Optimization of Cold-Formed Thin-Walled Cross-Sections in Portal Frames
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Formulation of the Optimization Problem
2.1. Objective for the Optimization Problem
2.2. Variables for the Optimization Problem
2.3. Constraints for the Optimization Problem
3. Structure for Optimization Examples
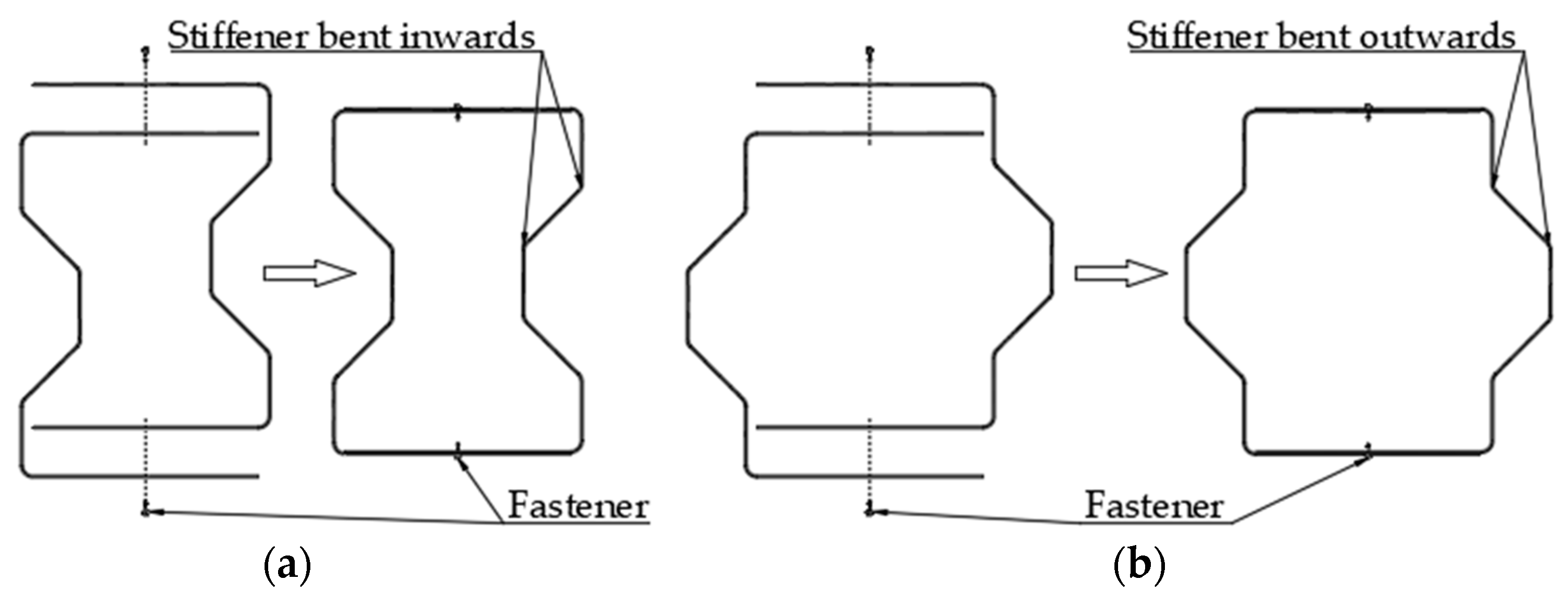
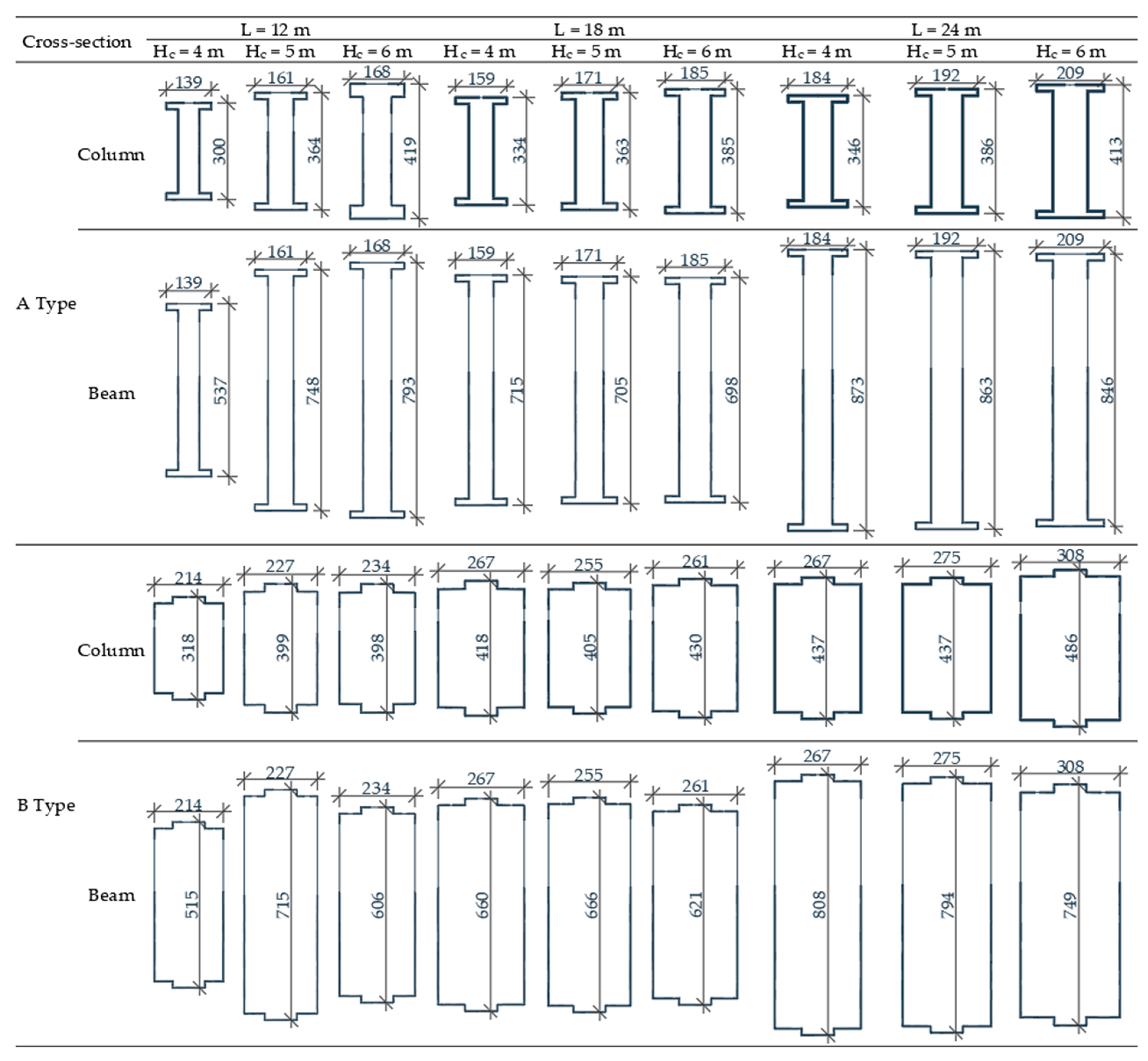
