Predicting Residual Flexural Strength of Corroded Prestressed Concrete Beams: Comparison of Chinese Code, Eurocode and ACI Standard
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Database of the Flexural Capacity of CPC Beams
2.1. Set up of the Experimental Database
2.2. Unification of Compressive Strength of Concrete
2.3. Unification of Corrosion Rate of Prestressed Steel
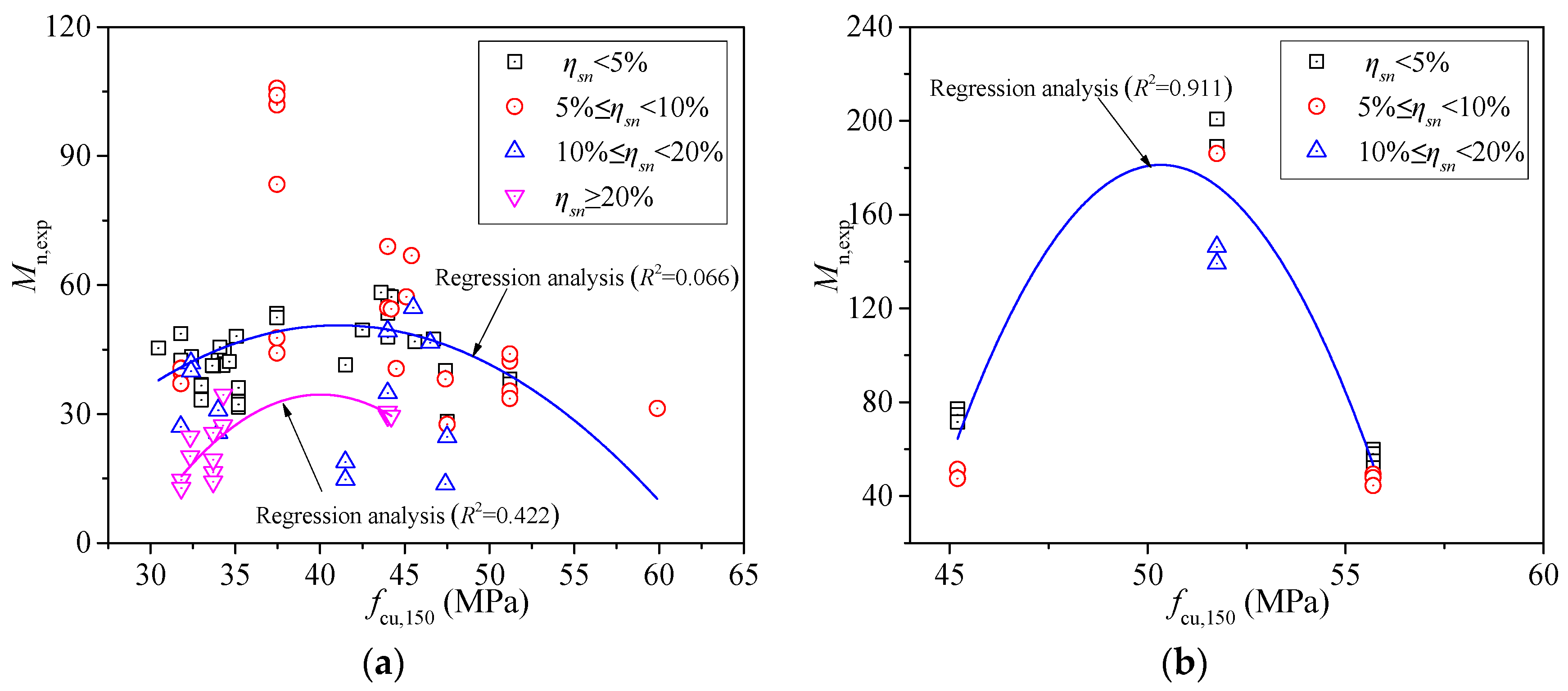
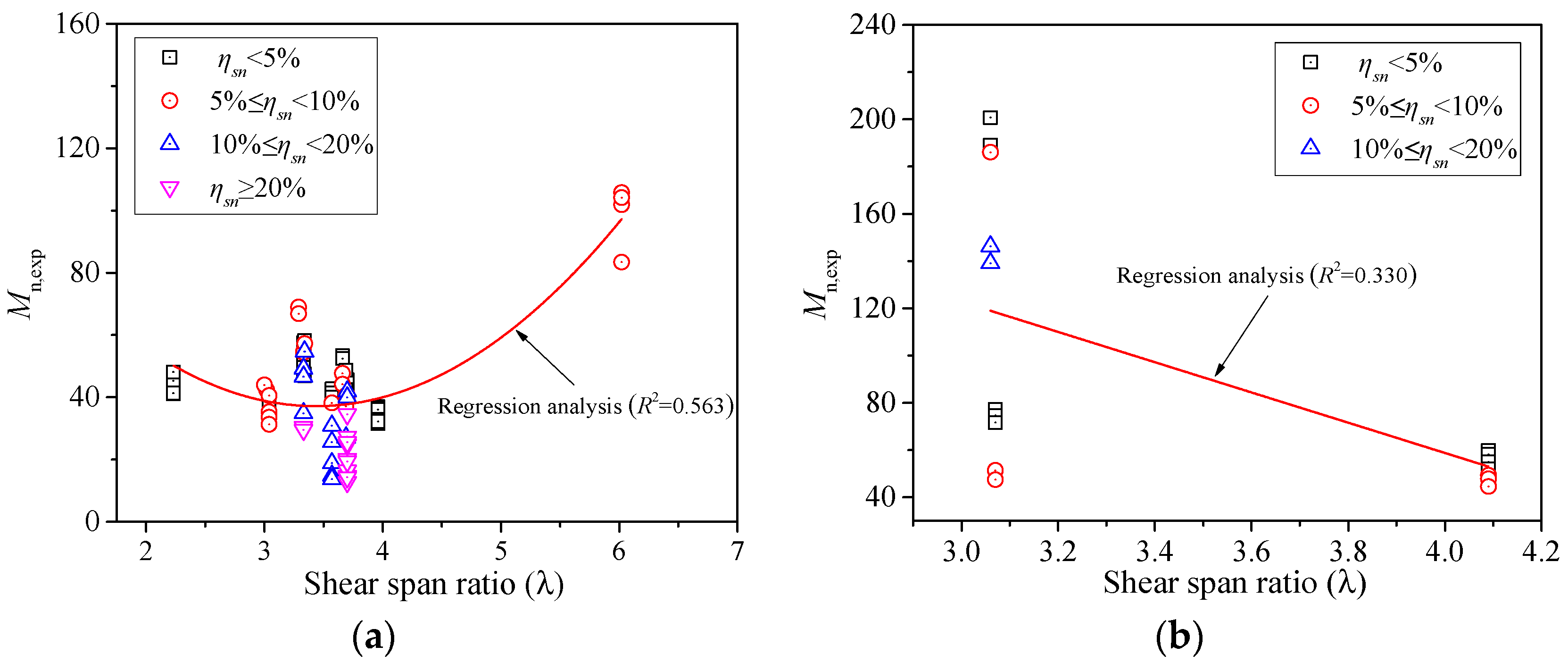
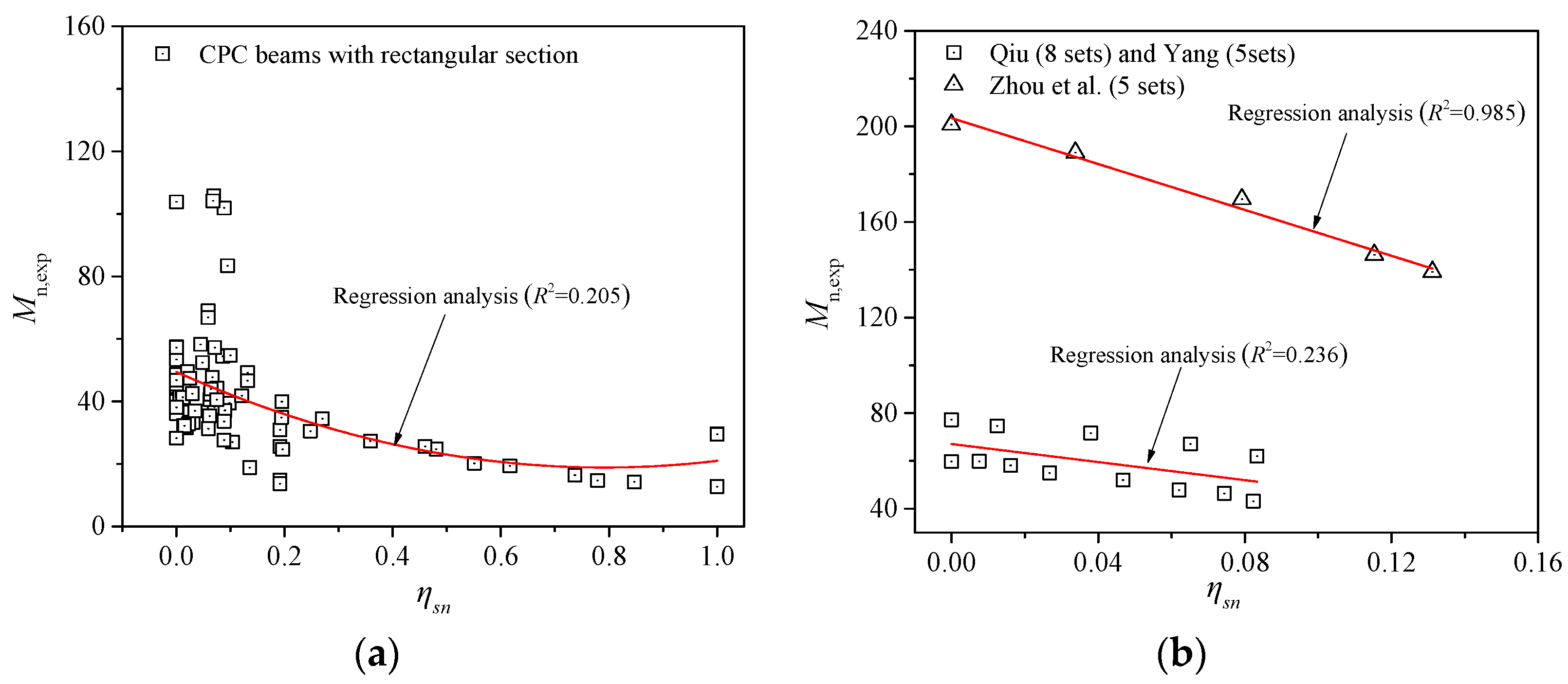
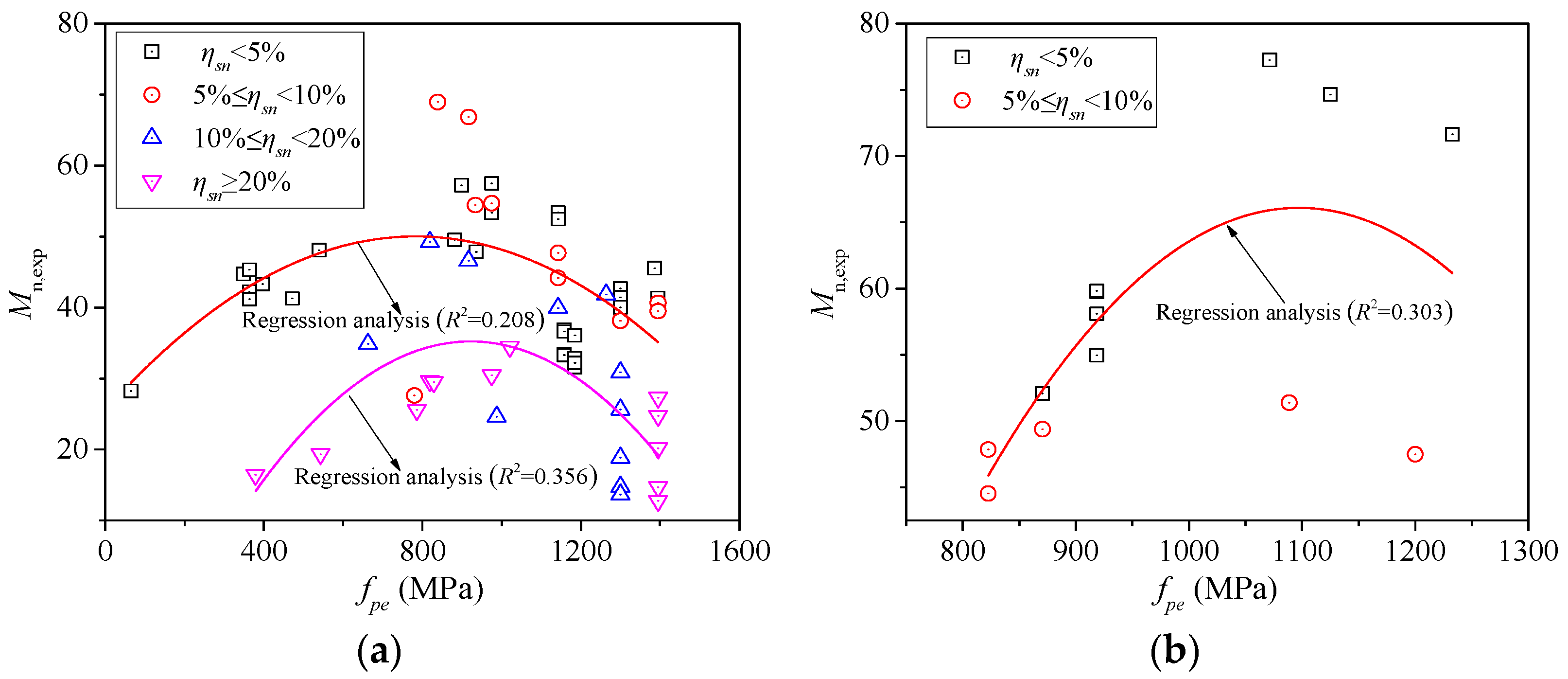
3. Effects of Parameters on the Flexural Strength of CPC Beams
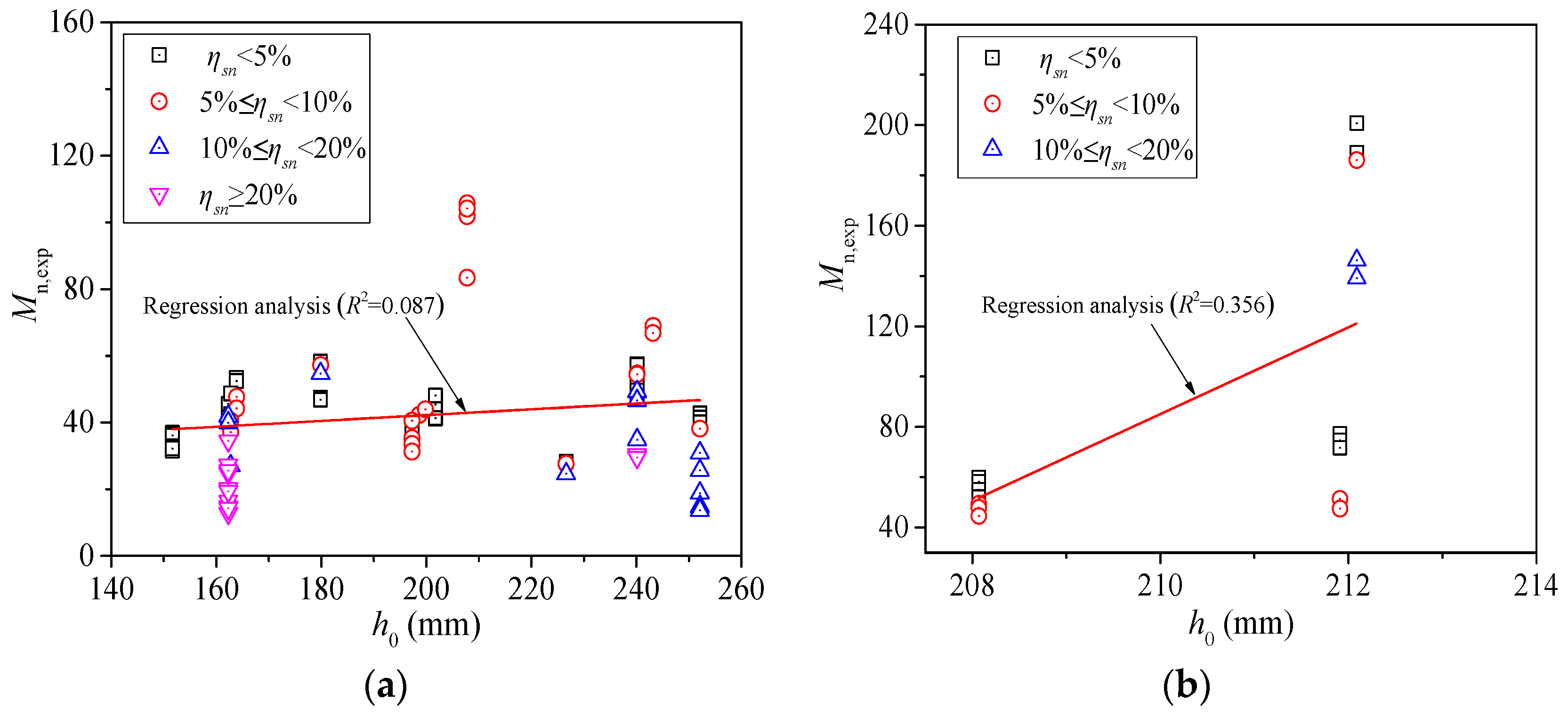
3.1. Beam’s Width and Effective Depth
3.2. Compressive Strength of Concrete and Shear Span Ratio
3.3. Corrosion Rate of Prestressed Steel
3.4. Prestressing Ratio (PPR) and Effective Prestress
4. Comparison between the Test Results and Predictions of Chinese Code, Eurocode and ACI Standard
4.1. GB50010-2010 (Chinese Code: Design Code for Concrete Structure, 2010)
4.2. EN 1992-1-1:2004+A1 (Eurocode 2: Design of Concrete Structure-Part 1-1: General Rules and Rules for Buildings, 2014)
4.3. ACI 318-19 (ACI Standard: Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete, 2019)
4.4. Calculation of the Flexural Capacity without Considering the Effects of Strand Corrosion
5. A Proposal for a Flexural Strength Model for CPC Beams on the Basis of the ACI Standard
5.1. Deterioration of Mechanical Properties of Corroded Prestressed Reinforcement
5.2. Proposal of New Model Based on ACI Standard
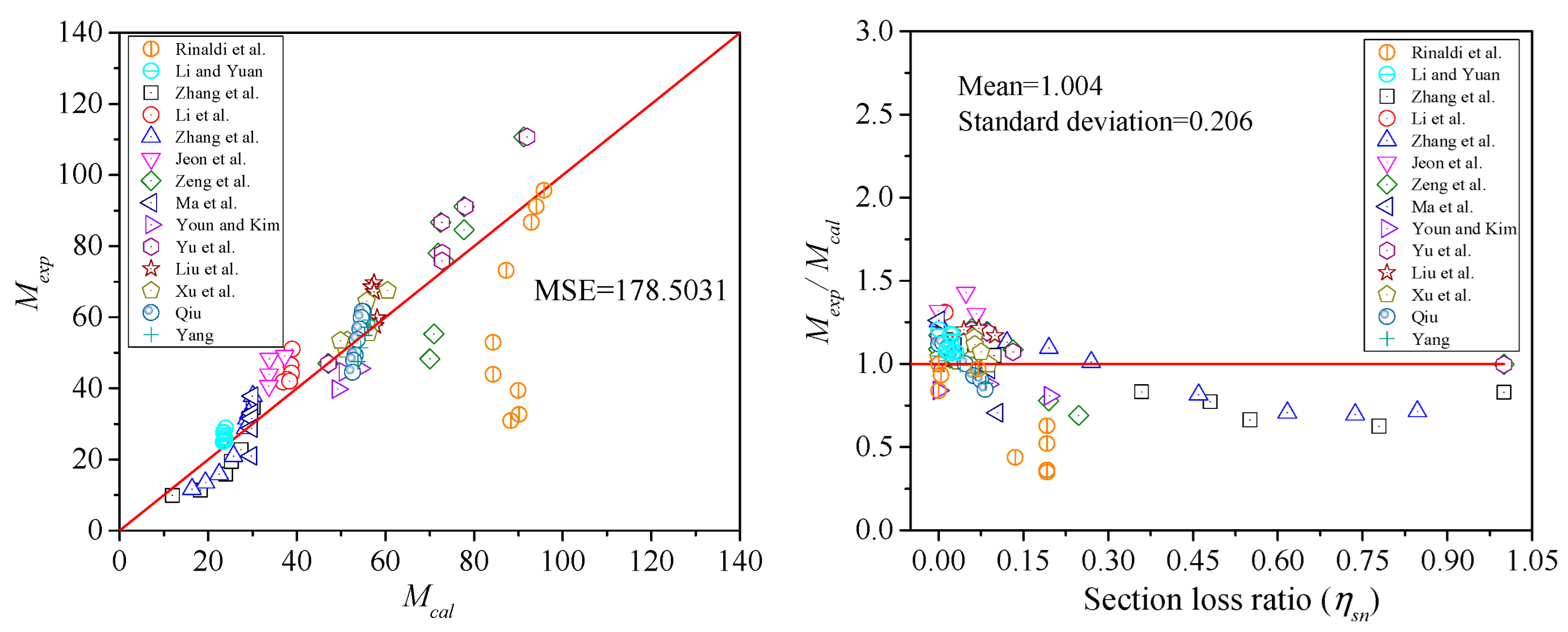
5.3. Verification of Proposed Model
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A0 | Cross-sectional area of the prestressed reinforcement |
| Amin | Minimum remaining cross-sectional area of the prestressed reinforcement after corrosion |
| Asc | Cross-sectional area of the compression non-prestressed reinforcement |
| Ast | Cross-sectional area of the tensile non-prestressed reinforcement |
