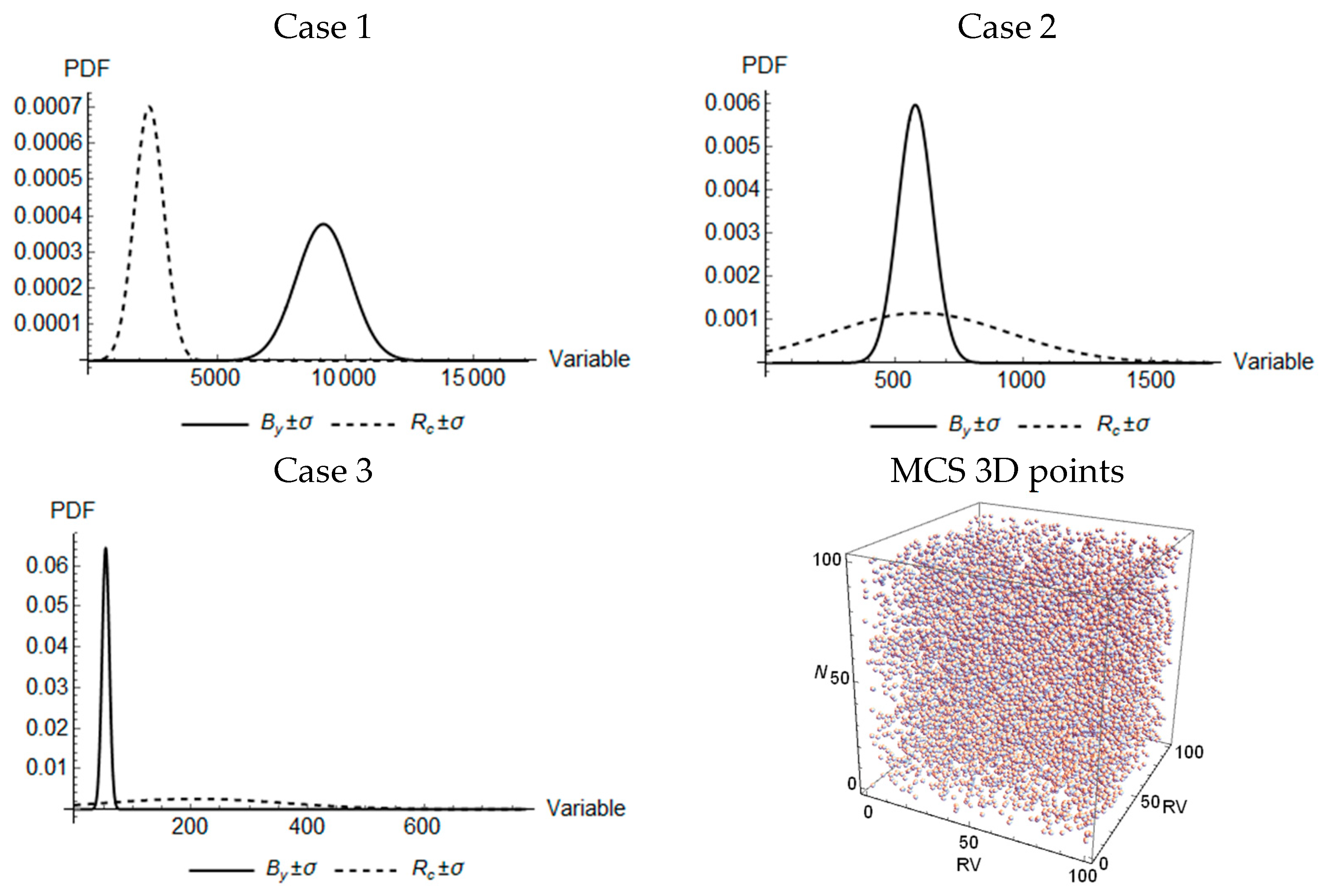
3.2.1. Probability of Failure for Pancake Collapse
3.2.2. Proposed Limit State Function
4. Analyses and Results
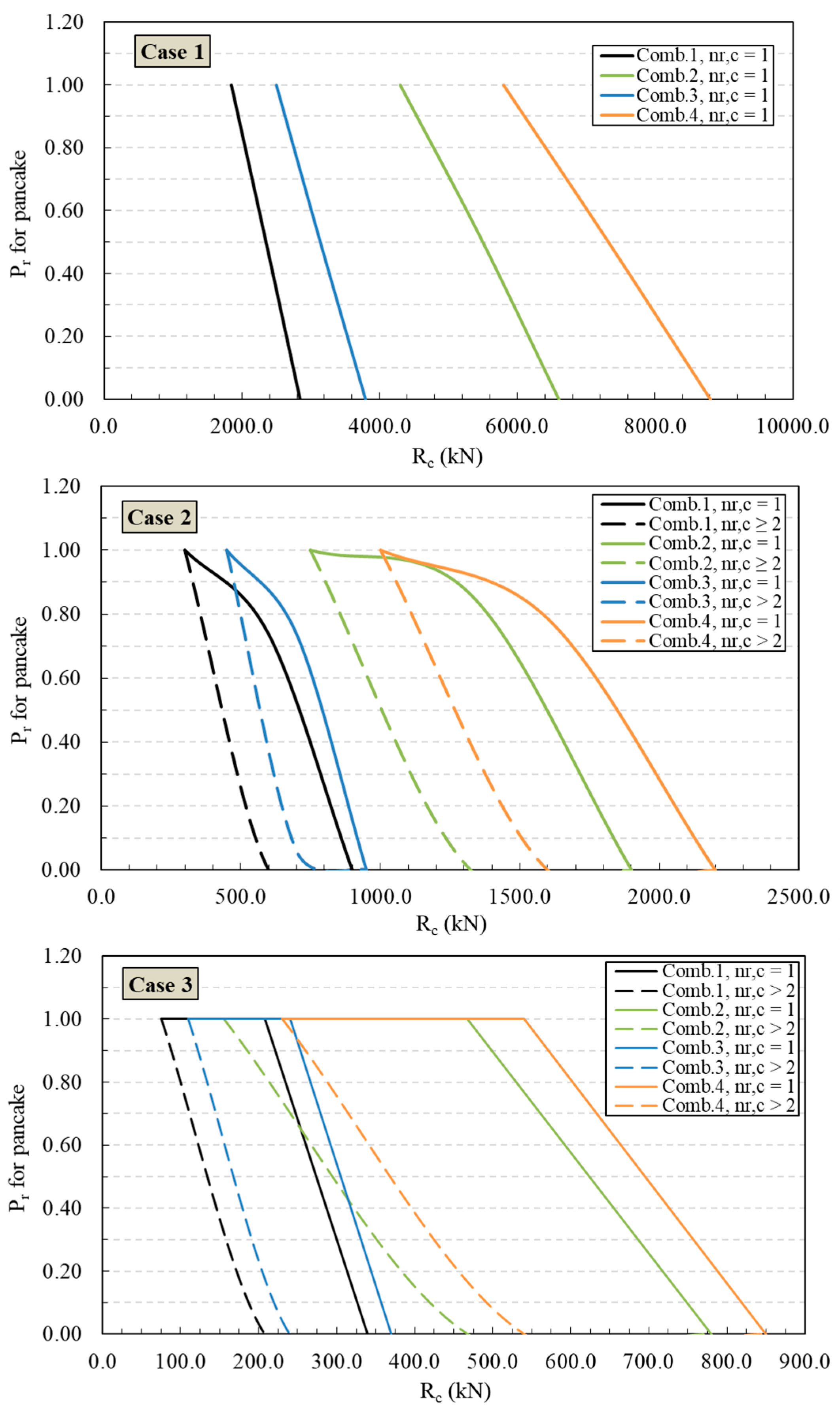
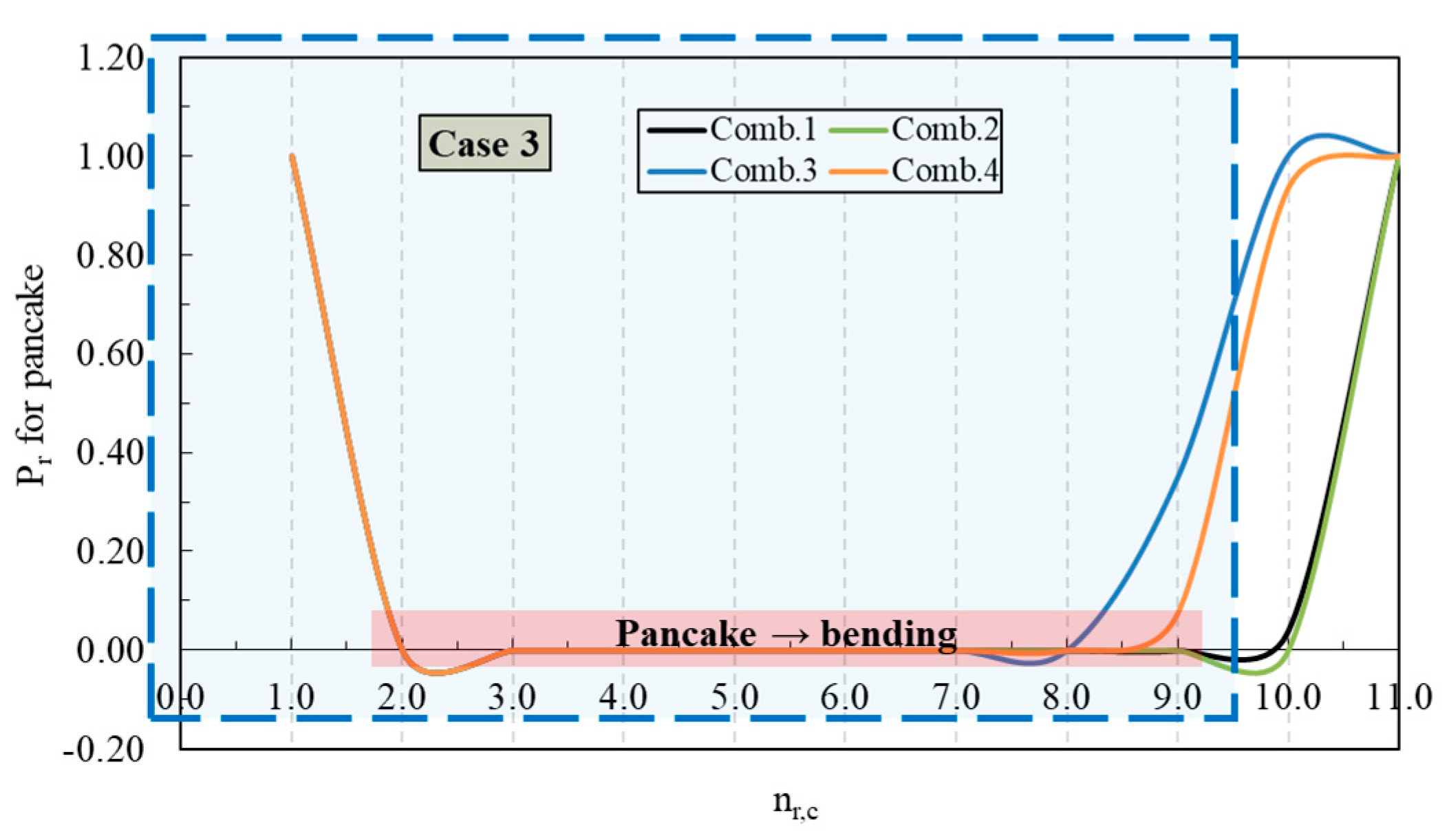
4.1. Scenarios for Pancake Collapse
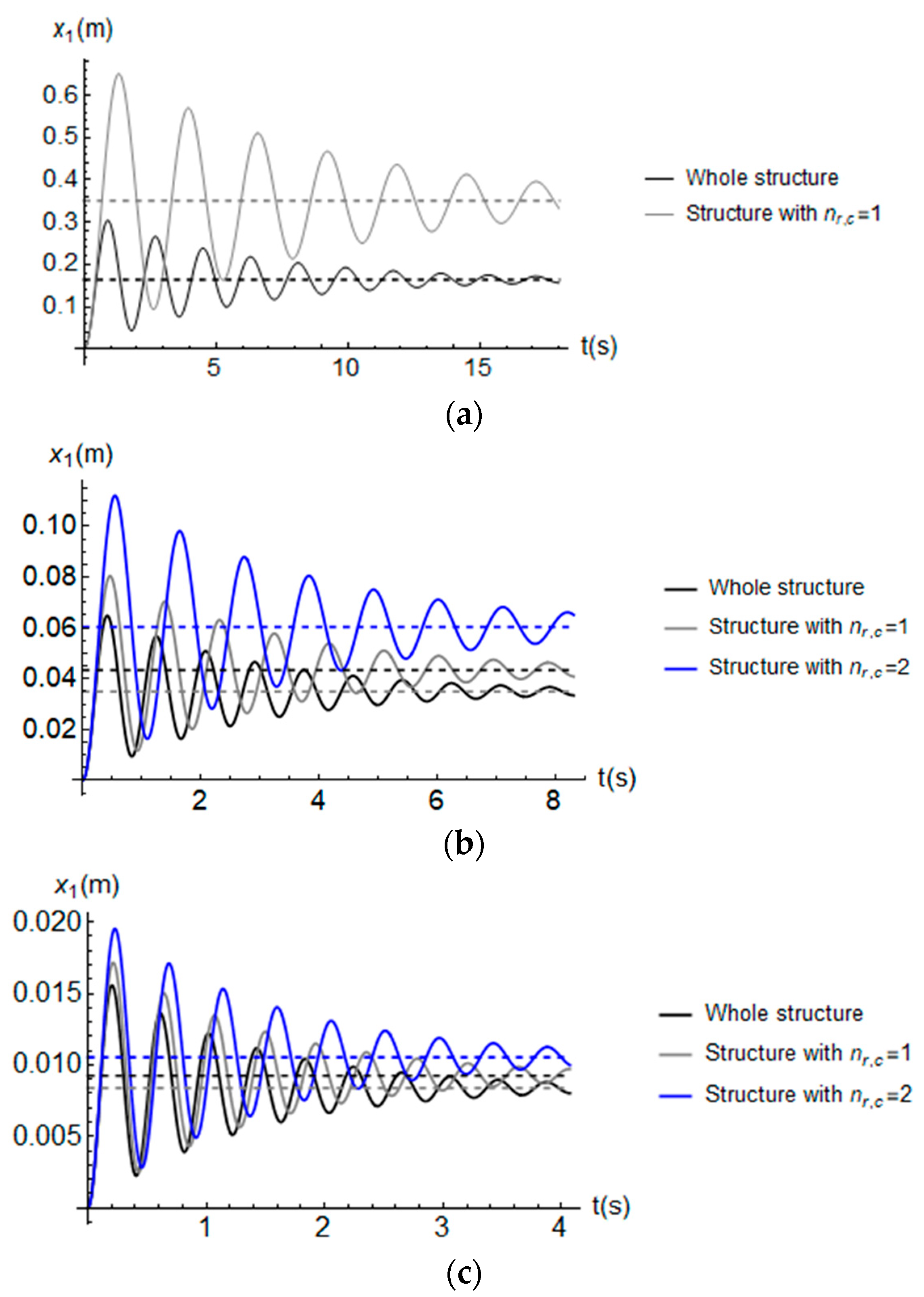
4.2. Dynamic Response of the Buildings
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pearson, C.; Delatte, N. Roman Point apartment tower collapse and its effect on building codes. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2005, 19, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.-G.; Xu, L. Upgrading of reinforced concrete frame using novel detailing technique for progressive collapse prevention. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 20, 5943–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Zeng, B.; Huang, L.-J.; Zhou, Z. Investigation on progressive collapse resistance of prestressed concrete frames with infilled walls. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 143, 106866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaia, B.M.; Masoero, E.; Wittel, F.K.; Herrmann, H.J. DEM simulations of the progressive collapse of framed structures. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Fracture (ICF 2009), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 12–17 July 2009; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Alshaikh, I.M.; Abu Bakar, B.; Alwesabi, E.A.; Abadel, A.A.; Alghamdi, H.; Altheeb, A.; Tuladhar, R. Progressive collapse behavior of steel fiber-reinforced rubberized concrete frames. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Biagi, V.; Chiaia, B. Complexity and robustness of frame structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 3723–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoero, E.; Wittel, F.K.; Chiia, B.M.; Herrmann, H.J. Parametric Study of the Progressive Collapse of 2D Framed Structures; 2009; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- EN 1998-4:2006; Eurocode 1: Actions on Structures, Part 1: Basis of Design. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 1994.