3.1. Cross-Section Geometry Definition
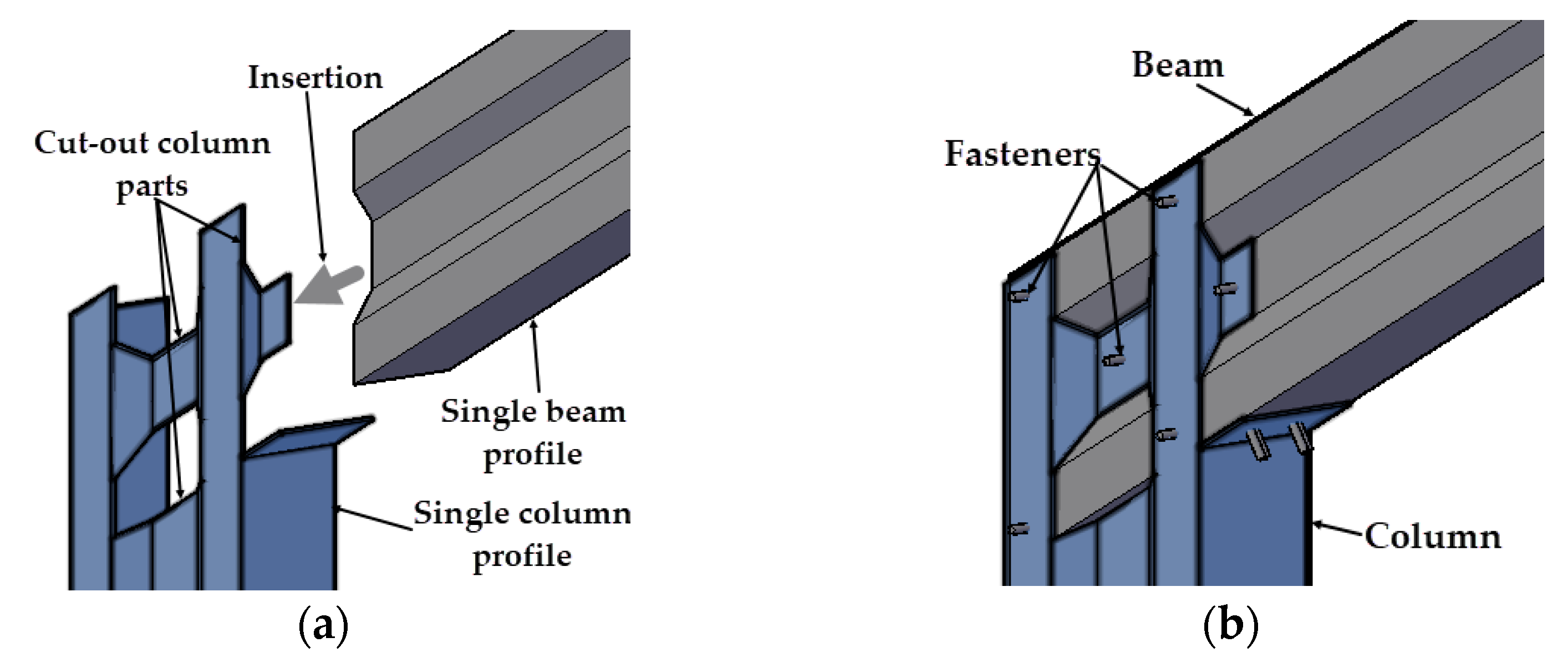
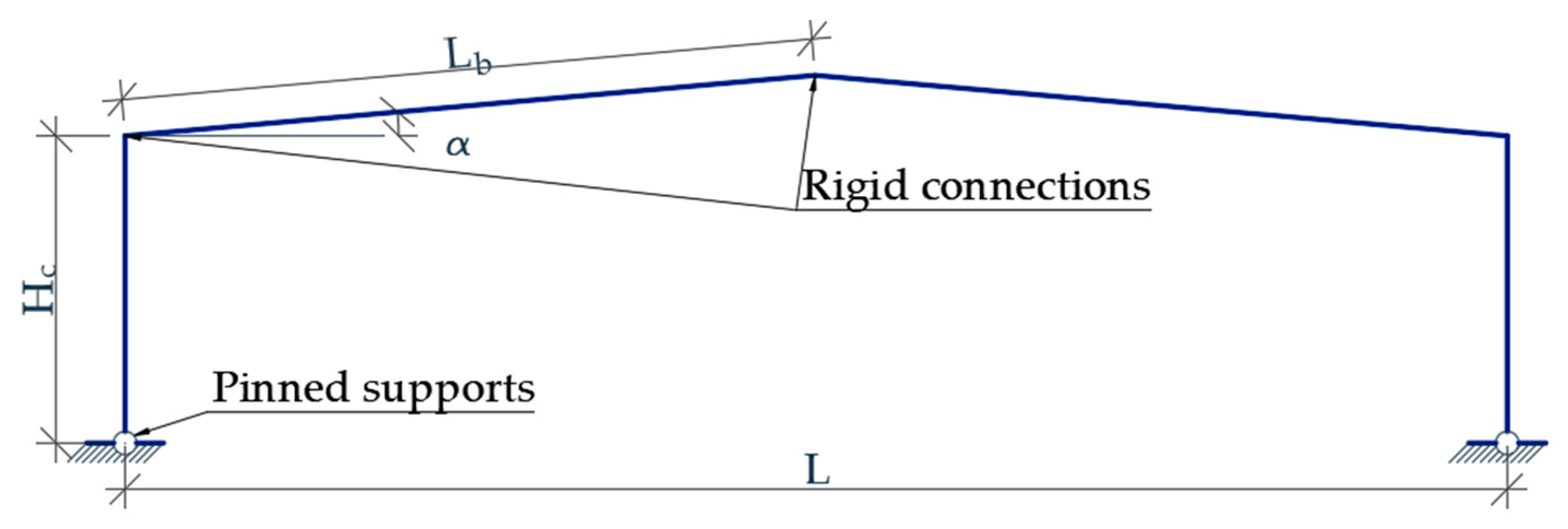
3.2. Structure Geometry
3.3. Portal Frame Loading and Displacements
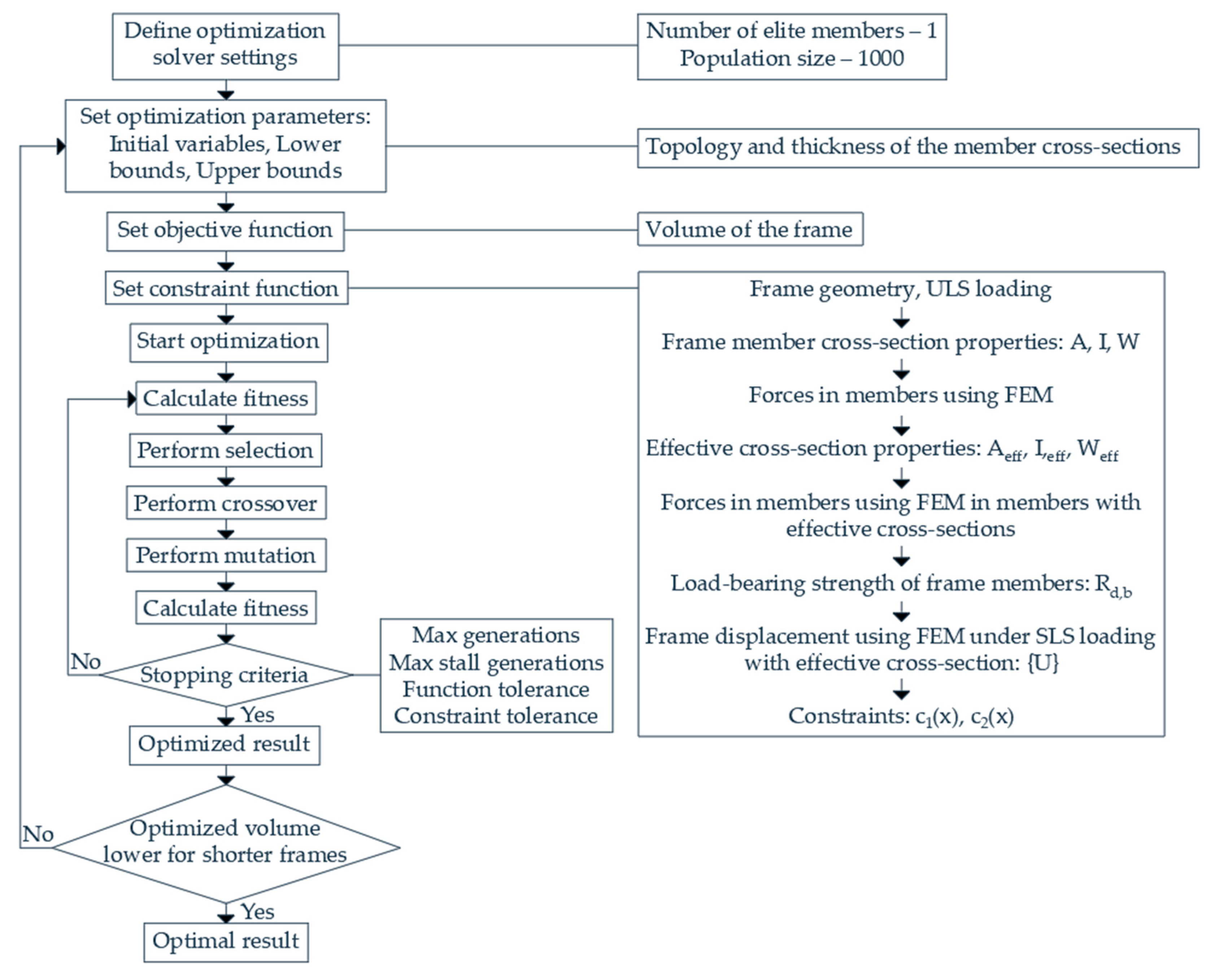
4. Optimization Algorithm
- Maximum Generations: The algorithm stops when the specified number of generations is reached. Set to 2000;
- Maximum Stall Generations: The algorithm stops if there is no significant improvement in fitness values over a set number of generations. Set to 50;
- Function Tolerance: The algorithm stops when the average relative change in fitness values over a specified number of generations falls below a certain threshold. Set to 0.000001;
- Constraint Tolerance: This criterion determines the feasibility of solutions concerning nonlinear constraints but is not a stopping criterion. Set to 0.001.