| A p | Original cross-sectional area of the tensile prestressed reinforcement |
| A′p | Cross-sectional area of the compression prestressed reinforcement |
| Apsη | Cross-sectional area of prestressed reinforcement after corrosion |
| a | Depth of equivalent rectangular stress block |
| as | Distance from the resultant force of the prestressed steel and the ordinary tensile steel bar to the edge of the beam Section in tension zone |
| b | Beam width, and the data in brackets are the flange width of the T-beam |
| d0 | Diameter of the prestressed reinforcement |
| dmin | Diameter of the prestressed reinforcement after corrosion |
| dp | Distance from extreme compression fiber to centroid of prestressed reinforcement |
| Ep | Elastic modulus of uncorroded prestressed reinforcement |
| Epη | Elastic modulus of corroded prestressed reinforcement |
| Es | Modulus of elasticity of the reinforcing steel |
| fck | Prismatic compressive strength of the concrete |
| fcu,150 | Cube compressive strength of concrete |
| fpe | Effective prestress |
| fps | Stress in prestressed reinforcement at nominal flexural strength |
| fpsη | Stress in corroded prestressed reinforcement at nominal flexural strength |
| fpt | Ultimate tensile strength of prestressed reinforcement |
| fpu0 | Ultimate tensile strength of uncorroded prestressed reinforcement |
| fpyt | Yield strength of the tensile prestressed reinforcement |
| fyc | Yield strength of compression non-prestressed reinforcement |
| fyt | Yield strength of tensile non-prestressed reinforcement |
| fcyl,150 | Compressive strength of concrete obtained from cylinder tests of 150 × 300 mm specimens |
| h | Beam depth, and the data in brackets are the flange depth of T-beam |
| h0 | Effective depth of the cross-section |
| Mcalη | Calculated the flexural capacity of CPC beams |
| Mexp | Experimental ultimate flexural capacity of CPC beams |
| Mu,exp | Normalized ultimate flexural stress |