- Carmona, H.A.; Wittel, F.K.; Kun, F.; Herrmann, H.J. Fragmentation processes in impact of spheres. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2008, 77, 051302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoero, E.; Darò, P.; Chiaia, B. Progressive collapse of 2D framed structures: An analytical model. Eng. Struct. 2013, 54, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-X.; Li, S.-T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Yi, W.-J. Beam torsion effect of monolithic precast concrete beam-column substructures during progressive collapse. Eng. Struct. 2023, 278, 115457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, D.; Lam, D.; Forth, J.; Ye, J.; Tsavdaridis, K.D. An evaluation of modelling approaches and column removal time on progressive collapse of building. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 153, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassis, A.G.; Izzuddin, B.A.; Elghazouli, A.Y.; Nethercot, D.A. Progressive collapse of multi-storey buildings due to sudden column loss—Part II: Application. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 1424–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoero, E.; Wittel, F.K.; Herrmann, H.J.; Chiaia, B.M. Progressive Collapse Mechanisms of Brittle and Ductile Framed Structures. J. Eng. Mech. 2010, 136, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Salvatori, M. Perché gli Edifici Cadono; Bombiani: Milan, Italy, 1997; p. 359. [Google Scholar]
- Medeot, R. The European Standard on Anti-Seismic Devices, New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering (NZSEE). In Proceedings of the 15th World Conference on Seismic Isolation, Energy Dissipation and Active Vibration Control of Structures, Wellington, New Zealand, 27–29 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zacchei, E.; Brasil, R. Semi-active tuned mass dampers under combined variable actions of friction forces and external disturbances. Arab. J. Geosci. 2023, 16, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Zhong, W.; Hao, J.; Song, X.; Tan, Z. Calculation of the resistance of an unequal span steel substructure against progressive collapse based on the component method. Eng. Struct. 2019, 182, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwondo, R.; Cunningham, L.; Gillie, M.; Bailey, C. Progressive collapse analysis of composite steel frames subject to fire following earthquake. Fire Saf. J. 2019, 103, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayegani, A.; Nouri, G. Application of Smart Dampers for Prevention of Seismic Pounding in Isolated Structures Subjected to Near-fault Earthquakes. J. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 26, 4069–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayegani, A.; Nouri, G. Seismic collapse probability and life cycle cost assessment of isolated structures subjected to pounding with smart hybrid isolation system using a modified fuzzy based controller. Structures 2022, 44, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Fabián, R.; Alvarez-Icaza, L. An adaptive observer for a shear building with an energy-dissipation device. Control. Eng. Pract. 2010, 18, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoero, E.; Wittel, F.K.; Herrmann, H.J.; Chiaia, B.M. Hierarchical Structures for a Robustness-Oriented Capacity Design. J. Eng. Mech. 2012, 138, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, R.W.; Penzien, J. Dynamics of Structures, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1976; 3a ed., 2003; p. 752. [Google Scholar]
- AutoCAD, version 2010; Autodesk, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2010.
- Shirinzadeh, M.; Haghollahi, A. Rehabilitation in Simple Steel Connections against Progressive Collapse due to Column Removal. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiel, S.E.; Naito, C.J.; Fallon, C.T. A non-emulative moment connection for progressive collapse resistance in precast concrete building frames. Eng. Struct. 2019, 179, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robot Structural Analysis, Professional 2020, Software, version 33.0.0.6930 (x64); Autodesk Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019.
