Investigating Large-Scale Tuned Liquid Dampers through Real-Time Hybrid Simulations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Objectives
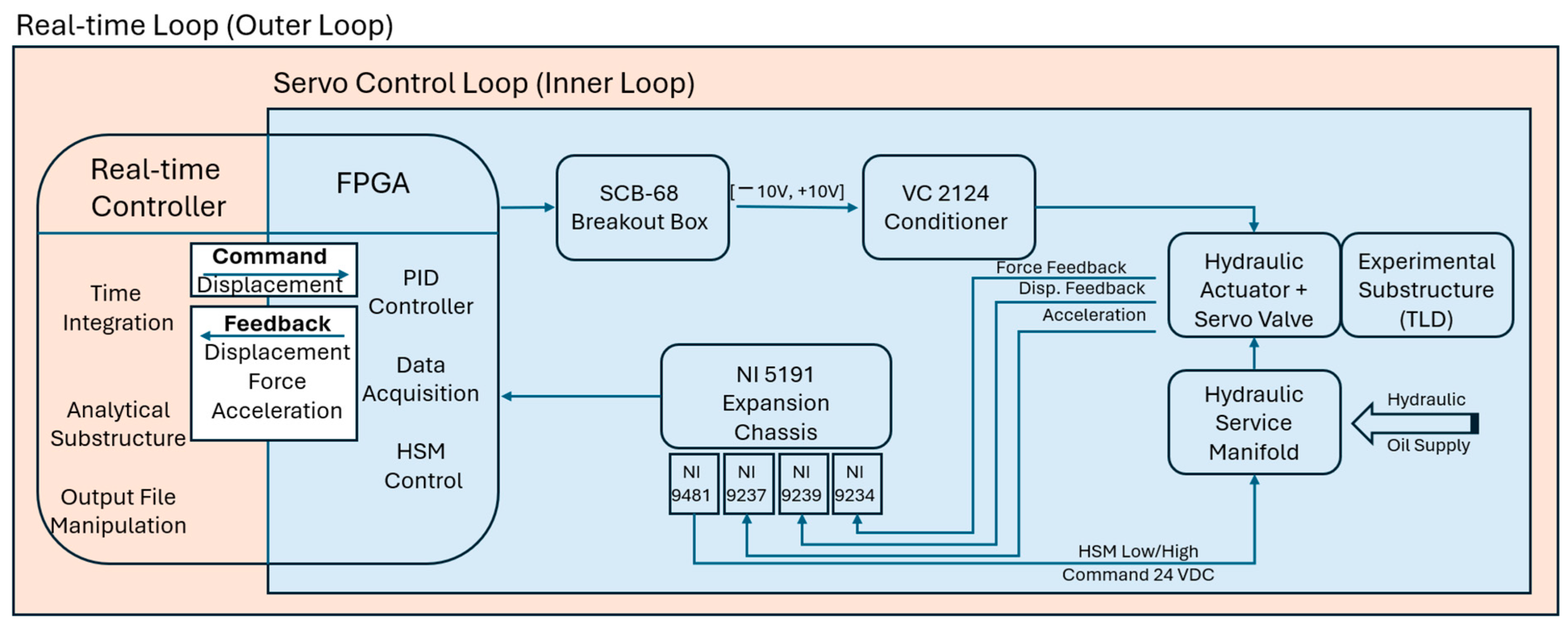
3. Real-Time Hybrid-Simulation Experimental Setup
3.1. Methodology: Real-Time Hybrid Simulation (RTHS)
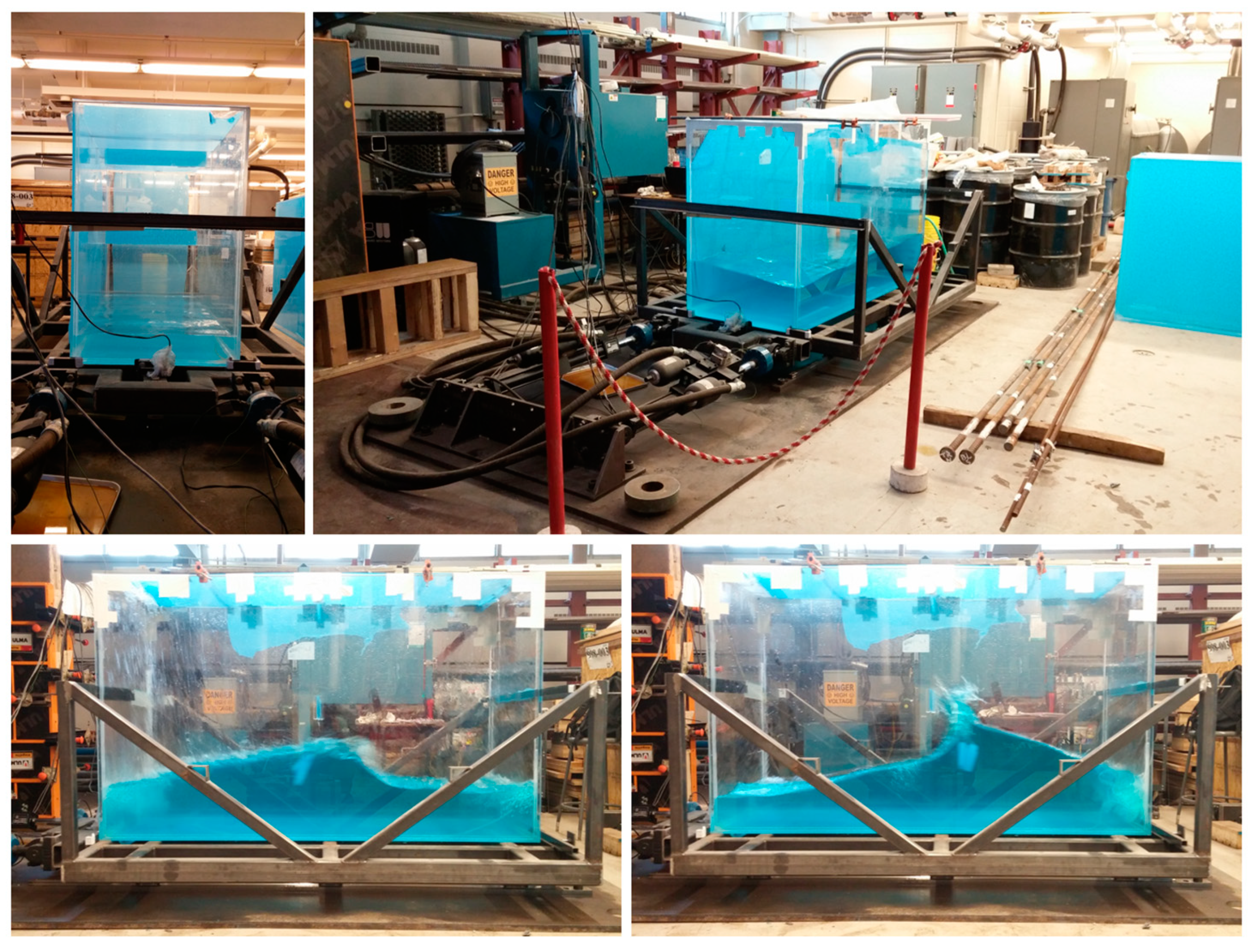
3.2. Mechanical Setup for Tests
3.3. Real-Time Hybrid Simulator
3.4. Software
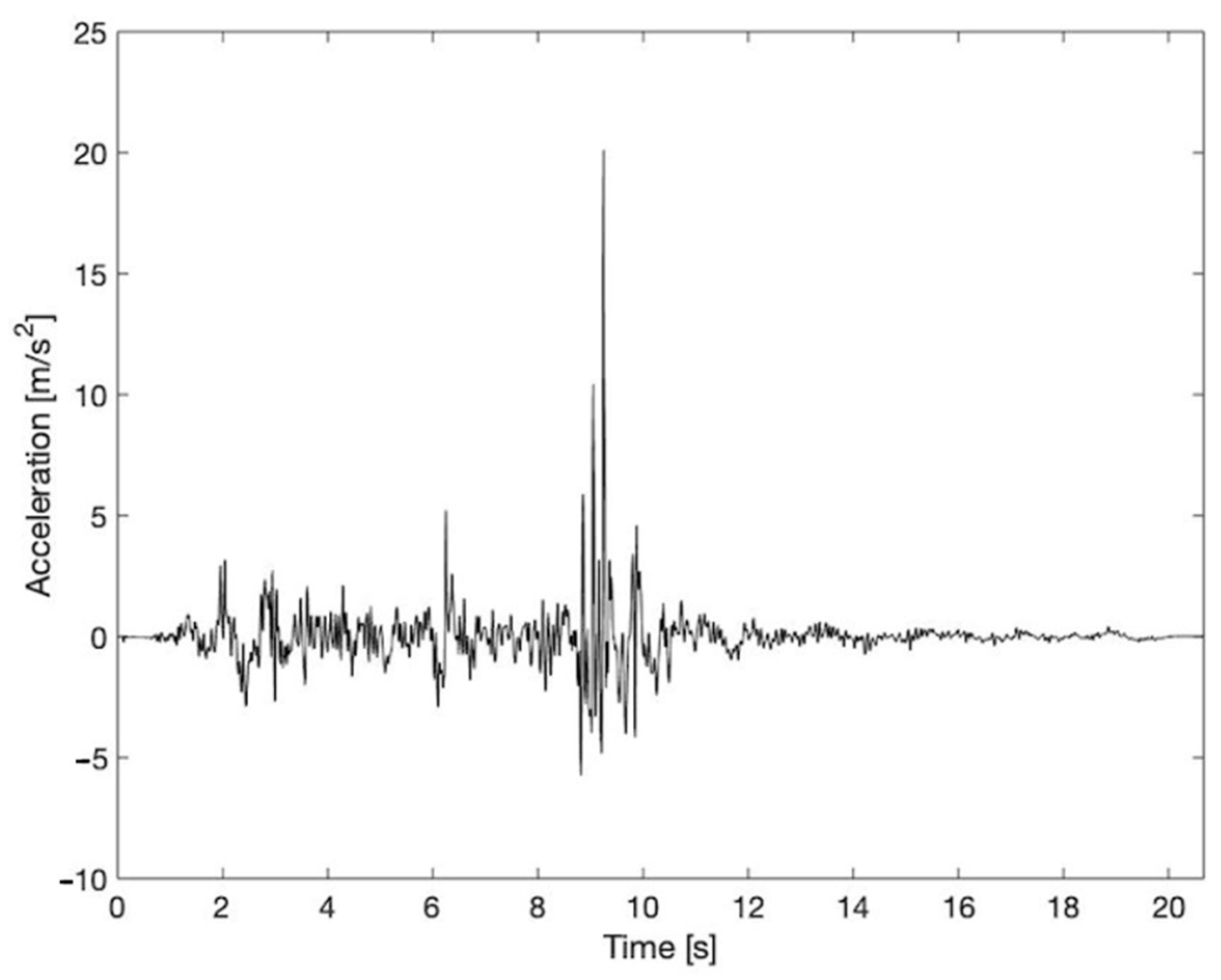
3.5. Ground Motions
3.6. Analytical and Experimental Substructures
4. RTHS of Linear/Nonlinear SDOF Equipped with Large-Scale TLD Subjected to Seismic Loading
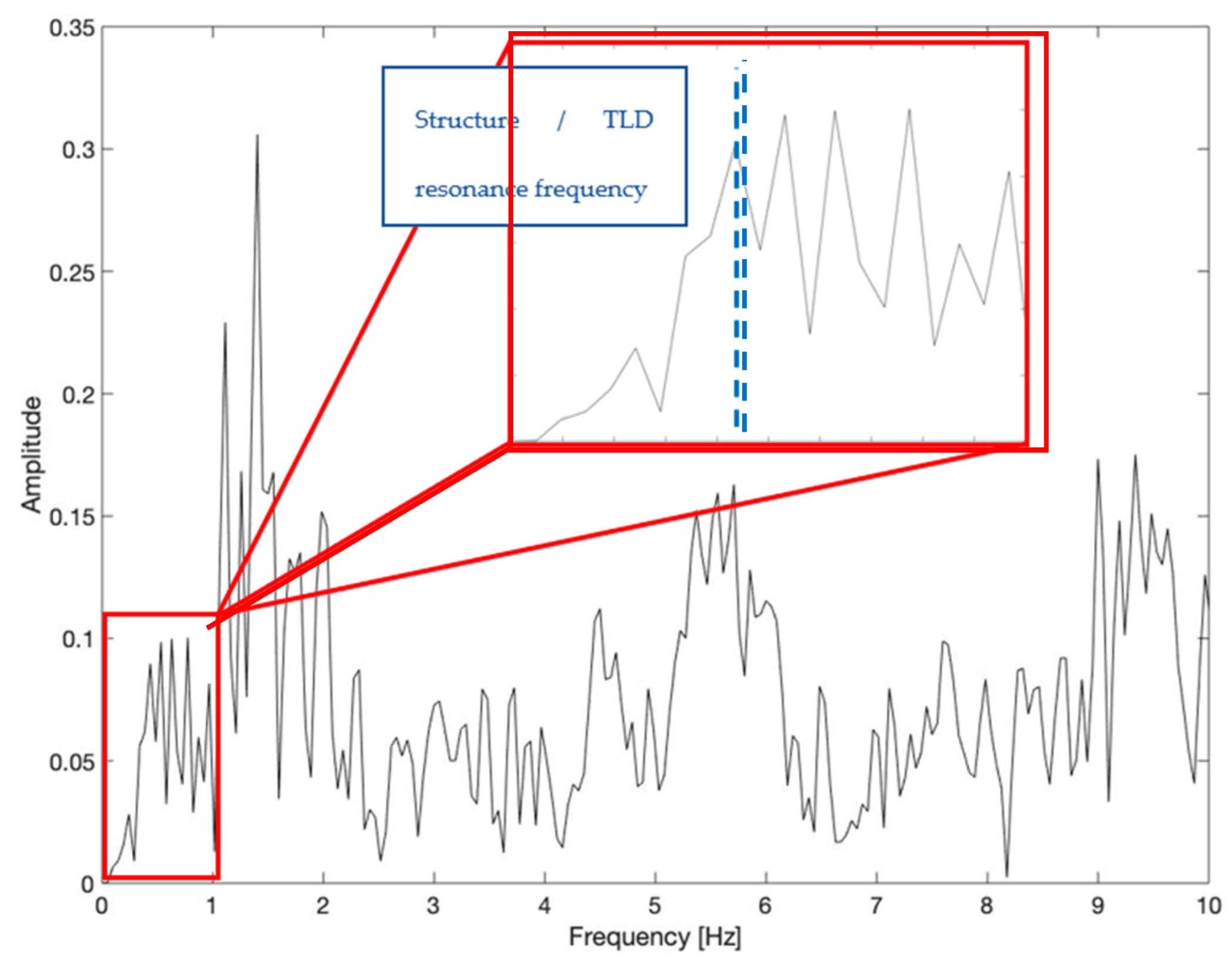
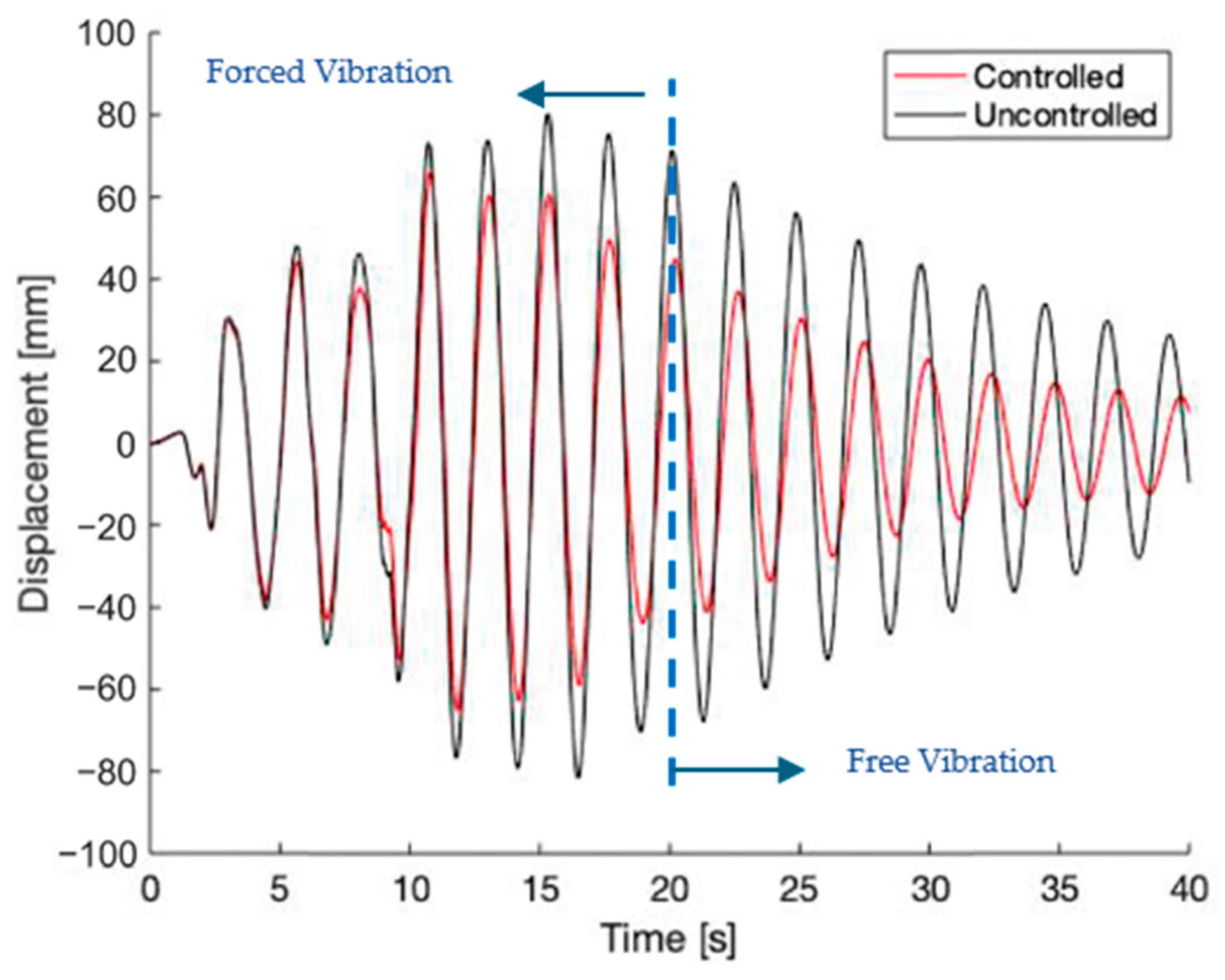
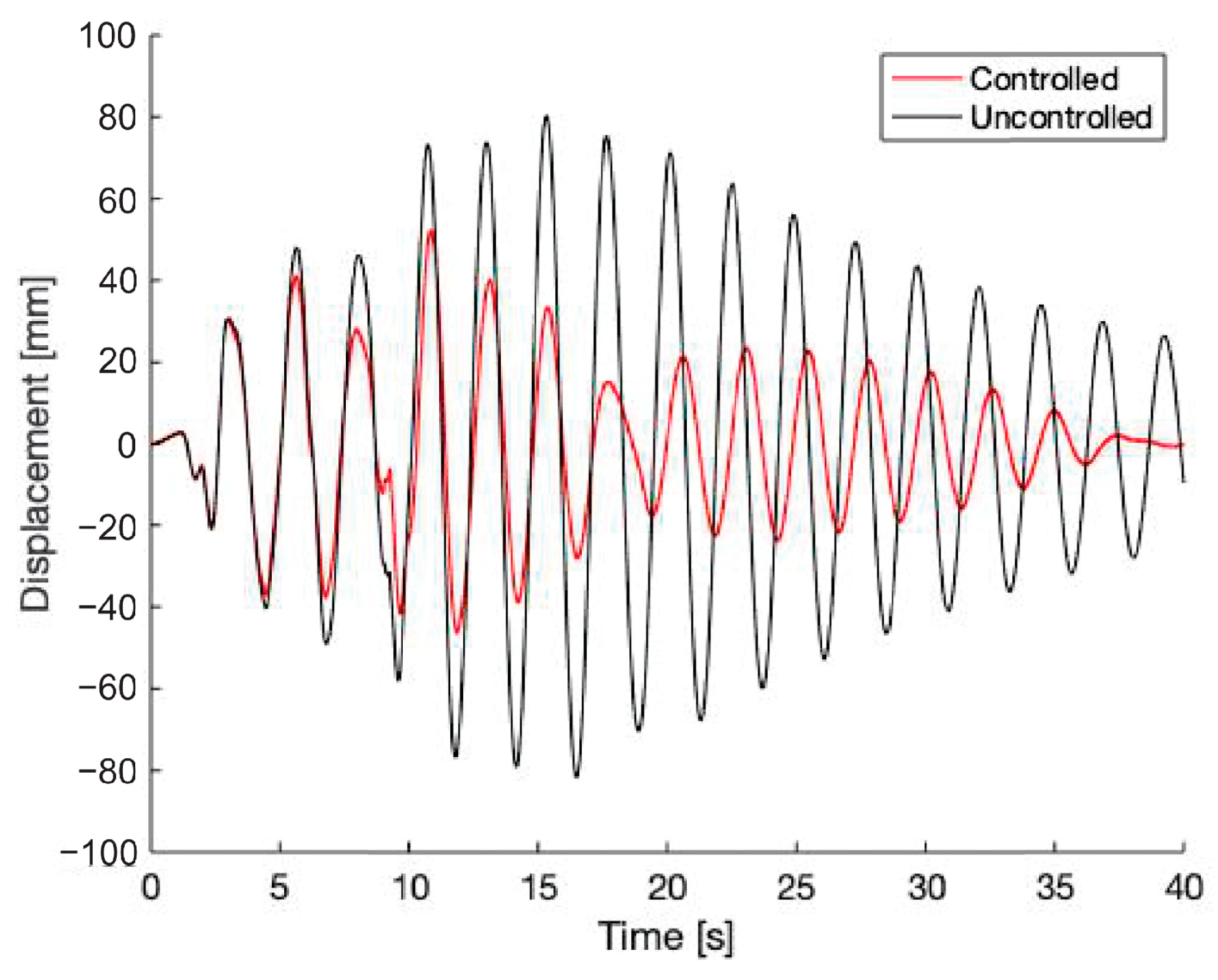
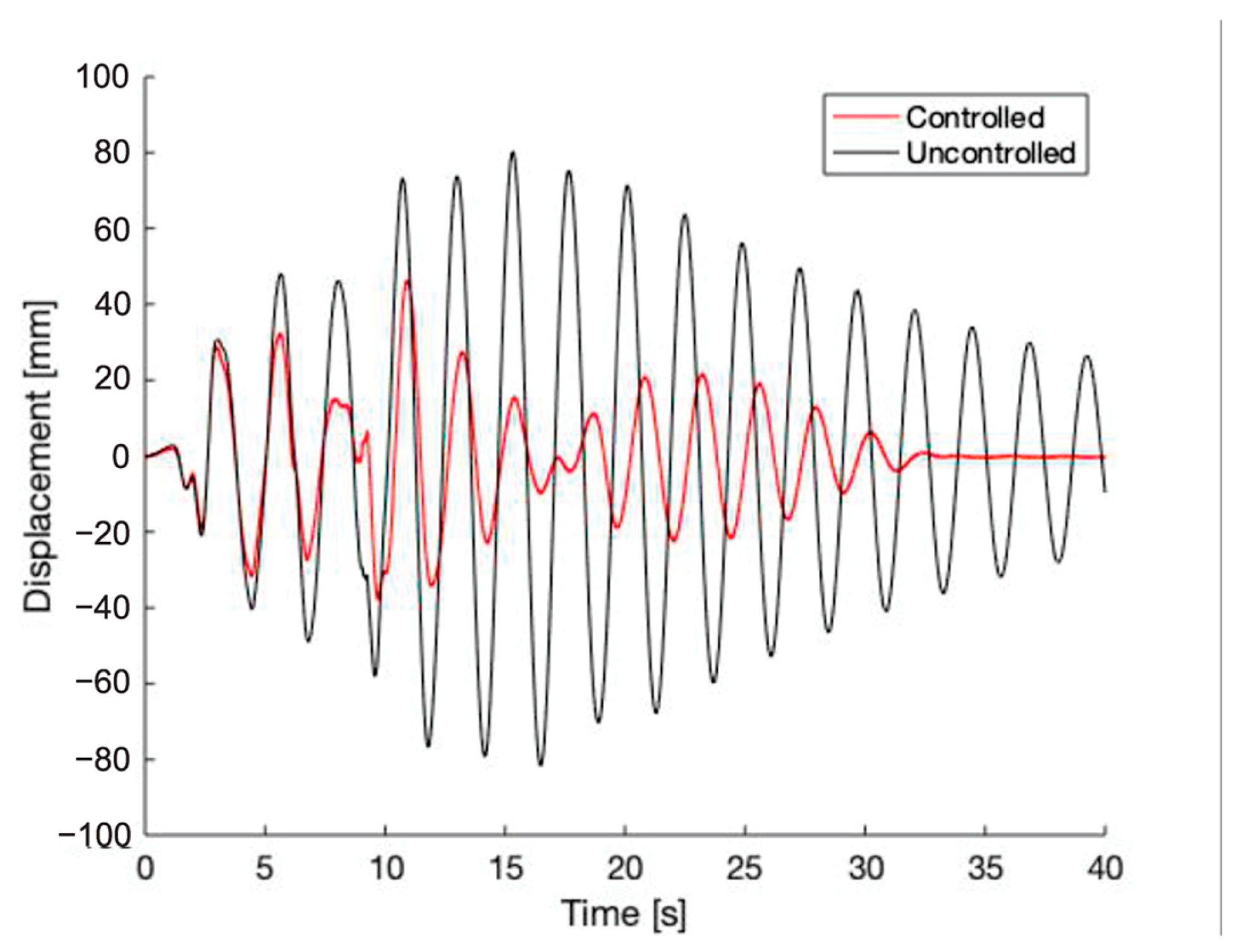
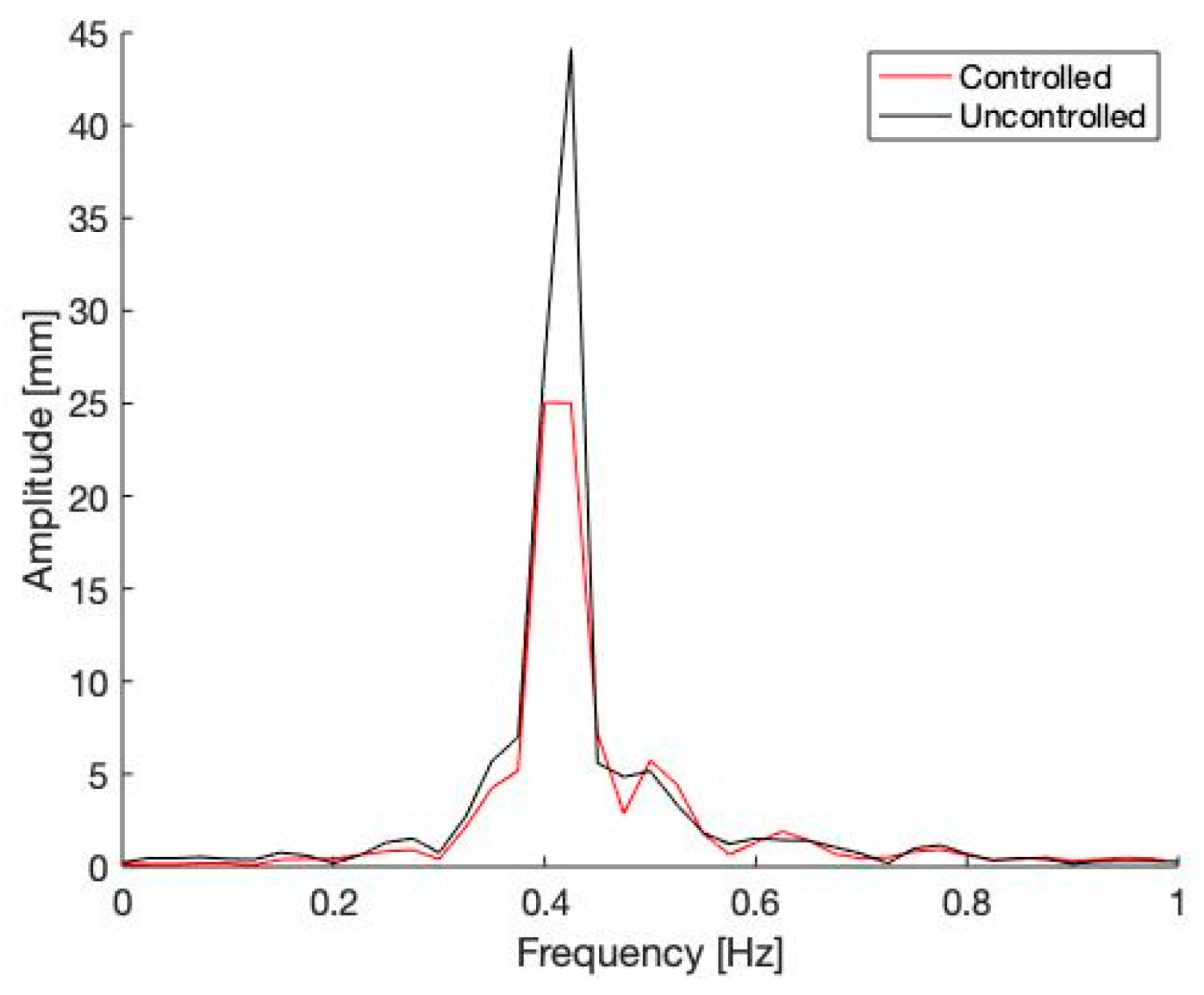
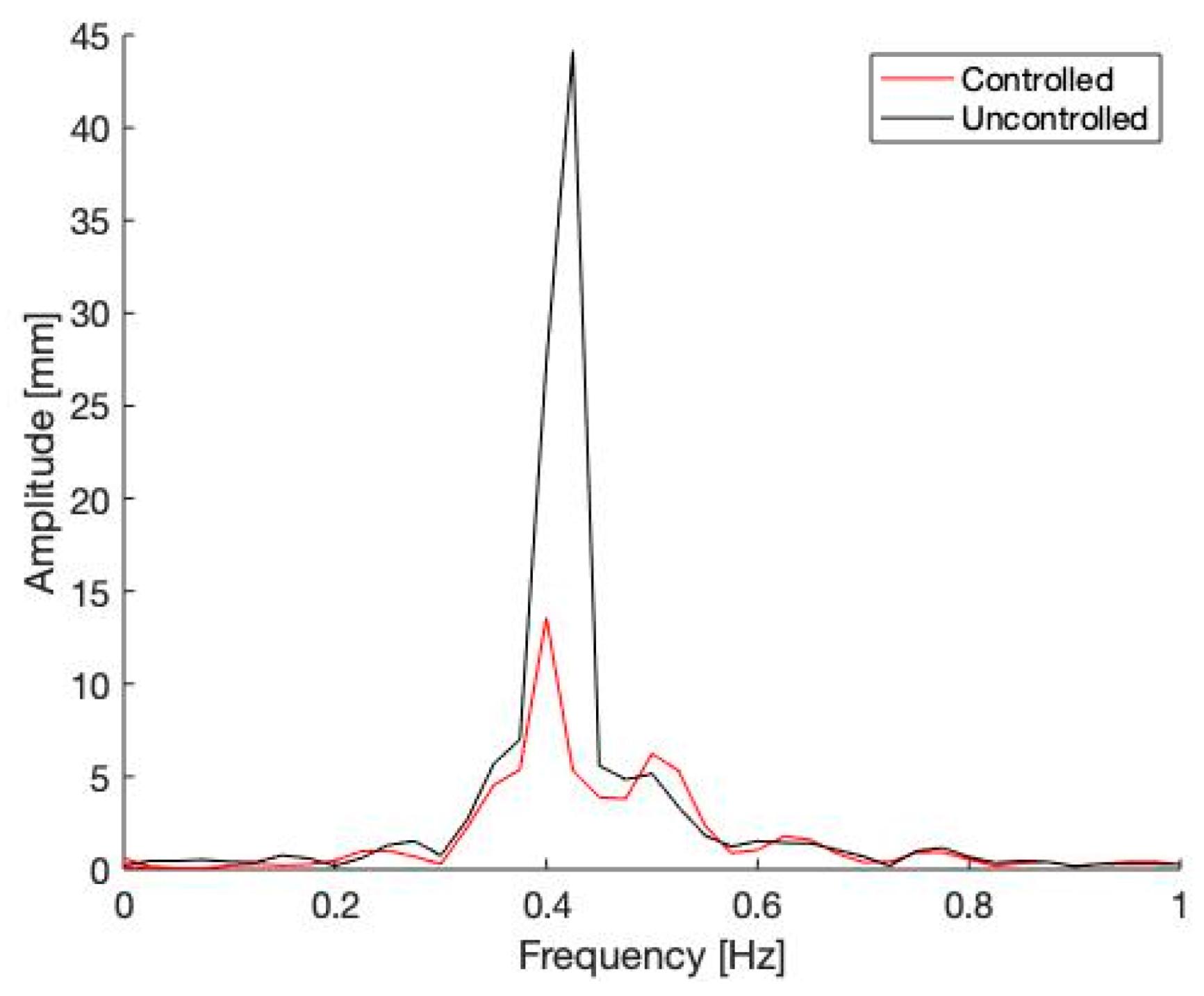
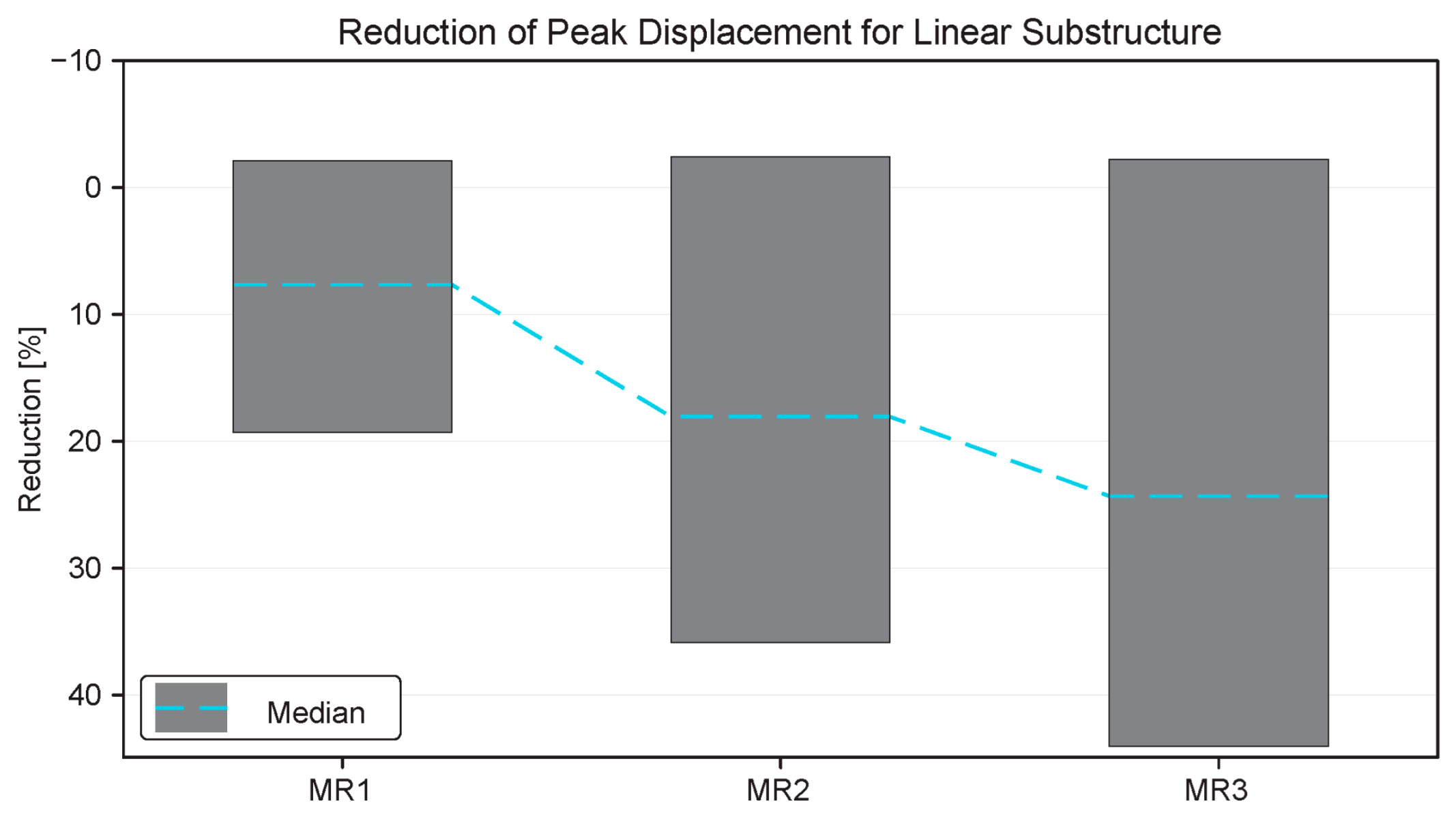
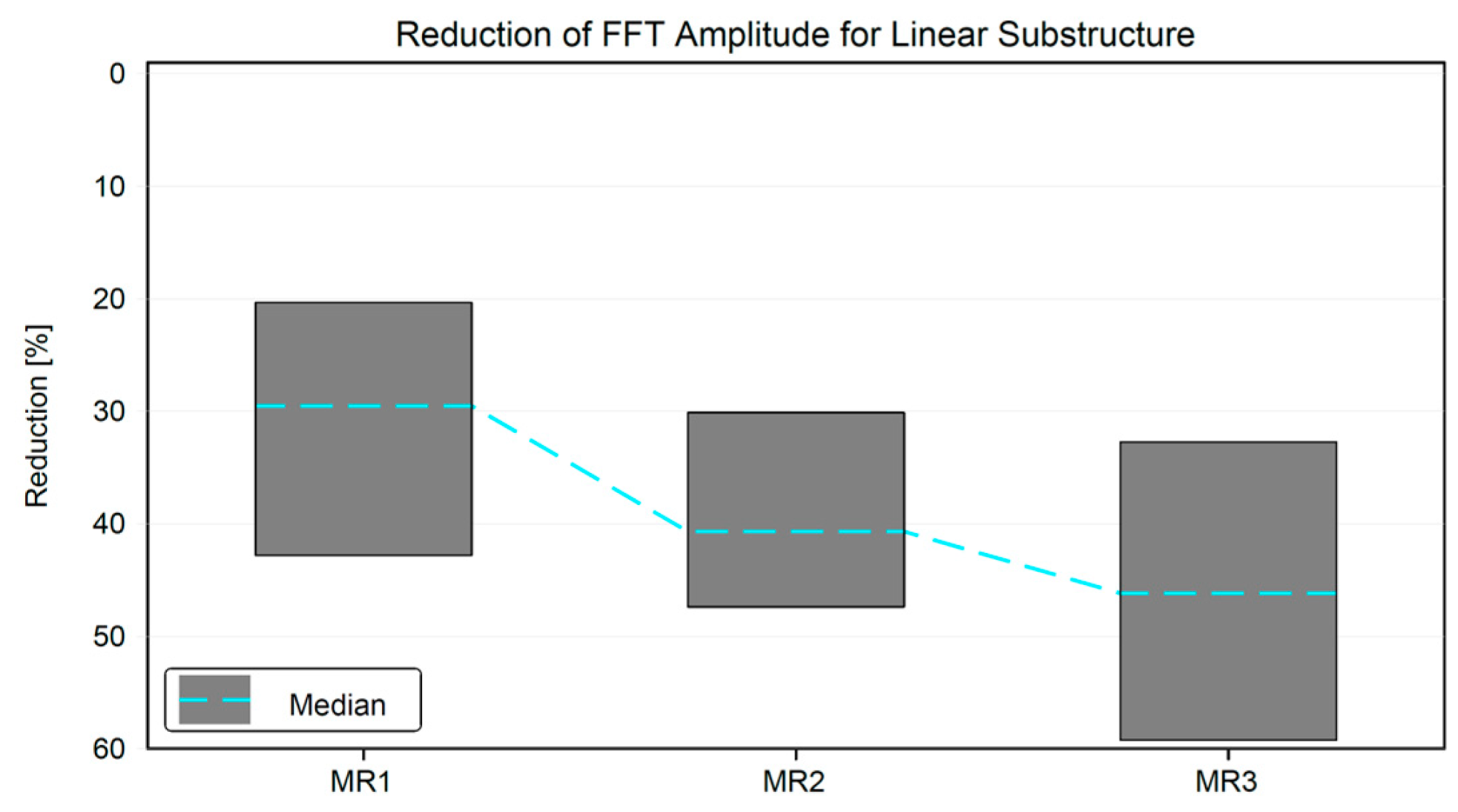
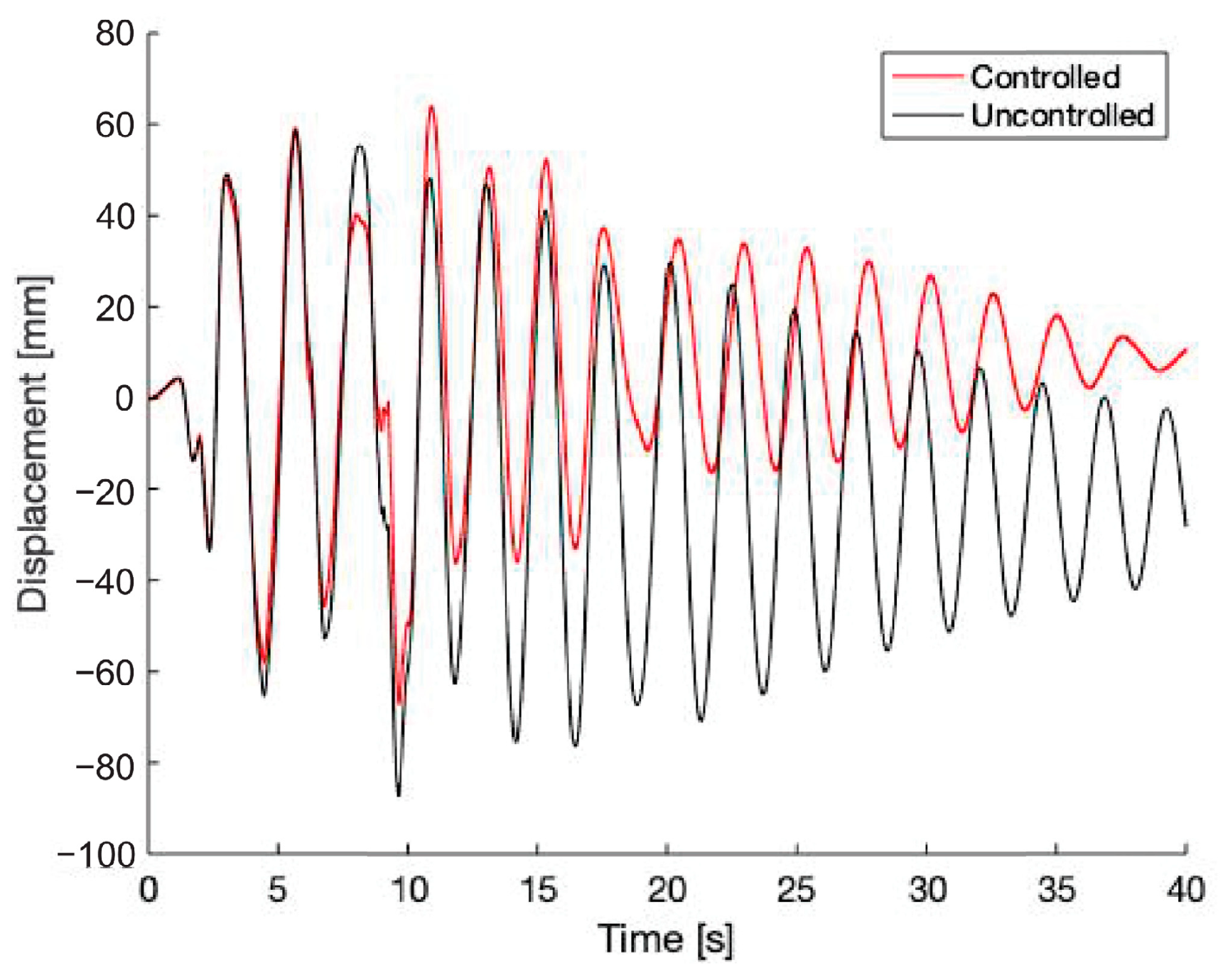
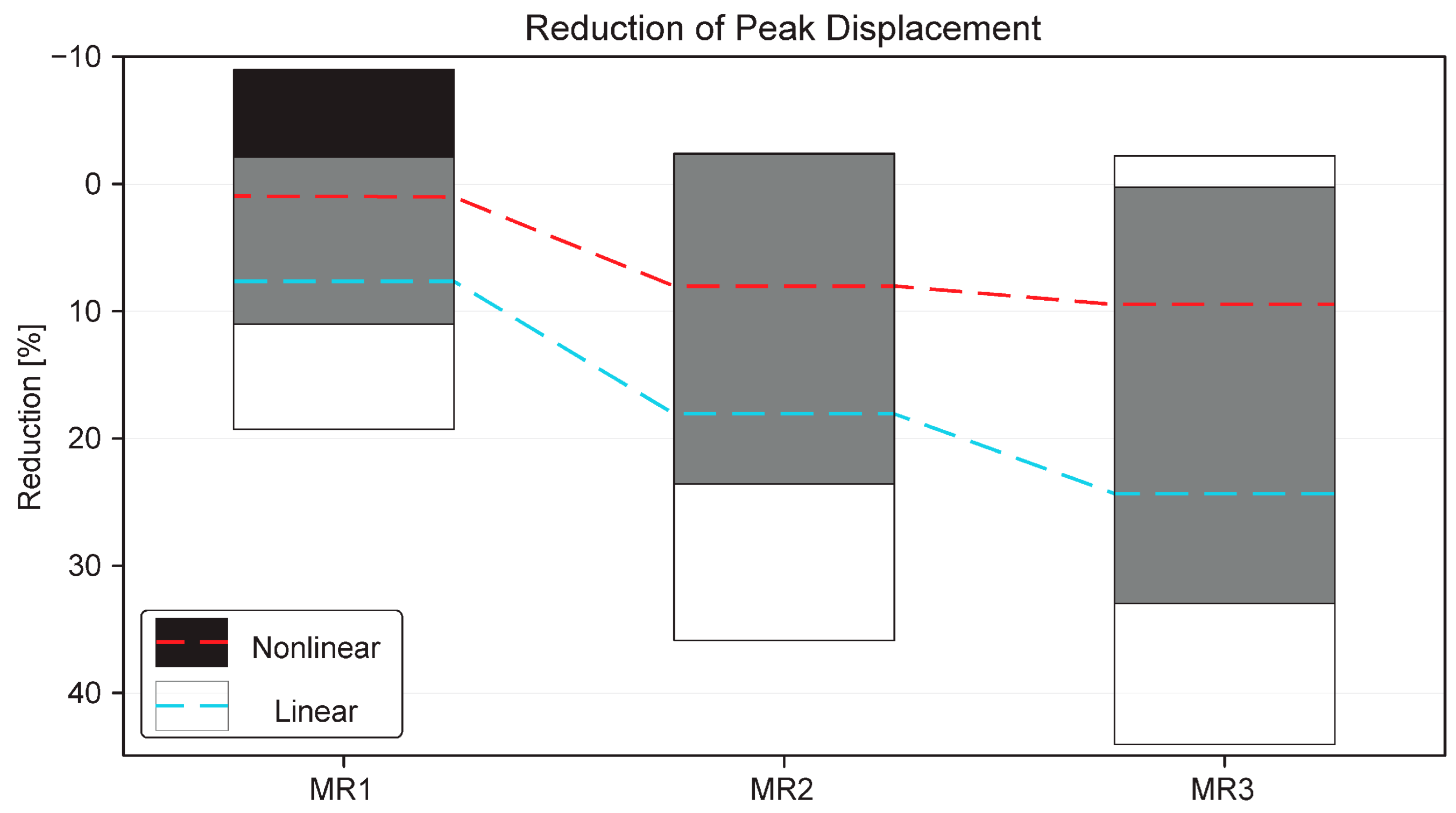
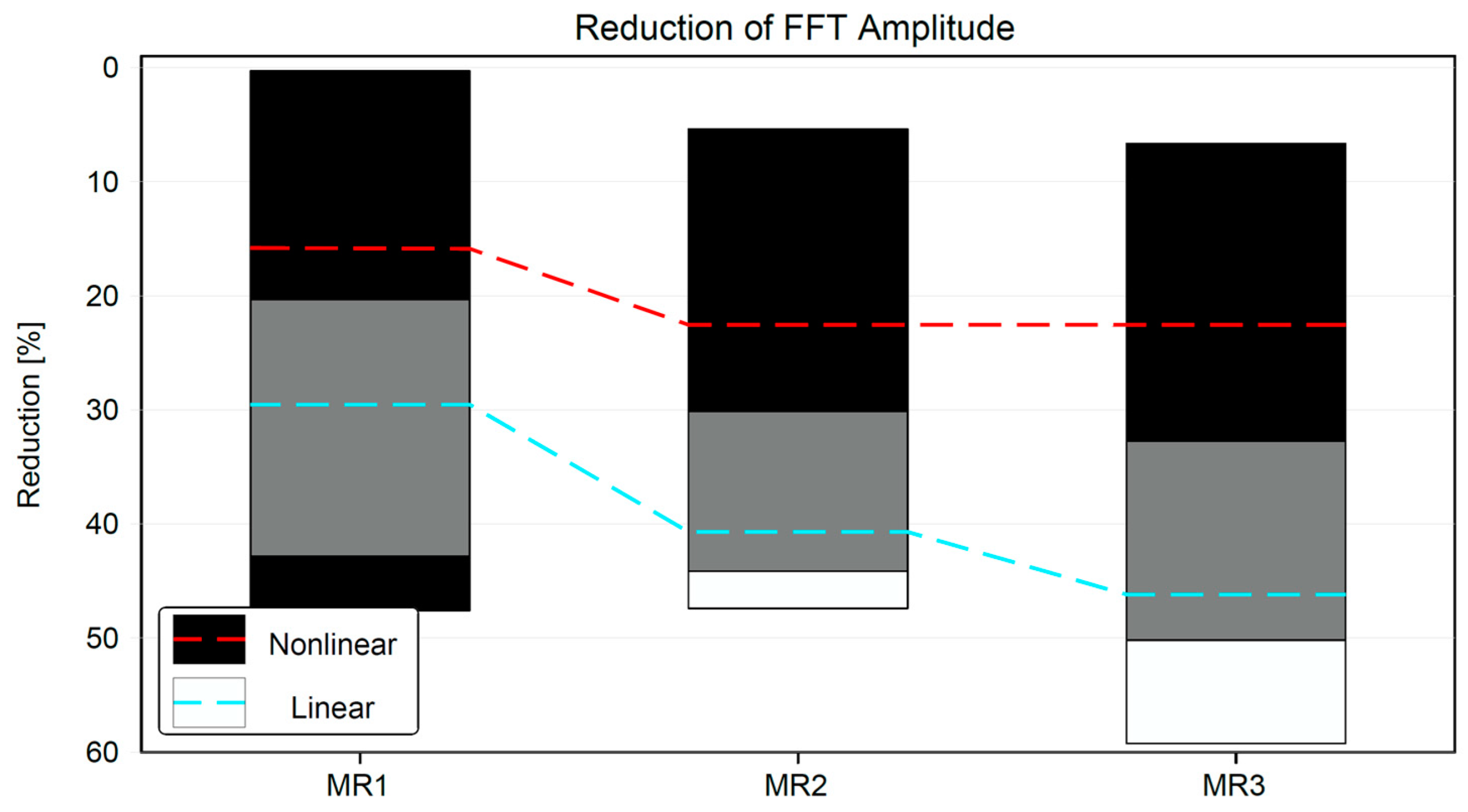
5. Linear Substructure Results
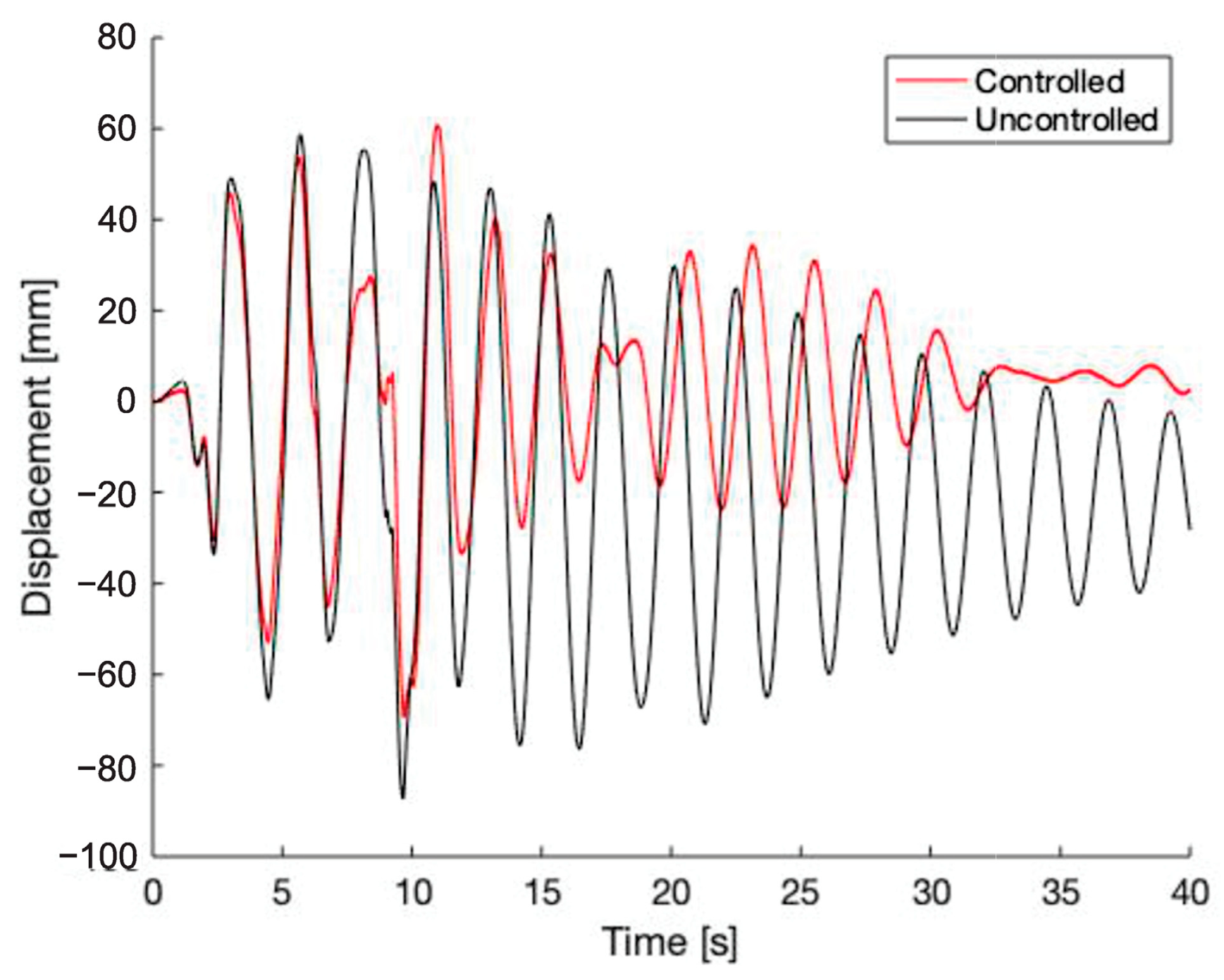
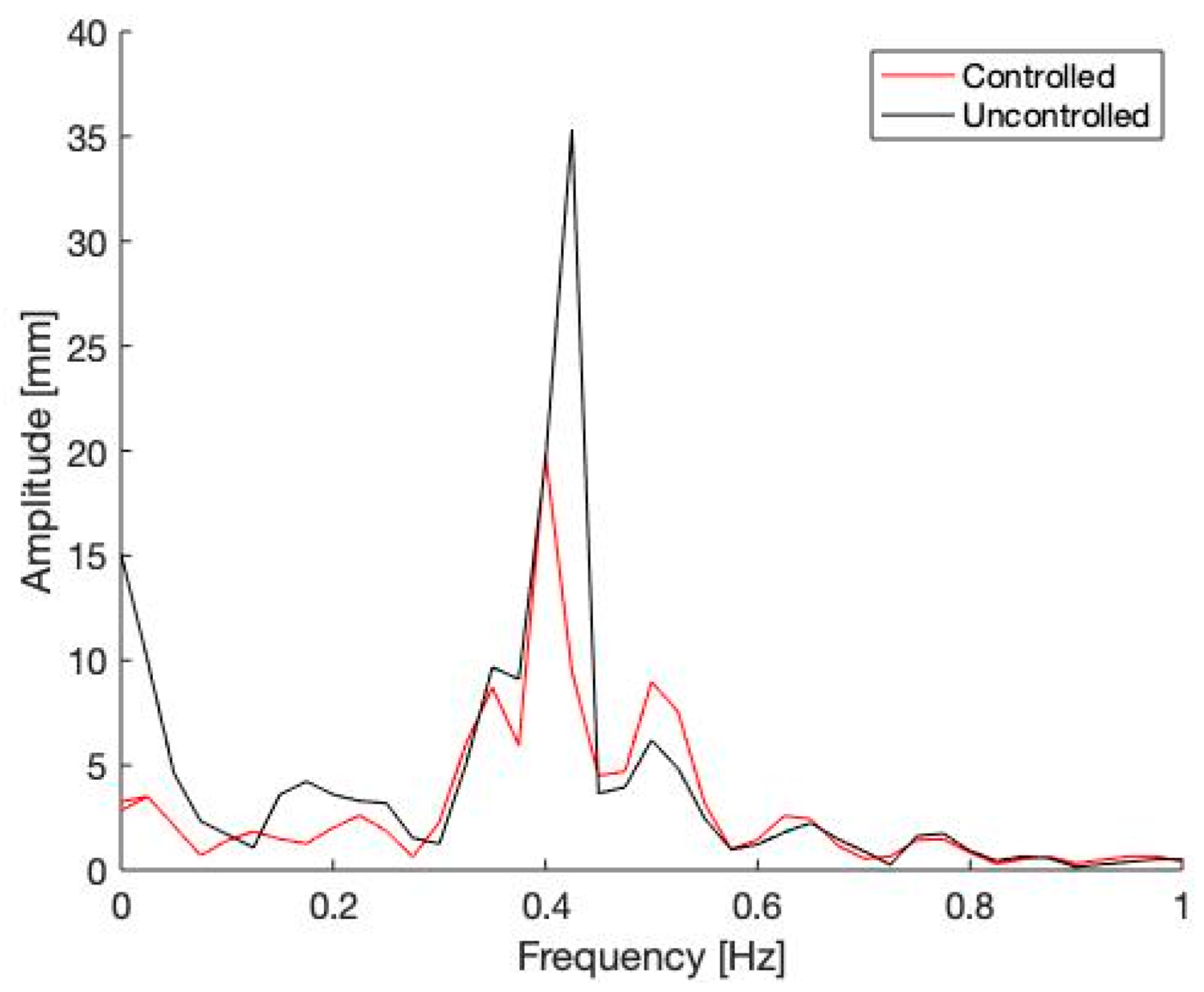
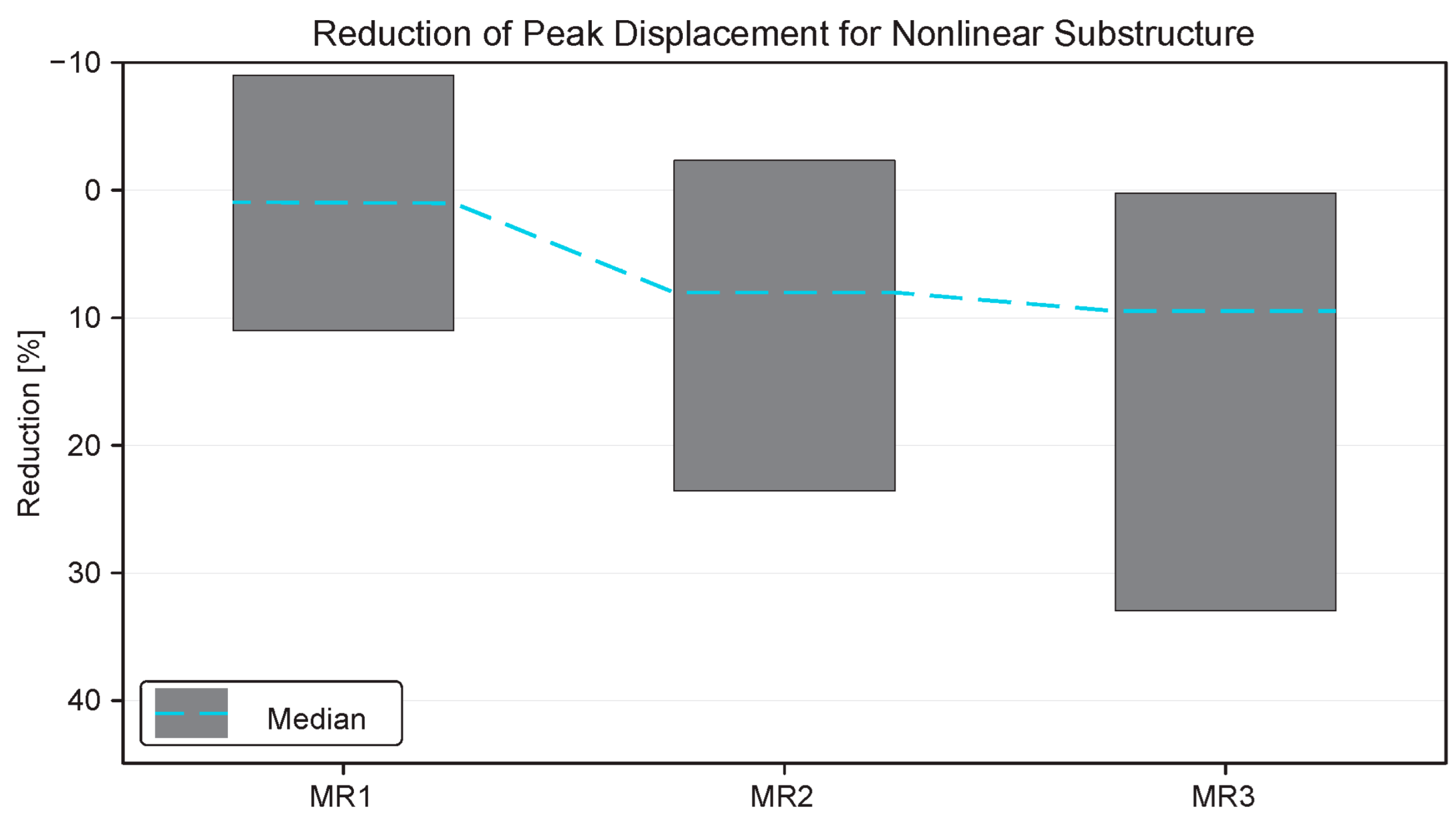
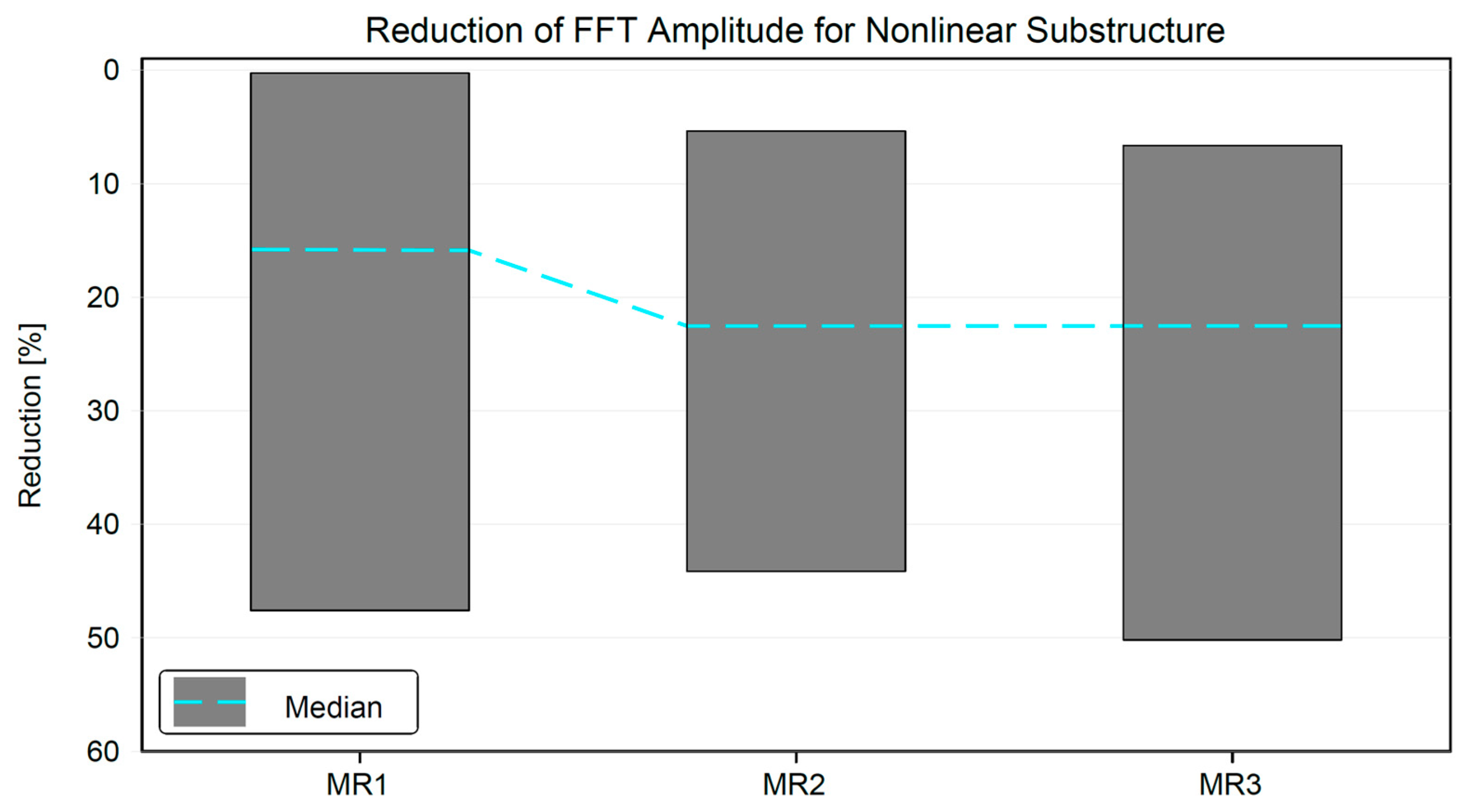
6. Nonlinear Substructure Results
7. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Y.; Chen, B. Integrated vibration control and health monitoring of building structures using semi-active friction dampers: Part I—Methodology. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 1789–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujino, Y.; Pacheco, B.M.; Chaiseri, P.; Sun, L.M. Parametric studies on tuned liquid damper (TLD) using circular containers by free-oscillation experiments. Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshu 1988, 5, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Fujii, K.; Sato, T.; Wakahara, T.; Kosugi, M. Wind-induced vibration of tall towers and practical applications of tuned sloshing dampers. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Serviceability of Buildings (Movements, Deformations, Vibrations), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 16–18 May 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, K.; Soong, T.; Chang, K.; Lai, M. Seismic behavior of reinforced concrete frame with added visco-elastic dampers. En-Gineering Struct. 1995, 17, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabraie, K.; Chan, R.; Huang, X.; Xie, Y.M. Shape optimization of metallic yielding devices for passive mitigation of seismic energy. Eng. Struct. 2010, 32, 2258–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S. A shape memory alloy-based reusable hysteretic damper for seismic hazard mitigation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ko, J.; Cao, D. Neuro-control of cable vibration using semi-active magneto-rheological dampers. Eng. Struct. 2003, 24, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Spencer, B.; Carlson, J.; Sain, M. Large-scale MR fluid dampers: Odeling and dynamic performance considerations. Eng. Struct. 2002, 24, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hwang, W.; Chiu, L.; Sheu, S. Flexibility of TLD to high-rise building by simple experiment and comparison. Comput. Struct. 1995, 57, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-M.; You, K.-P.; Ko, N.-H.; Yoon, S.-W. Use of TLD and MTLD for control of wind-induced vibration of tall buildings. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2006, 20, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NatHaz Research. tuned Liquid Dampers (TLDs) and Tuned Liquid Column Dampers (TLCDs) Research at NatHaz Modeling Laboratory. Available online: https://nathaz.nd.edu/research/liquid/liq_damp.html (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Reed, D.; Yu, J.; Yeh, H.; Gardarsson, S. Investigation of Tuned Liquid Dampers under Large Amplitude Excitation. J. Eng. Mech. 1998, 124, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.M.; Fujino, Y.; Pacheco, B.M.; Chaiseri, P. Modelling of tuned liquid damper (TLD). J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1992, 43, 1883–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wakahara, T.; Reed, D.A. A non-linear numerical model of the tuned liquid damper. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1999, 28, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, P.; Murudi, M.; Shah, A.; Popplewell, N. Tuned liquid dampers for controlling earthquake response of structures. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2000, 29, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, H.; Noji, T.; Yoshida, H.; Tatsumi, E.; Yamanaka, H.; Agrawal, A. Damping effects of a vibration control damper using sloshing of water. In Proceedings of the 10th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Madrid, Spain, 19–24 July 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.; Wu, Z.; Chen, K.; Tang, Y.; Yan, Y. An experimental study on the equivalent nonlinear model for a large-sized tuned liquid damper. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 73, 106754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocak, A.; Nigdeli, S.M.; Bekdaş, G.; Kim, S.; Geem, Z.W. Adaptive Harmony Search for Tuned Liquid Damper Optimization under Seismic Excitation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Sheng, J.; Dong, Y. Effects of tuned liquid dampers on the nonlinear seismic responses of high-rise structures using real-time hybrid simulations. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 70, 106333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekghasemi, H.; Ashasi-Sorkhabi, A.; Ghaemmaghami, A.R.; Mercan, O. Experimental and numerical investigations of the dynamic interaction of tuned liquid damper–structure systems. J. Vib. Control. 2013, 21, 2707–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, T.; Varum, H.; Teixeira-Dias, F.; Rodrigues, H.; Falcao-Silva, M.; Cost, A.; Guerreiro, L. Tuned liquid dampers simula-tion for earthquake response control of buildings. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2013, 12, 1007–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, K.; Reddy, G.; Venkatraj, V. Tuned liquid sloshing water damper: A robust device for seismic retrofitting. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. Monit. 2013, 4, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Shad, H.; Bin Adnan, A.; Behbahani, H.P. Performance Evaluation of Tuned Liquid Dampers on Response of a SDOF System Under Earthquake Excitation and Harmonic Load. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2013, 6, 3018–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-T.; Gui, Y.; Zhu, F.; Jin, F.; Zhou, M.-X. Real-time hybrid simulation of multi-story structures installed with tuned liquid damper. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2015, 23, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Li, X.; Sun, N.; Zhou, J.; Guan, J. Experimental and numerical study on tuned liquid dampers for controlling earth-quake response of jacket offshore platform. Mar. Struct. 2007, 20, 238–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemmaghami, A.; Kianoush, M.; Mardukhi, J. Numerical study on annular tuned liquid dampers for controlling the re-sponse of wind towers subjected to seismic loads. In Proceeding of the 15th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Lisbon, Portugal, 24–28 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaemmaghami, A.R.; Kianoush, R.; Mercan, O. Numerical modeling of dynamic behavior of annular tuned liquid dampers for the application in wind towers under seismic loading. J. Vib. Control 2015, 22, 3858–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, J.; Jin, F.; Altay, O. Real-time hybrid simulation of single and multiple tuned liquid column dampers for con-trolling seismic-induced response. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Advances in Experimental Structural Engineering, Illinoi, IL, USA, 19–21 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Choudhury, S. Seismic response control by tuned liquid dampers for low-rise RC frame buildings. Aust. J. Struct. Eng. 2017, 18, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, J.-T.; Jin, F.; Lu, L.-Q.; Gui, Y.; Zhou, M.-X. Real-time hybrid simulation of the size effect of tuned liquid dampers. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2017, 24, e1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashasi-Sorkhabi, A.; Mercan, O. Development, Implementation, and Verification of a User Configurable Platform for Re-al-time Hybrid Simulation. Smart Struct. Syst. 2014, 14, 1151–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashasi-Sorkhabi, A. Implementation, Verification and Application of Real-Time Hybrid Simulation. ProQuest Dissertations & Theses, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-K.; Park, E.C.; Min, K.-W.; Lee, S.-H.; Chun, L.; Park, J.-H. Real-time hybrid shaking table testing method for the per-formance evaluation of a tuned liquid damper controlling seismic response of building structures. J. Sound Vi-Bration 2006, 302, 596–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, P. Tuned Liquid Dampers for Control of Earthquake Response. In Proceedings of the 13th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1–6 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, R.; Taflanidis, A.; Lopez-Garcia, D. Characterization and design of tuned liquid dampers with floating roof considering abitrary tank cross-sections. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 368, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahin, S.; Shing, P. Pseudodynamic method for seismic testing. J. Struct. Eng. (ASCE) 1985, 111, 1482–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermitzakis, S.; Mahin, S. Development of Substructuring Techniques for On-Line Computer Controlled Seismic Performance Testing; Report UBC/EERC-85/04; Earthquake Engineering Research Center: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima, M.; Kato, H.; Takaoka, E. Development of real-time pseudodynamic testing. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1995, 21, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, T.; Inoue, M.; Konno, T.; Namita, Y. Real-time hybrid experimental system with actuator delay compensation and its application to a piping system with energy absorber. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1999, 28, 1121–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercan, O.; Ricles, J. Experimental Studies on real-time pseudodynamic (PSD) and hybrid PSD testing of structures with elastomeric dampers. J. Struct. Eng. 2009, 135, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashasi-Sorkhabi, A.; Malekghasemi, H.; Mercan, O. Implementation and verification of real-time hybrid simulation (RTHS) using a shake table for research and education. J. Vib. Control 2012, 21, 1459–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenson, R.; Lin, Y.Z.; Emmons, A.; Bass, B. Large-Scale Experimental Verification of Semiactive Control through Real-Time Hybrid Simulation. J. Struct. Eng. 2008, 134, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashasi-Sorkhabi, A.; Mercan, O. Experimental investigations of large scale TLD-structure interaction via real-time hybrid simulation. In Proceedings of the Resilient Infrastructure, CSCE, London, ON, Canada, 1–4 June 2016. [Google Scholar]





| # | Ground Motion | Magnitude | Location | Distance (km) | PGA (g) | Duration (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EQ1 | Erzincan Turkey 1992 | 6.69 | 95 Erzincan | 8.97 | 0.496 | 20.78 |
| EQ2 | Nahanni Canada 1985 | 6.76 | 6095 site 1 | 6.8 | 2.0508 | 20.56 |
| EQ3 | Kocaeli Turkey 1999 | 7.51 | Duzce | 98.22 | 0.312 | 27.185 |
| EQ4 | Duzce Turkey 1999 | 7.14 | Bolu | 41.27 | 0.728 | 55.9 |
| EQ5 | Chi-Chi Taiwan 1999 | 7.62 | CHY028 | 32.67 | 0.822 | 90 |
| EQ6 | Imperial Valley 1940 | 6.95 | El Centro, Array 09 | 12.99 | 0.3129 | 40.00 |