| m0 | Initial mass of the prestressed reinforcement before corrosion |
| mr | Remaining mass of the prestressed reinforcement after corrosion |
| PPR | Prestressing ratio |
| X | Maximum corrosion depth of the prestressed steel |
| x | Concrete depth of compression zone |
| ηsn | Section loss ratio of prestressed reinforcement |
| ηwt | Weight loss ratio of prestressed reinforcement |
| εcu2 | Ultimate compressive strain in the concrete |
| εsu0 | Ultimate strain of uncorroded prestressed reinforcement |
| εsuη | Ultimate strain of corroded prestressed reinforcement |
| λ | Shear span to depth ratio |
References
- Gu, X.L.; Jin, X.Y.; Zhou, Y. Prestressed Concrete Structures. In Basic Principles of Concrete Structures; Gu, X.L., Jin, X.Y., Zhou, Y., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 415–495. [Google Scholar]
- Nassiraei, H. Probability distribution models for the ultimate strength of tubular T/Y-joints reinforced with collar plates at room and different fire conditions. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 270, 113557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Wang, L.; Tang, S.H.; Cui, H.T.; Xie, X.N.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.H.; Yang, D.L.; Xiang, P. Investigations on the shearing performance of ballastless CRTS II slab based on quasi-distributed optical fiber sensing. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2023, 75, 103129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.N.; Ning, X.L. Prestressed Concrete. In Reinforced Concrete: Basic Theory and Standards; Ding, Y.N., Ning, X.L., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 355–401. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Strand Corrosion in Prestressed Concrete Structures, 1st ed.; Springers: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- ACI PRC-222.2R-14; Report on Corrosion of Prestressing Steels. American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2014.