Validation of Optimization Algorithm through Comparative Analysis
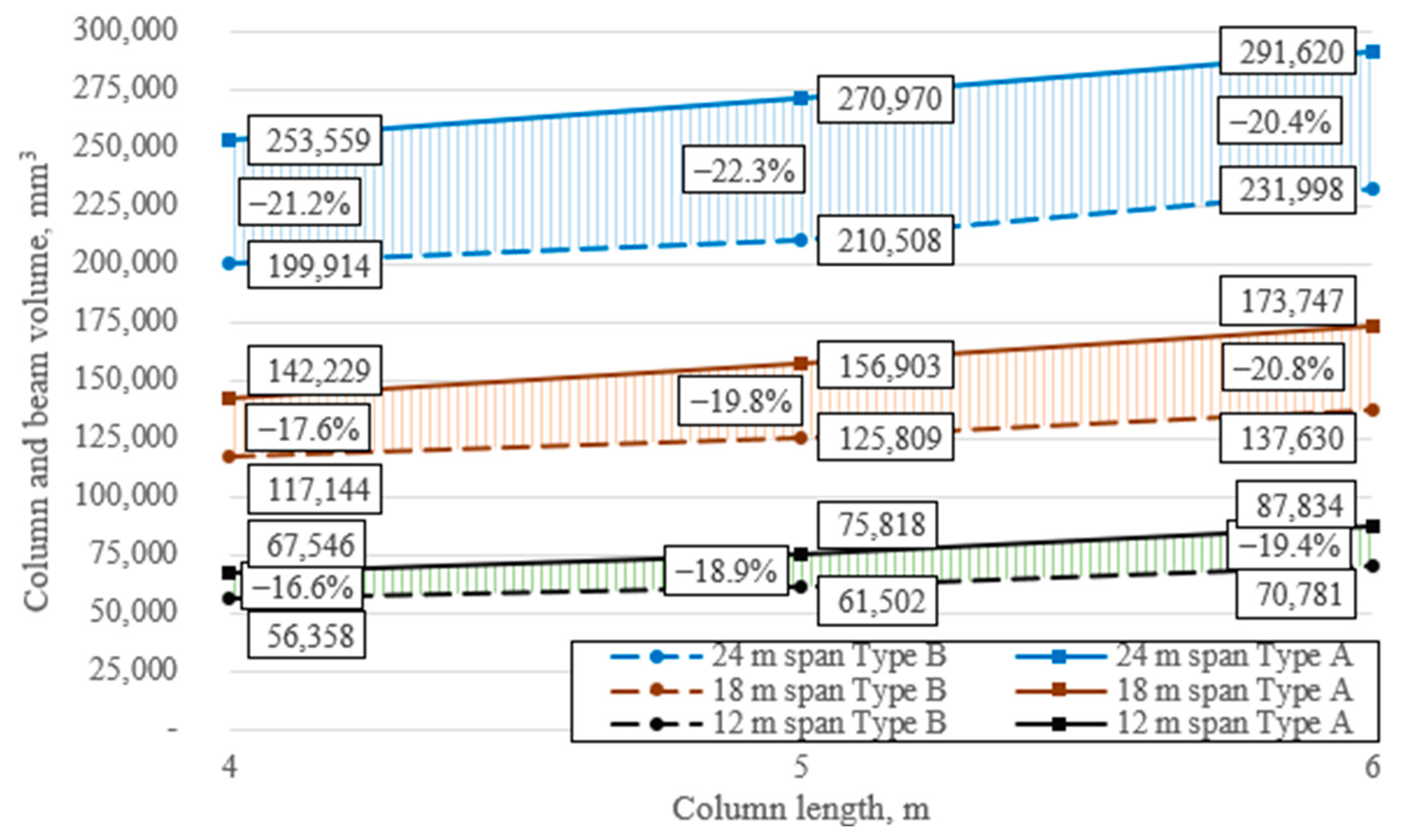
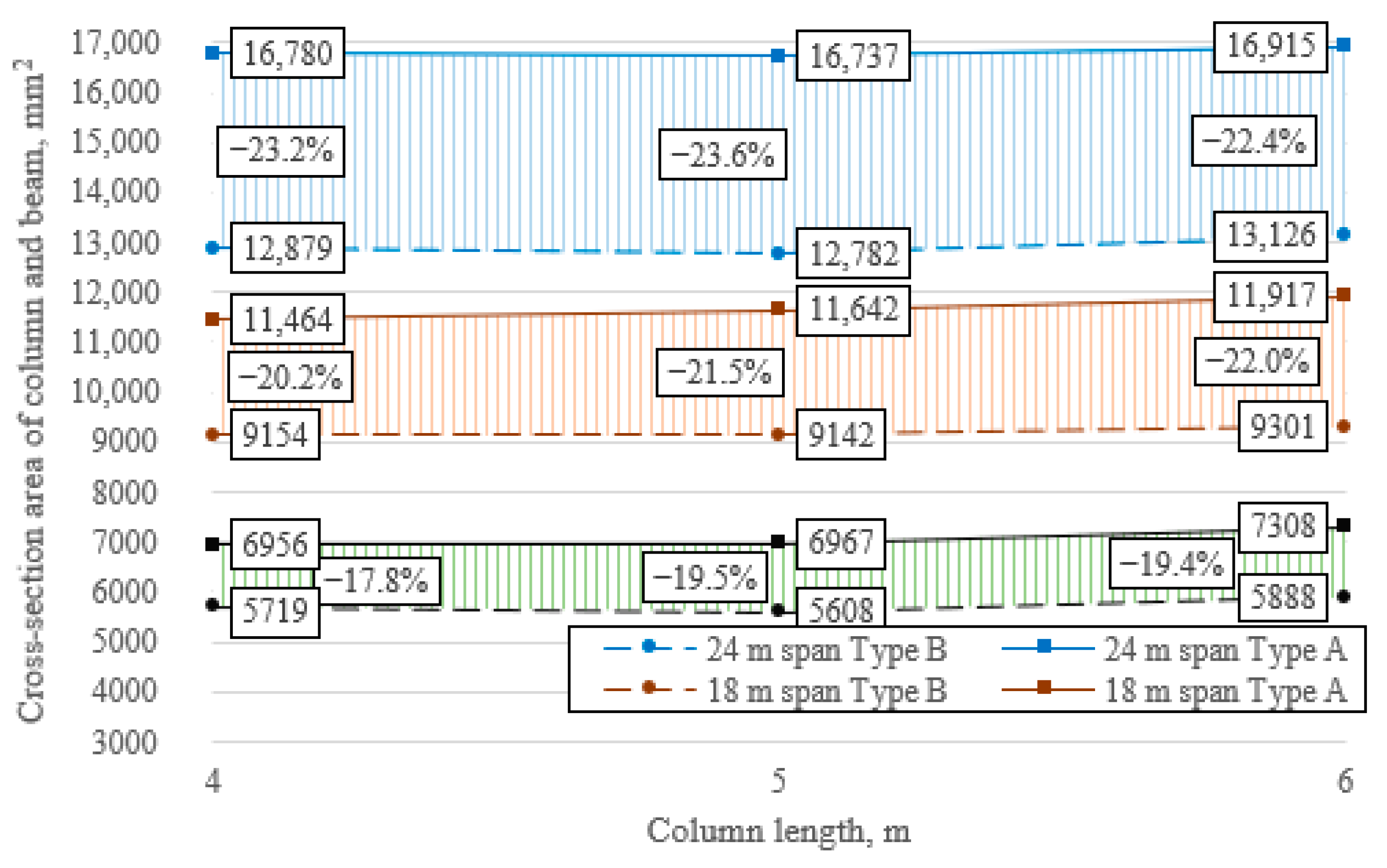
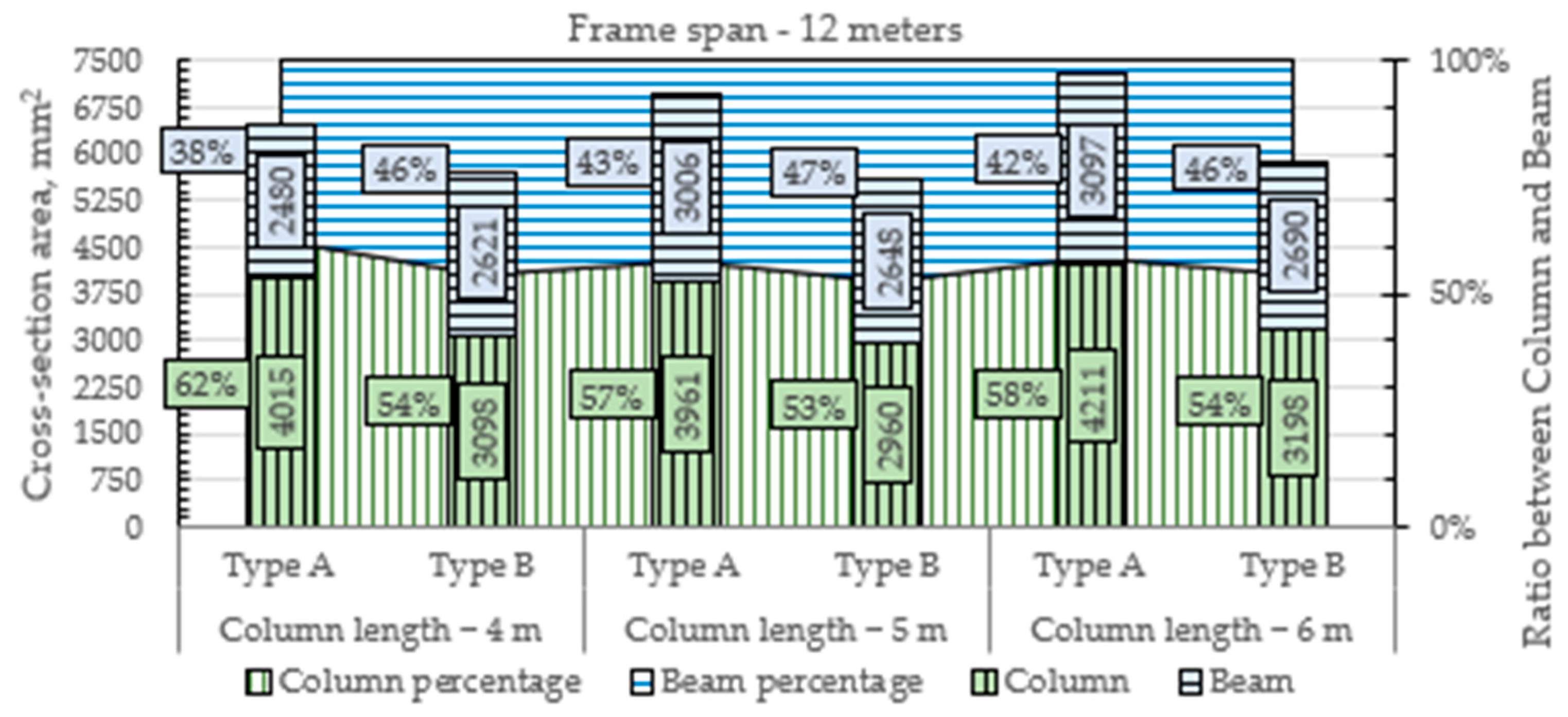
5. Optimized Examples and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| Notation | |||
| SLS | serviceability limit state | horizontal displacement | |
| ULS | ultimate limit state | maximum allowed horizontal displacement | |
| cross-section area of the beam | global displacement vector of the frame | ||
| cross-section area of the column | vertical displacement | ||
| cross-section area of the i-th member | maximum allowed vertical displacement | ||
| cross-section area of the i-th stiffener | Wi | wind load on portal frame members | |
| reduced cross-section area of the i-th stiffener | width of the i-th cross-section plate part | ||
| [BC] | boundary condition matrix | effective width of the i-th section plate part | |
| E | elasticity modulus | i-th constraint function | |
| global force vector | f | optimization objective function | |
| Gi | dead load on columns and beams | local force vector | |
| length of the column | fy | yielding strength | |
| moment of inertia of the i-th member | basic yield strength | ||
| global stiffness matrix of the frame | h | height of the cross-section | |
| L | portal frame span | k | number of stiffeners |
| length of the beam | stiffness matrix for members | ||
| length of the i-th member | lb | lower bounds | |
| buckling resistance to bending of the beam | n | number of variables | |
| buckling resistance to bending of the column | t | thickness of the cross-section | |
| bending moment in the beam for eff. sections | ub | upper bounds | |
| bending moment in the column for eff. sections | displacement vector of the i-th member | ||
| buckling resistance for torsion of the beam | i-th variable | ||
| buckling resistance for torsion of the column | shift of the centroid for beam cross-section | ||
| buckling resistance at y-y axis of the beam | shift of the centroid for column cross-section | ||
| buckling resistance at y-y axis of the column | α | portal frame beam pitch | |
| buckling resistance at z-z axis of the beam | γG | partial safety factor of the permanent action | |
| buckling resistance at z-z axis of the column | γQ | partial safety factor of the variable action | |
| axial force in the beam for eff. cross-sections | partial safety factor of the material | ||
| axial force in the column for eff. cross-sections | reduction factor of the i-th section plate part | ||
| design buckling resistance of the beam | compressive stress at the centerline of stiffener | ||
| design buckling resistance of the column | reduction factor of the stiffener cross-section | ||