- Zacchei, E.; Lyra, P.H.C. Recalibration of low seismic excitations in Brazil through probabilistic and deterministic analyses: Application for shear buildings structures. Struct. Concr. 2022, 24, 937–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram Mathematica 12; Software Version Number 12.0; Wolfram Research, Inc.: Champaign, IL, USA, 2019.
- Zacchei, E.; Nogueira, C.G. 2D/3D Numerical Analyses of Corrosion Initiation in RC Structures Accounting Fluctuations of Chloride Ions by External Actions. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 2105–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Broccardo, M.; Song, J. Hamiltonian Monte Carlo methods for Subset Simulation in reliability analysis. Struct. Saf. 2019, 76, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, C.G.; Yoshio, L.; Zacchei, E. Deterministic and probabilistic approaches for corrosion in RC structures: A direct proposed model to total service life predictions. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e01913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, C.G.; Leonel, E.D.; Coda, H.B. Probabilistic failure modelling of reinforced concrete structures subjected to chloride penetration. Int. J. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2012, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-C.; Yang, B.; Kang, S.-B.; Xu, S.-Q. A new method for progressive collapse analysis of steel frames. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 153, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luccioni, B.; Ambrosini, R.; Danesi, R. Analysis of building collapse under blast loads. Eng. Struct. 2004, 26, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liang, C. Risk Analysis for Cascade Reservoirs Collapse Based on Bayesian Networks under the Combined Action of Flood and Landslide Surge. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 2903935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Value for Each Case | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
| Number of columns, nc (-) | 3.0 | 6.0 | 12.0 |
| Number of storeys, ns (-) | 2.0 | 5.0 | 11.0 |
| Length of the beam, L (m) a | 20.0 | 9.0 | 4.0 |
| Height of the column, H (m) a | 16.50 | 6.50 | 3.0 |
| Concrete mass density, γc (kN/m3) | 25.0 | ||
| Case | Structural Frequency | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Structure | nr,c = 1.0 | nr,c = 2.0 | |
| Case 1 | 0.37 Hz (67.62 × 103 kg) | 0.32 Hz (63.44 × 103 kg) | - |
| Case 2 | 0.84 Hz (173.31 × 103 kg) | 0.83 Hz (171.67 × 103 kg) | 0.79 Hz (170.02 × 103 kg) |
| Case 3 | 1.79 Hz (373.06 × 103 kg) | 1.79 Hz (372.30 × 103 kg) | 1.77 Hz (371.54 × 103 kg) |
| Parameter | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moment yield threshold of the beam, By | μ (kN × m) a | 9137.17 | 580.18 | 53.97 |
| ±σ (kN × m) | 1057.40 | 67.03 | 6.20 | |
| CV (%) | 11.57 | 11.55 | 11.48 | |
| Compressive strength of the column, Rc | μ (kN) | 2357.91 | 597.46 | 206.34 |
| ±σ (kN) | 568.88 | 346.59 | 154.43 | |
| CV (%) | 24.13 | 58.01 | 74.84 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zacchei, E.; Gorla Nogueira, C. Scenarios of Progressive Pancake/Bending Collapse Considering Elastic/Plastic Reinforced Concrete Buildings. Buildings 2024, 14, 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14071948
Zacchei E, Gorla Nogueira C. Scenarios of Progressive Pancake/Bending Collapse Considering Elastic/Plastic Reinforced Concrete Buildings. Buildings. 2024; 14(7):1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14071948
Chicago/Turabian StyleZacchei, Enrico, and Caio Gorla Nogueira. 2024. "Scenarios of Progressive Pancake/Bending Collapse Considering Elastic/Plastic Reinforced Concrete Buildings" Buildings 14, no. 7: 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14071948
APA StyleZacchei, E., & Gorla Nogueira, C. (2024). Scenarios of Progressive Pancake/Bending Collapse Considering Elastic/Plastic Reinforced Concrete Buildings. Buildings, 14(7), 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14071948