- Woodward, R.J. Collapse of a segmental post-tensioned concrete bridge. In Transportation Research Record; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Campione, G. Simplified Model of PC Concrete Beams with Corroded Strands in Highway Viaduct: Case Study and Analytical Modeling. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2021, 35, 04021069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.N.; Au, F.K.; Mickleborough, N.; Lim, E.H.; Chan, K.Y.; Chung, P.H. Investigation Report on Prestressing Tendon Failure Incident at Concrete Viaduct of Shenzhen Bay Bridge-Hong Kong Section; Highways Department: Hong Kong, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.H.; Li, F.; Zhao, Y.G. An Investigation of Degradation of Mechanical Behaviour of Prestressing Strands Subjected to Chloride Attacking. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Durability of Concrete Structures, Shenzhen, China, 30 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.P.; Li, C.K.; Gu, X.L.; Zeng, Y.H. Variability in cross-sectional areas and tensile properties of corroded prestressing wires. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Ma, F.; Cao, B.; Mo, Z.; Liu, J.; Shi, R.; He, Z. Optimization of the Mechanical Properties of Bolted Connections between Concrete-Filled Tubular Columns and Steel Beam with Reinforcing Rings. Buildings 2024, 14, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C. Initial steps of corrosion and oxide characteristics. Struct. Concr. 2020, 21, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, C.H.; Nguyen, C.D.; Shim, C.S. Assessment of Mechanical Properties of Corroded Prestressing Strands. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.G.; Zhang, W.P.; Gu, X.L.; Ye, Z.W. Probability distribution model of stress impact factor for corrosion pits of high-strength prestressing wires. Eng. Struct. 2021, 230, 111686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Pan, Z.; Lun, P.; Zhan, Y.; Nie, Z.; Liu, Y.; Mo, Z.; He, Z. Research on Corrosion Rate Model of Reinforcement in Concrete under Chloride Ion Environments. Buildings 2023, 13, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.T.; Chen, W.Z.; Li, H.; Xu, J.S.; Zhang, B. Experiment and Probabilistic Prediction on Mechanical Properties of Corroded Prestressed Strands under Different Strain Levels. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2022, 34, 04022164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Y.M.; Wang, X.Z.; Tang, H. Effects of the position and chloride-induced corrosion of strand on bonding behavior between the steel strand and concrete. Structures 2023, 58, 105500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.M.; Yuan, Y.S. Experimental study on bending property of prestressed concrete beams with corroded steel strands. J. Build. Mater. 2010, 31, 78–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, Z.; Imperatore, S.; Valente, C. Experimental evaluation of the flexural behavior of corroded P/C beams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2267–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, C.H.; Shim, C.S. Flexural Behavior of Post-Tensioned Concrete Beams with Multiple Internal Corroded Strands. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.Q.; Gu, X.L.; Zeng, Y.H.; Zhang, W.P. Flexural behavior of Corrosion-Damaged prestressed concrete beams. Eng. Struct. 2022, 272, 114985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, H.; Mutsuyoshi, H.; Niitani, K. Influence of grouting condition on crack and load-carrying capacity of post-tensioned concrete beam due to chloride-induced corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Corrosion-induced flexural behavior degradation of locally ungrouted post-tensioned concrete beams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dai, L.Z.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, J.R. Effect of corrosion on deformation compatibility between prestressed reinforcement and concrete. J. Saf. Environ. 2014, 14, 5–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.G. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Flexural Performance of Corrosion-Affected High-Speed Rail Box Beam. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2014. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.D. Study on Flexural Performance and Reliability Analysis of Corrosion-Affected Simply-Supported Box Girder for High Speed Railway. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2016. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.H.; Lu, Z.H.; Li, H. Experimental study on flexural behavior of corroded high-speed railway box girder. Build. Struct. 