| Sk | snow load | ψ0 | combination factor |
References
- Usefi, N.; Sharafi, P.; Mortazavi, M.; Ronagh, H.; Samali, B. Structural performance and sustainability assessment of hybrid-cold formed modular steel frame. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 34, 101895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Mao, X.; He, L.; Yuan, J. Study on flexural and demountable behavior of a modular light-gauge steel framed wall. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2023, 29, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubina, D.; Ungureanu, V. Local/distortional and overall interactive buckling of thin-walled cold-formed steel columns with open cross-section. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 182, 110172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatheeshgar, P.; Bock, M.; Chandrasiri, D.; Suntharalingam, T. Assessment of Eurocode shear design provisions for cold-formed steel sections. Structures 2023, 47, 2066–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miranda Batista, E. Local-global buckling interaction procedures for the design of cold-formed columns: Effective width and direct method integrated approach. Thin-Walled Struct. 2009, 47, 1218–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, B.W. Review: The Direct Strength Method of cold-formed steel member design. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2008, 64, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camotim, D.; Martins, A.D.; Dinis, P.B. Towards the next-generation design of cold-formed steel structures. In Recent Trends in Cold-Formed Steel Construction; Yu, C., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 101–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Young, B. Finite element analysis and design of cold-formed steel built-up closed section columns with web stiffeners. Thin-Walled Struct. 2018, 131, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.R.; Maheshwari, P.B. Finite strip method for the analysis of diaphragm supported cylindrical shell. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 28, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.; Adany, S. New transverse extension modes for buckling analysis of thin-walled members by using the constrained finite strip method. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 179, 109634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebiano, R.; Camotim, D.; Gonçalves, R. GBTUL 2.0—A second-generation code for the GBT-based buckling and vibration analysis of thin-walled members. Thin-Walled Struct. 