| EQ7 | Northridge 1994 | 6.69 | Simi Valley-Katherine | 12.18 | 0.8774 | 24.99 |
| Net Length (mm) | Net Width (mm) | TLD Height (mm) | TLD MASS (kg) | Height of Water (mm) | Water Mass (kg) | Sloshing Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1978 | 779 | 1200 | 125 | 300 | 462 | 0.418 |
| Case # | M (kg) | Kf (N/m) | C (N.s/m) | Linear or Nonlinear | Vy N | MR % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 46,200 | 318,660 | 4853.4 | Linear | /// | 1 |
| 2 | 15,400 | 106,220 | 1617.8 | Linear | /// | 3 |
| 3 | 9240 | 63,732 | 970.67 | Linear | /// | 5 |
| 4 | 46,200 | 318,660 | 4853.4 | Nonlinear | 17,526 | 1 |
| 5 | 15,400 | 106,220 | 1617.8 | Nonlinear | 5842.1 | 3 |
| 6 | 9240 | 63,732 | 970.67 | Nonlinear | 3505.2 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashasi Sorkhabi, A.; Qiu, B.; Mercan, O. Investigating Large-Scale Tuned Liquid Dampers through Real-Time Hybrid Simulations. Buildings 2024, 14, 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14072017
Ashasi Sorkhabi A, Qiu B, Mercan O. Investigating Large-Scale Tuned Liquid Dampers through Real-Time Hybrid Simulations. Buildings. 2024; 14(7):2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14072017
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshasi Sorkhabi, Ali, Barry Qiu, and Oya Mercan. 2024. "Investigating Large-Scale Tuned Liquid Dampers through Real-Time Hybrid Simulations" Buildings 14, no. 7: 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14072017
APA StyleAshasi Sorkhabi, A., Qiu, B., & Mercan, O. (2024). Investigating Large-Scale Tuned Liquid Dampers through Real-Time Hybrid Simulations. Buildings, 14(7), 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14072017