2021, 51 (S1), 1514–1521. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.R.; Ma, Y.F.; Liu, Y.M. Flexural behavior of bonded post-tensioned concrete beams under strand corrosion. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2017, 313, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.Z.; Wang, L.; Bian, H.B.; Zhang, J.R.; Zhang, X.H.; Ma, Y.F. Flexural Capacity Prediction of Corroded Prestressed Concrete Beams Incorporating Bond Degradation. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2019, 32, 04019027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Z.Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.R. Calculation method for flexural capacity of corroded PC beams considering bond degradation. J. Disaster Prev. Mitig. Eng. 2020, 40, 639–646. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.H.; Zhou, Q.H.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.-G. A new empirical model for residual flexural capacity of corroded post-tensioned prestressed concrete beams. Structures 2021, 34, 4308–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, Y.; Nayak, G.; Bhat, R.; Kamath, M. A prediction model for flexural strength of corroded prestressed concrete beam using artificial neural network. Cogent Eng. 2023, 10, 2187657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Q.; Ge, W.J.; Cao, D.F. Mechanical behaviors of prestressed concrete beams after stress corrosion of prestressed reinforcement. J. Nanjing Univ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 38, 811–817. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.H.; Huang, Q.H.; Gu, X.L.; Zhang, W.P. Experimental Study on Bending Behavior of Corroded Post-Tensioned Concrete Beams. In Earth and Space 2010: Engineering, Science, Construction, and Operations in Challenging Environments; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Youn, S.; Kim, E.K. Deterioration of bonded post-tensioned concrete bridges and research topics on the strength evaluation in isarc. In Proceedings of the JSCE–KSCE Joint Seminar Maintenance and Management Strategy of Infrastructures in Japan and Korea, Kusatsu, Japan, 20 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Fan, Y.F.; Yu, J.; Li, Q.C. Flexural behavior test of corroded prestressed concrete beams under chloride environment. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2020, 37, 707–715. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.C.; Cao, Y.M.; Chen, Z.C.; Chen, M.C.; Fu, B.; Zhu, D.M. Study on flexural behavior of prestressed concrete beams under simulated acid rain corrosion. Chin. J. Comput. Mech. 2019, 36, 124–131. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- GB50010-2010; Design Code for Concrete Structure. China Building Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese)
- 1992-1-1:2004+A1:2014(E); Eurocode2: Design of Concrete Structures-Part 1-1: General Rules and Rules for Buildings. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2014.
- Xue, C.Y. Research on Bond Performance between Corroded Pre-Stressing Steel Strand and Concrete under Chloride Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, Changsha University of Science and Technology, Changsha, China, 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.H.; Li, H.; Li, W.G.; Zhao, Y.-G.; Tang, Z.; Sun, Z.H. Shear behavior degradation and failure pattern of reinforced concrete beam with chloride-induced stirrup corrosion. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2019, 22, 2998–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kani, G.N.J. The Riddle of Shear Failure and its Solution. ACI Struct. J. 1964, 61, 441–468. [Google Scholar]
- ACI 318-19; Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete. American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Sause, R.; Frangopol, D.M.; Li, A. Time-Dependent Reliability of PSC Box-Girder Bridge Considering Creep, Shrinkage, and Corrosion. J. Bridge Eng. 2011, 16, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
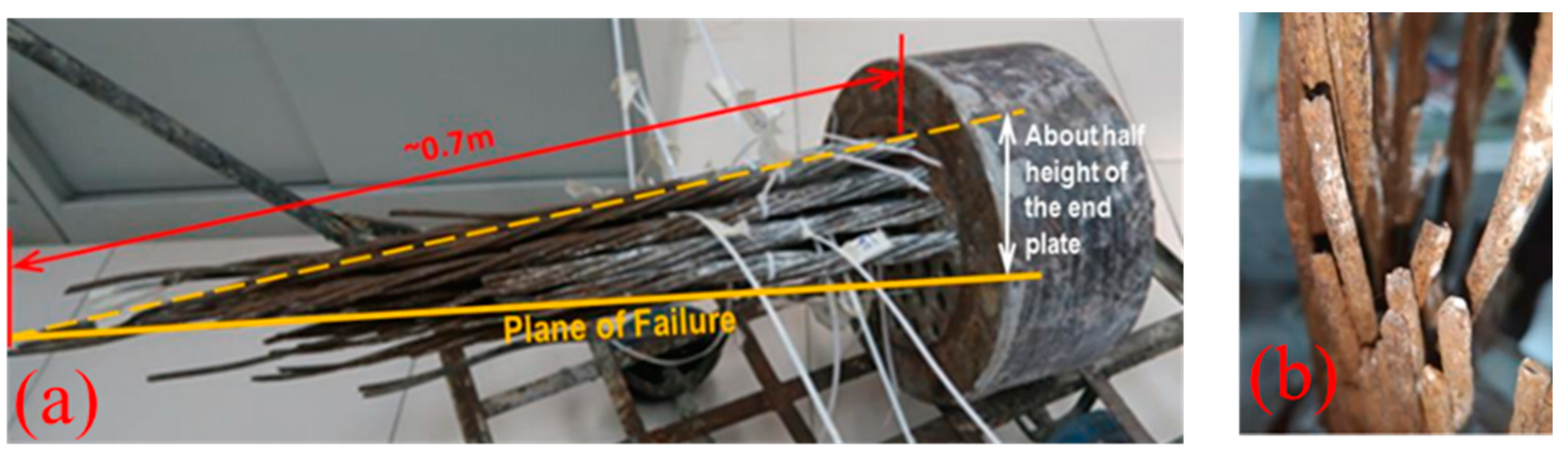
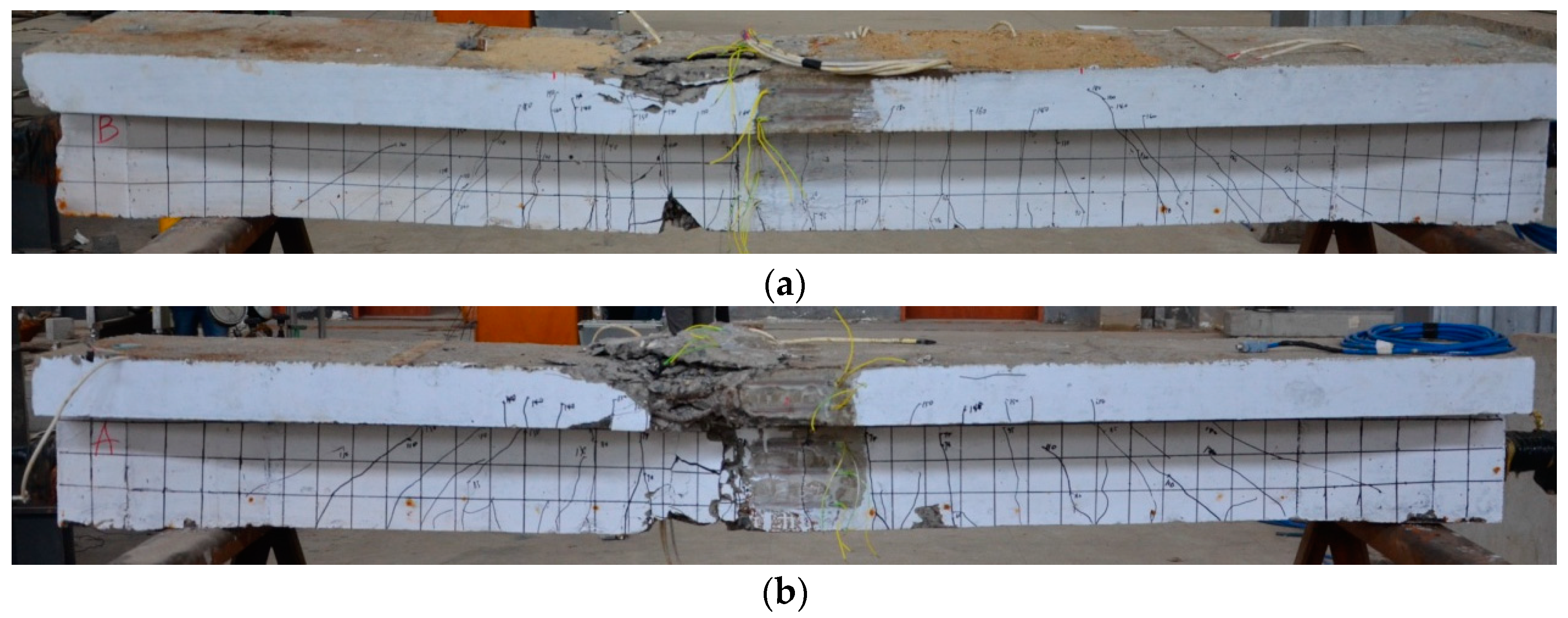
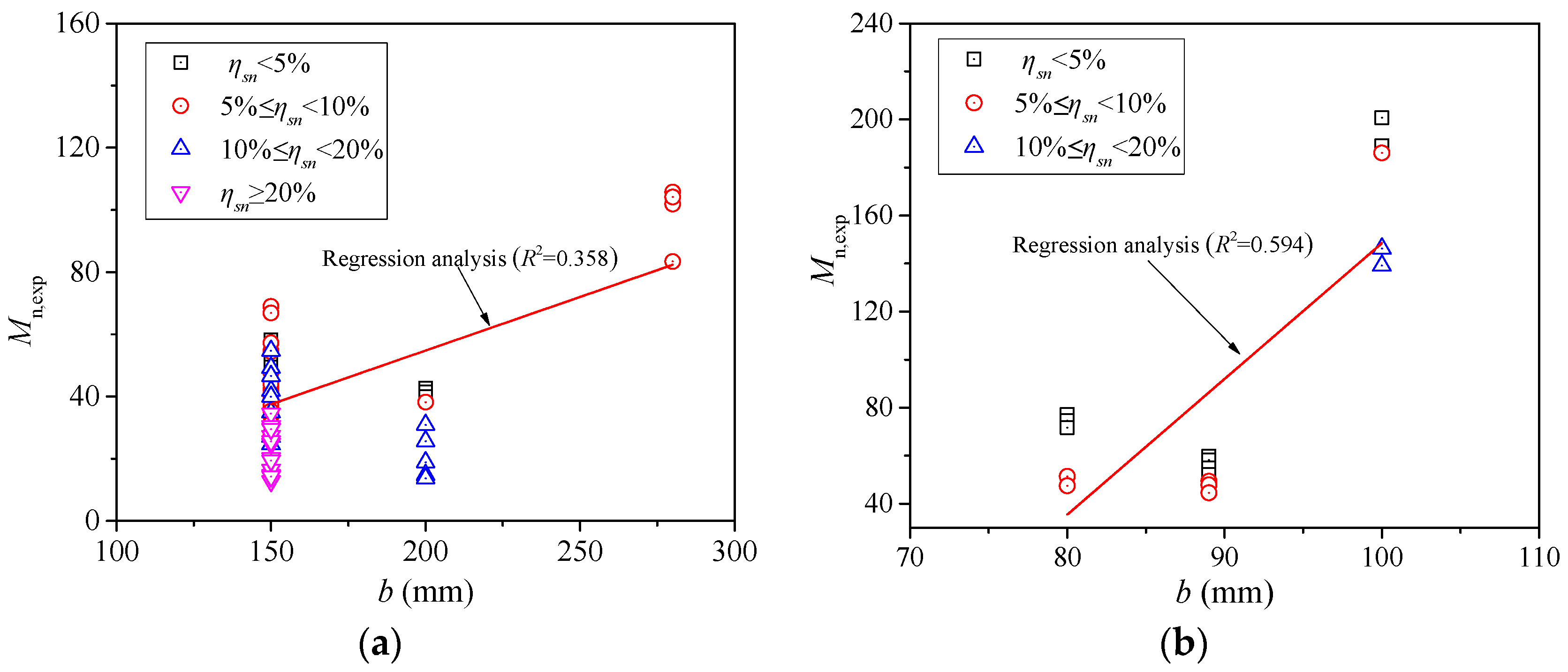

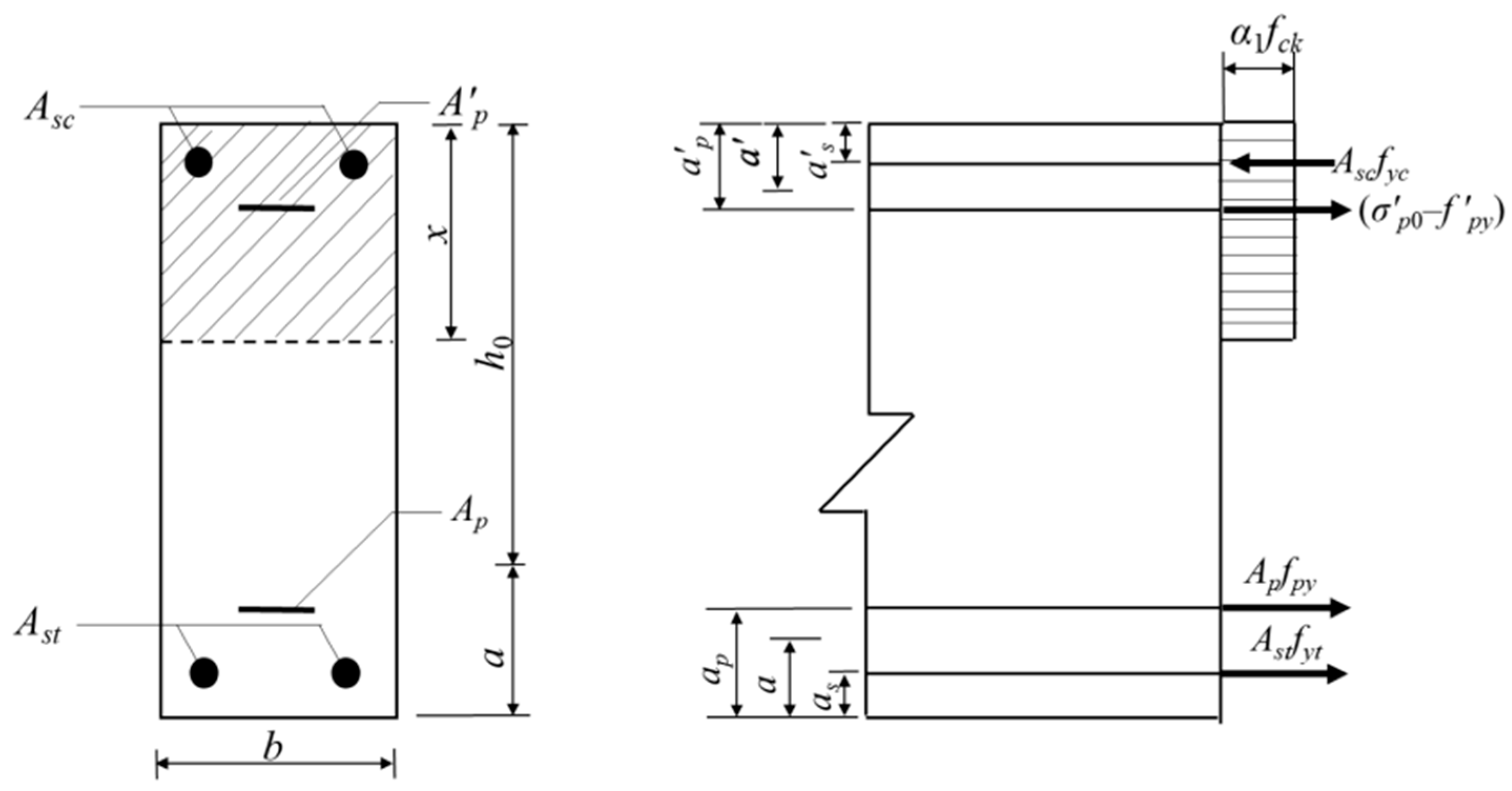
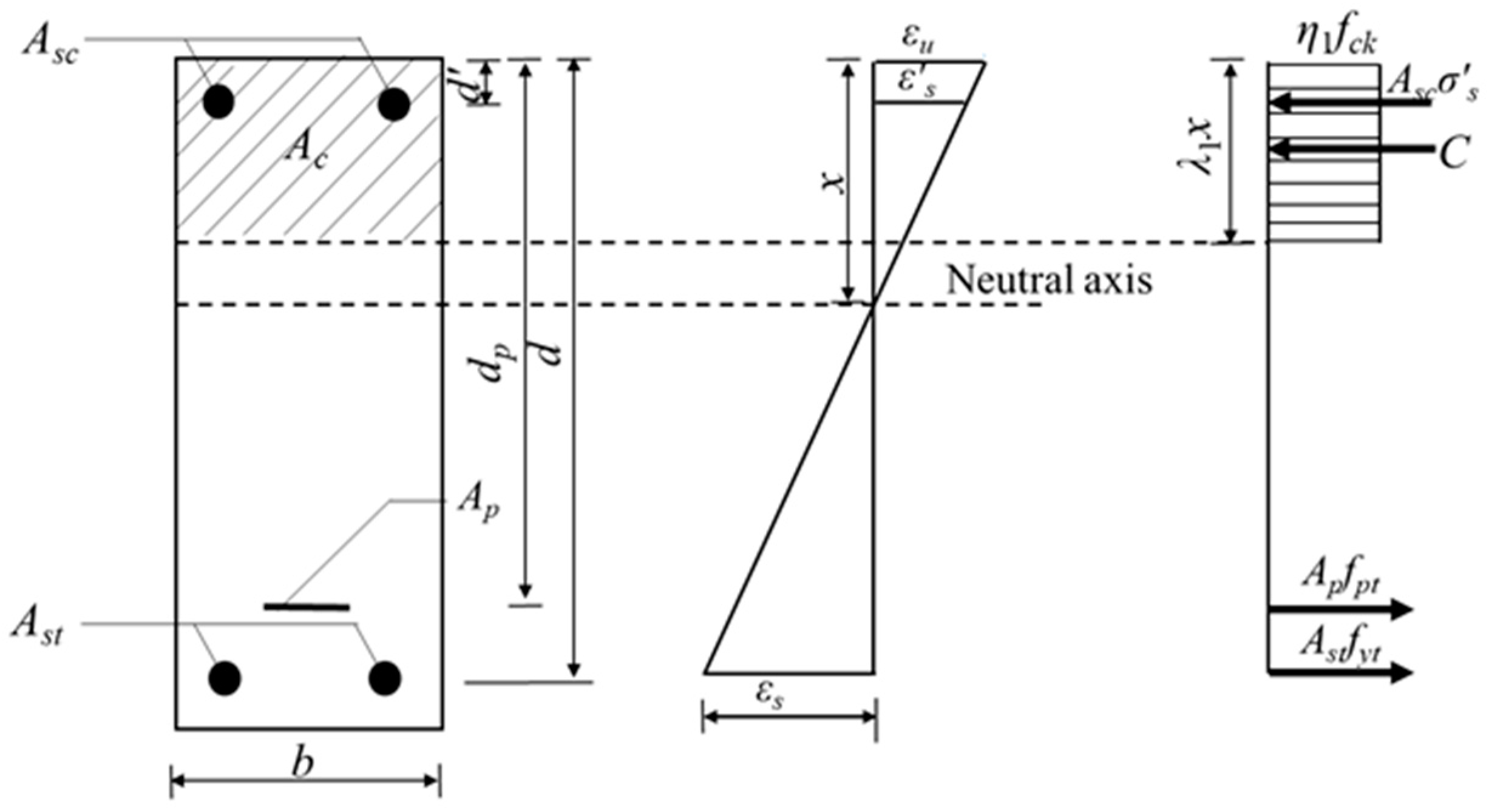
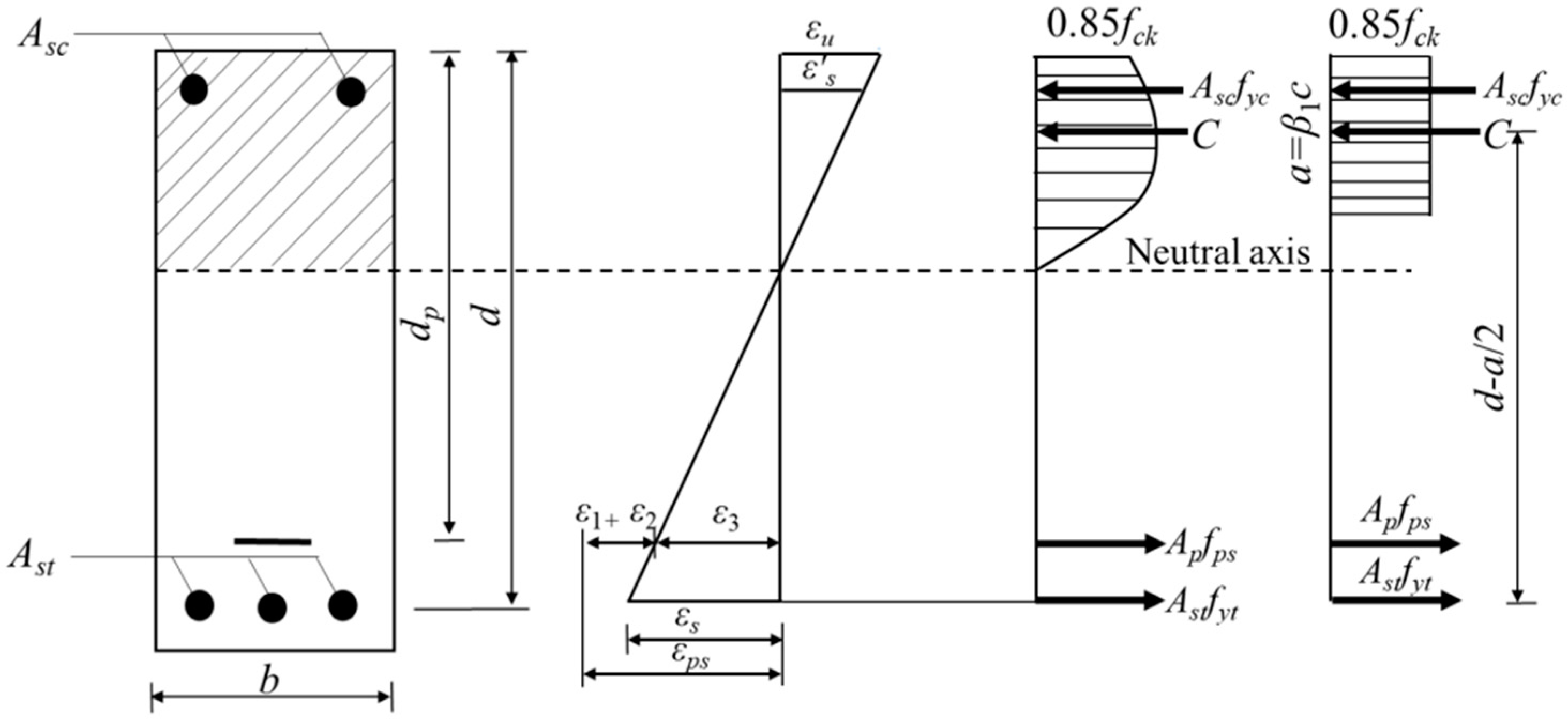

| Reference | Specimen | b (mm) | h (mm) | Concrete Strength (MPa) | Ast (mm2) | fyt (MPa) | Asc (mm2) | fyc (MPa) | Ap (mm2) | fpt (MPa) | Ep (N/mm2) | η | λ | Mexp (kN·m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rinaldi et al. [20] (9 sets) | NO.7 | 200 | 300 | 34 | 157 | 400 | 157 | 400 | 226.19 | 1976 | 195,000 | 0 | 3.57 | 73.20 |