2018, 124, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ádány, S.; Schafer, B.W. Generalized constrained finite strip method for thin-walled members with arbitrary cross-section: Primary modes. Thin-Walled Struct. 2014, 84, 150–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AISI S100-16; North American Specification for the Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structural Members. AISI: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- AS/NZS 4600:2005; Cold-Formed Steel Structures. Australian/New Zealand Standard: Sydney, Australia, 2005.
- EN 1993-1-3; Eurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures—Part 1–3: General Rules—Supplementary Rules for Cold-Formed Members and Sheeting. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2006.
- Shimoda, M.; Liu, Y.; Ishikawa, K. Optimum shape design of thin-walled cross sections using a parameter-free optimization method. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 148, 106603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Young, B. Experimental and numerical investigation on cold-formed steel zed section beams with complex edge stiffeners. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 194, 111315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jůza, J.; Jandera, M. Distortional buckling resistance of intermediate stiffeners in stainless steel cold-formed profiles. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 169, 108390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniunas, A.; Urbonas, K. Influence of the semi-rigid bolted steel joints on the frame behaviour. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2010, 16, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakir, Q.M.; Alliwe, R. Upgrading of Deficient Disturbed Regions in Precast RC beams with Near Surface Mounted (NSM) Steel Bars. J. Mater. Eng. Struct. 2020, 7, 167–184. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342247661 (accessed on 19 August 2024).
- Shakir, Q.M.; Hanoon, H.K. New models for reinforced concrete precast hybrid deep beams under static loads with curved hybridization. Structures 2023, 54, 1007–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hadary, M.R.; El-Aghoury, I.M.; Ibrahim, S.A.B. Behavior of different bolted connection configurations in frames composed of cold-formed sections. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Blum, H.B.; Roy, K.; Pouladi, P.; Uzzaman, A.; Lim, J.B.P. Cold-formed steel portal frame moment-resisting joints: Behaviour, capacity and design. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 183, 106718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1993-1-8; Eurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures—Part 1–8: Design of Joints. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2005.