| NO.8 | 200 | 300 | 34 | 157 | 400 | 157 | 400 | 226.19 | 1976 | 195,000 | 0.2 | 3.57 | 43.95 | |
| NO.9 | 200 | 300 | 34 | 157 | 400 | 157 | 400 | 226.19 | 1976 | 195,000 | 0.2 | 3.57 | 52.95 | |
| NO.2 | 200 | 300 | 41.5 | 157 | 400 | 157 | 400 | 226.19 | 1976 | 195,000 | 0 | 3.57 | 86.70 | |
| NO.3 | 200 | 300 | 41.5 | 157 | 400 | 157 | 400 | 226.19 | 1976 | 195,000 | 0.14 | 3.57 | 39.45 | |
| NO.1 | 200 | 300 | 41.5 | 157 | 400 | 157 | 400 | 226.19 | 1976 | 195,000 | 0.2 | 3.57 | 30.90 | |
| NO.4 | 200 | 300 | 47.4 | 157 | 400 | 157 | 400 | 226.19 | 1976 | 195,000 | 0 | 3.57 | 95.70 | |
| NO.6 | 200 | 300 | 47.4 | 157 | 400 | 157 | 400 | 226.19 | 1976 | 195,000 | 0.07 | 3.57 | 91.20 | |
| NO5 | 200 | 300 | 47.4 (fcu,150) | 157 | 400 | 157 | 400 | 226.19 | 1976 | 195,000 | 0.2 (ηwt) | 3.57 | 32.70 | |
| Li and Yuan [19] (9 sets) | PRB1 | 150 | 200 | 33.0 | 57 | 284 | 226 | 375 | 98.7 | 1913 | 195,000 | 0.0173 | 3.96 | 27.7 |
| PRB2 | 150 | 200 | 33.0 | 57 | 284 | 226 | 375 | 98.7 | 1913 | 195,000 | 0.0219 | 3.96 | 27.5 | |
| PRB3 | 150 | 200 | 33.0 | 57 | 284 | 226 | 375 | 98.7 | 1913 | 195,000 | 0.0224 | 3.96 | 25.1 | |
| PRB4 | 150 | 200 | 33.0 | 57 | 284 | 226 | 375 | 98.7 | 1913 | 195,000 | 0.0287 | 3.96 | 25.0 | |
| POB0 | 150 | 200 | 35.2 | 57 | 284 | 226 | 375 | 98.7 | 1913 | 195,000 | 0 | 3.96 | 28.9 | |
| POB1 | 150 | 200 | 35.2 | 57 | 284 | 226 | 375 | 98.7 | 1913 | 195,000 | 0.0094 | 3.96 | 25.8 | |
| POB2 | 150 | 200 | 35.2 | 57 | 284 | 226 | 375 | 98.7 | 1913 | 195,000 | 0.0151 | 3.96 | 25.3 | |
| POB3 | 150 | 200 | 35.2 | 57 | 284 | 226 | 375 | 98.7 | 1913 | 195,000 | 0.0198 | 3.96 | 26.3 | |
| POB4 | 150 | 200 | 35.2 (fcu,150) | 57 | 284 | 226 | 375 | 98.7 | 1913 | 195,000 | 0.0112 (ηwt) | 3.96 | 25.8 | |
| Zhang et al. [24] (8 sets) | PCB1 | 150 | 220 | 31.82 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.7790 | 3.70 | 11.4 |
| PCB2 | 150 | 220 | 31.82 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 1 | 3.70 | 9.9 | |
| PCB3 | 150 | 220 | 31.82 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.0635 | 3.70 | 31.5 | |
| PCB4 | 150 | 220 | 31.82 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.0982 | 3.70 | 30.6 | |
| PCB5 | 150 | 220 | 32.35 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.5510 | 3.70 | 15.9 | |
| PCB6 | 150 | 220 | 32.35 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.4804 | 3.70 | 19.5 | |
| PCB7 | 150 | 220 | 34.28 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.3589 | 3.70 | 22.8 | |
| PCB8 | 150 | 220 | 34.28 (fcu,150) | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.0128 (ηsn) | 3.70 | 34.5 | |
| Li et al. [34] (7 sets) | SCC0-2 | 150 | 250 | 34.37 | 308 | 360 | 100.6 | 254 | 201.1 | 622.83 | 205,000 | 0 | 2.23 | 46.53 |
| SCC2-1 | 150 | 250 | 34.65 | 308 | 360 | 100.6 | 254 | 201.1 | 622.83 | 205,000 | 0.0067 | 2.23 | 44.28 | |
| SCC2-2 | 150 | 250 | 32.42 | 308 | 360 | 100.6 | 254 | 201.1 | 622.83 | 205,000 | 0.0108 | 2.23 | 42.48 | |
| SCC2-3 | 150 | 250 | 33.73 | 308 | 360 | 100.6 | 254 | 201.1 | 622.83 | 205,000 | 0.0120 | 2.23 | 42.03 | |
| SCC2-4 | 150 | 250 | 30.47 | 308 | 360 | 100.6 | 254 | 201.1 | 622.83 | 205,000 | 0.0138 | 2.23 | 41.8 | |
| SCC1-3 | 150 | 250 | 33.65 | 308 | 360 | 100.6 | 254 | 201.1 | 622.83 | 205,000 | 0.0122 | 2.23 | 42.03 | |
| SCC4-1 | 150 | 250 | 35.07 (fcu,150) | 308 | 360 | 100.6 | 254 | 201.1 | 622.83 | 205,000 | 0.0113 (ηsn) | 2.23 | 51.03 | |
| Zhang et al. [29] (8 sets) | CB0 | 150 | 220 | 34.1 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0 | 3.70 | 37.8 |
| CB1 | 150 | 220 | 33.7 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.7370 | 3.70 | 13.5 | |
| CB2 | 150 | 220 | 33.7 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.4600 | 3.70 | 21 | |
| CB3 | 150 | 220 | 33.7 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.6170 | 3.70 | 15.9 | |
| CB4 | 150 | 220 | 33.7 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.8470 | 3.70 | 11.7 | |
| CB5 | 150 | 220 | 32.4 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.1210 | 3.70 | 33 | |
| CB6 | 150 | 220 | 32.4 | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.1950 | 3.70 | 31.5 | |
| CB7 | 150 | 220 | 34.3 (fcu,150) | 101 | 235 | 226 | 335 | 140 | 1910 | 195,000 | 0.2700 (ηsn) | 3.70 | 28.8 | |
| Jeon et al. [14] (4 sets) | RB | 150 | 220 | 37.46 | 157 | 400 | 265.46 | 400 | 140 | 1865 | 194,500 | 0 | 3.66 | 49.17 |
| QB | 150 | 220 | 37.46 | 157 | 400 | 265.46 | 400 | 140 | 1865 | 194,500 | 0.0482 | 3.66 | 48.3 | |
| MB1 | 150 | 220 | 37.46 | 157 | 400 | 265.46 | 400 | 140 | 1865 | 194,500 | 0.0667 | 3.66 | 43.92 | |
| MB2 | 150 | 220 | 37.46 (fcu,150) | 157 | 400 | 265.46 | 400 | 140 | 1865 | 194,500 | 0.0751 (ηsn) | 3.66 | 40.68 | |
| Zeng et al. [35] (9 sets) | L1 | 150 | 300 | 44 | 402 | 365 | 226 | 360 | 140 | 1950 | 203,000 | 0 | 3.33 | 91.12 |
| L2 | 150 | 300 | 44 | 402 | 365 | 226 | 360 | 140 | 1950 | 203,000 | 0.087 | 3.33 | 86.68 | |
| L3 | 150 | 300 | 44 | 402 | 365 | 226 | 360 | 140 | 1950 | 203,000 | 0.136 | 3.33 | 78.04 | |
| L4 | 150 | 300 | 44 | 402 | 365 | 226 | 360 | 140 | 1950 | 203,000 | 1 | 3.33 | 47 | |
| L5 | 150 | 300 | 44 | 402 | 365 | 226 | 360 | 140 | 1950 | 203,000 | 0.203 | 3.33 | 55.28 | |
| L6 | 150 | 300 | 44 | 760 | 370 | 226 | 360 | 140 | 1950 | 203,000 | 0.058 | 3.29 | 110.68 | |
| L7 | 150 | 300 | 44 | 402 | 365 | 226 | 360 | 140 | 1950 | 203,000 | 0 | 3.33 | 84.6 | |
| L8 | 150 | 300 | 44 | 402 | 365 | 226 | 360 | 140 | 1950 | 203,000 | 0.26 | 3.33 | 48.32 | |
| L9 | 150 | 300 | 44 (fcu,150) | 402 | 365 | 226 | 360 | 140 | 1950 | 203,000 | 0.017 (ηwt) | 3.33 | 75.84 | |
| Ma et al. [31] (5 sets) | B0 | 150 | 220 | 31.8 | 101 | 290 | 226 | 375 | 140 | 1910 | 193,000 | 0 | 3.69 | 37.8 |
| B1 | 150 | 220 | 31.8 | 101 | 290 | 226 | 375 | 140 | 1910 | 193,000 | 0.0270 | 3.69 | 33 | |
| B2 | 150 | 220 | 31.8 | 101 | 290 | 226 | 375 | 140 | 1910 | 193,000 | 0.0620 | 3.69 | 31.5 | |
| B3 | 150 | 220 | 31.8 | 101 | 290 | 226 | 375 | 140 | 1910 | 193,000 | 0.0910 | 3.69 | 28.8 | |
| B4 | 150 | 220 | 31.8 (fcu,150) | 101 | 290 | 226 | 375 | 140 | 1910 | 193,000 | 0.1060 (ηwt) | 3.69 | 21 | |
| Youn and Kim [36] (3 sets) | PC1 | 150 | 300 | 31 | 265.46 | 400 | 265.46 | 400 | 98.7 | 1834 | 195,000 | 0 | / | 45.6 |
| PC2 | 150 | 300 | 31 | 265.46 | 400 | 265.46 | 400 | 98.7 | 1834 | 195,000 | 0.0881 | / | 44.6 | |
| PC3 | 150 | 300 | 31 (fck) | 265.46 | 400 | 265.46 | 400 | 98.7 | 1834 | 195,000 | 0.1963 (ηsn) | / | 39.8 | |
| Yu et al. [22] (6 sets) | L1 | 150 | 300 | 44.2 | 402.1 | 365 | 226.2 | 359 | 140 | 1959 | 203,000 | 0 | 3.33 | 91.1 |
| L2 | 150 | 300 | 44.2 | 402.1 | 365 | 226.2 | 359 | 140 | 1959 | 203,000 | 0.087 | 3.33 | 86.7 | |
| L3 | 150 | 300 | 46.5 | 402.1 | 365 | 226.2 | 359 | 140 | 1959 | 203,000 | 0.136 | 3.33 | 78.0 | |
| L4 | 150 | 300 | 44.2 | 402.1 | 365 | 226.2 | 359 | 140 | 1959 | 203,000 | 1 | 3.33 | 47.0 | |
| L5 | 150 | 300 | 45.4 | 760.3 | 368 | 226.2 | 359 | 140 | 1959 | 203,000 | 0.058 | 3.29 | 110.7 | |
| L6 | 150 | 300 | 42.5 (fcu,150) | 402.1 | 365 | 226.2 | 359 | 140 | 1959 | 203,000 | 0.017 (ηwt) | 3.33 | 75.8 | |
| Jeon et al. [21] (5 sets) | CB1 | 280 | 380 | 37.46 | 157 | 400 | 265.46 | 400 | 138.7 | 1883 | 195,000 | 0.0949 | 6.02 | 181.75 |
| CB2 | 280 | 380 | 37.46 | 157 | 400 | 265.46 | 400 | 138.7 | 1883 | 195,000 | 0.0884 | 6.02 | 222.02 | |
| CB3 | 280 | 380 | 37.46 | 157 | 400 | 265.46 | 400 | 138.7 | 1883 | 195,000 | 0.0689 | 6.02 | 230.45 | |
| CB4 | 280 | 380 | 37.46 | 157 | 400 | 265.46 | 400 | 138.7 | 1883 | 195,000 | 0.068 | 6.02 | 226.92 | |
| RB5 | 280 | 380 | 37.46 (fcu,150) | 157 | 400 | 265.46 | 400 | 138.7 | 1883 | 195,000 | 0 (ηsn) | 6.02 | 226.31 | |
| Liu et al. [37] (5 sets) | B2 | 150 | 250 | 45.1 | 308 | 335 | 308 | 335 | 197.4 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.071 | 3.34 | 59.79 |
| B3 | 150 | 250 | 43.6 | 308 | 335 | 308 | 335 | 197.4 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.043 | 3.34 | 67.17 | |
| B5 | 150 | 250 | 45.5 | 308 | 335 | 308 | 335 | 197.4 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.102 | 3.34 | 57.63 | |
| B7 | 150 | 250 | 46.7 | 308 | 335 | 308 | 335 | 197.4 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.022 | 3.34 | 68.52 | |
| B9 | 150 | 250 | 45.6 (fcu,150) | 308 | 335 | 308 | 335 | 197.4 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0 (ηwt) | 3.34 | 69.66 | |
| Xu et al. [38] (8 sets) | PCB-1 | 150 | 250 | 51.2 | 226 | 400 | 226 | 400 | 140 | 1661 | 202,000 | 0 | 3.04 | 57.8 |
| PCB-2 | 150 | 250 | 51.2 | 226 | 400 | 226 | 400 | 140 | 1661 | 202,000 | 0.0322 | 3.04 | 56 | |
| PCB-3 | 150 | 250 | 51.2 | 226 | 400 | 226 | 400 | 140 | 1661 | 202,000 | 0.0611 | 3.04 | 53.5 | |
| PCB-4 | 150 | 250 | 51.2 | 226 | 400 | 226 | 400 | 140 | 1661 | 202,000 | 0.0895 | 3.04 | 50.9 | |
| PCB-5 | 150 | 250 | 51.2 | 308 | 400 | 226 | 400 | 140 | 1661 | 202,000 | 0.0623 | 3.02 | 64.5 | |
| PCB-6 | 150 | 250 | 51.2 | 402 | 400 | 226 | 400 | 140 | 1661 | 202,000 | 0.0635 | 3.00 | 67.5 | |
| PCB-7 | 150 | 250 | 59.9 | 226 | 400 | 226 | 400 | 140 | 1661 | 202,000 | 0.0582 | 3.04 | 55.5 | |
| PCB-8 | 150 | 250 | 44.5 (fcu,150) | 226 | 400 | 226 | 400 | 140 | 1661 | 202,000 | 0.0753 (ηwt) | 3.04 | 53.4 | |