- Bučmys, Ž.; Daniūnas, A.; Jaspart, J.P.; Demonceau, J.F. A component method for cold-formed steel beam-to-column bolted gusset plate joints. Thin-Walled Struct. 2018, 123, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Quan, G.; Kyvelou, P.; Teh, L.; Gardner, L. A practical numerical model for thin-walled steel connections and built-up members. Structures 2022, 38, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, Q.Y.; Li, H.; Ren, Q. Loading capacity prediction and optimization of cold-formed steel built-up section columns based on machine learning methods. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 180, 109826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatheeshgar, P.; Poologanathan, K.; Gunalan, S.; Tsavdaridis, K.D.; Nagaratnam, B.; Iacovidou, E. Optimised cold-formed steel beams in modular building applications. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parastesh, H.; Mohammad Mojtabaei, S.; Taji, H.; Hajirasouliha, I.; Bagheri Sabbagh, A. Constrained optimization of anti-symmetric cold-formed steel beam-column sections. Eng. Struct. 2021, 228, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.T.; Lim, J.B.P.; Tanyimboh, T.T.; Wrzesien, A.M.; Sha, W.; Lawson, R.M. Optimal design of cold-formed steel portal frames for stressed-skin action using genetic algorithm. Eng. Struct. 2015, 93, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.T.; Mojtabaei, S.M.; Hajirasouliha, I.; Ye, J.; Lim, J.B.P. Coupled element and structural level optimisation framework for cold-formed steel frames. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 168, 105867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzesien, A.M.; Lim, J.B.P.; Nethercot, D.A. Sustainable applications of cold-formed steel structures. In Recent Trends in Cold-Formed Steel Construction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 387–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinchen, R.; Rasmussen, K.J.R. Experiments on Long-Span Cold-Formed Steel Single C-Section Portal Frames. J. Struct. Eng. 2020, 146, 04019187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S. The Finite Element Method in Engineering, 6th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- EN 1993-1-5; Eurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures—Part 1–5: Plated Structural Elements. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2006.
- Stulpinas, M.; Daniūnas, A. An approach of web stiffener calculation in thin-walled columns. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2024, 30, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stulpinas, M.; Daniūnas, A. Selection of an Optimum Axially Compressed Closed Cross-Section Thin-Walled Built-Up Column. Lect. Notes Civ. Eng. 2024, 392, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, P.C. MATLAB Optimization Techniques; Apress: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 10149-3:2013; Hot Rolled Flat Products Made of High Yield Strength Steels for Cold-Forming—Part 3: Technical Delivery Conditions for Normalized or Normalized Rolled Steels. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2013.



| Member Type | Variable | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flange Half-Width | Cross-Section Half-Height | Stiffener Half-Web Coordinates | Cross-Section Thickness | |
| Column | ||||
| Beam | ||||
| Reference Section by Phan et al. [31] | Optimized Section, t = 3 mm | Optimized Section, h = 342.9 mm | Optimized Section, Unconstrained t, h | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Column | Beam | Column | Beam | Column | Beam | Column | Beam | |