| Qiu [26] (8 sets) | A0 | 89(265) | 240(75) | 55.7 | 100.6 | 350 | 100.6 | 350 | 140 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0 | 4.09 | 61.63 |
| A1 | 89(265) | 240(75) | 55.7 | 100.6 | 350 | 100.6 | 350 | 140 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.0033 | 4.09 | 61.71 | |
| A2 | 89(265) | 240(75) | 55.7 | 100.6 | 350 | 100.6 | 350 | 140 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.0124 | 4.09 | 59.93 | |
| A3 | 89(265) | 240(75) | 55.7 | 100.6 | 350 | 100.6 | 350 | 140 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.0237 | 4.09 | 56.7 | |
| A4 | 89(265) | 240(75) | 55.7 | 100.6 | 350 | 100.6 | 350 | 140 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.0452 | 4.09 | 53.72 | |
| A5 | 89(265) | 240(75) | 55.7 | 100.6 | 350 | 100.6 | 350 | 140 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.0615 | 4.09 | 49.39 | |
| A6 | 89(265) | 240(75) | 55.7 | 100.6 | 350 | 100.6 | 350 | 140 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.0747 | 4.09 | 47.86 | |
| A7 | 89(265) | 240(75) | 55.7 (fcu,150) | 100.6 | 350 | 100.6 | 350 | 140 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.0831 (ηwt) | 4.09 | 44.54 | |
| Yang [27] (5 sets) | B01 | 80(320) | 250(80) | 45.2 | 100.6 | 350 | 402.4 | 350 | 140 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0 | 3.07 | 59.2 |
| CB2 | 80(320) | 250(80) | 45.2 | 100.6 | 350 | 402.4 | 350 | 140 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.0085 | 3.07 | 57.2 | |
| CB3 | 80(320) | 250(80) | 45.2 | 100.6 | 350 | 402.4 | 350 | 140 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.0358 | 3.07 | 54.9 | |
| CB4 | 80(320) | 250(80) | 45.2 | 100.6 | 350 | 402.4 | 350 | 140 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.0648 | 3.07 | 51.4 | |
| CB5 | 80(320) | 250(80) | 45.2 (fcu,150) | 100.6 | 350 | 402.4 | 350 | 140 | 1860 | 195,000 | 0.0842 (ηwt) | 3.07 | 47.5 | |
| Zhou et al. [28] (5 sets) | A0 | 100(320) | 250(80) | 51.75 | 100.6 | 415.3 | 402.4 | 415.3 | 140 | 1980.8 | 195,000 | 0 | 3.06 | 220.33 |
| A1 | 100(320) | 250(80) | 51.75 | 100.6 | 415.3 | 402.4 | 415.3 | 140 | 1980.8 | 195,000 | 0.0313 | 3.06 | 207.51 | |
| A2 | 100(320) | 250(80) | 51.75 | 100.6 | 415.3 | 402.4 | 415.3 | 140 | 1980.8 | 195,000 | 0.0798 | 3.06 | 186.08 | |
| A3 | 100(320) | 250(80) | 51.75 | 100.6 | 415.3 | 402.4 | 415.3 | 140 | 1980.8 | 195,000 | 0.1184 | 3.06 | 160.56 | |
| A4 | 100(320) | 250(80) | 51.75 (fcu,150) | 100.6 | 415.3 | 402.4 | 415.3 | 140 | 1980.8 | 195,000 | 0.1353 (ηsn) | 3.06 | 152.74 |
| Compressive Strength of the Concrete | Yield Strength of the Longitudinal Tensile Reinforcement | Yield Strength of the Longitudinal Compression Reinforcement | Ultimate Tensile Strength of the Prestressed Reinforcement | Section Loss Ratio of the Prestressed Reinforcement | Shear Pan Ratio | Prestressed Reinforcement Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fcu,150 (MPa) | fyt (MPa) | fyc (MPa) | fpt (MPa) | ηsn | λ | ||
| Range | 30.47~59.9 | 235~415.3 | 254~415.3 | 622.83~1980.8 | 0~100% | 2.32~6.02 | 12.7 mm and 15.2 mm steel strands, 16 mm prestressed steel bar |
| Types of Code | AAE | MSE | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| GB50010-2010 [39] | 0.6186 | 1146.8869 | 0.5304 |
| EN 1992-1-1:2004+A1 [40] | 0.3868 | 371.4661 | 0.4676 |
| ACI 318-19 [44] | 0.2829 | 238.2815 | 0.3263 |
| The new proposal | 0.1990 | 178.5013 | 0.2764 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Pan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, H.; Ma, F.; Zheng, L. Predicting Residual Flexural Strength of Corroded Prestressed Concrete Beams: Comparison of Chinese Code, Eurocode and ACI Standard. Buildings 2024, 14, 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14072047
Li H, Pan Z, Yang Y, Wang X, Tang H, Ma F, Zheng L. Predicting Residual Flexural Strength of Corroded Prestressed Concrete Beams: Comparison of Chinese Code, Eurocode and ACI Standard. Buildings. 2024; 14(7):2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14072047
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hai, Zhicheng Pan, Yiming Yang, Xinzhong Wang, Huang Tang, Fanjun Ma, and Liangfei Zheng. 2024. "Predicting Residual Flexural Strength of Corroded Prestressed Concrete Beams: Comparison of Chinese Code, Eurocode and ACI Standard" Buildings 14, no. 7: 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14072047
APA StyleLi, H., Pan, Z., Yang, Y., Wang, X., Tang, H., Ma, F., & Zheng, L. (2024). Predicting Residual Flexural Strength of Corroded Prestressed Concrete Beams: Comparison of Chinese Code, Eurocode and ACI Standard. Buildings, 14(7), 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14072047