| Section | 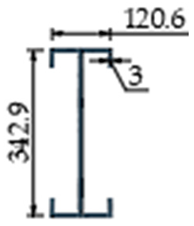 | 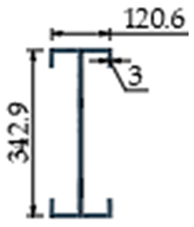 | 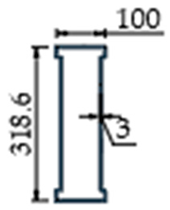 | 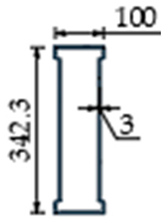 | 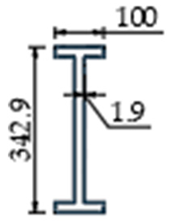 | 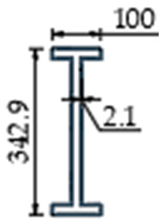 |  | 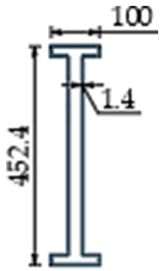 |
| Volume ratio to reference | - | 1.03 | 0.79 | 0.62 | ||||
| Load Combination | Permanent Actions | Variable Actions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leading Action | Accompanying Action | |||||
| Partial Factor (γG) | Action | Partial Factor (γQ) | Action | Partial Factor (γQ) | Combination Factor (ψ0) | |
| ULS | 1.35 | Snow | 1.5 | Wind | 1.5 | 0.6 |
| ULS | 1.35 | Wind | 1.5 | Snow | 1.5 | 0.7 |
| SLS | 1.0 | Snow | 1.0 | Wind | 1.0 | 0.6 |
| SLS | 1.0 | Wind | 1.0 | Snow | 1.0 | 0.7 |
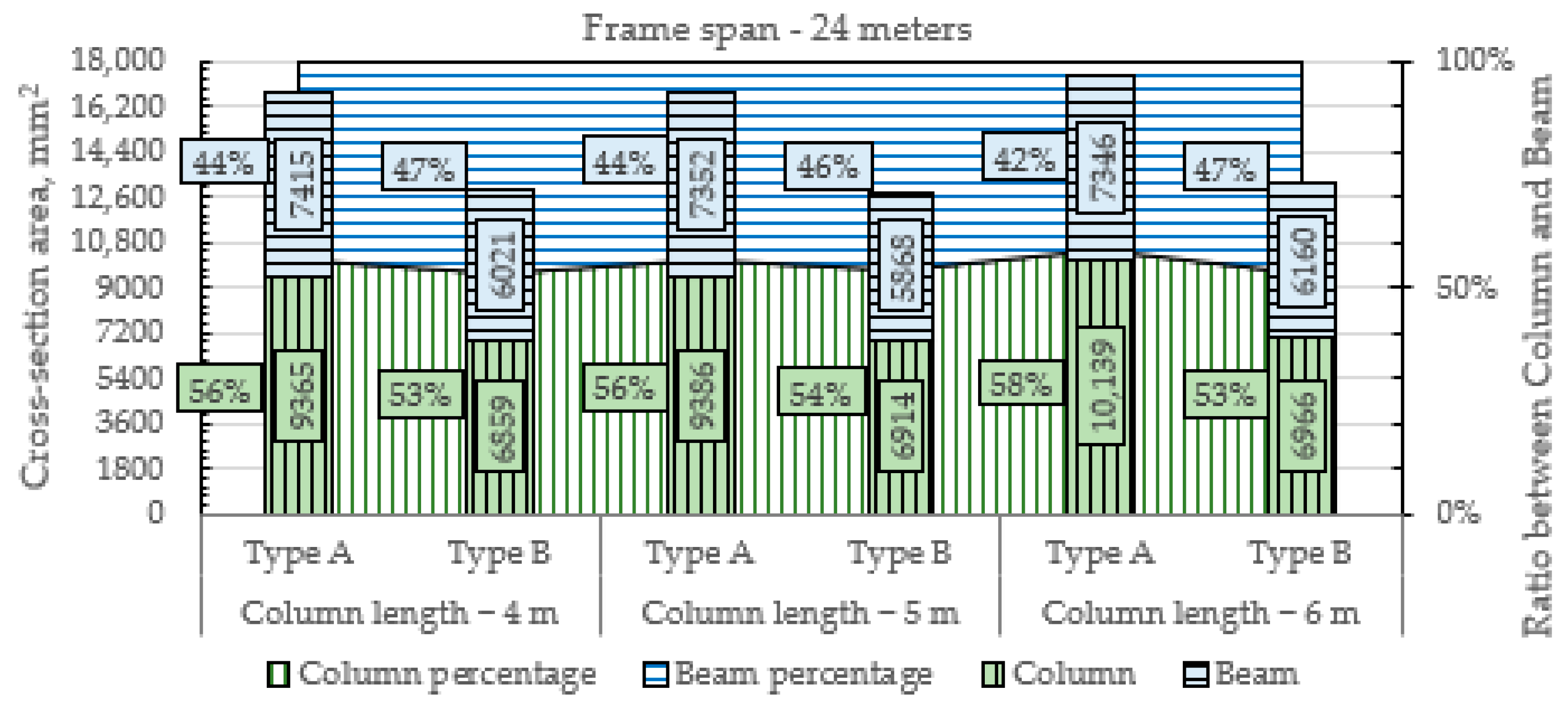
| Span | 12 m | 18 m | 24 m | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Column Length | 4 m | 5 m | 6 m | 4 m | 5 m | 6 m | 4 m | 5 m | 6 m | |||||||||
| Section Type | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B |
| Optimal volume, mm3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Column | 16,060 | 12,392 | 19,807 | 14,800 | 25,266 | 19,188 | 25,788 | 19,168 | 33,128 | 24,973 | 34,256 | 25,067 | 37,459 | 27,434 | 46,929 | 34,569 | 60,836 | 41,794 |
| Beam | 17,712 | 15,787 | 18,102 | 15,951 | 18,652 | 16,203 | 45,327 | 39,404 | 45,324 | 38,543 | 45,766 | 38,735 | 89,314 | 72,523 | 88,556 | 70,685 | 88,491 | 74,205 |
| Cross-section area, mm2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Column | 4015 | 3098 | 3961 | 2960 | 4211 | 3198 | 6447 | 4792 | 6626 | 4995 | 6851 | 5013 | 9365 | 6859 | 9386 | 6914 | 9584 | 6966 |
| Beam | 2941 | 2621 | 3006 | 2648 | 3097 | 2690 | 5017 | 4362 | 5017 | 4266 | 5066 | 4288 | 7415 | 6021 | 7352 | 5868 | 7331 | 6160 |
| Cross-section effective area, mm2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Column | 2878 | 2441 | 2718 | 2147 | 2813 | 2385 | 4845 | 3927 | 4854 | 4248 | 4902 | 4084 | 7217 | 5959 | 7102 | 6062 | 7074 | 5884 |
| Beam | 1770 | 1704 | 1647 | 1554 | 1673 | 1668 | 3048 | 2944 | 3028 | 2873 | 3018 | 2967 | 4503 | 4096 | 4461 | 4009 | 4591 | 4363 |
| Cross-section thickness, mm | ||||||||||||||||||
| Column | 3.08 | 2.45 | 2.58 | 2.04 | 2.52 | 2.19 | 4.39 | 3.06 | 4.19 | 3.36 | 4.07 | 3.17 | 5.79 | 4.26 | 5.44 | 4.26 | 5.20 | 3.90 |
| Beam | 1.66 | 1.58 | 1.31 | 1.27 | 1.28 | 1.43 | 2.25 | 2.12 | 2.22 | 2.08 | 2.19 | 2.18 | 2.78 | 2.56 | 2.74 | 2.51 | 2.86 | 2.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stulpinas, M.; Daniūnas, A. Optimization of Cold-Formed Thin-Walled Cross-Sections in Portal Frames. Buildings 2024, 14, 2565. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14082565
Stulpinas M, Daniūnas A. Optimization of Cold-Formed Thin-Walled Cross-Sections in Portal Frames. Buildings. 2024; 14(8):2565. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14082565
Chicago/Turabian StyleStulpinas, Mantas, and Alfonsas Daniūnas. 2024. "Optimization of Cold-Formed Thin-Walled Cross-Sections in Portal Frames" Buildings 14, no. 8: 2565. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14082565
APA StyleStulpinas, M., & Daniūnas, A. (2024). Optimization of Cold-Formed Thin-Walled Cross-Sections in Portal Frames. Buildings, 14(8), 2565. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14082565





